-
 Not All U.S. Pharmacists Are Equal: A Full-Time Versus Part-Time Comparison
Not All U.S. Pharmacists Are Equal: A Full-Time Versus Part-Time Comparison -
 Optimizing Drug Therapy in ECMO-Supported Critically Ill Adults: A Narrative Review and Clinical Guide
Optimizing Drug Therapy in ECMO-Supported Critically Ill Adults: A Narrative Review and Clinical Guide -
 Responsible Adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Pharmacy Practice: Perspectives of Regulators in Canada and the United States
Responsible Adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Pharmacy Practice: Perspectives of Regulators in Canada and the United States
Journal Description
Pharmacy
Pharmacy
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed, and open access journal dealing with pharmacy education and practice, and is published bimonthly online by MDPI. The Academy of Pharmaceutical Sciences (APS) is affiliated with Pharmacy and its members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 23.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: Reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Journal Clusters-Pharmaceutical Science: Scientia Pharmaceutica, Marine Drugs, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Pharmacy, Future Pharmacology, Pharmacoepidemiology, Drugs and Drug Candidates and Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry.
Impact Factor:
1.8 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.0 (2024)
Latest Articles
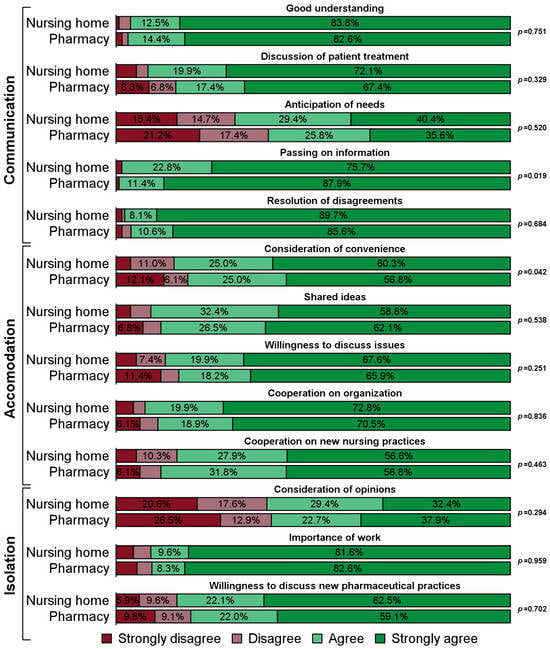
Impacts of Outsourcing Medication Repackaging in Nursing Homes: Quality and Areas of Pharmacy–Nursing Collaboration
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 182; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060182 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
The task of repackaging resident’s medication into medication organizers is increasingly outsourced from nursing homes to pharmacies, presenting an opportunity to redefine the interaction between nursing and pharmaceutical staff. This study investigated whether outsourcing medication repackaging changes the quality and subjects of collaboration
[...] Read more.
The task of repackaging resident’s medication into medication organizers is increasingly outsourced from nursing homes to pharmacies, presenting an opportunity to redefine the interaction between nursing and pharmaceutical staff. This study investigated whether outsourcing medication repackaging changes the quality and subjects of collaboration between the two professions. A cross-sectional survey was developed targeting heads of nursing in German nursing homes. A simple random sample of 1415 nursing homes was contacted by phone. Respondents participated either by phone or by online survey. Quality of collaboration was measured using Kenaszchuk’s Interprofessional Collaboration Scale (ICS) with its subscales Communication, Accommodation and Isolation. Topics of interaction were ascertained using items along a medication management phase model. Differences in response frequencies were analyzed using Fisher’s exact test. A total of 268 nursing homes participated (response: 18.9%). Of these, 132 (49.3%) had outsourced repackaging. Respondents at nursing homes with in-house medication repackaging rated the subscale Accommodation more favorably (p = 0.008), while Communication and Isolation showed no difference. Of the 13 individual ICS items, “passing on information” (Communication) was rated better by respondents at homes with outsourced repackaging (p = 0.019) and “consideration of convenience” (Accommodation) more favorably by respondents at homes with in-house repackaging (p = 0.042). Nursing staff at homes with outsourced medication repackaging interacted with pharmaceutical staff more frequently on medication changes (p < 0.001), but less frequently on tablet splitting (p = 0.035). In conclusion, outsourcing medication repackaging has a limited impact on the quality of interprofessional collaboration between the two professions but may have the potential to reduce ambiguities regarding splitting tablets.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacy Practice and Practice-Based Research)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
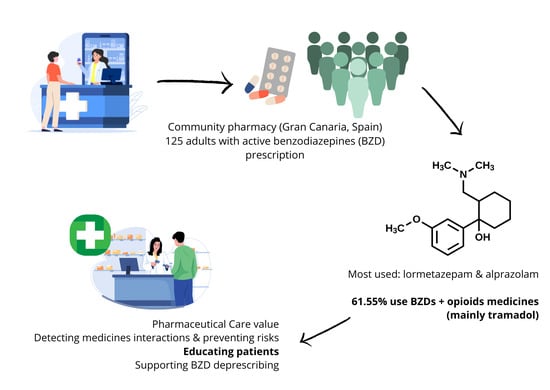
Benzodiazepine (BZD) Use and Patient Safety: Opportunities for Community Pharmacy Involvement in the Management of Drug Interactions
by
Juan Ramón Santana Ayala, Daida Alberto Armas, Veronica Hernández García, Armando Aguirre-Jaime, Ángel J. Gutiérrez, Soraya Paz-Montelongo, Arturo Hardisson de la Torre and Carmen Rubio Armendáriz
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 181; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060181 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
Introduction: During pharmaceutical care, community pharmacists play a crucial role by carrying out interventions aimed at preventing, detecting, and resolving drug-related problems (DRPs) and negative outcomes associated with medication (NOM), simultaneously enhancing patients’ knowledge about their treatments. The chronic use of Benzodiazepines (BZDs)
[...] Read more.
