Thrombus Imaging Features for Anterior Circulation Stroke: Their Impact on CTP Parameters and Natural Evolution of Infarct Progression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
2.2. Imaging Protocol and Analyses
2.3. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Subjects’ Characteristics
3.2. Outcome Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIS | acute ischemic stroke |
| CBS | clot burden score |
| CBV | cerebral blood volume |
| CTA | computed tomography angiography |
| CTP | computed tomography perfusion |
| ICA | internal carotid artery |
| NCCT | non-contrast computed tomography |
| Tmax | time-to-maximum value |
Appendix A
| Ischemic Core Volume | Hypoperfused Tissue Volume | Penumbra Volume | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β (95%CI) | R-Squared | p-Value | β (95%CI) | R-Squared | p-Value | β (95%CI) | R-Squared | p-Value | |
| Clot Burden Score | −2.2 (−4.1 to −0.3) | 0.33 | 0.02 | −8.7 (−12.8 to −4.5) | 0.49 | <0.001 | −6.3 (−10.2 to −2.4) | 0.33 | <0.01 |
| Thrombus length | 4.7 (−0.1 to 1.1) | 0.27 | 0.13 | 2.31 (1.1 to 3.6) | 0.41 | <0.01 | 1.83 (0.7 to 2.9) | 0.27 | <0.01 |
| Thrombus location | |||||||||
| ICA | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | ||||||
| Proximal M1 | −14.1 (−28.9 to 0.6) | 0.33 | 0.06 | −16.2 (−45.9 to 13.4) | 0.54 | 0.21 | −1.7 (−29.1 to 25.8) | 0.40 | 0.91 |
| Distal M1 | −14.6 (−30.1 to 0.9) | 0.33 | 0.06 | −27.9 (−58.8 to 3.1) | 0.54 | 0.08 | −12.9 (−41.5 to 15.8) | 0.40 | 0.37 |
| M2 | −19.3 (−32.9 to −4.8) | 0.33 | <0.01 | −58.6 (−86.3 to −30.1) | 0.54 | <0.001 | −38.8 (−64.4 to −13.1) | 0.40 | <0.01 |
| M3/M4 | −14.3 (−31.3 to 2.7) | 0.33 | 0.09 | −80.7 (−115.4 to −45.9) | 0.54 | <0.001 | −65.6 (−97.7 to −33.4) | 0.40 | <0.001 |
| Early Infarct Growth rate | Final Infarct Volume | Infarct Growth Volume | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β (95%CI) | R-Squared | p-Value | β (95%CI) | R-Squared | p-Value | β (95% CI) | R-Squared | p-Value | |
| Clot Burden Score | −1.4 (−3.5 to 0.6) | 0.13 | 0.17 | −16.8 (−28.9 to −4.7) | 0.27 | <0.01 | −17.2 (−30.1 to −4.5) | 0.24 | <0.01 |
| Thrombus length | 0.23 (−0.4 to 0.9) | 0.18 | 0.46 | 1.28 (−3.3 to 5.9) | 0.12 | 0.57 | 0.97 (−3.5 to 5.4) | 0.09 | 0.66 |
| Thrombus location | |||||||||
