Numerical Study of a Novel Kagome-Inspired Photonic Crystal Fiber-Based Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor for Detection of Blood Components and Analytical Targets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geometric Configuration of the Biosensing System
2.1. Production Feasibility Assessment for the Proposed Biosensor
2.1.1. Initial Preparation
2.1.2. Structuring Elliptical Air Holes
2.1.3. Stacking
2.1.4. Drawing Process
2.1.5. Plasmonic Coating (CVD) Process)
2.1.6. Post-Processing
2.1.7. Final Assembly and Sensing Setup
3. Methodology and Analysis of Findings
3.1. Determination of Biosensor Characteristics
3.2. Sensing Parameter Evaluation Through Increases in Plasmonic Material Thickness Beyond Optimal Levels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nankali, M.; Einalou, Z.; Asadnia, M.; Razmjou, A. High-Sensitivity 3D ZIF-8/PDA Photonic Crystal-Based Biosensor for Blood Component Recognition. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2021, 4, 1958–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Chowdhury, P.; Hossain, M.; Rahman, M.; Hossain, S. Hexagonal Hollow Core PCF-Based Blood Components Sensing: Design and Simulation. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2025, 83, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yang, H.; Sun, T.; Song, Q.; Yi, Z.; Yi, Y. Model Design and Study of a U-Channel Photonic Crystal Fib Optic Sensor for Measuring Glucose Concentration in Blood. Sensors 2025, 25, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdous, A.H.M.I.; Hosen, M.S.; Khandakra, K.; Kundu, D.; Bani, M.; Noor, K.S.; Tithi, S.A. Pioneering terahertz blood analysis: Hollow-core PCF with optimized sensitivity and low loss. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0319860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, G.T.; Hlaus, T.; Bass, K.J.; Seelhammer, T.G.; Culbertson, C.T. Sol−Gel Modified Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Microfluidic Devices with High Electroosmotic Mobilities and Hydrophilic Channel Wall Characteristics. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 1414–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versaevel, M.; Grevesse, T.; Riaz, M.; Lantoine, J.; Gabriele, S. Micropatterning Hydroxy-PAAm Hydrogels and Sylgard 184 Silicone Elastomers with Tunable Elastic Moduli. Meth. Cell Biol. 2014, 121, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Li, H.; McCourt, F.R.W. Ab initio potential energy functions, spectroscopy and thermal physics for krypton-contained rare gas dimers. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2022, 288, 108244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, A.; Khan, S.; Didar, T.F. Conventional and emerging strategies for the fabrication and functionalization of PDMS-based microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 3053–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.W.; Tilson, C. Distribution ratios of ethanol and water between whole blood, plasma, serum, and erythrocytes: Recommendations for interpreting clinical laboratory results in a legal context. J. Forensic Sci. 2023, 68, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogoda, K.; Charrier, E.; Janmey, P. A Novel Method to Make Polyacrylamide Gels with Mechanical Properties Resembling those of Biological Tissues. Bio-Protoc. 2021, 11, e4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.V.; Dennison, S.R.; Hayes, J.M.; Reddy, S.M. Evaluation of acrylamide-based molecularly imprinted polymer thin-sheets for specific protein capture—A myoglobin model. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2021, 7, 045025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, D.; Taya, S.A. A highly birefringent bend-insensitive porous core PCF for endlessly single-mode operation in THz regime: An analysis with core porosity. Appl. Nanosci. 2021, 11, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Prajapati, Y.K. Novel Bottom-Side Polished PCF-Based Plasmonic Biosensor for Early Detection of Hazardous Cancerous Cells. IEEE Trans. NanoBioscience 2023, 22, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Chaudhary, B.; Upadhyay, A.; Taya, S.A. Bottom side partially etched D-shaped PCF biosensor for early diagnosis of cancer cells. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2023, 138, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Upadhyay, A.; Chaudhary, B.; Sirohi, K.; Kumar, S. Enhanced Cu-Ni-TiO-BP Plasmonic Biosensor for Highly Sensitive Biomolecule Detection and SARS-CoV-2 Diagnosis. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, S.; Chaudhary, B.; Kumar, S. Black Phosphorus-Based Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor for DNA Hybridization. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2024, 52, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Chaudhary, B.; Kumar, R.; Upadhyay, A.; Kumar, S. A Numerical Analysis of Rectangular Open Channel Embedded TiO2-Au-MXene Employed PCF Biosensor for Brain Tumor Diagnosis. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 16047–16054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almawgani, A.H.M.; Alhamss, D.N.; Taya, S.A.; Hindi, A.T.; Upadhyay, A.; Singh, S.; Colak, I.; Pal, A.; Patel, S.K. Identification of four detrimental chemicals using square-core photonic crystal fiber in the regime of THz. J. Appl. Phys. 2023, 133, 243103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramola, A.; Shakya, A.K.; Vidyarthi, A.; Singh, S.; Talker, E.; Bergman, A. Next-generation photonic-crystal-fiber-based plasmonic sensor for heavy metal detection via spectroscopy and refractive index integration. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Optical Fiber Sensors, Porto, Portugal, 25–30 May 2025; pp. 1489–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, A.K.; Cheng, F.; Carmon, T. Ultracoherent emission by orthogonal lasers. Integr. Photonics Platf. III 2024, 13012, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, A.K.; Ramola, A.; Singh, S.; Vidyarthi, A. Optimized Design of Plasmonic Biosensor for Cancer Detection: Core Configuration and Nobel Material Coating Innovation. Plasmonics 2024, 20, 1789–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taya, S.A.; Colak, I.; Patel, S.K.; Pal, A.; Almawgani, A.H.M.; Ali, G.A. Highly sensitive sensor based on SPR nanostructure employing graphene and perovskite layers for the determination of blood hemoglobin concentration. Optik 2023, 281, 170857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.T.A.; Patnaik, R.; Huang, J.Y.; Campi, H.D.; Montorfano, L.; De Stefano, F.; Rosenthal, R.J.; Wexner, S.D. Leukopenia is an independent risk factor for early postoperative complications following incision and drainage of anorectal abscess. Color. Dis. 2023, 25, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Hao, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Di, F.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Y. Association between DIAPH1 variant and posterior circulation involvement with Moyamoya disease. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremese, E.; Bruno, D.; Varriano, V.; Perniola, S.; Petricca, L.; Ferraccioli, G. Serum Albumin Levels: A Biomarker to Be Repurposed in Different Disease Settings in Clinical Practice. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, A.K.; Vidyarthi, A. Comprehensive Study of Compression and Texture Integration for Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine Data Analysis. Technologies 2024, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramola, A.; Shakya, A.K.; Bergman, A. Finite Element Method-Based Modeling of a Novel Square Photonic Crystal Fiber Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor with a Au–TiO2 Interface and the Relevance of Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Sensor Optimization. Photonics 2025, 12, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramola, A.; Shakya, A.K.; Bergman, A. Comprehensive Analysis of Advancement in Optical Biosensing Techniques for Early Detection of Cancerous Cells. Biosensors 2025, 15, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.S.; Kumar, D.; Mishra, G.P.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, S. Plasmonic Biosensor with Gold and Titanium Dioxide Immobilized on Photonic Crystal Fiber for Blood Composition Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 8474–8481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeswari, D.; Revathi, A.A. Highly sensitive SPR-based PCF bio sensor for plasma cell detection in human blood for the detection of early stage cancer. Optik 2022, 258, 168897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabin, A.; Ahmed, K.; Rana, J.; Paul, B.K.; Luo, Y.; Vigneswaran, D. Titanium-Coated Dual-Core D-Shaped SPR-Based PCF for Hemoglobin Sensing. Plasmonics 2019, 14, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.-X.; Zhang, D.; Zhai, X.; Wang, L.-L.; Wen, S.-C. Phase-controlled topological plasmons in 1D graphene nanoribbon array. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 123, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedri-Knani, L.; Kaziz, S.; Dridi, C. Performance Prediction of a Highly Sensitive Optimized PCF-SPR Biosensor for Cancer Cell Detection Using MLP-Based ANN Model. IEEE Sens. J. 2025, 25, 17136–17143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Luo, B.; An, M.; Hu, T.; Lin, W.; Jia, H. A Highly Efficient D-Shaped Dual-Core PCF-SPR Sensor Coated with ITO Film for Refractive Index Detection. Plasmonics 2025, 20, 1379–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, A.K.; Singh, S. Design of novel Penta core PCF SPR RI sensor based on fusion of IMD and EMD techniques for analysis of water and transformer oil. Measurement 2022, 188, 110513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, A.K.; Singh, S. Designing of a Novel PCF Biosensor having Octagonal Core and based on SPR for Chemical and Heavy Metal Sensing. In Proceedings of the 2022 12th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence), Noida, India, 27–28 January 2022; pp. 