-
 Different Levels of Endemicity of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Brazil
Different Levels of Endemicity of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Brazil -
 AI-Generated Health Communication Material on Bird Flu Precautions Evaluation
AI-Generated Health Communication Material on Bird Flu Precautions Evaluation -
 Large Game Key in Tuberculosis Maintenance in Southern Portugal
Large Game Key in Tuberculosis Maintenance in Southern Portugal -
 Are We Missing Brucella spp. in Portugal?
Are We Missing Brucella spp. in Portugal? -
 Sterilizing Free-Roaming Cats Protects Public Health
Sterilizing Free-Roaming Cats Protects Public Health
Journal Description
Zoonotic Diseases
Zoonotic Diseases
- formerly Zoonoses - is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on various infectious diseases transmitted between animals and humans, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free to download, share, and reuse content. Authors receive recognition for their contribution when the paper is reused.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 34.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 5.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Zoonotic Diseases is a companion journal of Animals and Viruses.
Latest Articles
Methods for Rodent Control to Prevent Zoonotic Diseases: A Systematic Review of Studies from Africa
Zoonotic Dis. 2026, 6(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis6010004 - 29 Jan 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Background: Africa is a continent with diverse climates, landscapes, rainfall patterns, and vegetation types, all of which significantly influence its mammalian fauna, particularly small mammals. Rodents, which are highly diverse across the continent, serve as reservoirs for various zoonotic pathogens. Frequent human–rodent interactions
[...] Read more.
Background: Africa is a continent with diverse climates, landscapes, rainfall patterns, and vegetation types, all of which significantly influence its mammalian fauna, particularly small mammals. Rodents, which are highly diverse across the continent, serve as reservoirs for various zoonotic pathogens. Frequent human–rodent interactions heighten the risk of zoonotic disease transmission, posing a serious public health concern. Methods: This study conducted a comprehensive review of rodent control methods and their effectiveness in mitigating zoonotic diseases in Africa. Literature searches were performed using PubMed, Web of Science, ResearchGate, and Google Scholar. Additionally, one study was manually identified from the reference lists of the retrieved papers. Results: Thirteen relevant studies were identified, including seven field-based studies, five model evaluations, and one review. The distribution of studies varied by country, with the highest numbers conducted in Guinea (n = 3) and Nigeria (n = 3), followed by Sierra Leone (n = 2), Uganda (n = 2), Morocco (n = 1), Tanzania (n = 1), and Madagascar (n = 1). Two primary rodent control methods, kill traps and rodenticides, were used, targeting multimammate rats (Mastomys natalensis) and black/roof rats (Rattus rattus), the species most frequently encountered in human settings. Conclusion: Most studies examined short-term rodent management strategies, which proved insufficient in significantly reducing zoonotic disease prevalence. These findings highlight the need for Africa to adopt more sustainable, ecologically based rodent control approaches to effectively curb zoonotic risks in the long term.
Full article
Open AccessSystematic Review
Clinical Features and Epidemiology of Mpox in Saudi Arabia Post-2022 Re-Emergence: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Series
by
Ethar Alsulami, Roudin H. Alhasawi, Abdulaziz F. Samandar, Omnia A. Sulimani, Safia H. Alansari, Shahad A. Alshehri, Reem A. Alshehri, Saud A. Al-luhaypi and Mazin M. Aljabri
Zoonotic Dis. 2026, 6(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis6010003 - 28 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background: With the worldwide resurgence of Mpox in 2022, understanding its regional features is important. This systematic review aimed to provide an overview of the epidemiology, risk factors, clinical features, and outcomes of Mpox in Saudi Arabia to fill the knowledge gaps in
[...] Read more.
Background: With the worldwide resurgence of Mpox in 2022, understanding its regional features is important. This systematic review aimed to provide an overview of the epidemiology, risk factors, clinical features, and outcomes of Mpox in Saudi Arabia to fill the knowledge gaps in this area. Methods: Following the guidelines of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses, a systematic search was performed on PubMed, MEDLINE (via Ovid), Scopus and Wiley Online Library for case reports and series published on Mpox in Saudi Arabia after 2022. Results: Analysis included eight studies comprising a total of 410 patients with confirmatory data. The cohort was predominantly male (91%), with a mean age of 32.8 years. Extramarital sexual contact was the most frequently identified risk factor (28.8%), whereas most patients (63.4%) had unknown or denied exposure routes. The most common clinical manifestations were fever (97.1%) and rash (96.8%). Dermatological findings were usually pleomorphic. These included umbilicated pustules, crusted papules, and vesiculopustular lesions. Although management was primarily supportive, rare complications, such as keratitis and neurological deficits, were observed. Conclusions: In Saudi Arabia, Mpox primarily affects young adult males, particularly individuals with high-risk sexual behaviors. Much of this transmission remains undetermined, and better contact tracing and focused public health efforts are urgently required.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Vector-Borne Disease Spatial Epidemiology, Disease Ecology, and Zoonoses)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Temporal and Spatial Analysis of Vector-Tick Borne Spotted Fever in the State of São Paulo
by
Daniele Rosa Xavier de Melo, Michellin Pereira de Albuquerque, Fabricio dos Santos Menezes, Sílvia von Tiesenhausen de Sousa-Carmo and Adriano Pinter
Zoonotic Dis. 2026, 6(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis6010002 - 9 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Brazilian spotted fever (BSF) is a tick-borne acute febrile disease that can be lethal to humans, caused by the bacterium Rickettsia rickettsii. In the State of São Paulo, transmission occurs mainly through two tick species: Amblyomma sculptum and Amblyomma aureolatum. We
[...] Read more.
