Current Status of Multimodal Therapy for Oligometastatic Disease, Induced Oligometastatic Disease, and Oligo-Progressive Disease in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Oligometastatic Disease in EGFR-Mutated NSCLC
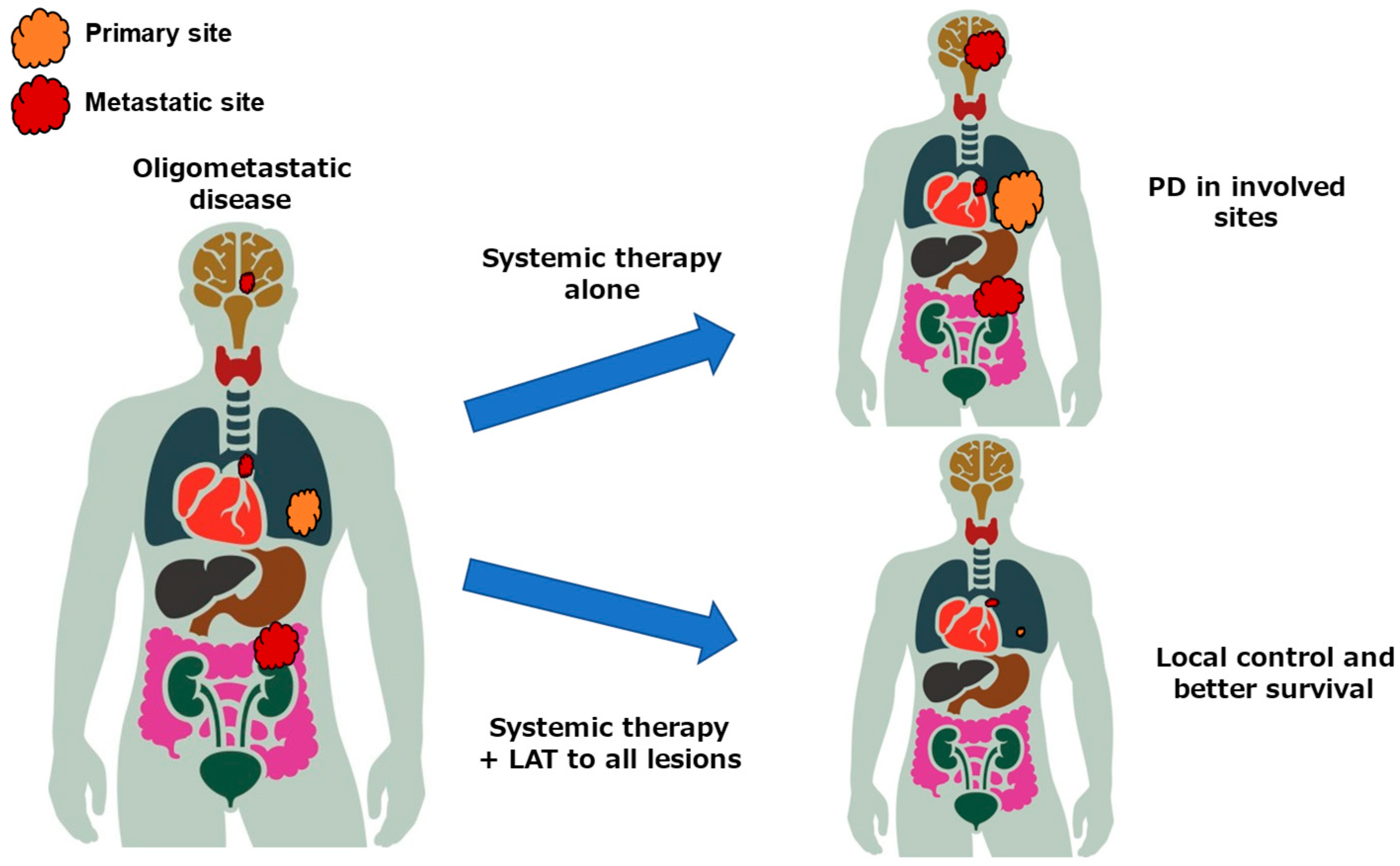
2.1. Concept of Oligometastatic Disease
2.2. Clinical Trials for Oligometastatic Disease
3. Oligo-Residual Disease in EGFR-Mutated NSCLC
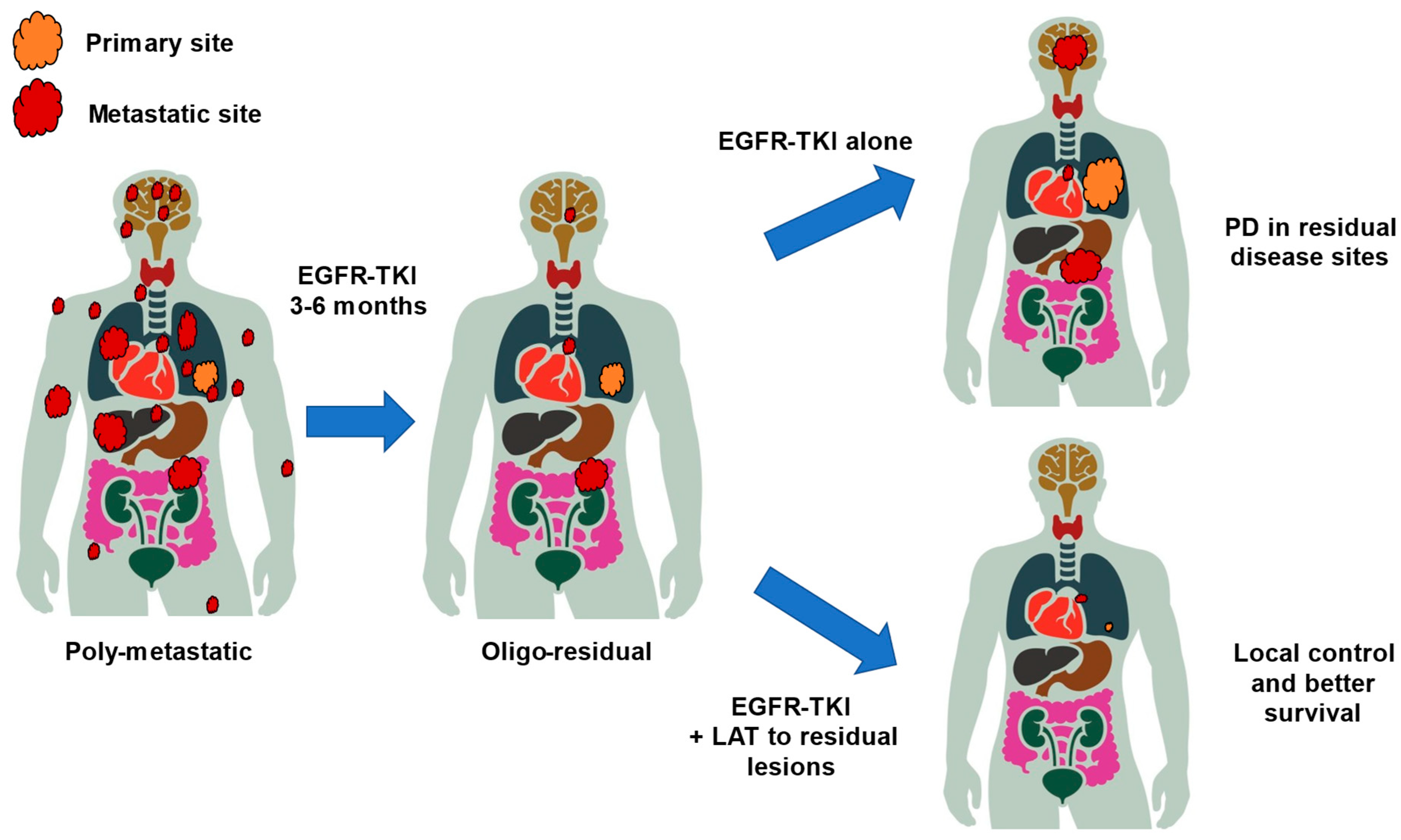
3.1. Concept of Oligo-Persistent Disease/Oligo-Residual Disease
3.2. Clinical Trials for Oligo-Residual Disease
4. Current Status of Oligo-PD
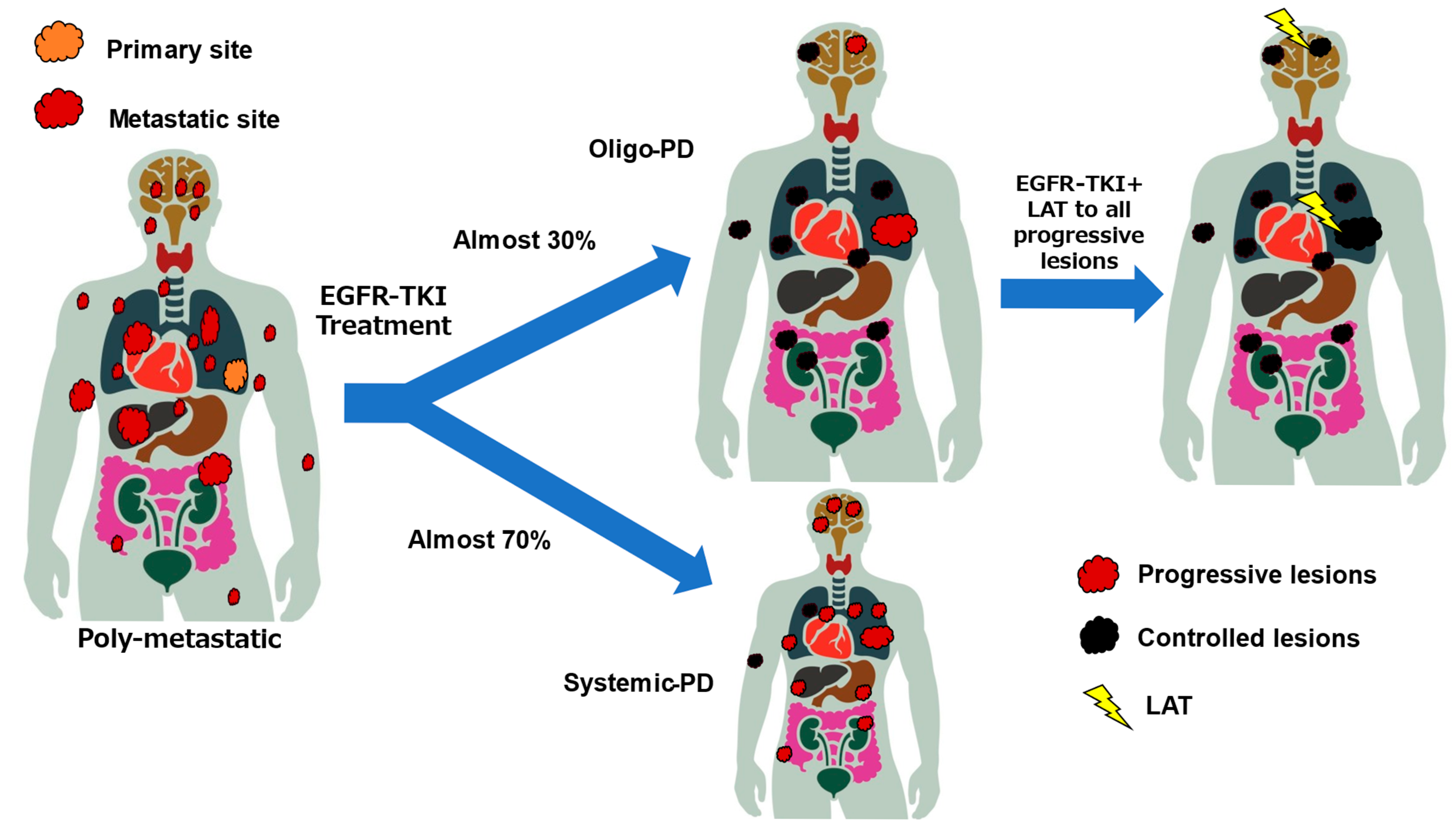
4.1. Concept of Oligo-PD
4.2. Definition of Oligo-PD
4.3. Current Status of Clinical Trials for Oligo-PD
4.4. Ongoing Trials for Oligo-PD
5. Local Ablative Therapy
5.1. Primary Site and Lung Metastases
5.2. Brain Metastases
5.3. Adrenal Gland Metastases
5.4. Bone Metastases
5.5. Liver Metastases
6. Summary
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitsudomi, T.; Morita, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Negoro, S.; Okamoto, I.; Tsurutani, J.; Seto, T.; Satouchi, M.; Tada, H.; Hirashima, T.; et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): An open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosell, R.; Carcereny, E.; Gervais, R.; Vergnenegre, A.; Massuti, B.; Felip, E.; Palmero, R.; Garcia-Gomez, R.; Pallares, C.; Sanchez, J.M.; et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maemondo, M.; Inoue, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Sugawara, S.; Oizumi, S.; Isobe, H.; Gemma, A.; Harada, M.; Yoshizawa, H.; Kinoshita, I.; et al. Gefitinib or Chemotherapy for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Mutated EGFR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.-C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.C.; Lu, S.; Felip, E.; Spira, A.I.; Girard, N.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Ostapenko, Y.; Danchaivijitr, P.; Liu, B.; et al. Amivantamab plus Lazertinib in Previously Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1486–1498. [Google Scholar]
- Planchard, D.; Jänne, P.A.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, J.C.; Yanagitani, N.; Kim, S.W.; Sugawara, S.; Yu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Geater, S.L.; et al. Osimertinib with or without Chemotherapy in EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1935–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, S.; Li, J.J.N.; Leighl, N.B. Mechanisms of osimertinib resistance and emerging treatment options. Lung Cancer 2020, 147, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, H.; Nadal, E.; Gray, J.E.; Ardizzoni, A.; Caria, N.; Puri, T.; Grohe, C. Overall Treatment Strategy for Patients with Metastatic NSCLC with Activating EGFR Mutations. Clin. Lung Cancer 2022, 23, e69–e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellman, S.; Weichselbaum, R.R. Oligometastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guckenberger, M.; Lievens, Y.; Bouma, A.B.; Collette, L.; Dekker, A.; deSouza, N.M.; Dingemans, A.-M.C.; Fournier, B.; Hurkmans, C.; Lecouvet, F.E.; et al. Characterisation and classification of oligometastatic disease: A European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology and European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer consensus recommendation. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, E18–E28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyengar, P.; Wardak, Z.; Gerber, D.E.; Tumati, V.; Ahn, C.; Hughes, R.S.; Dowell, J.E.; Cheedella, N.; Nedzi, L.; Westover, K.D.; et al. Consolidative Radiotherapy for Limited Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, e173501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.R.; Tang, C.; Zhang, J.; Blumenschein, G.R., Jr.; Hernandez, M.; Lee, J.J.; Ye, R.; Palma, D.A.; Louie, A.V.; Camidge, D.R.; et al. Local Consolidative Therapy Vs. Maintenance Therapy or Observation for Patients with Oligometastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Long-Term Results of a Multi-Institutional, Phase II, Randomized Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, D.A.; Olson, R.; Harrow, S.; Gaede, S.; Louie, A.V.; Haasbeek, C.; Mulroy, L.; Lock, M.