- Brief Report
Can Physical Activity, Sleep Parameters, and Sleep–Wake Patterns Predict Outcome of Combined Chronotherapy in Mood Disorder During Routine Clinical Practice? An Exploratory Study
- Stella J. M. Druiven,
- Olga Minaeva and
- Harriëtte Riese
- + 4 authors
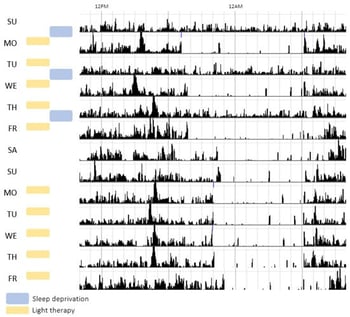
Background/Objectives: Combined chronotherapy (CCT), which combines repeated sleep deprivation and light therapy, is used in the clinical treatment of severe depression. Despite its potential to rapidly reduce depressive symptoms, CCT is infrequently used in clinical practice. We explored whether actigraphy-derived within-patient changes in physical activity, sleep parameters, and sleep–wake patterns prior to CCT can help identify those most likely to benefit from this treatment, supporting personalized mental health care. Methods: Actigraphy data from nine severely depressed patients were collected before, during, and after CCT. Data were assessed with a questionnaire on depressive symptoms (Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology—Self Report, IDS-SR) and actigraphy measures for sleep–wake patterns and physical activity: daily mean activity level, rhythm (intradaily variability (IV), interdaily stability (IS)), Midpoint of Sleep (MSF), time in bed, sleep efficiency (SE), and the fragmentation index (FI). Variables were compared before and after CCT by systematic visual inspection due to the small sample size. A prior set Minimal Clinically Important Difference (MCID) of a 30% change in IDS scores from before and the week after CCT was used to categorize patients as responders (n = 3) or nonresponders (n = 6) to CCT. Results: After CCT, for both responders and nonresponders, there was a notable decrease in IDS, IV and FI. Prior to CCT, responders, compared to nonresponders, were characterized with higher IDS, more time in bed and higher FI, while having lower SE. Conclusions: We concluded that actigraphy assessments during regular CCT are feasible and found preliminary evidence that patients with the most disrupted sleep–wake patterns prior to treatment may benefit most from CCT.
7 February 2026