Abstract
Influencer marketing has emerged as a crucial element in digital marketing, significantly shaping consumer behavior and online shopping preferences. This study examined the multidimensional impact of influencer marketing by analyzing engagement metrics, marketing effectiveness, and consumer decision-making processes, based on consumers in the Greek sector. Through a structured methodological framework, the research employed a questionnaire-based survey, statistical modeling, and Fuzzy Cognitive Mapping (FCM) scenarios to assess consumer interactions with influencer-driven content. Findings highlight that while influencer marketing enhances brand engagement and sales, its effectiveness varies based on content authenticity, transparency, and user trust. Additionally, consumer purchasing decisions are influenced by social media visibility, personalized marketing strategies, and digital platform usability. This study underscores the need for strategic influencer selection and information-driven marketing optimization to sustain long-term consumer engagement. These insights provide practical implications for businesses aiming to enhance digital marketing strategies and contribute to the ongoing discourse on social commerce and consumer-centric marketing models.
1. Introduction
The interpersonal contacts that develop satisfy people’s social needs for personal contact, and through interaction, the individual becomes able to maintain his/her social identity while receiving emotional support. Marketing is the activity, set of institutions, and processes that lead to the creation, communication, delivery, and exchange of offers for the purchase of products and services, which have value for the consumer public and society in general [1]. The main challenge for an online business is to make customers feel special, which can be implemented through digital marketing.
In the evolving landscape of digital marketing, social media and influencer marketing have emerged as pivotal forces reshaping consumer behavior. Social media platforms, with their vast reach and interactive capabilities, have become central to modern marketing strategies [2]. Influencer marketing, a subset of this digital realm, leverages the credibility and reach of popular individuals to shape consumer perceptions and drive purchasing decisions [3]. As influencers establish themselves as trusted voices within their niches, their endorsements and content play a significant role in influencing their followers’ attitudes and behaviors [4]. Understanding how these dynamics unfold requires a closer examination of the relationship between social media, influencer marketing, and consumer intentions.
Calderón et al. [5] emphasized that understanding the consumer behavior of a company’s clients is very important. Thus, companies should offer personalized shopping experiences while simultaneously improving both their services and products. Trudel [6] argued that consumer behavior is determined by external and internal factors, with external factors including terms such as accessibility, availability, and affordability of the product, that is, the products available for purchase and the products that customers can afford to buy.
Consumer behavior in the digital age is increasingly intertwined with social media marketing strategies. The rise of social media has transformed how consumers interact with brands, shifting the focus from traditional advertising methods to more personalized and engaging content [7]. Social media platforms provide a space for consumers to seek recommendations, reviews, and endorsements from influencers whom they perceive as authentic and relatable [8]. This shift has led to a growing interest in understanding how social media marketing impacts consumer decision-making processes. By exploring how consumers respond to influencer marketing efforts, researchers can gain insights into the effectiveness of these strategies and their influence on purchasing intentions [9].
The integration of digital marketing strategies with influencer marketing further underscores the need for research in this area. Digital marketing encompasses various online techniques and platforms designed to reach and engage target audiences [10]. Influencer marketing, as a specialized form of digital marketing, leverages influencers’ established relationships with their followers to enhance brand visibility and credibility. This approach has proven effective in driving consumer engagement and sales, making it essential to analyze its impact on consumer intentions. Investigating how influencer marketing campaigns affect consumer perceptions and behaviors can provide valuable insights for businesses seeking to optimize their digital marketing strategies and achieve better outcomes [11].
Given the increasing reliance on social media and influencer marketing in shaping consumer intentions, a comprehensive study is crucial to uncover the nuances of this relationship [12]. By examining how influencer marketing influences consumer intentions and decision-making, researchers can contribute to a deeper understanding of its effectiveness and strategic value [13]. This knowledge will not only benefit marketers aiming to refine their approaches but also provide consumers with a clearer perspective on the role of influencers in their purchasing decisions. As the digital marketing landscape continues to evolve, exploring the impact of influencer marketing on consumer intentions remains a critical area of inquiry.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: The present section presents an extant literature review of the examined topic. In the next section, the Research Methodology is discussed along with the formulation of the research hypotheses. Moreover, the development of the questionnaire and the study sample are also presented. Section 3 presents statistical analyses of the collected data to verify, or not, the research hypotheses, as well as the development of the Fuzzy Cognitive Mapping (FCM) scenarios. Finally, this paper concludes with the Discussion and Conclusions section, which offers clear insights and suggestions regarding the study’s findings and its limitations.
2. Literature Review
Influencer marketing has evolved into one of the most effective tools for digital engagement, surpassing traditional marketing methods in terms of consumer trust and ROI [14]. In 2023, the global influencer marketing industry was valued at $21.1 billion, more than doubling since 2019 [15]. This growth reflects a shift in consumer preferences toward peer-endorsed content, with nearly half of social media users making purchases influenced by influencer recommendations [16]. The effectiveness of influencer marketing lies in its ability to provide authentic, relatable content that resonates more than conventional digital ads, which are often perceived as intrusive [17].
Compared to traditional digital marketing, such as email campaigns, display ads, and search engine optimization, influencer marketing offers stronger emotional engagement and audience segmentation. While traditional strategies offer broad reach, influencers foster more personalized, trust-based interactions [18]. According to Beichert et al. [19], influencer marketing yields up to 11 times higher ROI than banner ads, due to increased click-through rates and higher conversion stemming from influencer credibility. Moreover, brands using micro- and nano-influencers report more loyal followings and niche-targeted results, challenging the one-size-fits-all logic of traditional approaches [20].
Several emerging trends define the current influencer marketing ecosystem. First, the rise of nano-influencers (under 10,000 followers) provides businesses access to niche markets with highly engaged audiences [21]. Second, long-term partnerships are replacing one-off collaborations to ensure continuity and trust between influencers and audiences [22]. Third, content diversification—especially in the form of short videos, livestreams, and behind-the-scenes reels—is improving campaign versatility [23]. Brands must also manage the balance between authenticity and promotional messaging. Excessive sales-driven content often results in ad fatigue and diminished trust [24], whereas value-driven storytelling is more likely to cultivate engagement [25].
As influencer marketing matures, ethical transparency becomes critical. Recent enforcement by regulatory agencies, such as the FTC’s 2024 mandate on disclosing sponsored content, emphasizes the importance of transparency [26]. Fake endorsements and undisclosed promotions now risk legal consequences, pushing influencers and brands to prioritize authenticity and accurate representation. Additionally, ethical practices influence campaign performance, as studies reveal that perceived honesty in influencer content significantly impacts consumer trust and purchase intention [27]. Ethical guidelines also vary across regions, suggesting a growing need for international harmonization of digital advertising regulations [28].
Table 1 below presents the literature review of the most recent and relevant studies. The research gap in the literature can be discerned and directly compared with our study. Based on these findings, the main research objective is settled.

