CrAssphage as a Human Enteric Viral Contamination Bioindicator in Marketed Bivalve Mollusks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. CrAssphage Quantification
2.2. CrAssphage as a Marker for Each Evaluated Enteric Virus
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
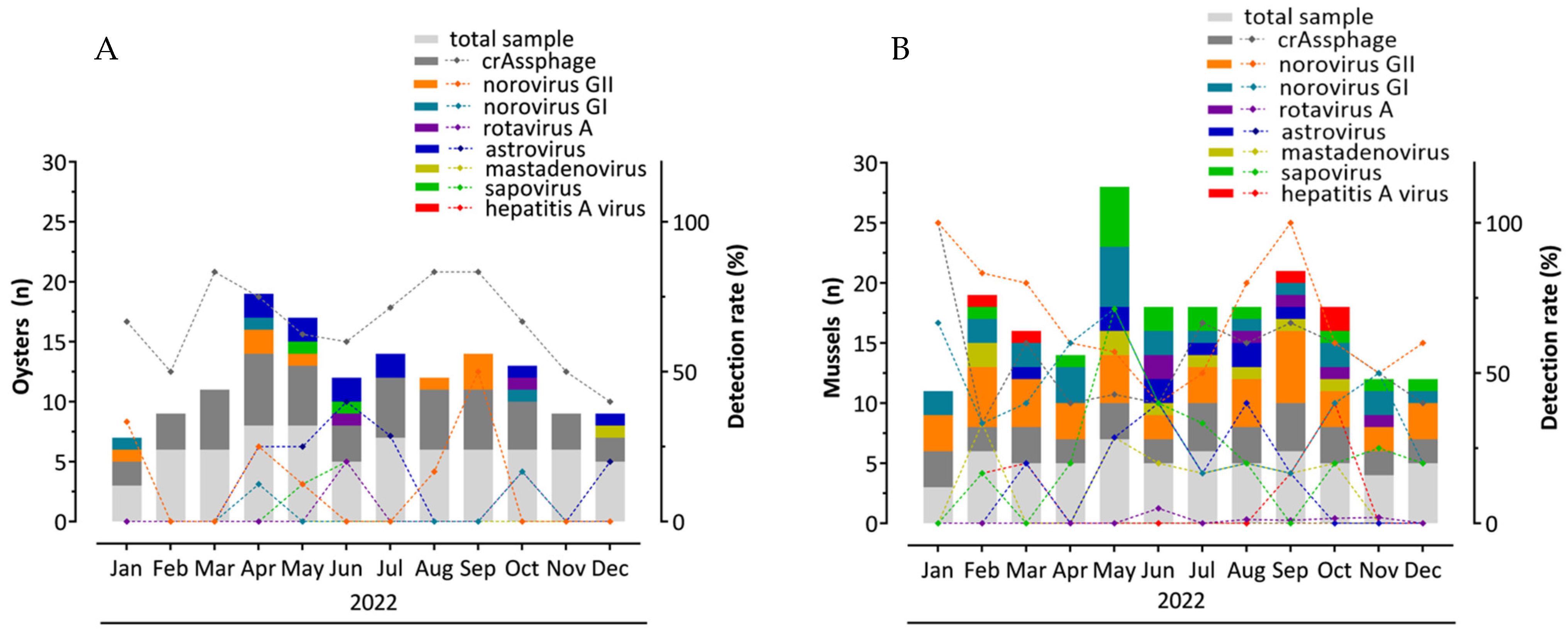
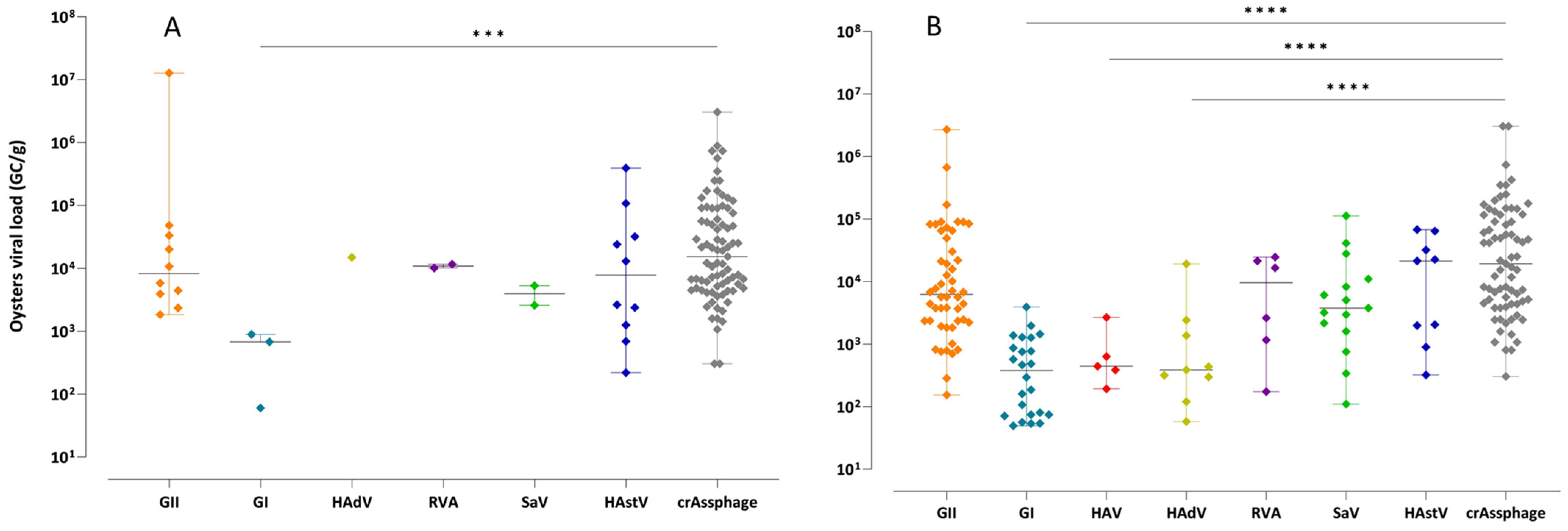
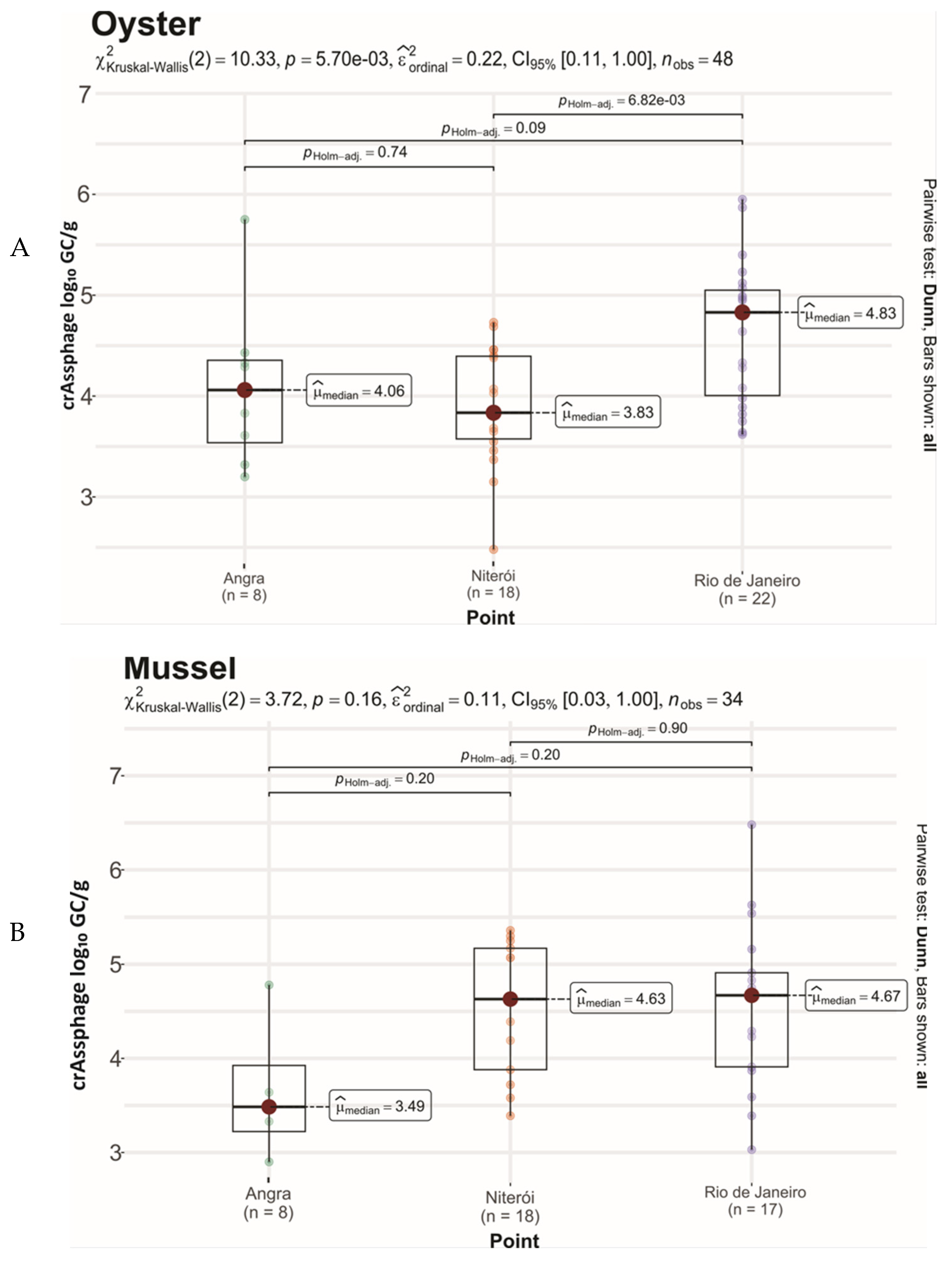
3.1. CrAssphage Detection
3.2. Evaluation of crAssphage as an Enteric Virus Detection Marker
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Fisheries and Aquaculture Projections to 2032; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024; Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/66538eba-9c85-4504-8438-c1cf0a0a3903/content (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Lin, D.; Chen, W.; Lin, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L. Viral Transmission in Sea Food Systems: Strategies for Control and Emerging Challenges. Foods 2025, 14, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joint FAO/WHO. Technical Guidance for the Development of the Growing Area Aspects of Bivalve Mollusc Sanitation Programmes, 2nd ed.; Food Safety and Quality Series; Joint FAO/WHO: Rome, Italy, 2021; ISBN 978-92-5-134591-7. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/344455/9789240030206-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- Joint FAO/WHO. Codex Alimentarius Commission. In Standard for Live and Raw Bivalve Molluscs (CXS 292-2008); FAO/WHO: Rome, Italy, 2015. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/sh-proxy/tr/?lnk=1&url=https%253A%252F%252Fworkspace.fao.org%252Fsites%252Fcodex%252FStandards%252FCXS%2B292-2008%252FCXS_292e_2015.