- Article
Dynamic Maintenance Optimization of the DS306 Detacher: A Preventive Approach and Operational Diagnosis
- Omar Kebour,
- Rabah Magraoui and
- Nadir Belgroune
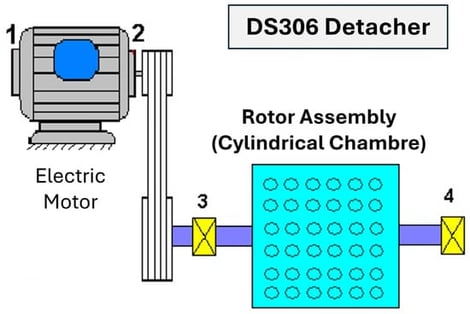
The dynamic behavior of the DS306 detacher, a critical component in industrial fiber processing lines, plays a decisive role in maintenance performance and overall operational reliability. This study introduces a strengthened preventive maintenance strategy that leverages vibration analysis and dynamic modeling with a strong emphasis on early fault anticipation. A detailed numerical finite element model of the detacher was developed to determine its natural frequencies, critical modes, and dynamic response under real operating conditions. Experimental vibration measurements were conducted to validate the numerical model and identify characteristic frequencies associated with imbalance and wear. The results show that the proposed predictive framework not only reproduces the machine’s dynamic behavior with high accuracy but also anticipates mechanical degradation trends well before the occurrence of critical failures. This early-warning capability allows maintenance teams to plan interventions proactively, significantly reducing unexpected downtime, avoiding cascading damage, and improving long-term equipment availability. Overall, the study provides a robust and practical methodology for dynamic diagnosis, fault prediction, and optimized preventive maintenance in industrial rotating machinery.
9 February 2026