Table 1.
Literature review.
Influencer marketing and online shopping behaviors have emerged as dominant forces shaping consumer decision-making and digital marketing strategies. While existing studies, such as those by Hudders and De Jans [30] as well as Li and Peng [31], have explored aspects like influencer trustworthiness and gender-specific effects, there is limited understanding of how influencer marketing impacts industries or demographics differently. Similarly, works by Aw and Agnihotri [32] and Cheah et al. [37] have highlighted challenges like over-endorsement and authenticity but have not sufficiently addressed the interplay between consumer engagement quality and industry-specific marketing effectiveness.
Furthermore, while Zhang et al. [33] and Sánchez Villegas et al. [36] have introduced simulation models and multimodal analyses, their practical application remains untested, particularly in real-world shopping behaviors across categories such as health, beauty, and technology. The literature often treats consumers as a homogeneous group, overlooking behavioral and demographic variations that influence satisfaction and loyalty in online shopping, as noted by Lopez-Dawn and Giovanidis [35].
Additionally, Doshi et al. [34] and Antoniou [38] have explored the theoretical implications of transparency and regulatory compliance in influencer marketing, yet these discussions lack empirical evidence to substantiate their impact on consumer trust and long-term engagement. Lastly, there is insufficient exploration of how technological advancements like AI personalization and augmented reality can mitigate concerns about product quality and foster continued online shopping.
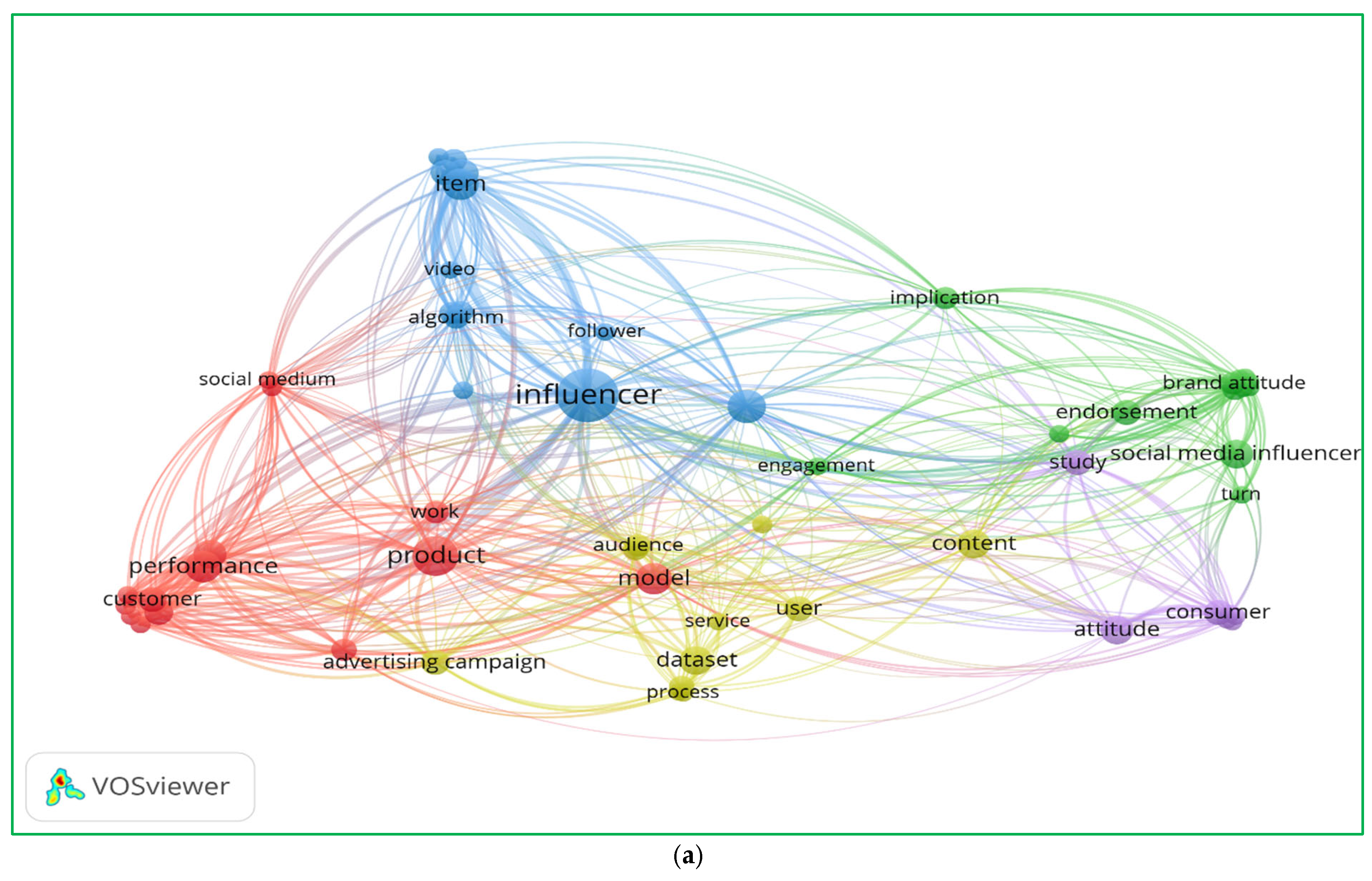
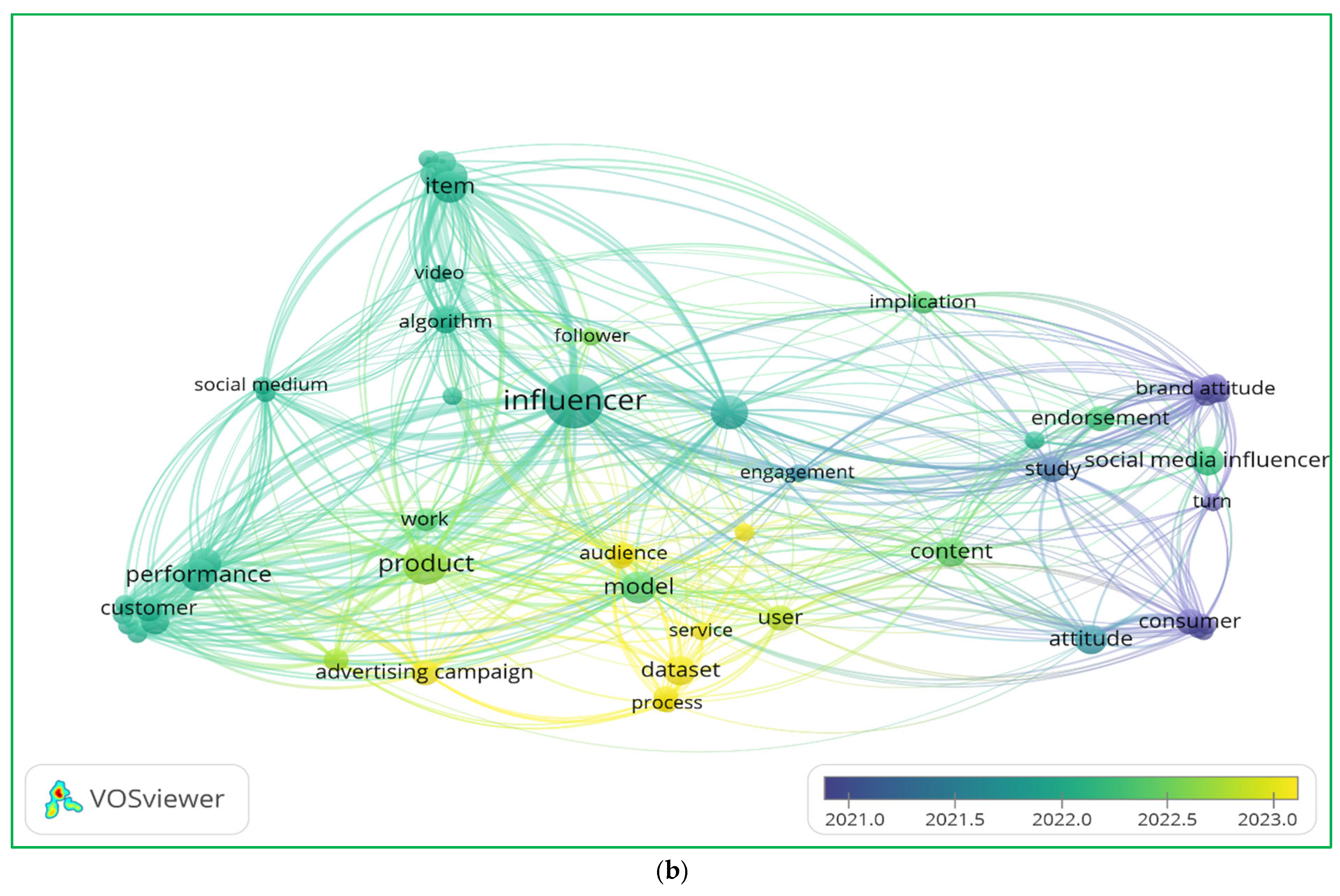
The following graphs (Figure 1) illustrate a bibliometric analysis of the literature on influencer marketing and social media strategies. The visualization highlights the clusters of relationships, key terms, and temporal trends in the field.
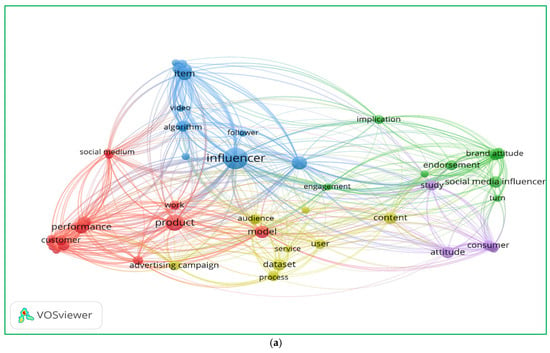
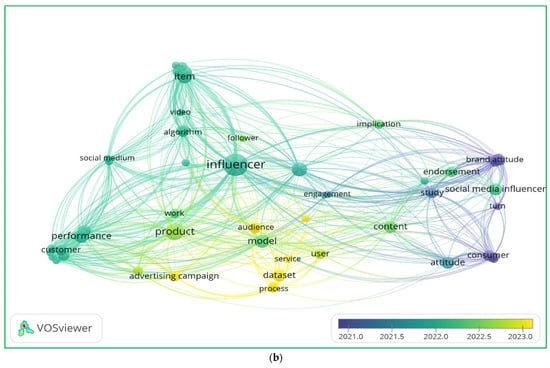
Figure 1.
Literature review of title–abstract keywords co-occurrence (a) as well as title–abstract and years of publications co-occurrence (b).
The analysis of the keyword co-occurrence figures highlights three key themes shaping influencer marketing research. First, technological advancements, such as algorithm-driven influencer selection, AI-enhanced content strategies, and video-based engagement, are increasingly central to digital marketing [39,40]. Second, consumer behavior and engagement dynamics play a pivotal role, as evidenced by the strong connections between brand attitude, social media influencers, and audience response metrics, reinforcing the need for content personalization and interactive consumer experiences [41,42]. Lastly, performance-driven influencer marketing strategies emphasize advertising campaigns, product visibility, and dataset-driven optimization, demonstrating the importance of data analytics in measuring influencer impact [43,44]. These insights suggest that future influencer marketing success will rely on AI-powered strategies, consumer-centric content, and precise performance tracking to enhance brand engagement and sales conversion. This paper aimed to bridge critical gaps, offering deeper insights into the interplay between influencer marketing strategies and consumer behavior.
Therefore, the research objective (RO) of the present research is: “to examine the multidimensional impact of influencer marketing, social media engagement strategies, and online shopping behaviors on consumer satisfaction, loyalty, and purchasing decisions across industries, demographics, and technological contexts”.
This study aimed to fill the identified gaps by:
- Examining the industry-specific and demographic variations in the effectiveness of influencer marketing activities, moving beyond the generalized findings of prior research.
- Exploring the qualitative dimensions of social media engagement strategies, such as authenticity and content quality, and their role in driving consumer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Assessing behavioral segmentation in shopping categories (e.g., health, beauty, and technology) to provide actionable insights for marketers in tailoring strategies.
- Integrating technological advancements such as AI-driven personalization and virtual try-ons into the analysis of online shopping behaviors, addressing concerns about product quality, and improving satisfaction.
- Providing empirical evidence on the dual nature of influencer marketing—both its benefits and challenges—and how it impacts consumer trust, loyalty, and purchase decisions.
By addressing these gaps, this study contributes to the ongoing discourse on digital marketing and consumer behavior, offering a nuanced understanding that bridges theoretical concepts with practical applications.
2.1. Social Media and Influencer Marketing
Social media platforms have transformed into powerful mass media channels that enable the dissemination of news and information on an unprecedented scale through user interaction. These platforms allow individuals to stay connected more frequently and intimately than ever before, fostering opportunities for self-education and interaction within an interconnected digital ecosystem [45]. The evolution of marketing science into “social marketing” highlights the critical role of these platforms in reshaping consumer engagement and promoting business objectives. For businesses to unlock the full potential of social media, they must adopt strategic approaches that emphasize community building, absorptive capacity, and timely implementation of innovative practices [32].
Social media’s interactive and dynamic environment has revolutionized traditional marketing practices, offering new opportunities for personalized brand promotion and consumer engagement. Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, Facebook, and YouTube are now indispensable tools in marketing strategies, providing brands with access to large, diverse audiences while enabling real-time communication and content delivery [30]. These platforms also empower businesses with tools for targeted advertising and data collection, facilitating a deeper understanding of consumer preferences and behaviors. The ability to quickly adapt to trends and deliver tailored content has positioned social media as a cornerstone of modern marketing strategies, enabling brands to maintain a competitive edge in an ever-changing digital landscape [13].
Influencer marketing, a specialized subset of social media marketing, has become a key strategy for leveraging the credibility and trust influencers have built with their audiences. Influencers, often regarded as opinion leaders in specific niches, bring a level of authenticity that traditional advertisements cannot match. Their endorsements resonate with followers on a personal level, driving higher engagement rates and significantly influencing consumer purchase decisions [46]. As a result, influencer marketing is increasingly integral to digital marketing efforts, with brands using these partnerships to amplify their reach and foster stronger connections with consumers [45].
However, influencer marketing is not without its challenges. The rapid evolution of social media platforms has heightened the need for brands and influencers to continuously adapt to remain relevant. Concerns surrounding authenticity, transparency in sponsored content, and influencer over-endorsement have led to growing consumer skepticism [47]. To address these issues, brands must prioritize transparent and ethical collaborations while investing in innovative strategies that maintain consumer trust and engagement. Continuous research and the integration of advanced analytics are essential to refining influencer marketing campaigns, ensuring their alignment with consumer expectations and sustained effectiveness in the digital marketing landscape [47].
2.2. Digital Consumers and Purchase Intention
A digital consumer refers to an individual who interacts, engages, and transacts with businesses, products, or services through digital platforms such as websites, mobile apps, and social media. These consumers rely heavily on technology and the internet to access information, compare options, and make purchasing decisions. They are characterized by their constant connectivity, preference for convenience, and ability to influence and be influenced through digital channels [40].
Digital consumers leverage multiple online tools and platforms, including search engines, social media, and e-commerce sites, to fulfill their needs. They expect personalized, seamless experiences and often prioritize brands that can offer instant access to products, services, and information [40]. Moreover, their behaviors are shaped by a variety of factors, including online reviews, influencer marketing, and targeted advertising campaigns, making them a dynamic and influential demographic in the digital economy.
Digital marketing has revolutionized consumer engagement, with influencer marketing becoming a cornerstone in shaping purchase intentions. Lee et al. [48] demonstrated how influencers sway consumer decisions by leveraging their relatability and credibility, particularly in industries like hospitality, where personal experiences matter. This relatability enhances trust and fosters a connection between the consumer and the product, often translating into higher purchase intentions. Furthermore, the digital consumer is increasingly drawn to authentic, engaging content that resonates with their values and lifestyle, which is why influencers are preferred over traditional advertising channels for creating impactful marketing campaigns [49].
The ability of influencers to create authentic content plays a pivotal role in shaping consumer attitudes and behaviors. Rachmad [45] highlighted how influencers craft content that aligns with audience interests, making marketing messages feel less intrusive and more aligned with the consumer’s identity. This personal touch not only boosts brand awareness but also increases engagement and conversion rates. However, Cheah et al. [37] warned of potential pitfalls, such as over-endorsement, which can lead to consumer skepticism. To sustain credibility and effectiveness, influencers must maintain transparency and authenticity in their campaigns, ensuring their endorsements align with their audience’s expectations [50].
While influencer marketing has proven effective, challenges such as influencer fraud and transparency issues threaten its credibility. Antoniou [38] discussed how unethical practices, including undisclosed sponsorships, can erode consumer trust, ultimately reducing campaign efficacy. The dynamic nature of digital consumer behavior further complicates the landscape, as preferences and engagement patterns shift rapidly. To address these challenges, Campbell and Farrell [51] suggested that brands must adopt a strategic approach when selecting influencers, focusing on alignment with brand values and audience demographics. This careful selection process is essential to maintain trust and foster meaningful consumer engagement.
As digital consumer behavior evolves, data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) are becoming integral to influencer marketing strategies. Aziz et al. [46] emphasized the importance of leveraging big data analytics to refine influencer partnerships, assess audience engagement, and optimize campaign outcomes. By incorporating advanced metrics such as engagement quality and audience authenticity, brands can make informed decisions and enhance the impact of their campaigns [52]. These data-driven strategies allow for continuous refinement, ensuring that influencer marketing remains an effective tool in driving purchase intentions in the ever-changing digital landscape.
2.3. Influencer Marketing and the Greek Market
Influencer marketing has gained significant traction in Greece, aligning with global trends that leverage social media personalities to enhance brand engagement. Theocharis and Papaioannou [53] examined Greek consumers’ responses to influencer marketing, revealing a positive reception and increased purchase intentions when influencers are perceived as authentic and trustworthy. This underscores the importance of selecting influencers whose values align with the brand to effectively penetrate the Greek market.
Greek consumers’ behavior closely aligns with that of Southeastern European consumers, such as those in Spain, Portugal, and Italy, particularly in their engagement with influencer marketing and digital brand interactions. Research indicates that social media-driven purchasing behavior and brand trust play a crucial role in consumer decision-making across these markets. Ruiz-Ariza et al. [54] found that Spanish and Portuguese consumers demonstrate high engagement with influencers, particularly in lifestyle, fashion, and travel sectors, mirroring the trends observed in Greece [53]. Similarly, Ingrassia et al. [55] highlighted that Italian consumers respond more positively to influencer campaigns when authenticity and cultural relatability are emphasized, a factor also critical in Greek consumer engagement [42].
Furthermore, tourism marketing studies in Italy and Spain have shown that regional influencers significantly impact travel choices, supporting findings that Greek social media users are influenced by content creators when selecting destinations [56]. However, Fraculj et al. [57] and Humprecht et al. [58] cautioned that the lack of transparency in sponsorship disclosures is a common concern across Southeastern European markets, reinforcing the need for ethical marketing practices to sustain consumer trust. These parallels suggest that Greek influencer marketing strategies can be effectively adapted to similar Southern European contexts, leveraging authenticity, transparency, and regional cultural relevance for maximum engagement.
In the tourism sector, Chatzigeorgiou [56] explored the impact of social media influencers on millennials’ behavioral intentions in rural Greek areas. The study found that influencers significantly affect travel decisions, suggesting that tourism marketers can use influencer partnerships to promote lesser-known destinations. This strategy not only broadens the appeal of rural tourism but also supports sustainable economic development in these regions.
Despite its potential, influencer marketing in Greece faces challenges, particularly concerning consumer skepticism and the need for transparency. Fraculj et al. [57] highlighted that undisclosed sponsorships can lead to consumer distrust, diminishing campaign effectiveness. Therefore, adherence to ethical guidelines and transparent disclosure of partnerships are crucial for maintaining consumer trust and maximizing the impact of influencer marketing strategies in the Greek market.
2.4. Research Hypotheses Formulation
For the deployment of the study, five main research hypotheses have been formed. These hypotheses involved specific questions and scales from the questionnaire, as described in the next section. Moreover, these hypotheses are linked to the research objective set at the beginning of the present section.
Recent studies underscore the transformative impact of influencer marketing on customer loyalty and profitability, with evidence suggesting these effects vary across industries and demographics. For example, Cheah et al. [37] highlighted that industries such as fashion and beauty experience stronger loyalty effects due to the emotional connection influencers create with their audiences. However, in technology or financial services, trust and expertise play a more significant role [31]. Additionally, demographic factors such as age and cultural context significantly moderate the effectiveness of influencer campaigns. Han et al. [29] found that younger demographics are more responsive to influencer endorsements, particularly on platforms like Instagram and TikTok, whereas older consumers prioritize trust and transparency. This hypothesis aligns with these findings, emphasizing the importance of tailoring influencer marketing strategies to specific industries and demographics to maximize customer loyalty and profitability.
Hypothesis 1 (H1):
“Influencer marketing activities enhance customer loyalty and profitability differently across industries or demographics”.
Consistency, authenticity, and engagement quality are critical determinants of effective social media marketing, as noted in the recent literature. Aw and Agnihotri [32] emphasized that consistent posting schedules maintain brand visibility, while authenticity fosters trust and deeper connections with audiences. Moreover, high-quality engagement, such as interactive content and timely responses to comments, enhances consumer perception of the brand [30]. Brands that maintain these attributes often see increased consumer trust and loyalty, driving purchase intentions. This hypothesis is strongly supported by Cheah et al. [37], who found that over-endorsement or lack of authenticity can reduce campaign effectiveness, further validating the necessity of authentic and consistent strategies in social media marketing.
Hypothesis 2 (H2):
“Consistency, authenticity, and engagement quality significantly influence the effectiveness of social media marketing strategies”.
Influencer marketing has been proven to impact consumer purchasing decisions positively and negatively. Rachmad [45] noted that authentic endorsements often lead to increased sales by leveraging the influencer’s credibility. However, Antoniou [38] cautioned that consumers are becoming more skeptical of influencer ads, especially when they lack transparency or appear overly commercialized. This skepticism can lead to annoyance and reduced engagement, as noted by Cheah et al. [37], who identified over-endorsement as a key factor in consumer disinterest. The dual nature of influencer marketing, as outlined in this hypothesis, highlights the need for a balanced approach where influencers maintain authenticity while avoiding saturation of sponsored content.
Hypothesis 3 (H3):
“Influencer marketing significantly impacts consumer purchasing decisions, with both positive and negative outcomes such as increased sales and perceived annoyance from ads”.
Recent research demonstrates that consumer satisfaction in online shopping is heavily influenced by product categories and behavioral factors. Sánchez Villegas et al. [36] highlighted that categories such as health and beauty rely on visual and descriptive content to meet consumer expectations, which directly correlates with satisfaction. Additionally, behavioral factors such as frequency of online purchases and prior experiences further shape satisfaction levels [35]. For instance, consumers with frequent exposure to online ads are more likely to exhibit higher satisfaction in specific categories, such as beauty products, due to familiarity and tailored offers. This hypothesis reflects these findings, emphasizing that understanding consumer behavior is essential for optimizing satisfaction in targeted product categories.
Hypothesis 4 (H4):
“Shopping behaviors in specific categories (e.g., health and beauty) influence online satisfaction, moderated by behavioral factors”.
The evolution of online shopping behavior is increasingly driven by concerns, preferences, and technological advancements. Aw and Agnihotri [32] highlighted that concerns such as product quality and data privacy remain significant barriers to consumer adoption. However, preferences for convenience and fast delivery, coupled with advancements like AI-driven personalization, are rapidly transforming online shopping experiences [37]. Moreover, technologies such as virtual try-ons and augmented reality enhance consumer confidence in making online purchases, particularly in categories like clothing and furniture [33]. This hypothesis aligns with recent findings, emphasizing that addressing consumer concerns and leveraging technology are crucial for sustaining and growing online shopping behavior.
Hypothesis 5 (H5):
“Consumer concerns, preferences, and technological advancements drive the evolution of continued online shopping behavior”.
3. Materials and Methods
The methodological framework of this study is systematically structured into five distinct stages: questionnaire design, data collection and sampling, validity and reliability testing, statistical analysis, and FCM scenarios’ development. These stages aim to ensure a rigorous and comprehensive approach to examine the impact of influencer marketing on consumer behavior and online shopping preferences.
- Stage 1: Questionnaire Design.
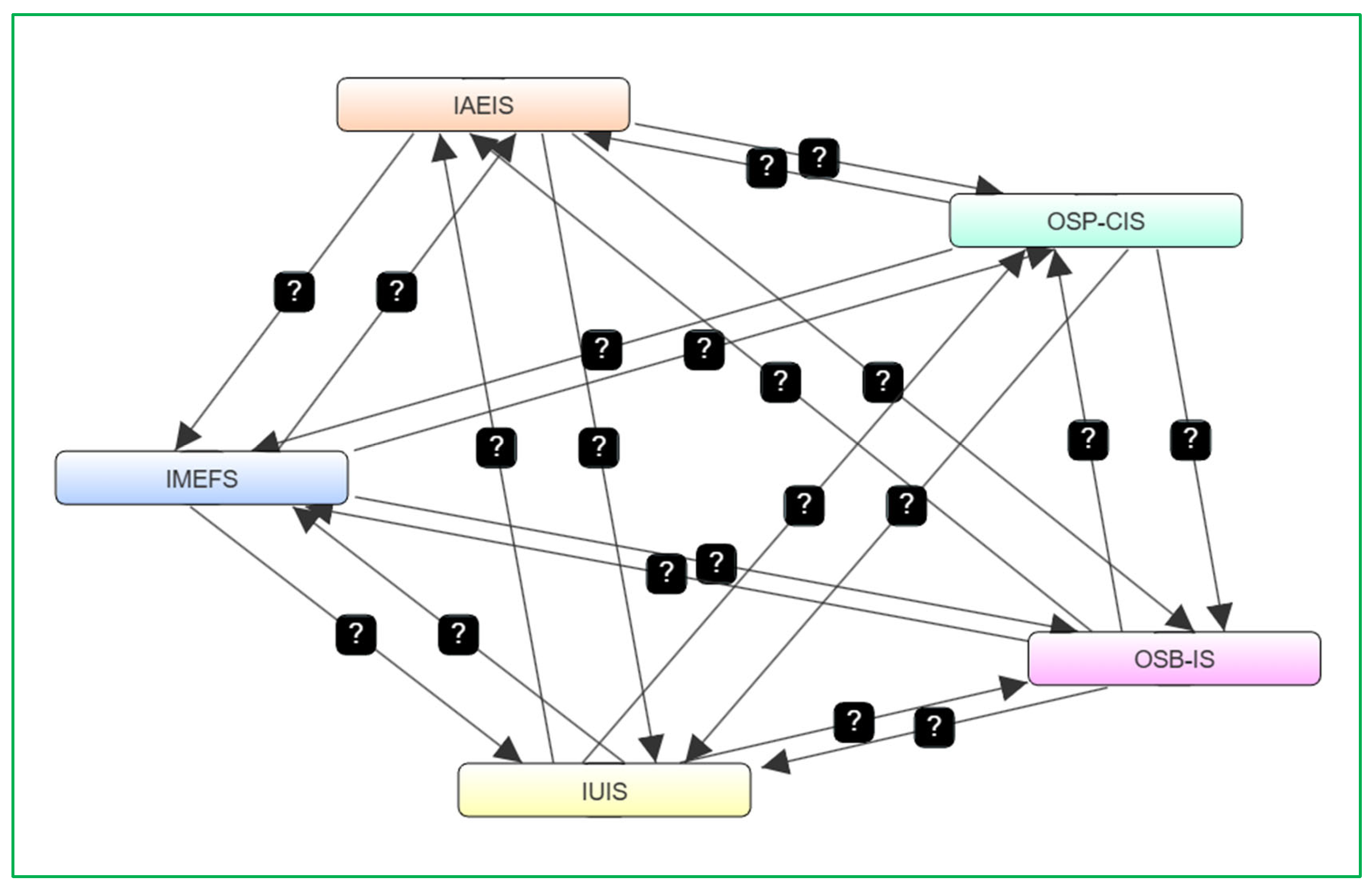
The questionnaire was meticulously developed to align with the study’s research objectives and consisted of 27 closed-ended questions organized across five core dimensions: Influencer Ads Engagement and Impact (IAEIS), Influencer Marketing Effectiveness Factors (IMEFS), Influencer Utility in Influencing Sales (IUIS), Online Shopping Behavior and Influencer Advertising Impact (OSB-IS), and Online Shopping Preferences and Consumer Intention (OSP-CIS). Each dimension targeted specific variables, such as consumer attitudes toward influencer ads, the effectiveness of marketing strategies, and preferences in online shopping behavior. To ensure clarity and relevance, the questions were customized and adapted to the context of this study, facilitating the collection of reliable, quantifiable data. The inclusion of clear instructions and assurances of respondent anonymity fostered trust and compliance among participants. Therefore, the mindmap of the relationship examined between the dependent variables of this study is presented in Figure 2.
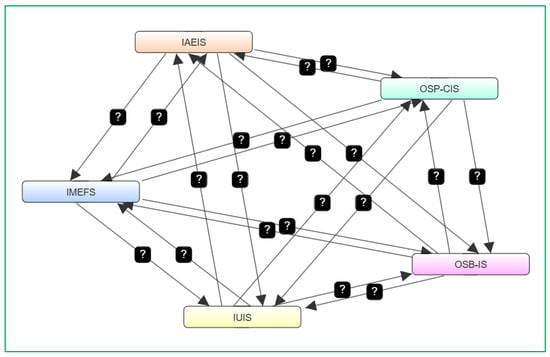
Figure 2.
FCM mindmap.
- Stage 2: Data Collection and Sampling.
Data collection was conducted using Stratified Random Sampling, a method chosen for its ability to capture variability between distinct subgroups while minimizing intragroup variability. This approach ensured a representative sample reflective of diverse consumer demographics and behaviors. The questionnaire was distributed via Google Forms and remained open for participation from 6 December 2023 to 20 March 2024, resulting in a total of 320 complete responses. Stratification criteria included demographic and behavioral characteristics to ensure heterogeneity and generalizability of the findings. Participants were informed of the ethical considerations of the study, including the confidentiality of their responses and the exclusive use of the data for academic purposes.
- Stage 3: Validity and Reliability Testing.
To validate the reliability of the questionnaire, Cronbach’s alpha coefficient was employed, with each scale exceeding the acceptable threshold of 0.6–0.7, confirming strong internal consistency. The rigorous testing of reliability and internal consistency ensured that the data collected was robust, allowing for meaningful analysis and interpretation of the study’s variables. This final stage solidified the methodological framework, enabling the derivation of valid insights into the dynamics of influencer marketing and online consumer behavior.
- Stage 4: Statistical Analysis.
The statistical analysis in Stage 4 followed a structured approach to examine the impact of influencer marketing on consumer behavior and online shopping preferences. First, descriptive statistics were applied to understand general trends and consumer engagement patterns with influencer ads. Next, multiple categorical regression models were developed to assess the predictive power of influencer engagement, marketing effectiveness, and consumer preferences on purchasing decisions. To further explore relationships between the dependent variables, Spearman’s correlation analysis identified key connections between influencer activity, consumer trust, and purchase intent. After answering the RQ and the research hypotheses of the study, an estimation of the relationships developed among the dependent variables was attempted. Thus, the utilization of Fuzzy Cognitive Mapping (FCM) analysis was discerned (Stage 5).
While Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) is indeed a robust analytical approach often used to capture complex relationships among latent constructs, it was not applied in this study for several methodological and practical reasons. This research focused on directly observable variables, such as views, likes, keyword use, and video duration, where linear regression offers transparent, interpretable, and statistically efficient estimates. Furthermore, the dataset’s structure did not meet some of the key assumptions required for SEM, such as latent construct specification and large sample sizes per construct [59]. As Shmueli et al. [60] argued, simpler predictive models are more appropriate when the primary goal is practical insight and application, especially in data-rich environments like YouTube analytics. Additionally, the study’s emphasis on exploratory relationships made regression more suitable than theory-driven confirmatory models like SEM. Future research could build on these findings using SEM to explore mediating effects, especially in contexts involving trust or emotional influence.
- Stage 5: FCM scenarios.
The Fuzzy Cognitive Map (FCM) model was developed to analyze causal relationships between influencer marketing factors and online consumer behavior. Ten FCM scenarios were simulated, varying the values of IAEIS, IMEFS, IUIS, OSB-IS, and OSP-CIS by +50% and −50% to observe their impact on purchasing behavior. The results revealed that higher influencer engagement (IAEIS) and utility in sales (IUIS) positively influence online shopping behavior, whereas reduced influencer marketing effectiveness (IMEFS) weakens consumer trust and purchase intent. The simulations also confirmed that transparent, well-structured influencer marketing strategies are crucial for sustaining consumer engagement. These FCM-based findings provide actionable insights for marketers to optimize influencer selection, enhance content authenticity, and improve digital marketing strategies for long-term consumer engagement and conversion success.
3.1. Questionnaire Formation
The questionnaire designed for this quantitative research comprises four sections (Appendix B) and was developed to align with the research questions, enhancing its validity. The questions were translated and customized for this study. The questionnaire included 27 primary closed-ended questions.
3.2. Data Origin and Retrieval
Stratified Random Sampling [61] was selected as the method for data collection, commonly employed by researchers to gather market research data from a representative and distinct group of participants. This method is particularly effective in studies where the variability within subgroups is smaller than between subgroups. The data were gathered through the completion of a questionnaire, which was distributed via Google Forms. The questionnaire was available to respondents between 6 December 2023 and 20 March 2024. A total of 320 individuals participated in the survey. Based on the total population of Greece (10,000,000 people) and the online sample size calculator “https://www.calculator.net/sample-size-calculator.html (accessed on 20 March 2024)”, this sample size is quite adequate (385 is the optimal size). In addition to providing instructions for completion, the questionnaire assured participants of their anonymity and clarified that the collected data would be used solely for research purposes.
3.3. Questionnaire Validity
For the subject of the present research (research on opinions–attitudes–perceptions), the necessary level of reliability, as expressed by the value of Cronbach’s alpha coefficient, must be between 0.6 and 0.7 and above to be considered reliable [62]. Reliability is the degree to which a questionnaire represents the actual results and opinions of the individuals. The greater is the score, the greater its reliability, provided that the set of questions and their subjects belong to the set of theoretically available questions on the topic under investigation [63]. In particular, the reliability of the answers according to Cronbach’s α coefficient is as follows:
- Scale 1: questions highlighting “Influencer Ads Engagement and Impact Scale (IAEIS)” (Question 8–12), with a = 0.670.
- Scale 2: question highlighting “Influencer Marketing Effectiveness Factors Scale (IMEFS)” (Question 7), with a = 0.893.
- Scale 3: questions highlighting “Influencers Utilization and Impact Scale (IUIS)” (Questions 1–6), with a = 0.908, which refers to a reliable sample.
- Scale 4: questions highlighting “Online Shopping Behavior and Influencer Advertising Impact Scale (OSB-IS)” (Questions 13–17), with a = 0.847, referring to a reliable sample.
- Scale 5: questions highlighting “Online Shopping Preferences and Consumer Intention Scale (OSP-CIS)” (Questions 18–20), with a = 0.769, which refers to a reliable sample.
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
The primary goal of the following descriptive statistics is to display the sample values, allowing for an initial interpretation of the survey results. Figure A1, Figure A2, Figure A3, Figure A4, Figure A5, Figure A6, Figure A7, Figure A8 and Figure A9, in Appendix A, present the basic demographic statistics of the questionnaire’s respondents. Table 2 shows the analysis of the respondents’ main demographic information to assess the generalizability of the research. Moreover, in Table 3, the results of the social media usage between the correspondents are presented.