Introduction: During pharmaceutical care, community pharmacists play a crucial role by carrying out interventions aimed at preventing, detecting, and resolving drug-related problems (DRPs) and negative outcomes associated with medication (NOM), simultaneously enhancing patients’ knowledge about their treatments. The chronic use of Benzodiazepines (BZDs) is known to be associated with risks such as tolerance, dependence, and cognitive impairment. Furthermore, the combined use of BZDs with other medications or alcohol may expose patients to significant drug interactions. Objectives: This study aimed to characterize and describe the clinical profile of patients using BZDs, to evaluate the extent of polypharmacy and potential drug interactions, to investigate their level of knowledge regarding BZD treatment, and ultimately, to propose evidence-based interventions from the community pharmacy to contribute to improving patient safety and minimizing risks associated with BZD use. Method: A cross-sectional, descriptive study was conducted in a single community pharmacy in Gran Canaria (Canary Islands, Spain). The study population comprised 125 adult patients with active BZD prescriptions. Data collection was performed through pharmacist–patient structured interviews using a questionnaire that included sociodemographic, clinical, and BZD knowledge variables. Results: Lormetazepam and alprazolam were the BZDs most frequently prescribed and dispensed. Potential drug interactions with other medications were detected in 38.4% of BZD users. Notably, 61.5% of patients using BZDs also reported the concurrent use of opioid analgesics, with tramadol being the most common opioid (48.1% of BZD users were also treated with tramadol). Statistically significant differences were observed between patients with and without BZD and other drug interactions in several adverse outcome variables, including the risk of falls (p = 0.003), cognitive impairment (p = 0.047), and urinary incontinence (p = 0.016). Existing BZD dependence is detected in 25% and 22.1% of cases, respectively. Patients’ knowledge of their BZD treatment revealed critical gaps, which are identified as a challenge and a clear opportunity for intervention through pharmaceutical care services. Conclusions: The findings underscore the essential and proactive role of community pharmacists in identifying and managing drug interactions, as well as in supporting deprescribing strategies through collaborative and interprofessional care models.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacy Practice and Practice-Based Research)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessPerspective
Advances in Drug and Vaccine Delivery for Low- and Middle-Income Healthcare Programs—The Case for Replacing Multi-Dose Vials with Prefilled Single-Dose Delivery Systems
by
Darin Zehrung and Michael J. Free
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 180; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060180 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The transition toward wide-scale use of single-dose administration systems such as prefilled syringes has primarily occurred in high-income countries due to economic considerations. This has resulted in a disparity of access to such technologies in low- and middle-income countries, which continue to utilize
[...] Read more.
The transition toward wide-scale use of single-dose administration systems such as prefilled syringes has primarily occurred in high-income countries due to economic considerations. This has resulted in a disparity of access to such technologies in low- and middle-income countries, which continue to utilize multi-dose vial-based presentations and syringes for parenteral delivery. Single-dose innovations currently available or in the product development pipeline represent the promise of enhanced access globally and the potential for public health impact. This perspective article discusses the reported benefits of pre-filled single-dose delivery systems compared to multi-dose vials, as well as the higher standards of infection control regulations and practices that resulted in the increasing use of and benefit from single-dose administration systems in high-income countries. We evaluated how these benefits and standards could enhance health initiatives in low- and middle-income countries. Finally, we explored the potential for making pre-filled single-dose delivery methods both accessible and affordable in low- and middle-income countries.
Full article
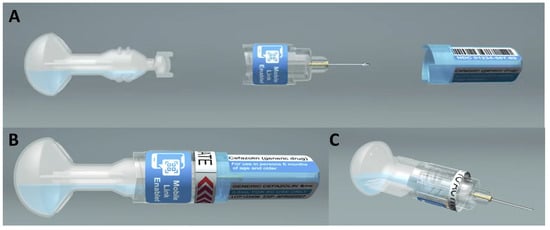
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Drug Repurposing for Inclusion of COVID-19-Related Indication: Field Study of the European Medicines Agency’s Response to the Pandemic
by
Antonio Ivanov, Violeta Getova-Kolarova and Ines Hababa-Ivanova
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 179; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060179 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
As one of the biggest challenges for healthcare in the 21st century, COVID-19 placed a sustained and intense demand on the European Medicines Agency’s resources and required constant adaptation and mobilization of different regulatory processes. In this situation, drug repurposing appeared as a
[...] Read more.
