How Much Area of a Pear Orchard Can One Honey Bee Colony Pollinate?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site and Plant Materials
2.2. Comparison of Pollination Effects Between Different Methods
2.2.1. Pollination Treatment
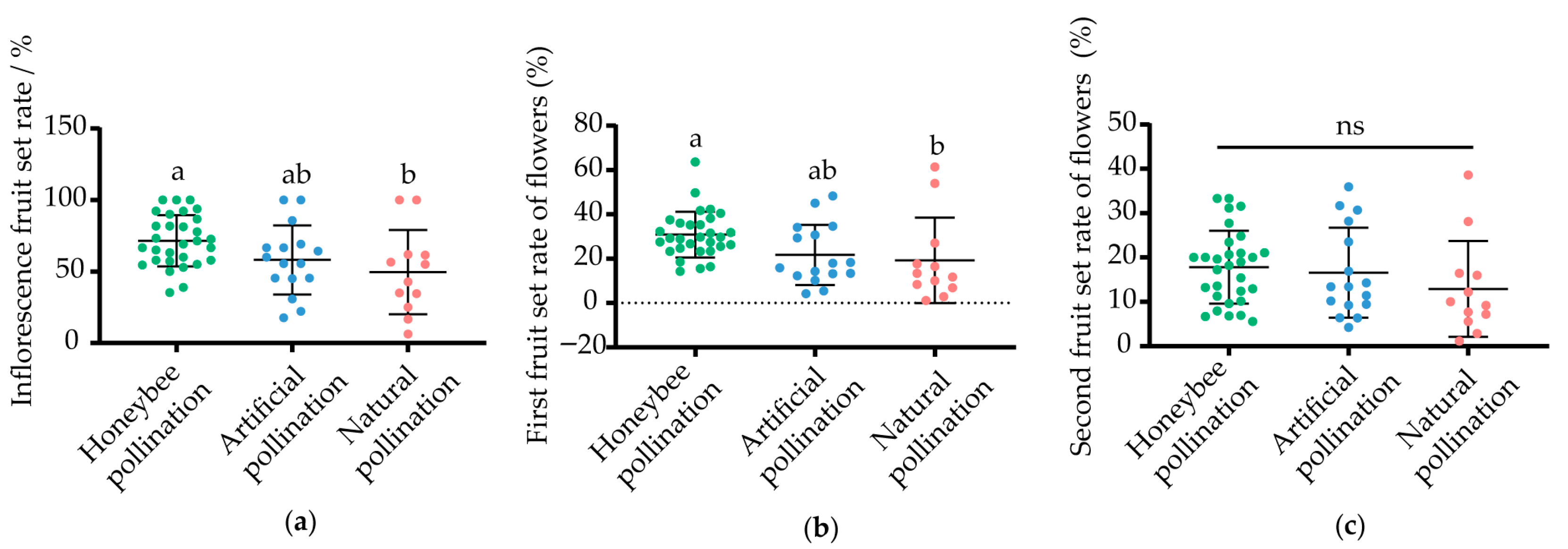
2.2.2. Fruit Set
