CGF-Conditioned Medium Modulates Astrocytic Differentiation and Invasiveness in U87MG Glioblastoma Cells
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of CGF and Conditional Medium
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
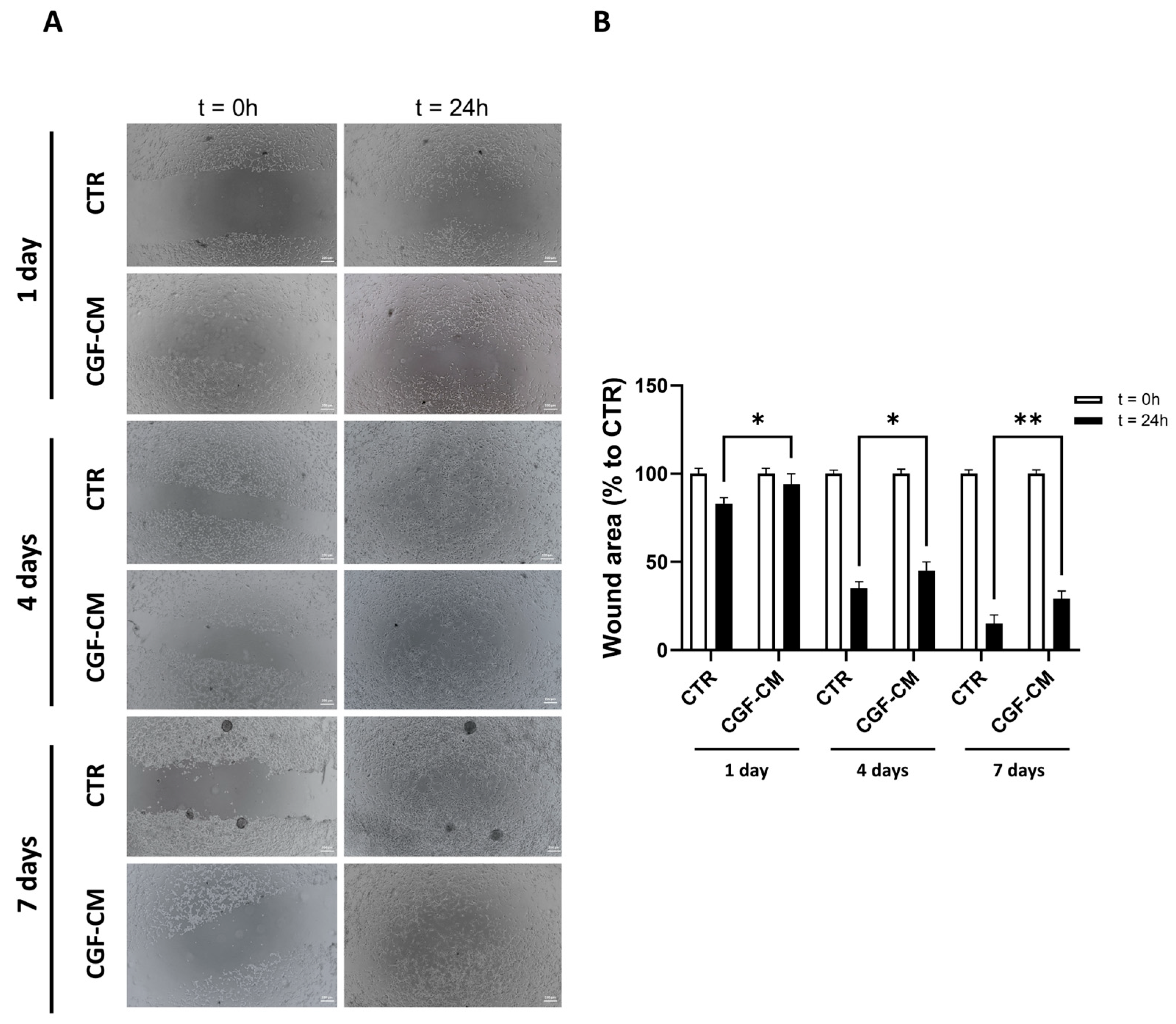
2.4. Scratch Wound Healing Assay
2.5. Real-Time PCR
2.6. Cell Counting and Growth Curve Protocol
2.7. Comet Assay
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. Immunohistochemistry and Hematoxylin-Eosin Staining
2.10. Dapi Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
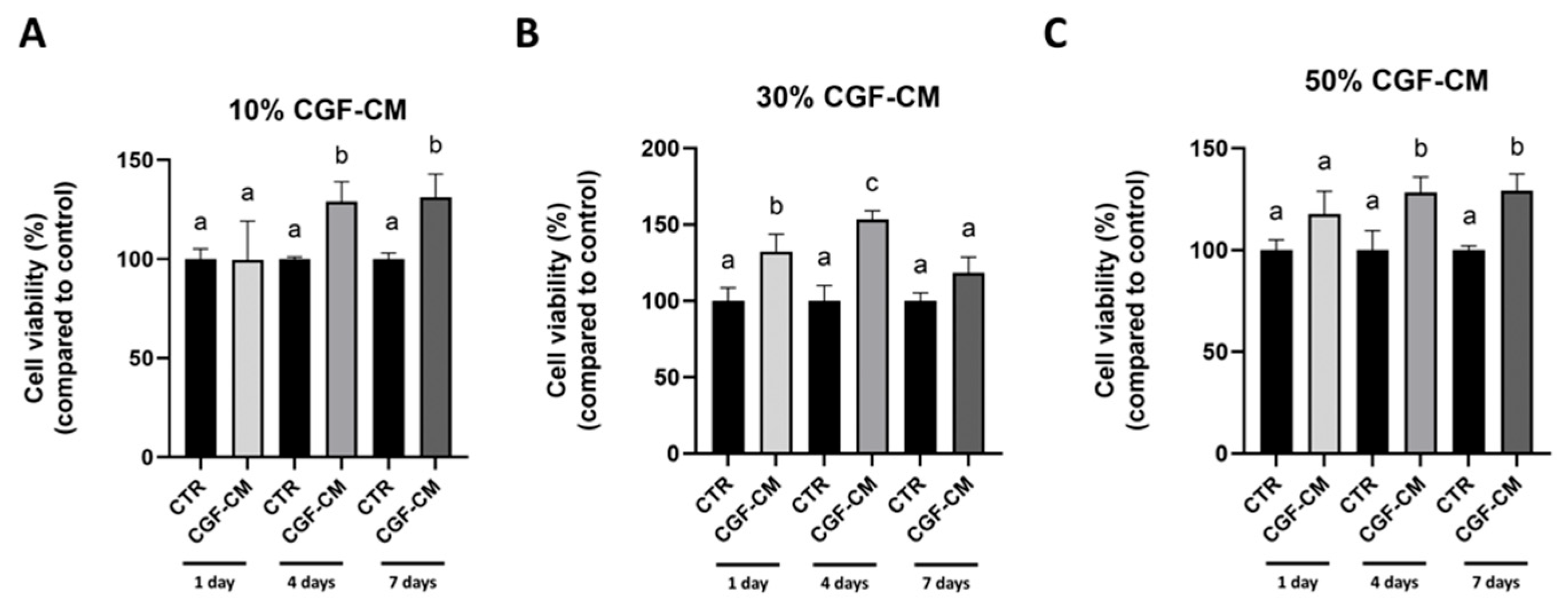
3.1. CGF-CM Modulates U87MG Cell Viability in a Concentration- and Time-Dependent Manner
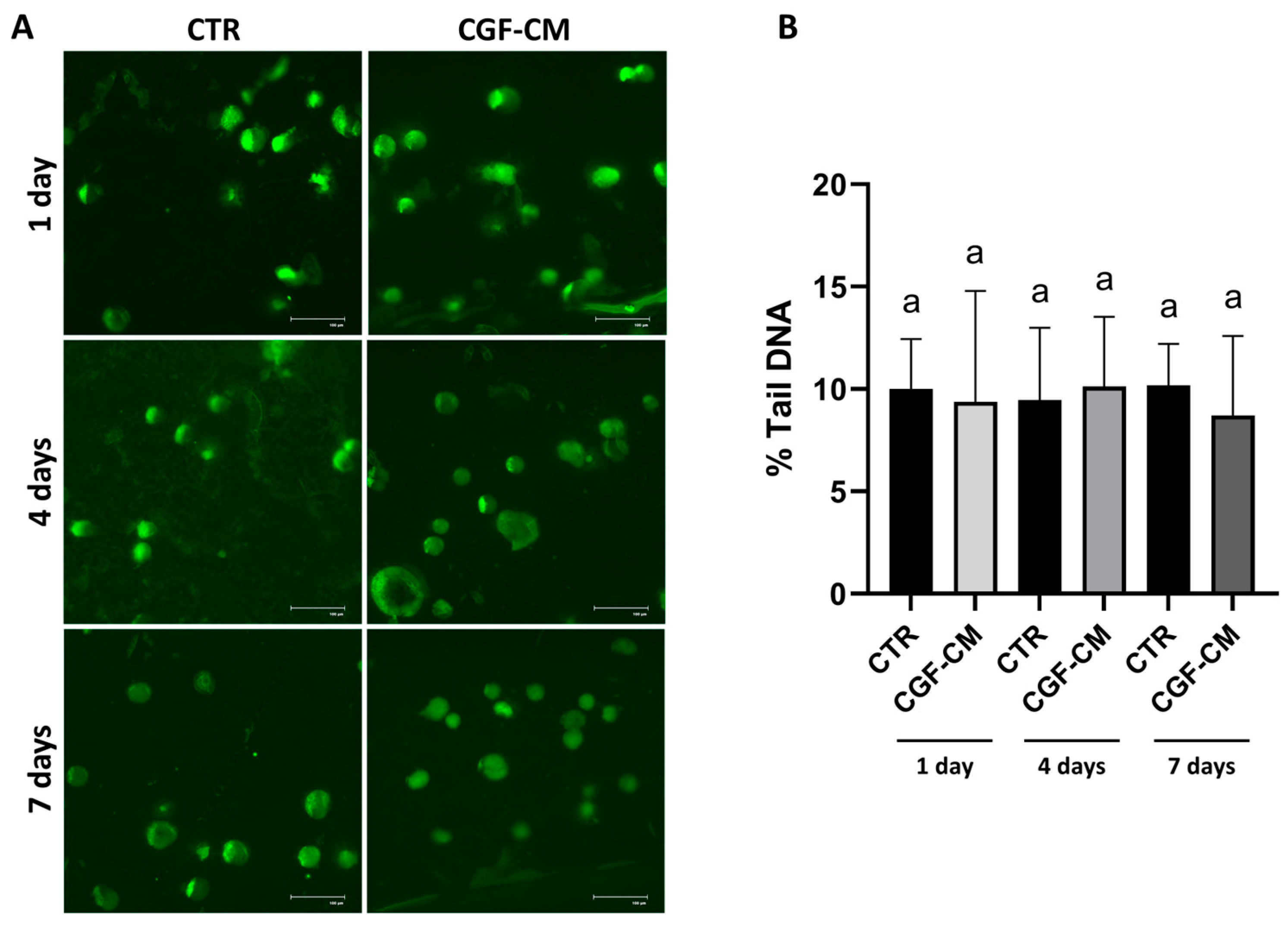
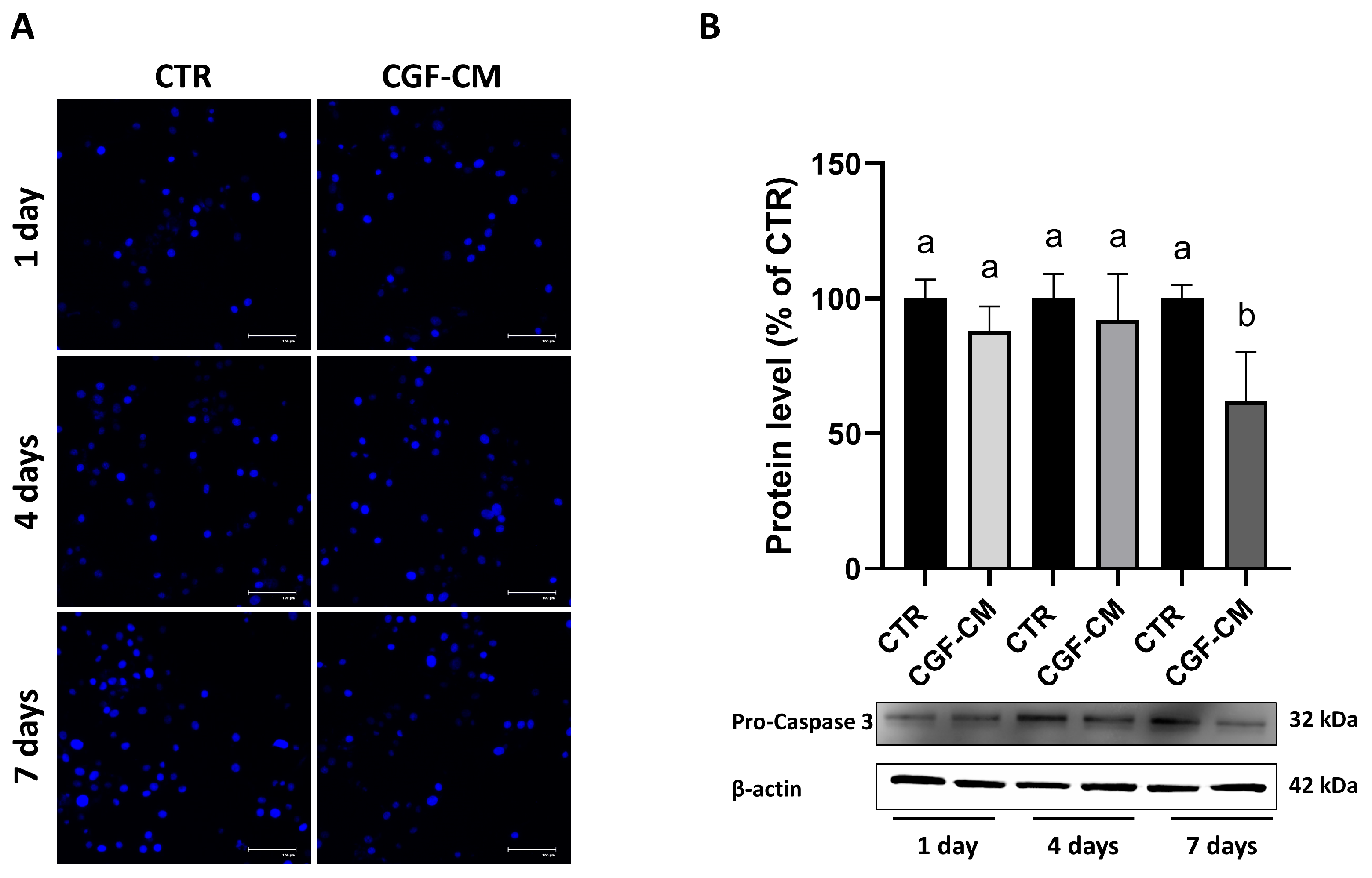
3.2. CGF-CM Does Not Cause DNA Damage
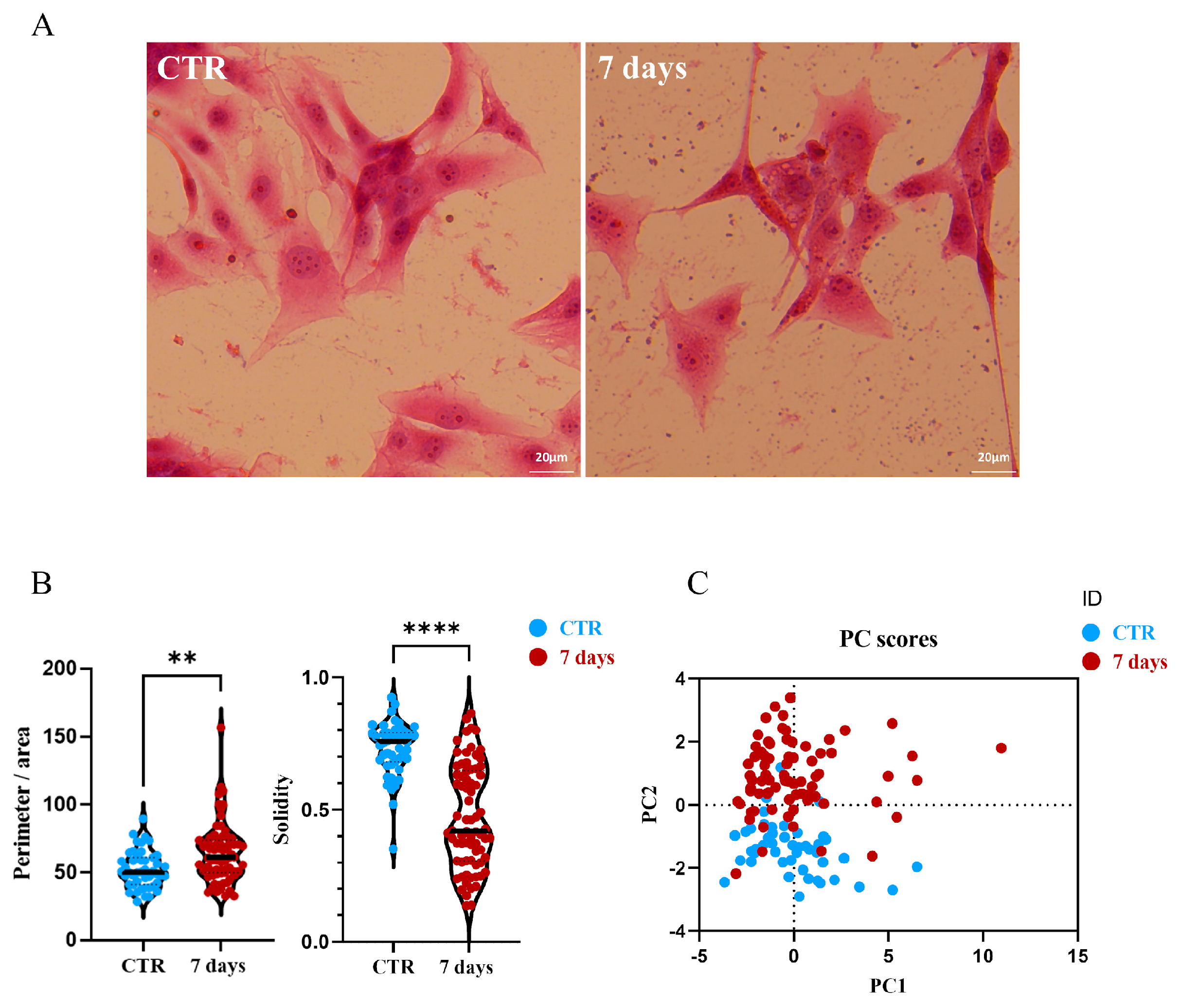
3.3. Effects on U87MG Morphometric Parameters After Treatment with CGF-CM
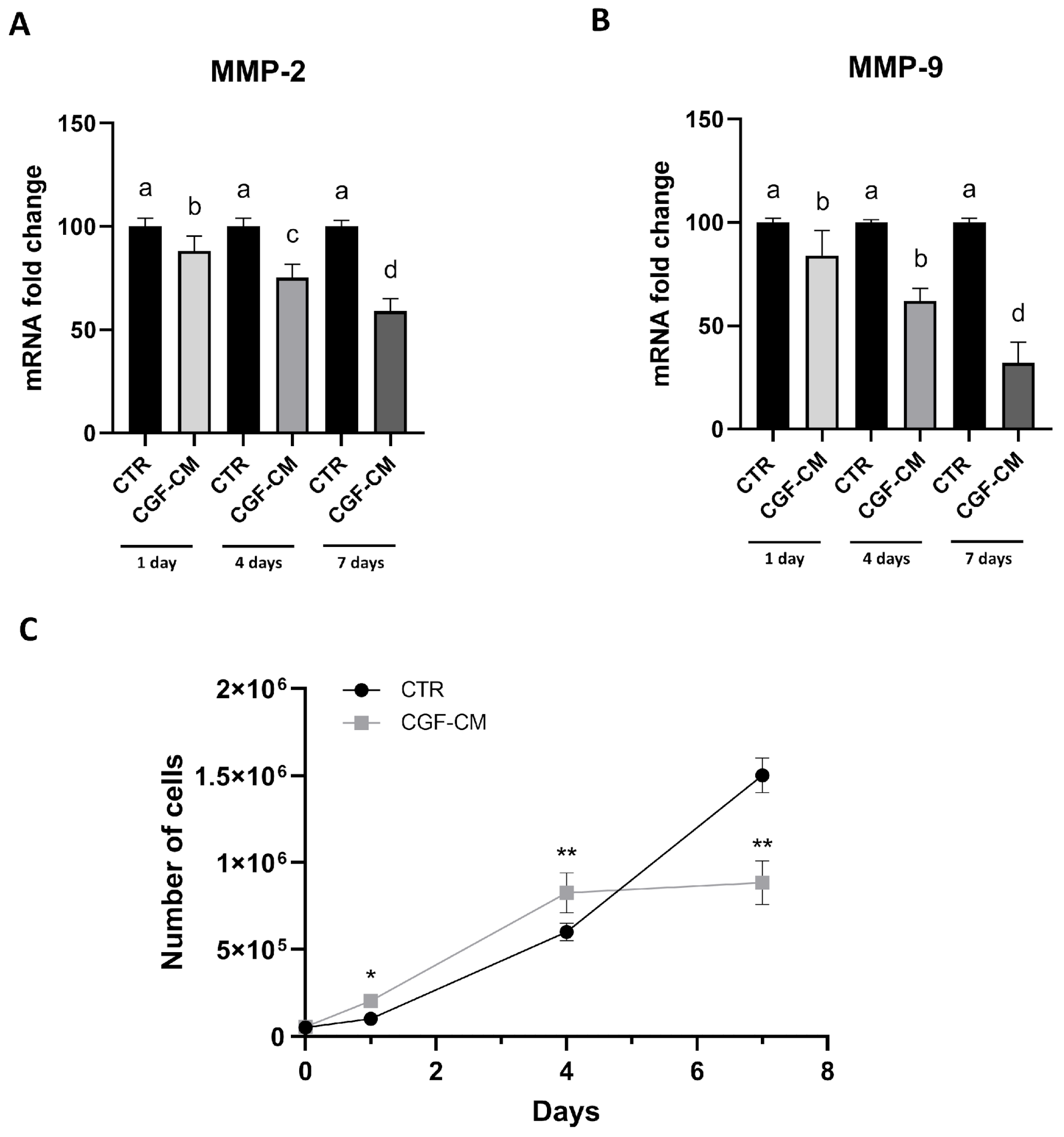
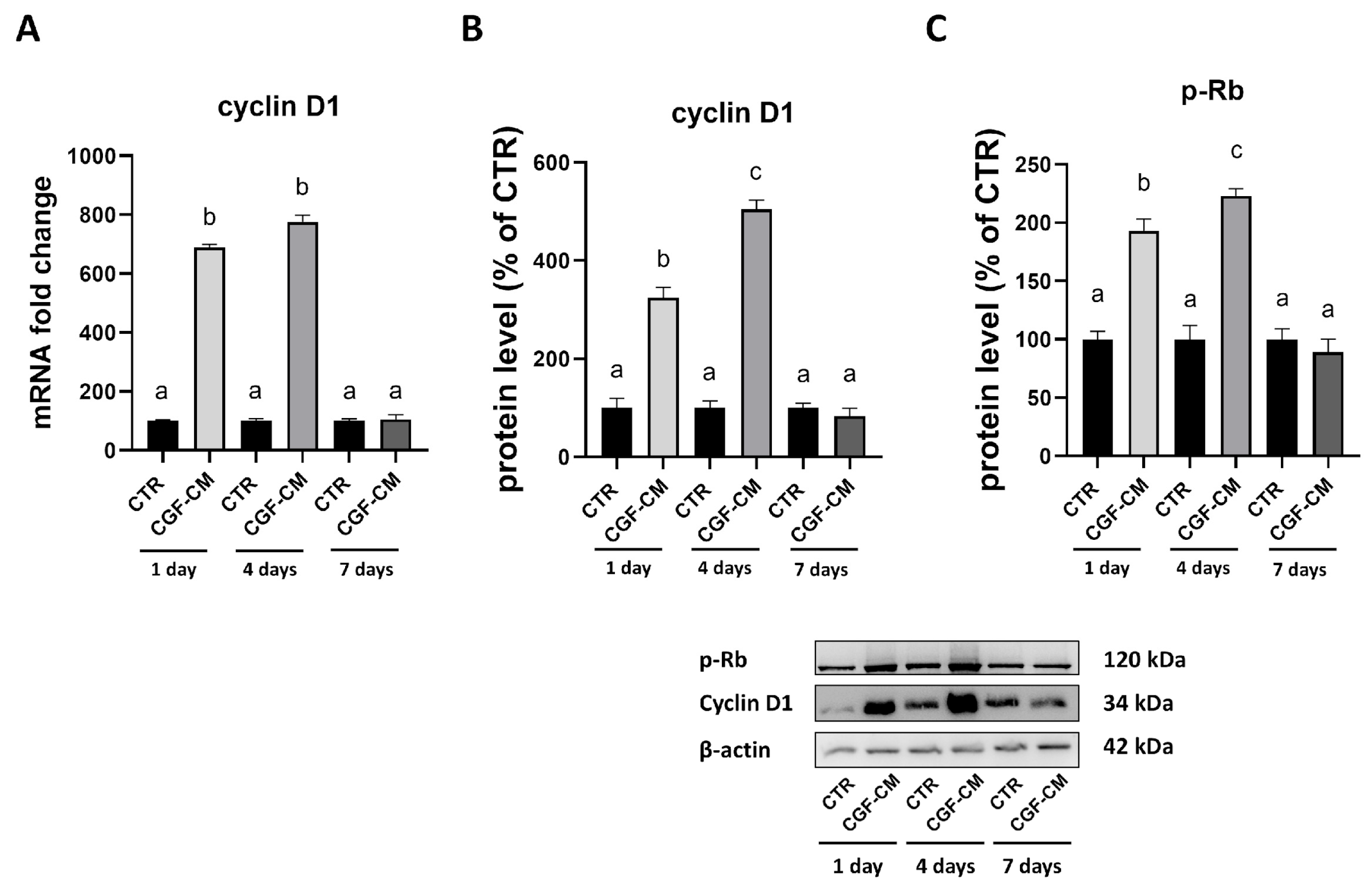
3.4. Effects of CGF-CM on U87MG Invasiveness and Proliferation
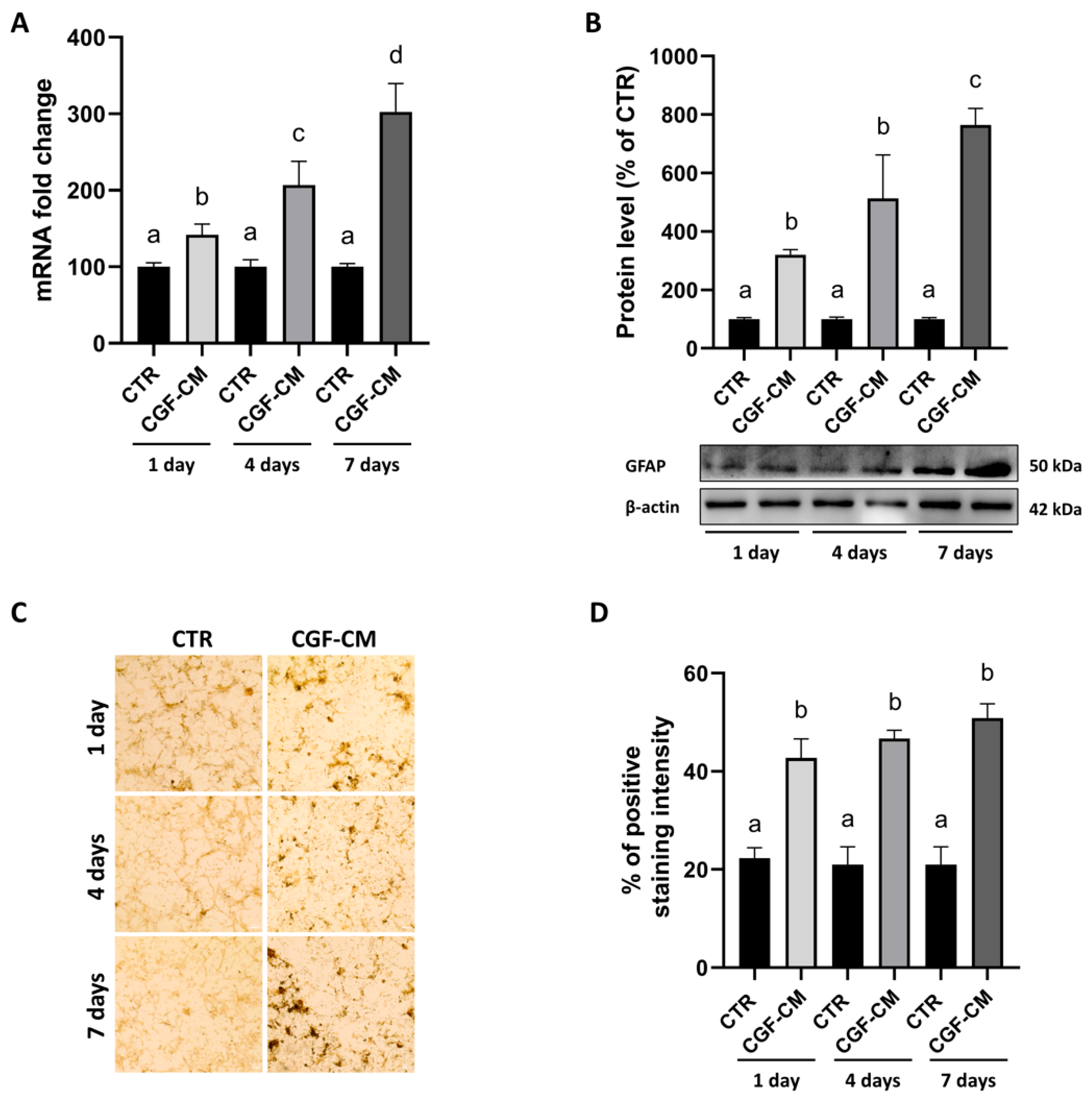
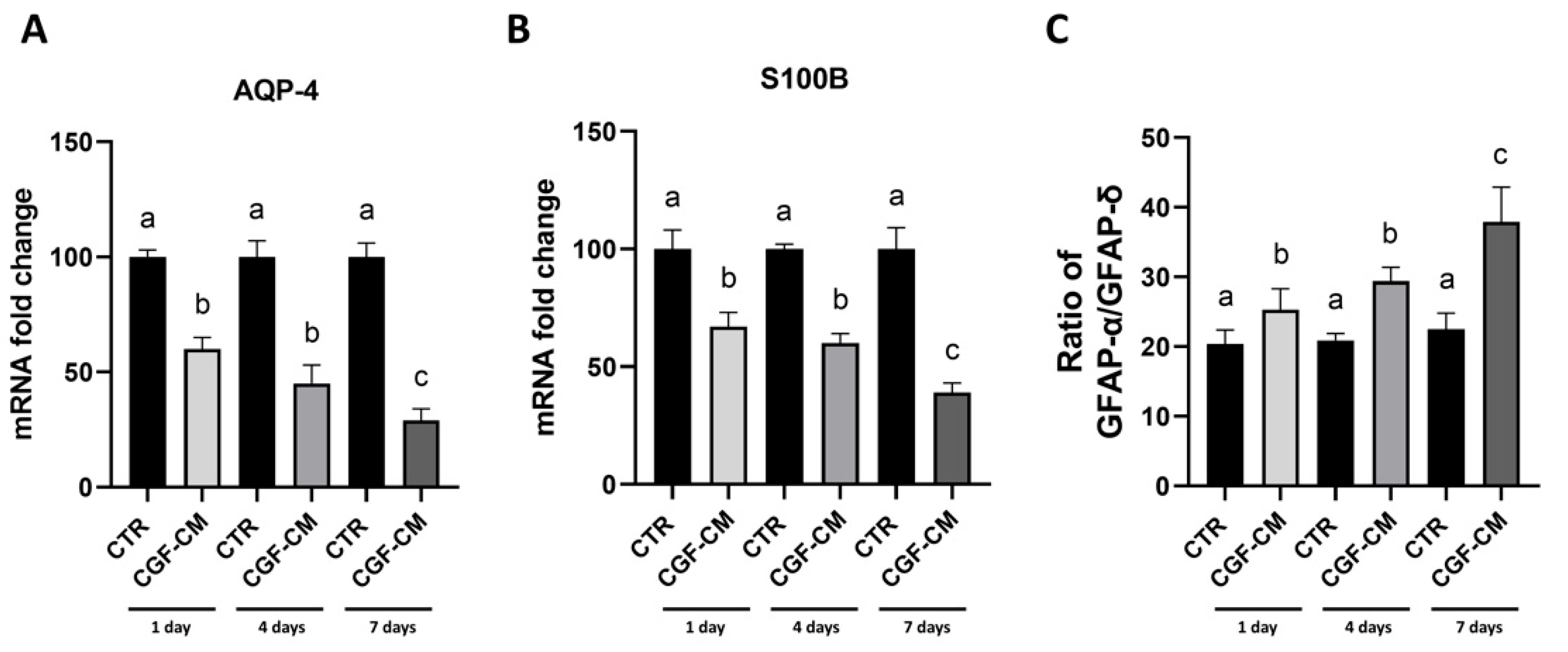
3.5. CGF-CM Promotes Astrocyte-Like Differentiation Features in U87MG Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodella, L.F.; Favero, G.; Boninsegna, R.; Buffoli, B.; Labanca, M.; Scarì, G.; Sacco, L.; Batani, T.; Rezzani, R. Growth factors, CD34 positive cells, and fibrin network analysis in concentrated growth factors fraction. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2011, 74, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, S.; Roffi, A.; Filardo, G.; Marcacci, M.; Kon, E. European Definitions, Current Use, and EMA Stance of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Sports Medicine. J. Knee Surg. 2015, 28, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, A.; Ferrante, F.; Stanca, E.; Damiano, F.; Gnoni, A.; Batani, T.; Carluccio, M.A.; Demitri, C.; Siculella, L. Release of VEGF from Dental Implant Surface (IML® Implant) Coated with Concentrated Growth Factors (CGF) and the Liquid Phase of CGF (LPCGF): In Vitro Results and Future Expectations. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannotti, L.; Di Chiara Stanca, B.; Spedicato, F.; Nitti, P.; Damiano, F.; Demitri, C.; Calabriso, N.; Carluccio, M.A.; Palermo, A.; Siculella, L.; et al. Progress in Regenerative Medicine: Exploring Autologous Platelet Concentrates and Their Clinical Applications. Genes 2023, 14, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabriso, N.; Stanca, E.; Rochira, A.; Damiano, F.; Giannotti, L.; Di Chiara Stanca, B.; Massaro, M.; Scoditti, E.; Demitri, C.; Nitti, P.; et al. Angiogenic Properties of Concentrated Growth Factors (CGFs): The Role of Soluble Factors and Cellular Components. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanca, E.; Calabriso, N.; Giannotti, L.; Nitti, P.; Damiano, F.; Stanca, B.D.C.; Carluccio, M.A.; De Benedetto, G.E.; Demitri, C.; Palermo, A.; et al. Analysis of CGF Biomolecules, Structure and Cell Population: Characterization of the Stemness Features of CGF Cells and Osteogenic Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochira, A.; Siculella, L.; Damiano, F.; Palermo, A.; Ferrante, F.; Carluccio, M.A.; Calabriso, N.; Giannotti, L.; Stanca, E. Concentrated Growth Factors (CGF) Induce Osteogenic Differentiation in Human Bone Marrow Stem Cells. Biology 2020, 9, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palermo, A.; Giannotti, L.; Di Chiara Stanca, B.; Ferrante, F.; Gnoni, A.; Nitti, P.; Calabriso, N.; Demitri, C.; Damiano, F.; Batani, T.; et al. Use of CGF in Oral and Implant Surgery: From Laboratory Evidence to Clinical Evaluation Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurita, M.; Otero, L.; Aguayo, C.; Bonilla, C.; Ferreira, E.; Parajón, A.; Vaquero, J. Cell therapy for spinal cord repair: Optimization of biologic scaffolds for survival and neural differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells. Cytotherapy 2010, 12, 522–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Burger, P.C.; Jouvet, A.