Table 2.
Participants’ demographics.

Table 3.
Participants’ social media usage.
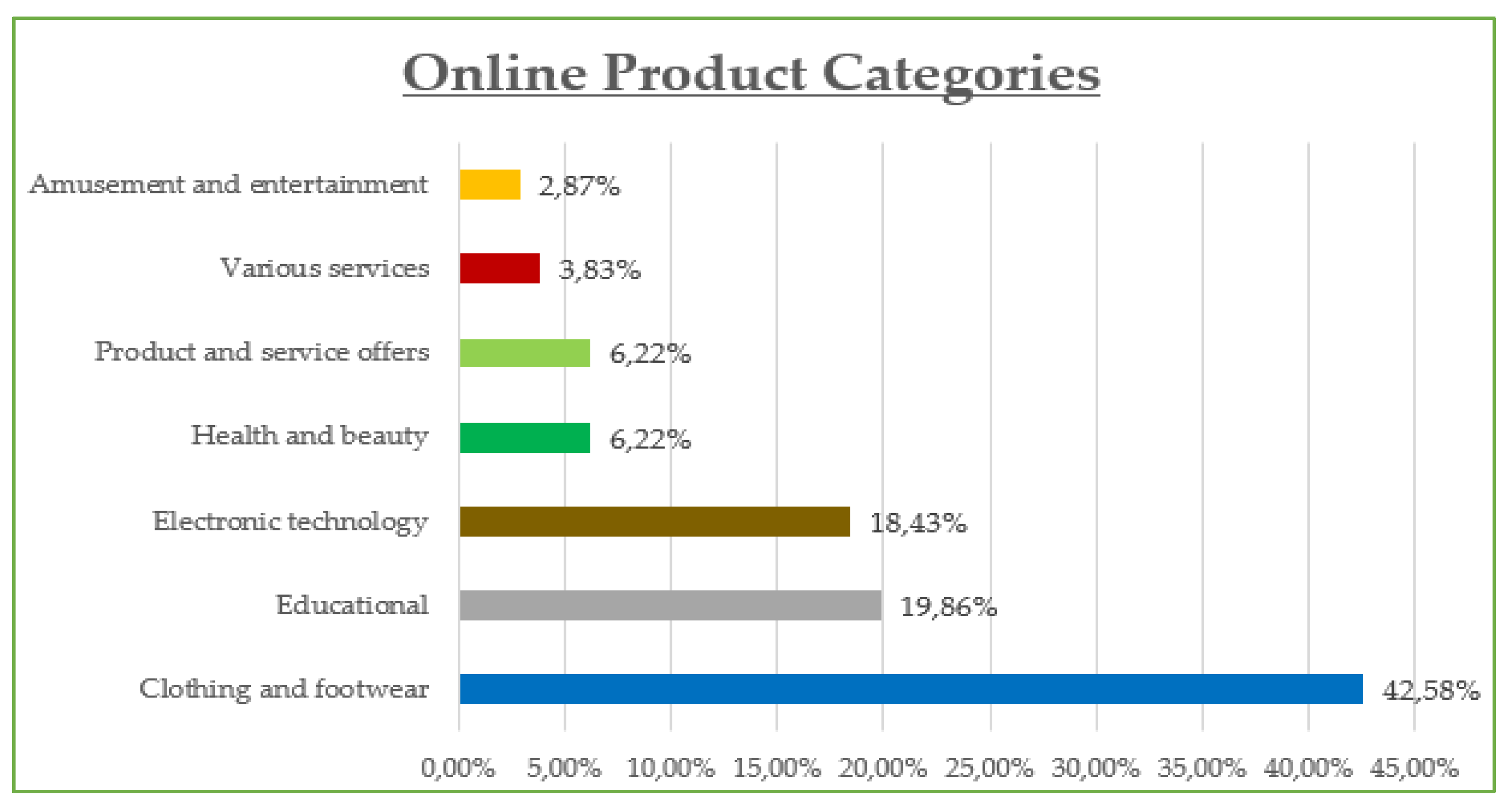
The demographic data reveal that the majority of participants are between 30 and 45 years old (42.8%) and are predominantly female (55%), with most holding at least a Bachelor’s degree (73% combined Bachelor and Master/Doctorate). Monthly income is relatively evenly distributed, though a notable portion (23.21%) earns €901–€1200, while a significant share (21.05%) exceeds €1500, suggesting moderate to high purchasing power. Professionally, most are public (32.5%) and private (24.2%) employees, with a strong representation of students and freelancers. In terms of marital status, the sample skews slightly toward single participants (48.8%) over married (45.5%). Social media usage is high, especially on Viber (86.1%) and Facebook (83.1%), with Instagram also playing a dominant role (72.6%). Most participants use social media for 1–3 h daily (43.54%), followed by 1 h (23.9%) and 3–5 h (19.14%). The most popular online shopping categories are clothing and footwear (42.58%), educational content (19.86%), and electronic technology (18.43%), highlighting a strong interest in both lifestyle and practical digital consumption.
The data across Table 4 and Table 5 illustrate significant differences in influencer ad engagement and online shopping behavior based on gender and age. Women report a higher mean score in both liking influencer posts (3.8 vs. 3.1) and purchasing from influencer ads (3.5 vs. 2.9) compared to men, while also showing less perceived ad annoyance (3.2 vs. 3.7). Furthermore, 68% of women follow influencers, in contrast to only 45% of men, suggesting that influencer marketing is notably more effective with female audiences. Age comparisons in Table 5 reveal that younger groups (18–24 and 25–34) display significantly higher online shopping satisfaction, trust in influencer ads, and engagement with online shopping and influencer content. In contrast, trust and engagement decrease sharply among those aged 45 and older, implying a generational gap in digital consumer behavior.

Table 4.
Influence of gender on influencer ad engagement and purchase behavior.

Table 5.
Age group comparison in online shopping behavior and trust.
Educational level also appears to shape attitudes toward influencer authenticity and promotional trust (Table 6). Participants with postgraduate degrees value authenticity the most (mean score: 4.4) and show the highest trust in promotional offers (4.1), along with the greatest agreement that ads boost sales (81%). This suggests that higher education levels correlate with both more critical and more engaged perspectives on digital marketing content. Similarly, employment status (Table 7) affects both exposure and response to social media marketing. Students and part-time employees spend more time on social media and are more likely to follow influencers and trust their content (mean trust scores: 4.2 and 4.0, respectively). Meanwhile, unemployed or non-working individuals display lower engagement and trust, pointing to the role of lifestyle and digital immersion in shaping influencer marketing effectiveness.

Table 6.
Educational level and attitudes toward influencer authenticity and sales promotions.

Table 7.
Employment status and time spent on social media platforms.
Lastly, income level significantly impacts the perceived value of influencer marketing and purchasing behavior (Table 8). Participants earning over €2000 monthly exhibit the highest perceived value in influencer marketing (4.2) and the greatest rate of purchases based on influencer content (68%), favoring premium products (65%). Conversely, those earning under €1000 show lower perceived value (3.5), fewer purchases (53%), and a strong preference for budget products (78%). This indicates that influencer campaigns may need to be tailored according to income segment, using aspirational messaging for high-income consumers and value-driven content for lower-income segments. Collectively, the tables reinforce the importance of demographic segmentation in influencer marketing strategy, highlighting how gender, age, education, employment, and income influence engagement, trust, and consumer action.

Table 8.
Income level and perceived value of influencer marketing.
4.2. Statistical Tests
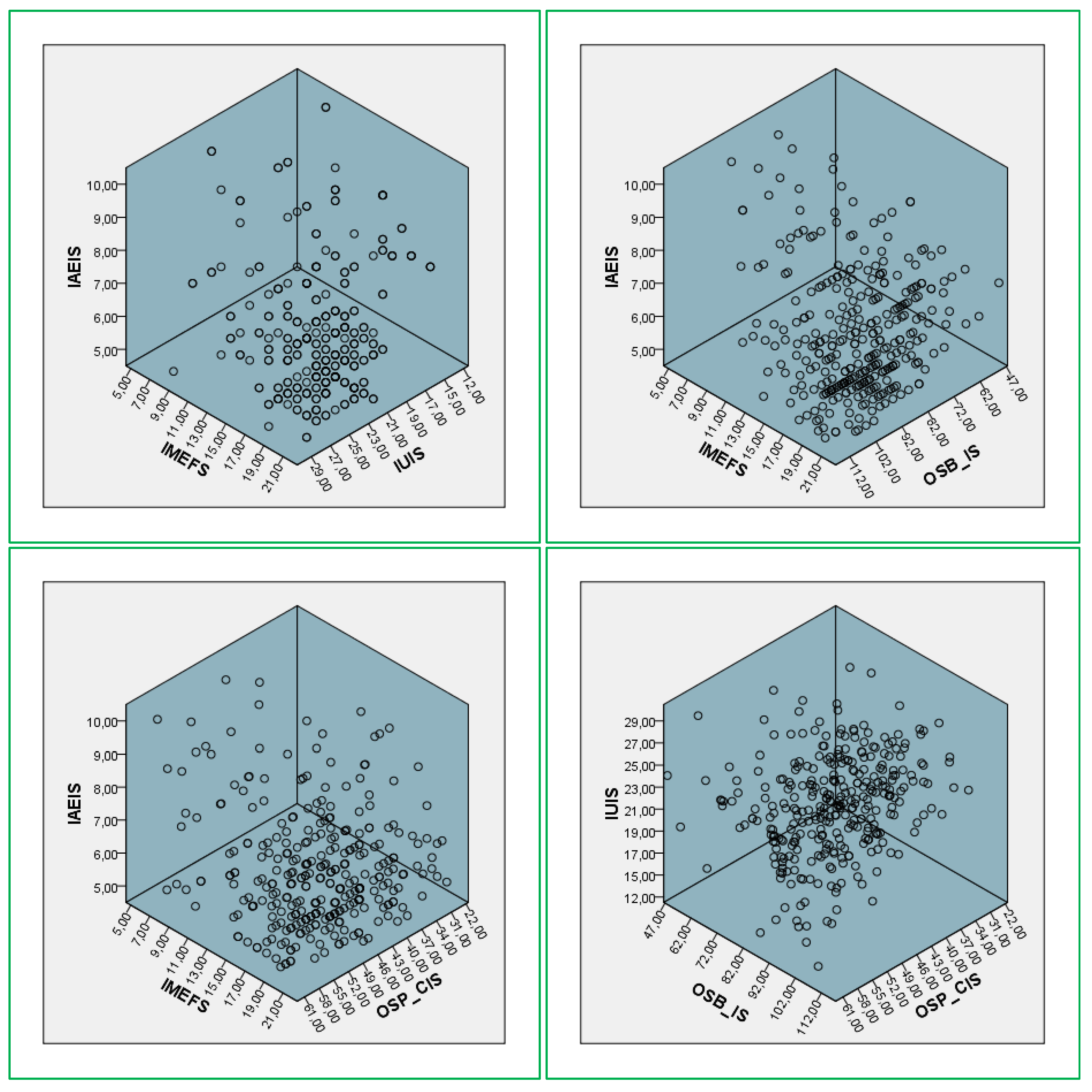
The results of the statistical analysis performed are presented in this section. The authors deployed simple linear regression models for the IAEIS, IMEFS, IUIS, OSB-IS, and OSP-CIS variables. The regression analysis for IAEIS (Influencer Activity Effectiveness in Influencing Sales) reveals significant findings with an R2 value of 1.000 (Table 9), indicating that the model explains all the variance in the dependent variable. The high F statistic (52,148.028, p < 0.001) confirms the robustness of the model. Among the predictors, shopping through influencer ads and keeping up with sales and promotions through influencer content show the strongest impact, with standardized coefficients of 0.355 and 0.360 (Table 10), respectively. This highlights that influencer marketing is particularly effective in driving customer engagement and enhancing sales through strategic promotions. The scatterplots (Figure 3) demonstrate a clear clustering in the higher ranges of IAEIS, indicating a consistent and significant relationship between influencer activities and their effectiveness in engaging consumers and boosting profitability.

Table 9.
IAEIS regression summary and ANOVA.

Table 10.
IAEIS regression coefficients.
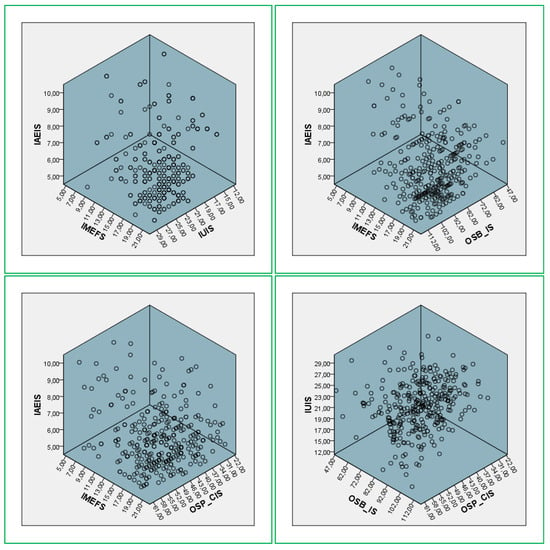
Figure 3.
3D Scatterplots between IAEIS, IMEFS, SMUIS, IUIS, OSB-IS, and OSP-CIS.
The IMEFS (Influence of Marketing Effectiveness on Social Media) model also demonstrates high explanatory power, with an R2 value of 0.987 (Table 11). This indicates that nearly all the variance in marketing effectiveness is accounted for by the model. The significant predictors include post content (standardized coefficient: 0.338), online offers (0.273), and customer engagement (0.261), underscoring the importance of high-quality content and targeted offers in driving consumer interaction on social media platforms (Table 12). This suggests that businesses must prioritize consistency and creativity in their digital marketing campaigns to achieve optimal engagement. The scatterplots (Figure 3) reveal a positive alignment between IMEFS and other variables, although the less linear relationship with IUIS (−0.359 **) hints at differences in how marketing effectiveness and influencer utility are perceived and applied across audiences.

Table 11.
IMEFS regression summary and ANOVA.

Table 12.
IMEFS regression coefficients.
For IUIS (Influencer Utility in Impacting Sales), the regression model is exceptionally robust, with an R2 of 1.000 (Table 13) and highly significant predictors (p < 0.001). Purchases made through influencer ads emerge as the strongest driver, with a standardized coefficient of 0.318, followed by businesses’ impact on customer purchases through influencers (0.301) (Table 14). Interestingly, the perceived annoyance from influencer ads (standardized coefficient: 0.283) is also significant, reflecting a dual impact where such ads can both attract and repel consumers. This finding highlights the nuanced role of influencer marketing, where the balance between engagement and consumer fatigue is critical. The scatterplots (Figure 3) display a wide distribution with clusters around key variables, emphasizing the variability in consumer responses to influencer marketing efforts.

Table 13.
IUIS regression summary and ANOVA.

Table 14.
IUIS regression coefficients.
The regression analysis for OSB-IS (Online Shopping Behavior Influenced by Social Media) yields an R2 value of 0.749 (Table 15), indicating moderate explanatory power. Key predictors include the usability of a friendly and responsive website (standardized coefficient: 0.131) and store offers (0.140), which significantly influence online shopping behavior (Table 16). These findings suggest that while influencer marketing plays a role, practical factors such as website design and clear promotional offers are critical in shaping consumer purchasing behavior. The scatterplots (Figure 3) show clustering at moderate values of OSB-IS, reflecting that while these factors are important, there is room for improvement in addressing usability and communication of offers to optimize consumer behavior.

Table 15.
OSB-IS regression summary and ANOVA.

Table 16.
OSB-IS regression coefficients.
The OSP-CIS (Online Shopping Preferences and Consumer Satisfaction) model demonstrates strong explanatory power, with an R2 value of 0.924 (Table 17). Predictors such as a preference for online shopping (standardized coefficient: 0.326) and encouragement of friends and relatives to shop online (0.257) significantly influence consumer satisfaction and continued behavior (Table 18). Additionally, concerns about product descriptions and promotional images (0.117) are also significant, emphasizing the importance of trust in the online shopping experience. The scatterplots (Figure 3) reveal positive trends between OSP-CIS and its predictors, with higher scores corresponding to increased consumer satisfaction and engagement. These results underline the critical role of trust, accurate product representation, and social recommendations in driving continued online shopping behavior.

Table 17.
OSP-CIS regression summary and ANOVA.

Table 18.
OSP-CIS regression coefficients.
The Spearman’s correlation coefficients highlight interconnected relationships between the variables (Table 19). Positive correlations, such as between IAEIS and IUIS (0.244 **), reflect the alignment between influencer marketing activities and their utility in driving consumer purchases. However, negative correlations, such as between IMEFS and IAEIS (−0.146 **), indicate some divergence in how marketing strategies are perceived across different metrics. The scatterplots (Figure 3) visually capture these relationships, with clusters and distributions emphasizing areas of alignment and variability. Overall, the findings underscore the importance of influencer marketing, high-quality content, trust, and usability in driving customer loyalty, satisfaction, and profitability. By leveraging these insights, businesses can refine their digital marketing strategies to maximize their impact on consumer behavior.