As one of the biggest challenges for healthcare in the 21st century, COVID-19 placed a sustained and intense demand on the European Medicines Agency’s resources and required constant adaptation and mobilization of different regulatory processes. In this situation, drug repurposing appeared as a promising potential approach in quickly emerging health crises due to its main advantage of reducing the time and cost for addition of new indications since it uses products proven to be of high quality, safe, and effective. We performed an analysis of European Public Assessment Reports for medicinal products authorized for the SARS-CoV-2 infection by the European Medicines Agency, showing a total of eight products with this indication, three (37.5%) of which used repurposing as a mechanism for development (remdesivir, tocilizumab, and anakinra). The application of this mechanism by these medicines highlights the importance of the life cycle stage at which repositioning is undertaken, which resulted in different volumes of data submitted in the respective European Public Assessment Reports. The participation of organizations other than the marketing authorization holder in key stages in the drug development process of repurposed products was once again confirmed, which emphasizes the need to regulate this interaction.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Drug Repurposing: Strengthening Outcomes of Existing Pharmaceuticals to Shift Emerging Health Challenges)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mining of Adverse Event Signals Associated with Fluticasone Furoate/Umeclidinium/Vilanterol Triple Therapy: A Post-Marketing Analysis Based on FAERS
by
Jiajun Chen, Ying Qiao, Gaoxing Qiao, Xiaocan Jia and Jicun Zhu
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 178; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060178 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a major global health burden. The fluticasone furoate (FF)/umeclidinium (UMEC)/vilanterol (VI) triple therapy provides new treatment, but its long-term real-world safety lacks evidence. A post-marketing analysis used the FAERS database to identify adverse event (AE) signals for
[...] Read more.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a major global health burden. The fluticasone furoate (FF)/umeclidinium (UMEC)/vilanterol (VI) triple therapy provides new treatment, but its long-term real-world safety lacks evidence. A post-marketing analysis used the FAERS database to identify adverse event (AE) signals for FF/UMEC/VI. Disproportionality methods including reporting odds ratio (ROR), proportional reporting ratio (PRR), information component (IC), and empirical Bayesian geometric mean (EBGM), were applied to detect AE signals, focusing on reports from third quarter (Q3) 2019 to Q3 2024. Among 16,238 reports listing FF/UMEC/VI as primary suspect, significant AE signals occurred in ‘injury, poisoning and procedural complications’ (n = 9067, ROR 2.46, PRR 2.08, IC 1.06, EBGM 2.08), and ‘respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders’ (n = 6567, ROR 4.87, PRR 4.15, IC 2.05, EBGM 4.13). A total of 196 significantly disproportionate preferred terms (PTs) were identified, including previously undocumented AEs such as chronic eosinophilic rhinosinusitis, dysphonia, and vocal cord dysfunction. This post-marketing safety study revealed significant signals for dysphonia and vocal cord dysfunction associated with FF/UMEC/VI, suggesting that clinicians should remain vigilant for these events.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Telepharmacy Consultations (TPCs) in Local Pharmacies—A Bi-Centric Survey of Customer Opinions
by
Nathalie Floch, Philipp Harand, Chris Graichen and Thilo Bertsche
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 177; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060177 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Telepharmacy consultations (TPCs) became a routine element of pharmacy operations. However, there is limited data available on local pharmacy customer feedback related to TPC. Methods: A customer survey was developed seeking feedback on TPC. The pharmacy customers were invited to
[...] Read more.
Background: Telepharmacy consultations (TPCs) became a routine element of pharmacy operations. However, there is limited data available on local pharmacy customer feedback related to TPC. Methods: A customer survey was developed seeking feedback on TPC. The pharmacy customers were invited to complete the survey in two local pharmacies in Germany. The survey and corresponding informed consent form were approved by the Ethics Committee. Results: In total, 178 pharmacy customers were enrolled (median age 41–50 years). From those, 37% agreed when asked whether they were generally interested in TPC. A total of 37% had the nearest pharmacy 5–15 min from their home. A total of 42% visited their pharmacy quarterly. A total of 36% used technical devices in median 1–2 h per days. A total of 33% classified their own digital skills at least as sufficient. A total of 59% would use their smartphone as a potential device for TPC. A total of 83% rated it as (slightly) important that the pharmacist providing TPC can be heard clearly. A total of 76% each (strongly) agreed that an argument for TPC would include limited mobility or pandemic/quarantine. A total of 33% (strongly) agreed that a key argument against TPC were technical requirements. A total of 75% considered situations of immobility to be the most important future perspective for TPC. Conclusions: Many pharmacy customers see TPC as an opportunity, e.g., in cases of limited mobility or during pandemic or quarantine. However, the use of appropriate technology can be a limiting factor.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacy Practice and Practice-Based Research)
►▼
Show Figures
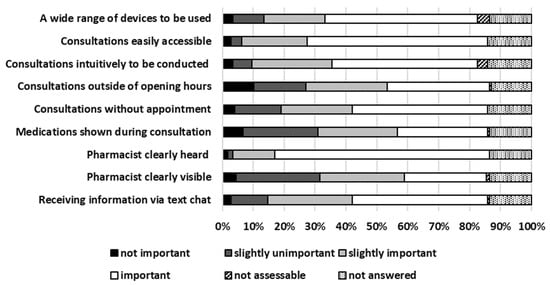
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Large Language Models for Drug-Related Adverse Events in Oncology Pharmacy: Detection, Grading, and Actioning
by
Md Muntasir Zitu, Ashish Manne, Yuxi Zhu, Wasimul Bari Rahat and Samar Binkheder
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 176; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060176 - 3 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Preventable medication harm in oncology is often driven by drug-related adverse events (AEs) that trigger order changes such as holds, dose reductions, delays, rechallenges, and enhanced monitoring. Much of the evidence needed to make these decisions lives in unstructured clinical texts, where large
[...] Read more.
Preventable medication harm in oncology is often driven by drug-related adverse events (AEs) that trigger order changes such as holds, dose reductions, delays, rechallenges, and enhanced monitoring. Much of the evidence needed to make these decisions lives in unstructured clinical texts, where large language models (LLMs), a type of artificial intelligence (AI), now offer extraction and reasoning capabilities. In this narrative review, we synthesize empirical studies evaluating LLMs and related NLP systems applied to clinical text for oncology AEs, focusing on three decision-linked tasks: (i) AE detection from clinical documentation, (ii) Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) grade assignment, and (iii) grade-aligned actions. We also consider how these findings can inform pharmacist-facing recommendations for order-level safety. We conducted a narrative review of English-language studies indexed in PubMed, Ovid MEDLINE, and Embase. Eligible studies used LLMs on clinical narratives and/or authoritative guidance as model inputs or reference standards; non-text modalities and non-empirical articles were excluded. Nineteen studies met inclusion criteria. LLMs showed the potential to detect oncology AEs from routine notes and often outperformed diagnosis codes for surveillance and cohort construction. CTCAE grading was feasible but less stable than detection; performance improved when outputs were constrained to CTCAE terms/grades, temporally anchored, and aggregated at the patient level. Direct evaluation of grade-aligned actions was uncommon; most studies reported proxies (e.g., steroid initiation or drug discontinuation) rather than formal grade-to-action correctness. While prospective, real-world impact reporting remained sparse, several studies quantified scale advantages and time savings, supporting an initial role as high-recall triage with pharmacist adjudication. Overall, the evidence supports near-term, pharmacist-in-the-loop use of AI for AE surveillance and review, with CTCAE-structured, citation-backed outputs delivered into the pharmacist’s electronic health record order-verification workspace as reviewable artifacts. Future work must standardize reporting and CTCAE/version usage, and measure grade-to-action correctness prospectively, to advance toward order-level decision support.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessBrief Report
Cost Analysis of Multidose Drug Dispensing (MDD) System Implementation in a Community Pharmacy in Portugal
by
Ana Reis, Ângelo Jesus and Maria Luisa Martín
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 175; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060175 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Community pharmacies are increasingly delivering structured services to support chronic disease management, such as Multidose Drug Dispensing (MDD). This strategy can improve adherence and safety, but evidence of its economic feasibility in Portuguese pharmacies remains limited. Objective: To estimate the cost of
[...] Read more.