Brazilian spotted fever (BSF) is a tick-borne acute febrile disease that can be lethal to humans, caused by the bacterium Rickettsia rickettsii. In the State of São Paulo, transmission occurs mainly through two tick species: Amblyomma sculptum and Amblyomma aureolatum. We analyzed trends in BSF incidence and mortality in relation to the spatial distribution of these vector species in the State of São Paulo from 2007 to 2017 and evaluated clinical outcomes according to hospitalization location. In A. sculptum areas, incidence and mortality showed significant increasing trends between 2007 and 2015 (p-value < 0.05). In contrast, A. aureolatum areas exhibited a significant decrease in incidence (p-value < 0.05), while mortality remained stable throughout the study period. Lethality was substantially higher in cases associated with A. aureolatum than in those linked to A. sculptum (67.1% versus 55.0%, p-value = 0.037). Most patients received care in hospitals located near the probable site of infection. Incidence and mortality patterns differed sharply between vector-specific areas, with notably higher mortality in A. aureolatum-related cases. These findings highlight the importance of incorporating vector distribution into surveillance, prevention, and clinical management strategies to better address the distinct epidemiological contexts within the State of São Paulo.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Nursing Students’ Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices Toward Monkeypox Virus: A Cross-Sectional Survey at the University of Palermo, 2022
by
Barbara Ravazzolo, Francesco Leonforte, Letizia Cascio, Clara Ferrara, Federico Li Causi, Francesco Armetta, Maria Lampasona, Rinaldo Stefano Miceli, Carlo Fantini, Klara Komici and Alberto Firenze
Zoonotic Dis. 2026, 6(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis6010001 - 25 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Human monkeypox is a zoonotic disease caused by the monkeypox virus (MPXV), endemic in Central and West Africa. A significant 2022 outbreak affected 104 countries, driven by increased susceptibility due to the cessation of smallpox vaccination, global travel, and interactions with infected
[...] Read more.
Background: Human monkeypox is a zoonotic disease caused by the monkeypox virus (MPXV), endemic in Central and West Africa. A significant 2022 outbreak affected 104 countries, driven by increased susceptibility due to the cessation of smallpox vaccination, global travel, and interactions with infected animals. Strengthening surveillance, public health measures, and raising awareness are essential for early diagnosis, vaccination acceptance, and preventing future outbreaks. Methods: The survey was distributed to 645 nursing students of the University of Palermo between July 2022 and August 2022, and we estimated the knowledge, attitudes and behaviors through a KAP Survey. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize the data, while chi-squared, Fisher’s exact, and Student’s t-tests were employed to analyze differences between groups, with statistical significance set at p < 0.05. At least 80% of the students surveyed had already taken the microbiology exam, as microbiology is studied in the first year of the Bachelor of Science in Nursing program at the University of Palermo. Results: The survey showed a predominantly young, female nursing student population with limited knowledge of monkeypox, as only 3.88% demonstrated adequate understanding. Despite this, attitudes toward prevention were positive, with 82.64% scoring adequately and 41.09% expressing strong willingness to get vaccinated. Knowledge improved with academic progression (p = 0.005), while attitudes and behaviors remained consistent. These findings imply a critical gap in education; the limited knowledge, especially regarding transmission and severity, may lead to an underestimation of the risks associated with global infectious diseases. This underscores the need to better prepare future healthcare professionals for public health emergencies Conclusions: The study found that nursing students had limited knowledge of monkeypox, especially regarding epidemiology and disease severity. Despite positive attitudes toward vaccination, some behaviors reflected an underestimation of global infection risks. Knowledge improved with academic progression, underscoring the importance of education. Targeted educational programs are needed to enhance awareness and preparedness for future outbreaks.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Mapping Socio-Environmental Drivers of Zoonotic Diseases in Brazil
by
Vitor Daniel Sousa and Diego Simeone
Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5(4), 36; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5040036 - 16 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Zoonotic diseases represent an important interface between socio-environmental change and public health, yet integrative assessments linking ecological and social determinants remain limited in tropical regions. This study mapped how socio-environmental drivers have shaped research patterns on zoonotic diseases in Brazil. We integrated socio-environmental
[...] Read more.
Zoonotic diseases represent an important interface between socio-environmental change and public health, yet integrative assessments linking ecological and social determinants remain limited in tropical regions. This study mapped how socio-environmental drivers have shaped research patterns on zoonotic diseases in Brazil. We integrated socio-environmental data from empirical evidence with statistical modeling to evaluate temporal trends, thematic associations, and geographic distribution across six major zoonoses: leishmaniasis, Chagas disease, leptospirosis, yellow fever, Brazilian spotted fever, and hantavirus infection. Research output increased after 2010, particularly for leishmaniasis, Chagas disease, and leptospirosis, reflecting growing recognition of land-use change and socioeconomic vulnerability as key drivers of disease risk. Network analyses revealed strong thematic connections between zoonoses and land-use or socioeconomic factors, whereas climate change remained underrepresented. Spatially, research efforts were concentrated in the Amazon and Cerrado biomes, underscoring both ecological significance and persistent regional disparities in knowledge production. These findings demonstrate that Brazil’s zoonotic research landscape mirrors broader socio-environmental pressures, where deforestation, poverty, and climatic variability jointly influence disease dynamics. Strengthening geographically inclusive and environmentally informed research frameworks that integrate climate, land-use, and surveillance data will be essential to improve early-warning systems and guide sustainable, cross-sectoral public health policies.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Navigating Zoonotic Landscapes: From Genomic Insights to Ethical Frontiers
by
Alaa A. A. Aljabali, Abdelrahim Alqudah, Rasha M. Bashatwah, Rawan Alsharedeh, Esam Qnais, Omar Gammoh, Vijay Mishra, Yachana Mishra, Mohamed El-Tanani and Taher Hatahet
Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5(4), 35; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5040035 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Viral zoonoses represent a critical intersection of global health, ecology, and ethical issues. Pathogens that pass from animals to humans. This review examines the complex landscape of viral zoonoses, including their mechanisms, impact, and mitigation strategies. We begin with insights into the historical
[...] Read more.
