-
 Predictive Factors of Cytomegalovirus Colonic Reactivation in Patients with Active Ulcerative Colitis
Predictive Factors of Cytomegalovirus Colonic Reactivation in Patients with Active Ulcerative Colitis -
 Elements in the 5′ Untranslated Region of Viral RNA Important for HIV Gag Recognition and Cross-Packaging
Elements in the 5′ Untranslated Region of Viral RNA Important for HIV Gag Recognition and Cross-Packaging -
 First Report of Paralytic Rabies in a Lowland Tapir (Tapirus terrestris) in Argentina
First Report of Paralytic Rabies in a Lowland Tapir (Tapirus terrestris) in Argentina -
 The In Situ Structure of T-Series T1 Reveals a Conserved Lambda-Like Tail Tip
The In Situ Structure of T-Series T1 Reveals a Conserved Lambda-Like Tail Tip -
 Exploring the Contribution of TLR7 to Sex-Based Disparities in Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)-Induced Inflammation and Immunity
Exploring the Contribution of TLR7 to Sex-Based Disparities in Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)-Induced Inflammation and Immunity
Journal Description
Viruses
Viruses
is a peer-reviewed, open access journal of virology, published monthly online by MDPI. The Spanish Society for Virology (SEV), Canadian Society for Virology (CSV), Italian Society for Virology (SIV-ISV), Australasian Virology Society (AVS), Brazilian Society for Virology (BSV) and others are affiliated with Viruses and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, Embase, PubAg, AGRIS, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Virology) / CiteScore - Q1 (Infectious Diseases)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 18.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journal: Zoonotic Diseases.
Impact Factor:
3.5 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.7 (2024)
Latest Articles
Maternal Obesity Modifies the Impact of Active SARS-CoV-2 Infection on Placental Pathology
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 1013; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071013 - 18 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: Obesity during pregnancy is associated with an elevated risk of severe COVID-19, including higher rates of maternal complications, intensive care admission, and adverse neonatal outcomes. The impact of combination of SARS-CoV-2 infection and maternal obesity in placental pathology has not been properly
[...] Read more.
Background: Obesity during pregnancy is associated with an elevated risk of severe COVID-19, including higher rates of maternal complications, intensive care admission, and adverse neonatal outcomes. The impact of combination of SARS-CoV-2 infection and maternal obesity in placental pathology has not been properly investigated. Aim: To compare the histopathological changes in the placenta induced by active SARS-CoV-2 infection in obese and non-obese patients. Methods: This retrospective cohort study included human placentas from non-obese women and pre-gestationally obese women with active SARS-CoV-2 infection (SARS and OB+SARS, respectively), and placentas from non-obese women and pre-gestationally obese women without SARS-CoV-2 infection (control and OB, collected in the post- and pre-pandemic periods, respectively). Results: A higher (50%) occurrence of ischemic injury and subchorionic fibrin deposits and a 15 × higher risk of occurrence of these lesions were found in the OB+SARS group, in relation to control. In contrast, a 10% lower risk of developing chorangiosis in the OB+SARS group than the OB group was observed. Conclusions: An increased risk of lesions related to both maternal and fetal malperfusion and ischemic injury and a lower risk for chorangiosis exist in placentas from obese women affected by SARS-CoV-2 infection. Importantly, these differences were not observed in placentas from non-obese women.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue SARS-CoV-2, COVID-19 Pathologies, Long COVID, and Anti-COVID Vaccines)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
CrAssphage as a Human Enteric Viral Contamination Bioindicator in Marketed Bivalve Mollusks
by
Isabella Rodrigues Negreiros, Natália Lourenço dos Santos, Bruna Barbosa de Paula, Bruna Lopes Figueiredo, Marcelo Luiz Lima Brandão, José Paulo Gagliardi Leite, Marize Pereira Miagostovich and Carina Pacheco Cantelli
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 1012; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071012 - 18 Jul 2025
Abstract
CrAssphage, a bacteriophage that infects human gut-associated Bacteroides spp., has emerged as a potential anthropogenic fecal pollution indicator in environmental matrices. This study investigated the presence and concentration of crAssphages in bivalve mollusks (oysters and mussels) marketed in three cities in the state
[...] Read more.
CrAssphage, a bacteriophage that infects human gut-associated Bacteroides spp., has emerged as a potential anthropogenic fecal pollution indicator in environmental matrices. This study investigated the presence and concentration of crAssphages in bivalve mollusks (oysters and mussels) marketed in three cities in the state of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, sampled from January to December 2022. CrAssphages were detected during the study period in 66.7% (48/72) of sampled oysters and 54.8% (34/62) of sampled mussels, at median concentrations of 1.9 × 104 and 4.2 × 104 genome copies (GC)/g, respectively. These levels were 1–2 log10 higher than those observed for major human enteric viruses, including norovirus genogroups GI and GII, sapovirus, human mastadenovirus (HAdV), rotavirus A, human astrovirus (HAstV), and hepatitis A virus. CrAssphage specificity and sensitivity were calculated for all viruses. Moderate correlations between crAssphage (log10 GC/g) and norovirus GI and GII, HAdV, SaV, and HAstV (Spearman’s rho = 0.581-0.464, p < 0.001) were observed in mussels. Altogether, the data support the use of crAssphage as a molecular indicator of human viral contamination in shellfish, with potential application in routine environmental and food safety monitoring in production areas.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Role of Bacteriophage in Intestine Microbial Communities)
Open AccessArticle
Investigation of the Mouse Infection Model for Echovirus 18
by
Lei Xiang, Linlin Zhai, Guanyong Ou, Wei Zhao, Yang Yang and Chenguang Shen
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 1011; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071011 - 18 Jul 2025
Abstract
Echovirus 18, a member of the B group of enteroviruses, is a significant etiological agent of aseptic meningitis and viral encephalitis in children. In this study, we investigated the pathogenicity of E18 by establishing a mouse infection model after comparing various mouse strains
[...] Read more.
