Journal Description
Biology
Biology
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal of biological sciences, published monthly online by MDPI. The Spanish Society for Nitrogen Fixation (SEFIN) and Federation of European Laboratory Animal Science Associations (FELASA) are affiliated with Biology and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, PubAg, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Biology) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Agricultural and Biological Sciences)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 17.4 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
3.5 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.0 (2024)
Latest Articles
Comparative Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis Revealed Key Pathways and Hub Genes Related to Gill Raker Development in Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix)
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1797; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121797 - 17 Dec 2025
Abstract
The silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) is a filter-feeding fish species, characterized by significant morphological transformations in its filter-feeding apparatus, particularly the gill rakers, which are closely associated with dietary changes throughout its development. Despite the importance of these morphological innovations, the
[...] Read more.
The silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) is a filter-feeding fish species, characterized by significant morphological transformations in its filter-feeding apparatus, particularly the gill rakers, which are closely associated with dietary changes throughout its development. Despite the importance of these morphological innovations, the molecular mechanisms driving these changes remain largely unexplored. To investigate this, we employed an integrative approach combining scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and comparative transcriptomics to examine the gill rakers at five critical developmental stages (6, 15, 30, 45, and 60 days post-hatching, dph). SEM analysis revealed a structural evolution from sparse, bump-like protrusions to a dense, interlocking mesh. Simultaneously, transcriptomic analysis identified 10,184 differentially expressed genes (DEGs), which showed significant enrichment in pathways such as Focal Adhesion, ECM-Receptor Interaction, and the PI3K-Akt Signaling Pathway. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) indicated a coordinated upregulation of collagen and integrin gene families during the early developmental transition (6 vs. 15 dph), highlighting their crucial role in the formation of the sieve structure. This study reveals the molecular mechanisms of gill raker development in silver carp, providing initial insights into genetic regulation of morphology for ecological adaptation. The findings connect developmental biology, evolutionary biology, and ecology.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Genetics and Evolutionary Biology of Aquatic Organisms)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Environmental DNA Metabarcoding Reveals Divergent Patterns of Biodiversity, Community Assembly, and Environmental Sensitivity Across Taxa in Adjacent Rivers
by
Yimei Wei, Jingwei Zhang, Shuping Wang, Zhenjun Tian, Xiaolong Lin, Yongkun Yu and Yangwei Bai
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1796; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121796 - 17 Dec 2025
Abstract
The differentiated responses of biological groups to environmental change are central to river ecosystem management; however, the shared and distinct environmental selection processes that shape their spatial patterns remain understudied. We investigated two adjacent rivers with contrasting environmental conditions and applied eDNA metabarcoding
[...] Read more.
The differentiated responses of biological groups to environmental change are central to river ecosystem management; however, the shared and distinct environmental selection processes that shape their spatial patterns remain understudied. We investigated two adjacent rivers with contrasting environmental conditions and applied eDNA metabarcoding to characterize the eukaryotic plankton and fish communities. The alpha diversity showed no significant river-to-river difference for either group, but beta diversity differed strongly, indicating high spatial turnover. Both groups exhibited distance–decay relationships, which were stronger in plankton, whose community assembly was mainly stochastic; in contrast, fish assembly was predominantly deterministic. Community variation in both groups was significantly associated with physical and chemical factors—electrical conductivity (EC), the potential of hydrogen (pH), water temperature (WT), dissolved oxygen (DO), chemical oxygen demand (COD), and biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5)—while plankton also responded to nutrient variables, including total phosphorus (TP), total nitrogen (TN), and ammonium nitrogen (NH4-N). Collectively, our results emphasize differential environmental selection across biological groups and provide a basis for designing targeted river restoration and water quality improvement strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Evolution, Genetics, and Conservation of Wildlife Respond to Environmental Changes)
►▼
Show Figures
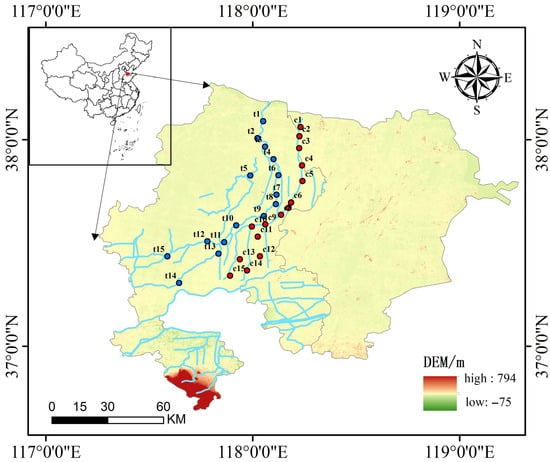
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Hospital-Based Genomic Surveillance of Klebsiella pneumoniae: Trends in Resistance and Infection
by
Erica Olund-Matos, Ricardo Franco-Duarte, André Santa-Cruz, Maria Nogueira, Margarida Correia-Neves, Diana Lopes, Rui Jorge Silva, Margarida Ribeiro Araújo, Inês Monteiro Araújo, Ana Filipa Martins, Carolina Maia Nogueira, Alberta Faustino, Pedro G. Cunha, Pedro Soares and Teresa Rito
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1795; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121795 - 16 Dec 2025
Abstract
Klebsiella pneumoniae (Kp) is a leading cause of hospital-acquired infections representing a growing threat driven by emerging multidrug resistance (MDR) and hypervirulence. In this study, we aim to characterise the genomic and epidemiological landscape of Kp in a Portuguese regional hospital (Braga) lacking
[...] Read more.
