Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Emerging Foot-and-Mouth Disease, Bluetongue, and Peste Des Petits Ruminants in Algeria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
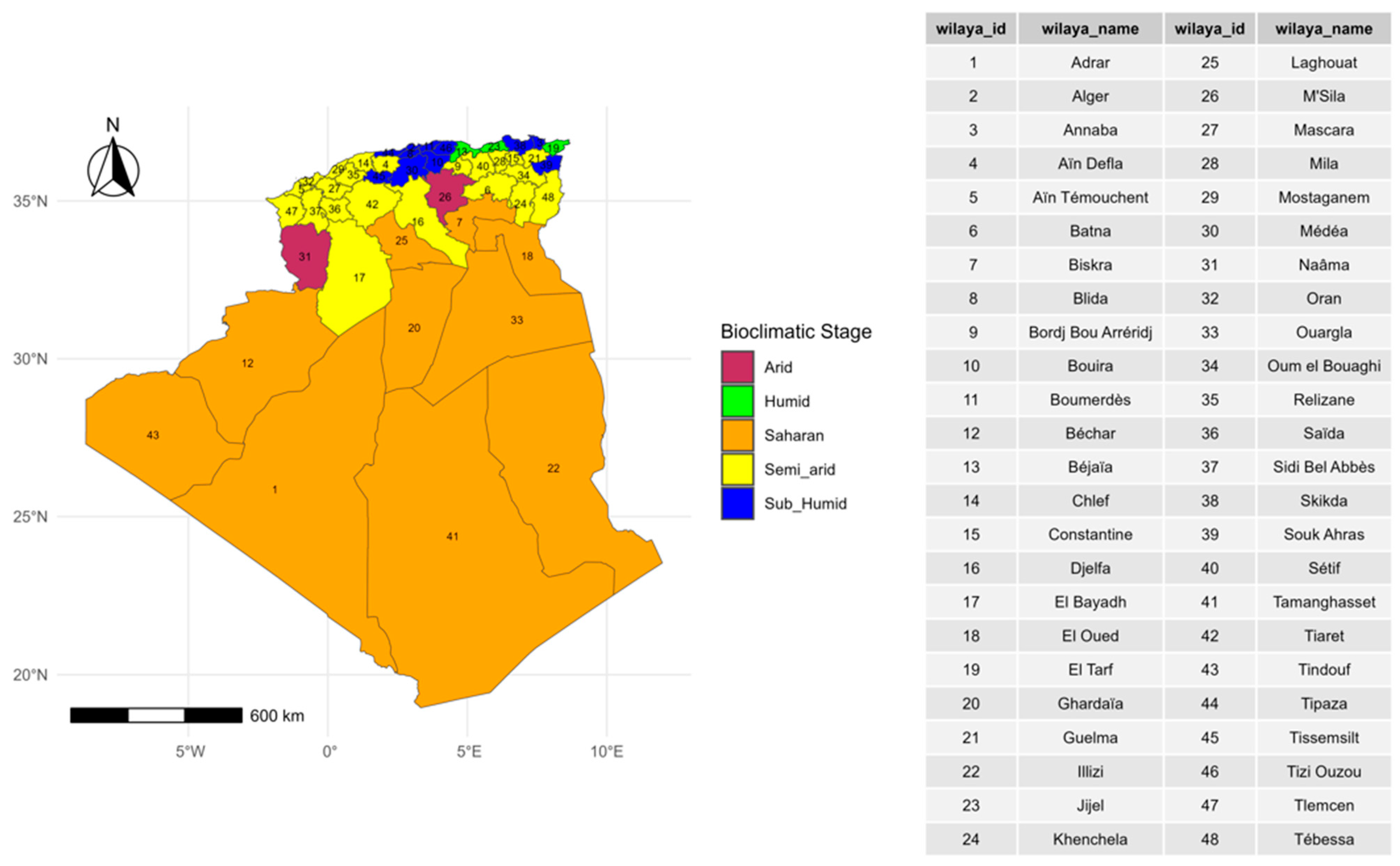
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Data
2.2.1. The Study Period
2.2.2. Data Sources
2.2.3. Data Analyses
Description of Spatiotemporal Patterns