Viral zoonoses represent a critical intersection of global health, ecology, and ethical issues. Pathogens that pass from animals to humans. This review examines the complex landscape of viral zoonoses, including their mechanisms, impact, and mitigation strategies. We begin with insights into the historical context and significance of these diseases and then explore spillover mechanisms influenced by genetic, ecological, and anthropogenic factors. This review covers the host range, transmission dynamics, and immunological barriers, including viral detection, adaptation, and immune evasion. Genomic insights have revealed the genetic determinants of host switching and adaptation, illuminating the dynamics of viral spillover events. We emphasize the anticipation and prevention of zoonotic events, highlighting surveillance, early warning systems, and the “One Health” approach. Using case studies of outbreaks such as Ebola, avian influenza, and COVID-19, this review examines the real-world consequences of zoonotic diseases. We then discuss interventions, including mitigation strategies and vaccination, and their ethical and social implications. Drawing on past outbreaks, we provide recommendations for the future, aiming to balance human health, conservation, and animal welfare. This review aims to inform professionals, academics, and policymakers by offering a multidisciplinary perspective on the complex world of viral zoonoses and strategies to protect global health.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Enduring Warning: A Holistic Comparison of the Establishment and Spread of P. falciparum Evolutionary Lineage Malaria in Ancient Rome and the Threat of Zoonotic P. knowlesi Malaria in Modern Southeast Asia
by
Mark Orsag, Giovanni Meledandri, Amanda McKinney and Melissa Clouse
Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5(4), 34; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5040034 - 12 Nov 2025
Abstract
Our article presents a holistic analysis aimed at discerning patterns from ancient–modern comparative contexts of malaria. The article’s interdisciplinary and consilient methodology is drawn from a range of disciplines: the humanities and social sciences, medical knowledge (particularly epidemiology and pathology), molecular phylogenetics, demography,
[...] Read more.
Our article presents a holistic analysis aimed at discerning patterns from ancient–modern comparative contexts of malaria. The article’s interdisciplinary and consilient methodology is drawn from a range of disciplines: the humanities and social sciences, medical knowledge (particularly epidemiology and pathology), molecular phylogenetics, demography, archaeology, paleopathology, numismatics, complex systems theory, etc. The article begins with a detailed exploration of a 463 BCE epidemic event that likely marked the, ultimately transformative, debut of P. falciparum evolutionary lineage malaria for ancient Roman civilization. It is important to note that the concept of evolutionary lineage is defined herein as a sequence of organisms, descended from a common ancestor and culminating, for the present at least, in the form existing currently. An interdisciplinary retrospective diagnosis methodology is utilized to establish, with what we believe to be a high degree of probability, a conclusion that effectively marks the beginning point for the ancient side of our comparative example. The deep interdisciplinary/historical methods used to elucidate the ancient side of the disease equation both lead to a clear conclusion and suggest potential modern analogies or even “prophecies.” These are used to highlight the threats emanating from the current spread of zoonotic P. knowlesi malaria in Southeast Asia. The article also utilizes six broader holistic and interdisciplinary factors in its contextual and comparative analysis: (A) political, military and security contexts; (B) the effects of cultural perceptions; (C) the role of climate and climate change; (D) additional anthropogenic environmental factors; (E) perceptions, practices and capabilities of prevailing medical systems and (F) holistic underlying states of the health of affected populations.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Occurrence, Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles, and Multidrug Resistance Characterization of Campylobacter spp. Isolated from Domestic Pets in Kelantan, Malaysia
by
Chinedu Amaeze Frank, Mohammed D. Goni, Nor Fadhilah Kamaruzzaman, Hafeez A. Afolabi, Mohammed S. Gaddafi, Aliyu Yakubu and Shamsaldeen Ibrahim Saeed
Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5(4), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5040033 - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Campylobacter spp. are significant zoonotic pathogens, increasingly recognized for their role in the transmission of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) between animals and humans. This study aims to determine the occurrence, antimicrobial resistance profiles, and characterization of multidrug resistance indices of Campylobacter spp. isolated from
[...] Read more.
Campylobacter spp. are significant zoonotic pathogens, increasingly recognized for their role in the transmission of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) between animals and humans. This study aims to determine the occurrence, antimicrobial resistance profiles, and characterization of multidrug resistance indices of Campylobacter spp. isolated from domestic pets in Kelantan, Malaysia. Methods: Rectal swabs (n = 150) were collected from both healthy and diarrheic cats. Campylobacter spp. were isolated and confirmed by PCR, and antimicrobial susceptibility was assessed using the disk diffusion method. Results: Campylobacter spp. were detected in 35.3% of cats (53/150; SE = 0.04; 95% CI: 28.1–43.3%), with C. upsaliensis identified as the predominant species (33.3%; SE = 0.05; 95% CI: 24.5–43.6%), followed by C. jejuni (17.8%; SE = 0.04; 95% CI: 11.3–26.9%) and C. coli (7.8%; SE = 0.03; 95% CI: 3.8–15.2%). Isolates exhibited high resistance rates to amoxicillin (90.6%), ampicillin (81.1%), tetracycline (67.9%), erythromycin (62.3%), and sulphonamides (54.7%). Conclusion: The study reveals a substantial prevalence of Campylobacter spp. and notable levels of antimicrobial resistance among feline isolates, highlighting the zoonotic threat in Malaysia. These findings emphasize the importance of integrated surveillance and prudent antimicrobial stewardship under a One Health framework.