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, A.K.; Singh, S. Performance Analysis of a Developed Optical Sensing Setup Based on the Beer-Lambert Law. Plasmonics 2024, 19, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Ren, F.; Zhou, D.; Li, Y. Highly Sensitive PCF-SPR RI Sensor for Cancer Detection Using Gold/Graphene/Ti3C2Tx-MXene Hybrid Layer. Plasmonics 2025, 20, 2279–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveena, S.; Senthilnathan, K. Performance Enhancement of Gold Coated D-shaped PCF Sensor Using Monolayer MoS2. Plasmonics 2025, 20, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Iftekher, A.N.M.; Etu, M.F.; Rashmi, W.R.; Abbas, S. Dual Peak Double Resonance Sensing Using a Dual Plasmonic Material PCF-SPR Sensor. Plasmonics 2023, 18, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadeh, A.; Rash-Ahmadi, S. A surface plasmon resonance sensor based on photonic crystal fiber composed of magnesium fluoride and graphene layers to detect aqueous solutions. Opt. Quant. Electron. 2024, 56, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Rahman, I.; Chakrabarti, K.; Tabata, H.; Ramaraj, S.G.; Eid, M.M.A.; Rashed, A.N.Z.; Razzak, S.M.A. Advanced low loss PCF-based SPR sensor for enhanced sensor length configurations flexibility with exceptional superior sensing performance capability. Appl. Phys. A 2025, 131, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Kumar, S.; Kaushik, B.K. (INVITED) Advances in photonic crystal fiber: Sensing and supercontinuum generation applications. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2022, 72, 102982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Ono, L.K.; Qi, Y.; Oughaddou, H. Recent Advances in Phosphorene: Structure, Synthesis, and Properties. Small 2024, 20, 2303115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Shen, T.; Feng, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. PCF sensor coated with Au-graphene/MXene for a low refractive index and a wide detection range. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2022, 39, 3329–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, R.; Wan, H.; Shi, W.; Liang, H.; Lou, Y. Design and Theoretical Analysis of High-Sensitive Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor Based on Au/Ti 3C2Tx-MXene Hybrid Layered D-Shaped Photonic Crystal Fiber. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 18160–18167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, W.; Song, D.; Yan, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Suzuki, T.; Ohishi, Y.; et al. An Antiinterference Temperature Sensor Based on Mach-Zehnder Interferometer Using Kagome Hollow-Core Photonic Crystal Fiber. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 8426–8434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokoua, E.N.; Mousavi, S.A.; Jasion, G.T.; Richardson, D.J.; Poletti, F. Loss in hollow-core optical fibers: Mechanisms, scaling rules, and limits. Adv. Opt. Photon. 2023, 15, 1–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Das, S.K.; Chakraborty, S.R.; Deb, A. Investigation of Optical Properties of Zinc-Oxide Thin Films Deposited on Various Substrates: A Simulation Study. J. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2018, 4, 58–67. [Google Scholar]
- Ramola, A.; Marwaha, A.; Singh, S. Design and investigation of a dedicated PCF SPR biosensor for CANCER exposure employing external sensing. Appl. Phys. A 2021, 127, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayana, A.; Gummagol, N.B.; Patil, P.S.; Sharma, P.; Rajendra, B.V. Nonlinear optical properties of zinc oxide thin films. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 175, 110820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatian, B. Fitting refractive-index data with the Sellmeier dispersion formula. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 4477–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthil, R.; Anand, U.; Krishnan, P. Hollow-core high-sensitive photonic crystal fiber for liquid-/gas-sensing applications. Appl. Phys. A 2021, 127, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuad, M.H.; Nayan, M.F.; Mahmud, R.R. Advances in Surface Plasmon Resonance-Based PCF and MIM Sensors. Plasmonics 2025, 20, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, A.K.; Ramola, A.; Singh, S.; Van, V. Design of an ultra-sensitive bimetallic anisotropic PCF SPR biosensor for liquid analytes sensing. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 9233–9255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, R.; Singh, R.K. Mie scattering of tightly focused beams by a core-shell nanoparticle. Opt. Commun. 2024, 557, 130306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.S.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, S. Au-TiO2 Coated Photonic Crystal Fiber Based SPR Refractometric Sensor for Detection of Cancerous Cells. IEEE Trans. NanoBioscience 2023, 22, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, S.; Kadoya, S.; Michihata, M.; Takahashi, S. Novel absolute length measurement method for etalon sensor using optical comb pulsed interference and harmonic etalon reflections. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2023, 34, 055205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COMSOL Multiphysics Software for Optimizing Designs. Available online: https://www.comsol.com/ (accessed on 2 October 2023).