| ICA | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | ||||||
| Proximal M1 | −1.8 (−17.6 to 13.9) | 0.19 | 9.81 | −142.8 (−228.9 to −56.7) | 0.37 | <0.01 | −156.2 (−240.3 to −72.1) | 0.37 | <0.01 |
| Distal M1 | −7.8 (−24.3 to 8.9) | 0.19 | 0.35 | −114.4 (−205.1 to −23.8) | 0.37 | 0.01 | −106.5 (−193.2 to −19.8) | 0.37 | 0.02 |
| M2 | −9.1 (−23.4 to 5.5) | 0.19 | 0.22 | −172.8 (−259.8 to −85.7) | 0.37 | <0.001 | −166.6 (−251.2 to −82.1) | 0.37 | <0.001 |
| M3/M4 | −5.4 (−23.6 to 12.8) | 0.19 | 0.55 | −118.9 (−223.9 to −13.8) | 0.37 | 0.03 | −116.3 (−219.7 to −12.8) | 0.37 | 0.03 |
References
- Fiehler, J.; Knudsen, K.; Thomalla, G.; Goebell, E.; Rosenkranz, M.; Weiller, C.; Röther, J.; Zeumer, H.; Kucinski, T. Vascular occlusion sites determine differences in lesion growth from early apparent diffusion coefficient lesion to final infarct. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2005, 26, 1056–1061. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Puetz, V.; Dzialowski, I.; Hill, M.D.; Subramaniam, S.; Sylaja, P.; Krol, A.; O’REilly, C.; Hudon, M.E.; Hu, W.Y.; Coutts, S.B.; et al. Intracranial thrombus extent predicts clinical outcome, final infarct size and hemorrhagic transformation in ischemic stroke, The clot burden score. Int. J. Stroke 2008, 3, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarraj, A.; Hassan, A.E.; Grotta, J.; Blackburn, S.; Day, A.; Abraham, M.; Sitton, C.; Dannenbaum, M.; Cai, C.; Pujara, D.; et al. Early Infarct Growth Rate Correlation with Endovascular Thrombectomy Clinical Outcomes, Analysis from the SELECT Study. Stroke 2021, 52, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, H.C.; Treurniet, K.M.; Dutra, B.G.; Jansen, I.G.H.; Boers, A.M.; Santos, E.M.; Berkhemer, O.A.; Dippel, D.W.; van der Lugt, A.; van Zwam, W.H.; et al. Associations Between Collateral Status and Thrombus Characteristics and Their Impact in Anterior Circulation Stroke. Stroke 2018, 49, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Almekhlafi, M.A.; Cognard, C.; McTaggart, R.; Blackham, K.; Biondi, A.; van der Lugt, A.; Majoie, C.B.L.M.; van Zwam, W.H.; van der Worp, H.B.; et al. Which patients with acute stroke due to proximal occlusion should not be treated with endovascular thrombectomy? Neuroradiology 