Echovirus 18, a member of the B group of enteroviruses, is a significant etiological agent of aseptic meningitis and viral encephalitis in children. In this study, we investigated the pathogenicity of E18 by establishing a mouse infection model after comparing various mouse strains and injection methods. Two-day-old IFNAR1 knockout mice infected with clinical isolates of E18 exhibited symptoms such as lethargy, hind limb paralysis, and even mortality. Similarly, some two-day-old C57BL/6J mice displayed comparable symptoms; however, the incidence was lower than that observed in IFNAR1 knockout mice. No similar symptoms were noted in any Balb/c mice. Significant pathological changes were observed in skeletal muscle, brain tissue, and other organs of symptomatic mice; among these tissues, skeletal muscle demonstrated the highest viral load. The established infection model using two-day-old IFNAR1 knockout mice provides valuable insights into further investigations regarding its pathological injury mechanisms as well as the protective effects conferred by antibodies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Viruses)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Wheat Resistance Genes on Wheat Curl Mite Fitness and Wheat Streak Mosaic Dynamics Under Single and Mixed Infections
by
Saurabh Gautam and Kiran R. Gadhave
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 1010; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071010 - 18 Jul 2025
Abstract
The wheat curl mite (WCM, Aceria tosichella Keifer), a complex of eriophyid mite species, transmits wheat streak mosaic virus (WSMV) and Triticum mosaic virus (TriMV), which in single or mixed infections cause wheat streak mosaic (WSM) disease—a major threat to wheat production across
[...] Read more.
The wheat curl mite (WCM, Aceria tosichella Keifer), a complex of eriophyid mite species, transmits wheat streak mosaic virus (WSMV) and Triticum mosaic virus (TriMV), which in single or mixed infections cause wheat streak mosaic (WSM) disease—a major threat to wheat production across the U.S. Great Plains. Resistant wheat cultivars bearing Cmc3 and Cmc4 (targeting WCM), Wsm1 and Wsm2 (targeting WSMV), and Wsm1 (targeting TriMV) are widely used to manage this pest–pathogen complex. However, comprehensive studies investigating how these resistance mechanisms influence both vector biology and virus transmission remain scarce. To address this gap, we evaluated disease development and WCM fitness across nine wheat cultivars with differential resistance profiles under single and mixed infections of WSMV and TriMV. We found strong viral synergy in co-infected plants, with TriMV accumulation markedly enhanced during mixed infections, irrespective of host genotype. Symptom severity and virus titers (both WSMV and TriMV) were highest in the cultivars carrying Wsm2, suggesting a potential trade-off in resistance effectiveness under mixed infection pressure. While mite development time (egg to adult) was unaffected by host genotype or infection status, mite fecundity was significantly reduced on infected plants carrying Wsm1 or Wsm2, but not on those with Cmc3 and Cmc4. Notably, virus accumulation in mites was reduced on the cultivars with Cmc3 and Cmc4, correlating with virus titers in the host tissues. Our findings highlight the complex interplay between host resistance, virus dynamics, and vector performance. Cultivars harboring Cmc3 and Cmc4 may offer robust field-level protection by simultaneously suppressing mite reproduction and limiting virus accumulation in both plant and vector.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular and Biological Virus-Plant-Insect Vector Interactions)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Overexpression of Interleukin-17 Modulates Responses to Marek’s Disease Virus Infection and Tumor Formation in Chickens
by
Nitish Boodhoo, Katherine Blake, Fatemeh Fazel, Janan Shoja Doost and Shayan Sharif
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 1009; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071009 - 18 Jul 2025
Abstract
Marek’s Disease Virus (MDV) is a highly contagious pathogen in chickens, resulting in immunosuppression and T-cell lymphomas. Understanding the role of host cytokines in MDV pathogenesis is crucial for developing effective interventions. This study investigated the in vivo effects of overexpressing avian interleukin-17
[...] Read more.
Marek’s Disease Virus (MDV) is a highly contagious pathogen in chickens, resulting in immunosuppression and T-cell lymphomas. Understanding the role of host cytokines in MDV pathogenesis is crucial for developing effective interventions. This study investigated the in vivo effects of overexpressing avian interleukin-17 (IL-17) in Marek’s disease virus infection model and its impact on T-cell populations. We utilized a recombinant pCDNA3.1 plasmid that expresses IL-17 at days 4 and 10 post-MDV infection in chickens. Our findings demonstrate that IL-17 overexpression significantly enhanced MDV replication. However, treatment with the plasmid expressing IL-17 led to a reduction in MD disease severity. Additionally, IL-17 treatment markedly altered the frequency of CD4+ and CD8α+ αβ T-cells. Specifically, at 21-dpi, there was an increase in CD3+ CD8α+ αβ T cells and a decrease in CD3+ CD4+ αβ T-cells within the spleen of chickens treated with the plasmid expressing IL-17. These modulatory effects suggest a possible mechanism by which IL-17 facilitates immune system cell activation and enhances viral persistence. This study underscores the pivotal role of IL-17 in MDV infection dynamics and offers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Marek's Disease Virus)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Emerging Foot-and-Mouth Disease, Bluetongue, and Peste Des Petits Ruminants in Algeria
by
Ilhem Zouyed, Sabrina Boussena, Nacira Ramdani, Houssem Eddine Damerdji, Julio A. Benavides and Hacène Medkour
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 1008; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071008 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD), bluetongue (BT), and Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR) are major emerging and re-emerging viral infections affecting ruminants. These diseases can threaten livestock health, food security, and economic stability in low- and middle-income countries, including Algeria. However, their dynamics remain mostly
[...] Read more.