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Ministério da Agricultura e Pecuária (MAPA). Portaria SDA/MAPA nº 884, de 6 de Setembro de 2023; Ministério da Agricultura e Pecuária: Brasília, Brazil, 2023. Available online: https://www.in.gov.br/en/web/dou/-/portaria-sda/mapa-n-884-de-6-de-setembro-de-2023-510078795 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Prez, V.E.; Gil, P.M.; Temprana, C.F.; Cuadrado, P.R.; Martínez, L.; Giordano, M.O.; Masachessi, G.; Isa, M.B.; Ré, V.; Pavan, J.; et al. Quantification of Human Infection Risk Caused by Rotavirus in Surface Waters from Córdoba, Argentina. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, J.P.S.; Sena, K.; Hodgers, L.; Palmer, A.; Toze, S. Comparative Enteric Viruses and Coliphage Removal during Wastewater Treatment Processes in a Sub-Tropical Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Zhao, F.; Tong, L.; Wang, S.; Zhou, D. Contamination, Bioaccumulation Mechanism, Detection, and Control of Human Norovirus in Bivalve Shellfish: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 62, 8972–8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desdouits, M.; Reynaud, Y.; Philippe, C.; Le Guyader, F.S.L.G. A Comprehensive Review for the Surveillance of Human Pathogenic Microorganisms in Shellfish. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joint FAO/WHO. Microbiological Risk Assessment of Viruses in Foods: Part 1: Food Attribution, Analytical Methods and Indicators—Meeting Report; Microbiological Risk Assessment Series, No. 49; Joint FAO/WHO: Rome, Italy, 2024. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/379637/9789240101074-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Lowther, J.A.; Cross, L.; Stapleton, T.; Gustar, N.E.; Walker, D.I.; Sills, M.; Treagus, S.; Pollington, V.; Lees, D.N. Use of F-Specific RNA Bacteriophage to Estimate Infectious Norovirus Levels in Oysters. Food Environ. Virol. 2019, 11, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haramoto, E.; Kitajima, M.; Kishida, N.; Konno, Y.; Katayama, H.; Asami, M.; Akiba, M. Occurrence of Pepper Mild Mottle Virus in Drinking Water Sources in Japan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7413–7418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symonds, E.M.; Nguyen, K.H.; Harwood, V.J.; Breitbart, M. Pepper