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Yaremko, B.P.; et al. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for the Comprehensive Treatment of Oligometastatic Cancers: Long-Term Results of the SABR-COMET Phase II Randomized Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2830–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyawaki, T.; Kenmotsu, H.; Kodama, H.; Nishioka, N.; Miyawaki, E.; Mamesaya, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Omori, S.; Ko, R.; Wakuda, K.; et al. Association between oligo-residual disease and patterns of failure during EGFR-TKI treatment in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective study. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.F.; Jeng, M.Y.; Ma, J.; Agrawal, P.; Dunne, E.; Boe, L.A.; Kris, M.G.; Huang, J.; Veeraraghavan, H.; Gomez, D.; et al. Outcomes After Radiation for Oligoprogressive Disease Sites in Patients with EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer Treated with Osimertinib. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2025, 9, e2500047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusthoven, K.E.; Hammerman, S.F.; Kavanagh, B.D.; Birtwhistle, M.J.; Stares, M.; Camidge, D.R. Is there a role for consolidative stereotactic body radiation therapy following first-line systemic therapy for metastatic lung cancer? A patterns-of-failure analysis. Acta Oncol. 2009, 48, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyawaki, T.; Wakuda, K.; Kenmotsu, H.; Miyawaki, E.; Mamesaya, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Omori, S.; Ono, A.; Naito, T.; Murakami, H.; et al. Proposing synchronous oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer based on progression after first-line systemic therapy. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Halabi, H.; Sayegh, K.; Digamurthy, S.R.; Niemierko, A.; Piotrowska, Z.; Willers, H.; Sequist, L.V. Pattern of Failure Analysis in Metastatic EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer Treated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors to Identify Candidates for Consolidation Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Zhu, X.R.; Zhang, C.C.; Yu, W.; Zhang, B.; Shen, T.L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Fu, X.L. Analysis of Progression Patterns and Failure Sites of Patients with Metastatic Lung Adenocarcinoma with EGFR Mutations Receiving First-line Treatment of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.H.; Rimner, A.; Foster, A.; Zhang, Z.; Woo, K.M.; Yu, H.A.; Riely, G.J.; Wu, A.J. Patterns of initial and intracranial failure in metastatic EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer treated with erlotinib. Lung Cancer 2017, 108, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobbini, E.; Bertolaccini, L.; Giaj-Levra, N.; Menis, J.; Giaj-Levra, M. Epidemiology of oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer: Results from a systematic review and pooled analysis. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 3339–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gennari, A.; André, F.; Barrios, C.H.; Cortés, J.; de Azambuja, E.; DeMichele, A.; Dent, R.; Fenlon, D.; Gligorov, J.; Hurvitz, S.A.; et al. ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for the diagnosis, staging and treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1475–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, A.; Hendriks, L.E.L.; Berghmans, T.; Faivre-Finn, C.; GiajLevra, M.; GiajLevra, N.; Hasan, B.; Pochesci, A.; Girard, N.; Greillier, L.; et al. EORTC Lung Cancer Group survey on the definition of NSCLC synchronous oligometastatic disease. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 122, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingemans, A.-M.C.; Hendriks, L.E.L.; Berghmans, T.; Levy, A.; Hasan, B.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Giaj-Levra, M.; Giaj-Levra, N.; Girard, N.; Greillier, L.; et al. Definition of Synchronous Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer—A Consensus Report. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 2109–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conibear, J.; Chia, B.; Ngai, Y.; Bates, A.T.; Counsell, N.; Patel, R.; Eaton, D.