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD), bluetongue (BT), and Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR) are major emerging and re-emerging viral infections affecting ruminants. These diseases can threaten livestock health, food security, and economic stability in low- and middle-income countries, including Algeria. However, their dynamics remain mostly unknown, limiting the implementation of effective preventive and control measures. We analyzed outbreak data reported by Algerian veterinary authorities and the WAHIS database from 2014 to 2022 for FMD; from 2006 to 2020 for BT; and from 2011 to 2022 for PPR to investigate their spatiotemporal patterns and environmental drivers. Over these periods, Algeria reported 1142 FMD outbreaks (10,409 cases; 0.16/1000 incidence), 167 BT outbreaks (602 cases; 0.018/1000), and 222 PPR outbreaks (3597 cases; 0.096/1000). Small ruminants were the most affected across all diseases, although cattle bore the highest burden of FMD. BT primarily impacted sheep, and PPR showed a higher incidence in goats. Disease peaks occurred in 2014 for FMD, 2008 for BT, and 2019 for PPR. Spatial analyses revealed distinct ecological hotspots: sub-humid and semi-arid zones for FMD and BT, and semi-arid/Saharan regions for PPR. These patterns may be influenced by species susceptibility, animal movement, trade, and climatic factors such as temperature and rainfall. The absence of consistent temporal trends and the persistence of outbreaks suggest multiple drivers, including insufficient vaccination coverage, under-reporting, viral evolution, and environmental persistence. Our findings underscore the importance of targeted species- and region-specific control strategies, including improved surveillance, cross-border coordination, and climate-informed risk mapping. Strengthening One Health frameworks will be essential to mitigate the re-emergence and spread of these diseases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Microbes, Infections and Spillovers, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
A Strand-Specific Quantitative RT-PCR Method for Detecting vRNA, cRNA, and mRNA of H7N9 Avian Influenza Virus in a Mouse Model
by
Bo Wang, Guangwen Wang, Yi-han Wang, Xuwei Liu, Manman Li, Huihui Kong, Hualan Chen, Li Jiang and Chengjun Li
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 1007; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071007 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
Avian influenza virus (AIV) remains a persistent threat to both the poultry industry and human health. Among the AIV subtypes posing public health threats, H7N9 AIV is responsible for five epidemic waves of human infection in China. Here, a detection system based on
[...] Read more.
Avian influenza virus (AIV) remains a persistent threat to both the poultry industry and human health. Among the AIV subtypes posing public health threats, H7N9 AIV is responsible for five epidemic waves of human infection in China. Here, a detection system based on a mouse model was established, which can simultaneously and quantitatively analyze the dynamic changes in the viral genomic RNA (vRNA), complementary RNA (cRNA), and messenger RNA (mRNA) of H7N9 AIV by using reverse transcription primers with tag sequences to reverse transcribe the three species of RNAs into corresponding cDNA templates, which are then absolutely quantified using the TaqMan quantitative PCR method. This system specifically targets the PB2 and NA genes and, for the first time, enables a spatiotemporal analysis of all three viral RNA species within an animal model. Our results revealed that H7N9 AIV exhibits characteristic replication kinetics, with all three species of viral RNAs showing a rapid increase followed by a certain degree of decline. This system offers a powerful tool for us to further advance our understanding of the replication dynamics of AIV in mice.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses: Prevention, Diagnosis, Treatment: 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Non-Coding RNAs and Immune Evasion in Human Gamma-Herpesviruses
by
Tablow S. Media, Laura Cano-Aroca and Takanobu Tagawa
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 1006; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071006 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
Herpesviruses are DNA viruses that evade the immune response and persist as lifelong infections. Human gamma-herpesviruses Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and Kaposi’s sarcoma herpesvirus (KSHV) are oncogenic; they can lead to cancer. Oncogenic viruses are responsible for 10–15% of human cancer development, which can
[...] Read more.
Herpesviruses are DNA viruses that evade the immune response and persist as lifelong infections. Human gamma-herpesviruses Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and Kaposi’s sarcoma herpesvirus (KSHV) are oncogenic; they can lead to cancer. Oncogenic viruses are responsible for 10–15% of human cancer development, which can have poor prognoses. Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are RNAs that regulate gene expression without encoding proteins, and are being studied for their roles in viral immune evasion, infection, and oncogenesis. ncRNAs are classified by their size, and include long non-coding RNAs, microRNAs, and circular RNAs. EBV and KSHV manipulate host ncRNAs, and encode their own ncRNAs, regulating host processes and immune responses. Viral ncRNAs regulate host functions by post-transcriptionally modifying host RNAs, and by serving as mimics of other host RNAs, promoting immune evasion. ncRNAs in gamma-herpesvirus infection are also important for tumorigenesis, as dampening immune responses via ncRNAs can upregulate pro-tumorigenic pathways. Emerging topics such as RNA modifications, target-directed miRNA degradation, competing endogenous RNA networks, and lncRNA/circRNA–miRNA interactions provide new insights into ncRNA functions. This review compares ncRNAs and the mechanisms of viral immune evasion in EBV and KSHV, while also expanding on recent developments in the roles of ncRNAs in immune evasion, viral infection, and oncogenesis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Understanding the Oncogenesis of Human Herpesviruses through Their Critical Comparisons)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Serum sICAM-1 and Galectin-3 Levels in Diabetic Patients with COVID-19
by
Busra Karahan, Dogan Nasir Binici, Omer Karasahin, Sibel İba Yilmaz, Ahmet Kiziltunc and Filiz Mercantepe
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 1005; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071005 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
Introduction: This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic and prognostic value of soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) and galectin-3 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) diagnosed with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Participants and Method: This prospective observational study included 45 adult
[...] Read more.