Full article
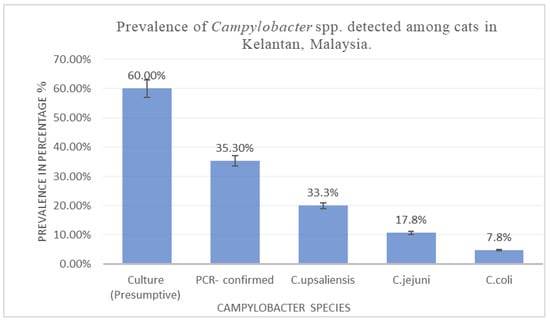
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Drivers and Consequences of Viral Zoonoses: Public Health and Economic Perspectives
by
Anirban Banik and Soumya Basu
Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5(4), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5040032 - 3 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Viral zoonoses or viral pathogens transmitted from animals to humans—constitute a rapidly intensifying global health and economic challenge. They are responsible for an estimated 2.5 billion illnesses and 2.7 million deaths annually, representing nearly 60% of all infectious diseases and 75% of newly
[...] Read more.
Viral zoonoses or viral pathogens transmitted from animals to humans—constitute a rapidly intensifying global health and economic challenge. They are responsible for an estimated 2.5 billion illnesses and 2.7 million deaths annually, representing nearly 60% of all infectious diseases and 75% of newly emerging infections. Recent outbreaks, including Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Ebola, Nipah, and avian influenza, underscore their capacity to overwhelm health systems, with COVID-19 alone projected to reduce global Gross Domestic Product by USD 22 trillion by 2025 and impose annual healthcare costs of USD 2–3 trillion. Beyond mortality and morbidity, zoonotic events disrupt trade, depress rural livelihoods, and inflict agricultural losses exceeding USD 100 billion per outbreak, with impacts disproportionately borne by low- and middle-income countries. Hotspot regions across tropical North and South America, Asia, and Central Africa remain especially vulnerable due to accelerating land use change, climate variability, and intensified wildlife–human interfaces. While the Global One Health Index highlights high regional heterogeneity, with sub-Saharan Africa scoring lowest, a critical gap persists between the conceptual strength of One Health and its operationalization in resource-limited settings. This review synthesizes evidence on drivers, clinical manifestations, and socioeconomic burdens of viral zoonoses, while highlighting novel perspectives on equity gaps, co-infection dynamics, and limitations of global preparedness initiatives. We argue that current strategies remain over-reliant on donor-driven agendas and insufficiently integrated across sectors. Addressing future zoonotic threats requires prioritizing surveillance in high-risk geographies, integrating epidemiological and economic data for preparedness planning, and supporting context sensitive One Health approaches that confront political, financial, and structural barriers to implementation.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Acute Phase Extrapulmonary Effects of a High-Dose Influenza A Virus Infection in a Mouse Model of Obesity
by
Saranya Vijayakumar, Saurav Pantha, Brian Wolfe, Qi Zhang, Shristy Budha Magar, Tawfik Aboellail and Santosh Dhakal
Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5(4), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5040031 - 16 Oct 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Influenza A viruses (IAVs) primarily cause respiratory illness but can also induce extrapulmonary effects, which may be aggravated by obesity. This study evaluated the impact of obesity on virus replication, histopathological changes, and cytokine/chemokine profiles in extrapulmonary sites during the acute phase, following
[...] Read more.
Influenza A viruses (IAVs) primarily cause respiratory illness but can also induce extrapulmonary effects, which may be aggravated by obesity. This study evaluated the impact of obesity on virus replication, histopathological changes, and cytokine/chemokine profiles in extrapulmonary sites during the acute phase, following a high-dose IAV infection. Diet-induced non-obese mice or mice with obesity were inoculated intranasally with either vehicle (medium) or 103 TCID50 of the 2009 pandemic H1N1 IAV. At 3 days post-infection (dpi), the lungs, blood, and various extrapulmonary tissues were collected for virus titration, histopathological analysis, and cytokine/chemokine quantification. IAV infection resulted in comparable virus titers (6–7 log10 TCID50/mL) and histopathological scores (p > 0.05 in each case) in the lungs of mice with or without obesity. Replicating viruses were not detected in the extrapulmonary sites, and histopathological scores did not differ significantly between the two groups. However, analysis of fold changes in five cytokines/chemokines (i.e., IL-6, IL-1β, TNFα, MCP-1, and IFNγ) revealed site-specific differences. IL-6 was significantly higher (p < 0.05) in the lungs and perirenal adipose tissue, and showed a higher trend in the kidney (0.05 ≤ p ≤ 0.1); IL-1β had a higher trend in the lungs; TNFα was significantly lower in the kidney but showed a higher trend in the lungs; while MCP-1 was significantly lower in the lungs, plasma, and inguinal adipose tissue of mice with obesity compared to non-obese mice. Future studies should consider a broader range of IAV strains/subtypes, doses, time points, and inflammatory markers to better understand how obesity affects extrapulmonary outcomes.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Conservation and Zoonotic Risk Implications of Egyptian Fruit Bats Amid Marburg Virus Disease Outbreaks in Tanzania and the Broader Sub-Saharan African Region
by
Edson Kinimi, Lee Joo-Yeon, Lee Jeong-Su, Lim Hee-Young, Min Su Yim and Gerald Misinzo
Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5(4), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5040030 - 9 Oct 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The Marburg virus (MARV) is a zoonotic pathogen that causes a high case fatality rate of up to 100% in humans. In response to Marburg virus disease (MVD) outbreaks in the Kagera region, an ecological investigation was initiated to map the population and
[...] Read more.