Mild Mottle Virus: A Plant Pathogen with a Greater Purpose in (Waste)Water Treatment Development and Public Health Management. Water Res. 2018, 144, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusiñol, M.; Fernandez-Cassi, X.; Hundesa, A.; Vieira, C.; Kern, A.; Eriksson, I.; Ziros, P.; Kay, D.; Miagostovich, M.; Vargha, M.; et al. Application of Human and Animal Viral Microbial Source Tracking Tools in Fresh and Marine Waters from Five Different Geographical Areas. Water Res. 2014, 59, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesté, E.; Pascual-Benito, M.; Martín-Díaz, J.; Blanch, A.R.; Lucena, F.; Muniesa, M.; Jofre, J.; García-Aljaro, C. Dynamics of CrAssphage as a Human Source Tracking Marker in Potentially Faecally Polluted Environments. Water Res. 2019, 155, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Greaves, J.; Arp, L.; Stone, D.; Bibby, K. Comparative Fate of CrAssphage with Culturable and Molecular Fecal Pollution Indicators during Activated Sludge Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutilh, B.E.; Cassman, N.; McNair, K.; Sanchez, S.E.; Silva, G.G.Z.; Boling, L.; Barr, J.J.; Speth, D.R.; Seguritan, V.; Aziz, R.K.; et al. A Highly Abundant Bacteriophage Discovered in the Unknown Sequences of Human Faecal Metagenomes. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shkoporov, A.N.; Khokhlova, E.V.; Fitzgerald, C.B.; Stockdale, S.R.; Draper, L.A.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. ΦCrAss001 represents the most abundant bacteriophage family in the human gut and infects Bacteroides intestinalis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffron, J.; Mayer, B.K. Virus Isoelectric Point Estimation: Theories and Methods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 87, e02319-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, K.; Cooper, D.M.; McDonald, J.E.; Malham, S.K.; de Rougemont, A.; Jones, D.L. Seasonal