Table 19.
Spearman’s correlation coefficients.
4.3. FCM Scenarios’ Development
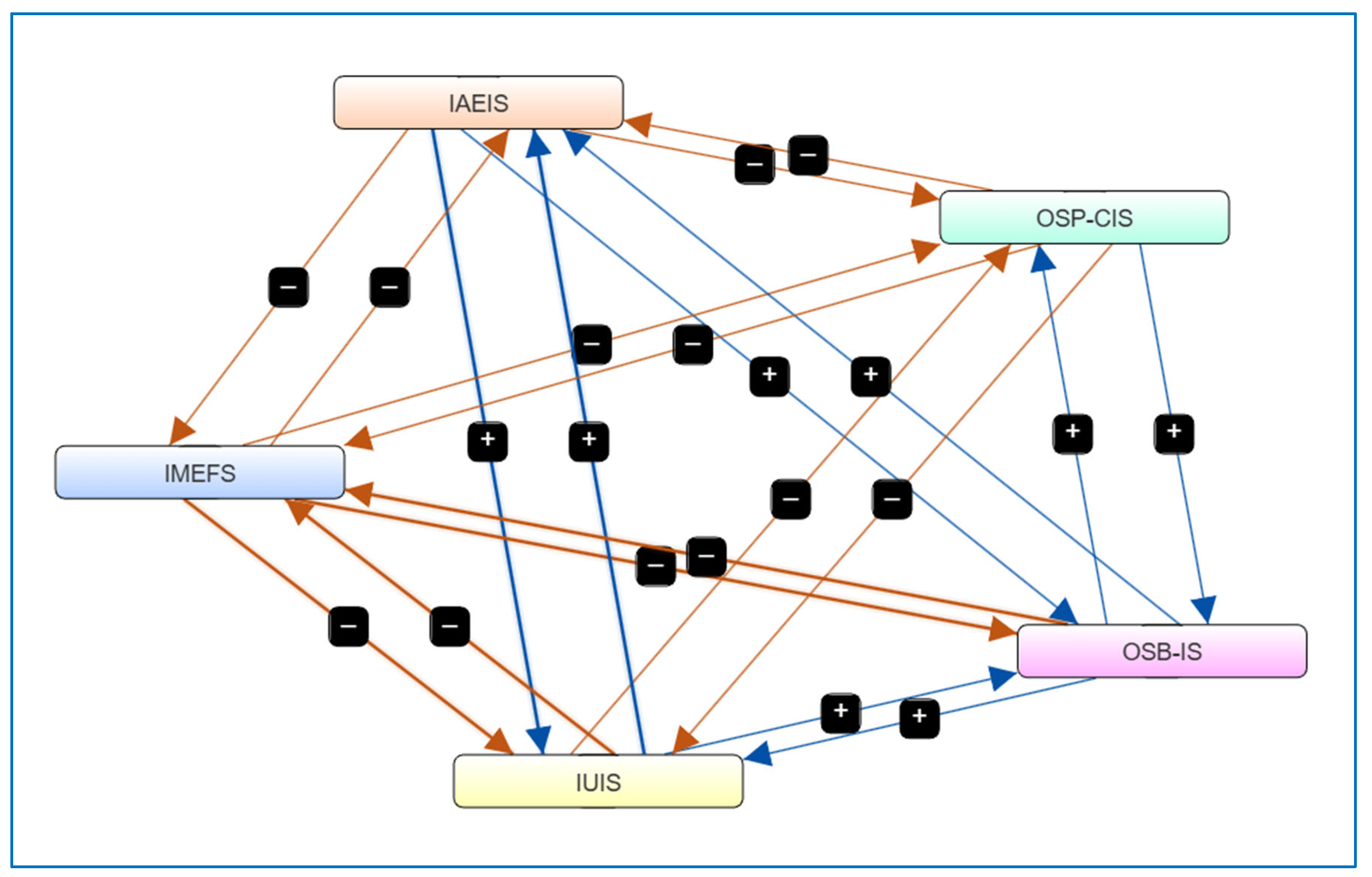
In this section, the FCM mindmap has been enhanced by adding the variable correlations (Pearson) based on the statistical analysis that preceded it. FCM is a computational modeling technique used to represent and analyze complex systems by depicting causal relationships between key variables. The provided FCM diagram consists of multiple interconnected nodes, each representing a concept, with directed edges indicating the causal influence between them. These influences are denoted by positive (+) and negative (−) signs, signifying reinforcing and inhibiting relationships, respectively [64]. The color-coded nodes and directed arrows in Figure 4 illustrate the feedback loops and interactions among different components, which can be useful for decision making, scenario analysis, and policy evaluation in dynamic environments [65].
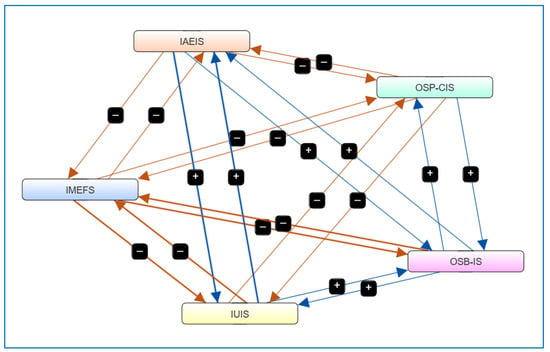
Figure 4.
FCM model deployment.
The development of the FCM model was informed by the statistical correlations identified in earlier stages of the analysis, particularly the Spearman and Pearson coefficients. These values were used to construct the directional weights among concepts, thereby ensuring empirical grounding of the causal pathways. Each node in the FCM represents a construct validated through prior regression models and supported by theoretical justification.
The interaction of factors in this FCM indicates a multidimensional system where certain variables, such as IMEFS, IAEIS, and OSB-IS, play crucial roles in influencing other components. The positive-weighted edges (blue arrows) suggest direct positive correlations, meaning an increase in one factor leads to an increase in another. Conversely, the negative-weighted edges (brown arrows) depict inverse relationships, implying a regulatory or opposing effect. These features enable stakeholders to simulate different intervention strategies and assess their impact, particularly in fields such as strategic decision-making, business intelligence, and risk management [66].
To validate the FCM scenarios, ten simulations were executed by varying the core variables (IAEIS, IMEFS, IUIS, OSB-IS, OSP-CIS) by ±50%. These variations allow for the sensitivity testing of each factor’s influence across the model. The causal directions and weights were iteratively tested through expert judgment and cross-checked against the statistical outcomes to confirm internal consistency.
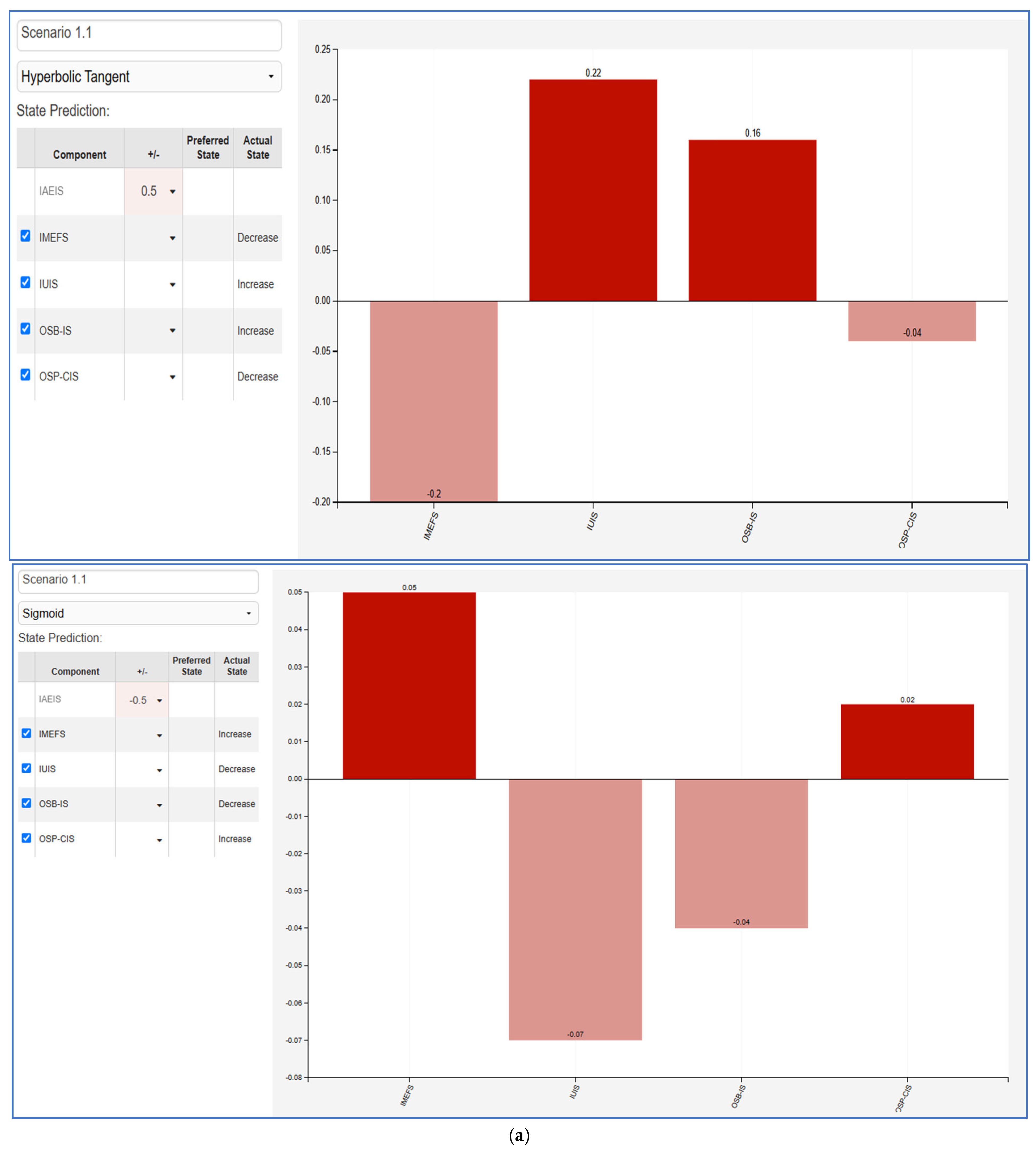
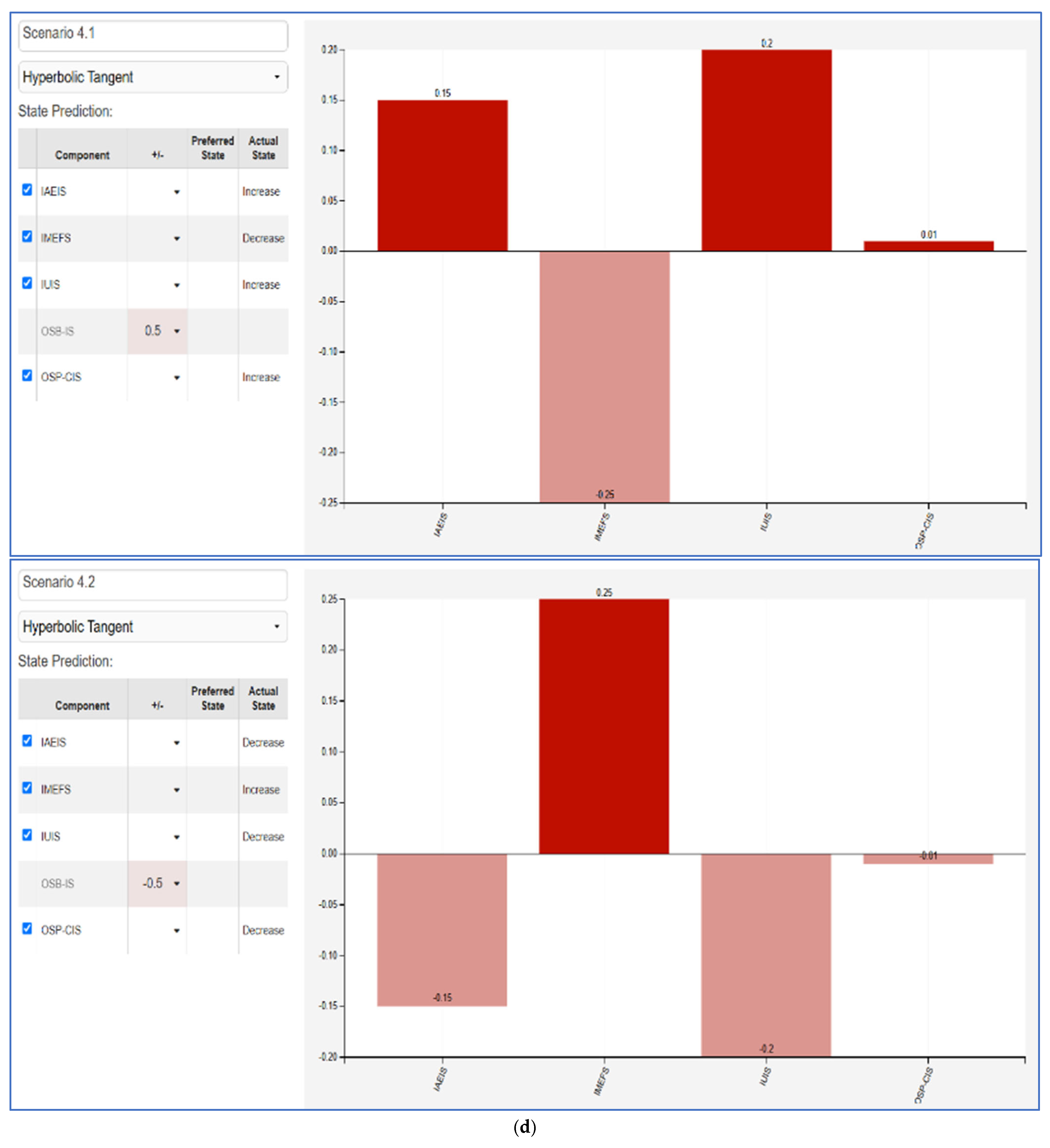
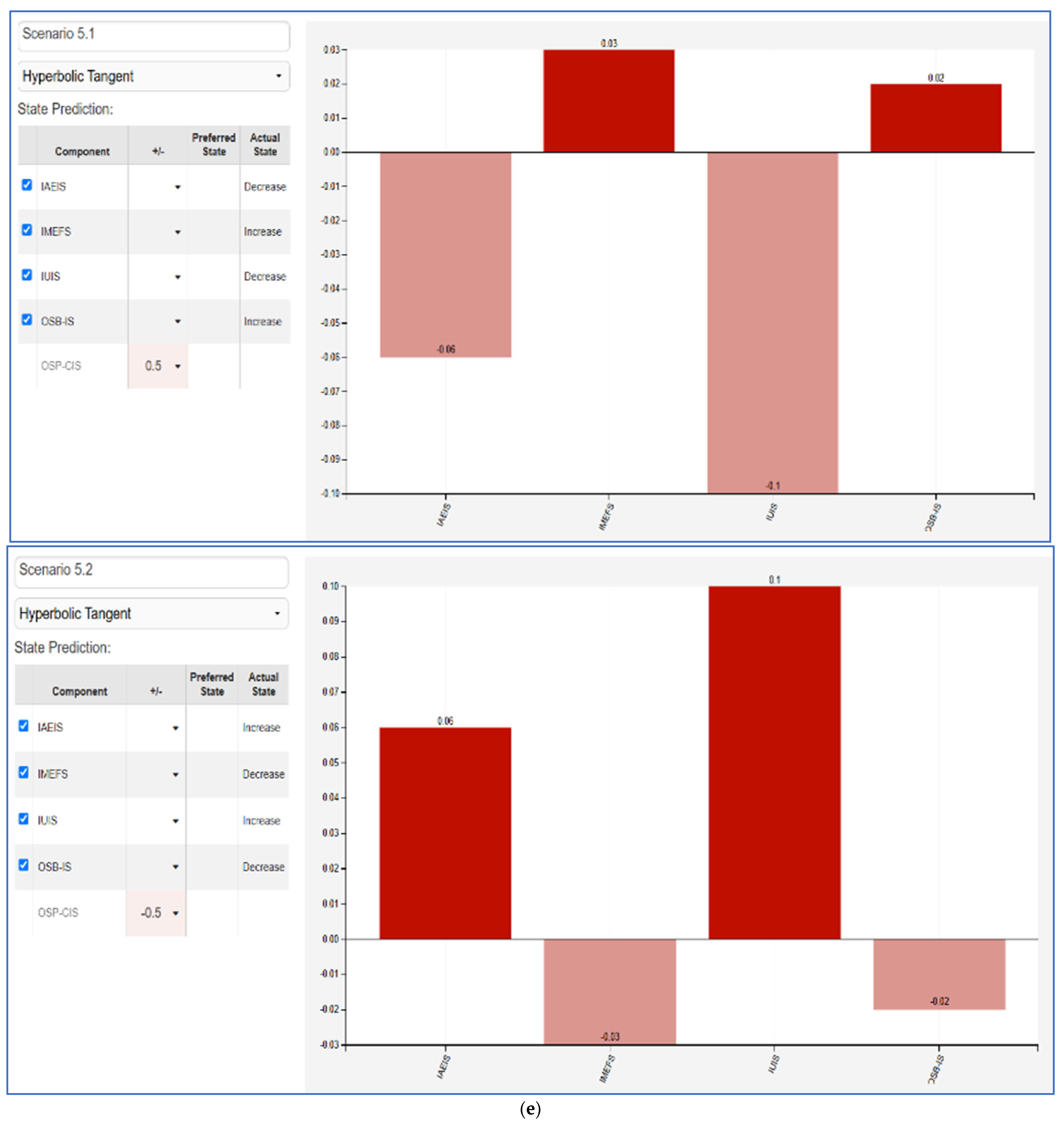
The Fuzzy Cognitive Map (FCM) scenarios illustrate the impact between varying influencer marketing factors and key consumer behaviors. Each scenario evaluates a +50% and −50% change in a given factor—Influencer Ads Engagement and Impact (IAEIS), Influencer Marketing Effectiveness Factors (IMEFS), Influencer Utility in Influencing Sales (IUIS), Online Shopping Behavior and Influencer Advertising Impact (OSB-IS), and Online Shopping Preferences and Consumer Intention (OSP-CIS). The results highlight the nonlinear effects of influencer-driven marketing efforts on consumer engagement, shopping behaviors, and decision making.
- IAEIS (Figure 5a): Increasing influencer ads engagement positively impacts IUIS and OSB-IS, indicating that higher engagement leads to greater effectiveness in influencing sales and online shopping behavior. Conversely, reducing IAEIS leads to a decline in these metrics, showcasing the importance of maintaining high engagement levels for advertising success.
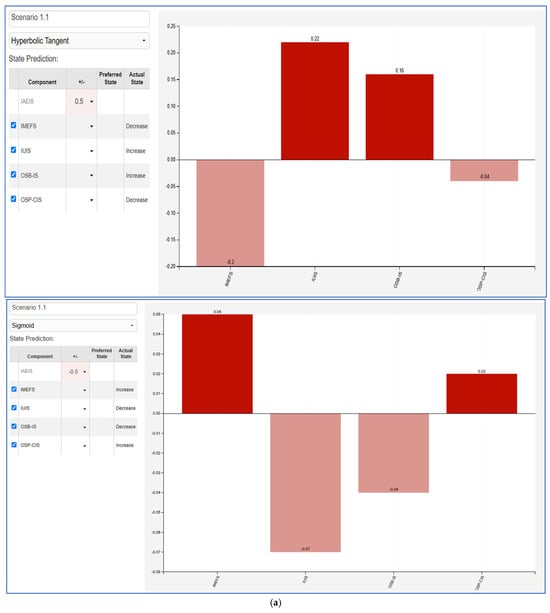
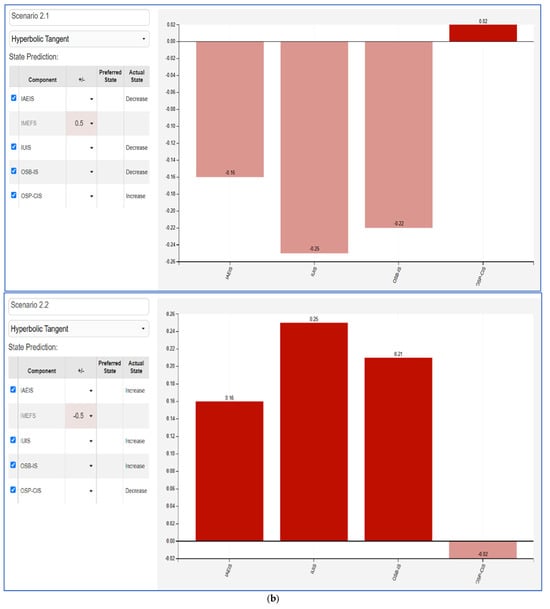
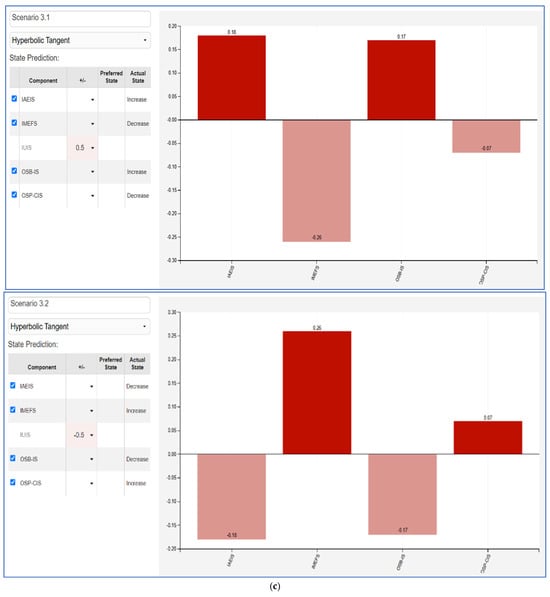
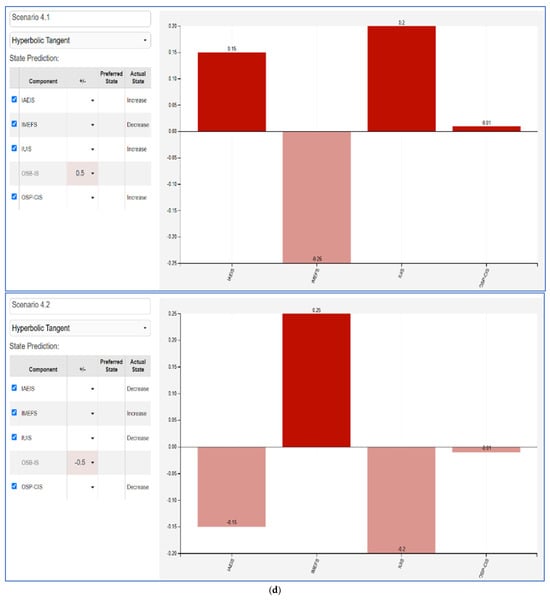
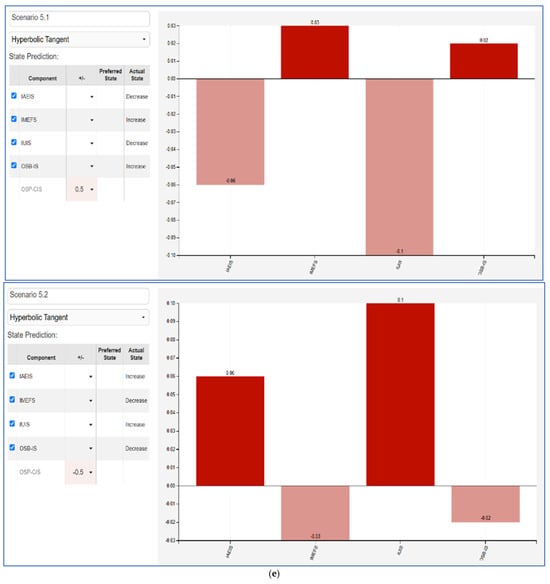 Figure 5. FCM scenarios. (a) IAEIS variation +50% (left), −50% right; (b) IMEFS variation +50% (left), −50% right; (c) IUIS variation +50% (left), −50% right; (d) OSB-IS variation +50% (left), −50% right; (e) OSP-CIS variation +50% (left), −50% right.
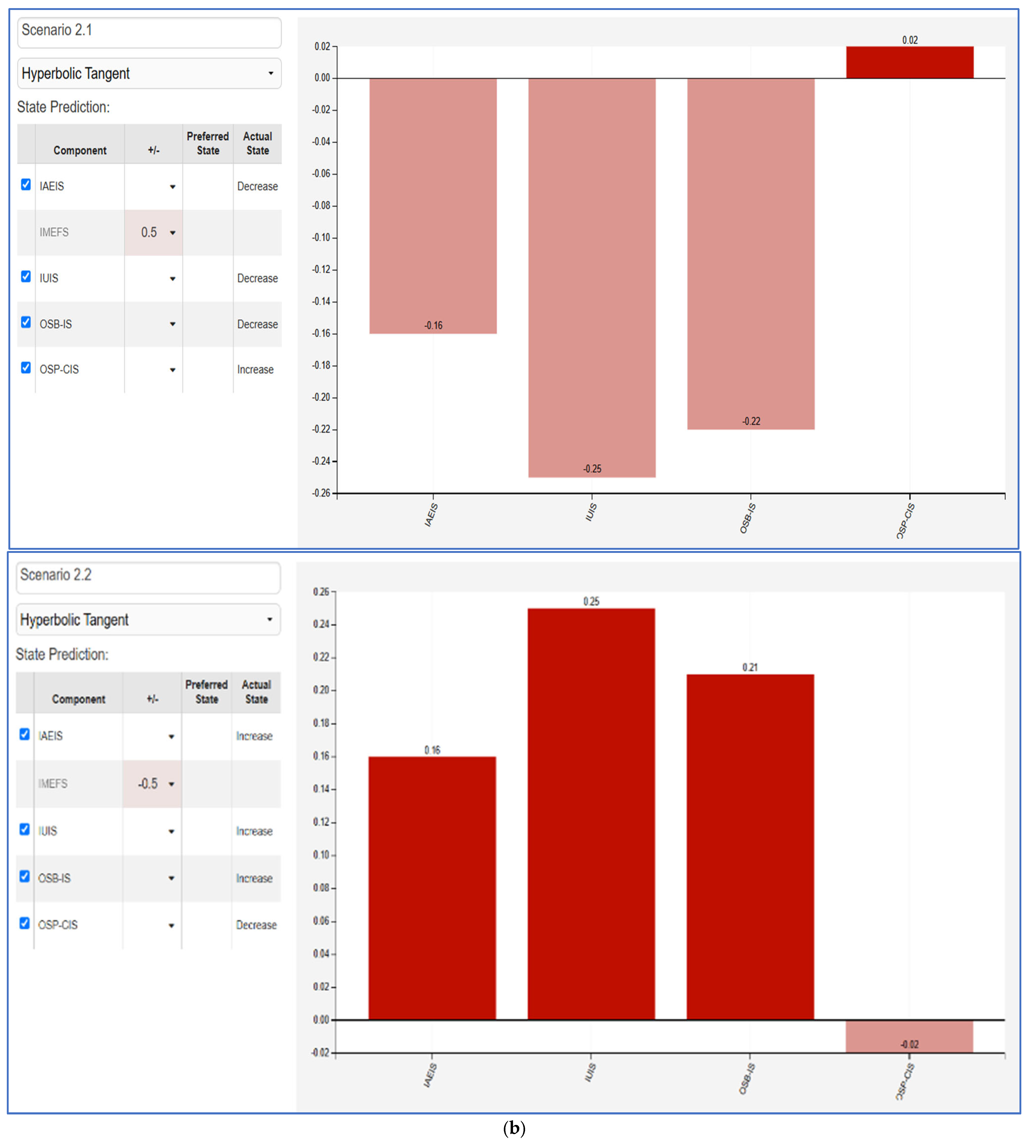
Figure 5. FCM scenarios. (a) IAEIS variation +50% (left), −50% right; (b) IMEFS variation +50% (left), −50% right; (c) IUIS variation +50% (left), −50% right; (d) OSB-IS variation +50% (left), −50% right; (e) OSP-CIS variation +50% (left), −50% right. - IMEFS (Figure 5b): A positive shift in influencer marketing effectiveness strengthens consumer intention (OSP-CIS) and IUIS, suggesting that well-targeted and high-quality influencer strategies significantly enhance purchasing decisions. In contrast, a decline results in a negative impact on online shopping behaviors, reinforcing the necessity of optimized influencer selection and marketing execution.
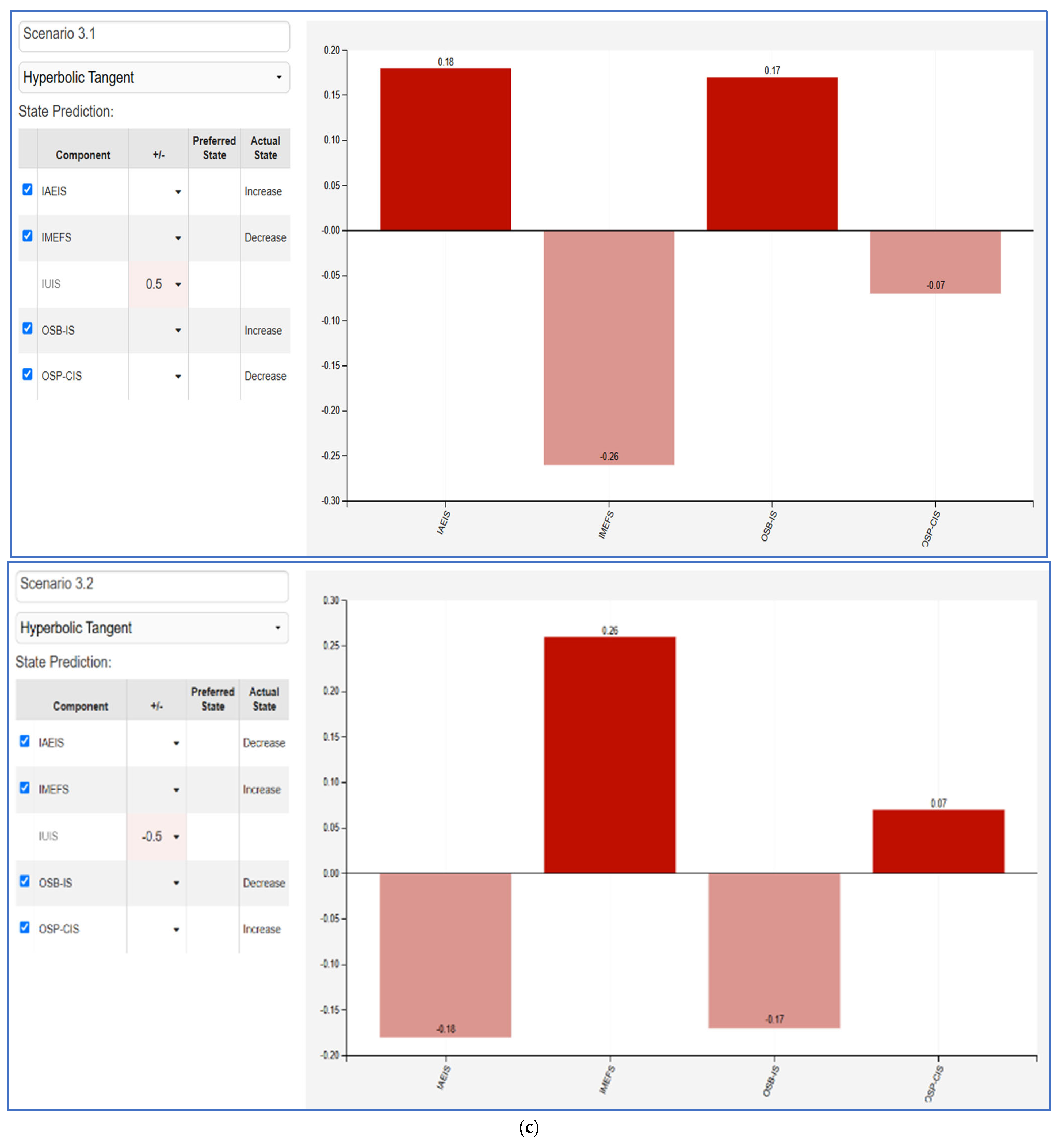
- IUIS (Figure 5c): Increasing influencer utility in influencing sales directly improves consumer engagement and online shopping behaviors, particularly OSB-IS. However, a negative shift leads to a sharp decline in OSB-IS and OSP-CIS, emphasizing that influencer-driven sales influence must be strategically enhanced to maintain online consumer trust.
- OSB-IS (Figure 5d): A positive shift in online shopping behavior influenced by influencer advertising enhances IUIS and IAEIS, suggesting that effective influencer advertising can significantly boost both sales and engagement. However, a decline results in a decrease across most factors, highlighting the need for consistent influencer-driven marketing strategies.
- OSP-CIS (Figure 5e): Changes in online shopping preferences and consumer intention show that higher consumer intent correlates with improved influencer effectiveness (IMEFS) and online shopping behavior (OSB-IS). A decline leads to worsening influencer impact and consumer engagement, suggesting that maintaining strong consumer trust and preference for influencer-driven marketing is critical for sustained effectiveness.
5. Discussion
This study offers a comprehensive examination of how influencer marketing affects consumer behavior and online shopping dynamics. The findings provide robust support for the formulated hypotheses, answering research questions centered around influencer engagement, trust, content strategies, and consumer purchasing decisions. H1 is fully supported, indicating that influencer marketing activities significantly enhance customer loyalty and profitability. This supports prior studies by Aw and Agnihotri [32] as well as Li and Peng [31], which stressed that consistent and personalized influencer strategies can foster strong consumer–brand relationships and long-term engagement. The regression analysis confirmed that high influencer activity (IAEIS) directly relates to increased consumer engagement and loyalty, underlining the pivotal role influencers play in digital commerce environments.
H2 also receives strong empirical support, confirming that consistency, authenticity, and high engagement quality in influencer posts enhance marketing effectiveness (IMEFS). These findings are consistent with the findings that emphasized that relatability and authenticity are critical to audience trust and conversion [30,37]. High-quality content, especially when aligned with user interests, significantly boosts the effectiveness of social media campaigns. These outcomes suggest marketers should invest in audience-aligned messaging strategies, leveraging influencers whose personas resonate with their target demographics to drive meaningful engagement.
H3 reveals a dual impact of influencer marketing: while influencer promotions positively impact purchasing decisions, consumers also report fatigue and annoyance when exposed to excessive endorsements. This duality echoes the findings of Antoniou [38], who warned of over-commercialization and its potential to erode brand credibility. Brands must therefore strike a balance between promotion and authentic engagement to avoid alienating their audiences. Transparent communication, limited ad frequency, and relevance to the audience’s interests are essential to mitigating negative sentiment.
The partial confirmation of H4 demonstrates that online shopping satisfaction (OSB-IS) is significantly shaped by category-specific shopping behavior (e.g., health and beauty, apparel), moderated by digital usability and communication clarity. These findings align with studies by López and Giovanidis [35], which underscored the importance of intuitive website design and targeted communication in enhancing the user experience. Businesses must prioritize seamless navigation and personalized offers to meet the expectations of today’s digital consumers. These strategies are essential when targeting younger, digitally native audiences with high usability standards.
H5 is strongly supported, illustrating that trust, preferences, and technological features are key drivers of continued online shopping behavior (OSP-CIS). This aligns with the trust-centric findings [33] and studies by Sánchez Villegas et al. [36], affirming that transparent product representation and peer recommendations significantly influence purchase decisions. Influencer marketing that reinforces product reliability and social proof contributes to higher consumer satisfaction and behavioral consistency. This suggests a shift towards socially mediated commerce, where consumer decisions are shaped by both individual preferences and social validation mechanisms.
The Fuzzy Cognitive Map (FCM) analysis confirms that increases in influencer activity (IAEIS), marketing effectiveness (IMEFS), and influencer-driven impact (IUIS) lead to stronger consumer trust and online shopping engagement. Conversely, a reduction in these elements weakens campaign effectiveness. These results are consistent with the evolving influencer marketing literature, which emphasizes the value of trust, credibility, and targeted content strategies in shaping online consumer engagement [54,67]. The integration of FCM provided a dynamic lens through which interdependencies among influencer marketing variables and consumer behavior were visualized. The outcomes of each scenario were triangulated with empirical findings from the regression analysis, reinforcing the linkage between the modeled causal inferences and real-world behavioral responses of online consumers.