Introduction: This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic and prognostic value of soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) and galectin-3 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) diagnosed with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Participants and Method: This prospective observational study included 45 adult patients (≥18 years) with T2D and confirmed COVID-19 who were followed in the Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology departments between May and June 2022. The control group consisted of 45 healthy volunteers without chronic illness who were presented to the internal medicine outpatient clinic. In addition to routine laboratory biomarkers assessed at hospital admission, the serum levels of sICAM-1 and galectin-3 were measured via ELISA kits. Results: The median age of the patients was 66 years (range: 41–77), and 23 (51.1%) were male. Hypertension was the most common comorbidity in addition to diabetes. Compared with those in the control group, the serum levels of both galectin-3 and sICAM-1 were significantly elevated in patients with COVID-19 and T2D (p < 0.001). However, there was no significant difference in galectin-3 or sICAM-1 levels between survivors and nonsurvivors (p = 0.240 and p = 0.266, respectively). Conclusion: Galectin-3 and sICAM-1 demonstrated stronger diagnostic utility than conventional biomarkers in T2D patients with COVID-19. The elevated levels of these markers may reflect the underlying systemic inflammation observed in diabetic patients with COVID-19. The strong correlation between galectin-3 and sICAM-1 suggests a potential link in their inflammatory regulation, although causality cannot be inferred.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue COVID-19 Complications and Co-infections)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Innovating Quality Control and External Quality Assurance for HIV-1 Recent Infection Testing: Empowering HIV Surveillance in Lao PDR
by
Supaporn Suparak, Kanokwan Ngueanchanthong, Petai Unpol, Siriphailin Jomjunyoung, Wipawee Thanyacharern, Sirilada Pimpa Chisholm, Nitis Smanthong, Pojaporn Pinrod, Thitipong Yingyong, Phonepadith Xangsayarath, Sinakhone Xayadeth, Virasack Somoulay, Theerawit Tasaneeyapan, Somboon Nookhai, Archawin Rojanawiwat and Sanny Northbrook
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 1004; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071004 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
Quality assurance programs are critical to ensuring the consistency and reliability of point-of-care surveillance test results. In 2022, we launched Laos’ inaugural quality control (QC) and external quality assessment (EQA) program for national HIV recent infection surveillance. Our study aims to implement the
[...] Read more.
Quality assurance programs are critical to ensuring the consistency and reliability of point-of-care surveillance test results. In 2022, we launched Laos’ inaugural quality control (QC) and external quality assessment (EQA) program for national HIV recent infection surveillance. Our study aims to implement the first QC and EQA program for national HIV recent infection surveillance in Laos, utilizing non-infectious dried tube specimens (DTS) for quality control testing. This initiative seeks to monitor and assure the quality of HIV infection surveillance. We employed the Asante HIV-1 Rapid Test for Recent Infection (HIV-1 RTRI) point-of-care kit, using plasma specimens from the Thai Red Cross Society to create dried tube specimens (DTS). The DTS panels, including HIV-1 negative, HIV-1 recent, and HIV-1 long-term samples, met ISO 13528:2022 standards to ensure homogeneity and stability. These panels were transported from the Thai National Institute of Health (Thai NIH) to the Laos National Center for Laboratory and Epidemiology (NCLE) and subsequently shipped to 12 remote laboratories at ambient temperature. The laboratory results were electronically transmitted to Thai NIH 15 days after receiving the panel for performance analysis. The concordance results with the sample types were scored, and laboratories that achieved 100% concordance across all sample panels were considered to have satisfactorily met the established standards. Almost all laboratories demonstrated satisfactory results with 100% concordance across all sample panels during all three rounds of QC: 11 out of 12 (92%) in June, 10 out of 12 (83%) in July, and 11 out of 12 (91%) in August. The two rounds of EQA performed in June and August 2022 were satisfied by 8 out of 11 (72%) and 5 out of 10 (50%) laboratories, respectively. QC and EQA monitoring identified errors such as testing protocol mistakes and insufficient DTS panel dissolution, leading to improvements in HIV recency testing quality. Laboratories that reported errors were corrected and implemented further preventive actions. The QC and EQA program for HIV-1 RTRI identified errors in HIV recent infection testing. Implementing a specialized QC and EQA program for DTS marks a significant advancement in improving the accuracy and consistency of HIV recent infection surveillance. Continuous assessment is vital for addressing recurring issues.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Virology and Viral Diseases)
Open AccessReview
Laboratory Diagnosis of Hendra and Nipah: Two Emerging Zoonotic Diseases with One Health Significance
by
Shaun van den Hurk, Aurelle Yondo and Binu T. Velayudhan
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 1003; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071003 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
Hendra virus (HeV) and Nipah virus (NiV) are two highly pathogenic RNA viruses with zoonotic potential, which can cause severe diseases with high mortality rates (50–100%) in humans and animals. Given this context, these viruses are classified as Biosafety Level 4 (BSL-4) pathogens,
[...] Read more.