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Kleihues, P. The 2007 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, M.; Conti, V.; Palermo, G.; De Maria, L.; Iaconetta, G. Advancements in Glioma Care: Focus on Emerging Neurosurgical Techniques. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, M.; Iaconetta, G.; Palermo, G.; Fiorindi, A.; Schaller, K.; De Maria, L. Clustering Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Time Series in Glioblastoma Characterization: A Review of the Evolution, Applications, and Potentials. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Banik, N.L.; Ray, S.K. N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl) retinamide induced both differentiation and apoptosis in human glioblastoma T98G and U87MG cells. Brain Res. 2008, 1227, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, F.; Luan, Y.; Cai, J.; Wu, S.; Mai, J.; Gu, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, K.; Lin, Y.; Xiao, X.; et al. The Anti-Warburg Effect Elicited by the cAMP-PGC1α Pathway. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Han, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhao, P.; Liang, S.; Xu, K. Autologous platelet-rich plasma promotes neurogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells in vitro. Int. J. Neurosci. 2013, 123, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caja, L.; Bellomo, C.; Moustakas, A. Transforming growth factor β and bone morphogenetic protein actions in brain tumors. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccirillo, S.G.; Reynolds, B.A.; Zanetti, N.; Lamorte, G.; Binda, E.; Broggi, G.; Brem, H.; Olivi, A.; Dimeco, F.; Vescovi, A.L. Bone morphogenetic proteins inhibit the tumorigenic potential of human brain tumour-initiating cells. Nature 2006, 444, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano, L.; Pistollato, F.; Rampazzo, E.; della Puppa, A.; Abbadi, S.; Frasson, C.; Volpin, F.; Indraccolo, S.; Scienza, R.; Basso, G. BMP2 Sensitizes Glioblastoma Stem-like Cells to Temozolomide by Affecting HIF-1α Stability and MGMT Expression. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.H.; Jang, S.; Lee, S.C.; Jeong, H.S.; Park, J.S.; Han, J.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Cho, Y.B. Effect of neural-induced mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma on facial nerve regeneration in an acute nerve injury model. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emel, E.; Ergün, S.S.; Kotan, D.; Gürsoy, E.B.; Parman, Y.; Zengin, A.; Nurten, A. Effects of insulin-like growth factor-I and platelet-rich plasma on sciatic nerve crush injury in a rat model. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 114, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsani, E.; Buffoli, B.; Bonazza, V.; Brunelli, G.; Monini, L.; Inchingolo, F.; Ballini, A.; Rezzani, R.; Rodella, L.F. In vitro effects of concentrated growth factors (CGF) on human SH-SY5Y neuronal cells. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Panek, W.K.; Pituch, K.C.; Miska, J.; Kim, J.W.; Rashidi, A.; Kanojia, D.; Lopez-Rosas, A.; Han, Y.; Yu, D.; Chang, C.L.; et al. Local Application of Autologous Platelet-Rich Fibrin Patch (PRF-P) Suppresses Regulatory T Cell Recruitment in a Murine Glioma Model. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 5032–5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeton, M.; Kanski, R.; Stassen, O.M.J.A.; Sluijs, J.A.; Geerts, D.; van Tijn, P.; Wiche, G.; van Strien, M.E.; Hol, E.M. Silencing GFAP Isoforms in Astrocytoma Cells Disturbs Laminin-Dependent Motility and Cell Adhesion. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 2942–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, S.H.; Sándor, G.K.; Kim, Y.D. Comparison of platelet-rich plasma (PRP), platelet-rich fibrin (PRF), and concentrated growth factor (CGF) in rabbit-skull defect healing. Arch. Oral Biol. 2014, 59, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metlerska, J.; Fagogeni, I.; Nowicka, A. Efficacy of Autologous Platelet Concentrates in Regenerative Endodontic Treatment: A Systematic Review of Human Studies. J. Endod. 2019, 45, 20–30.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijiritsky, E.; Assaf, H.D.; Kolerman, R.; Mangani, L.; Ivanova, V.; Zlatev, S. Autologous Platelet Concentrates (APCs) for Hard Tissue Regeneration in Oral Implantology, Sinus Floor Elevation, Peri-Implantitis, Socket Preservation, and Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (MRONJ): A Literature Review. Biology 2022, 11, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Wan, G.Z. Effect of concentrated growth factors on beagle periodontal ligament stem cells in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wan, G.J.; Yu, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhen, G.D.; Zhan, G.B. Effect of concentrated growth factor (CGF) on the promotion of osteogenesis in bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5876–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, G.S.; Chen, W.; Jian, G.B. A comparative evaluation of concentrated growth factor and platelet-rich fibrin on the proliferation, migration, and differentiation of human stem cells of the apical papilla. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Son, G.G.; Chai, J.; Gou, X.; Yuan, G.; Chen, Z. Effects of concentrated growth factor on proliferation, migration, and differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells in vitro. J. Tissue Eng. 2018, 9, 2041731418817505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Hou, Y.; Son, G.P.; Zhou, M.; Nie, M.; Liu, X. Modulation of proliferation and differentiation of gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells by concentrated growth factors: Potential implications in tissue engineering for dental regeneration and repair. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hon, G.S.; Li, L.; Cai, W.; Jian, G.B. The potential application of concentrated growth factor in regenerative endodontics. Int. Endod. J. 2019, 52, 646–655. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Qiao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, W.; Hon, G.S.; Pan, J.; Jian, G.B. The potential application of concentrated growth factor in pulp regeneration: An in vitro and in vivo study. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberheim, N.A.; Takano, T.; Han, X.; He, W.; Lin, J.H.C.; Wang, F.; Xu, Q.; Wyatt, J.D.; Pilcher, W.; Ojemann, J.G.; et al. Uniquely hominid features of adult human astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 3276–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makale, M. Cellular mechanobiology and cancer metastasis. Birth Defects Res. Part C Embryo Today Rev. 2007, 81, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Yang, L.; Guo, S. All-trans retinoic acid inhibits migration, invasion and proliferation, and promotes apoptosis in glioma cells in vitro. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 2833–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, N.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y. BHLHE41 promotes U87 and U251 cell proliferation via ERK/cyclinD1 signaling pathway. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 7657–7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žugec, M.; Furlani, B.; Castañon, M.J.; Rituper, B.; Fischer, I.; Broggi, G.; Caltabiano, R.; Barbagallo, G.M.V.; Di Rosa, M.; Tibullo, D.; et al. Plectin plays a role in the migration and volume regulation of astrocytes: A potential biomarker of glioblastoma. J. Biomed. Sci. 2024, 31, 14–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.L.; Wang, X.; Lou, J.C.; Ma, X.C.; Zhang, B. The potential roles of aquaporin 4 in malignant gliomas. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 32345–32355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, I.Y.; Chen, X.; Da Fonseca, A.; Wu, S.; Ren, H.; Badie, S.; Sadeghi, S.; Ouyang, M.; et al. S100B promotes glioma growth through chemoattraction of myeloid-derived macrophages. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3764–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Mao, X.; Ye, L.; Cheng, H.; Dai, X. The Role of the S100 Protein Family in Glioma. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 3022–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenholz, I.; Heizmann, C.W.; Fritz, G. S100 proteins in mouse and man: From evolution to function and pathology (including an update of the nomenclature). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 322, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, R.; Petrescu, G.E.D.; Gorgan, R.M.; Brehar, F.M. GFAPδ: A Promising Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 859247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stassen, O.M.J.A.; van Bodegraven, E.; Giuliani, F.; Moeton, M.; Kanski, R.; Sluijs, J.A.; van Strien, M.E.; Kamphuis, W.; Robe, P.A.J.; Hol, E.M. Gfapδ/Gfapα Ratio Directs Astrocytoma Gene Expression Towards a More Malignant Profile. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 88104–88121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uceda-Castro, R.; van Asperen, J.V.; Vennin, C.; Sluijs, J.A.; van Bodegraven, E.J.; Margarido, A.S.; Robe, P.A.J.; van Rheenen, J.; Hol, E.M. GFAP Splice Variants Fine-Tune Glioma Cell Invasion and Tumour Dynamics by Modulating Migration Persistence. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Name | Sequences (5′-3′) | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | F: ATGGCCTTCCGTGTCCCCAC R: ACGCCTGCTTCACCACCTTC | NM_014364.5 |
| Cycline D1 | F: TCTACACCGACAACTCCATCCG R: TCTGGCATTTTGGAGAGGAAGTG | NM_053056.3 |
| MMP-2 | F: AGCGAGTGGATGCCGCCTTTAA R: CATTCCAGGCATCTGCGATGAG | NM_001302508.1 |