Background: Community pharmacies are increasingly delivering structured services to support chronic disease management, such as Multidose Drug Dispensing (MDD). This strategy can improve adherence and safety, but evidence of its economic feasibility in Portuguese pharmacies remains limited. Objective: To estimate the cost of implementing and operating an MDD system in a community pharmacy, informing reimbursement models and policy. Methods: A micro-costing approach assessed fixed and variable expenses for serving polymedicated elderly patients. Costs were calculated in euros (2024/2025) and expressed per working day based on 253 annual preparation days. Results: First-year costs totaled €70,985.68, including €8184.00 for setup, €21,579.00 for supplies, and €41,222.68 for staff salaries. The daily operating cost was €280.58, with labour representing the major expense. A break-even analysis indicated sustainability with around 700 users at €10/month. Conclusion: Although requiring significant initial investment, MDD can become financially viable through scaling, workflow efficiency, and supportive reimbursement strategies.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
“But Will It Last?”: Examining How Pharmacy Staff Perceptions Influence Beliefs About the Sustainability of a Pharmacy-Based Intervention Targeting Older Adult Over-the-Counter (OTC) Medication Misuse
by
Aaron M. Gilson, Katherine G. Moore, Stephanie M. Resendiz, Emily L. Hoffins, Shiying Mai, Jamie A. Stone and Michelle A. Chui
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 174; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060174 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
Sustaining a well-designed healthcare intervention justifies the resources allocated during its conceptualization and implementation and maximizes its clinical benefits, but staff influences on sustainment have been studied insufficiently. This study evaluates the effects of pharmacy staff (i.e., pharmacists/technicians) perceptions about the sustainability of
[...] Read more.
Sustaining a well-designed healthcare intervention justifies the resources allocated during its conceptualization and implementation and maximizes its clinical benefits, but staff influences on sustainment have been studied insufficiently. This study evaluates the effects of pharmacy staff (i.e., pharmacists/technicians) perceptions about the sustainability of Senior SafeTM, a U.S. pharmacy-based intervention to reduce older adult over-the-counter (OTC) medication misuse. Three months after introducing Senior Safe into 67 pharmacies in a large Midwestern health-system, all pharmacy staff (N = 279) received a survey invitation. Fifty-nine pharmacists and 94 technicians completed the survey. Using logistic regression modeling for the 14 belief-based survey items, and staff roles (pharmacist or technician), the final factors significantly predicting staff views that Senior Safe was sustainable were as follows: perceiving Senior Safe as well-integrated into leadership operations (OR = 5.606, p < 0.001) and believing the intervention reduced OTC misuse (OR = 8.217, p < 0.001). Also, technicians were more confident than pharmacists about Senior Safe’s sustainment and its OTC misuse reduction success. Overall, an intervention’s sustainability relies on those using it. Since the principal predictor of maintaining Senior Safe was its perceived effectiveness, increasing staff buy-in and awareness of an intervention’s benefits may be central to its long-term viability. With an aging U.S. population, sustainable solutions to older adult medication misuse remain critical.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Barriers and Opportunities in Cancer Pain Management: A Qualitative Study on Pharmacists’ Role
by
Evangelos Aliferis, George Koulierakis, Christina Dalla and Tina Garani-Papadatos
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 173; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060173 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: Cancer pain remains a critical issue for patients’ quality of life, affecting their physiology, psychology, and social relationships. Despite the widely recognized role of pharmacists in pain management, their involvement in palliative care in Greece remains limited. This study focuses on exploring
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Cancer pain remains a critical issue for patients’ quality of life, affecting their physiology, psychology, and social relationships. Despite the widely recognized role of pharmacists in pain management, their involvement in palliative care in Greece remains limited. This study focuses on exploring the perceptions and experiences of pharmacists regarding their role in cancer pain management, identifying barriers, required skills, and proposing strategies for their integration in the multidisciplinary team. Μaterials and Μethods: Qualitative research was conducted through semi-structured interviews with seven pharmacists in the Attica region. The interviews were recorded, transcribed, and thematically analyzed. Results: The analysis revealed four main themes: (1) limited access to medical records and challenges in pharmaceutical decision-making, (2) lack of institutional frameworks and a culture of collaboration, (3) need for specialized education and continuous training, and (4) understaffing and bureaucracy, faced by pharmacists. Discussion: This study highlights the underutilized role of pharmacists in cancer pain management in Greece. Barriers such as restricted access to patient records, weak interdisciplinary collaboration, insufficient training, and bureaucratic constraints limit their contribution. Structured frameworks and collaborative cultures can enhance pharmacists’ involvement, while education and continuous training are essential to strengthen their legitimacy within care teams. Digital tools can improve access to patient information and support evidence-based decisions. Conclusions: Pharmacists’ integration in the patient’s management team has significant benefits for the patient’s quality of life. Strengthening pharmacists’ involvement in cancer pain management requires the establishment of collaborations, continuous education, bureaucratic simplification, and the integration of digital tools. The development of practical resources, such as educational guides, can play a pivotal role in enhancing the quality of care provided.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Capturing Value: How Health-System Specialty Pharmacies Define and Document Pharmacist Interventions
by
Autumn D. Zuckerman, Karen C. Thomas, Erica Diamantides, Shannan Takhar, Rushabh Shah, Kelsi Conant, Thom Platt and Christian Rhudy
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 172; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060172 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
Standardized pharmacist intervention practices and documentation among health-system specialty pharmacies could improve understanding of the pharmacists’ role and value in this setting. This study describes current health-system specialty pharmacies’ intervention practices. A survey developed by a volunteer committee subgroup was distributed to two
[...] Read more.