Spatiotemporal Ecological Regression Model
Global Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
Local Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis (LISA)
3. Results
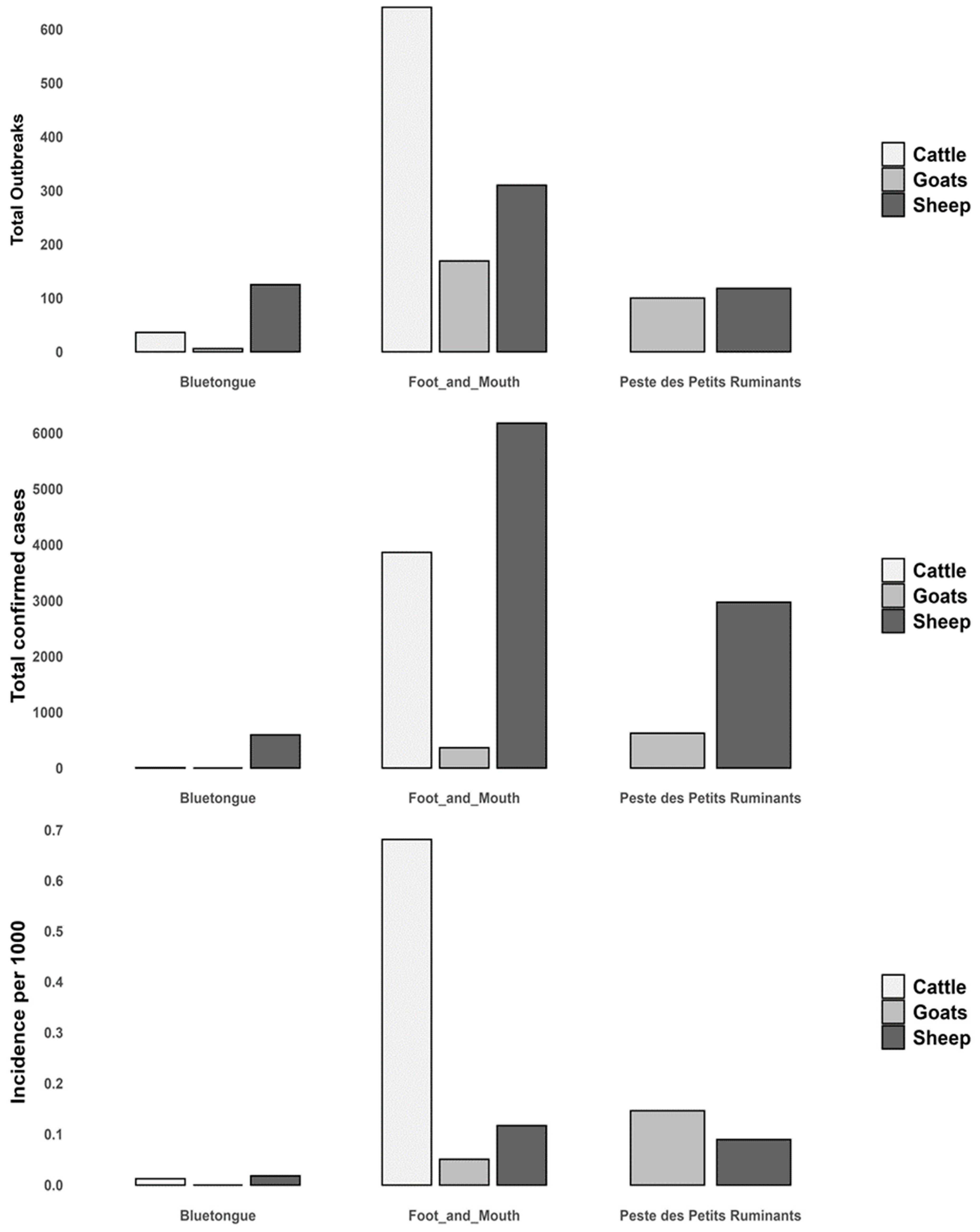
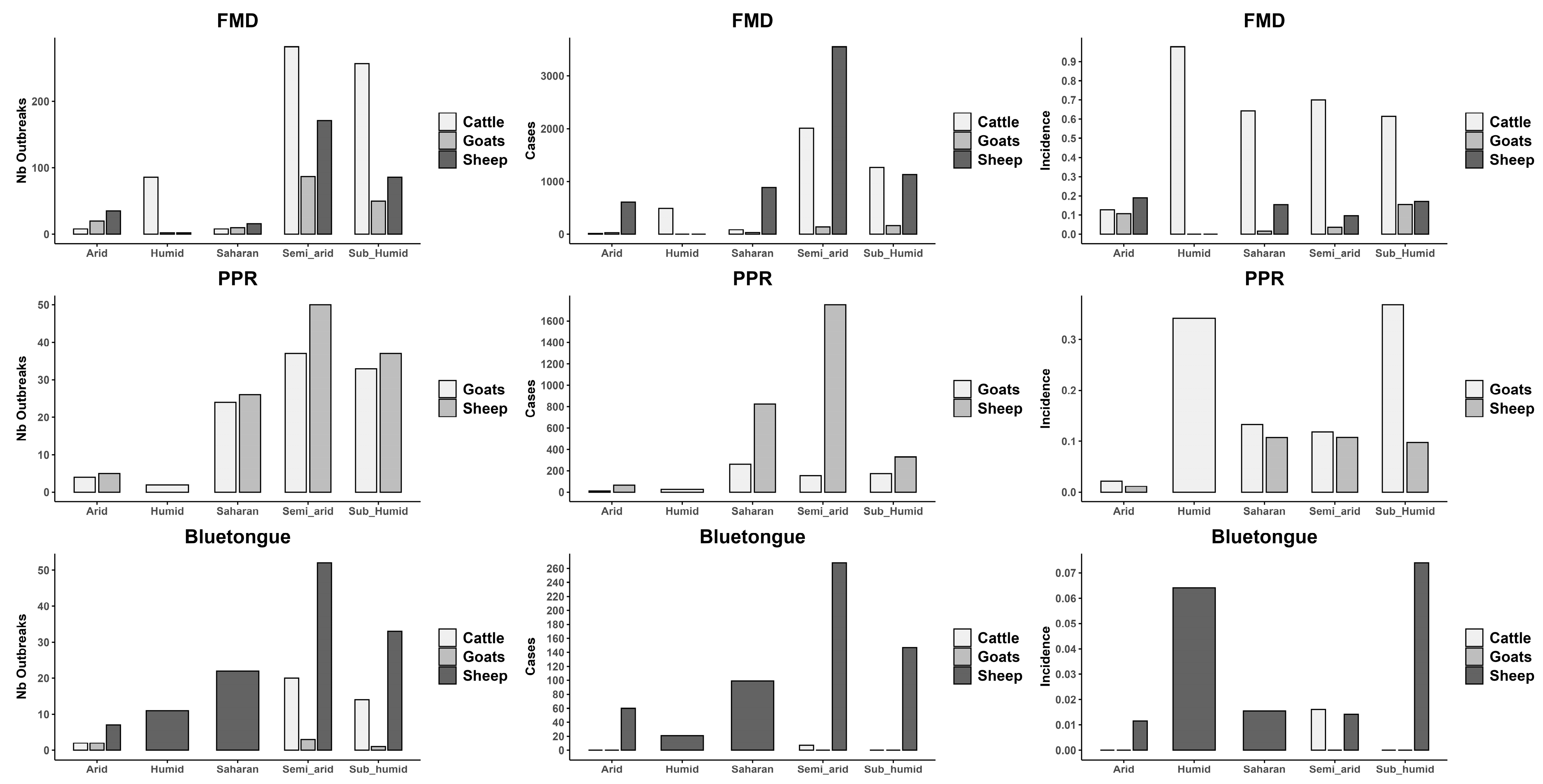
3.1. Disease Burden by Livestock Species
3.2. Temporal Trend
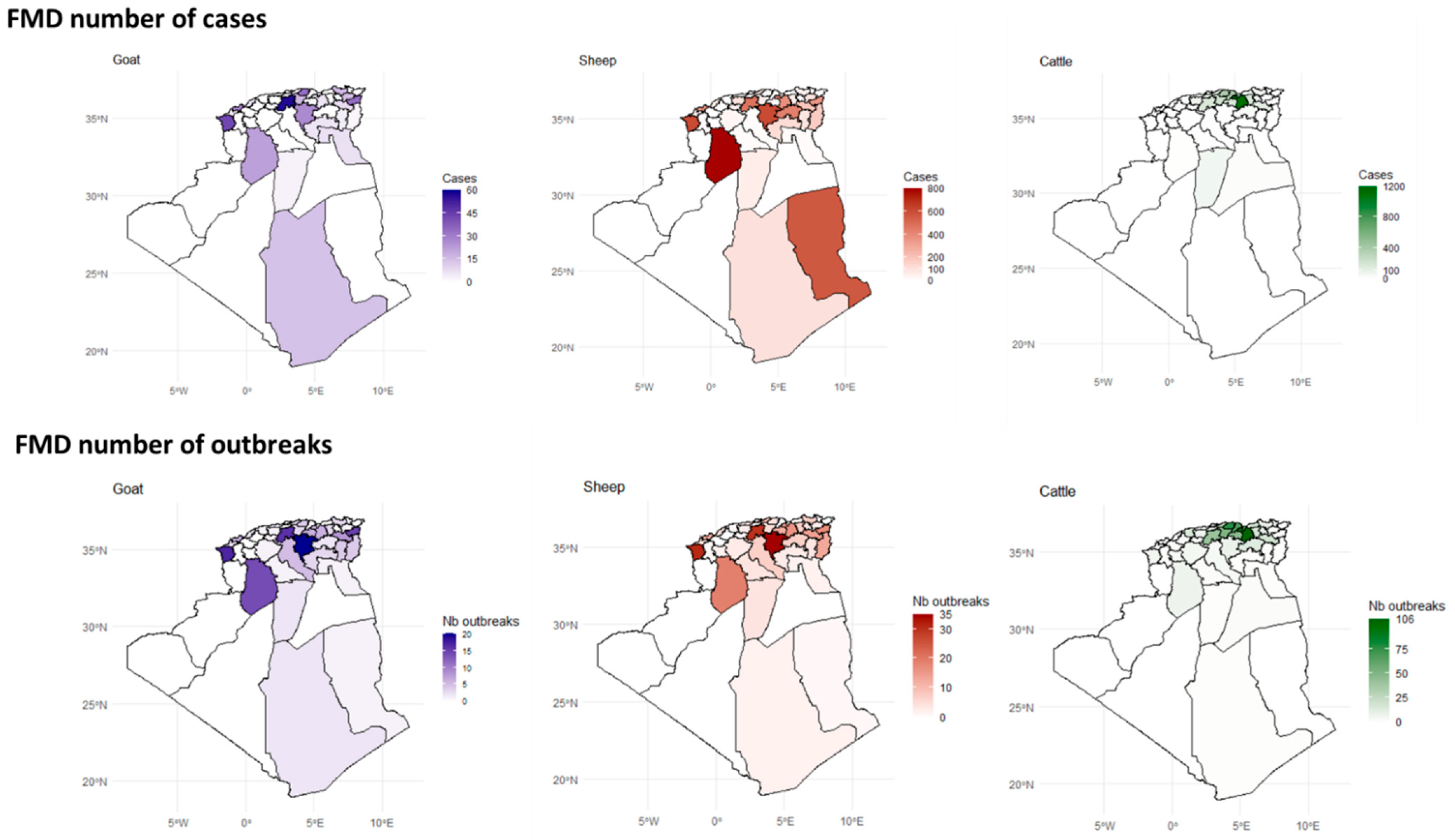
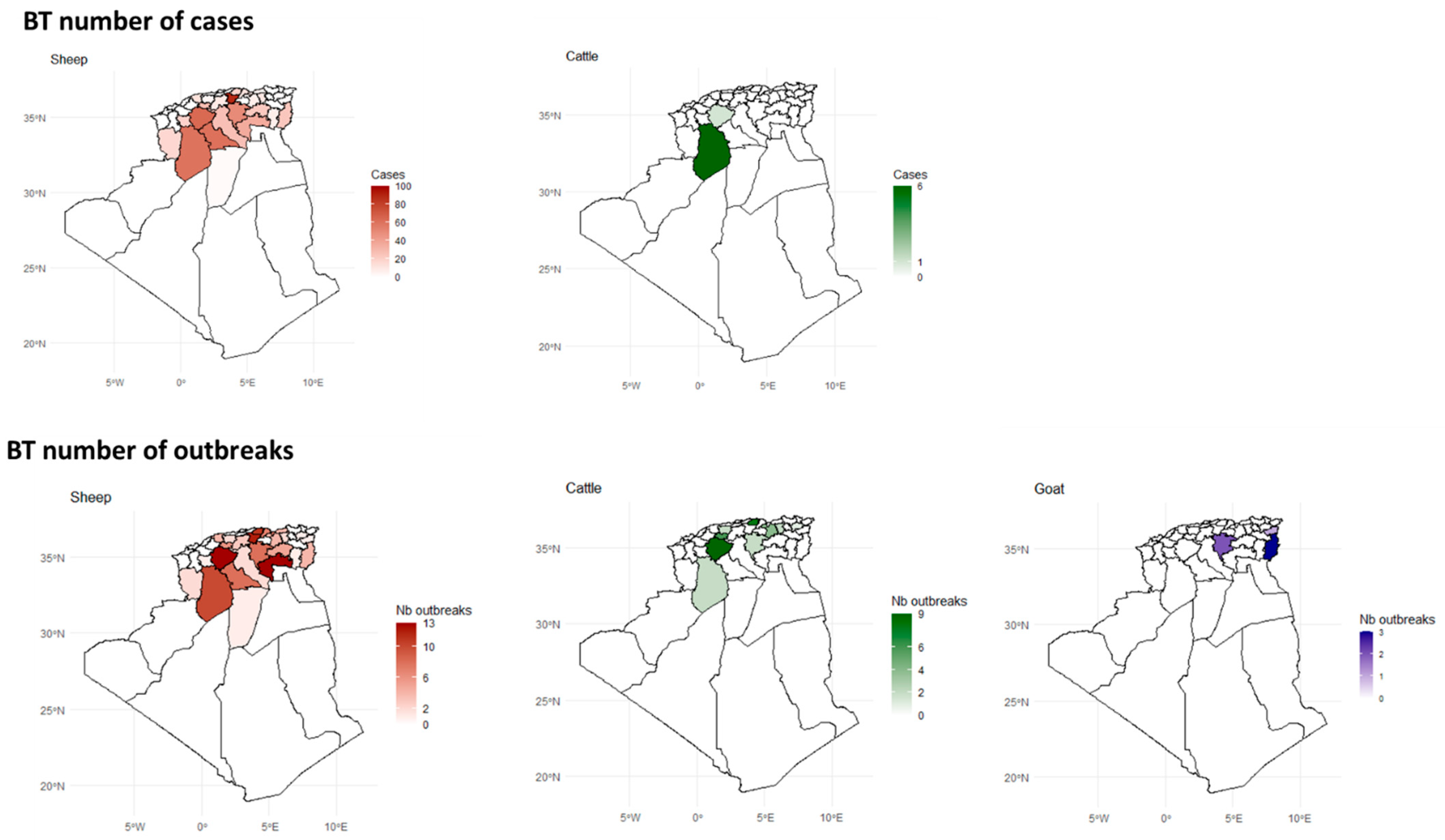
3.3. Spatial Distribution