Klebsiella pneumoniae (Kp) is a leading cause of hospital-acquired infections representing a growing threat driven by emerging multidrug resistance (MDR) and hypervirulence. In this study, we aim to characterise the genomic and epidemiological landscape of Kp in a Portuguese regional hospital (Braga) lacking prior genomic data. We performed whole-genome sequencing of 115 Kp isolates collected from colonisation and infection cases. Phylogenetic, resistance, and virulence profiles were integrated with clinical and epidemiological data. Genomic analysis revealed high diversity, with 83.5% of isolates forming evolutionary clusters. Several novel sequence types (STs), as ST2623 and ST1562, were detected for the first time in Portugal to our knowledge. ST45, uncommonly associated with carbapenem resistance, emerged as dominant with multiple blaKPC-3-positive isolates. Results suggest active transmission of carbapenem resistance genes. One hypervirulent carbapenem-resistant ST13 warrants careful surveillance. Virulence-associated yersiniabactin was common (66.9%) but other hypervirulence loci were rare. Epidemiologically, MDR-Kp was associated with older hospitalised patients with prior antibiotic use and invasive procedures, while community-acquired infections were genetically diverse and affected younger patients with comorbidities. An unusually low number of respiratory infections was observed, likely reflecting strict COVID-19 mitigation measures. Although widespread dissemination of hypervirulent or MDR clones was not evident, the emergence of high-risk lineages and the detection of ongoing gene transmission episodes underscore the need for ongoing genomic surveillance. Immediate mitigation strategies could include reducing device use and hospital transfers, given the high prevalence of colonisation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Microbiology)
►▼
Show Figures
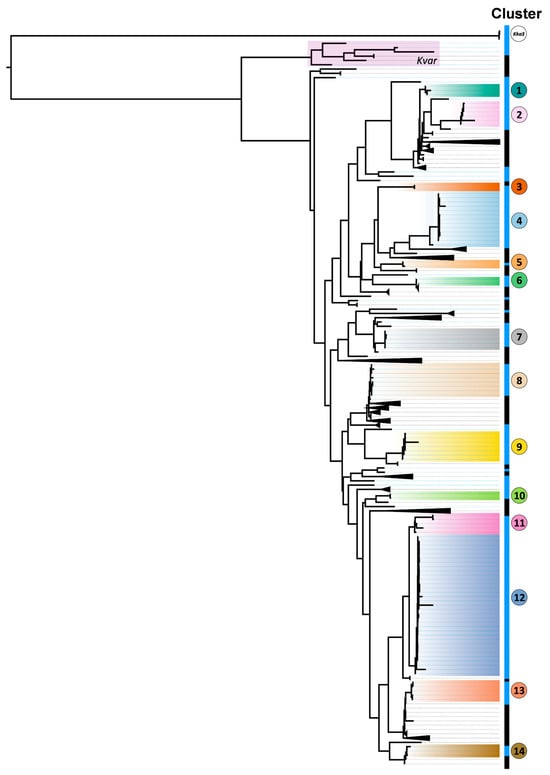
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Complete Mitochondrial Genomes of Spotted Forest Musk Deer (Moschus berezovskii) from Huanglong Mountain, Shaanxi, China, and Phylogenetic Analysis of Moschidae
by
Kuo Sun, Xiao Tan, Lei Zhang, Ying Dai, Kun Bian, Feiran Li, Lijuan Suo, Xiaojuan Du, Chao Yang and Jie Tang
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1794; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121794 - 16 Dec 2025
Abstract
Musk deer (Moschidae), a primitive lineage within Ruminantia, are distributed across East Asia and have long been of interest in molecular phylogenetic research. The spotted forest musk deer from Huanglong (HL) Mountain in Shaanxi, China, has long been morphologically classified as Moschus moschiferus
[...] Read more.
Musk deer (Moschidae), a primitive lineage within Ruminantia, are distributed across East Asia and have long been of interest in molecular phylogenetic research. The spotted forest musk deer from Huanglong (HL) Mountain in Shaanxi, China, has long been morphologically classified as Moschus moschiferus (Siberian musk deer). However, its true taxonomic status has remained uncertain due to the lack of comprehensive molecular evidence. Moreover, studies on mitochondrial genome (mitogenome) variation within Moschidae, particularly at the intraspecific level, remain limited. To date, few phylogenetic analyses of Moschidae have incorporated all available complete mitochondrial genomes from public databases. In this study, we sequenced and assembled the complete mitogenomes of two spotted musk deer individuals from Huanglong Mountain, Shaanxi, China, and identified them as M. berezovskii (forest musk deer) by phylogenetic analysis. All available complete mitochondrial genomes of Moschidae were also included in the phylogenetic reconstruction. The average complete mitogenome length of M. berezovskii distributed in HL was 16,355 bp, and comprises 13 protein-coding genes (PCGs), two ribosomal RNA genes, and 22 transfer RNA genes. Phylogenetic analysis and genetic distance indicate that the taxonomic identity of the HL Mountain population as M. berezovskii supports the monophyly of M. berezovskii and provides a robust phylogenetic framework for clarifying evolutionary relationships within the family.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Genetic Variability within and between Populations)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Unraveling a 150-Year-Old Enigma: Psalidodon rivularis (Acestrorhamphidae: Acestrorhampinae), a Species Complex or a Polymorphic Species?
by
Igor Henrique Rodrigues-Oliveira, Priscila Martins de Assis, Luiz Guilherme Pereira Pimentel, Rafael Augusto Silva Soares, Iuri Batista da Silva, Renan Rodrigues Rocha, Fabiano Bezerra Menegidio, Rubens Pasa and Karine Frehner Kavalco
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1793; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121793 - 16 Dec 2025
Abstract
Psalidodon rivularis, a fish endemic to the São Francisco River Basin and known as “piaba do córrego,” has long been regarded as a widely distributed species complex, exhibiting remarkable morphological and cytogenetic variation, even in sympatry. This study aims to determine whether
[...] Read more.
Psalidodon rivularis, a fish endemic to the São Francisco River Basin and known as “piaba do córrego,” has long been regarded as a widely distributed species complex, exhibiting remarkable morphological and cytogenetic variation, even in sympatry. This study aims to determine whether P. rivularis represents a single polymorphic species or a group of cryptic species. We analyzed meristic, morphometric, and karyotypic data from 419 specimens identified as P. rivularis, as well as from the related species Astyanax turmalinensis and Hyphessobrycon santae. Additionally, we inferred the phylogeny of the group using NGS data from 25 individuals, incorporating both mitochondrial and nuclear genomic sequences. Our integrative results support the recognition of at least five distinct species within the P. rivularis complex. The true P. rivularis (called morphotype 1) has 46 chromosomes, while the others have 50 and differ in both morphology and distribution. One of these corresponds to Psalidodon santae comb. nov.—which includes A. turmalinensis as a junior synonym—and three others are newly described species. These findings clarify the diversity of fishes in the São Francisco River Basin and highlight the importance of conserving its unique freshwater ecosystems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Population Genomics in Biodiversity Conservation in the Neotropics)
►▼
Show Figures
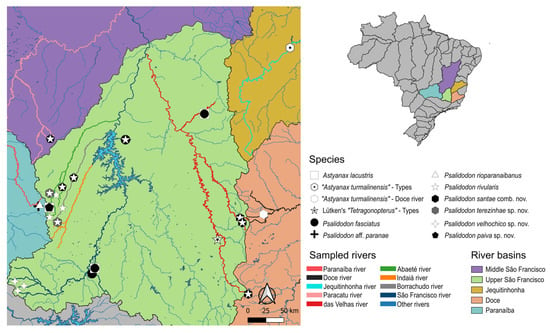
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Malaria Parasite Cell Classification Using Transfer Learning with State-of-the-Art CNN Architectures
by
Azhar Ali Laghari, Wazir Muhammad, Mudasar Latif Memon, Ayaz Hussain and Akash Kumar
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1792; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121792 - 16 Dec 2025
Abstract
Malaria remains a critical global health challenge for doctors and healthcare practitioners, particularly clinicians involved in initial treatment. Inaccurate diagnosis of malaria-infected cells often leads to delayed or inappropriate treatment, increasing the risk of severe complications or death. Traditional microscopic diagnosis is time-consuming
[...] Read more.