Hendra virus (HeV) and Nipah virus (NiV) are two highly pathogenic RNA viruses with zoonotic potential, which can cause severe diseases with high mortality rates (50–100%) in humans and animals. Given this context, these viruses are classified as Biosafety Level 4 (BSL-4) pathogens, thus limiting research studies. Despite the high case fatalities, there are currently no human vaccines available for either virus, owing in part to the limitations in research and hesitancy in funding. In the absence of widespread vaccination, diagnostic tests are crucial for the rapid identification of cases and disease surveillance. This review synthesizes current knowledge on the epidemiology, transmission dynamics, and pathogenesis of NiV and HeV to contextualize a detailed assessment of the available diagnostic tools. We examined molecular and serological assays, including RT-PCR, ELISA, and LAMP, highlighting sample sources, detection windows, and performance. Diagnostic considerations across human and animal hosts are discussed, with emphasis on outbreak applicability and field-readiness, given the need for diagnostic assays that are suitable for use in low-income areas. Further development of diagnostic assays, including isothermal amplification tests and other next-generation approaches, is recommended to fill the gap in rapid, point-of-care diagnostics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Virology and Viral Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
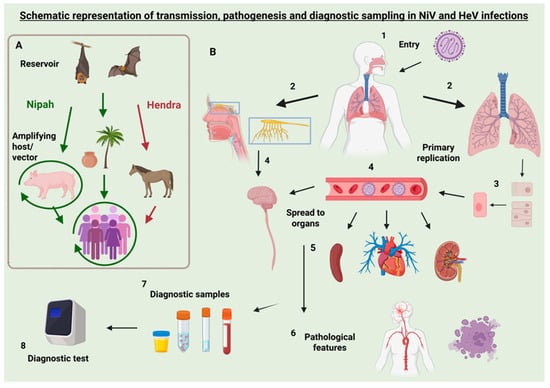
Figure A1
Open AccessReview
Age Matters: Key Contributors to Interferon Toxicity in Infants During Influenza Virus Infection
by
Abigail P. Onufer and Alison J. Carey
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 1002; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071002 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
Respiratory viral infections are a leading cause of early childhood hospitalizations in the United States. Neonatal immune responses are reliant on innate mechanisms during the first few months of life. Interferons (IFNs) are a key component of this response. These antiviral cytokines are
[...] Read more.
Respiratory viral infections are a leading cause of early childhood hospitalizations in the United States. Neonatal immune responses are reliant on innate mechanisms during the first few months of life. Interferons (IFNs) are a key component of this response. These antiviral cytokines are produced early in infection and aid in viral control and clearance. Although generally considered protective in the setting of respiratory viral infections, the recent literature has suggested that IFNs may exacerbate disease. In the process of promoting an antiviral environment, IFNs impede cell proliferation, contribute to pulmonary barrier disruption, and generate reactive oxygen species. This is not tolerated in the rapidly developing neonatal lung. Therefore, IFNs contribute to pathogenesis in the influenza-infected neonate. This review focuses on the potential mechanisms that drive IFN-induced toxicity in neonates and prospective therapeutics to mitigate this toxicity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Interferon Signaling in Viral Pathogenesis)
►▼
Show Figures
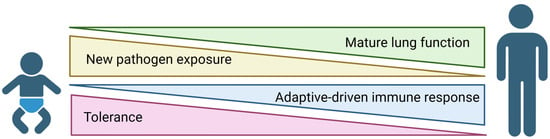
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Genomic Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 in Ukraine from May 2022 to March 2024 Reveals Omicron Variant Dynamics
by
Anna Iaruchyk, Jason Farlow, Artem Skrypnyk, Serhii Matchyshyn, Alina Kovalchuk, Iryna Demchyshyna, Mykhailo Rosada, Aron Kassahun Aregay and Jarno Habicht
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 1000; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071000 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
In Ukraine, SARS-CoV-2 detection and national genomic surveillance have been complicated by full-scale war, limited resources, and varying levels of public health infrastructure impacted across the country. Following the Spring of 2022, only a paucity of data have been reported describing the prevalence
[...] Read more.
In Ukraine, SARS-CoV-2 detection and national genomic surveillance have been complicated by full-scale war, limited resources, and varying levels of public health infrastructure impacted across the country. Following the Spring of 2022, only a paucity of data have been reported describing the prevalence and variant dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 in the country. Comparative whole genome analysis has overtaken diagnostics as the new gold standard for detecting and tracing emerging variants while showing utility to rapidly inform diagnostics, vaccine strategies, and health policy. Herein, we provide an updated report characterizing the dynamics and prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in Ukraine from 1 May 2022 to 31 March 2024. The present study extends previous reports for disease incidence Waves 1–4 in Ukraine with the addition herein of Waves 5, 6, and 7, occurring from August to November 2022 (Wave 5), February to May 2023 (Wave 6), and October 2023 to January 2024 (Wave 7). During the study period, the national Case Fatality Rate (CFR) fluctuated between 0.46% and 1.74%, indicating a consistent yet modest rate when compared to the global average. The epidemiological dynamics of Variants of Concern (VOCs) in Ukraine reflected global patterns over this period, punctuated by the rise of the BA.5 lineage and its subsequent replacement by the Omicron subvariants XBB and JN.1. Our analysis of variant dispersal patterns revealed multiple potential spatiotemporal introductions into Ukraine from Europe, Asia, and North America. Our results highlight the importance of ongoing genomic surveillance to monitor variant dynamics and support global efforts to control and mitigate COVID-19 disease risks as new variants arise.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Coronaviruses)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A More Rapid Method for Culturing LUHMES-Derived Neurons Provides Greater Cell Numbers and Facilitates Studies of Multiple Viruses
by
Adam W. Whisnant, Stephanie E. Clark, José Alberto Aguilar-Briseño, Lorellin A. Durnell, Arnhild Grothey, Ann M. Miller, Steven M. Varga, Jeffery L. Meier, Charles Grose, Patrick L. Sinn, Jessica M. Tucker, Caroline C. Friedel, Wendy J. Maury, David H. Price and Lars Dölken
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 1001; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071001 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
The ability to study mature neuronal cells ex vivo is complicated by their non-dividing nature and difficulty in obtaining large numbers of primary cells from organisms. Thus, numerous transformed progenitor models have been developed that can be routinely cultured, then scaled, and differentiated
[...] Read more.