The Marburg virus (MARV) is a zoonotic pathogen that causes a high case fatality rate of up to 100% in humans. In response to Marburg virus disease (MVD) outbreaks in the Kagera region, an ecological investigation was initiated to map the population and ecological threat to the reservoir host of MARV: Egyptian fruit bats. The investigation conducted from October 2023 to December 2024 included interviews with local authorities to locate all known autochthonous bat colonies in the region. Bat species confirmation was performed using high-resolution melting analysis (HRMA) and DNA barcoding, targeting two mitochondrial genes: cytochrome oxidase 1 (COI) and 16S rRNA. We found five considerably large cave-dwelling Egyptian fruit bat colonies (with approximately 100,000 individuals) at the geolocations between 1°06′04.2″ and 2°26′35.8″ S latitude and 30°40′49.7″ and 31°51′19.8″ E longitude. The study also provides the first confirmed identification of Egyptian fruit bats (Rousettus aegyptiacus) (accession numbers: PV700530-PV700534) in major bat colonies in the Kagera River Basin ecosystem. Cave-dwelling Egyptian fruit bats in mines face higher risks, and thus, attention is needed to prevent this species from becoming more vulnerable to extinction. The loss of bat roosting sites and subsequent population declines are primarily driven by the destructive practice of burning car tyres and logs, a method used to eliminate colonies through toxic smoke and heat. The collection of guano and partially eaten fruits in mining caves, as well as daily contact with Egyptian fruit bats in mines, homes, and churches, have become major potential risk factors for MARV transmission to humans. Increased threats to bats in the Kagera region warrant the implementation of conservation strategies that ensure the survival of the bat populations and inform policies on MVD risk reduction in Tanzania and the broader East African region.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Epidemiological Survey of Human Zoonotic Fascioliasis and Schistosomiasis in the Lake Victoria and Southern Highland Ecological Zones of Tanzania
by
Godlisten Shedrack Materu, Jahashi Nzalawahe, Mita Eva Sengupta, Anna-Sofie Stensgaard, Abdul Katakweba, Yasinter Silvester, Gerald P. Mwing’a, Birgitte J. Vennervald and Safari Kinung’hi
Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5(4), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5040029 - 5 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Zoonotic fascioliasis and schistosomiasis, caused by trematode parasites transmitted by freshwater snails, are neglected tropical diseases of both medical and veterinary importance. There are critical knowledge gaps regarding the transmission dynamics of these infections in humans and animals, particularly in endemic African
[...] Read more.
Background: Zoonotic fascioliasis and schistosomiasis, caused by trematode parasites transmitted by freshwater snails, are neglected tropical diseases of both medical and veterinary importance. There are critical knowledge gaps regarding the transmission dynamics of these infections in humans and animals, particularly in endemic African communities. Therefore, the current study aimed to determine the burden of human zoonotic schistosomiasis and fascioliasis among different age groups, focusing on the Lake Victoria zone and the Southern Highlands of Tanzania. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted among preschool-aged children, school-aged children, and adults. A total of 1557 stool and urine samples were collected, 400 from preschool children, 804 from school-aged children, and 353 from adults. Stool samples were processed using the Kato–Katz technique and the formol-ether concentration method to detect Schistosoma mansoni and Fasciola spp., respectively. Urine samples were examined for Schistosoma haematobium infection using the urine filtration method. Data were analyzed using Stata version 17. The t-tests or one-way ANOVA were used to assess statistical differences in the mean egg counts of S. mansoni and S. haematobium between exposure groups. Results: The overall prevalence of S. haematobium was 4.9%, S. mansoni was 1.2% with no significant differences across age groups, but with a statistically significant difference between sexes 1.8%. Males had a higher prevalence of both S. haematobium and S. mansoni infections compared to females. The prevalence of Fasciola infection was 0.9%, with the highest prevalence found in adults (≥18 years). Conclusions: Zoonotic schistosomiasis and fascioliasis are prevalent in the study area, affecting individuals across all age groups. This is the first study to report the presence of Fasciola infection in both the Lake Victoria zone and the Southern Highlands of Tanzania. These findings call for the Ministry of Health, through the Tanzania NTD Control Program, to recognize fascioliasis as a high-priority disease and include it in the national master plan.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Different Levels of Endemicity of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Brazil
by
Dilceu Silveira Tolentino Júnior, Heberson Teixeira da Silva, Alessandro Martins Ribeiro, Ana Mécia Ribeiro Amador, Bruno Oliveira Souza e Silva, Bárbara Mendes Guimarães, Manuella Botelho Laure Nogueira, Hellen Karine Campos Teixeira and Eliseu Miranda de Assis
Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5(4), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5040028 - 29 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Brazil is the first of the 12 priority countries in Latin America with the highest number of cases of American cutaneous leishmaniasis (ACL). This study estimated the prevalence of ACL in Brazil and classified the states according to the different levels of endemicity
[...] Read more.