Malaria remains a critical global health challenge for doctors and healthcare practitioners, particularly clinicians involved in initial treatment. Inaccurate diagnosis of malaria-infected cells often leads to delayed or inappropriate treatment, increasing the risk of severe complications or death. Traditional microscopic diagnosis is time-consuming and requires expert skills, resulting in variability and inconsistency in results. These challenges are further complicated by the complexity of malaria symptoms, which overlap with other febrile illnesses, making clinical diagnosis unreliable without laboratory confirmation. To address these challenges, this study explores deep-learning-based approaches, particularly leveraging state-of-the-art pretrained convolutional neural network (CNN) models, for automated malaria parasite detection and classification from microscopic blood smear images. Transfer learning is an effective approach to handling issues such as limited labeled data, time-consuming training, and domain-specific variations in medical image classification. By leveraging pretrained models trained on large-scale datasets like ImageNet, transfer learning enables the reuse of learned features, significantly accelerating the adaptation process for malaria detection and other medical imaging tasks. We used eight pretrained models for malaria parasite classification such as VGG16, VGG19, Inception-v3, ResNet-18, ResNet-34, ResNet-50, ResNet-101, and Xception. In particular, ResNet-50 and ResNet-101 achieved accuracies of approximately 89%, respectively, while Xception reached around 88% accuracy. In comparison, VGG-16 achieved a lower overall accuracy of about 80% due to a recall trade-off despite high precision. These metrics highlight meaningful improvements over simpler architectures and validate the efficacy of our transfer learning approach for automated malaria detection. The proposed models were fine-tuned on extensive labeled datasets comprising parasitized and uninfected cells. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations were conducted using metrics such as precision, recall, F1-score, and support. Our experimental results demonstrate that ResNet-50, ResNet-101, and Xception exhibit strong balanced performance with higher accuracy, while VGG-16 shows a trade-off of high precision but lower recall for parasitized cells.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Hope for the Forgotten: Tackling Endemic Parasitic Diseases with New Tools and Ideas)
►▼
Show Figures
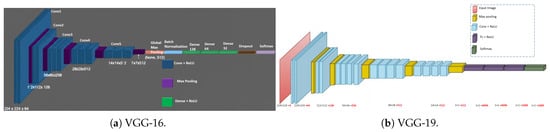
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Rumen Microbial Diversity and Metabolome Analysis Reveals the Effects of Alkaline Metal Ion Complexes on Muscle Quality of Lambs
by
Yang Zi, Yilin Yang, Mingyue Li, Yalin Li, Ziyi An, Mengjiao Liu, Chi Ma, Feng Gao and Changqing Li
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1791; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121791 - 16 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study investigated the effects of dietary supplementation with an alkaline metal ion complex (AMIC) on growth performance, meat quality, rumen microbiota, and metabolome in Hu lambs. Fifty lambs were randomly assigned to either a control group (basal diet) or an AMIC group
[...] Read more.
This study investigated the effects of dietary supplementation with an alkaline metal ion complex (AMIC) on growth performance, meat quality, rumen microbiota, and metabolome in Hu lambs. Fifty lambs were randomly assigned to either a control group (basal diet) or an AMIC group (basal diet + 0.15% AMIC) for 60 days. The results showed that AMIC significantly increased carcass weight, Longissimus dorsi area, crude protein, intramuscular fat, ash content, and meat luminosity (L*). Amino acid profiles and key flavor compounds were elevated, while off-flavor hydrocarbons were reduced. 16S rRNA sequencing revealed that AMIC altered rumen microbiota composition, enriching butyrate-producing genera such as Butyrivibrio and Saccharofermentans. Metabolomic analysis identified 398 differentially expressed metabolites, with upregulated pathways including butanoate metabolism and xylene degradation. Correlation analyses indicated strong associations between specific microbial taxa, metabolites, and meat quality traits. These findings suggest that AMIC enhances meat quality by modulating rumen microbial ecology and metabolic pathways, leading to improved nutrient deposition and flavor development. This study provides novel insights into the microbe–metabolite–muscle axis in ruminants and supports the use of AMIC as a dietary strategy for quality lamb production.
Full article
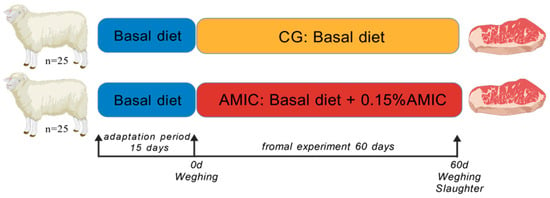
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Prospects for Development and Commercialisation of Allogeneic CAR-Based Therapies for Autoimmune Disease
by
Madeleine Osborne and John Maher
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1790; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121790 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
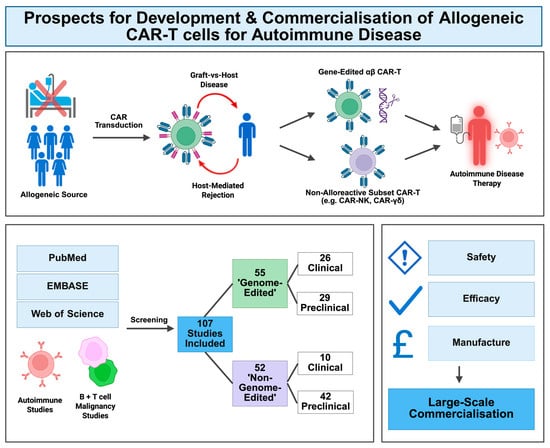
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapies represent a promising therapeutic approach for refractory autoimmune diseases. Although autologous CAR-T cells have achieved success thus far, they require expensive, individualised manufacturing, limiting their commercialisation potential. Allogeneic alternatives could overcome these scalability barriers, providing ‘off-the-shelf’ treatments,
[...] Read more.