and Spatial Dynamics of Enteric Viruses in Wastewater and in Riverine and Estuarine Receiving Waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachler, E.; Bibby, K. Metagenomic Evaluation of the Highly Abundant Human Gut Bacteriophage CrAssphage for Source Tracking of Human Fecal Pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinek, O.; Mazankova, K.; Kramna, L.; Odeh, R.; Alassaf, A.; Ibekwe, M.U.; Ahmadov, G.; Mekki, H.; Abdullah, M.A.; Bashir, M.E.; et al. Quantitative CrAssphage Real-Time PCR Assay Derived from Data of Multiple Geographically Distant Populations. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.P.; Teng, Y. Integrating Metagenomic and Bayesian Analyses to Evaluate the Performance and Confidence of CrAssphage as an Indicator for Tracking Human Sewage Contamination in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 4992–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantelli, C.P.; Tavares, G.C.L.; Sarmento, S.K.; Burlandy, F.M.; Fumian, T.M.; Maranhão, A.G.; da Silva, E.d.S.R.F.; Horta, M.A.P.; Miagostovich, M.P.; Yang, Z.; et al. Assessment of Gastroenteric Viruses in Marketed Bivalve Mollusks in the Tourist Cities of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2022. Viruses 2024, 16, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, N.L.; Burlandy, F.M.; Figueiredo, A.S.; Lopes, B.F.; Villar, L.M.; Maranhão, A.G.; Salgado, C.R.S.; Brandão, M.L.L.; Miagostovich, M.P.; Leite, J.P.G.; et al. Occurrence and Molecular Characterization of Human Astrovirus and Hepatitis a Virus in Bivalve Mollusks Marketed in Tourist Cities in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Food Environ. Virol. 2025, 17, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 15216-1:2017; Microbiology of Food a Chain—Horizontal Method for Determination of Hepatitis A Virus and Norovirus in Food Using Real-Time RT-PCR—Part 1: Method for Quantification. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 2017, pp. 1–48.