Standardized pharmacist intervention practices and documentation among health-system specialty pharmacies could improve understanding of the pharmacists’ role and value in this setting. This study describes current health-system specialty pharmacies’ intervention practices. A survey developed by a volunteer committee subgroup was distributed to two health-system specialty pharmacy group email distribution lists. The survey evaluated the types of tasks considered to be clinical or non-clinical interventions; who could perform interventions; where and how they were documented; data elements included in documentation; and how intervention data were classified, used, reviewed, and shared with internal or external stakeholders. Twenty-four institutions responded to the survey. Tasks within medication management, adverse drug events/monitoring, and education domains were more commonly considered clinical interventions; tasks in the health maintenance and coordination of care domains were more frequently considered non-clinical interventions or not considered to be interventions. Interventions were completed by pharmacists (at 100% of sites) and were mostly documented in the electronic health record (92%). Intervention data were primarily collected to meet accreditation purposes (96%) or for quality auditing and review (88%). No respondents shared intervention data with patients. Results demonstrate areas of alignment and variance in intervention definition and documentation among health-system specialty pharmacies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacy Practice and Practice-Based Research)
►▼
Show Figures
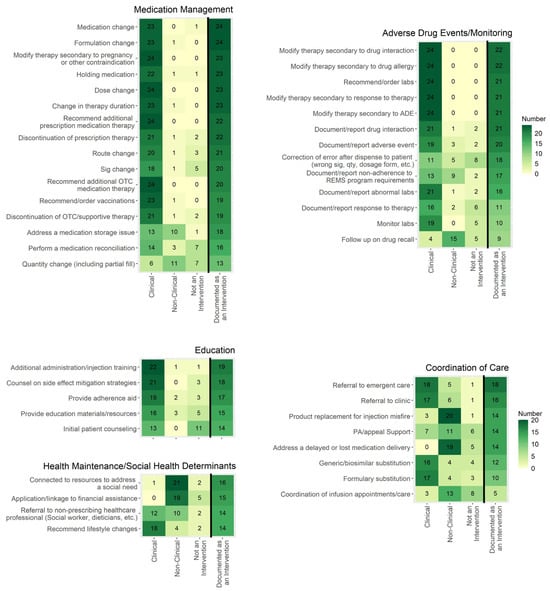
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Job Satisfaction Among Pharmacists Graduating from a University in Northern Sweden: A Comparative Analysis
by
Maria Gustafsson, Helena Norberg and Sofia Mattsson
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 171; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060171 - 22 Nov 2025
Abstract
Job satisfaction plays a critical role in shaping professional outcomes, as it has been positively associated with enhanced performance and greater motivation. Conversely, insufficient job satisfaction may contribute to higher rates of staff turnover, professional burnout, and intentions to leave the profession. The
[...] Read more.
Job satisfaction plays a critical role in shaping professional outcomes, as it has been positively associated with enhanced performance and greater motivation. Conversely, insufficient job satisfaction may contribute to higher rates of staff turnover, professional burnout, and intentions to leave the profession. The objective was to investigate job satisfaction among pharmacists educated at Umeå University in Sweden over time and to explore factors affecting job satisfaction. A survey was distributed to pharmacy graduates who had completed web-based pharmacy programs at Umeå University between 2019 and 2023. Questions regarding job satisfaction and factors related to it were included. The response rate was 38%. The results were compared with results from a previous investigation (graduation years 2015–2018) to enable comparisons over time. Compared to findings from the previous survey, job satisfaction was lower in the present study (76.4% vs. 91.4%, p = 0.004). Both greater opportunities for continuing professional development (CPD) and the perception that the knowledge and skills gained during education are beneficial in the current job were associated with high job satisfaction (OR: 5.360; 95% CI: 1.896–15.156 and OR: 3.983; 95% CI: 1.255–12.642, respectively). Understanding factors contributing to job satisfaction can help employers improve retention and work environment.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Medication Use by Older Adults with Frailty: A Scoping Review
by
Rishabh Sharma, Tanaya Sharma, Brent McCready-Branch, Arshia Chauhan, Caitlin Carter, SooMin Park, Imra Hudani, Prapti Choudhuri and Tejal Patel
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 170; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060170 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
Frailty among older adults heightens their risk of negative health outcomes, and medication use plays a major role in this increased vulnerability. Various aspects of medication use elevate the risk of poor outcomes in individuals with frailty. The current scoping review was designed
[...] Read more.