Brazil is the first of the 12 priority countries in Latin America with the highest number of cases of American cutaneous leishmaniasis (ACL). This study estimated the prevalence of ACL in Brazil and classified the states according to the different levels of endemicity in the period from 2014 to 2024. This is a retrospective and cross-sectional study of ACL cases registered in Brazil by the Information System for Notifiable Diseases of the Ministry of Health. The predominant cases were male (73.2%), brown (65.0%), aged between 20 and 39 (41.5%), with a low level of education (44.4%), 0.5% in pregnant women, 80% of cases were confirmed by laboratory criteria, and 90% were classified as cutaneous. A total of 182,072 autochthonous cases were recorded, with a prevalence of 89.6 cases per 100,000 population. Two states were classified as having high intense endemicity; three were classified as having medium intense endemicity; four were classified as having low intense endemicity; five states were classified as having moderate endemicity; and 13 were classified as having low endemicity. The municipality of Presidente Figueiredo, Amazonas, had the highest prevalence of ACL (5503.1%), while Belo Horizonte had the lowest prevalence (72.2%). The month with the highest average number of cases was January with 1731 (with a standard deviation of 364; upper limit of 1933; lower limit of 1572). The heterogeneity of endemicity among States suggests that social and environmental determinants influence the dynamics of ACL transmission. All sociodemographic, clinical, and epidemiological categories, when compared with the different levels of endemicity, showed significant effects (p < 0.05), except for the variable gestational status in high disease endemicity. The inclusion of these variables significantly improved the model’s ability to predict the dependent variable.
Full article
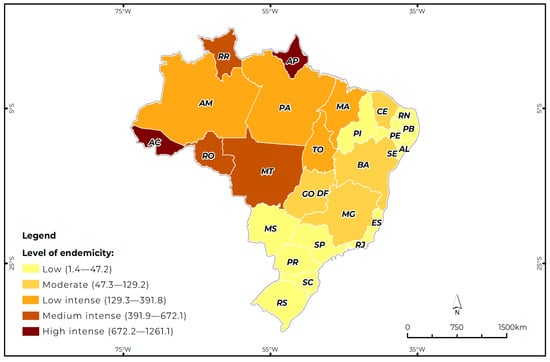
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Cross-Sectional Survey of Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices Toward Mpox Among One Health Stakeholders in Nigeria
by
Nafi’u Lawal, Muhammad Bashar Jibril, Muhammad Bashir Bello, Abdurrahman Jibril Hassan, Mustapha Umar Imam, Samira Rabiu Anka, Maryam Abida Alhassan, Bello Magaji Arkilla and Aminu Shittu
Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5(4), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5040027 - 25 Sep 2025
Abstract
Mpox has re-emerged as a global public health threat, particularly in endemic regions such as Nigeria, where human, animal, and environmental health sectors intersect. To inform surveillance and control strategies, this study assessed the knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) toward Mpox among One
[...] Read more.
Mpox has re-emerged as a global public health threat, particularly in endemic regions such as Nigeria, where human, animal, and environmental health sectors intersect. To inform surveillance and control strategies, this study assessed the knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) toward Mpox among One Health stakeholders in Nigeria. A cross-sectional survey was conducted among 492 participants from human, veterinary, and environmental health sectors using a structured questionnaire. Descriptive statistics, ordinal logistic regression, and margins analysis were used to evaluate levels and predictors of KAP. Results showed that 33.7% of respondents had low knowledge, 43.5% moderate, and 22.8% high. While 62.6% demonstrated high attitude scores, only 48.2% reported moderate preventive practices. Gender was significantly associated with attitudes, with females having lower odds of expressing higher attitudes than males (OR = 0.70, 95% CI: 0.49–1.00, p = 0.052), and margins analysis revealed a predicted probability of high attitude at 56% for females and 64% for males. Multivariable modeling for practice was not pursued because model fit did not improve compared to univariable results, and sparse data led to unstable estimates, thus offering no added explanatory power. These findings underscore persistent knowledge gaps and gender-related disparities that may hinder effective Mpox response. Targeted risk communication and capacity building are recommended to strengthen One Health preparedness in Nigeria.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Zoonotic Diseases: Understanding the Intersection Between Animal and Human Health)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Are We Missing Brucella spp. in Portugal? The First Nationwide Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Retrospective Serological Study of Brucella canis (2013–2025)
by
Ricardo Lopes, Hugo Lima de Carvalho, Ana Cristina Ferreira, Andreia Garcês, Cátia Fernandes, Ana Rita Silva, Ana Patrícia Lopes, Luís Cardoso, Elsa Leclerc Duarte and Ana Cláudia Coelho
Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5(4), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5040026 - 24 Sep 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Brucella canis is a neglected zoonotic pathogen associated with canine reproductive disorders and emerging public health concerns. This study presents the first nationwide systematic review and meta-analysis of Brucella spp. in Portugal, integrated with a 13-year retrospective seroepidemiological investigation (2013–2025) of B. canis
[...] Read more.