The ability to study mature neuronal cells ex vivo is complicated by their non-dividing nature and difficulty in obtaining large numbers of primary cells from organisms. Thus, numerous transformed progenitor models have been developed that can be routinely cultured, then scaled, and differentiated to mature neurons. In this paper, we present a new method for differentiating one such model, the Lund human mesencephalic (LUHMES) dopaminergic neurons. This method is two days faster than some established protocols, results in nearly five times greater numbers of mature neurons, and involves fewer handling steps that could introduce technical variability. Moreover, it overcomes the problem of cell aggregate formation that commonly impedes high-resolution imaging, cell dissociation, and downstream analysis. While recently established for herpes simplex virus type 1, we demonstrate that LUHMES neurons can facilitate studies of other herpesviruses, as well as RNA viruses associated with childhood encephalitis and hemorrhagic fever. This protocol provides an improvement in the generation of large-scale neuronal cultures, which may be readily applicable to other neuronal 2D cell culture models and provides a system for studying neurotrophic viruses. We named this method the Streamlined Protocol for Enhanced Expansion and Differentiation Yield, or SPEEDY, method.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Virology and Viral Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Seroprevalence of Equine Influenza Virus Antibodies in Horses from Four Localities in Colombia
by
Juliana Gonzalez-Obando, Jeiczon Jaimes-Dueñez, Angélica Zuluaga-Cabrera, Jorge E. Forero, Andrés Diaz, Carlos Rojas-Arbeláez and Julian Ruiz-Saenz
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 999; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070999 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
Equine influenza is a highly contagious disease caused by the equine influenza virus (EIV). The occurrence of EIV outbreaks in America is associated with low levels of vaccination coverage. In Colombia, no seroprevalence evaluation has been carried out to estimate the distribution of
[...] Read more.
Equine influenza is a highly contagious disease caused by the equine influenza virus (EIV). The occurrence of EIV outbreaks in America is associated with low levels of vaccination coverage. In Colombia, no seroprevalence evaluation has been carried out to estimate the distribution of the virus within the country. Our aim was to perform a sero-epidemiological survey of equine influenza infections and to identify associated risk factors in horses from four departments of Colombia. Serological testing was carried out by using an ELISA for the detection of IgG antibodies against the influenza A virus. The evaluation of epidemiological variables, clinical manifestations, and vaccination history was carried out through the application of a data collection instrument. Among the 385 horses analyzed, 27% of the samples tested positive, with a higher prevalence in Study 1 from horses with respiratory symptoms (40.4%) than in Study 2 from horses without clinical signs (16.1%). Only horses housed in stables had higher odds of testing positive. The study also revealed that unvaccinated horses were 68% less likely to test positive than vaccinated horses were. This research highlights a significant gap in vaccination coverage and the presence of antibodies even in asymptomatic horses. Management factors such as activity type and housing should be considered when strategies for EIV prevention are developed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Viral Diseases of Livestock and Diagnostics, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Spatiotemporal Distribution and Risk Factors of African Swine Fever Outbreak Cases in Uganda for the Period 2010–2023
by
Eddie M. Wampande, Robert Opio, Simon P. Angeki, Corrie Brown, Bonto Faburay, Rose O. Ademun, Kenneth Ssekatawa, David D. South, Charles Waiswa and Peter Waiswa
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 998; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070998 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
This paper describes the spatiotemporal distribution and risk factors of African Swine Fever (ASF) in Uganda for the period of 2010 through 2023. The study utilized a comprehensive dataset from monthly reports (2010–2023) from District Veterinary Officers (DVOs), the Ministry of Agriculture, Animal
[...] Read more.