Frailty among older adults heightens their risk of negative health outcomes, and medication use plays a major role in this increased vulnerability. Various aspects of medication use elevate the risk of poor outcomes in individuals with frailty. The current scoping review was designed to explore medication use in older adults with frailty in primary care, focusing on the prevalence of potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs), polypharmacy, medication adherence, and their role in contributing to adverse drug events. This scoping review was conducted using the Arksey and O’Malley, supplemented by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) guidelines. A search of the literature was conducted from inception to November 2023 in Ovid EMBASE, PubMed (MEDLINE), Scopus, EBSCOhost CINAHL, and Ovid International Pharmaceutical Abstracts. Studies which met the eligibility criteria included older adults with frailty (≥65 years) living at home, defined frailty criteria, and assessment of medication use. Out of the 4726 studies screened, 223 were included, conducted across 39 countries. Frailty prevalence varied widely from 0.9% to 89.2%. Polypharmacy (5–9 medications) and hyper-polypharmacy (≥10 medications) were notably more common among individuals with frailty, with polypharmacy rates ranging from 1.3% to 96.4%. Twelve studies reported PIM prevalence among individuals with varying levels of frailty, ranging from 2.4% to 95.9%. This scoping review highlights the challenges and complexities involved in understanding the relationship between medication use and frailty in older adults.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacy Practice and Practice-Based Research)
►▼
Show Figures
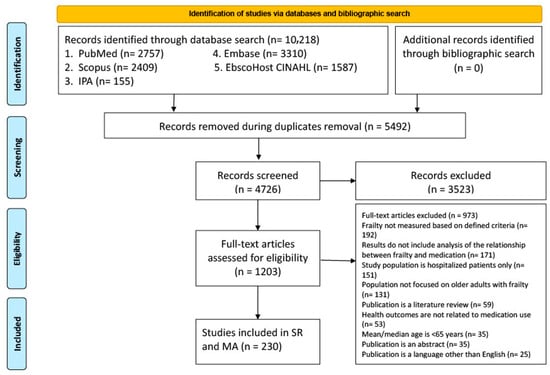
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Monoclonal Antibodies as a Breakthrough in Personalised Leukaemia Therapy: What Pharmacists and Doctors Should Know
by
Anastasiia Ryzhuk, Sergiy M. Kovalenko, Marine Georgiyants, Kateryna Vysotska and Victoriya Georgiyants
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 169; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060169 - 20 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are an important medical innovation in modern medicine. They are an effective therapy for several subtypes of leukaemia but may have undesirable effects, which may be minimised through the provision of interdisciplinary care including a pharmacist. The goals of this
[...] Read more.
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are an important medical innovation in modern medicine. They are an effective therapy for several subtypes of leukaemia but may have undesirable effects, which may be minimised through the provision of interdisciplinary care including a pharmacist. The goals of this narrative review were twofold: first, to summarise the literature on the side effects of mAbs and the challenges of their preparation, and to provide recommendations for the safe preparation of mAb drug formulations for clinicians. Second, to suggest clinical roles for pharmacists to improve patient safety and clinical outcomes for leukaemia patients receiving mAb therapy. The review covers data from 178 scientific and official sources of information on the types of targeted immunobiological drugs for the treatment of various types of leukaemia. The results are a detailed description of the possible side effects from mAb therapy and a list of suggested actions that can be taken to prevent them. Pharmaceutical aspects of the use of mAbs, such as pharmacoeconomics, compounding and stability, are also discussed. The discussion is organised according to the current classification of leukaemia. The drugs considered include blinatumomab, inotuzumab ozogamicin, gemtuzumab ozogamicin, rituximab, ofatumumab, obinutuzumab, and alemtuzumab. The review offers a comprehensive resource to equip pharmacists and other clinicians to optimise mAb therapy and promote the safe use of these novel therapies.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Modifying Supportive Care Medications in Combination Therapy with Pertuzumab, Trastuzumab, and Taxane Anticancer Drugs
by
Mina Takagi, Shinichiro Maeda, Makiko Maeda, Yasushi Fujio and Sachiko Hirobe
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 168; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060168 - 17 Nov 2025
Abstract
Chemotherapy for breast cancer includes pertuzumab and trastuzumab regimens with docetaxel (PHD) or paclitaxel (PHP). Current approaches for using supportive care drugs to manage the side effects of PHD and PHP are unclear. Here, we investigated the occurrence of side effects before and
[...] Read more.
Chemotherapy for breast cancer includes pertuzumab and trastuzumab regimens with docetaxel (PHD) or paclitaxel (PHP). Current approaches for using supportive care drugs to manage the side effects of PHD and PHP are unclear. Here, we investigated the occurrence of side effects before and after supportive care medications were modified by discontinuing antipyretic analgesics. We retrospectively analyzed adverse events that occurred within 24 h of treating 76 patients with PHD or PHP. The frequencies of adverse effects in the groups before and after modification did not differ significantly (45.5% [15/33] and 44.2% [19/43], respectively). Severity also did not significantly differ between the groups. Therefore, discontinuing antipyretic analgesics as supportive care drugs had little effect on the frequency of side effects. Symptoms of feeling hot, pyrexic, and flushed were frequent, and their severity increased in the group after the support drugs were modified. Discontinuation of supportive care medications, including antipyretic analgesics, might affect the severity of certain symptoms and lead to the development of side effects that require medical intervention. Overall, our findings indicate the need to consider premedication with antipyretic analgesics, including further analysis of the risk factors that can predict symptoms.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacy Practice and Practice-Based Research)
►▼
Show Figures
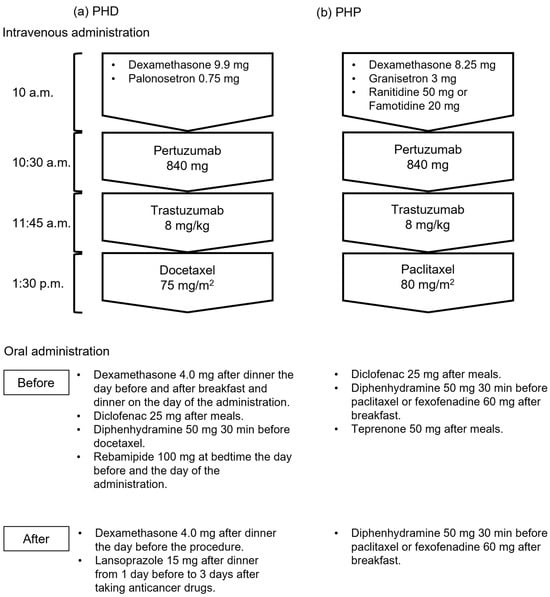
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pharmacist Intervention Models in Drug–Drug Interaction Management in Prescribed Pharmacotherapy
by
Ivana Samardžić, Ivana Marinović, Iva Marović, Nikolina Kuča and Vesna Bačić Vrca
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 167; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060167 - 17 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Drug–drug interactions (DDIs) are one of the most common problems related to drug administration which represent a risk for patient safety. Considering their position in the healthcare system, pharmacists should be more proactively involved in DDI management. The paper shows representation of DDI
[...] Read more.