Brucella canis is a neglected zoonotic pathogen associated with canine reproductive disorders and emerging public health concerns. This study presents the first nationwide systematic review and meta-analysis of Brucella spp. in Portugal, integrated with a 13-year retrospective seroepidemiological investigation (2013–2025) of B. canis in dogs across mainland Portugal and Insular Autonomous Regions. Among 132 canine serum samples, a seropositivity of 23.48% was observed using an immunochromatographic assay confirmed by indirect immunofluorescence (IFAT). Significant associations were identified with seasonality (p < 0.001) and breed (p = 0.001), while sex and age were not statistically significant. Municipal-level analysis revealed marked heterogeneity, with Trofa showing the highest seropositivity (58.82%) and a pooled odds ratio of 11.28 (95% CI: 2.90–43.94; p < 0.001). In parallel, meta-analyses of published data estimated a pooled seroprevalence of 2.42% in animals (95% CI: 1.79–3.13) and 10.57% in humans (95% CI: 8.80–12.47), underscoring the broader burden of Brucella spp. exposure in Portugal. These findings suggest underdiagnosis of canine brucellosis and highlight the need for enhanced surveillance in high-risk breeds and regions. The study reinforces the importance of integrated One Health strategies to improve early detection, control, and prevention of B. canis infection in both veterinary and public health contexts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Zoonotic Diseases: Understanding the Intersection Between Animal and Human Health)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessCase Report
First Confirmed Human Case of Rickettsia parkeri Strain Atlantic Rainforest Infection on the North Coast of São Paulo State, Brazil
by
Michellin Pereira de Albuquerque, Cassiano Barbosa, Marcelo Bahia Labruna, Luis Filipe Mucci, Ludia Barboza Leite, Daniele Rosa Xavier de Melo, Thiago Fernandes Martins and Adriano Pinter
Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5(3), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5030025 - 15 Sep 2025
Abstract
Rickettsia parkeri strain Atlantic rainforest is an emerging pathogen in Brazil, but human infections remain rarely reported. We report the first confirmed case in the municipality of Caraguatatuba on the northern coast of São Paulo State, Brazil. A 37-year-old man was bitten by
[...] Read more.
Rickettsia parkeri strain Atlantic rainforest is an emerging pathogen in Brazil, but human infections remain rarely reported. We report the first confirmed case in the municipality of Caraguatatuba on the northern coast of São Paulo State, Brazil. A 37-year-old man was bitten by an Amblyomma ovale tick while visiting a forested area. Six days later, he developed a papular skin lesion with a necrotic center at the tick bite site, accompanied by regional lymphadenopathy, myalgia, and flu-like symptoms. Ticks parasitizing both the patient and his dog were collected, along with the eschar. Two ticks were analyzed for Rickettsia isolation, and R. parkeri was successfully isolated from one infected specimen. The patient’s infection was confirmed by molecular testing through the PCR amplification of the gltA and ompA genes from an eschar inoculation sample. This represents the sixth confirmed case of rickettsiosis caused by R. parkeri in Brazil, and it reinforces the need for increased epidemiological surveillance in endemic regions for spotted fever caused by this pathogen. With the increasing recognition of R. parkeri in South America, further research is needed to better understand its transmission dynamics, clinical manifestations, and potential public health impact.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Vector-Borne Disease Spatial Epidemiology, Disease Ecology, and Zoonoses)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Geospatial Model Suggests Sterilizing Free-Roaming Domestic Cats Reduces Potential Risk of Toxoplasma gondii Infection
by
Sue M. Neal, Peter J. Wolf and Melanie E. Anderson
Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5(3), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5030024 - 27 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Although trap-neuter-return (TNR) is a popular method for managing free-roaming domestic cat populations, a common criticism is that sterilization fails to mitigate the public health risks posed by free-roaming cats. One of these risks is the environmental contamination of Toxoplasma gondii, a
[...] Read more.
Although trap-neuter-return (TNR) is a popular method for managing free-roaming domestic cat populations, a common criticism is that sterilization fails to mitigate the public health risks posed by free-roaming cats. One of these risks is the environmental contamination of Toxoplasma gondii, a parasite that can be spread in the feces of actively infected felids (both domestic and wild). In healthy humans, toxoplasmosis tends to be mild or asymptomatic; however, the disease can have severe consequences (e.g., for pregnant women) and even be fatal in immunocompromised individuals. Previous research has examined the extent to which free-roaming domestic cats might contaminate sites frequented by young children (e.g., schools and parks). However, the model used included several assumptions that are not reflective of sterilized cats in an urban setting (e.g., smaller home range). By properly accounting for several key factors (e.g., reproductive status, home range), our modeling revealed considerably lower rates of potential incursions by sterilized free-roaming cats than those reported previously. More importantly, our results show that sterilization contributes to a considerable reduction in the risk of environmental contamination; TNR therefore appears to be a valuable harm reduction strategy in mitigating the risks of T. gondii infection.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Epidemiological-Based Study of SARS-CoV-2 in Faisalabad
by
Sana Ullah, Muhammad Waseem Khan, Qurat-ul-Ain, Khushbu Farva, Niaz Muhammad Khan and Hayat Ullah
Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5(3), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5030023 - 25 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) raced around the world across different populations; there needs to be a consolidated effort to understand the divergence of the epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2. Population-based epidemiological characteristics studies measure the extent of SARS-CoV-2 infection in a country.
[...] Read more.