3.4. Bioclimatic Associations with Disease Outbreaks
3.5. Spatiotemporal Ecological Regression Model
3.5.1. FMD
3.5.2. BT
3.5.3. PPR
3.6. Global Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
3.6.1. FMD
3.6.2. BT
3.6.3. PPR
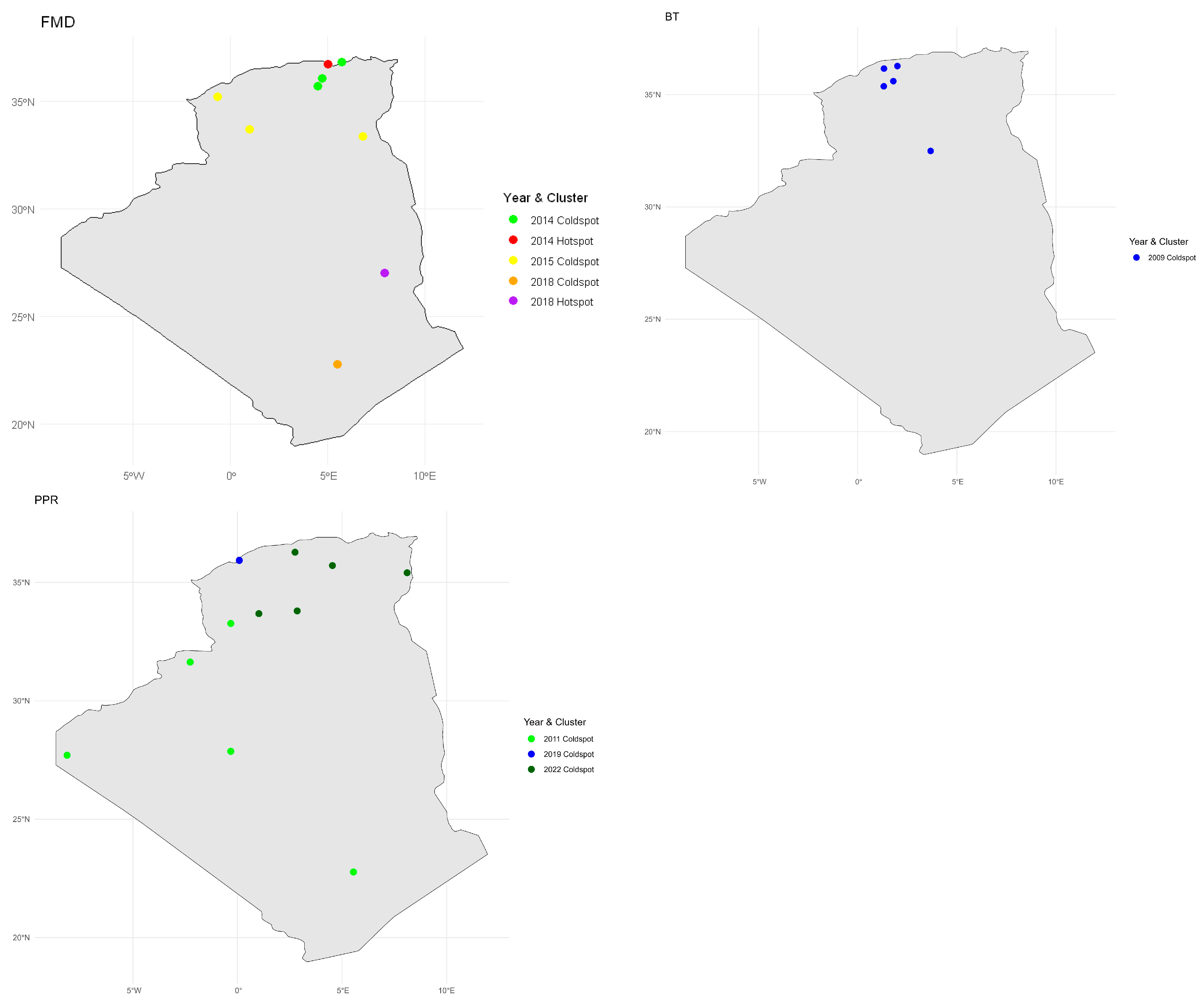
3.7. Local Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis (LISA)
3.7.1. FMD
3.7.2. BT
3.7.3. PPR
4. Discussion
4.1. Disease Burden by Livestock Species
4.2. Temporal Trend
4.3. Spatial Distribution
4.4. Bioclimatic Associations with Disease Outbreaks
5. Recommendations for Prevention and Control of FMD, BT, and PPR in Algeria
- -
- Species-specific local surveillance and control: Target interventions in areas with the highest disease burden. Current vaccination strategies should be re-evaluated in terms of cost-effectiveness and geographic targeting.