- Li, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Kang, W.; Deng, N.; Zhuang, X.; Zhou, X. Research progress of ultrafine alumina fiber prepared by sol-gel method: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 127744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, Y.; Xu, B.; Wei, Z.; Cheng, T.; Wang, X. Modified D-type surface plasmon resonance (SPR)-based photonic crystal fiber (PCF) for application as a polarization filter and refractive index sensor. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2023, 51, 162–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.S.; Kalam, M.A.E.; Faisal, M. PCF Based Four-Channel SPR Biosensor with Wide Sensing Range. IEEE Trans. NanoBiosci. 2024, 23, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, H.; Pereira, M.F. Recent Progress in Light Polarization Control Schemes for Silicon Integrated Photonics. Laser Photonics Rev. 2024, 18, 2301025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parandin, F.; Heidari, F.; Aslinezhad, M.; Parandin, M.M.; Roshani, S.; Roshani, S. Design of 2D photonic crystal biosensor to detect blood components. Opt. Quant. Electron. 2022, 54, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, R.; Suaganya, T.; Robinson, S. Design and Analysis of 2D Photonic Crystal Based Biosensor to Detect Different Blood Components. Photonic Sens. 2019, 9, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Ahmed, F.; Roy, S.; Paul, B.K.; Aktar, M.N.; Vigneswaran, D.; Islam, M.S. Refractive Index-Based Blood Components Sensing in Terahertz Spectrum. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 3368–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirunavakkarasu, P.M.; Khan, A.A.; Noor, A.S.M.; Saidin, N.B.; Waqas, N. Au coated etched FBG SPR sensor for the detection of ethanol in aqueous solution. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2024, 82, 103584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.K.; Singh, M. Plasmonic Elliptical Nanohole Array for On-Chip Human Blood Group Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 27224–27230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Iftekher, A.N.M.; Noor, F.; Khan, M.R.H.; Reza, M.T.; Nishat, M.M. AZO-coated plasmonic PCF nanosensor for blood constituent detection in near-infrared and visible spectrum. Appl. Phys. A 2022, 128, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayalakshmi, D.; Manimegalai, C.T.; Selvakumar, P. Bi-core photonic crystal fiber for blood component detection. J. Opt. 2023, 52, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

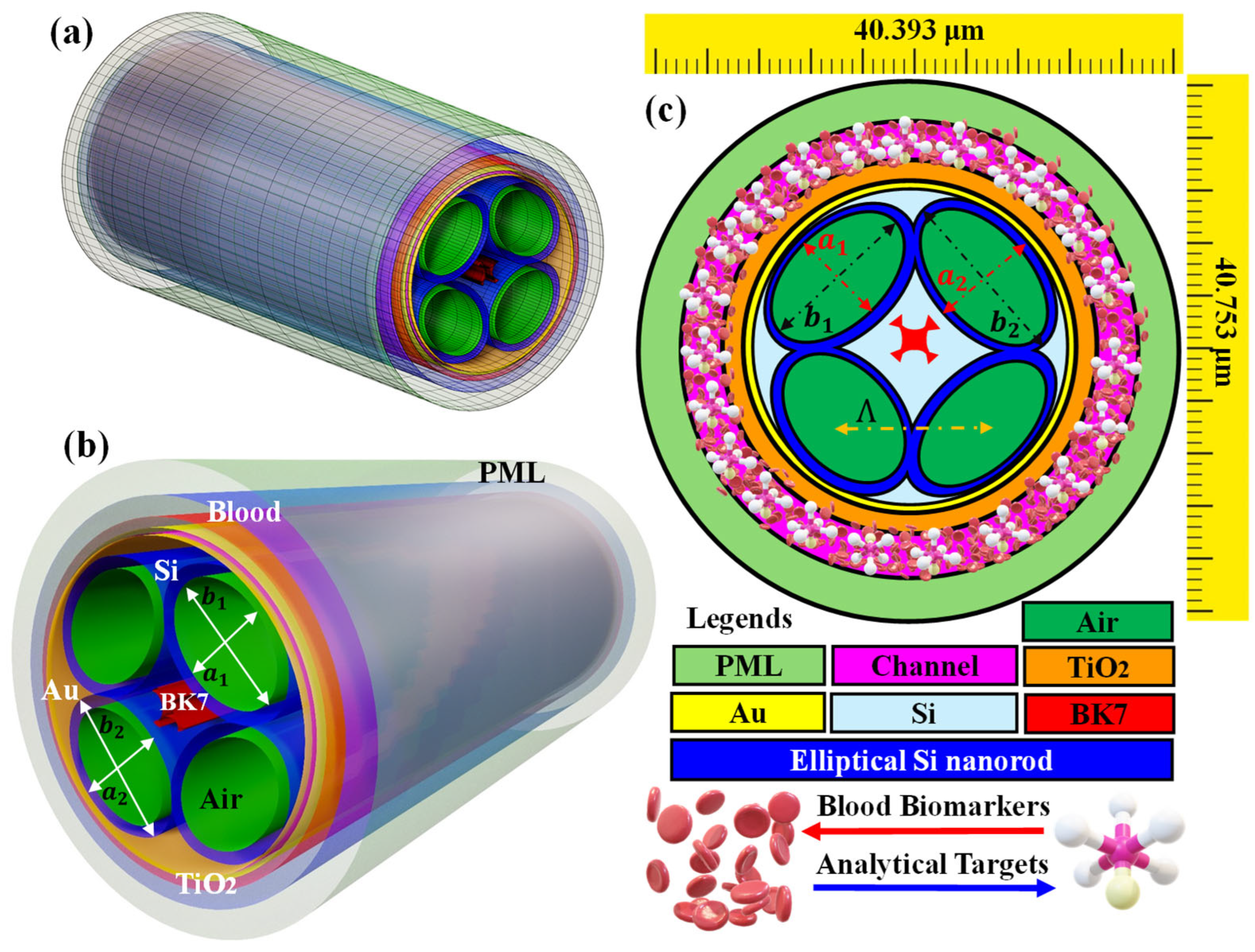


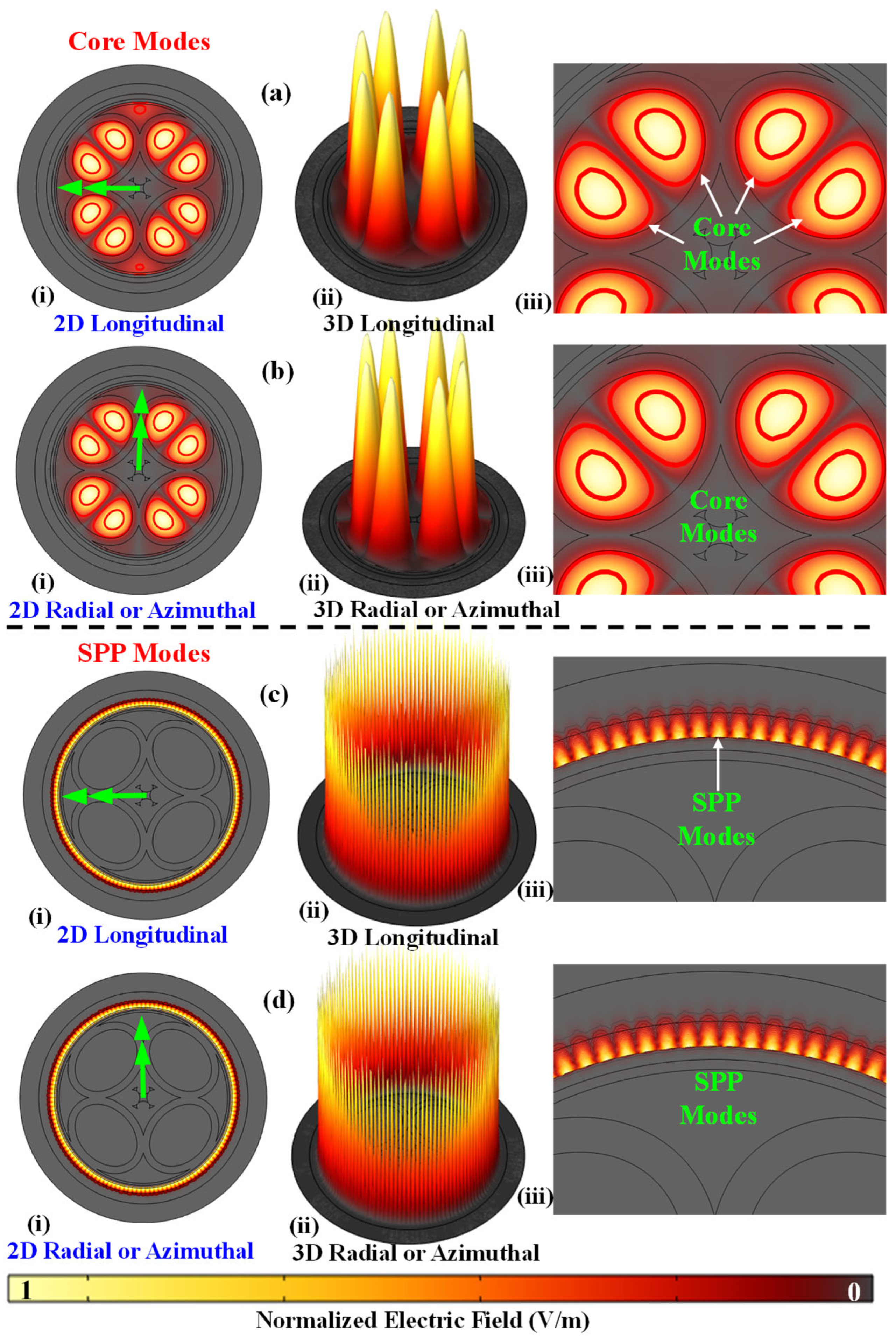
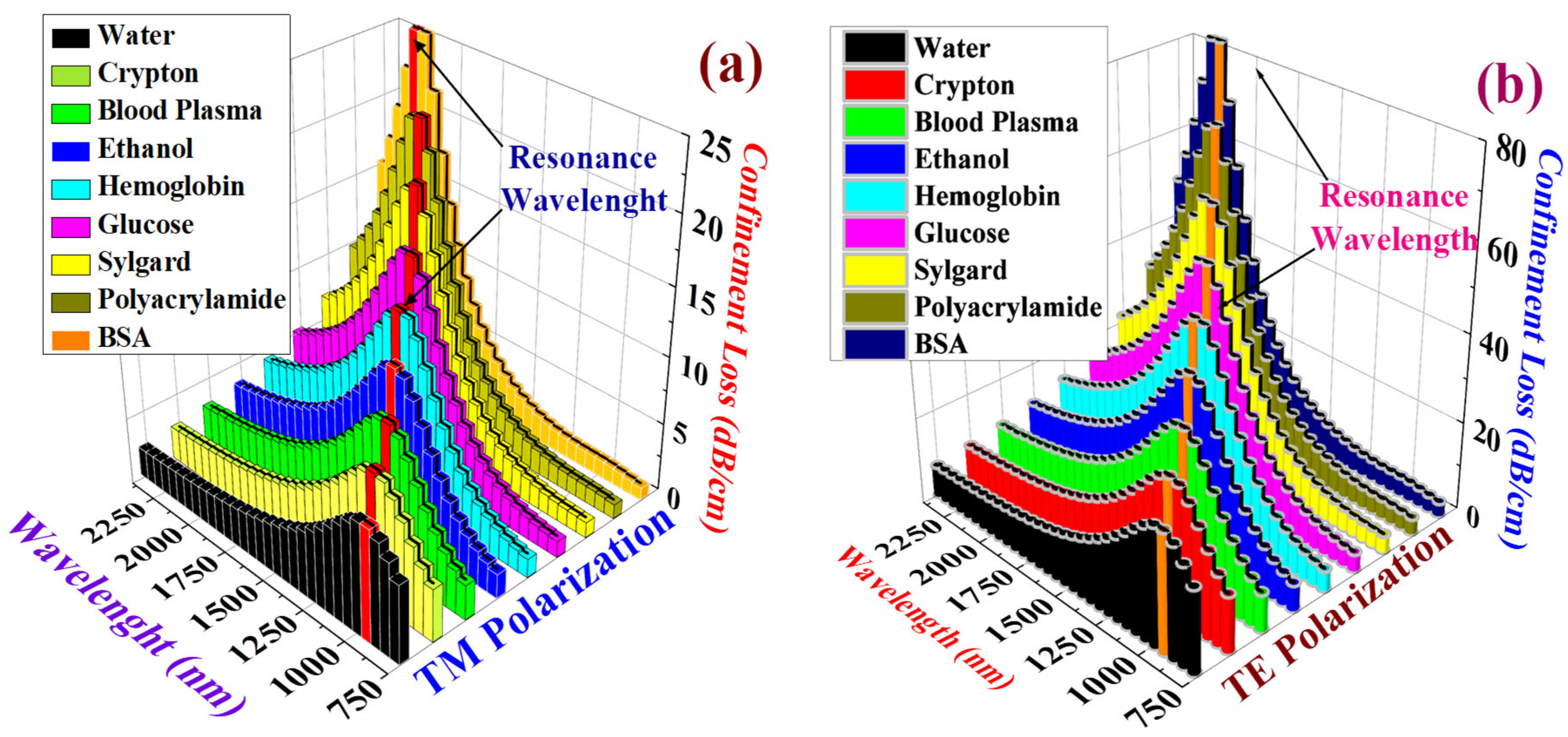






| Blood Biomarker and Target Analytes | Refractive Index | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 1.330 | [64] |
| Crypton | 1.340 | [65] |
| Plasma | 1.350 | [66] |
| Ethanol | 1.360 | [67] |
| Hemoglobin (Hb) | 1.380 | [68] |