2019, 61, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sillanpää, N.; Saarinen, J.; Rusanen, H.; Elovaara, I.; Dastidar, P.; Soimakallio, S. Location of the clot and outcome of perfusion defects in acute anterior circulation stroke treated with intravenous thrombolysis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, I.; Demchuk, A.; Hopyan, J.; Zhang, L.; Gladstone, D.; Wong, K.; Martin, M.; Symons, S.; Fox, A.; Aviv, R. CT angiography clot burden score and collateral score, Correlation with clinical and radiologic outcomes in acute middle cerebral artery infarct. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, B.; Gawlitza, M.; Schob, S.; Hobohm, C.; Raviolo, M.; Hoffmann, K.-T.; Lobsien, D. Distance to thrombus in acute middle cerebral artery occlusion, A predictor of outcome after intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2015, 46, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.C.; Parsons, M.W. Imaging selection for acute stroke intervention. Int. J. Stroke 2018, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, R.G.; Jadhav, A.P.; Haussen, D.C.; Bonafe, A.; Budzik, R.F.; Bhuva, P.; Yavagal, D.R.; Ribo, M.; Cognard, C.; Hanel, R.A.; et al. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 Hours after Stroke with a Mismatch between Deficit and Infarct. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, G.W.; Marks, M.P.; Kemp, S.; Christensen, S.; Tsai, J.P.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; McTaggart, R.A.; Torbey, M.T.; Kim-Tenser, M.; Leslie-Mazwi, T.; et al. Thrombectomy for Stroke at 6 to 16 Hours with Selection by Perfusion Imaging. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagal, A.; Wintermark, M.; Nael, K.; Bivard, A.; Parsons, M.; Grossman, A.W.; Khatri, P. Automated CT perfusion imaging for acute ischemic stroke, Pearls and pitfalls for real-world use. Neurology 2019, 93, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albers, G.W. Use of imaging to select patients for late window endovascular therapy. Stroke 2018, 49, 2256–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bivard, A.; Levi, C.; Spratt, N.; Parsons, M. Perfusion CT in Acute Stroke, A Comprehensive Analysis of Infarct and Penumbra. Radiology 2013, 267, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedraza, S.; Puig, J.; Blasco, G.; Daunis-I-Estadella, J.; Boada, I.; Bardera, A.; Castellanos, M.; Serena, J. Reliability of the ABC/2 Method in Determining Acute Infarct Volume. J. Neuroimaging 2012, 22, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, E.M.; Sohn, S.I.; Mishra, S.; Almekhlafi, M.A.; Eesa, M.; D’eSterre, C.D.; Qazi, A.A.; Puig, J.; Goyal, M.; Demchuk, A.M.; et al. Thrombus Characteristics Are Related to Collaterals and Angioarchitecture in Acute Stroke. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 42, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagal, A.; Aviv, R.; Sucharew, H.; Reddy, M.; Hou, Q.; Michel, P.; Jovin, T.; Tomsick, T.; Wintermark, M.; Khatri, P. Collateral clock is more important than time clock for tissue fate a natural history study of acute ischemic strokes. Stroke 2018, 49, 2102–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boers, A.M.; Jansen, I.G.; Berkhemer, O.A.; Yoo, A.J.; Lingsma, H.F.; Slump, C.H.; Roos, Y.B.; van Oostenbrugge, R.J.; Dippel, D.W.; van der Lugt, A.; et al. Collateral status and tissue outcome after intra-arterial therapy for patients with acute ischemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 3589–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.C.; Christensen, S.; Tress, B.M.; Churilov, L.; Desmond, P.M.; Parsons, M.W.; Barber, P.A.; Levi, C.R.; Bladin, C.; Donnan, G.A.; et al. Failure of collateral blood flow is associated with infarct growth in ischemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawlitza, M.; Friedrich, B.; Hobohm, C.; Schaudinn, A.; Schob, S.; Quäschling, U.; Hoffmann, K.-T.; Lobsien, D. Distance to Thrombus in Acute Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Predicts Target Mismatch and Ischemic Penumbra. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparotti, R.; Grassi, M.; Mardighian, D.; Frigerio, M.; Pavia, M.; Liserre, R.; Magoni, M.; Mascaro, L.; Padovani, A.; Pezzini, A. Perfusion CT in patients with acute ischemic stroke treated with intra-arterial thrombolysis, Predictive value of infarct core size on clinical outcome. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannoni, S.; Cereda, C.W.; Sirimarco, G.; Lambrou, D.; Strambo, D.; Eskandari, A.; Dunet, V.; Wintermark, M.; Michel, P. Collaterals are a major determinant of the core but not the penumbra volume in acute ischemic stroke. Neuroradiology 2019, 61, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, A.; Yu, F.; Zhang, M.; Shan, Y.; Guo, D.; Shakya, M.R.; Bai, X.; Ma, Q.; Jiao, L.; Lu, J. Multimodal CT imaging characteristics may predict post-reperfusion infarct volume in wake-up stroke patients. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2023, 13, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirimarco, G.; Strambo, D.; Nannoni, S.; Labreuche, J.; Cereda, C.; Dunet, V.; Puccinelli, F.; Saliou, G.; Meuli, R.; Eskandari, A.; et al. Predicting Penumbra Salvage and Infarct Growth in Acute Ischemic Stroke, A Multifactor Survival Game. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treurniet, K.M.; Yoo, A.J.; Berkhemer, O.A.; Lingsma, H.F.; Boers, A.M.; Fransen, P.S.; Beumer, D.; Berg, L.A.v.D.; Sprengers, M.E.; Jenniskens, S.F.; et al. Clot Burden Score on Baseline Computerized Tomographic Angiography and Intra-Arterial Treatment Effect in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2016, 47, 2972–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saarinen, J.; Rusanen, H.; Sillanpää, N. Collateral score complements clot location in predicting the outcome of intravenous thrombolysis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1892–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguida, G.; Shuaib, A. Collateral circulation in ischemic stroke, an updated review. J. Stroke 2023, 25, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wu, W.; Tali, E.T.; Yuh, W.T. Oligemia, penumbra, infarction, understanding hypoperfusion with neuroimaging. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2018, 28, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munsch, F.; Planes, D.; Fukutomi, H.; Marnat, G.; Courret, T.; Micard, E.; Chen, B.; Seners, P.; Dubos, J.; Planche, V.; et al. Dynamic evolution of infarct volumes at MRI in ischemic stroke due to large vessel occlusion. Neurology 2024, 102, e209427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalet, L.; Boutelier, T.; Christen, T.; Raguenes, D.; Debatisse, J.; Eker, O.F.; Becker, G.; Nighoghossian, N.; Cho, T.