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapies represent a promising therapeutic approach for refractory autoimmune diseases. Although autologous CAR-T cells have achieved success thus far, they require expensive, individualised manufacturing, limiting their commercialisation potential. Allogeneic alternatives could overcome these scalability barriers, providing ‘off-the-shelf’ treatments, although they raise the issues of graft-vs-host reactions and host-mediated rejection. To mitigate such risks, gene-edited αβ T cells or non-alloreactive host cells (e.g., NK cells, γδ T cells) may be used. This review evaluates evidence of the functionality and commercial potential of various allogeneic CAR-T solutions for autoimmunity. Searches were conducted of PubMed, EMBASE and Web of Science to extract clinical and preclinical studies of allogeneic CAR-T cells, for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and B or T cell malignancies. In light of the paucity of data on autoimmune disease, the latter were included to facilitate extrapolation to the autoimmune setting. A total of 107 studies were included. The available clinical outcomes of efficacy and safety, as well as preclinical key findings, are reported. Current developments and potential future improvements for safety, effectiveness and cost-effective manufacture are then discussed. The findings of this review demonstrate the promising therapeutic potential of allogeneic CAR-T for autoimmune disease, with scope for the further optimisation of safety and scalable manufacture to facilitate commercialisation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cancer Biology)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Genome-Wide Identification and Comprehensive Analysis of the GS Gene Family in Hordeum vulgare Under Low Nitrogen Stress
by
Yaping Pei, Juncheng Wang, Lirong Yao, Erjing Si, Ke Yang, Baochun Li, Yaxiong Meng, Xiaole Ma, Hong Zhang, Xunwu Shang and Huajun Wang
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1789; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121789 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
Glutamine synthetase (GS; EC 6.3.1.2) is a key enzyme for primary assimilation and re-assimilation of ammonium in higher plants. Although several GS gene families have been reported for several cereal crops, systematic studies for barley (Hordeum vulgare) under different nitrogen treatment
[...] Read more.
Glutamine synthetase (GS; EC 6.3.1.2) is a key enzyme for primary assimilation and re-assimilation of ammonium in higher plants. Although several GS gene families have been reported for several cereal crops, systematic studies for barley (Hordeum vulgare) under different nitrogen treatment conditions are still lacking. In this study, we combined genome-wide bioinformatics mining with transcriptome analysis to characterize the HvGS gene family in two different genotypes of barley (nitrogen-efficient W26 and nitrogen-sensitive W20) and their responses to low nitrogen stress. Four HvGS genes were retrieved from the barley genome and named HvGS1–HvGS4. These genes were comprehensively analyzed in terms of chromosomal distribution, physicochemical properties, subcellular localization, intron-exon structure, conserved motifs, promoter cis-acting elements, evolutionary relationships, and predicted protein–protein interactions. Leaves and roots were sampled and subjected to RNA-seq analysis at 3, 18, and 21 days of low-nitrogen stress, which revealed significant expression differences among genotypes and tissues. In W26, low nitrogen (0.4 mmol·L−1) induced synergistic expression of HvGS1 and HvGS4 and suppressed expression of plastidic HvGS2, whereas W20 up-regulated the expression of HvGS1 and HvGS3 mainly in the root system. Combined GO/KEGG enrichment analysis and metabolomic characterization of the differentially expressed genes highlighted nitrogen metabolism, glutathione turnover, and amino acid biosynthesis as key hubs in the tolerant genotypes. Our results provide a genome-wide analysis of the barley GS family and highlight HvGS1 and HvGS4 as candidate genes for functional validation toward improved nitrogen use efficiency.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Potential of Genetics and Plant Breeding in Crop Improvement)
►▼
Show Figures
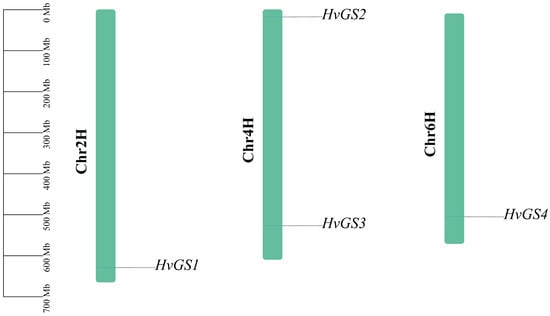
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Mechanisms of Soil Conditioner and Switchgrass in Improving Saline–Alkali Soil: A Field Study in a Semi-Arid Area
by
Yixuan Li, Qing Liu, Longfei Kang, Kaiyu Zhang, Qiang Li and Feng Ai
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1788; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121788 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
Chemical and plant-based strategies have become increasingly critical for the remediation of saline–alkali soils. However, the underlying mechanisms driving improvements in soil quality and ecological functionality remain insufficiently understood. In this study, we adopted a synergistic remediation approach that integrated multiple switchgrass (
[...] Read more.
Chemical and plant-based strategies have become increasingly critical for the remediation of saline–alkali soils. However, the underlying mechanisms driving improvements in soil quality and ecological functionality remain insufficiently understood. In this study, we adopted a synergistic remediation approach that integrated multiple switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) cultivars with a coal-based soil amendment to enhance saline–alkali land. A field experiment was conducted using five switchgrass varieties (YM-1, YM-2, YM-3, YM-4, and YM-5), each receiving a uniform application of the coal-based soil conditioner at 10 t ha−1. A traditional control group was not included in this study, as the experimental design focused on direct comparisons between varieties. Our results showed that soil ionic composition played a significant role in shaping microbial activity. Notably, we found that YM-5 treatment exhibited the highest relative soil microbial abundance (22.1%) under the condition of soil amendments. Furthermore, the YM-5 treatment significantly reduced soil Na+ content and exchangeable sodium percentage (ESP) (p < 0.05), outperforming other treatments. Compared to YM-2, the YM-5 treatment also resulted in substantial increases in soil organic carbon (SOC) and available potassium (AK), increases of 78.28% and 54.3%, respectively. In addition to enhancing physicochemical parameters, the integration of switchgrass and amendment promoted soil biological vitality. For example, the YM-2 treatment achieved a 7.4% increase in catalase (CAT) activity and a 6.3% reduction in soil pH compared to YM-3, indicating improved redox balance and acid–base regulation. Collectively, these findings provide direct empirical evidence supporting the effectiveness of switchgrass–amendment combinations in saline–alkali soil restoration. Among the tested cultivars, YM-5 demonstrated superior ecological performance and is recommended as the most suitable genotype for saline–alkali soil amelioration when used in conjunction with coal-based amendments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multi-omics Approaches in Agricultural Crops to Unravel Responses to Environmental Stresses and Advance Sustainable Agriculture)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Impact of Neurotoxin Proteins Trafficked by Primary Cilia and Extracellular Vesicles in Neurodegenerative Diseases
by
Riley Danna, Soham Kondle, Orr Amar, Michayla Mabourakh, Gratiana Chen, Wala B. Fadol and Ashraf M. Mohieldin
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1787; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121787 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs), including Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Parkinson’s Disease (PD), and Huntington’s Disease (HD), share pathologic mechanisms including oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and protein aggregation. However, they differ in age of onset and clinical progression. Emerging evidence highlights primary cilia (PC) as a
[...] Read more.
Neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs), including Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Parkinson’s Disease (PD), and Huntington’s Disease (HD), share pathologic mechanisms including oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and protein aggregation. However, they differ in age of onset and clinical progression. Emerging evidence highlights primary cilia (PC) as a key regulator of neuronal aging and the progression of these diseases. Dysfunctional PC may impair key signaling pathways, such as Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) and Wnt, promote oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage, and epigenetic instability. PC may also influence intercellular communication by regulating the biogenesis of exosomes and modulating tunneling nanotube (TNT) formation, both of which propagate toxic proteins between neurons. Mechanistically, the regulation of ciliary length is disrupted in AD, which leads to ciliary dysfunction that interferes with signaling pathways and promotes the aggregation of amyloid-beta. This amyloid-beta is then propagated through TNTs and exosomes, spreading neuronal damage. In PD, the accumulation of alpha-synuclein (α-syn) also impairs cilia function, thereby compromising the cell’s response to oxidative stress. This results in the formation of abnormal TNTs and defective exosome-mediated clearance, ultimately contributing to neurodegeneration. Similarly, the mutant huntingtin protein aggregates within primary cilia in HD, morphologically disrupting them by obstructing intraflagellar transport. Damaged cilia are also associated with increased TNT formation and the exosomal release of toxic proteins, which leads to mitochondrial and epigenetic instability, ultimately promoting neuronal aging. Together, targeting ciliary function and its downstream regulation of TNTs and exosomes may provide a novel approach for slowing or halting disease progression across neurodegenerative diseases.
Full article
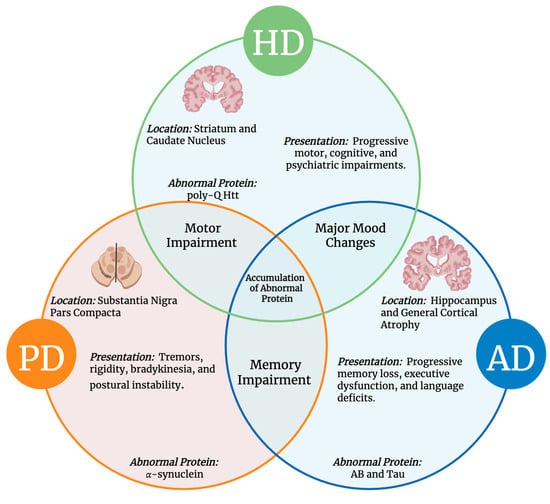
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Isolation and Probiotic Functions of Bacillus subtilis and Its Inhibitory Effects on Colitis
by
Ningning Guan, Chang Li, Wei Liu, Qiong Wu, Jiajia Zhu, Ting Gao, Hui Song, Rui Guo, Fangyan Yuan, Yongxiang Tian, Keli Yang and Danna Zhou
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1786; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121786 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
Bacillus subtilis, as a probiotic feed additive, has been increasingly applied in livestock and poultry farming. In the present study, the environmental tolerance of a strain of Bacillus subtilis, isolated from a goat farm, was investigated. This article conducts a series
[...] Read more.
Bacillus subtilis, as a probiotic feed additive, has been increasingly applied in livestock and poultry farming. In the present study, the environmental tolerance of a strain of Bacillus subtilis, isolated from a goat farm, was investigated. This article conducts a series of experiments on the obtained strains. The results demonstrated that the isolated strain exhibits strong tolerance to high temperatures, acidic and alkaline conditions, and high concentrations of bile salts. Furthermore, its self-aggregation rate exceeded 60% after 24 h. Whole-genome sequencing revealed that the genomes of the isolated strains were functionally annotated, identifying genes associated with amino acid metabolism, vitamin biosynthesis, and other metabolic pathways. Based on this genomic analysis, the present study further evaluated the anti-inflammatory effects of a Bacillus subtilis strain isolated in a murine model of colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium (DSS). The analyses revealed that the DSS-treated group exhibited significantly reduced expression of intestinal tight junction proteins ZO-1 and Occludin, along with elevated expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, compared to the PBS control group. Following oral administration of 1 × 108 CFU/mL Bacillus subtilis isolated strain suspension, the DSS-treated mice showed increased expression of ZO-1 and Occludin and decreased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines. These results indicate that the isolated strain of Bacillus subtilis has a protective effect against colitis and demonstrates probiotic potential.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Microbiology)
►▼
Show Figures
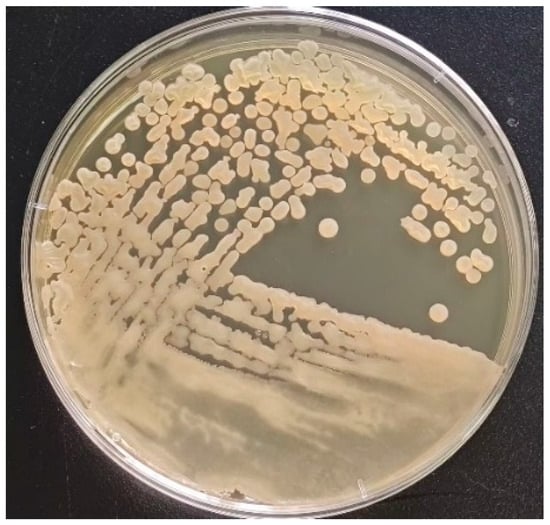
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Seasonal Variation of Shoreline Fish Assemblages at Two Stations in the Southern Branch of the Yangtze River Estuary
by
Bo Feng, Guangpeng Feng, Xuzhe Gu, Ju Yang and Qingbo Zhang
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1785; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121785 - 14 Dec 2025
Abstract
The Yangtze River Estuary is one of the most productive estuarine ecosystems in the western Pacific, supporting diverse fish communities that sustain ecosystem functioning. This study investigated the seasonal patterns and community structure of intertidal fish assemblages to provide a baseline for future
[...] Read more.