| MMP-9 | F: GCCACTACTGTGCCTTTGAGTC R: CCCTCAGAGAATCGCCAGTACT | NM_004994.3 |
| GFAP | F: CTGGAGAGGAAGATTGAGTCGC R: ACGTCAAGCTCCACATGGACCT | NM_002055.5 |
| AQP-4 | F: GCCATCATTGGAGCAGGAATCC R: ACTCAACCAGGAGACCATGACC | NM_153010 |
| S100B | F: GGAGACGGCGAATGTGACTT R: GAACTCGTGGCAGG CAGTAGTAA | NM_006272.3 |
| GFAP-α | F: CCCACTCTGCTTTGACTGAGC R: CCTTCTTCGGCCTTAGAGGG | NM_002055.5 |
| GFAP-δ | F: GTGGTAAAGGTGGTGAGTCCTT R: AGAGGCTGCTGCTTGCTC | NM_001242376.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giannotti, L.; Di Chiara Stanca, B.; Spedicato, F.; Demitri, C.; Stanca, E.; Palermo, A.; Ferrante, F.; Damiano, F.; De Sangro, M.A.; Abbruzzese, L.; et al. CGF-Conditioned Medium Modulates Astrocytic Differentiation and Invasiveness in U87MG Glioblastoma Cells. Biology 2025, 14, 1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101461
Giannotti L, Di Chiara Stanca B, Spedicato F, Demitri C, Stanca E, Palermo A, Ferrante F, Damiano F, De Sangro MA, Abbruzzese L, et al. CGF-Conditioned Medium Modulates Astrocytic Differentiation and Invasiveness in U87MG Glioblastoma Cells. Biology. 2025; 14(10):1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101461
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiannotti, Laura, Benedetta Di Chiara Stanca, Francesco Spedicato, Christian Demitri, Eleonora Stanca, Andrea Palermo, Franco Ferrante, Fabrizio Damiano, Maria Antonietta De Sangro, Luciano Abbruzzese, and et al. 2025. "CGF-Conditioned Medium Modulates Astrocytic Differentiation and Invasiveness in U87MG Glioblastoma Cells" Biology 14, no. 10: 1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101461
APA StyleGiannotti, L., Di Chiara Stanca, B., Spedicato, F., Demitri, C., Stanca, E., Palermo, A., Ferrante, F., Damiano, F., De Sangro, M. A., Abbruzzese, L., & Siculella, L. (2025). CGF-Conditioned Medium Modulates Astrocytic Differentiation and Invasiveness in U87MG Glioblastoma Cells. Biology, 14(10), 1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101461