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) raced around the world across different populations; there needs to be a consolidated effort to understand the divergence of the epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2. Population-based epidemiological characteristics studies measure the extent of SARS-CoV-2 infection in a country. The current research study was designed to report epidemiological data from Pakistan. For this purpose, 246 SARS-CoV-2-infected patients were included in the study. For SARS-CoV-2 confirmation, viral samples were collected from all the study participants; SARS-CoV-2 infection was confirmed by viral nucleic acid detection using a nucleic acid detection kit. After SARS-CoV-2 confirmation, all the study participants were interviewed for epidemiological data through a detailed questionnaire. The study results showed that the disease ratio was higher between 30 and 59 years (51.21%) of age. The male ratio (55.28%) was higher compared to the female ratio (44.71%). The patients’ illiteracy and low socioeconomic status were 32.52% and 59.75%, respectively. The majority of the patients (97.56%) had cough, smell or taste disturbance (79.67%), or fever (76.42%), and 70.73% had fatigue. For comorbidities, a higher ratio was observed for diabetes (38.61%), hypertension (36.17%), and respiratory disease (16.26%). The vaccination status analysis revealed that 51.21% of patients had not received routine immunizations, and 65.5% were un-vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2. Notably, not a single patient was vaccinated for influenza vaccine. The current research study concluded that SARS-CoV-2 was more prevalent in individuals who were middle aged, male, and had low socio-economic status. The most common symptoms were cough, smell or taste disturbance, and fever. The patients’ vaccination status highlights a critical gap in preventive healthcare and shows the need to strengthen vaccination awareness and accessibility in the population to reduce vulnerability to future outbreaks. Future research should focus on investigating the impact of COVID-19 outcomes on comorbidities such as diabetes and hypertension.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of an Artificial Intelligence-Generated Health Communication Material on Bird Flu Precautions
by
Ayokunle A. Olagoke, Comfort Tosin Adebayo, Joseph Ayotunde Aderonmu, Emmanuel A. Adeaga and Kimberly J. Johnson
Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5(3), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5030022 - 1 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The 2025 avian influenza A(H5N1) outbreak has highlighted the urgent need for rapidly generated health communication materials during public health emergencies. Artificial intelligence (AI) systems offer transformative potential to accelerate content development pipelines while maintaining scientific accuracy and impact. We evaluated an AI-generated
[...] Read more.
The 2025 avian influenza A(H5N1) outbreak has highlighted the urgent need for rapidly generated health communication materials during public health emergencies. Artificial intelligence (AI) systems offer transformative potential to accelerate content development pipelines while maintaining scientific accuracy and impact. We evaluated an AI-generated health communication material on bird flu precautions among 100 U.S. adults. The material was developed using ChatGPT for text generation based on CDC guidelines and Leonardo.AI for illustrations. Participants rated perceived message effectiveness, quality, realism, relevance, attractiveness, and visual informativeness. The AI-generated health communication material received favorable ratings across all dimensions: perceived message effectiveness (3.83/5, 77%), perceived message quality (3.84/5, 77%), realism (3.72/5, 74%), relevance (3.68/5, 74%), attractiveness (3.62/5, 74%), and visual informativeness (3.35/5 67%). Linear regression analysis revealed that all features significantly predicted perceived message effectiveness in unadjusted and adjusted models (p < 0.0001), e.g., multivariate analysis of outcome on perceived visual informativeness showed β = 0.51, 95% CI: 0.37–0.66, p < 0.0001. Also, mediation analysis revealed that visual informativeness accounted for 23.8% of the relationship between material attractiveness and perceived effectiveness. AI tools can enable real-time adaptation of prevention guidance during epidemiological emergencies while maintaining effective risk communication.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Large Game as a Key Factor in the Maintenance of Tuberculosis in a Multi-Species Scenario in Southern Portugal: A Preliminary Statistical Study
by
Maria Pureza Ferreira, Madalena Vieira-Pinto, Yolanda Vaz and Ana Carolina Abrantes
Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5(3), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis5030021 - 22 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Knowing the specific characteristics and animal tuberculosis risk factors present and applying good practices are crucial points in combating tuberculosis (TB) in a Mediterranean multi-species scenario. The objective of this work is to statistically analyze the association between the existence of TB in
[...] Read more.
Knowing the specific characteristics and animal tuberculosis risk factors present and applying good practices are crucial points in combating tuberculosis (TB) in a Mediterranean multi-species scenario. The objective of this work is to statistically analyze the association between the existence of TB in areas with a marked game–livestock interface, with various complementary factors found in 30 extensive farms in southern Portugal, such as the number of animals of each large game species present in the territory and the frequency of their sightings. Collecting this information, an inferential statistical analysis was conducted to obtain information on the association type between TB occurrence in the farms and the presence of highlighted factors. The main statistical results show an association between the presence of large game species and TB occurrence in the analyzed areas. Thus, in a multi-species scenario, large game species are a crucial component in TB maintenance, namely when stricter contact occurs. This could be one of the reasons why TB continues to circulate and why the eradication process is so difficult; the risk of zoonotic transmission is evident. It is crucial to apply biosecurity tools to improve the alignment and structure of natural resource management strategies.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Agriculture, Animals, Veterinary Sciences, Antibiotics, Zoonotic Diseases
Animal Diseases in Agricultural Production Systems: Their Veterinary, Zoonotic, and One Health Importance, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Ewa Tomaszewska, Beata Łebkowska-Wieruszewska, Tomasz Szponder, Joanna Wessely-SzponderDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
Infectious Disease Reports, Insects, IJERPH, Pathogens, TropicalMed, Zoonotic Diseases
Vector-Borne Disease Spatial Epidemiology, Disease Ecology, and Zoonoses
Topic Editors: Chad L. Cross, Louisa Alexandra MessengerDeadline: 31 December 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Zoonotic Diseases
Viral Zoonotic Diseases and Spillover Risks
Guest Editor: Jonathon D. Gass, Jr.Deadline: 31 May 2026
Special Issue in
Zoonotic Diseases
Emerging Zoonotic Viruses: Transmission, Evolution, and Public Health Challenges
Guest Editors: Mohammed Rohaim, Muhammad MunirDeadline: 30 June 2026