-H.; Canet-Soulas, E.; et al. Clinical imaging of the penumbra in ischemic stroke, from the concept to the era of mechanical thrombectomy. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 861913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pensato, U.; Demchuk, A.M.; Menon, B.K.; Nguyen, T.N.; Broocks, G.; Campbell, B.C.; Vasquez, D.A.G.; Mitchell, P.J.; Hill, M.D.; Goyal, M.; et al. Cerebral infarct growth, pathophysiology, pragmatic assessment, and clinical implications. Stroke 2025, 56, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venema, S.M.U.; Dankbaar, J.W.; van der Lugt, A.; Dippel, D.W.; van der Worp, H.B. Cerebral collateral circulation in the era of reperfusion therapies for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2022, 53, 3222–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortimer, A.M.; Simpson, E.; Bradley, M.D.; Renowden, S.A. Computed tomography angiography in hyperacute ischemic stroke, prognostic implications and role in decision-making. Stroke 2013, 44, 1480–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
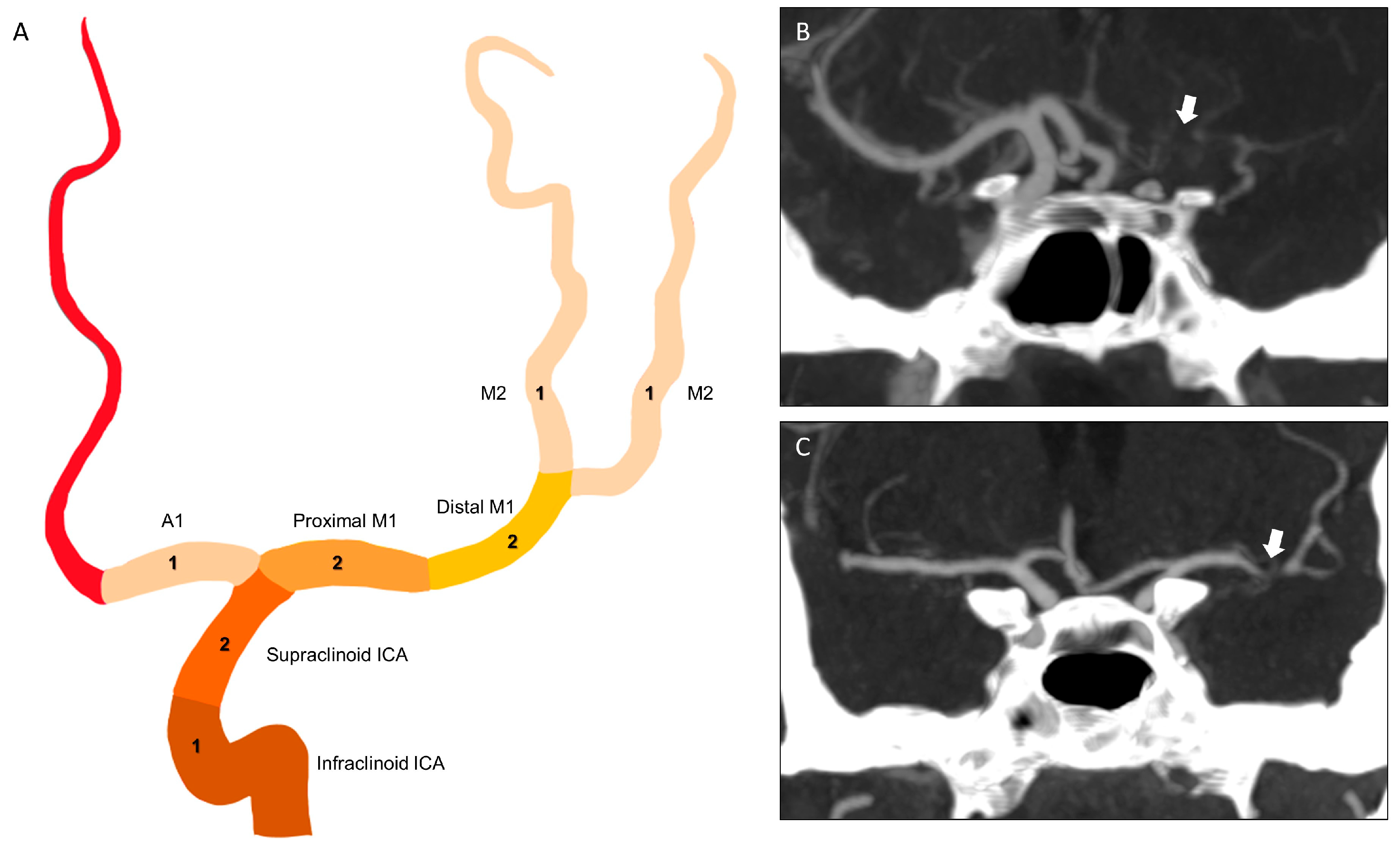

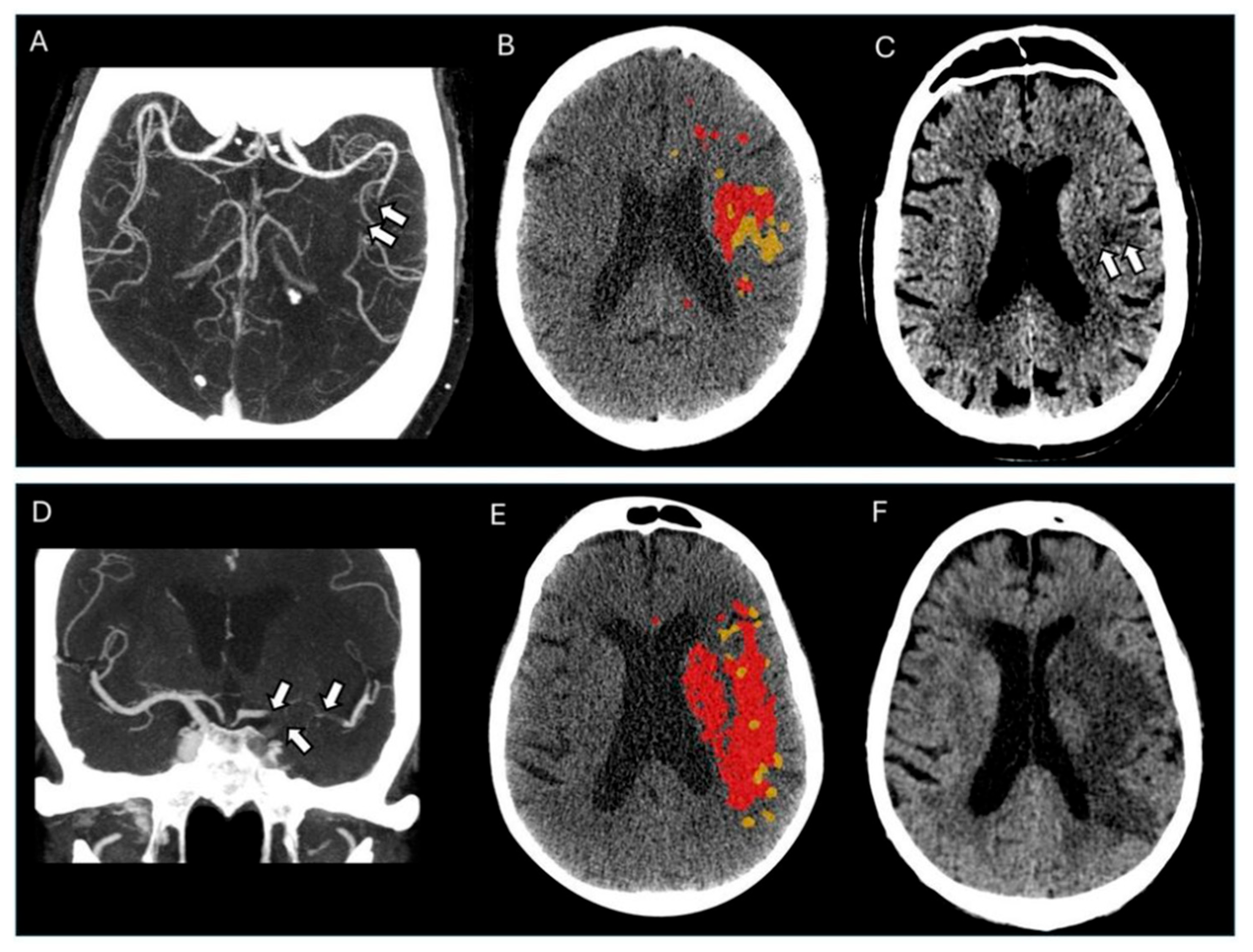
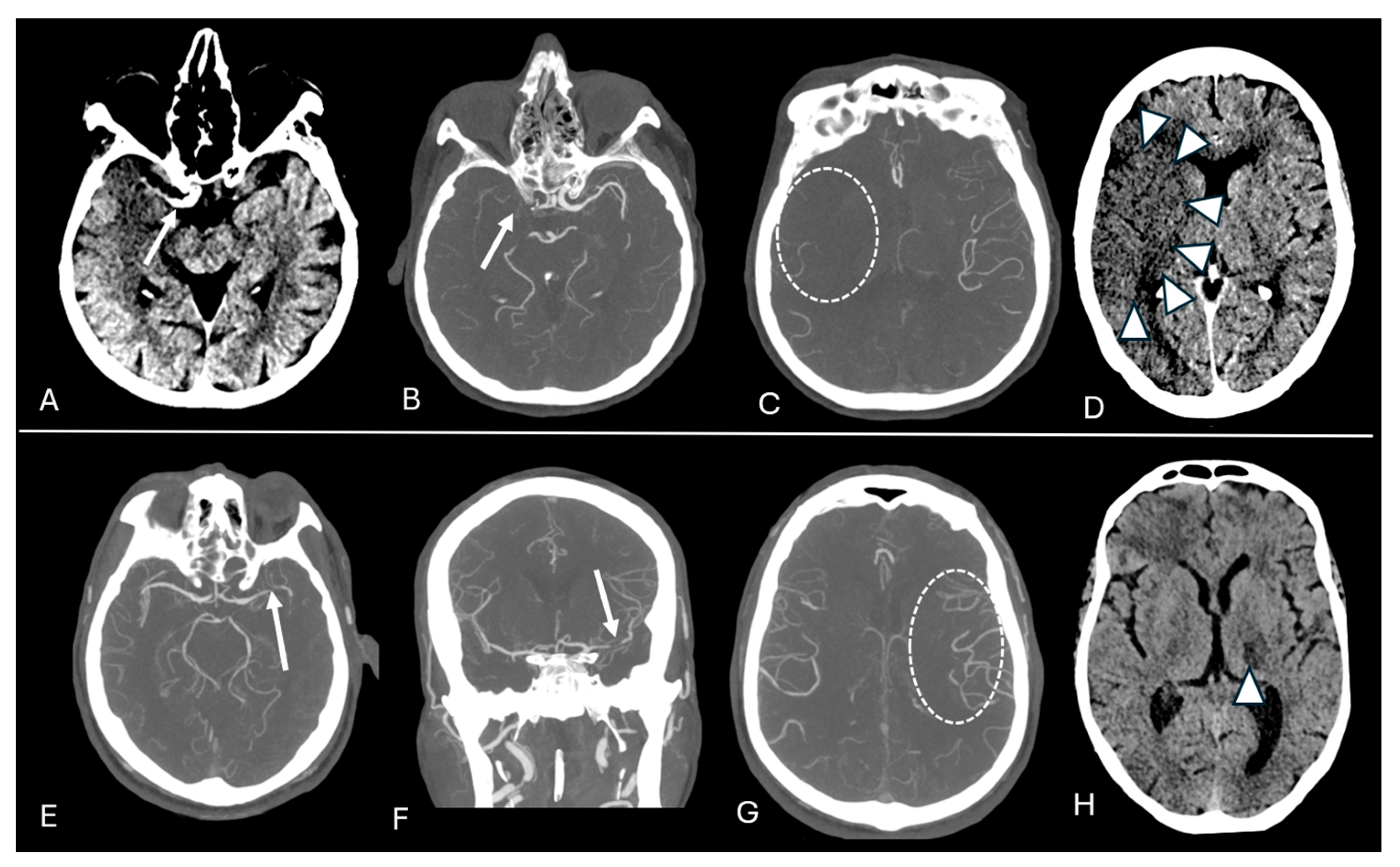
| Total = 81 Patients | |
|---|---|
| Clinical variables | |
| Age, median (IQR) | 62 (55, 77) |
| Male sex, n (%) | 45 (55.6) |
| Baseline NIHSS, median (IQR) | 11.5 (6, 16) |
| Stroke ictus, min—median (IQR) | 120 (60, 215) |
| Systolic blood pressure, mm Hg, median (IQR) | 150 (130, 180) |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mm Hg—median (IQR) | 90 (80, 100) |
| Baseline glucose, mg/dL—median (IQR) | 130 (112, 171) |
| Medical history | |
| Current smoker | 19 (25) |
| Hypertension | 45 (67.1) |
| Diabetes | 17 (22.4) |
| Arterial fibrillation | 17 (22.4) |
| Dyslipidemia | 6 (7.9) |
| Peripheral artery disease | 4 (5.3) |
| Previous stroke | 8 (10.5) |
| Previous myocardial infarction | 6 (7.9) |
| Anticoagulation | 4 (5.3) |
| Imaging variables | |
| ASPECTS, median (IQR) | 7 (5, 8) |
| Occlusion location, n (%) | |
| ICA-i | 5 (6.2) |
| ICA-t | 15 (18.5) |
| Proximal M1 | 12 (14.8) |
| Distal M1 | 15 (18.5) |
| M2 | 19 (23.5) |
| M3 | 13 (16) |
| M4 | 2 (2.5) |
| Tandem occlusion, n (%) | 4 (5.5) |
| CBS, median (IQR) | 6 (5, 9) |
| Collateral score, n (%) | |