The Yangtze River Estuary is one of the most productive estuarine ecosystems in the western Pacific, supporting diverse fish communities that sustain ecosystem functioning. This study investigated the seasonal patterns and community structure of intertidal fish assemblages to provide a baseline for future habitat assessments. Seasonal surveys conducted from May to December 2024 recorded 47 fish species belonging to 10 orders, 18 families, and 37 genera. Cyprinidae contributed the highest proportion of species (42.55%). Dominant species identified by the index of relative importance-including Cynoglossus gracilis, Coilia nasus, and Lateolabrax japonicus—characterized the seasonal assemblage structure. The assemblages were dominated by sedentary species (82.98%), and demersal fishes accounted for 48.94% of the species. Carnivorous taxa (57.45%) dominated the trophic guilds. Diversity indices indicated moderate diversity (H′: 1.797–2.441; C: 0.788–0.892; D: 1.724–4.770; J′: 0.6318–0.8642). Similarity analysis based on Jaccard’s index (Cj) showed the highest overlap between spring and summer (Cj = 0.5000) and the lowest between spring and winter (Cj = 0.1714); spring–autumn and summer–autumn were approximately 0.30, indicating moderate overlap. ABC curves yielded slightly negative W values in spring and summer and positive values in autumn and winter (W = −0.066 to 0.276), indicating moderately disturbed assemblages in spring–summer and less disturbed communities in autumn–winter. Overall, the study provides a seasonal baseline of intertidal fish assemblages in nearshore waters of the southern branch of the Yangtze River Estuary, which can provide useful ecological context for future assessments of nursery and feeding habitats of juvenile Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Young Researchers in Conservation Biology and Biodiversity)
►▼
Show Figures
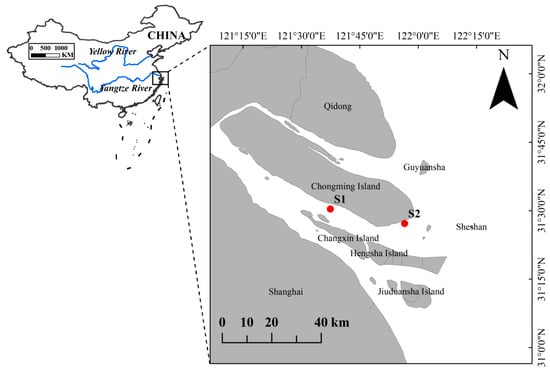
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Rethinking the Evolution of Tubulin Polymerization Promoting Proteins
by
Ferenc Orosz
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1784; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121784 - 14 Dec 2025
Abstract
TPPP (tubulin polymerization promoting protein)-like proteins are found throughout the living world. The individual members of this protein family are distinguished according to how many times and how completely their characteristic structural element, the p25alpha domain, is found in them. Phylogenomic occurrences of
[...] Read more.
TPPP (tubulin polymerization promoting protein)-like proteins are found throughout the living world. The individual members of this protein family are distinguished according to how many times and how completely their characteristic structural element, the p25alpha domain, is found in them. Phylogenomic occurrences of the members of the family differ from each other. Animals, fungi, algae, and various groups of unicellular organisms have their characteristic proteins. The two phylogenomic multi-supergroups, Opimoda+ and Diphoda+, show very different patterns in the occurrence of TPPP types. By using BLAST search in protein and nucleotide databases, we found that the previously known phylogenomic distribution is not strictly true, e.g., fungal type TPPPs are not only found in fungi. We primarily analyzed the Opisthokonta clade but also examined broader relationships. It was confirmed that the occurrence of TPPPs/genes is linked to the presence of the eukaryotic flagellum. A TPPP that contains the entire p25alpha domain twice and occurs only in Opisthokonta was identified. We also identified a TPPP in choanoflagellates and in the uncertainly classified Opisthokonta Tunicaraptor unikontis, which was previously known only in the Diphoda+ clade. On the other hand, we found an Opisthokonta (Opimoda+)-specific TPPP in a Heterolobosea (Diphoda+). Based on these results, we need to rethink the evolutionary history of TPPPs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Evolutionary Biology)
►▼
Show Figures
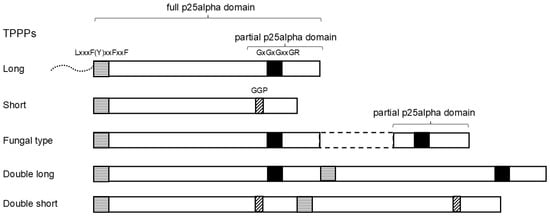
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Genome-Wide Identification of PGRP Gene Family and Its Role in Dendrolimus kikuchii Immune Response Against Bacillus thuringiensis Infection
by
Yanjiao Tang, Zizhu Wang, Qiang Guo, Xue Fu, Ning Zhao, Bin Yang and Jielong Zhou
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1783; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121783 - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Peptidoglycan recognition proteins (PGRPs) are conserved pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that play key roles in insect innate immunity by binding bacterial peptidoglycan (PGN) and activating downstream signaling pathways. The Dendrolimus kikuchii, a major defoliator of coniferous forests in southern China, has incompletely
[...] Read more.
Peptidoglycan recognition proteins (PGRPs) are conserved pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that play key roles in insect innate immunity by binding bacterial peptidoglycan (PGN) and activating downstream signaling pathways. The Dendrolimus kikuchii, a major defoliator of coniferous forests in southern China, has incompletely characterized immune defenses. This study systematically identified the PGRP gene family in D. kikuchii based on genome-wide data, identifying 10 PGRP genes with typical PGRP/Amidase_2 conserved domains, including 6 PGRP-S proteins and 4 PGRP-L proteins. Additionally, to further investigate the evolutionary relationships of these PGRP genes, a maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree was constructed using PGRP amino acid sequences from 6 different insect species, along with the 10 PGRP amino acid sequences from D. kikuchii. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that the DkikPGRP genes of D. kikuchii are distributed across distinct evolutionary branches and share high homology with PGRP genes from other insects, suggesting a close evolutionary relationship between the PGRP genes of D. kikuchii and those of other insect species. Transcriptome profiling revealed that DkikPGRP-S1, -S2, -S3, -S4, and -S5 were upregulated in the midgut, fat body, and hemolymph after Bt infection, showing tissue- and time-specific immune responses. Functional assays using siRNA knockdown demonstrated distinct roles of DkikPGRP-S4 and DkikPGRP-S5: DkikPGRP-S5 mainly promoted antimicrobial peptide (AMP) expression, including attacin, lebocin, lysozyme, and cecropin, whereas DkikPGRP-S4 showed a complex regulatory pattern, enhancing lebocin and lysozyme but suppressing attacin without affecting gloverin or cecropin. Silencing either gene significantly increased larval mortality upon Bt challenge. These results highlight the specialized immune regulatory functions of PGRPs in D. kikuchii, provide new insights into host–pathogen interactions, and suggest potential molecular targets for sustainable pest management strategies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Contrasting Evolutionary Trajectories: Differential Population Dynamics and Gene Flow Patterns in Sympatric Halimeda discoidea and Halimeda macroloba
by
Yichao Tong, Wei Liu, Yuqing Sun, Jinlin Liu and Qunhui Yang
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1782; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121782 - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Calcareous tropical green macroalgae of the genus Halimeda are key reef-builders, yet the drivers of their diversification and population dynamics remain poorly understood. This study analyzed the species diversity of Halimeda in the Xisha (Paracel) Islands based on tufA gene sequences, focusing
[...] Read more.