This paper describes the spatiotemporal distribution and risk factors of African Swine Fever (ASF) in Uganda for the period of 2010 through 2023. The study utilized a comprehensive dataset from monthly reports (2010–2023) from District Veterinary Officers (DVOs), the Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Industry and Fisheries (MAAIF), and the Food and Agriculture Organization, Uganda. Using GPS coordinates, ASF cases were mapped using QGIS to show ASF distribution and spread in Uganda. Moran’s I analysis was used to delineate clusters of ASF. A total of 1521 ASF cases were recorded. The data show that cases of ASF were disseminated throughout the country, with more cases of ASF documented in the central region and border districts (hotspots for ASF), and few cases were reported in Acholi, Karamoja, and Lango, Ankole, West Nile, and Kigezi sub-regions. The time series analysis revealed incidences of ASF disease occurring year-round; notable peak cases were observed in some districts, and districts with ≥30,000 pigs reported higher cases of ASF. The Moran’s I (≥1) analysis showed that ASF is either aggregated (p = 0.01), especially in central districts bordering Tanzania and lake shores, or sporadic in occurrence. The disease was present in 66% of the districts, with ASF occurring throughout the year. More cases were aggregated in central and border districts and districts with large pig populations (≥30,000). Sporadic cases were reported in districts bordering the DRC, Sudan, Kenya, the lake shores, Karamoja, Acholi, and Lango sub-regions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Viruses)
►▼
Show Figures
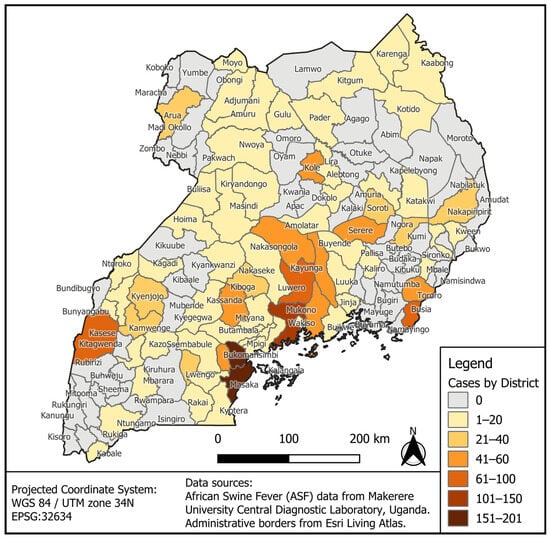
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Soluble Neuropilin-1 as a Marker for Distinguishing Bacterial and Viral Sepsis in Critically Ill Patients—A Prospective, Multicenter, Observational Study
by
Fabian Perschinka, Georg Franz Lehner, Timo Mayerhöfer, Frank Hartig, Birgit Zassler, Johannes Bösch, Dietmar Fries, Romuald Bellmann and Michael Joannidis
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 997; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070997 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
Sepsis causes millions of deaths each year. Rapid, targeted therapy can reduce mortality rates. Both bacterial and viral pathogens can trigger sepsis, but the utility of commonly used inflammatory markers for differentiation remains controversial. Moreover, little is known about the time courses of
[...] Read more.
Sepsis causes millions of deaths each year. Rapid, targeted therapy can reduce mortality rates. Both bacterial and viral pathogens can trigger sepsis, but the utility of commonly used inflammatory markers for differentiation remains controversial. Moreover, little is known about the time courses of alternative inflammatory parameters. The aim of this prospective, two-center observational study was to investigate the differences in the course of soluble Neuropilin-1 (sNRP-1) levels between bacterial and viral sepsis over a 7-day period. To be included, adult patients had to meet the SEPSIS-3 criteria and be diagnosed with either a bacterial or viral pathogen. Immunosuppressed patients were excluded. While IL-6, PCT, and CRP levels decreased consistently over time, sNRP-1 levels remained elevated in the bacterial group throughout the entire ICU stay. PCT (p < 0.001) and CRP (p = 0.016) levels were significantly associated with the course of sNRP-1. The AUC of sNRP-1 was 0.777 for discriminating between bacterial and viral infections on day 1. sNRP-1 remained stable and significantly higher in bacterial than in viral infections. Furthermore, the AUC values for discrimination ranged from acceptable to good, depending on the day of the ICU stay. sNRP-1 may serve as a potential tool to differentiate between bacterial and viral pathogens in sepsis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Viral Sepsis: Pathogenesis, Diagnostics and Therapeutics)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Characterization of a STAT-1 Knockout Mouse Model for Machupo Virus Infection and Pathogenesis
by
Stephanie R. Monticelli, Ana I. Kuehne, Russell R. Bakken, Susan R. Coyne, Kenise D. Lewis, Jo Lynne W. Raymond, Xiankun Zeng, Joshua B. Richardson, Zebulon Lapoint, Jennifer L. Williams, Christopher P. Stefan, Jeffrey R. Kugelman, Jeffrey W. Koehler and Andrew S. Herbert
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 996; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070996 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
Machupo virus (MACV), a member of the Arenaviridae family and causative agent of Bolivian hemorrhagic fever, results in lethality rates of 25–35% in humans. Mice lacking the signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT-1−/−) have previously been shown to succumb
[...] Read more.
Machupo virus (MACV), a member of the Arenaviridae family and causative agent of Bolivian hemorrhagic fever, results in lethality rates of 25–35% in humans. Mice lacking the signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT-1−/−) have previously been shown to succumb to MACV infection within 7–8 days via the intraperitoneal route. Despite these reports, we observed partial lethality in STAT-1−/− mice following challenge with wild-type MACV. Serial sampling studies to evaluate the temporal progression of infection and pathologic changes after challenge revealed a two-phase disease course. The first phase was characterized by viral load and pathological lesions in the spleen, liver, and kidney followed by a second, lethal phase, defined by high viral titers and inflammation in the brain and spinal cord resulting in neurological manifestations and subsequent mortality. Tissue adaptation in the brains of challenged STAT-1−/− mice resulted in a fully lethal model in STAT-1−/− mice (mouse-adapted; maMACV). A similar two-phase disease course was observed following maMACV challenge, but more rapid dissemination of the virus to the brain and overall pathology in this region was observed. The outcome of these studies is a lethal small rodent model of MACV that recapitulates many aspects of human disease.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Virology and Viral Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Biological, Molecular, and Physiological Characterization of Four Soybean Mosaic Virus Isolates Present in Argentine Soybean Crops
by
Mariel Maugeri, Marianela Rodríguez, Nicolas Bejerman, Irma G. Laguna and Patricia Rodríguez Pardina
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 995; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070995 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
Soybean mosaic virus (SMV) causes systemic infections in soybean plants, leading to chlorotic mosaic and significant yield losses. In Argentina, during the 1990s, three isolates were collected in Marcos Juárez (MJ), Manfredi (M), and Northwestern Argentina (NOA), along with the “Planta Vinosa” (PV)
[...] Read more.