| 0% filling of the occluded territory | 12 (14.8) |
| 0–50% filling of the occluded territory | 21 (25.9) |
| 50–100% filling of the occluded territory | 25 (30.9) |
| 100% filling of the occluded territory | 23 (28.4) |
| Hyperdense artery sign, n (%) | 48 (60) |
| Thrombus length—mm, median (IQR) | 12.6 (7.5, 18) |
| CTP parameters | |
| Infarct core volume, mL—median (IQR) | 7.6 (1.6, 25) |
| Hypoperfused tissue volume, mL—median (IQR) | 74.6 (27.2, 123) |
| Penumbra volume, mL—median (IQR) | 50.5 (21.7, 100) |
| Early infarct growth rate, mL/h—median (IQR) | 39.7 (22.2, 151) |
| Follow-up imaging variables * | |
| Follow-up scan date, median (IQR) | 2 (1, 4) |
| Final infarct volume, mL—median (IQR) | 50 (22.7, 154) |
| Infarct growth volume, mL—median (IQR) | 116 (32, 252) |
| Ischemic Core Volume | Hypoperfused Tissue Volume | Penumbra Volume | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β (95%CI) | R-Squared | p-Value | β (95%CI) | R-Squared | p-Value | β (95%CI) | R-Squared | p-Value | |
| Clot Burden Score | −3.9 (−5.7 to −2.1) | 0.18 | <0.001 | −12.2 (−16.1 to −8.4) | 0.34 | <0.001 | −7.9 (−11.3 to −4.6) | 0.22 | <0.001 |
| Thrombus length | 0.88 (0.2 to 1.5) | 0.08 | <0.01 | 2.87 (1.6 to 4.1) | 0.23 | <0.001 | 1.99 (0.9 to 3.1) | 0.17 | <0.001 |
| Thrombus location | |||||||||
| ICA | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | ||||||
| Proximal M1 | −6.3 (−23.5 to 10.7) | 0.13 | 0.46 | −7.7 (−40.3 to 24.8) | 0.39 | 0.63 | 0.5 (−27.3 to 28.4) | 0.31 | 0.96 |
| Distal M1 | −13.3 (−31.2 to 4.5) | 0.13 | 0.14 | −25.9 (−60.1 to 8.1) | 0.39 | 0.13 | −10.7 (−39.8 to 18.4) | 0.31 | 0.47 |
| M2 | −23.5 (−39.3 to −7.7) | 0.13 | <0.001 | −64.3 (−94.5 to −34.1) | 0.39 | <0.001 | −38.8 (−64.6 to −13.1) | 0.31 | <0.001 |
| M3/M4 | −28.4 (−45.5 to −11.9) | 0.13 | <0.001 | −102.4 (−135.1 to −69.8) | 0.39 | <0.001 | −72.1 (−99.9 to −44.1) | 0.31 | <0.001 |
| Early Infarct Growth Rate | Final Infarct Volume | Infarct Growth Volume | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β (95% CI) | R-Squared | p-Value | β (95% CI) | R-Squared | p-Value | β (95% CI) | R-Squared | p-Value | |
| Clot Burden Score | −2.3 (−4.2 to −0.5) | 0.07 | 0.01 | −22.8 (−33.4 to −12.3) | 0.25 | <0.001 | −22.7 (−32.9 to −12.6) | 0.27 | <0.001 |