Calcareous tropical green macroalgae of the genus Halimeda are key reef-builders, yet the drivers of their diversification and population dynamics remain poorly understood. This study analyzed the species diversity of Halimeda in the Xisha (Paracel) Islands based on tufA gene sequences, focusing on evaluating the genetic diversity, population structure, and historical dynamics of two widespread species—Halimeda discoidea and Halimeda macroloba. The results indicate new records of Halimeda cylindracea and Halimeda cf. stuposa in the Xisha (Paracel) Islands. More importantly, H. discoidea and H. macroloba exhibited significantly different evolutionary histories. Specifically, H. discoidea showed a highly fragmented population structure, restricted gene flow, and a multimodal mismatch distribution, suggesting a complex historical process or long-term stability. In contrast, H. macroloba exhibited lower population differentiation, extensive gene flow, and non-significant neutrality test results, indicating long-term demographic stability without recent, drastic population events. Further validation based on gene flow analysis and divergence time estimation revealed that the lineage divergence of H. discoidea is older, while H. macroloba represents a lineage with a relatively younger evolutionary origin restricted to the Indo-Pacific region. This striking dichotomy clearly illustrates the interplay between intrinsic species-specific traits (e.g., dispersal capacity) and extrinsic historical factors (e.g., paleo-oceanographic events), leading to contrasting evolutionary outcomes among widespread marine taxa. By elucidating how differing evolutionary histories influence patterns of genetic diversity, this study provides a predictive framework for evaluating the resilience and guiding conservation priorities for critical marine calcifiers in the context of rapid environmental change.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Microbial Drivers of Aquatic Ecosystem Function: From Genomes to Biogeochemical Cycles)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Toxic Impacts of Trichlorfon on Tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum): Molecular Evidence of Oxidative, Metabolic and Apoptotic Stress
by
Hallana Cristina Menezes da Silva, Daniele Aparecida Matoso, André Gentil da Silva, Ana Lúcia Silva Gomes, Wallice Paxiúba Duncan and Roberto Ferreira Artoni
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1781; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121781 - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: The intensification of aquaculture has led to increased use of chemical agents, such as trichlorfon, for controlling parasitic infections in farmed fish. While effective, this organophosphate compound may exert toxic effects even at sublethal concentrations, posing risks to economically important species such
[...] Read more.
Background: The intensification of aquaculture has led to increased use of chemical agents, such as trichlorfon, for controlling parasitic infections in farmed fish. While effective, this organophosphate compound may exert toxic effects even at sublethal concentrations, posing risks to economically important species such as tambaqui (C. macropomum). This study investigated the molecular effects of trichlorfon on the expression of genes involved in stress response, energy metabolism, and apoptosis in juvenile tambaqui. Methods: Fish were exposed to two sublethal concentrations of trichlorfon (30% and 50% LC50–96 h, equivalent to 0.261 and 0.435 mg/L) for 48, 72, and 96 h. Expression levels of fkbp5, p53, pim-2, pir, me1, bbox1, and higd1a were quantified in liver tissue using qPCR. Results: fkbp5 and p53 were strongly upregulated at 48 h, indicating acute stress and genotoxic activation. me1 and pim-2 were also upregulated, reflecting activation of compensatory energy metabolism and anti-apoptotic survival pathways. bbox1 showed an early induction followed by collapse at 96 h, while higd1a and pir exhibited delayed overexpression at 96 h, suggesting mitochondrial hypoxia and inflammation. Conclusions: Trichlorfon triggers a multifaceted toxic response characterized by initial activation of compensatory pathways (stress response, antioxidant defense, and anti-apoptotic mechanisms) followed by late-phase metabolic collapse, mitochondrial hypoxia, and inflammation, with both time- and dose-dependent effects. These findings demonstrate that even sublethal concentrations disrupt hepatic homeostasis and support the use of these genes as molecular biomarkers for environmental monitoring in aquaculture.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Metabolic and Stress Responses in Aquatic Animals)
►▼
Show Figures
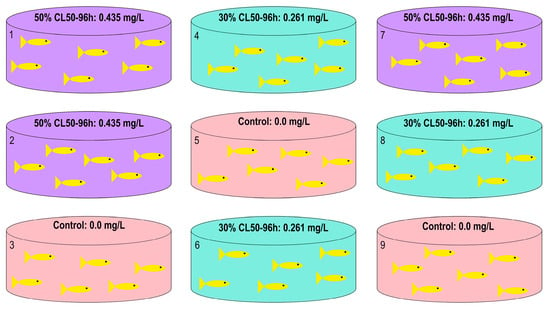
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Life History of the Giant Looper Moth Ascotis selenaria (Lepidoptera: Geometridae) in Eucalyptus Plantations and the Effect of Adult Mating Age on Fecundity
by
Shuai Yuan, Mengjun Yang, Rijiao He, Bin Liu, Sijia Wang, Zhende Yang and Ping Hu
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1780; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121780 - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
Ascotis selenaria has recently shifted hosts to become a major defoliator in Southern China’s eucalyptus plantations. To facilitate Integrated Pest Management (IPM), we investigated the genetic origins, life history, and reproductive bio-ecology of this population. Mitochondrial COI analysis revealed that the Southern China
[...] Read more.
Ascotis selenaria has recently shifted hosts to become a major defoliator in Southern China’s eucalyptus plantations. To facilitate Integrated Pest Management (IPM), we investigated the genetic origins, life history, and reproductive bio-ecology of this population. Mitochondrial COI analysis revealed that the Southern China population aligns phylogenetically with South Asian clades, distinct from Northern China populations. Life table analysis confirmed six larval instars, with the final instar exhibiting exponential consumption, accounting for 79.68% of total food intake. Reproductive assays demonstrated significant protandry and a novel bimodal ovarian maturation rhythm (peaking on days 3 and 7). Crucially, female fecundity declined sharply after a 3-day mating delay, and mating with older males severely reduced egg hatchability in older females. These findings suggest that control thresholds must shift from visual damage assessment to monitoring early-instar larvae (1st–3rd instars). Furthermore, the combination of protandry and reproductive sensitivity implies that mating disruption strategies must be deployed prior to male emergence. This study provides the biological basis for a dual-window IPM framework targeting this emerging pest.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Ecological Regulation of Forest and Grassland Pests)
►▼
Show Figures
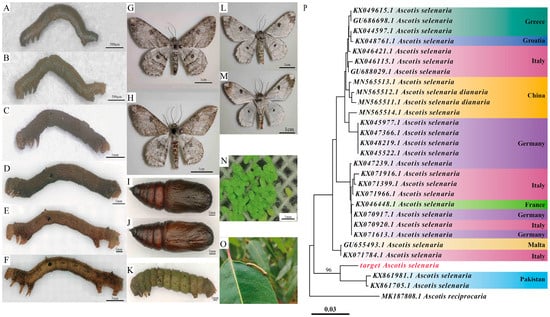
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Stability Analysis of a Nonautonomous Diffusive Predator–Prey Model with Disease in the Prey and Beddington–DeAngelis Functional Response
by
Yujie Zhang, Tao Jiang, Changyou Wang and Qi Shang
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1779; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121779 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Based on existing models, this paper incorporates some key ecological factors, thereby obtaining a class of eco-epidemiological models that can more objectively reflect natural phenomena. This model simultaneously integrates disease dynamics within the prey population and the Beddington–DeAngelis functional response, thus achieving an
[...] Read more.