From a theoretical perspective, this study validates the Source Credibility Theory and Elaboration Likelihood Model [66] by demonstrating how influencer trustworthiness and message relevance influence consumer attitudes. It also contributes to the literature on digital marketing strategy, particularly how influencer traits, engagement quality, and platform usability interplay to shape consumer behavior. Practically, it offers actionable guidance to marketers and platform designers, highlighting the importance of selecting credible influencers, personalizing content, and investing in user-centered digital environments.
6. Conclusions
6.1. Theoretical, Practical, and Managerial Implications
This study provides critical insights into the practical and theoretical aspects of influencer marketing and its impact on consumer behavior, offering significant contributions to both academic literature and managerial practices. The findings of this study hold substantial value for businesses seeking to leverage influencer marketing effectively. Influencer marketing has evolved as a key strategy for businesses aiming to enhance brand visibility, consumer engagement, and profitability [68]. This study has highlighted that attributes such as consistency in influencer posts, authentic content, and engagement quality significantly influence the effectiveness of influencer campaigns. These findings are aligned with Masuda et al. [69], who emphasized that influencer authenticity and character traits mediate consumer purchase intentions, reinforcing the importance of selecting relatable influencers to ensure campaign success.
Moreover, the study’s results underline the necessity of balancing promotional activities with engaging and non-intrusive content to address consumer concerns about ad fatigue and perceived annoyance. Nisar and Whitehead [70] argued that social media platforms must focus on fostering meaningful brand interactions to build loyalty. This study complements these findings by demonstrating that engagement quality and trust in influencers are critical factors for sustaining consumer interest, suggesting that businesses should incorporate feedback mechanisms to refine influencer campaigns continually.
While this study focused on Greek consumers, its findings align with global trends in influencer marketing. For instance, Lou and Yuan [71] demonstrated that message value and influencer credibility enhance consumer trust and purchase intentions on social media platforms. Similarly, Garg and Bakshi [72] found that beauty vloggers’ credible attributes, such as trustworthiness and expertise, significantly influence consumer trust and purchase intentions in the Indian context. However, regional differences also emerge. In Southeast Asia, consumers place a high value on influencer authenticity and expertise, but user reviews and peer recommendations often carry more weight than influencer endorsements [73]. These variations underscore the importance of cultural and market-specific factors in shaping the effectiveness of influencer marketing strategies.
The significance of user-friendly digital platforms in shaping consumer purchasing behavior is another critical practical insight. This study reveals that responsive website design, clear navigation, and effective promotional communication are vital for enhancing online shopping satisfaction. This aligns with Moran et al. [74], who found that tailored message content and platform design play pivotal roles in driving user engagement in the media industry. Businesses should therefore invest in optimizing their digital touchpoints to ensure a seamless consumer experience.
From a theoretical perspective, this study expands existing knowledge by integrating various dimensions of influencer marketing and online consumer behavior into a cohesive framework. The validation of hypotheses related to influencer marketing effectiveness (e.g., H1, H3) underscores the multidimensional role of influencers in shaping consumer attitudes and behaviors. This study contributes to the growing literature on digital marketing by emphasizing the interplay between influencer authenticity, content quality, and consumer trust, which are central themes in recent works by Chen et al. [75].
The interconnected nature of influencer impact suggests that brands must adopt strategic influencer selection, maintain content transparency, and optimize engagement metrics to sustain long-term effectiveness [76,77]. Theoretically, this aligns with the Source Credibility Theory, which highlights that an influencer’s expertise, trustworthiness, and attractiveness directly affect audience engagement, as well as the Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM), which suggests that consumers’ process influencer content either rationally or emotionally, influencing purchasing decisions [78].
Practically, brands can implement AI-driven tools to analyze engagement metrics, predict audience behavior, and identify high-performing influencers using machine learning. AI-powered sentiment analysis can help track consumer reactions in real time, allowing brands to refine messaging and optimize content strategies [40]. Additionally, blockchain technology can enhance transparency in influencer marketing, minimizing fraudulent activities such as fake engagement and follower inflation [78]. Long-term businesses should leverage predictive analytics to anticipate consumer behavior trends, ensuring that marketing strategies remain adaptive, personalized, and impactful.
This study offers valuable insights for managers aiming to enhance influencer marketing strategies. Selecting authentic influencers aligned with brand values is essential for building trust and engagement [79]. Managers should balance promotional content with non-intrusive, engaging material to avoid ad fatigue and maintain consumer loyalty [80]. Optimizing digital platforms for user experience—through intuitive design and clear messaging—can further support online engagement [74]. Tools like AI-driven analytics and sentiment tracking can help refine content in real time, while blockchain technologies may improve transparency and reduce fraud in influencer partnerships [81,82]. Overall, a strategic blend of authenticity, personalization, and technological support is key to effective influencer campaigns. Moreover, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can effectively leverage influencer marketing by collaborating with micro-influencers, who typically offer higher engagement at lower costs, and by encouraging user-generated content to extend reach without incurring significant promotional expenses.
Furthermore, this study bridges gaps in the literature regarding consumer heterogeneity and behavioral factors. While earlier research, such as Wijekoon et al. [78], highlighted the need for segmentation strategies based on consumer psychographics, this study adds to this discussion by demonstrating how demographic and behavioral factors influence consumer responses to influencer marketing. These findings highlight the importance of adapting influencer campaigns to align with the preferences of specific consumer segments, paving the way for more personalized and effective marketing strategies [79].
This study also reinforces the theoretical framework of social media marketing as a dynamic and evolving field. By showcasing the role of trust, transparency, and technological advancements in shaping online consumer behavior, it complements the work of Mallipeddi et al. [80], who developed frameworks for optimizing influencer selection. This study’s emphasis on practical factors, such as usability and clear communication, provides a broader perspective on how digital marketing strategies [80] can be refined to align with evolving consumer expectations.
Marketers and businesses should prioritize partnering with authentic influencers whose values align with their brand, as authenticity significantly boosts consumer trust and engagement. Content should be engaging yet non-intrusive to avoid ad fatigue, while digital platforms must offer user-friendly experiences through responsive design and clear messaging. Employing AI tools for real-time sentiment analysis and engagement tracking can refine campaigns dynamically, while blockchain technologies can enhance transparency and combat fake metrics. For policymakers, developing and enforcing clear guidelines around influencer disclosure and ethical practices is essential to ensure consumer protection and credibility in digital advertising ecosystems.
6.2. Limitations and Future Research Directions
Despite its contributions, this study is not without limitations. One primary limitation is the cross-sectional nature of the research design, which restricts the ability to examine long-term consumer behavior trends [82]. Longitudinal studies could provide deeper insights into the evolving dynamics of influencer marketing and its sustained impact on consumer loyalty and profitability. Additionally, while this study emphasized the role of demographic and behavioral factors, it did not fully explore the influence of cultural contexts, which is critical in the globalized digital marketplace. Future research should address this gap by examining how cultural differences shape consumer perceptions and responses to influencer marketing, as suggested by Pop et al. [83]. Moreover, the analysis does not differentiate between types of influencers (e.g., micro vs. macro), nor does it investigate how emerging technologies such as virtual influencers and AI-driven content shape marketing outcomes—both of which offer promising directions for future inquiry. Finally, as with many studies involving user feedback, there is a risk of self-reported data being influenced by social desirability bias, which may affect the accuracy of consumer perceptions and engagement metrics; future research could mitigate this by incorporating behavioral tracking or triangulating with platform analytics.
