- Article
Exploring the Potential of Transdermal Nanobilosomal Gel for Magnified Anti-Inflammatory Efficacy of Thymol for Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Deepti Tripathi,
- Ranjit Singh and
- Gul Naz Fatima
- + 2 authors
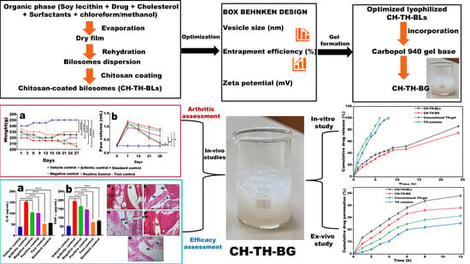
This research aims to develop a chitosan-coated, TH-loaded nanobilosomal gel (CH-TH-BG) to magnify the transdermal delivery and anti-inflammatory efficacy of thymol (TH) for the management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Initially, chitosan-coated, TH-loaded bilosomes (CH-TH-BLs) were prepared and optimized by Box–Behnken design. The optimized CH-TH-BLs exhibited enhanced entrapment efficiency (83.52%) and a positive zeta potential (+36.3 mV). Further, the optimized lyophilized CH-TH-BLs were incorporated into the carbopol gel (CH-TH-BG) and characterized thoroughly. The CH-TH-BG exhibited superior pharmaceutical properties, including high drug content (98.65 ± 1.43%), optimal viscosity (10,400 ± 12.6 cps), excellent spreadability (5.33 ± 0.15 cm), extrudability, and a slightly acidic pH (5.40 ± 0.10), which resembles the pH of human skin. In vitro drug release revealed that the developed gel exhibited a biphasic release pattern, with a rapid release followed by sustained release. Notably, ex vivo results revealed a ~2.0-fold increase in permeation flux and a ~2.8-fold increase in skin retention compared to the TH solution. In vivo results confirmed a significant reduction in paw edema and pro-inflammatory biomarkers (TNF-α and IL-6), alongside recovery of body weight and ankle joints. In conclusion, the CH-TH-BG is a transformative transdermal platform for effective management of RA.
10 February 2026