| Glucose (40 gm/100 mL) | 1.400 | [1] |
| Sylgard | 1.430 | [65] |
| Polyacrylamide (PA) | 1.452 | [1] |
| Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) | 1.470 | [1] |
| Blood Components and Target Analytes | Shift | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| αCL | RW | αCL | RW | ΔαCL | |RW| | |
| Water | 3.48 | 841 | 8.74 | 862 | 5.26 | 21 |
| Crypton | 4.39 | 1012 | 10.47 | 1011 | 6.08 | 01 |
| Plasma | 6.43 | 1185 | 15.63 | 1163 | 9.20 | 22 |
| Ethanol | 7.48 | 1374 | 18.42 | 1331 | 10.94 | 43 |
| Hb | 8.64 | 1576 | 26.42 | 1509 | 17.78 | 67 |
| Glucose | 9.52 | 1787 | 32.42 | 1693 | 22.90 | 94 |
| Sylgard | 14.32 | 1827 | 48.96 | 1891 | 34.64 | 64 |
| PA | 19.42 | 2087 | 63.82 | 2097 | 44.40 | 10 |
| BSA | 24.82 | 2382 | 79.84 | 2365 | 55.02 | 17 |
| Blood Components | TM pol. | TE pol. | Shift | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| αCL | RW | αCL | RW | αCL | |RW| | |
| Water | 07.12 | 982.0 | 18.11 | 991.0 | 10.99 | 09 |
| Crypton | 08.52 | 1134 | 24.12 | 1129 | 15.60 | 05 |
| Plasma | 11.63 | 1285 | 34.42 | 1277 | 22.79 | 08 |
| Ethanol | 16.47 | 1453 | 44.34 | 1439 | 27.87 | 14 |
| Hb | 22.18 | 1642 | 56.18 | 1613 | 34.00 | 29 |
| Glucose | 29.16 | 1842 | 75.11 | 1987 | 45.95 | 145 |
| Sylgard | 34.45 | 1878 | 89.18 | 2175 | 54.73 | 297 |
| PA | 39.42 | 2103 | 99.52 | 2376 | 60.10 | 273 |
| BSA | 48.12 | 2352 | 123.4 | 2619 | 75.28 | 267 |