Furthermore, while this study identified key predictors of online shopping behavior, it did not delve deeply into the technological advancements shaping these trends, such as the use of AI and machine learning in personalizing consumer experiences. Apart from that, the authors did not apply cross-validation techniques such as train/test splitting, as the primary aim was exploratory rather than predictive. However, future research could enhance result robustness and generalizability by employing cross-validation methods, as recommended by Kuhn and Johnson [84] as well as Hastie et al. [85]. Exploring these aspects could offer valuable insights into the future trajectory of digital marketing strategies [82]. Future studies should also investigate the ethical dimensions of influencer marketing, including disclosure practices, influencer authenticity, and consumer protection, which remain underexplored in the current research. Furthermore, future research should explore platform-specific dynamics by comparing how features unique to Instagram, TikTok, or YouTube, such as Stories, Reels, and live streaming, shape user engagement and purchasing behavior. Such a comparative platform analysis would help isolate design-driven influences on consumer response. Additionally, adopting longitudinal or experimental research designs could enhance causal inference and offer deeper insights into the sustained impact of influencer marketing on loyalty and behavioral change.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.P.M., N.T.G. and D.P.S.; methodology, S.P.M., N.T.G. and D.P.S.; software, S.P.M., N.T.G. and D.P.S.; validation, S.P.M., N.T.G. and D.P.S.; formal analysis, S.P.M., N.T.G. and D.P.S.; investigation, S.P.M., N.T.G. and D.P.S.; resources, S.P.M., N.T.G. and D.P.S.; data curation, S.P.M., N.T.G. and D.P.S.; writing—original draft preparation, S.P.M., N.T.G. and D.P.S.; writing—review and editing, S.P.M., N.T.G. and D.P.S.; visualization, S.P.M., N.T.G. and D.P.S.; supervision, S.P.M., N.T.G. and D.P.S.; project administration, S.P.M., N.T.G. and D.P.S.; funding acquisition, S.P.M., N.T.G. and D.P.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of Agricultural University of Athens.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data available in a publicly accessible repository: https://thyme.dbbee.com/dashboard/Collect.wbsp?ProjectName=Project_696HC (accessed on 29 November 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
Demographics Visualization
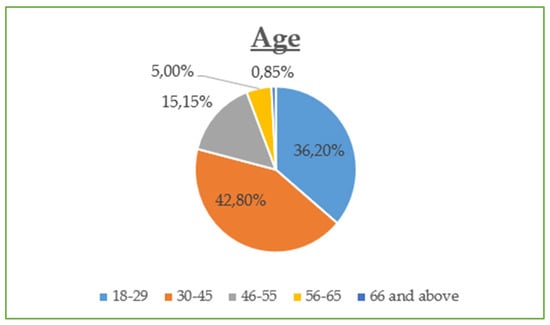
Figure A1.
Age.
Figure A1.
Age.
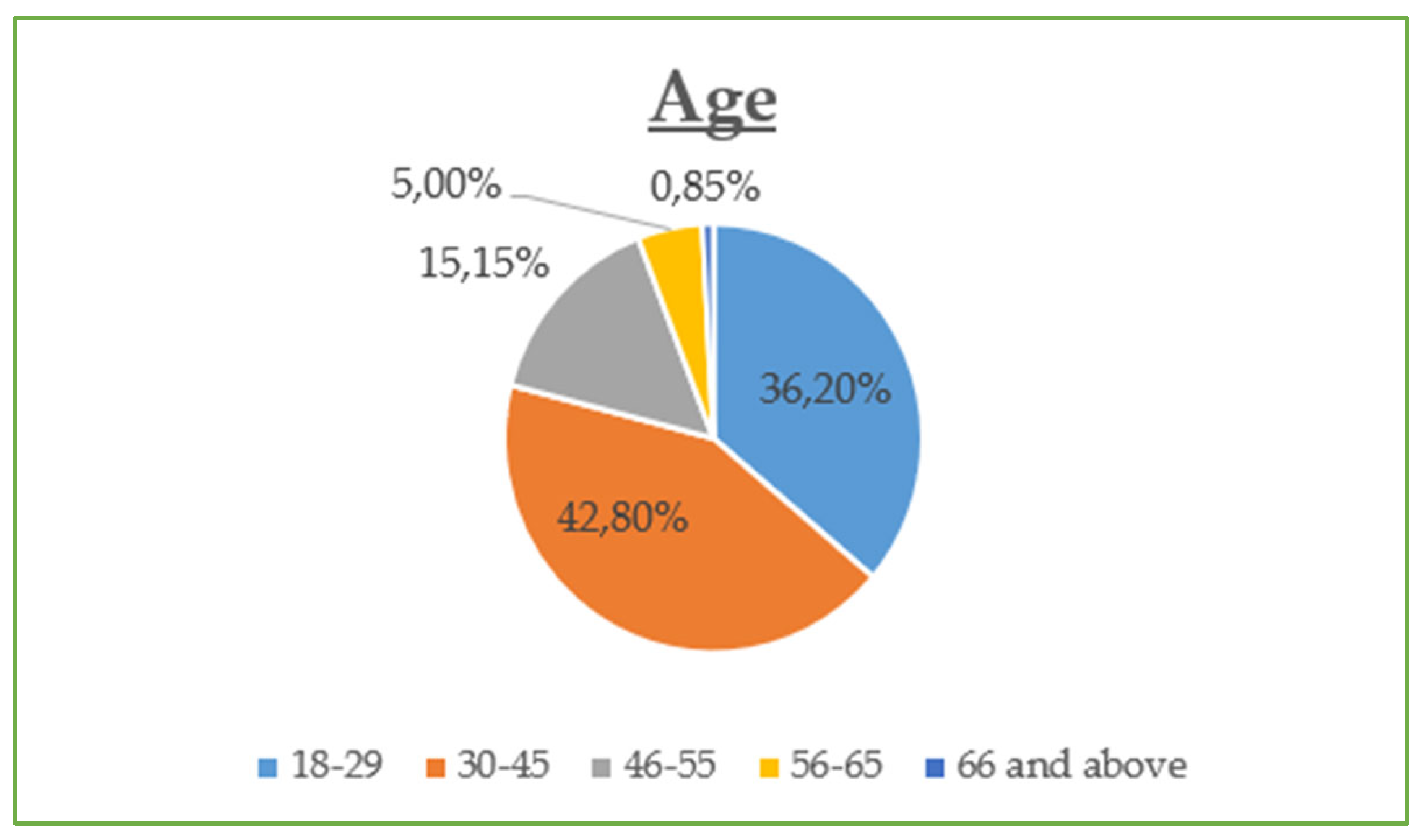
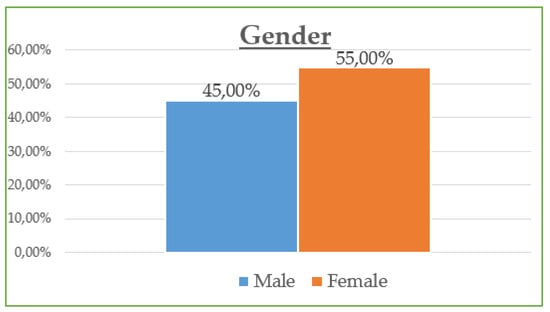
Figure A2.
Gender.
Figure A2.
Gender.
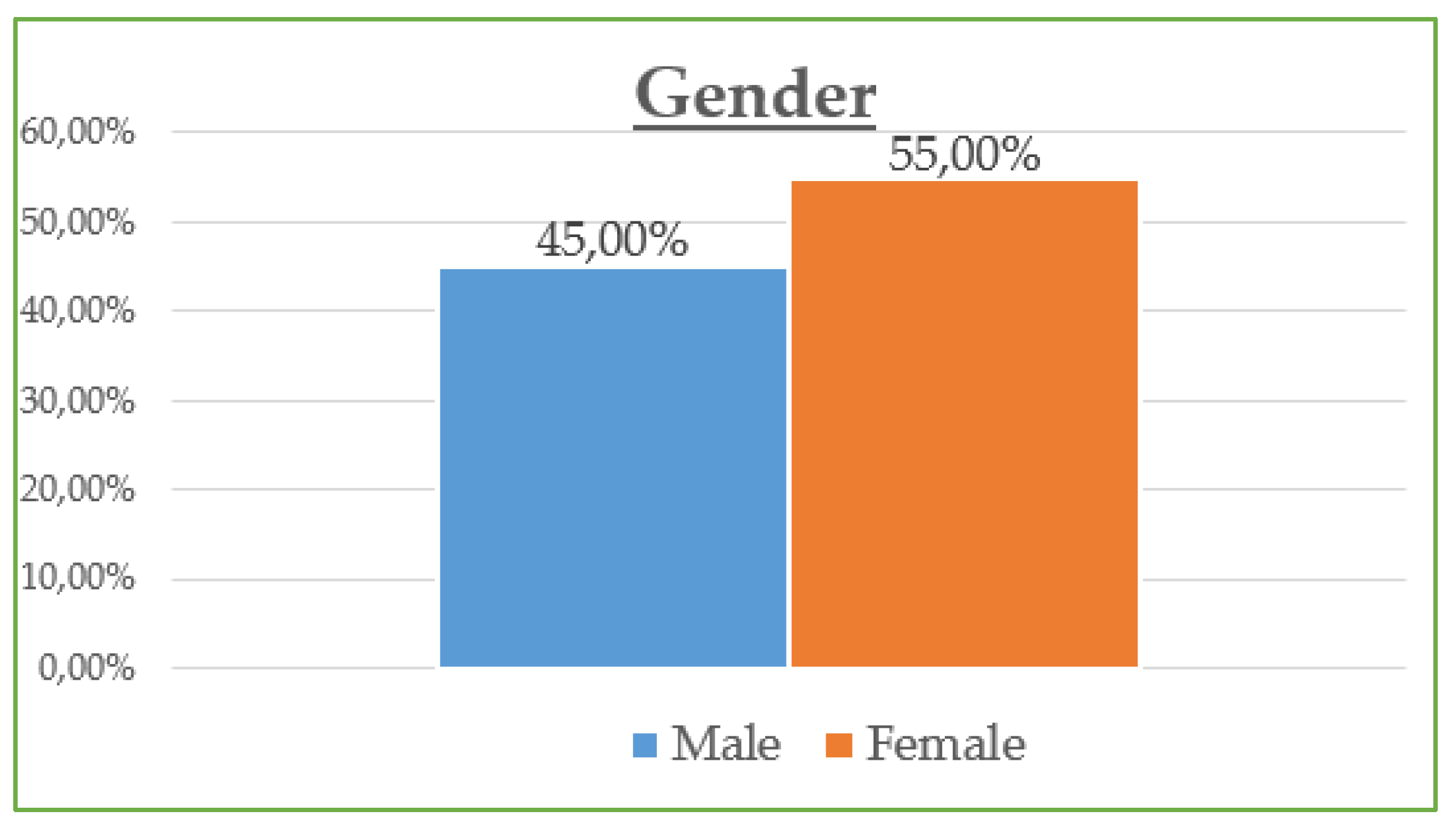
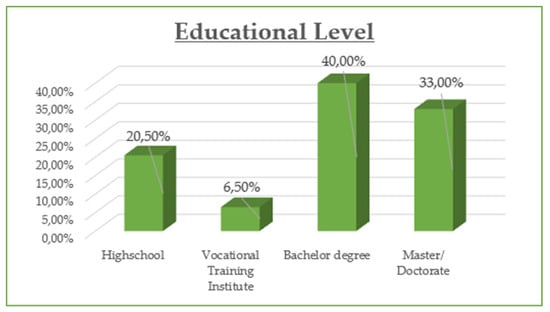
Figure A3.
Education level.
Figure A3.
Education level.
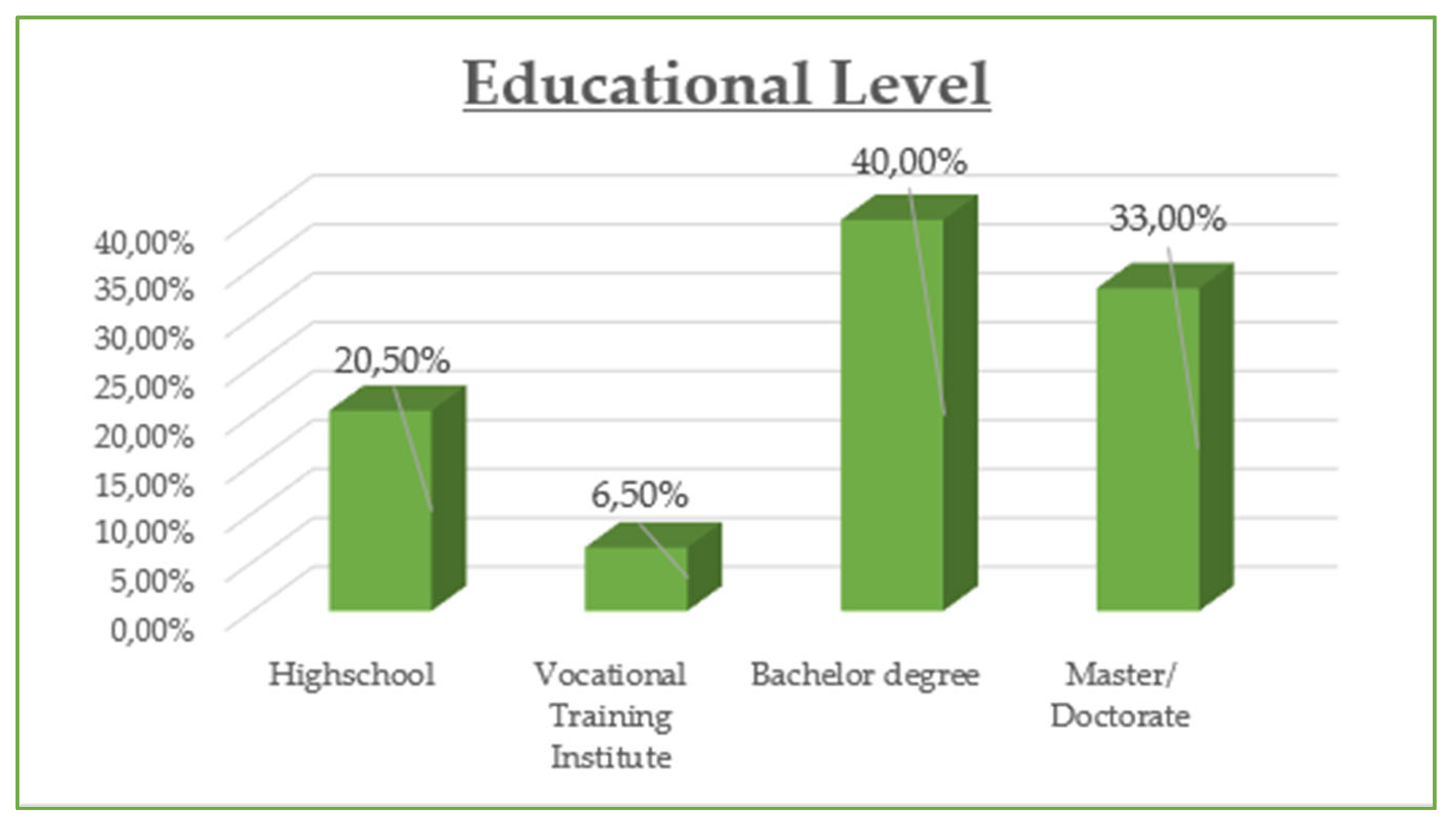
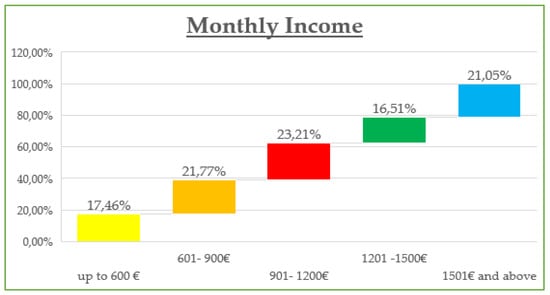
Figure A4.
Monthly income.
Figure A4.
Monthly income.
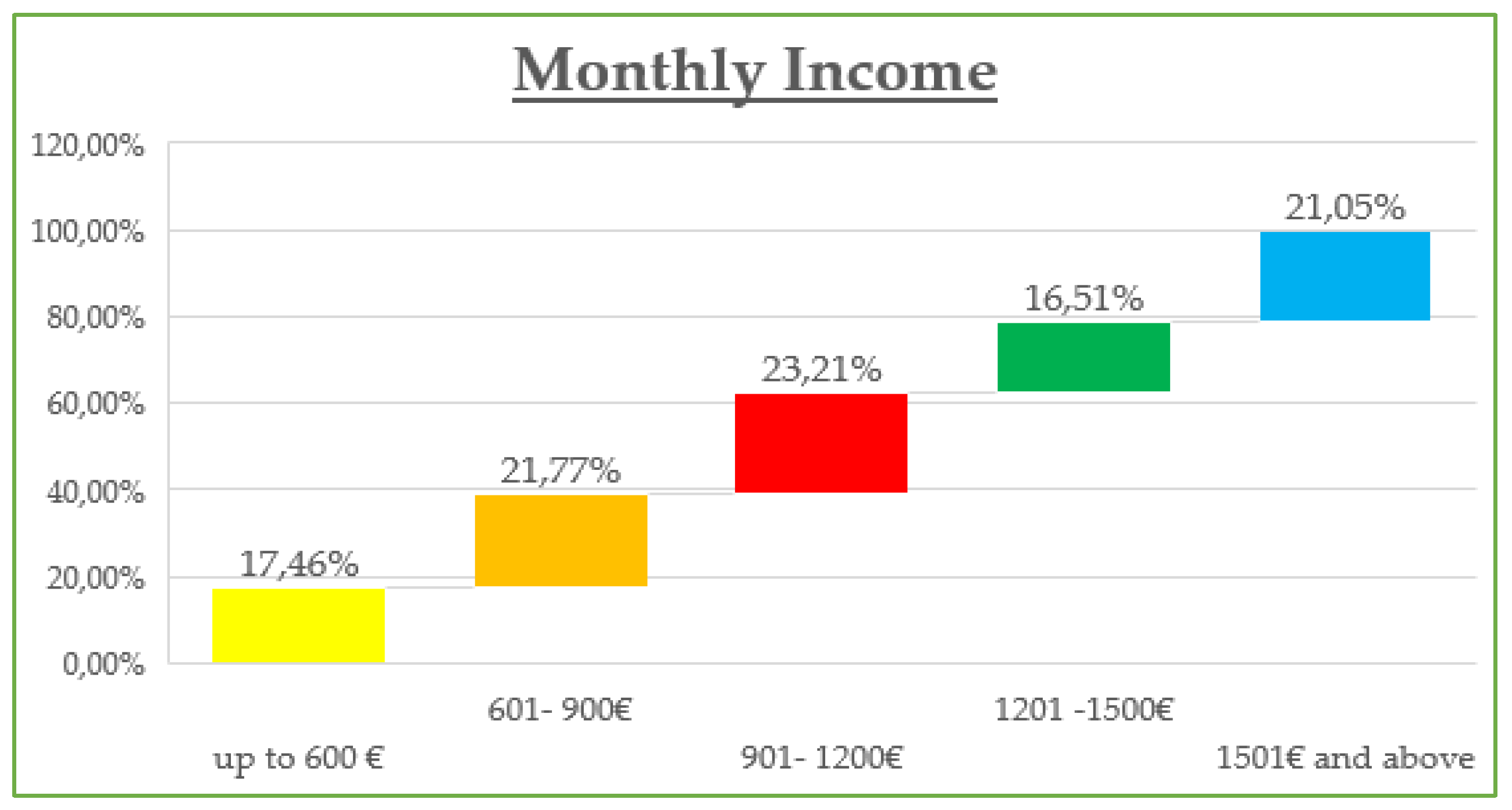
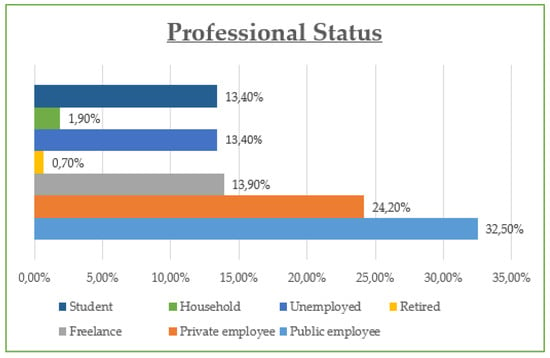
Figure A5.
Professional status.
Figure A5.
Professional status.
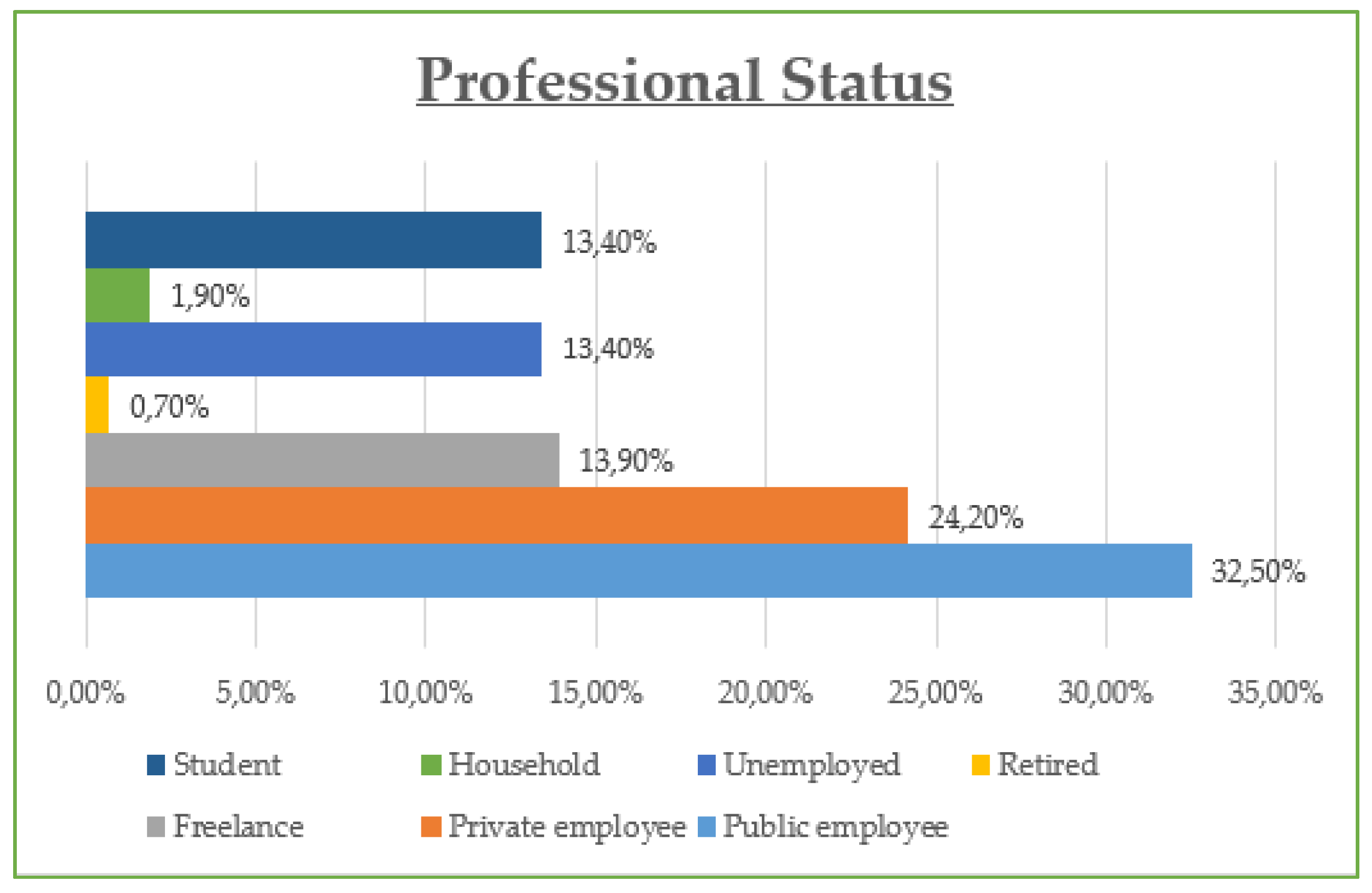
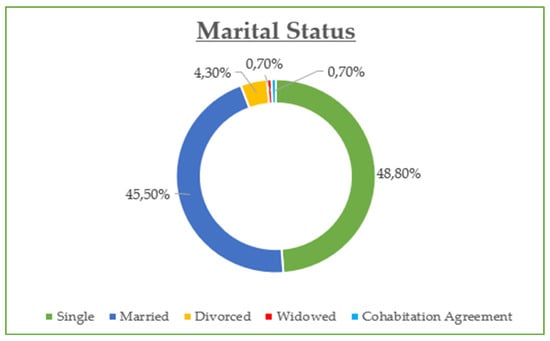
Figure A6.
Marital status.
Figure A6.
Marital status.
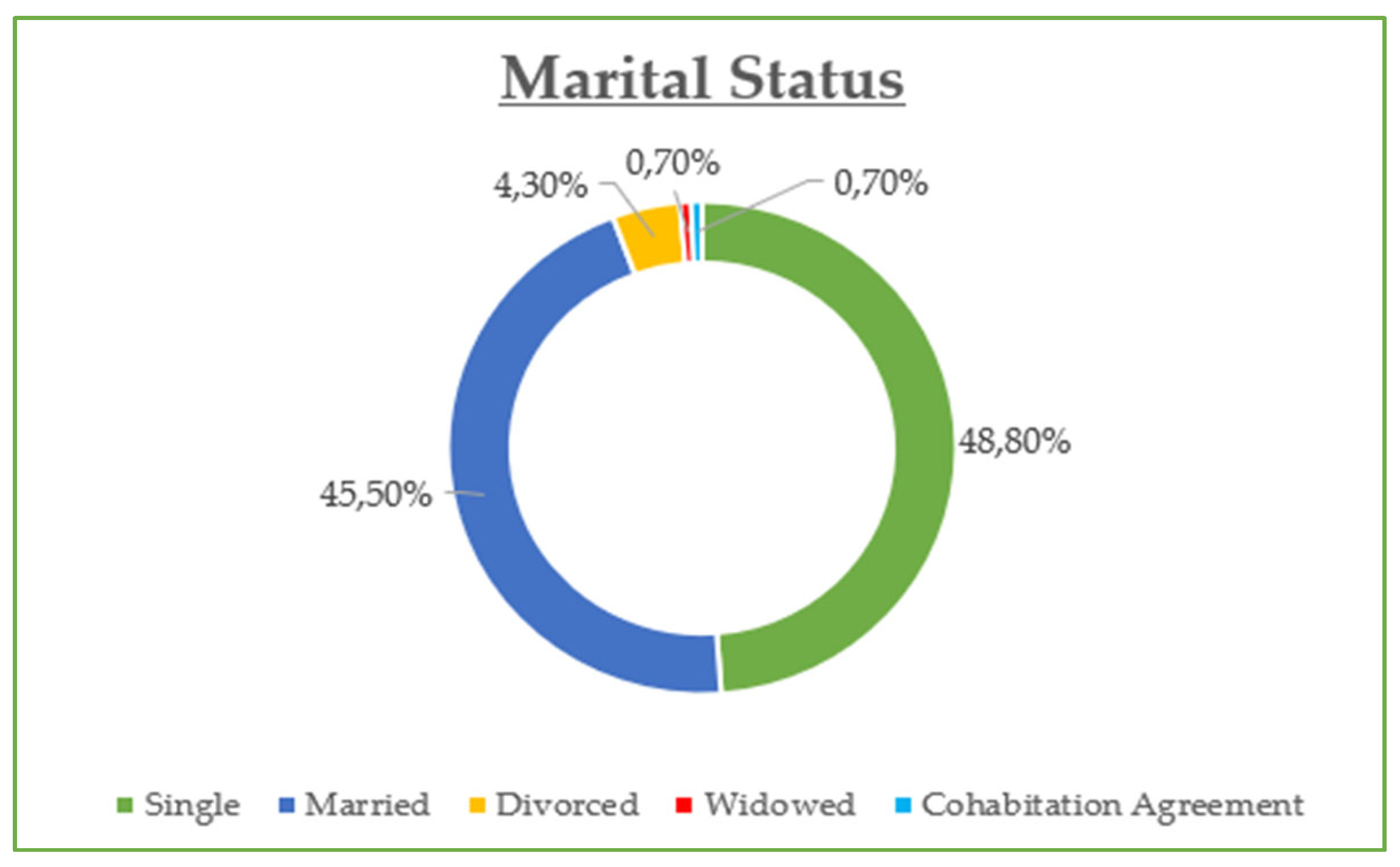
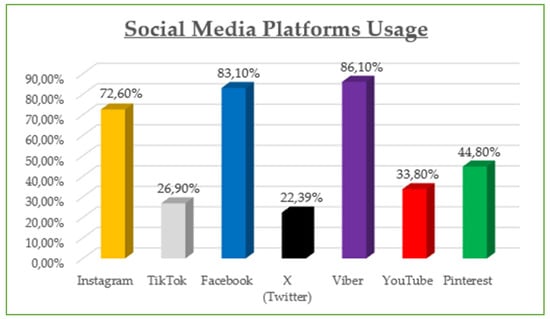
Figure A7.
Social media platform usage.
Figure A7.
Social media platform usage.
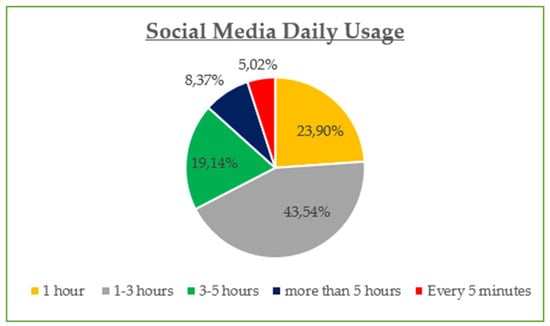
Figure A8.
Social media daily usage.
Figure A8.
Social media daily usage.
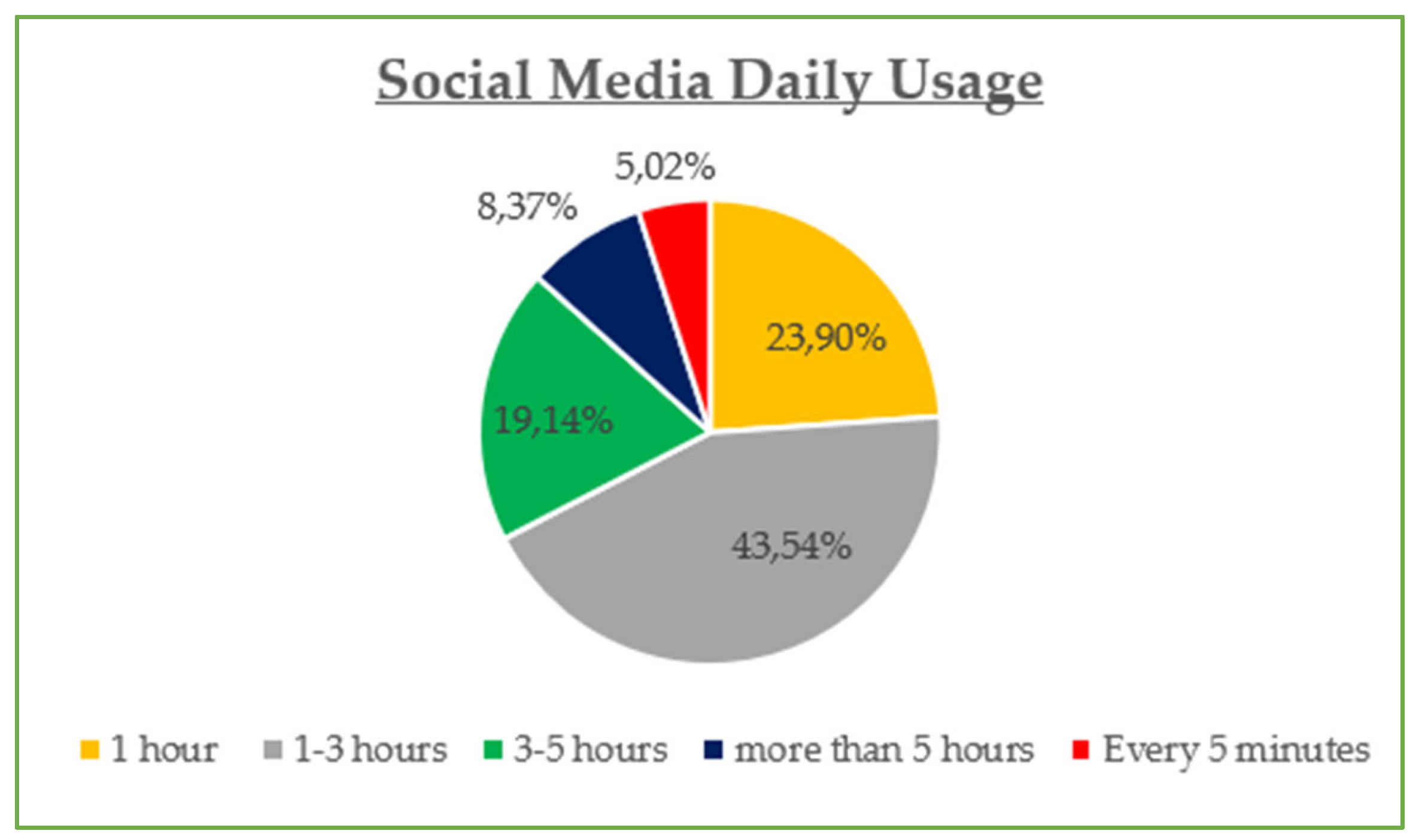
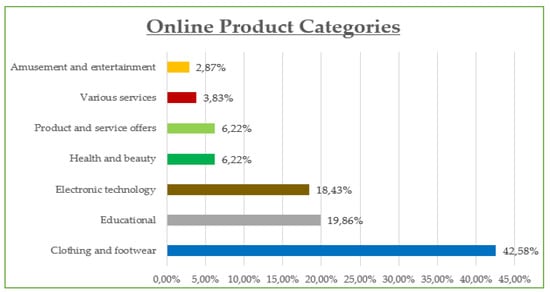
Figure A9.
Online search by product categories.
Figure A9.
Online search by product categories.
Appendix B
Questionnaire
Section 1—The Role of Digital Marketing through Social Media
- Do you schedule through social media, personal, or business appointments?
1—Strongly Disagree 2—Disagree 3—I neither disagree/nor agree 4—Agree 5—Strongly Agree
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Strongly Disagree | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | Strongly Agree |
- 2.
- In your professional or academic occupation, have influencer ads helped you through product promotion?
1—Strongly Disagree 2—Disagree 3—I neither disagree/nor agree 4—Agree 5—Strongly Agree
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Strongly Disagree | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | Strongly Agree |
- 3.
- Do businesses impact your purchases through influencers?
1—Strongly Disagree 2—Disagree 3—I neither disagree/nor agree 4—Agree 5—Strongly Agree
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Strongly Disagree | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | Strongly Agree |
- 4.
- Does the promotion of products and services through influencer marketing increase business sales?
1—Strongly Disagree 2—Disagree 3—I neither disagree/nor agree 4—Agree 5—Strongly Agree
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Strongly Disagree | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | Strongly Agree |
- 5.
- Have you bought something you saw in influencer ads?
1—Strongly Disagree 2—Disagree 3—I neither disagree/nor agree 4—Agree 5—Strongly Agree
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Strongly Disagree | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | Strongly Agree |
- 6.
- Are influencer ads annoying?
1—Strongly Disagree 2—Disagree 3—I neither disagree/nor agree 4—Agree 5—Strongly Agree
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Strongly Disagree | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | Strongly Agree |
- 7.
- What factors are important for a business using influencer marketing? Choose only one answer.
1—not important at all
2—little important
3—not much either
4—very important
5—very important
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Consistency and regularity of posts | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| Post Content | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| Customer engagement (customer service) | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| Online Offers | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
- 8.
- Do you shop through influencer marketing ads?
□ YES
□ NO
- 9.
- If businesses integrate influencer activity into their marketing, will they achieve better financial results and customer loyalty?
□ YES
□ NO
- 10.
- Do you think influencer marketing is the best way for businesses to reach a targeted audience?
□ YES
□ NO
- 11.
- Do you keep up with sales and product promotions through influencer ads?
□ YES
□ NO
- 12.
- Have you ever benefited from a sale or purchase of a product that you saw or learned about through influencer ads?
□ YES
□ NO
- 13.
- Which of the following actions do you perform the most? Choose for each row only one answer.
1—not at all 2—a little 3—neither a little nor a lot 4—a lot 5—a lot
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| I open commercial ads from influencers that appear | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| I pay attention to what is offered from influencer ads | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| Influencer ads are relevant to my interests | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| Ads play a role for me in my purchases | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| I buy products I have seen advertised on social media | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| I buy products that I have seen on influencer profiles | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| I follow influencers to keep up to date with new products and offers | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| I invite friends to take advantage of offers I receive | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| Recommend friends to buy products shown through influencer ads | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| I like posts from companies that feature products or offers through influencers | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
- 14.
- Which category of products and ads promoted by influencers are you most interested in? Choose only one answer.
□ Electronic technology products
□ Various Services
□ Product and service offers
□ Clothing and footwear
□ Fun and Entertainment
□ Health and Beauty
□ Education
Section 2—Consumer Behavior and Digital Marketing
- 15.
- What reasons influenced you to increase online shopping from e-stores?
1—not at all 2—a little 3—neither a little nor a lot 4—a lot 5—a lot
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Because of the fear of contact with the virus | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| Due to store offers | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| Because of influencer ads | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| Due to the restrictive measures | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| Because of the influencers/celebrities who got something online | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| Due to the discounts or promotions of shops | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
- 16.
- In which product–service category did your purchases increase the most? (one answer).
□ Electronic technology products
□ Product and service offers
□ Clothing and footwear
□ Various Services
□ Fun and Entertainment
□ Health and Beauty
□ Education
- 17.
- What influenced you the most in your purchase? (one answer).
□ The name of the store and its reputation
□ The previous customer reviews
□ The wide variety of products and services
□ The good prices of products and services
□ The fast and immediate delivery of the products
□ The good and friendly format of the shopping site and easy navigation
Section 3—The consumer’s attitude towards e-marketing through e-shops
- 18.
- Are you concerned that the product you ordered from the online store was not as expected according to its descriptions and promotional images?
□ not at all □ a little □ neither much nor a little □ much □ too much
- 19.
- Is online shopping preferable to physical shopping? Choose for each row only one answer.
1—Strongly Disagree 2—Disagree 3—I neither disagree/nor agree 4—Agree 5—Strongly Agree
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Yes, because I don’t have to go from there | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| Yes, I don’t have to wait in line at the checkout | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| Yes, I don’t have to wait in line when entering | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| Yes, I appreciate the convenience of online shopping | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| Yes, online shopping takes less time than yes I visit a store | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| No, it is inconvenient to wait at home for delivery | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| Yes, I don’t need to go to the store | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