Drug–drug interactions (DDIs) are one of the most common problems related to drug administration which represent a risk for patient safety. Considering their position in the healthcare system, pharmacists should be more proactively involved in DDI management. The paper shows representation of DDI intervention models in each DDI category. This research enrolled outpatients prescribed pharmacotherapies from 40 randomly selected community pharmacies. DDIs were analyzed using Lexicomp® Lexi-InteractTM Online (Lexi-Comp, Inc., Hudson, NY, USA) software. Clinical pharmacists’ panel, according to the necessary interventions, determined an independent model of pharmacist interventions (category 1) and models that require cooperation with physicians (category 2) for DDI management. In total, 4107 patients were enrolled in the study. Mean patient age was 67.5; they were mostly women (56.5%) and had on average of 3.4 diagnosis and 5.5 prescription drugs. Overall, 14,175 potential clinically significant DDIs were identified: 83.3% of C, 15.4% of D, and 1.3% of X category. At least one potential DDI was found in 78.6% of patients. Models of pharmacist DDI interventions in collaboration with a physician (category 2) were more prevalent than independent models (category 1): 57.5% vs. 42.5% in C category DDIs, 97.8% vs. 2.2% in D category, and 100% vs. 0% in category X DDIs. This research aimed to gain an insight into the distribution of interventions in DDI management models between physicians and pharmacists, which can contribute to more efficient pharmaceutical care and visibility.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Experiences Reported by People with Epilepsy During Antiseizure Medication Shortages in the UK: A Cross-Sectional Survey
by
Eric Amankona Abrefa Kyeremaa, Tom Shillito, Caroline Smith, Charlotte Lawthom, Sion Scott and David Wright
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 166; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060166 - 10 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
(1) Background: Medication shortages have become increasingly common in the UK. However, there is limited evidence regarding the experiences of people with epilepsy and their caregivers during these shortages. The aim of this study is to explore the extent and impact of ASM
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: Medication shortages have become increasingly common in the UK. However, there is limited evidence regarding the experiences of people with epilepsy and their caregivers during these shortages. The aim of this study is to explore the extent and impact of ASM shortages on people with epilepsy and their caregivers across the UK. (2) Methods: A cross-sectional online survey was distributed between January and April, 2024 by epilepsy charities. Participants included people with epilepsy and caregivers. The survey collected demographic information, types of ASM respondents were prescribed, experiences of shortages, and the impact of shortages. Data were analysed descriptively, and subgroup analyses were conducted by medication type. (3) Results: A total of 1549 responded, of whom 1312 were people with epilepsy and their carers who were included in the analysis with a mean age of 43 years. A total of 941 respondents (71.7%) reported difficulty obtaining their prescribed ASM in the past year. Shortages were most frequently reported for sodium valproate (60.8%), lamotrigine (65.2%), carbamazepine (92.6%), clobazam (82.6%), topiramate (81.5%), zonisamide (74.0%), levetiracetam (62.8%), lacosamide (71.0%), and brivaracetam (70.5%). A total of 529 (40.4%) of the participants reported that stress and/or anxiety caused by medication shortages was associated with recurrent seizures. We did not ask whether patients missed medications because of these difficulties. (4) Conclusions: ASM shortages are a widespread issue for people with epilepsy in the UK, leading to treatment disruptions and psychological distress. Addressing supply change limitations and identifying effective approaches to preventing the substitution of ASMs brands by clinicians may potentially reduce this problem.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Bedside Medication Management: Pharmacy Technicians Managing Patient Medication Supply to Improve Nursing Productivity and Patient Safety
by
Tom W. Simpson, Duncan S. Mckenzie, Rosina G. Guastella and Michael J. Ryan
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 165; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060165 - 7 Nov 2025
Abstract
Audits of medication charts conducted by Royal Hobart Hospital Pharmacy revealed that dose omission was the most common medication error experienced by patients. Investigation of these errors also found that nurses spend significant time organising medication for inpatients. To address the issues contributing
[...] Read more.
Audits of medication charts conducted by Royal Hobart Hospital Pharmacy revealed that dose omission was the most common medication error experienced by patients. Investigation of these errors also found that nurses spend significant time organising medication for inpatients. To address the issues contributing to these problems, an alternative model of medication management was implemented and tested. This model of bedside medication management involves medication supply managed by ward pharmacy technicians who review charts daily for changes to medicines and obtain the medicines needed for each patient. Outcomes on two intervention wards showed that the model, combined with technician involvement in controlled medicines stock management, resulted in 29.78 h of nursing time released to patient care per 20-bed ward per week, for an investment of 22.28 h of ward pharmacy technician time; a 75% reduction in delayed doses; a 44% reduction in missed doses; and an average decrease of two hours in the turnaround time for supply of inpatient medication. Introducing bedside medication management and controlled medicines stock management activities can release 1.34 h of nursing time to patient care for every hour of ward pharmacy technician time (at a lower hourly salary cost), decrease dose delays and omissions, and improve patient safety.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
The Spectrum of Clinical Pharmacy Services in a Non-University Hospital—A Comprehensive Characterization Including a Risk Assessment for Drug-Related Problems and Adverse Drug Reactions
by
Olaf Zube, Wiebke Schlüter, Johanna Dicken, Jan Hensen and Thilo Bertsche
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 164; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060164 - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Clinical pharmacy services (CPS) have been shown to confer significant advantages in patient care. It remains to be clarified how CPS resources are allocated across routine care settings. It remains to be clarified which recommendations are made to resolve the drug-related problems
[...] Read more.