Soybean mosaic virus (SMV) causes systemic infections in soybean plants, leading to chlorotic mosaic and significant yield losses. In Argentina, during the 1990s, three isolates were collected in Marcos Juárez (MJ), Manfredi (M), and Northwestern Argentina (NOA), along with the “Planta Vinosa” (PV) isolate, which causes severe necrosis in some cultivars. These isolates were freeze-dried and stored at −70 °C for several years. They were recovered by mechanical inoculation and biologically, molecularly, and physiologically characterized for the first time. Three of the four isolates showed low genetic divergence in the P1, CI, and CP genes. Although SMV-NOA and SMV-PV had high nucleotide sequence identity, they differed in pathogenicity, seed mottling, and transmission efficiency by seeds or aphids. SMV-NOA caused early changes in photosystem II quantum efficiency (ɸPSII) and malondialdehyde (MDA) content before symptom expression (BS). After symptom development (LS), SMV-M significantly increased MDA, total soluble sugars, and starch compared to the other isolates. Thus, early changes in ɸPSII and sugars may influence late viral symptoms. Likewise, SMV-MJ induced more severe symptoms in the susceptible Davis cultivar than in Don Mario 4800. Therefore, our results demonstrate genomic, biological, and physiological differences among SMV isolates and variable interactions of SMV-MJ with two soybean cultivars.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Viral Diseases of Major Crops)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Cytoplasmic Tail of Ovine Herpesvirus 2 Glycoprotein B Affects Cell Surface Expression and Is Required for Membrane Fusion
by
Colleen M. Lynch, Maria K. Herndon, McKenna A. Hull, Daniela D. Moré, Katherine N. Baker, Cristina W. Cunha and Anthony V. Nicola
Viruses 2025, 17(7), 994; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070994 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
Ovine herpesvirus 2 (OvHV-2) causes the fatal veterinary disease malignant catarrhal fever (MCF). Fusion is an essential step in the host cell entry of enveloped viruses and is an important target for vaccine development. OvHV-2 cannot be propagated in vitro, so a robust
[...] Read more.
Ovine herpesvirus 2 (OvHV-2) causes the fatal veterinary disease malignant catarrhal fever (MCF). Fusion is an essential step in the host cell entry of enveloped viruses and is an important target for vaccine development. OvHV-2 cannot be propagated in vitro, so a robust virus-free cell–cell membrane fusion assay is necessary to elucidate its entry mechanism. OvHV-2 cell–cell fusion requires three conserved herpesviral envelope glycoproteins: gB, gH, and gL. OvHV-2 fusion activity is detectable but low. We hypothesize that enhancing the cell surface expression of gB, which is the core herpesviral fusogen, will increase cell–cell fusion. We generated C-terminal truncation mutants of gB and determined their cell surface expression, subcellular distribution, and fusion activity. Two mutants, including one that lacked the entire cytoplasmic tail domain, failed to function in the cell–cell fusion assay, despite wild-type levels of surface expression. This suggests that the OvHV-2 gB cytoplasmic tail is critical for fusion. A gB mutant truncated at amino acid 847 showed increased surface expression and fusion relative to the wild type. This suggests that the robust fusion activity of gB847 is the result of increased surface expression. gB847 may be used in place of wild-type gB in an improved, more robust OvHV-2 fusion assay.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Viruses)
►▼
Show Figures
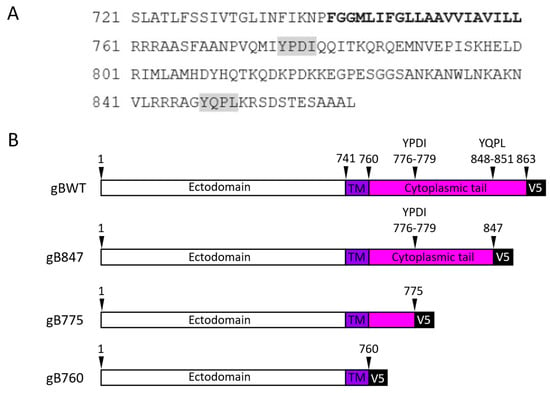
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Viruses Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
30 October–2 November 2025
The 11th Wuhan International Symposium on Modern Virology & Viruses 2025 Conference

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Viruses
Spumaretroviruses: Research and Applications
Guest Editors: Arifa Khan, Marcelo A. Soares, Dirk Lindemann, Martin LöcheltDeadline: 30 July 2025
Special Issue in
Viruses
Viral Resistance
Guest Editor: Maria Antonia De FrancescoDeadline: 31 July 2025
Special Issue in
Viruses
Mass Spectrometry and Viral Analysis
Guest Editor: Paul D. GershonDeadline: 31 July 2025
Special Issue in
Viruses
Virus-Host Protein Interactions
Guest Editor: Benoit CoulombeDeadline: 31 July 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Viruses
Mathematical Modeling of Viral Infection
Collection Editors: Amber M. Smith, Ruian Ke