- 20.
- Intention and consumer behavior. Choose for each row only one answer.
1—Strongly Disagree 2—Disagree 3—I neither disagree/nor agree 4—Agree 5—Strongly Agree
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| I will recommend the online stores to anyone they ask my opinion | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| I am positive about online shopping | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| Online shopping is my first preference now in markets | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| I encourage friends and family to buy from e-stores | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
| The next period of months and years continue to buy online | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ |
Section 4—Demographics
The data taken as demographics are respondents’ gender, age group, educational level, marital status, employment status, monthly family income, and social media usage.
- 21.
- Gender.
□ Man
□ Woman
- 22.
- Age.
□ 18–29
□ 30–45
□ 46–55
□ 56–65
□ 66 and above
- 23.
- Educational Level.
□ Primary School graduate
□ Middle School graduate
□ High School Graduate
□ Vocational Training Institute
□ Bachelor Degree
□ Master/Doctorate
- 24.
- Marital Status.
□ Single
□ Married
□ Divorced
□ Widowed
□ Cohabitation Agreement
- 25.
- Professional status.
□ Public employee
□ Private employee
□ Freelance
□ Retired
□ Unemployed
□ Household
□ Student
- 26.
- Monthly Family Income.
□ up to 600 €
□ 601–900€
□ 901–1200€
□ 1201–1500€
□ 1501€ and above
- 27.
- Which social media account do you have? (multiple answers).
□ Instagram
□ TikTok
□ Facebook
□ Twitter
□ Viber
□ YouTube
□ Pinterest
- 28.
- How often do you use them daily?
□ 1 h
□ 1–3 h
□ 3–5 h
□ more than 5 h
□ I check them almost every 5 min
References
- Armstrong, G. Marketing: An Introduction; Pearson Education: Winston-Salem, NC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Larimo, J.; Leonidou, L.C. Social media marketing strategy: Definition, conceptualization, taxonomy, validation, and future agenda. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2021, 49, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrontis, D.; Makrides, A.; Christofi, M.; Thrassou, A. Social media influencer marketing: A systematic review, integrative framework and future research agenda. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2021, 45, 617–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapitan, S.; Van Esch, P.; Soma, V.; Kietzmann, J. Influencer marketing and authenticity in content creation. Australas. Mark. J. 2022, 30, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, H.; Cervera, A.; Molla, A. Brand assessment: A key element of marketing strategy. J. Prod. Brand Manag. 1997, 6, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudel, R. Sustainable consumer behavior. Consum. Psychol. Rev. 2019, 2, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, L.M.; Tang, T. Strategic Social Media: From Marketing to Social Change; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ardley, B.; Craig, C.; Hunt, A.; May, C. Product endorsements on instagram: Consumer perceptions of influencer authenticity. Open J. Bus. Manag. 2022, 10, 1196–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdi, B.A.; Alshurideh, M.; Akour, I.; Tariq, E.; AlHamad, A.; Alzoubi, H. The effect of social media influencers’ characteristics on consumer intention and attitude toward Keto products purchase intention. Int. J. Data Netw. Sci. 2022, 6, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffey, D.; Ellis-Chadwick, F. Digital Marketing; Pearson: Harlow, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Adesokan, A.; Rahman, A.B.; Tsiropoulou, E.E. INFLUTRUST: Trust-Based Influencer Marketing Campaigns in Online Social Networks. Future Internet 2024, 16, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, K.; Rajagopal, P.; Kulow, K. Unfaithful brands: How brand attachment can lead to negative responses to influencer marketing campaigns. J. Consum. Psychol. 2024, 00, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Ren, P.; Tang, M. How Social Media as a Digital Marketing Strategy Influences Chinese Students’ Decision to Study Abroad in the United States: A Model Analysis Approach. J. Linguist. Educ. Res. 2024, 6, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.V.; Kim, S.; Chakravarty, A. Influence of pull marketing actions on marketing action effectiveness of multichannel firms: A meta-analysis. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2023, 51, 310–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, B. Contemporary Trends in Innovative Marketing Strategies; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Azhar, M.; Akhtar, M.J.; Rahman, M.N.; Khan, F.A. Measuring buying intention of generation Z on social networking sites: An application of social commerce adoption model. J. Econ. Adm. Sci. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Baek, T.H. Are virtual influencers friends or foes? Uncovering the perceived creepiness and authenticity of virtual influencers in social media marketing in the United States. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2024, 40, 5042–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Rayne, D.; Salo, J.; Yiu, C.S. Battle of influence: Analysing the impact of brand-directed and influencer-directed social media marketing on customer engagement and purchase behaviour. Australas. Mark. J. 2025, 33, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beichert, M.; Bayerl, A.; Goldenberg, J.; Lanz, A. Revenue generation through influencer marketing. J. Mark. 2024, 88, 40–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.H.; Hung, K.; Tse, D.K. Comparing E-Commerce Micro-and Macroinfluencers in TikTok Videos: Effects of Strategies on Audience Likes, Audience Shares, and Brand Sales. J. Interact. Advert. 2023, 23, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibawa, R.C.; Pratiwi, C.P.; Larasati, H. The role of nano influencers through Instagram as an effective digital marketing strategy. In Proceedings of the Conference Towards ASEAN Chairmanship 2023 (TAC 23 2021), Bogor, Indonesia, 13–15 December 2021; Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2021; pp. 223–233. [Google Scholar]
- Gamarra, G.; Dias, Á.L.; Pereira, L.F. The influence of social and environmental responsibility on customer-based brand equity. Prog. Ind. Ecol. Int. J. 2024, 17, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Shalini. Influencer Marketing Evolution: Unveiling the Power of Data Analytics and AI for Strategic Campaign Excellence. In Advances in Data Analytics for Influencer Marketing: An Interdisciplinary Approach. Information Systems Engineering and Management; Dutta, S., Rocha, Á., Dutta, P.K., Bhattacharya, P., Singh, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 9, pp. 125–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, C.W.; Chow, T.C.; Li, C. Bridging the trust gap in influencer marketing: Ways to sustain consumers’ trust and assuage their distrust in the social media influencer landscape. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2023, 39, 3445–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, C.F.; Ferreira, A.G.; Cardoso, R.M. The influence of storytelling on the consumer–brand relationship experience. J. Mark. Anal. 2023, 11, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, L.R.; Helveston, M.; Robinson, Z. Influencer Speech-Torts. Marquette Law Sch. Leg. Stud. Pap. Georget. Law J. 2024, 24, 2–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Dutta, P.K.; Kaunert, C. Online User Choices Data Analytics and Privacy in Digital Marketing: Legal-Ethical Landscapes in the Digital-Futuristic Arena Projecting Multiple Layers of Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain. In Advances in Data Analytics for Influencer Marketing: An Interdisciplinary Approach. Information Systems Engineering and Management; Dutta, S., Rocha, Á., Dutta, P.K., Bhattacharya, P., Singh, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 9, pp. 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duivenvoorde, B.; Goanta, C. The regulation of digital advertising under the DSA: A critical assessment. Comput. Law Secur. Rev. 2023, 51, 105870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, L.; Fan, W. Cost-effective social media influencer marketing. Inf. J. Comput. 2023, 35, 138–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudders, L.; De Jans, S. Gender effects in influencer marketing: An experimental study on the efficacy of endorsements by same-vs. other-gender social media influencers on Instagram. Int. J. Advert. 2022, 41, 128–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Peng, Y. Influencer marketing: Purchase intention and its antecedents. Mark. Intell. Plan. 2021, 39, 960–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, E.C.X.; Agnihotri, R. Influencer marketing research: Review and future research agenda. J. Mark. Theory Pract. 2024, 32, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Yan, R. LLM-Driven Agents for Influencer Selection in Digital Advertising Campaigns. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.15105. [Google Scholar]
- Doshi, R.; Ramesh, A.; Rao, S. Modeling influencer marketing campaigns in social networks. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2022, 10, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Dawn, R.; Giovanidis, A. Optimal Influencer Marketing Campaign Under Budget Constraints Using Frank-Wolfe. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Villegas, D.; Goanta, C.; Aletras, N. A Multimodal Analysis of Influencer Content on Twitter. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.03064. [Google Scholar]