Background: Clinical pharmacy services (CPS) have been shown to confer significant advantages in patient care. It remains to be clarified how CPS resources are allocated across routine care settings. It remains to be clarified which recommendations are made to resolve the drug-related problems (DRP) identified by CPS and which adverse drug reactions (ADR) actually arise from the identified DRP. Methods: Following positive ethical approval, patient chart analyses, evaluation of pharmacy documentation on CPS and pharmacist interviews were performed to characterize CPS at all medical departments of the Bundeswehr Hospital Hamburg. We developed and pre-tested instruments for standardization: A Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for the practical exercise and documentation of CPS by the pharmacists performing them, a standardized form (checklist) for retrospective data collection as part of this study, and a standardized questionnaire for conducting the pharmacist interviews including a risk assessment according to the NCC-MERP score. Results: In total, 1000 CPS were documented in 504 patients (mean age: 69.95 years; 229 female) on 16,705 treatment days. A total of 66.87% CPS was initiated when pharmacists participated in ward rounds. In all CPS, “Indications” was the topic addressed most frequently (37.70%). “Agents for obstructive respiratory diseases” was the most frequently involved drug class (11.32%). The most frequent processing time per CPS was 16–30 min (48.61%). The number of CPS ranged from 0.36/100 treatment days in dermatology to 12.47 in oncology. Severity of 358 DRP was classified “very severe” (5.03%), “severe” (42.74%), “moderate” (34.36%), “low” (15.08%), “very low” (1.40%), or “without impact” (1.40%). The probability of DRP occurrence was classified as “high” in 13.13% and “very high” in 3.35%. In 15.36% of the DRP, an ADR actually occurred. In 504 patients, 932 specific recommendations were forwarded to solve the DRP identified during CPS. Of those, 53.97% were implemented. Conclusions: In almost all CPS, a considerable number of DRP with serious clinical consequences were identified. Half of the forwarded recommendations were implemented.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacy Practice and Practice-Based Research)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessment of Job Satisfaction and Intention to Quit Job Among Pharmacists in Saudi Arabia
by
Ashwaq Alharthi, Maha Aleiban, Abdulrahman Alwhaibi, Moureq Alotaibi, Yousef Almutairi and Sultan Alghadeer
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 163; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060163 - 5 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Job satisfaction is an essential element for organizational functions. Working entities would not effectively operate without employee contentment. This study aimed to determine the level of job satisfaction among pharmacists and investigate its correlation with demographic variables and professional personal experience. Methods:
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Job satisfaction is an essential element for organizational functions. Working entities would not effectively operate without employee contentment. This study aimed to determine the level of job satisfaction among pharmacists and investigate its correlation with demographic variables and professional personal experience. Methods: A cross-sectional online survey targeting registered pharmacists in Saudi Arabia was conducted from September to November 2024 using an IRB-approved structured questionnaire adapted from validated instruments. Reliability and validity were confirmed (Cronbach’s α = 0.8), and a target sample of 380 was calculated to ensure representativeness. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, chi-squared tests, and univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses utilizing SPSS v28, with significance set at p < 0.05. Results: A total of 330 pharmacists responded to the survey, representing 86.8% of the calculated sample size. Of those, 57% were male and 68.5% were staffing pharmacists. More than half of participants had professional experience of ≤5 years (57.3%), while 31.8% had 5 to 15 years of experience. Approximately 60% of participants worked in shift systems and reported dissatisfaction with their pay (70%) and lack of benefits (66.7%). Of all participants, only 26.4% confirmed satisfaction with their job and no intention to quit, while 23% clearly reported job dissatisfaction and an intention to quit; the rest of the participants were undecided (50.6%). Significant correlations were found between job satisfaction and variables such as education, current position, organization type, monthly income, and professional experience. Additionally, most of the items assessing professional personal experience such as working in a shift system, working as a team member, gaining financial benefits, and having accomplishments or growth opportunities at work were significantly correlated with job satisfaction. Opportunities for professional development, promotion, and a positive work environment were also frequently selected as factors contributing to job satisfaction (60.6%, 75.2% and 75.5%, respectively). Interestingly, motivation showed minimal impact on participants’ opinions regarding job satisfaction and decisions over whether to quit their jobs. Finally, occupation and age were found to significantly influence work environments, promotions, and opportunities, which consequently impact participants’ satisfaction towards their jobs. Conclusions: Our findings indicate that Saudi pharmacists experience low-to-moderate job dissatisfaction, with a significant percentage considering quitting form their jobs. Improving monetary rewards, recognition, and career advancement opportunities could improve job satisfaction and retention in this crucial workforce.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmacy Workflow Optimization: Strategies for Enhancing Efficiency and Patient Satisfaction)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Pharmacy Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomedicines, JCM, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Pharmacy, IJMS, Molecules, Biophysica
Peptoids and Peptide Based Drugs
Topic Editors: Laura Zaccaro, Annarita Del Gatto, Galia MaayanDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
JCM, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Pharmacy, Healthcare
Optimization of Drug Utilization and Medication Adherence
Topic Editors: Enrica Menditto, Sara Mucherino, Ignacio Aznar-LouDeadline: 30 October 2026
Topic in
Biomedicines, Future Pharmacology, Pharmacy, IJMS, Biomolecules, Genes
Prospects of Multi-Target Agonists in Metabolic and Epigenetic Medicine
Topic Editors: Riham Abouleisa, Yanming LiDeadline: 30 November 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Pharmacy
The AI Revolution in Pharmacy Practice and Education
Guest Editor: Maree SimpsonDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Pharmacy
The Evolving Role of the Pharmacist in Improving Vaccination Uptake
Guest Editor: Mary BushellDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
Pharmacy
Advancing Pharmacy Education: Integrating Science and Clinical Practice
Guest Editors: Ryoichi Fujiwara, Frank YuDeadline: 15 April 2026
Special Issue in
Pharmacy
Drug Repurposing: Strengthening Outcomes of Existing Pharmaceuticals to Shift Emerging Health Challenges
Guest Editors: Ilko Getov, Hristina LebanovaDeadline: 30 April 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Pharmacy
New Insights into Pharmacy Teaching and Learning during COVID-19
Collection Editors: Darko Modun, Ana Seselja Perisin