- Stachler, E.; Kelty, C.; Sivaganesan, M.; Li, X.; Bibby, K.; Shanks, O.C. Quantitative CrAssphage PCR Assays for Human Fecal Pollution Measurement. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9146–9154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, S.H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, S.H.; Vinjé, J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, G.W. Evaluation of CrAssphages as a Potential Marker of Human Viral Contamination in Environmental Water and Fresh Leafy Greens. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1374568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trullols, E.; Ruisánchez, I.; Rius, F.X. Validation of Qualitative Analytical Methods. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2004, 23, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, T. How to Read a Paper: Papers That Report Diagnostic or Screening Tests. BMJ 1997, 315, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamovi, version 2.6.24; The Jamovi Project; [Computer Software]. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Farkas, K.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; Walker, D.I.; McDonald, J.E.; Malham, S.K.; Jones, D.L. Critical Evaluation of CrAssphage as a Molecular Marker for Human-Derived Wastewater Contamination in the Aquatic Environment. Food Environ. Virol. 2019, 11, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venuti, I.; Cuevas-Ferrando, E.; Falcó, I.; Girón-Guzmán, I.; Ceruso, M.; Pepe, T.; Sánchez, G. Presence of Potentially Infectious Human Enteric Viruses and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Mussels from the Campania Region, Italy: Implications for Consumer’s Safety. Food Environ. Virol. 2025, 17, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyawali, P.; Devane, M.; Scholes, P.; Hewitt, J. Application of CrAssphage, F-RNA Phage and Pepper Mild Mottle Virus as Indicators of Human Faecal and Norovirus Contamination in Shellfish. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas-Ferrando, E.; Allende, A.; Pérez-Cataluña, A.; Truchado, P.; Hernández, N.; Gil, M.I.; Sánchez, G. Occurrence and Accumulation of Human Enteric Viruses and Phages in Process Water from the Fresh Produce Industry. Foods 2021, 10, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabar, M.A.; Honda, R.; Haramoto, E. CrAssphage as an Indicator of Human-Fecal Contamination in Water Environment and Virus Reduction in Wastewater Treatment. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demoliner, M.; Filippi, M.; Gularte, J.S.; de Almeida, P.R.; da Silva, M.S.; Pereira, V.M.d.A.G.; Hansen, A.W.; Girardi, V.; Ferreira, H.L.; Spilki, F.R. Comparison of Metagenomic Protocols for Virome Data Generation from Environmental Matrices and Stool Samples: Insights into Viral Diversity and Fecal Contamination Indicators. Total Environ. Microbiol. 2025, 1, 100008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lioe, T.S.; Sun, L.; Adriaenssens, E.; McCarthy, A.; Sekar, R. Validation of CrAssphage Microbial Source Tracking Markers and Comparison with Bacteroidales Markers for Detection and Quantification of Faecal Contaminations in Surface Water. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 336, 125403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suplicy, F.M.; Vianna, L.F.d.N.; Rupp, G.S.; Novaes, A.L.T.; Garbossa, L.H.P.; de Souza, R.V.; Guzenski, J.; da Costa, S.W.; Silva, F.M.; dos Santos, A.A. Planning and Management for Sustainable Coastal Aquaculture Development in Santa Catarina State, South Brazil. Rev. Aquac. 2015, 9, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, R.V.; Moresco, V.; Miotto, M.; Souza, D.S.M.; de Campos, C.J.A. Prevalence, Distribution and Environmental Effects on Faecal Indicator Bacteria and Pathogens of Concern in Commercial Shellfish Production Areas in a Subtropical Region of a Developing Country (Santa Catarina, Brazil). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Aljaro, C.; Ballesté, E.; Muniesa, M.; Jofre, J. Determination of CrAssphage in Water Samples and Applicability for Tracking Human Faecal Pollution. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1775–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Estatística e Geografia (IBGE). Cidades e Estados do Brasil. 2024. Available online: https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/ (accessed on 3 June 2025).