- -
- Cross-border collaboration: As TADs readily spread across national borders, joint surveillance and harmonized vaccination campaigns with neighboring countries are essential.
- -
- Climatic and environmental data integration: Incorporate these data into predictive models, especially for vector-borne diseases like BT, to improve forecasting and preparedness.
- -
- Molecular epidemiology and wildlife studies: Further investigation is needed into viral evolution and the role of wildlife reservoirs in disease transmission.
- -
- Advanced spatiotemporal modeling: Use predictive models to identify high-risk areas and timeframes, enabling efficient, timely, and evidence-based interventions.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torres-Velez, F.; Havas, K.A.; Spiegel, K.; Brown, C. Transboundary animal diseases as re-emerging threats—Impact on one health. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2019, 36, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ghonemy, M.R. Food security and rural development in North Africa. Middle East. Stud. 1993, 29, 445–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatzel, K.; Tankari, M.R.; Shah, M.; Choudhury, S.; Badiane, O.; von Braun, J. Meat, Milk and More: Policy Innovations to Shepherd Inclusive and Sustainable Livestock Systems in Africa; Malabo Montpellier Panel Livestock Report; Publisher International Food Policy Research Institute: Dakar, Senegal, 2020; pp. 1–87. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10568/143667 (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Upton, M. The Role of Livestock in Economic Development and Poverty Reduction. Food Agric. Organ. Pro-Poor Livest. Policy Initiat. Work. Pap. 2004, 10, 1–57. Available online: https://ideas.repec.org/p/ags/faopwp/23783.html (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- Horemans, B. Transboundary animal diseases: Diseases with a strong social and economic impact. FAO Newsletter. 2013, 3, 1–3. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/45cabd33-7758-425d-81a4-80679df4b009/content (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Seimenis, A.; Morelli, D.; Mantovani, A. Zoonoses in the Mediterranean region. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2006, 42, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- ONS: Office National des Statistiques. Available online: https://www.ons.dz/spip.php?article2918 (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Mokhtari, F.; Houari, M.A. Economic Growth and Government Subventions for Agriculture Sector in Algeria: An ARDL Model. Arab Econ. Bus. J. 2016, 11, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, S. North Africa: A regional overview of bluetongue virus, vectors, surveillance and unique features. Vet. Ital. 2004, 40, 43–46. Available online: https://www.izs.it/vet_italiana/2004/40_3/11.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2025). [PubMed]
- De Nardi, M.; Lamin Saleh, S.M.; Batten, C.; Oura, C.; Di Nardo, A.; Rossi, D. First evidence of peste des petits ruminants (PPR) virus circulation in Algeria (Sahrawi territories): Outbreak investigation and virus lineage identification. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2012, 59, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouguedour, R.; Ripani, A. Review of the foot and mouth disease situation in North Africa and the risk of introducing the disease into Europe. Rev. Sci. Tech. Int. Off. Epizoot. 2016, 35, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzoni, G.; Calzolari, M.; Foglia, E.A.; Bregoli, A.; Nardo, A.D.; Sghaier, S.; Madani, H.; Chiapponi, C.; Grazioli, S.; Relmy, A.; et al. Characterization of the O/ME-SA/Ind-2001d foot-and-mouth disease virus epidemic recorded in the Maghreb during 2014–2015. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e2641–e2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njeumi, F.; Velascogil, G.; Besbes, B. K-01 FAO’s work for the development of the sheep subsector. Anim. Sci. Proc. 2023, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, S.; Muniraju, M.; Altan, E.; Baazizi, R.; Raj, G.D.; Mahapatra, M. Emergence of PPR and its threat to Europe. Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 142, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albina, E.; Kwiatek, O.; Minet, C.; Lancelot, R.; Servan de Almeida, R.; Libeau, G. Peste des Petits Ruminants, the next eradicated animal disease? Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 165, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OIE. Global Strategy for the Control and Eradication of PPR. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/items/3a081556-4053-499c-856b-b087dce7e604 (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Rushton, J.; Lyons, N. Economic impact of bluetongue: A review of the effects on production. Vet. Ital. 2015, 51, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardjadj, M. History of Foot-and-mouth disease in North African countries. Vet. Ital. 2018, 54, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardjadj, M. Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) in the Maghreb and its threat to southern European countries. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 49, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzoni, G.; Bregoli, A.; Grazioli, S.; Barbieri, I.; Madani, H.; Omani, A.; Sadaoui, H.; Bouayed, N.; Wadsworth, J.; Bachanek-Bankowska, K.; et al. Foot-and-mouth disease outbreaks due to an exotic virus serotype A lineage (A/AFRICA/G-IV) in Algeria in 2017. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardjadj, M.; Kouidri, B.; Metref, D.; Luka, P.D.; Ben-Mahdi, M.H. Seroprevalence, distribution and risk factor for peste des petits ruminants (PPR) in Algeria. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 122, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardjadj, M.; Ben-Mahdi, M.-H.; Luka, P.D. First serological and molecular evidence of PPRV occurrence in Ghardaïa district, center of Algeria. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2015, 47, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baazizi, R.; Mahapatra, M.; Clarke, B.D.; Ait-Oudhia, K.; Khelef, D.; Parida, S. Peste des petits ruminants (PPR): A neglected tropical disease in Maghreb region of North Africa and its threat to Europe. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cêtre-Sossah, C.; Madani, H.; Sailleau, C.; Nomikou, K.; Sadaoui, H.; Zientara, S.; Maan, S.; Maan, N.; Mertens, P.; Albina, E. Molecular epidemiology of bluetongue virus serotype 1 isolated in 2006 from Algeria. Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 91, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardjadj, M.; Luka, P.D. Molecular epidemiology of foot and mouth disease, bluetongue and pest de petites ruminants in Algeria: Historical perspective, diagnosis and control. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 15, 2474–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Madani, H.; Casal, J.; Alba, A.; Allepuz, A.; Cêtre-Sossah, C.; Hafsi, L.; Kount-Chareb, H.; Bouayed-Chaouach, N.; Saadaoui, H.; Napp, S. Animal diseases caused by Orbiviruses, Algeria. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 2325–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daget, P. Le bioclimat Mediterraneen: Analyse des formes climatiques par le systeme d’Emberger. Vegetatio 1977, 34, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SGG Algérie. Journal Officiel de la République Algérienne Démocratique et Populaire. Décret Présidentiel n° 95-433 du 25 Rajab 1416 Correspondant au 18 Décembre 1995. Available online: www.joradp.dz (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- R Core Team. The R Project for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Rea, L.M.; Parker, R.A. Designing and Conducting Survey Research: A Comprehensive Guide, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Jossey-Bass, CA, USA, 2014; 352p. [Google Scholar]
- Dormann, C.F.; Elith, J.; Bacher, S.; Buchmann, C.; Carl, G.; Carré, G.; Marquéz, J.R.G.; Gruber, B.; Lafourcade, B.; Leitão, P.J.; et al. Collinearity: A review of methods to deal with it and a simulation study evaluating their performance. Ecography 2013, 36, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.C.; Trivedi, P.K. Regression-based tests for overdispersion in the Poisson model. J. Econom. 1990, 46, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbe, J.M. Methods of estimation. In Negative Binomial Regression, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Model selection and multimodel inference. In A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hartig, F. DHARMa: Residual Diagnostics for Hierarchical (Multi-Level/Mixed) Regression Models. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/DHARMa/vignettes/DHARMa.html (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Moran, P.A.P. Notes on continuous stochastic phenomena. Biometrika 1950, 37, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselin, L. Local indicators of spatial association—LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghonaim, A.H.; Rouby, S.R.; Hopo, M.G.; Li, W. Foot-and-mouth disease: A persistent challenge for the livestock industry. In Veterinary Virology of Domestic and Pet Animals, Latest ed.; Wang, L., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; Urbana, IL, USA, 2025; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo de Rueda, C.; de Jong, M.C.M.; Eblé, P.L.; Dekker, A. Estimation of the transmission of foot-and-mouth disease virus from infected sheep to cattle. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 58. Available online: http://www.veterinaryresearch.org/content/45/1/58 (accessed on 30 May 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporale, M.; Di Gialleonorado, L.; Janowicz, A.; Wilkie, G.; Shaw, A.; Savini, G.; Van Rijn, P.A.; Mertens, P.; Di Ventura, M.; Palmarini, M. Virus and host factors affecting the clinical outcome of bluetongue virus infection. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10399–10411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLachlan, N.J. Bluetongue: Pathogenesis and duration of viraemia. Vet. Ital. 2004, 40, 462–467. Available online: https://www.izs.it/vet_italiana/2004/40_4/462.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2025). [PubMed]
- Coetzee, P.; van Vuuren, M.; Venter, E.H.; Stokstad, M. A review of experimental infections with bluetongue virus in the mammalian host. Virus Res. 2014, 182, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belbis, G.; Zientara, S.; Bréard, E.; Sailleau, C.; Caignard, G.; Vitour, D.; Attoui, H. Chapter Seven—Bluetongue Virus: From BTV-1 to BTV-27. In Advances in Virus Research, 1st ed.; Beer, M., Höper, D., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 99, pp. 161–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Maherchandani, S.; Kashyap, S.K.; Singh, S.V.; Sharma, S.; Chaubey, K.K.; Ly, H. Peste des petits ruminants virus infection of small ruminants: A comprehensive review. Viruses 2014, 6, 2287–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, K.; Madani, T.; Ben Cheikh el Hocine, T.; Merrouche, L. Systèmes d’élevage associés à l’agriculture dans les hautes plaines de Sétif: Etude des caractéristiques des exploitations agricoles ayant des caprins. Rech. Agron. 2002, 6, 79–94. Available online: https://asjp.cerist.dz/en/article/75536 (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO); World Reference Laboratory for Foot-and-Mouth Disease (WRLFMD); World Reference Laboratory Reports (World Organisation for Animal Health [OIE]/FAO). FMD Molecular Epidemiology Reports for Algeria. 