Based on existing models, this paper incorporates some key ecological factors, thereby obtaining a class of eco-epidemiological models that can more objectively reflect natural phenomena. This model simultaneously integrates disease dynamics within the prey population and the Beddington–DeAngelis functional response, thus achieving an organic combination of ecological dynamics, epidemic transmission, and spatial movement under time-varying environmental conditions. The proposed framework significantly enhances ecological realism by simultaneously accounting for spatial dispersal, predator–prey interactions, disease transmission within prey species, and seasonal or temporal variations, providing a comprehensive mathematical tool for analyzing complex eco-epidemiological systems. The theoretical results obtained from this study can be summarized as follows: Firstly, the existence and uniqueness of globally positive solutions for any positive initial data are rigorously established, ensuring the well-posedness and biological feasibility of the model over extended temporal scales. Secondly, analytically tractable sufficient conditions for uniform population persistence are derived, which elucidate the mechanisms of species coexistence and biodiversity preservation even under sustained epidemiological pressure. Thirdly, by employing innovative applications of differential inequalities and fixed point theory, the existence and uniqueness of a positive spatially homogeneous periodic solution in the presence of time-periodic coefficients are conclusively demonstrated, capturing essential rhythmicities inherent in natural systems. Fourthly, through a sophisticated combination of the upper and lower solution method for parabolic partial differential equations and Lyapunov stability theory, the global asymptotic stability of this periodic solution is rigorously established, offering a powerful analytical guarantee for long-term predictive modeling. Beyond theoretical contributions, these research findings provide actionable insights and quantitative analytical tools to tackle pressing ecological and public health challenges. They facilitate the prediction of thresholds for maintaining ecosystem stability using real-world data, enable the analysis and assessment of disease persistence in spatially structured environments, and offer robust theoretical support for the planning and design of wildlife management and conservation strategies. The derived criteria support evidence-based decision-making in areas such as controlling zoonotic disease outbreaks, maintaining ecosystem stability, and mitigating anthropogenic impacts on ecological communities. A representative numerical case study has been integrated into the analysis to verify all of the theoretical findings. In doing so, it effectively highlights the model’s substantial theoretical value in informing policy-making and advancing sustainable ecosystem management practices.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Whole-Genome Resequencing Analysis Reveals the Local Ancestry and Selection of Kongshan Cattle
by
Mengmeng Bai, Kai Yang, Xiaohui Ma, Chenqi Bian, Wei Wang, Jun Yi, Ningbo Chen, Chuzhao Lei and Xiaoting Xia
Biology 2025, 14(12), 1778; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121778 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Kongshan cattle is an indigenous breed from Sichuan Province, China, characterized by their excellent meat quality, high fertility, strong disease resistance, and remarkable environmental adaptability. However, their genomic diversity has not been systematically studied. In this work, we performed whole-genome sequencing of 30
[...] Read more.
Kongshan cattle is an indigenous breed from Sichuan Province, China, characterized by their excellent meat quality, high fertility, strong disease resistance, and remarkable environmental adaptability. However, their genomic diversity has not been systematically studied. In this work, we performed whole-genome sequencing of 30 Kongshan cattle from a breeding farm and integrated these data with 113 representative commercial and indigenous cattle breeds worldwide to investigate their population structure and genetic diversity. We further analyzed the ancestral contributions to the development of the breed. The population structure revealed that Kongshan cattle possess four types of ancestral components: East Asian indicine (0.5974), East Asian taurine (0.3464), European taurine (0.0483), and Indian indicine (0.0079). The population also exhibits high nucleotide diversity, second only to pure East Asian indicine cattle. We inferred the ancestry of each variable site in the genome and, in combination with integrated haplotype score analysis, identified candidate genes related to meat quality (ME1, ENPP2, GPD2, PDZRN4, and TMTC2), immunity (MCM6, MAP3K6, PIP4K2A, CDC6, CDC25B, PTAFR, ZC3H10, and NEK6), and environmental adaptability (KCNJ15, BECN1, AOC2, DUSP5, and ST3GAL4). These findings provide valuable insights into the evolutionary history and ancestral origins of Kongshan cattle and contribute to the broader understanding, conservation, and sustainable utilization of indigenous Chinese cattle genetic resources.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Bioinformatics)
►▼
Show Figures
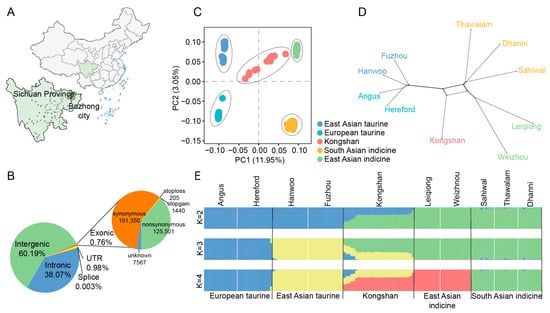
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Biology Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Microbiology, Bioengineering, Biology, Environments, Microorganisms
Environmental Bioengineering and Geomicrobiology
Topic Editors: Xian-Chun Zeng, Deng LiuDeadline: 20 December 2025
Topic in
Biology, Biomolecules, Cancers, Cells, IJMS
RNAs and Phase Separation Phenomena
Topic Editors: Ana Lúcia Leitão, Afshin Beheshti, Francisco J. EnguitaDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Agrochemicals, Agronomy, Insects, IJMS, Marine Drugs, Toxins, Agriculture, Biology
Research on Natural Bioactive Product-Based Pesticidal Agents—2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Min Lv, Hui XuDeadline: 28 February 2026
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Toxics, IJERPH, Biology, Cancers, Radiation
Disease Risks from Environmental Radiological Exposure
Topic Editors: Valentina Venuti, Francesco CaridiDeadline: 1 April 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Biology
Computational Modeling of Drug Delivery
Guest Editors: Dingding Han, Arezoo M. ArdekaniDeadline: 25 December 2025
Special Issue in
Biology
Organ-on-a-Chip: Biology Meets Technology
Guest Editor: Julia MantajDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Biology
Arthropods as Vectors of Human and Animal Pathogens: Vector Ecology and Disease Transmission
Guest Editor: Panpim ThongsripongDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Biology
Living Resources of the Deep Sea: Biological Profiles and Environmental Linkages
Guest Editors: Zuozhi Chen, Longshan LinDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Biology
Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria: Mechanisms and Applications
Collection Editor: Bernard R. Glick
Topical Collection in
Biology
Feature Papers in Microbial Biology
Collection Editors: Pabulo Rampelotto, Juan Carlos Gutiérrez
Topical Collection in
Biology
Abiotic Stress in Plants and Resilience: Recent Advances
Collection Editors: Chengliang Sun, Weiwei Zhou
Topical Collection in
Biology
Gap Junctions and Connexins in Physiology, Pharmacology and Disease
Collection Editors: Yi Zhu, Sebastian Curti, Xinbo Li