- Edwards, R.A.; Vega, A.A.; Norman, H.M.; Ohaeri, M.; Levi, K.; Dinsdale, E.A.; Cinek, O.; Aziz, R.K.; McNair, K.; Barr, J.J.; et al. Global Phylogeography and Ancient Evolution of the Widespread Human Gut Virus CrAssphage. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honap, T.P.; Sankaranarayanan, K.; Schnorr, S.L.; Ozga, A.T.; Warinner, C.; Lewis, C.M. Biogeographic Study of Human Gut-Associated CrAssphage Suggests Impacts from Industrialization and Recent Expansion. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachler, E.; Akyon, B.; de Carvalho, N.A.; Ference, C.; Bibby, K. Correlation of CrAssphage QPCR Markers with Culturable and Molecular Indicators of Human Fecal Pollution in an Impacted Urban Watershed. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7505–7512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, S.J.; Hu, W.S.; Koo, O.K. Evaluation of CrAssphage as a Human-Specific Microbial Source-Tracking Marker in the Republic of Korea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mafumo, N.; Bezuidt, O.K.I.; le Roux, W.; Makhalanyane, T.P. CrAssphage May Be Viable Markers of Contamination in Pristine and Contaminated River Water. mSystems 2023, 8, e01282-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Brighton, K.; Chen, J.; Shuai, D.; Aw, T.G. Quantification of Particle-Associated Viruses in Secondary Treated Wastewater Effluent. Food Environ. Virol. 2025, 17, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Juel, A.I.; Eytcheson, S.; Munir, M.; Aw, T.G.; Molina, M. Temporal and Spatial Relationships of CrAssphage and Enteric Viral and Bacterial Pathogens in Wastewater in North Carolina. Water Res. 2023, 239, 120008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karkman, A.; Pärnänen, K.; Larsson, D.G.J. Fecal pollution can explain antibiotic resistance gene abundances in anthropogenically impacted environments. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesté, E.; Blanch, A.R.; Mendez, J.; Sala-comorera, L.; Maunula, L.; Monteiro, S.; Farnleitner, A.H.; Tiehm, A.; Jofre, J.; García-aljaro, C. Bacteriophages Are Good Estimators of Human Viruses Present in Water. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 619495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Bai, X.; Li, Y.; Jing, L.; Chen, R.; Teng, Y. Source identification of antibiotic resistance genes in a peri-urban river using novel crAssphage marker genes and metagenomic signatures. Water Res. 2019, 167, 115098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crank, K.; Li, X.; North, D.; Ferraro, G.B.; Iaconelli, M.; Mancini, P.; La Rosa, G.; Bibby, K. CrAssphage abundance and correlation with molecular viral markers in Italian wastewater. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Threndyle, R.E.; Kurylyk, B.L.; Huang, Y.; Johnston, L.H.; Jamieson, R.C. CrAssphage as an indicator of groundwater-borne pollution in coastal ecosystems. Environ. Res. Commun. 2022, 4, 051001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Lobos, A.; Senkbeil, J.; Peraud, J.; Gallard, J.; Harwood, V.J. Evaluation of the novel crAssphage marker for sewage pollution tracking in storm drain outfalls in Tampa, Florida. Water Res. 2018, 131, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, K.; Walker, D.I.