2017. Available online: https://www.wrlfmd.org/ (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Baazizi, R.; Mimoune, N.; Mokhefi, M.E.; Raza, M.; Chahed, A.; Hussain, T. Knowledge and behavior of cattle and sheep owners and herders regarding foot-and-mouth disease in Northern Algeria. Vet. World 2019, 12, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guessoum, M.; Adnane, M.; Baazizi, R.; Derguini, M.S. Spatial and temporal distribution of foot-and-mouth disease outbreaks in Algeria from 2014 to 2022. Vet. World 2024, 17, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athambawa, M.J.; Kubota, S.; Kono, H. Knowledge affecting foot-and-mouth disease vaccination behavior: Traditional dairy farmers in the dry zone of Sri Lanka. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xaydalasouk, K.; Innoula, N.; Putthana, V.; Chanthavongsa, K.; Snoeck, C.J.; Hübschen, J.M.; Oudomphone, P.; Chan, B.; Muller, C.P.; Black, A.P.; et al. High seroprevalence of foot and mouth disease in Laos: Call for nationwide vaccination campaigns and disease surveillance. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 68, 2345–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielke, S.R.; Lendzele, S.; Delgado, A.H.; Abdoulmoumini, M.; Dickmu, S.; Garabed, R. Patterns of foot-and-mouth disease virus detection in environmental samples in an endemic setting. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1157538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukai, K.; Kawaguchi, R.; Nishi, T.; Ikezawa, M.; Yamada, M.; Seeyo, K.B.; Morioka, K. Risk of transmission of foot-and-mouth disease by wild animals: Infection dynamics in Japanese wild boar following direct inoculation or contact exposure. Vet. Res. 2022, 53, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahiya, S.S.; Subramaniam, S.; Mohapatra, J.K.; Rout, M.; Biswal, J.K.; Giri, P.; Nayak, V.; Singh, R.P. Foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype O exhibits phenomenal genetic lineage diversity in India during 2018–2022. Viruses 2023, 15, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagerman, A.D.; South, D.D.; Sondgerath, T.C.; Patyk, K.A.; Sanson, R.L.; Schumacher, R.S.; Delgado, A.H.; Magzamen, S. Temporal and geographic distribution of weather conditions favorable to airborne spread of foot-and-mouth disease in the coterminous United States. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 161, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandersen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Reid, S.M.; Hutchings, G.H.; Donaldson, A.I. Quantities of infectious virus and viral RNA recovered from sheep and cattle experimentally infected with foot-and-mouth disease virus O UK 2001. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arzt, J.; Pacheco, J.M.; Stenfeldt, C.; Rodriguez, L.L. Pathogenesis of virulent and attenuated foot-and-mouth disease virus in cattle. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, P.S.; Wittmann, E.J. Bluetongue virus in the Mediterranean basin 1998–2001. Vet. J. 2002, 164, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, P.S.; Boorman, J. The transmission and geographical spread of African horse sickness and bluetongue viruses. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1995, 89, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guichard, S.; Guis, H.; Tran, A.; Garros, C.; Balenghien, T.; Kriticos, D.J. Worldwide niche and future potential distribution of Culicoides imicola, a major vector of bluetongue and African horse sickness viruses. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Cabello, L.; Utrilla-Trigo, S.; Calvo-Pinilla, E.; Moreno, S.; Nogales, A.; Ortego, J.; Marín-López, A. Viral vector vaccines against bluetongue virus. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpar, H.O.; Bramwell, V.W.; Veronesi, E.; Darpel, K.E.; Pastoret, P.P.; Mertens, P.P.C. Bluetongue virus vaccines past and present. In Bluetongue; Mellor, P.S., Baylis, M., Mertens, P.P.C., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2009; pp. 397–428. [Google Scholar]
- Kalthoum, S.; Sghaier, S.; Ben Hassine, T.; Teodori, L.; Spedicato, M.; Guesmi, K.; Gharbi, R.; Hajlaoui, H.; Bel Haj, M.B.; Khalfaoui, W.; et al. Risk-based serological survey of bluetongue and the first evidence of bluetongue virus serotype 26 circulation in Tunisia. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 1671–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Salem, A.; Ben Aicha, E.; Kalthoum, S.; Dhaouadi, A.; Hajlaoui, H.; Bel Haj, M.B.; Ben Slimen, I.; Khalfaoui, W.; Gharbi, R.; Guesmi, K.; et al. Estimation of the economic impact of a bluetongue serotype 4 outbreak in Tunisia. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1310202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rijn, A.P. Prospects of next-generation vaccines for bluetongue. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, P. Highly efficient vaccines for Bluetongue virus and a related Orbivirus based on reverse genetics. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2020, 44, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardjadj, M.; Luka, P.D.; Ben-Mahdi, M.H. Assessing the immune response of commercial peste des petits ruminant’s vaccine in sheep and goats in Algeria. J. Vet. Sci. Med. Diagn. 2015, 4, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencherif, S. L’élevage Pastoral et la Céréaliculture Dans la Steppe Algérienne. Évolution et Possibilités de Développement. Ph.D. Thesis, AgroParisTech, Paris, France, 2011. Available online: https://pastel.hal.science/pastel-00586977 (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Banyard, A.C.; Parida, S.; Batten, C.; Oura, C.; Kwiatek, O.; Libeau, G. Global distribution of peste des petits ruminants virus and prospects for improved diagnosis and control. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2885–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantip, S.E.; Shamaki, D.; Farougou, S. Peste des petits ruminants in Africa: Meta-analysis of virus isolation in molecular epidemiology studies. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2019, 86, e1–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouslikhane, M. Les mouvements transfrontaliers d’animaux et de produits d’origine animale et leur rôle dans l’épidémiologie des maladies animales en Afrique. In Proceedings of the 21e Conférence de la Commission Régionale OIE-Afrique, Rabat, Maroc, 16–20 February 2015; pp. 1–8. Available online: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/eng/Publications_%26_Documentation/docs/pdf/TT/2015_AFR2_Bouslikhane_F.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Lezaar, Y.; Manneh, M.; Apolloni, A.; Berrada, J.; Bouslikhane, M. Transboundary livestock network in Africa: How circulate pathogens and where to act to prevent the epizootics spread? Epidemiol. Open J. 2023, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purse, B.V.; Mellor, P.S.; Rogers, D.J.; Samuel, A.R.; Mertens, P.P.; Baylis, M. Erratum: Climate change and the recent emergence of bluetongue in Europe. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.C.; Carrondo, M.J.T.; Alves, P.M. Strategies for improved stability of peste des petits ruminants vaccine. Vaccine 2011, 29, 4983–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Njeumi, F.; Parida, S.; Benfield, C.T.O. Progress towards eradication of peste des petits ruminants through vaccination. Viruses 2021, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakri, F.; Embarki, T.; Parida, S.; Bamouh, Z.; Jazouli, M.; Mahapatra, M.; Tadlaoui, K.; Fassi-Fihri, O.; Richardson, C.D.; Elharrak, M. Re-emergence of peste des petits ruminants virus in 2015 in Morocco: Molecular characterization and experimental infection in Alpine goats. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 197, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benavides, J.A.; Rojas Paniagua, E.; Hampson, K.; Valderrama, W.; Streicker, D.G. Quantifying the burden of vampire bat rabies in Peruvian livestock. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variable | SE | IRR | IRR 95% CI | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FMD | Year (2014) | 19.55 | 29.08 | 6.75–96.70 | <0.0001 |
| Year (2018) | 13.78 | 17.47 | 3.51–78.45 | <0.001 | |
| Species (Cattle) | 4.42 | 12.57 | 4.19–36.69 | <0.0001 | |
| Species (Sheep) | 5.31 | 15.67 | 7.76–31.34 | <0.001 | |
| Quarter (2) | 27.64 | 16.83 | 0.69–1492.24 | 0.086 | |
| PPR | Quarter (4) | 1.79 | 3.25 | 0.98–9.04 | 0.033 |
| Quarter (1) | 1.97 | 3.81 | 1.21–9.67 | 0.010 | |
| Species (Sheep) | 1.31 | 4.32 | 2.35–7.88 | <0.001 | |
| BT | Quarter (3) | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.00–0.34 | 0.006 |
| Quarter (4) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00–0.23 | 0.0021 | |
| Species (Sheep) | 162.68 | 155.53 | 20.02–1208.25 | <0.0001 |
| Disease | Year | Wilaya | Latitude | Longitude | Incidence Rate | LISA I | p-Value | Cluster |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FMD | 2018 | Tamanghasset | 22.7697 | 5.548 | 0.49 | −0.19 | 0.001 | Coldspot |
| 2018 | Illizi | 26.9997 | 7.9707 | 6.91 | 2.45 | 0.029 | Hotspot | |
| 2015 | El_Oued | 33.3714 | 6.8554 | 0.01 | −0.08 | 0.000 | Coldspot | |
| 2015 | El_Bayadh | 33.6829 | 1.0217 | 0.06 | −0.92 | 0.000 | Coldspot | |
| 2015 | Sidi_Bel_Abbès | 35.2007 | −0.6323 | 0.02 | −0.01 | 0.000 | Coldspot | |
| 2014 | M’Sila | 35.7142 | 4.5422 | 0.24 | −0.39 | 0.041 | Coldspot | |
| 2014 | Bordj_Bou_Arréridj | 36.0774 | 4.7611 | 0.25 | −0.44 | 0.020 | Coldspot | |
| 2014 | Béjaïa | 36.7222 | 5.0503 | 2.03 | 0.71 | 0.044 | Hotspot | |
| 2014 | Jijel | 36.8321 | 5.7617 | 0.12 | −0.56 | 0.016 | Coldspot | |
| PPR | 2011 | Tamanghasset | 22.7697 | 5.548 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.000 | Coldspot |
| 2011 | Tindouf | 27.7 | −8.1528 | 0.32 | −0.72 | 0.000 | Coldspot | |
| 2011 | Adrar | 27.8668 | −0.3196 | 0.02 | −0.34 | 0.000 | Coldspot | |
| 2011 | Béchar | 31.6348 | −2.2641 | 0.18 | −0.03 | 0.000 | Coldspot | |
| 2011 | Naâma | 33.2672 | −0.3196 | 0.06 | −0.16 | 0.000 | Coldspot | |
| 2022 | El_Bayadh | 33.6829 | 1.0217 | 0.04 | −0.83 | 0.000 | Coldspot | |
| 2022 | Laghouat | 33.797 | 2.8558 | 0.00 | −0.17 | 0.000 | Coldspot | |
| 2022 | Tébessa | 35.4088 | 8.1155 | 0.02 | −0.03 | 0.000 | Coldspot | |
| 2022 | M’Sila | 35.7142 | 4.5422 | 0.00 | −0.14 | 0.000 | Coldspot | |
| 2019 | Mostaganem | 35.927 | 0.0872 | 0.11 | −0.43 | 0.042 | Coldspot | |
| 2022 | Médéa | 36.2641 | 2.7539 | 0.00 | −0.08 | 0.000 | Coldspot | |
| BT | 2009 | Ghardaïa | 32.4921 | 3.6776 | 0.01 | −0.25 | 0.00 | Coldspot |
| 2009 | Tiaret | 35.371 | 1.3169 | 0.02 | −0.10 | 0.00 | Coldspot | |
| 2009 | Tissemsilt | 35.6015 | 1.799 | 0.12 | −0.82 | 0.00 | Coldspot | |
| 2009 | Chlef | 36.1596 | 1.3259 | 0.06 | −0.02 | 0.00 | Coldspot | |
| 2009 | Aïn_Defla | 36.2741 | 2.0017 | 0.03 | −0.05 | 0.00 | Coldspot |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zouyed, I.; Boussena, S.; Ramdani, N.; Damerdji, H.E.; Benavides, J.A.; Medkour, H. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Emerging Foot-and-Mouth Disease, Bluetongue, and Peste Des Petits Ruminants in Algeria. Viruses 2025, 17, 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071008
Zouyed I, Boussena S, Ramdani N, Damerdji HE, Benavides JA, Medkour H. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Emerging Foot-and-Mouth Disease, Bluetongue, and Peste Des Petits Ruminants in Algeria. Viruses. 2025; 17(7):1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071008
Chicago/Turabian StyleZouyed, Ilhem, Sabrina Boussena, Nacira Ramdani, Houssem Eddine Damerdji, Julio A. Benavides, and Hacène Medkour. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Emerging Foot-and-Mouth Disease, Bluetongue, and Peste Des Petits Ruminants in Algeria" Viruses 17, no. 7: 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071008
APA StyleZouyed, I., Boussena, S., Ramdani, N., Damerdji, H. E., Benavides, J. A., & Medkour, H. (2025). Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Emerging Foot-and-Mouth Disease, Bluetongue, and Peste Des Petits Ruminants in Algeria. Viruses, 17(7), 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17071008