| Modes/Year Design/Ref. | Blood Components | SW (nm RIU−1) | SA (RIU−1) | SR (RIU) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TM pol./ 2022/ EMD/ [29] | Water- Plasma | 2000 | 249.1 | 5.0 × 10−5 |
| Plasma- WBC | 3000 | 333.2 | 3.3 × 10−5 | |
| WBC-Hb | 4400 | 574.3 | 2.2 × 10−5 | |
| Hb-RBC | 12,400 | NA | 8.6 × 10−6 | |
| TM pol. TE pol./ 2022/ EMD/ [69] | Water | 1750 | 2576.38 | 5.7 × 10−5 |
| Plasma | ||||
| WBC | ||||
| Hb | ||||
| RBC | ||||
| Water | 1950 | 5078.99 | 5.1 × 10−5 | |
| Plasma | ||||
| WBC | ||||
| Hb | ||||
| RBC | ||||
| TM pol. 2022/ IMD/ [70] | RBC | 6680 | 5663 | NA |
| WBC | ||||
| Hb | ||||
| Plasma | ||||
| Water | ||||
| TE pol./ 2022/ IMD/ [70] | RBC | 6930 | 5623 | NA |
| WBC | ||||
| Hb | ||||
| Plasma | ||||
| Water | ||||
| Proposed Work TM pol. 2025/ EMD Design Kagome Model | Water | 17,100 | 71,224 | 5.8 × 10−6 |
| Crypton | 17,300 | 63,488 | 5.7 × 10−6 | |
| Plasma | 18,900 | 59,722 | 5.2 × 10−6 | |
| Ethanol | 10,100 | 52,684 | 9.9 × 10−6 | |
| Hb | 10,550 | 44,621 | 9.4 × 10−6 | |
| Glucose | 1333.33 | 36,722 | 7.5 × 10−6 | |
| Sylgard | 11,818.18 | 23,648 | 8.4 × 10−6 | |
| PA | 16,388.88 | 15,428 | 6.1 × 10−6 | |
| Proposed Work TE pol. 2025/ EMD Design Kagome Model | Water | 14,900 | 58,112 | 6.7 × 10−6 |
| Crypton | 15,200 | 51,224 | 6.5 × 10−6 | |
| Plasma | 16,800 | 43,178 | 5.9 × 10−6 | |
| Ethanol | 8900 | 38,622 | 1.1 × 10−5 | |
| Hemoglobin | 9200 | 34,411 | 1.0 × 10−5 | |
| Glucose | 6600 | 26,422 | 1.5 × 10−5 | |
| Sylgard | 9363.63 | 18,742 | 1.0 × 10−5 | |
| PA | 14,888.88 | 9848 | 6.7 × 10−6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramola, A.; Shakya, A.K.; Droby, A.; Bergman, A. Numerical Study of a Novel Kagome-Inspired Photonic Crystal Fiber-Based Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor for Detection of Blood Components and Analytical Targets. Biosensors 2025, 15, 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080539
Ramola A, Shakya AK, Droby A, Bergman A. Numerical Study of a Novel Kagome-Inspired Photonic Crystal Fiber-Based Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor for Detection of Blood Components and Analytical Targets. Biosensors. 2025; 15(8):539. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080539
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamola, Ayushman, Amit Kumar Shakya, Ali Droby, and Arik Bergman. 2025. "Numerical Study of a Novel Kagome-Inspired Photonic Crystal Fiber-Based Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor for Detection of Blood Components and Analytical Targets" Biosensors 15, no. 8: 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080539
APA StyleRamola, A., Shakya, A. K., Droby, A., & Bergman, A. (2025). Numerical Study of a Novel Kagome-Inspired Photonic Crystal Fiber-Based Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor for Detection of Blood Components and Analytical Targets. Biosensors, 15(8), 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080539