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Fenwick, J.; Forster, M.; et al. Study protocol for the SARON trial: A multicentre, randomised controlled phase III trial comparing the addition of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy and radical radiotherapy with standard chemotherapy alone for oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e020690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, D.A.; Olson, R.; Harrow, S.; Correa, R.J.M.; Schneiders, F.; Haasbeek, C.J.A.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Lock, M.; Yaremko, B.P.; Bauman, G.S.; et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for the comprehensive treatment of 4–10 oligometastatic tumors (SABR-COMET-10): Study protocol for a randomized phase III trial. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibdewal, A.; Agarwal, J.P.; Srinivasan, S.; Mummudi, N.; Noronha, V.; Prabhash, K.; Patil, V.; Purandare, N.; Janu, A.; Kannan, S. Standard maintenance therapy versus local consolidative radiation therapy and standard maintenance therapy in 1–5 sites of oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer: A study protocol of phase III randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e043628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garon, E.B.; Peterson, P.; Rizzo, M.T.; Kim, J.S. Overall Survival and Safety with Pemetrexed/Platinum ± Anti-VEGF Followed by Pemetrexed ± Anti-VEGF Maintenance in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Pooled Analysis of 4 Randomized Studies. Clin. Lung Cancer 2022, 23, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Bai, Y.F.; Verma, V.; Yu, R.L.; Tian, W.; Ao, R.; Deng, Y.; Zhu, X.Q.; Liu, H.; Pan, H.X.; et al. Randomized Trial of First-Line Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor With or Without Radiotherapy for Synchronous Oligometastatic EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2023, 115, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhou, F.; Liu, H.; Jiang, T.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, C. Consolidative Local Ablative Therapy Improves the Survival of Patients with Synchronous Oligometastatic NSCLC Harboring EGFR Activating Mutation Treated with First-Line EGFR-TKIs. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.R.; Blumenschein, G.R.; Lee, J.J.; Hernandez, M.; Ye, R.; Camidge, D.R.; Doebele, R.C.; Skoulidis, F.; Gaspar, L.E.; Gibbons, D.L.; et al. Local consolidative therapy versus maintenance therapy or observation for patients with oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer without progression after first-line systemic therapy: A multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauml, J.M.; Mick, R.; Ciunci, C.; Aggarwal, C.; Davis, C.; Evans, T.; Deshpande, C.; Miller, L.; Patel, P.; Alley, E.; et al. Pembrolizumab After Completion of Locally Ablative Therapy for Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase 2 Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, M.; Huang, W.; Zhang, J.; Wei, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ye, S.; Gong, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Thoracic Radiotherapy Improves the Survival in Patients with EGFR-Mutated Oligo-Organ Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: A Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled, Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haratake, N.; Shimokawa, M.; Seto, T.; Yoshioka, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Nakagawa, K.; Mitsudomi, T. Survival benefit of using pemetrexed for EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer in a randomized phase III study comparing gefitinib to cisplatin plus docetaxel (WJTOG3405). Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 27, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Lee, J.-S.; Fan, Y.; Marinis, F.d.; Okamoto, I.; Inoue, T.; Cid, J.R.R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, C.-T.; Jimenez, E.D.L.M.; et al. Pemetrexed and platinum with or without pembrolizumab for tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI)-resistant, EGFR-mutant, metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC: Phase 3 KEYNOTE-789 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, LBA9000. [Google Scholar]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Shaw, A.T. Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, O.S.H.; Lam, K.C.; Li, J.Y.C.; Choi, F.P.T.; Wong, C.Y.H.; Chang, A.T.Y.; Mo, F.K.F.; Wang, K.; Yeung, R.M.W.; Mok, T.S.K. ATOM: A phase II study to assess efficacy of preemptive local ablative therapy to residual oligometastases of NSCLC after EGFR TKI. Lung Cancer 2020, 142, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, Y.Y.; Gomez, D.R.; Antonoff, M.B.; Robichaux, J.P.; Tran, H.; Shorter, M.K.; Bohac, J.M.; Negrao, M.V.; Le, X.; Rinsurogkawong, W.; et al. Local Consolidation Therapy (LCT) After First Line Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI) for Patients with EGFR Mutant Metastatic Non-small-cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Koom, W.S.; Byun, H.K.; Yang, G.; Kim, M.S.; Park, E.J.; Ahn, J.B.; Beom, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Shin, S.J.; et al. Metastasis-Directed Radiotherapy for Oligoprogressive or Oligopersistent Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Color. Cancer 2022, 21, e78–e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Peng, L.; Liang, F.; Chu, L.; Chu, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Guo, T.; Jiang, S.; Pang, Y.; et al. Safety and efficacy of consolidative stereotactic radiotherapy for oligo-residual EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer after first-line third-generation EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors: A single-arm, phase 2 trial. eClinicalMedicine 2024, 76 (Suppl. S17), 102853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, P.; Gong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Han, G.; Meng, R.; Chen, Y.; Yang, M.; Shen, Q.; et al. EGFR-TKIs plus stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for stage IV Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A prospective, multicenter, randomized, controlled phase II study. Radiother. Oncol. 2023, 184, 109681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doebele, R.C.; Pilling, A.B.; Aisner, D.L.; Kutateladze, T.G.; Le, A.T.; Weickhardt, A.J.; Kondo, K.L.; Linderman, D.J.; Heasley, L.E.; Franklin, W.A.; et al. Mechanisms of resistance to crizotinib in patients with ALK gene rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, A.; Verma, V.; Simone, C.B., 2nd; Chetty, I.J.; Chun, S.G.; Donington, J.; Edelman, M.J.; Higgins, K.A.; Kestin, L.L.; Movsas, B.; et al. American Radium Society Appropriate Use Criteria for Radiation Therapy in Oligometastatic or Oligoprogressive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 112, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gettinger, S.N.; Wurtz, A.; Goldberg, S.B.; Rimm, D.; Schalper, K.; Kaech, S.; Kavathas, P.; Chiang, A.; Lilenbaum, R.; Zelterman, D.; et al. Clinical Features and Management of Acquired Resistance to PD-1 Axis Inhibitors in 26 Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, A.J.; Rizvi, H.; Memon, D.; Luo, J.; Preeshagul, I.R.; Sauter, J.L.; Plodkowski, A.J.; Vanderbilt, C.; Miller, M.L.; Hellmann, M.D. Acquired resistance to PD-1 blockade in NSCLC. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. S15), 9621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzetti, C.; Tiseo, M.; Lagrasta, C.; Nizzoli, R.; Guazzi, A.; Leonardi, F.; Gasparro, D.; Spiritelli, E.; Rusca, M.; Carbognani, P.; et al. Comparison between epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene expression in primary non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and in fine-needle aspirates from distant metastatic sites. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, K.; Murakami, I.; Yu, H.; Ellison, K.; Shimoji, M.; Genova, C.; Rivard, C.J.; Mitsudomi, T.; Hirsch, F.R. Heterogeneity of EGFR Aberrations and Correlation with Histological Structures: Analyses of Therapy-Naive Isogenic Lung Cancer Lesions with EGFR Mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1711–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schuler, A.; Huser, J.; Schaer, S.; Schmid, S.; Scherz, A.; Gautschi, O.; Mauti, L.A.; Von Briel, T.; Waibel, C.; Wannesson De Nicola, L.; et al. 365P Patterns of progression on first-line osimertinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A Swiss cohort study. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S1584–S1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Popat, S.; Kerr, K.; Novello, S.; Smit, E.F.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Mok, T.S.; Reck, M.; Van Schil, P.E.; Hellmann, M.D.; et al. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29 (Suppl. S4), iv192–iv237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Wood, D.E.; Aisner, D.L.; Akerley, W.; Bauman, J.R.; Bharat, A.; Bruno, D.S.; Chang, J.Y.; Chirieac, L.R.; DeCamp, M.; et al. NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 2.2023. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2023, 21, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basler, L.; Kroeze, S.G.; Guckenberger, M. SBRT for oligoprogressive oncogene addicted NSCLC. Lung Cancer 2017, 106, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weickhardt, A.J.; Scheier, B.; Burke, J.M.; Gan, G.; Lu, X.; Bunn, P.A., Jr.; Aisner, D.L.; Gaspar, L.E.; Kavanagh, B.D.; Doebele, R.C.; et al. Local ablative therapy of oligoprogressive disease prolongs disease control by tyrosine kinase inhibitors in oncogene-addicted non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukuya, T.; Takahashi, T.; Naito, T.; Kaira, R.; Ono, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Tsuya, A.; Kenmotsu, H.; Murakami, H.; Harada, H.; et al. Continuous EGFR-TKI administration following radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer patients with isolated CNS failure. Lung Cancer 2011, 74, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.J.; Yang, J.T.; Guttmann, D.M.; Shaverdian, N.; Shepherd, A.F.; Eng, J.; Gelblum, D.; Xu, A.J.; Namakydoust, A.; Iqbal, A.; et al. Consolidative Use of Radiotherapy to Block (CURB) Oligoprogression—Interim Analysis of the First Randomized Study of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Patients with Oligoprogressive Metastatic Cancers of the Lung and Breast. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 111, 1325–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagawa, Y.; Furuta, H.; Uemura, T.; Watanabe, N.; Shimizu, J.; Horio, Y.; Kuroda, H.; Inaba, Y.; Kodaira, T.; Masago, K.; et al. Efficacy of local therapy for oligoprogressive disease after programmed cell death 1 blockade in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 4442–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheinheimer, S.; Heussel, C.P.; Mayer, P.; Gaissmaier, L.; Bozorgmehr, F.; Winter, H.; Herth, F.J.; Muley, T.; Liersch, S.; Bischoff, H.; et al. Oligoprogressive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer under Treatment with PD-(L)1 Inhibitors. Cancers 2020, 12, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, F.; Guckenberger, M.; Popat, S.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Andratschke, N.; Riddell, A.; Hanna, G.G.; Hiley, C.; Prakash, V.; Nair, A.; et al. EP08.03-005 HALT—Targeted Therapy with or without Dose-Intensified Radiotherapy in Oligo-Progressive Disease in Oncogene Addicted Lung Tumours. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17 (Suppl. S9), S492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, S.; Berk, L.; Chang, E.; Chow, E.; Hahn, C.; Hoskin, P.; Howell, D.; Konski, A.; Kachnic, L.; Lo, S.; et al. Palliative Radiotherapy for Bone Metastases: An ASTRO Evidence-Based Guideline. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 79, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, S.; Jiang, W.; Mou, B.; Lund, C.R.; Liu, M.; Bergman, A.M.; Schellenberg, D.; Alexander, A.S.; Carolan, H.; Atrchian, S.; et al. Progression-Free Survival and Local Control After SABR for up to 5 Oligometastases: An Analysis From the Population-Based Phase 2 SABR-5 Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 114, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, H.; Shirato, H.; Nagata, Y.; Hiraoka, M.; Fujino, M.; Gomi, K.; Karasawa, K.; Hayakawa, K.; Niibe, Y.; Takai, Y.; et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for operable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: Can SBRT be comparable to surgery? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, 1352–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuks, Z.; Kolesnick, R. Engaging the vascular component of the tumor response. Cancer Cell 2005, 8, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rose, F.; Cozzi, L.; Navarria, P.; Ascolese, A.M.; Clerici, E.; Infante, M.; Alloisio, M.; Testori, A.; Toschi, L.; Finocchiaro, G.; et al. Clinical Outcome of Stereotactic Ablative Body Radiotherapy for Lung Metastatic Lesions in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Oligometastatic Patients. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 28, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virbel, G.; Cox, D.G.; Olland, A.; Falcoz, P.E.; Le Fevre, C.; Schott, R.; Antoni, D.; Noel, G. Outcome of lung oligometastatic patients treated with stereotactic body irradiation. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 945189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muacevic, A.; Wowra, B.; Siefert, A.; Tonn, J.-C.; Steiger, H.-J.; Kreth, F.W. Microsurgery plus whole brain irradiation versus Gamma Knife surgery alone for treatment of single metastases to the brain: A randomized controlled multicentre phase III trial. J. Neuro Oncol. 2008, 87, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, H.; Shirato, H.; Tago, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Toyoda, T.; Hatano, K.; Kenjyo, M.; Oya, N.; Hirota, S.; Shioura, H.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2006, 295, 2483–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, D.W.; Scott, C.B.; Sperduto, P.W.; Flanders, A.E.; Gaspar, L.E.; Schell, M.C.; Werner-Wasik, M.; Demas, W.; Ryu, J.; Bahary, J.P.; et al. Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: Phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 2004, 363, 1665–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collen, C.; Christian, N.; Schallier, D.; Meysman, M.; Duchateau, M.; Storme, G.; De Ridder, M. Phase II study of stereotactic body radiotherapy to primary tumor and metastatic locations in oligometastatic nonsmall-cell lung cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1954–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruysscher, D.; Wanders, R.; van Baardwijk, A.; Dingemans, A.-M.C.; Reymen, B.; Houben, R.; Bootsma, G.; Pitz, C.; van Eijsden, L.; Geraedts, W.; et al. Radical Treatment of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Synchronous Oligometastases: Long-Term Results of a Prospective Phase II Trial (Nct01282450). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhuang, H.; Guo, X.; Song, Y.; Ju, X.; Wang, P.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, H. Clinical efficacy of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) for adrenal gland metastases: A multi-center retrospective study from China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plichta, K.; Camden, N.; Furqan, M.; Hejleh, T.A.; Clamon, G.H.; Zhang, J.; Flynn, R.T.; Bhatia, S.K.; Smith, M.C.; Buatti, J.M.; et al. SBRT to adrenal metastases provides high local control with minimal toxicity. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 2, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudra, S.; Malik, R.; Ranck, M.C.; Farrey, K.; Golden, D.W.; Hasselle, M.D.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Salama, J.K. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for curative treatment of adrenal metastases. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 12, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casamassima, F.; Livi, L.; Masciullo, S.; Menichelli, C.; Masi, L.; Meattini, I.; Bonucci, I.; Agresti, B.; Simontacchi, G.; Doro, R. Stereotactic radiotherapy for adrenal gland metastases: University of Florence experience. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzese, C.; Franceschini, D.; Cozzi, L.; D’Agostino, G.; Comito, T.; De Rose, F.; Navarria, P.; Mancosu, P.; Tomatis, S.; Fogliata, A.; et al. Minimally Invasive Stereotactical Radio-ablation of Adrenal Metastases as an Alternative to Surgery. Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 49, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Voglhuber, T.; Kessel, K.A.; Oechsner, M.; Vogel, M.M.E.; Gschwend, J.E.; Combs, S.E. Single-institutional outcome-analysis of low-dose stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) of adrenal gland metastases. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, Y.; Takeda, Y.; Hirano, S.; Ito, H.; Aruga, T. Role of radiotherapy for local control of asymptomatic adrenal metastasis from lung cancer. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 34, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, E.; van der Linden, Y.M.; Roos, D.; Hartsell, W.F.; Hoskin, P.; Wu, J.S.; Brundage, M.D.; Nabid, A.; Tissing-Tan, C.J.; Oei, B.; et al. Single versus multiple fractions of repeat radiation for painful bone metastases: A randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R.; Ding, K.; Brundage, M.; Meyer, R.M.; Nabid, A.; Chabot, P.; Coulombe, G.; Ahmed, S.; Kuk, J.; Dar, A.R.; et al. Effect of Radiotherapy on Painful Bone Metastases: A Secondary Analysis of the NCIC Clinical Trials Group Symptom Control Trial SC.23. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprave, T.; Verma, V.; Förster, R.; Schlampp, I.; Bruckner, T.; Bostel, T.; Welte, S.E.; Tonndorf-Martini, E.; Nicolay, N.H.; Debus, J.; et al. Randomized phase II trial evaluating pain response in patients with spinal metastases following stereotactic body radiotherapy versus three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 128, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, A.J.; Tao, R.; Rebueno, N.C.; Christensen, E.N.; Allen, P.K.; Wang, X.A.; Amini, B.; Tannir, N.M.; Tatsui, C.E.; Rhines, L.D.; et al. Outcomes for Spine Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy and an Analysis of Predictors of Local Recurrence. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.L.; Soliman, H.; Myrehaug, S.; Lee, Y.K.; Ruschin, M.; Atenafu, E.G.; Campbell, M.; Maralani, P.; Yang, V.; Yee, A.; et al. Imaging-Based Outcomes for 24 Gy in 2 Daily Fractions for Patients with de Novo Spinal Metastases Treated with Spine Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Rhines, L.D.; Shiu, A.S.; Yang, J.N.; Selek, U.; Gning, I.; Liu, P.; Allen, P.K.; Azeem, S.S.; Brown, P.D.; et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for management of spinal metastases in patients without spinal cord compression: A phase 1–2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.L.; Myrehaug, S.; Soliman, H.; Husain, Z.A.; Tseng, C.-L.; Detsky, J.; Ruschin, M.; Atenafu, E.G.; Witiw, C.D.; Larouche, J.; et al. Mature Local Control and Reirradiation Rates Comparing Spine Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy with Conventional Palliative External Beam Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 114, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erler, D.; Brotherston, D.; Sahgal, A.; Cheung, P.; Loblaw, A.; Chu, W.; Soliman, H.; Chung, H.; Kiss, A.; Chow, E.; et al. Local control and fracture risk following stereotactic body radiation therapy for non-spine bone metastases. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 127, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, Q.N.; Chun, S.G.; Chow, E.; Komaki, R.; Liao, Z.; Zacharia, R.; Szeto, B.K.; Welsh, J.W.; Hahn, S.M.; Fuller, C.D.; et al. Single-Fraction Stereotactic vs Conventional Multifraction Radiotherapy for Pain Relief in Patients with Predominantly Nonspine Bone Metastases: A Randomized Phase 2 Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerici, E.; Comito, T.; Franzese, C.; Di Brina, L.; Tozzi, A.; Iftode, C.; Navarria, P.; Mancosu, P.; Reggiori, G.; Tomatis, S.; et al. Role of stereotactic body radiation therapy in the treatment of liver metastases: Clinical results and prognostic factors. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2020, 196, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, B.D.; Mannina, E.M.; Althouse, S.K.; Maluccio, M.A.; Cárdenes, H.R. Long-term safety and efficacy of stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatic oligometastases. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 6, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez Romero, A.; Keskin-Cambay, F.; van Os, R.M.; Nuyttens, J.J.; Heijmen, B.J.M.; Ijzermans, J.N.M.; Verhoef, C. Institutional experience in the treatment of colorectal liver metastases with stereotactic body radiation therapy. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2017, 22, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez Romero, A.; Schillemans, W.; van Os, R.; Koppe, F.; Haasbeek, C.J.; Hendriksen, E.M.; Muller, K.; Ceha, H.M.; Braam, P.M.; Reerink, O.; et al. The Dutch-Belgian Registry of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Liver Metastases: Clinical Outcomes of 515 Patients and 668 Metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 109, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Trial | Status | Criteria for Metastatic Lesions | Study Design | Primary Outcome | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02893332 (Sindas study) | Completed | 1–5 | Phase III | PFS | 1st-generation EGFR-TKI with SBRT to all lesions vs. 1st-generation EGFR-TKI alone |
| NCT04908956 | Recruiting | 1–5 | Single-arm phase II | Safety PFS | Osimertinib with SBRT to all lesions |
| NCT05167851 | Not yet recruiting | 1–5 | Randomized phase II | PFS | Lazertinib with SBRT to all lesions vs. Lazertinib alone |
| NCT05277844 (TARGET-01) | Recruiting | 1–5 | Randomized phase II | PFS | EGFR-TKI (or ALK-TKI) with SBRT to all lesions vs. EGFR-TKI (or ALK-TKI) alone * |
| Trial | Status | Criteria for Residual | Length of Induction EGFR-TKI Treatment | Study Design | Primary Outcome | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT01941654 (ATOM study) | Completed | 1–5 | 12–14 weeks | Single-arm phase II | PFS | SBRT to all residual disease following induction of treatment with 1st-generation EGFR-TKI alone |
| NCT03410043 (NORTHSTAR Study) | Not recruiting | N.A. | 6–12 weeks | Randomized phase II | PFS | Surgery or RT to all residual disease following induction of treatment with Osimertinib vs. Osimertinib alone |
| jRCTs041220115 (ORIHALCON trial/WJOG13920L) | Recruiting | 1–3 | 90–120 days | Randomized phase II | PFS | SBRT to all residual disease following induction of treatment with Osimertinib vs. Osimertinib alone |
| Trial | Criteria for Progressive Lesions | Study Design | Primary Outcome | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04970693 | 3–5 | Non-randomized phase II | PFS | Furmonertinib with RT to all progressive lesions |
| NCT02759835 | N.A | Non-randomized phase II | PFS | Osimertinib with LAT to all progressive lesions |
| NCT04216121 (LAT-FLOSI) | 1–3 | Observational study | PFS2 | Osimertinib with LAT to all progressive lesions |
| NCT03256981 (HALT) | 1–3 | Randomized phase II/III study | PFS | SBRT for all progressive lesions, followed by continued TKI vs. continued TKI I |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miyawaki, T.; Kenmotsu, H.; Ko, R.; Oshima, M.; Shukuya, T.; Shikama, N.; Takahashi, K. Current Status of Multimodal Therapy for Oligometastatic Disease, Induced Oligometastatic Disease, and Oligo-Progressive Disease in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 2202. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132202
Miyawaki T, Kenmotsu H, Ko R, Oshima M, Shukuya T, Shikama N, Takahashi K. Current Status of Multimodal Therapy for Oligometastatic Disease, Induced Oligometastatic Disease, and Oligo-Progressive Disease in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(13):2202. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132202
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiyawaki, Taichi, Hirotsugu Kenmotsu, Ryo Ko, Masaki Oshima, Takehito Shukuya, Naoto Shikama, and Kazuhisa Takahashi. 2025. "Current Status of Multimodal Therapy for Oligometastatic Disease, Induced Oligometastatic Disease, and Oligo-Progressive Disease in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 13: 2202. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132202
APA StyleMiyawaki, T., Kenmotsu, H., Ko, R., Oshima, M., Shukuya, T., Shikama, N., & Takahashi, K. (2025). Current Status of Multimodal Therapy for Oligometastatic Disease, Induced Oligometastatic Disease, and Oligo-Progressive Disease in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers, 17(13), 2202. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132202