| Thrombus length | 0.38 (−0.26 to 1.02) | 0.02 | 0.24 | 3.5 (−0.58 to 7.62) | 0.05 | 0.06 | 3.1 (−0.78 to 7.03) | 0.05 | 0.11 |
| Thrombus location | |||||||||
| ICA | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | ||||||
| Proximal M1 | −0.53 (−17.6 to 16.5) | 0.01 | 0.95 | −134.5 (−233.5 to −45.5) | 0.29 | <0.001 | −155.9 (−240.9 to −70.9) | 0.33 | <0.001 |
| Distal M1 | −4.4 (−22.3 to 13.6) | 0.01 | 0.62 | −105.4 (−199.7 to −10.9) | 0.29 | 0.02 | −109.4 (−197.1 to −21.8) | 0.33 | 0.01 |
| M2 | −10.7 (−26.6 to 5.1) | 0.01 | 0.18 | −197.7 (−286.7 to −108.7) | 0.29 | <0.001 | −196.9 (−279.6 to −114.1) | 0.33 | <0.001 |
| M3/M4 | −16.1 (−33.1 to −1.0) | 0.01 | 0.06 | −185.6 (−280.1 to −91.2) | 0.29 | <0.001 | −182.9 (−270.5 to −95.4) | 0.33 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dutra, B.G.; Alves, H.C.B.R.; Gagliardi, V.; Gagliardi, R.J.; Pacheco, F.T.; Maia, A.C.M., Jr.; da Rocha, A.J. Thrombus Imaging Features for Anterior Circulation Stroke: Their Impact on CTP Parameters and Natural Evolution of Infarct Progression. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15100464
Dutra BG, Alves HCBR, Gagliardi V, Gagliardi RJ, Pacheco FT, Maia ACM Jr., da Rocha AJ. Thrombus Imaging Features for Anterior Circulation Stroke: Their Impact on CTP Parameters and Natural Evolution of Infarct Progression. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(10):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15100464
Chicago/Turabian StyleDutra, Bruna G., Heitor C. B. R. Alves, Vivian Gagliardi, Rubens J. Gagliardi, Felipe T. Pacheco, Antonio C. M. Maia, Jr., and Antônio J. da Rocha. 2025. "Thrombus Imaging Features for Anterior Circulation Stroke: Their Impact on CTP Parameters and Natural Evolution of Infarct Progression" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 10: 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15100464
APA StyleDutra, B. G., Alves, H. C. B. R., Gagliardi, V., Gagliardi, R. J., Pacheco, F. T., Maia, A. C. M., Jr., & da Rocha, A. J. (2025). Thrombus Imaging Features for Anterior Circulation Stroke: Their Impact on CTP Parameters and Natural Evolution of Infarct Progression. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(10), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15100464