- Cheah, C.W.; Koay, K.Y.; Lim, W.M. Social media influencer over-endorsement: Implications from a moderated-mediation analysis. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2024, 79, 103831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, A. When likes go rogue: Advertising standards and the malpractice of unruly social media influencers. J. Media Law 2024, 16, 74–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Wamba, S.F.; Gunasekaran, A.; Dubey, R.; Childe, S.J. How to improve firm performance using big data analytics capability and business strategy alignment? Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 182, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffey, D.; Smith, P.R. Digital Marketing Excellence: PLANNING, Optimizing and Integrating Online Marketing; Routledge: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, A.; Kumar, A.; Kant, R.; Jaiswal, D. Impact of fashion influencers on consumers’ purchase intentions: Theory of planned behaviour and mediation of attitude. J. Fash. Mark. Manag. 2024, 28, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Kapoor, D.; Gupta, R. Role of influencer–follower congruence in influencing followers’ food choices and brand advocacy: Mediating role of perceived trust. Br. Food J. 2024, 126, 4055–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B.; Kishore, K.; Gokhale, N. Social media influencers and consumer engagement: A review and future research agenda. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2023, 47, 2106–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallevig, A. The Distributed Creative Brand Image: Integrating Digital Influencer Collaboration into Omnichannel Marketing Communication. In Digital Transformation for Fashion and Luxury Brands: Theory and Practice; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 249–270. [Google Scholar]
- Rachmad, Y.E. The Future of Influencer Marketing: Evolution of Consumer Behavior in the Digital World; PT. Sonpedia Publishing: Jambi, Indonesia, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, K.; Dua, S.; Gupta, P. Revolutionizing Influencer Marketing: Harnessing the Power of Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI). In Advances in Data Analytics for Influencer Marketing: An Interdisciplinary Approach; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 41. [Google Scholar]
- Kotler, P.; Pfoertsch, W.; Sponholz, U. H2H Marketing: The Genesis of Human-to-Human Marketing; Haas, M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, P.Y.; Koseoglu, M.A.; Qi, L.; Liu, E.C.; King, B. The sway of influencer marketing: Evidence from a restaurant group. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2021, 98, 103022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozuem, W.; Willis, M. Influencer marketing. In Digital Marketing Strategies for Value Co-Creation: Models and Approaches for Online Brand Communities; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 209–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellman, M.L.; Stoldt, R.; Tully, M.; Ekdale, B. Ethics of authenticity: Social media influencers and the production of sponsored content. J. Media Ethics 2020, 35, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.; Farrell, J.R. More than meets the eye: The functional components underlying influencer marketing. Bus. Horiz. 2020, 63, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.S.; Sihi, D.; Muzellec, L. Implementing Big Data Analytics in Marketing Departments: Mixing Organic and Administered Approaches to Increase Data-Driven Decision Making. Informatics 2021, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharis, D.; Papaioannou, E. Consumers’ responses on the emergence of influencer marketing in Greek market place. Int. J. Technol. Mark. 2020, 14, 283–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ariza, A.; Ruiz, J.R.; de la Torre-Cruz, M.; Latorre-Román, P.; Martínez-López, E.J. Influencia del nivel de atracción hacia la actividad física en el rendimiento académico de los adolescentes. Rev. Latinoam. De Psicol. 2016, 48, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrassia, M.; Altamore, L.; Columba, P.; Raffermati, S.; Lo Grasso, G.; Bacarella, S.; Chironi, S. Mediterranean Diet, Sustainability, and Tourism—A Study of the Market’s Demand and Knowledge. Foods 2023, 12, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzigeorgiou, C. Modelling the impact of social media influencers on behavioural intentions of millennials: The case of tourism in rural areas in Greece. J. Tour. Herit. Serv. Mark. 2017, 3, 25–29. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3747699 (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Fraculj, M.; Antolović, K.; Pale, D. Influencer Marketing as a Contemporary Tool in Brand Promotion. Oeconomicus 2021, 16, 49. Available online: https://openurl.ebsco.com/EPDB%3Agcd%3A10%3A30584426/detailv2?sid=ebsco%3Aplink%3Ascholar&id=ebsco%3Agcd%3A149517504&crl=c&link_origin=scholar.google.com (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Humprecht, E.; Esser, F.; Van Aelst, P. Resilience to Online Disinformation: A Framework for Cross-National Comparative Research. Int. J. Press/Politics 2020, 25, 493–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Hair, J.F. Partial least squares structural equation modeling. In Handbook of Market Research; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 587–632. [Google Scholar]
- Shmueli, G.; Ray, S.; Estrada, J.M.V.; Chatla, S.B. The elephant in the room: Predictive performance of PLS models. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 4552–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, N.; Kadilar, C. Ratio and product estimators in stratified random sampling. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2009, 139, 2552–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lance, C.E.; Butts, M.M.; Michels, L.C. The sources of four commonly reported cutoff criteria what did they really say? Organizational Research Methods 2006, 9, 202–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ary, D.; Jacobs, L.; Sorensen, C.; Walker, D. Introduction to Research in Education. Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kosko, B. Fuzzy cognitive maps. Int. J. Man-Mach. Stud. 1986, 24, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, E.I.; Salmeron, J.L. Methods and algorithms for fuzzy cognitive map-based modeling. In Fuzzy Cognitive Maps for Applied Sciences and Engineering: From Fundamentals to Extensions and Learning Algorithms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Stach, W.; Kurgan, L.; Pedrycz, W.; Reformat, M. Genetic learning of fuzzy cognitive maps. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2005, 153, 371–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, S. How digitalized interactive platforms create new value for customers by integrating B2B and B2C models? An empirical study in China. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 142, 694–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, S.; Tanton, S. Valuable Content Marketing: How to Make Quality Content Your Key to Success. Kogan Page Publishers: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, H.; Han, S.H.; Lee, J. Impacts of influencer attributes on purchase intentions in social media influencer marketing: Mediating roles of characterizations. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 174, 121246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, T.M.; Whitehead, C. Brand interactions and social media: Enhancing user loyalty through social networking sites. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 62, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, C.; Yuan, S. Influencer Marketing: How Message Value and Credibility Affect Consumer Trust of Branded Content on Social Media. J. Interact. Advert. 2019, 19, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, M.; Bakshi, A. Exploring the impact of beauty vloggers’ credible attributes, parasocial interaction, and trust on consumer purchase intention in influencer marketing. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 2024, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mili.eu. Unveiling the World of Influencer Marketing in Southeast Asia: From Follower Trends to Deinfluencers. 2023. Available online: https://www.mili.eu/sg/insights/unveiling-the-world-of-influencer-marketing-in-southeast-asia-from-follower-trends-to-deinfluencers (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Moran, G.; Muzellec, L.; Johnson, D. Message content features and social media engagement: Evidence from the media industry. J. Prod. Brand Manag. 2020, 29, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qin, Z.; Yan, Y.; Huang, Y. The Power of Influencers: How Does Influencer Marketing Shape Consumers’ Purchase Intentions? Sustainability 2024, 16, 5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, R.E.; Cacioppo, J.T.; Petty, R.E.; Cacioppo, J.T. The Elaboration Likelihood Model of Persuasion; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Byoung-Goo, K.I.M. A Study on the Change and Development Strategies of E-Commerce Industry in China. J. Ind. Distrib. Bus. 2024, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijekoon, A.; Salunke, S.; Athaide, G.A. Customer heterogeneity and innovation-based competitive strategy: A review, synthesis, and research agenda. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2021, 38, 315–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, J.; Weinstein, A. Business psychographics revisited: From segmentation theory to successful marketing practice. J. Mark. Manag. 2009, 25, 315–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallipeddi, R.R.; Kumar, S.; Sriskandarajah, C.; Zhu, Y. A framework for analyzing influencer marketing in social networks: Selection and scheduling of influencers. Manag. Sci. 2022, 68, 75–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.A.; Weiss, A.M.; Stewart, D.W. Marketing Champions: Practical Strategies for Improving Marketing’s Power, Influence, and Business Impact; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, D.; Bratton, S.; McKee, J. Social Media Marketing; AG Printing & Publishing: Embakasi, Nairobi, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pop, R.A.; Săplăcan, Z.; Dabija, D.C.; Alt, M.A. The impact of social media influencers on travel decisions: The role of trust in consumer decision journey. Curr. Issues Tour. 2022, 25, 823–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Johnson, K. Applied Predictive Modeling; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J.H.; Friedman, J.H. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).