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; McDonald, J.E.; Hillary, L.S.; Malham, S.K.; Jones, D.L. Viral indicators for tracking domestic wastewater contamination in the aquatic environment. Water Res. 2020, 181, 115926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toribio-Avedillo, D.; Ballesté, E.; García-Aljaro, C.; Stange, C.; Tiehm, A.; CSánchez-Cid, C.; Mulogo, E.; Nasser, A.; Santos, R.; Nemes, K.; et al. The reliability of CrAssphage in human fecal pollution detection: A cross-regional MST marker assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 382, 125399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Commercial Site | Bivalve | Origin/Farm–City | n | CrAssphage Detection (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per Species/Site | p-Value | Total/Site | ||||
| Angra dos Reis | Oyster | Ilha Grande Bay, Angra dos Reis (same farm) | 25 | 8 (32.0) | 0.0109 | 12/50 (24.0) |
| Mussel | 25 | 4 (16.0) | ||||
| Niterói | Oyster | Florianópolis, farm X | 25 | 22 (88) | 0.0646 | 35/40 (87.5) |
| Mussel | Sampled from any point in Niterói | 15 | 13 (86.7) | |||
| Rio de Janeiro | Oyster | Florianópolis, farm Y | 22 | 18 (81.8) | 0.0121 | 35/44 (79.5) |
| Mussel | Sampled from any point in Rio de Janeiro | 22 | 17 (77.3) | |||
| Bivalve | Parameter | Viruses | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Norovirus GII | Norovirus GI | Sapovirus | Astrovirus | Rotavirus A | Mastadenovirus | Hepatitis A Virus | ||
| Oyster | Sensitivity | 0.7 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.5 | - |
| Specificity | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.7 | |
| Mussel | Sensitivity | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Specificity | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | |
| Viral Concentrations log10 GC/g | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bivalve | Parameters | Norovirus GII | Sapovirus | Mastadenovirus | Rotavirus A | Norovirus GI | Hepatitis A Virus | Astrovirus | |
| CrAssphage log10 GC/g | Oyster | rho, p-level | 0.024 | 0.227 | −0.139 | 0.102 | −0.053 | - | 0.389 *** |
| Mussel | rho, p-level | 0.536 *** | 0.488 *** | 0.537 *** | 0.287 * | 0.581 *** | 0.252 * | 0.464 *** | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Negreiros, I.R.; dos Santos, N.L.; de Paula, B.B.; Figueiredo, B.L.; Brandão, M.L.L.; Leite, J.P.G.; Miagostovich, M.P.; Cantelli, C.P. CrAssphage as a Human Enteric Viral Contamination Bioindicator in Marketed Bivalve Mollusks. Viruses 2025, 17, 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071012
Negreiros IR, dos Santos NL, de Paula BB, Figueiredo BL, Brandão MLL, Leite JPG, Miagostovich MP, Cantelli CP. CrAssphage as a Human Enteric Viral Contamination Bioindicator in Marketed Bivalve Mollusks. Viruses. 2025; 17(7):1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071012
Chicago/Turabian StyleNegreiros, Isabella Rodrigues, Natália Lourenço dos Santos, Bruna Barbosa de Paula, Bruna Lopes Figueiredo, Marcelo Luiz Lima Brandão, José Paulo Gagliardi Leite, Marize Pereira Miagostovich, and Carina Pacheco Cantelli. 2025. "CrAssphage as a Human Enteric Viral Contamination Bioindicator in Marketed Bivalve Mollusks" Viruses 17, no. 7: 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071012
APA StyleNegreiros, I. R., dos Santos, N. L., de Paula, B. B., Figueiredo, B. L., Brandão, M. L. L., Leite, J. P. G., Miagostovich, M. P., & Cantelli, C. P. (2025). CrAssphage as a Human Enteric Viral Contamination Bioindicator in Marketed Bivalve Mollusks. Viruses, 17(7), 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071012