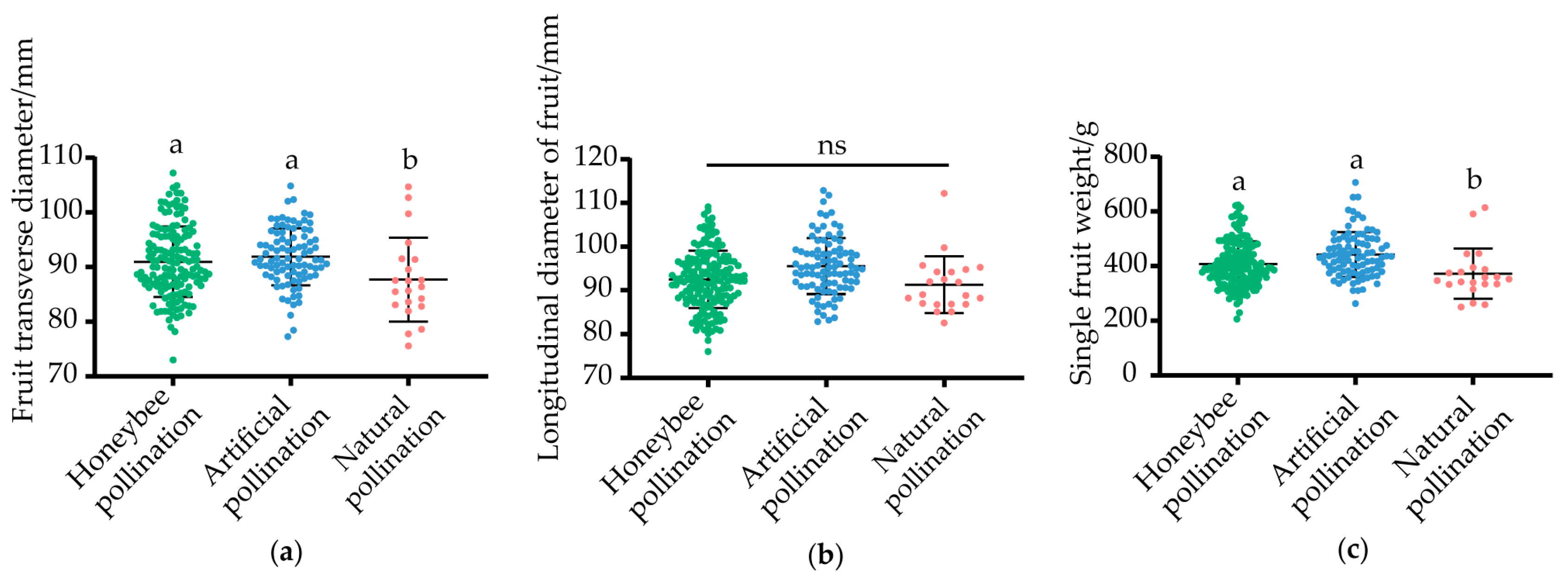
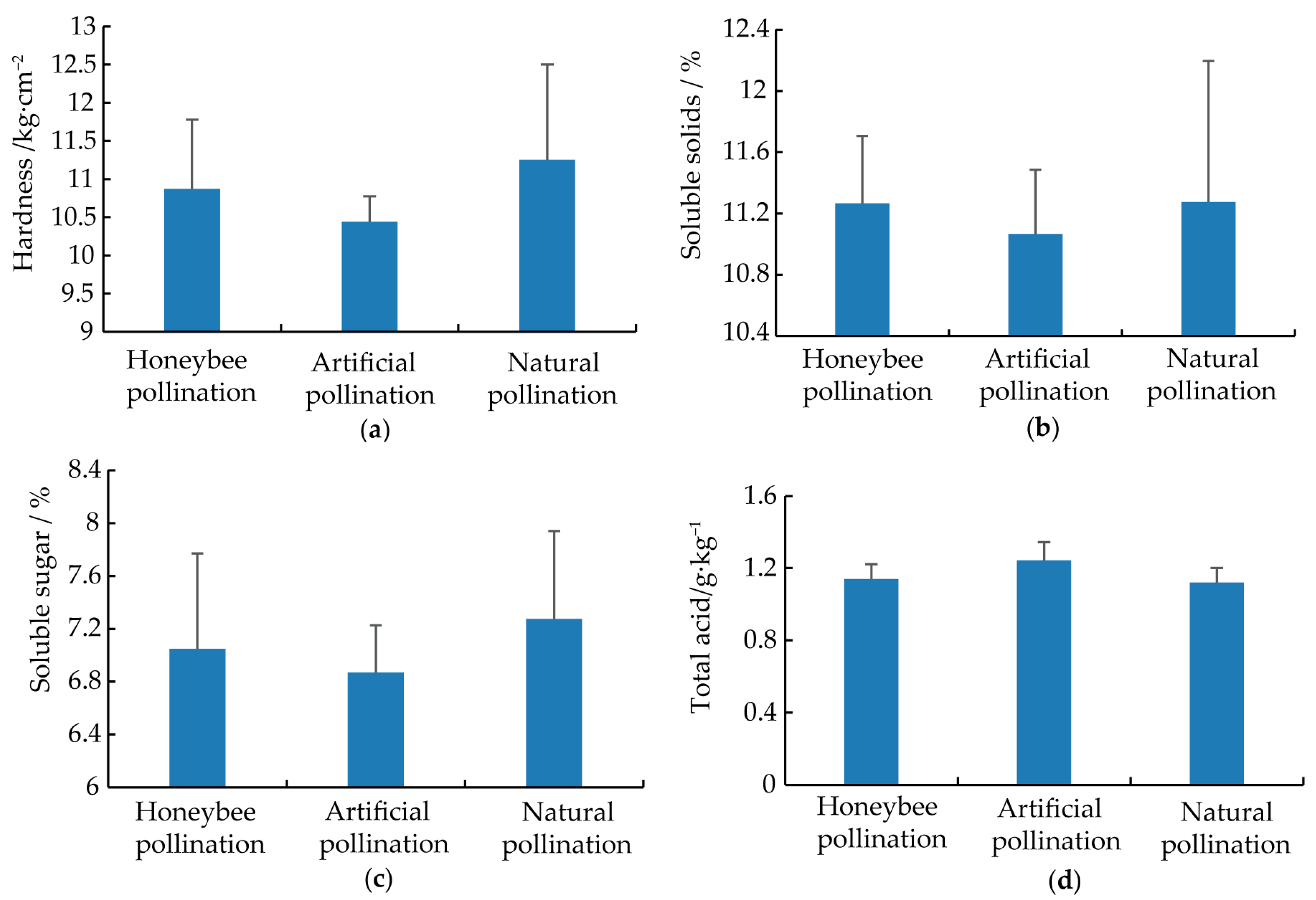
2.2.3. Fruit Quality
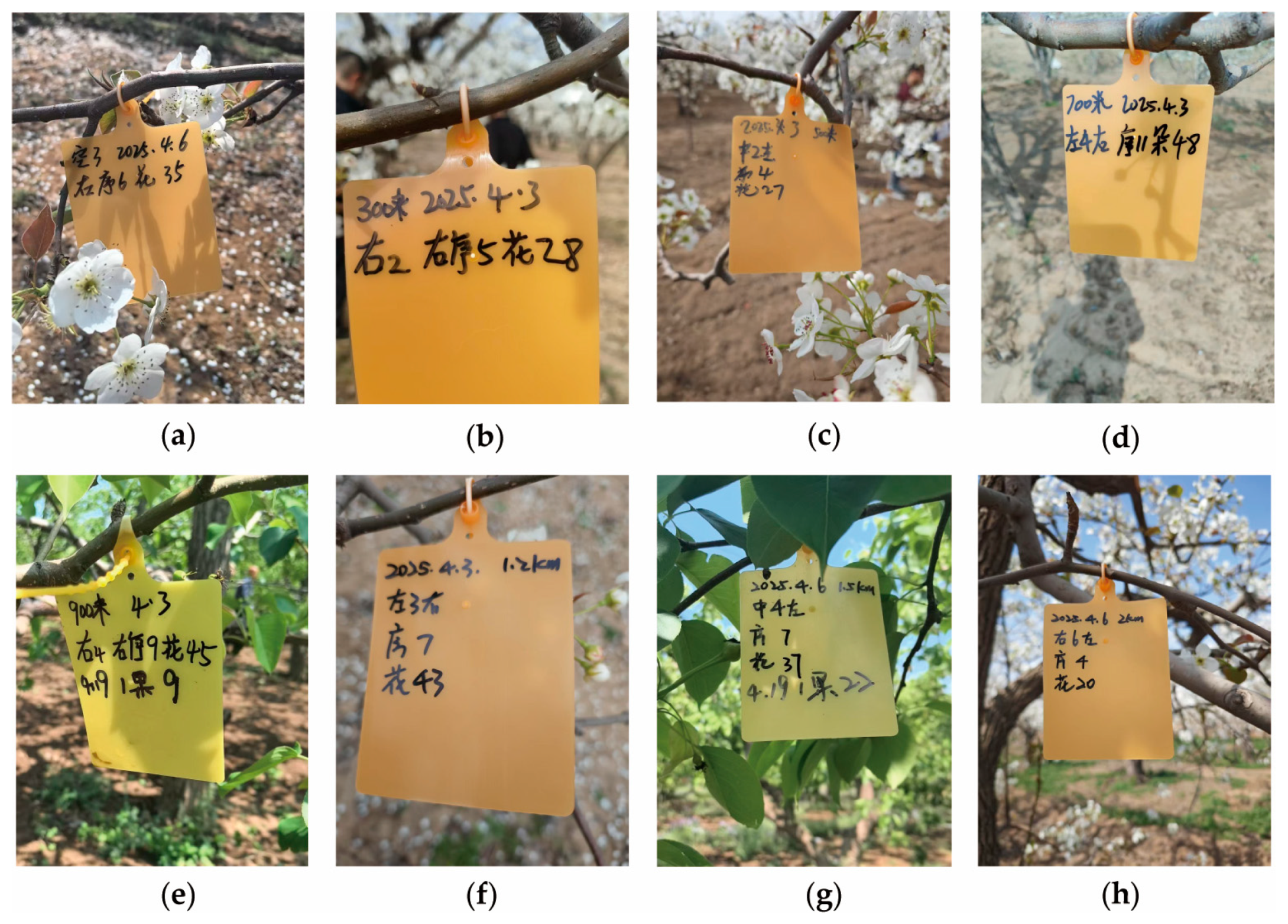
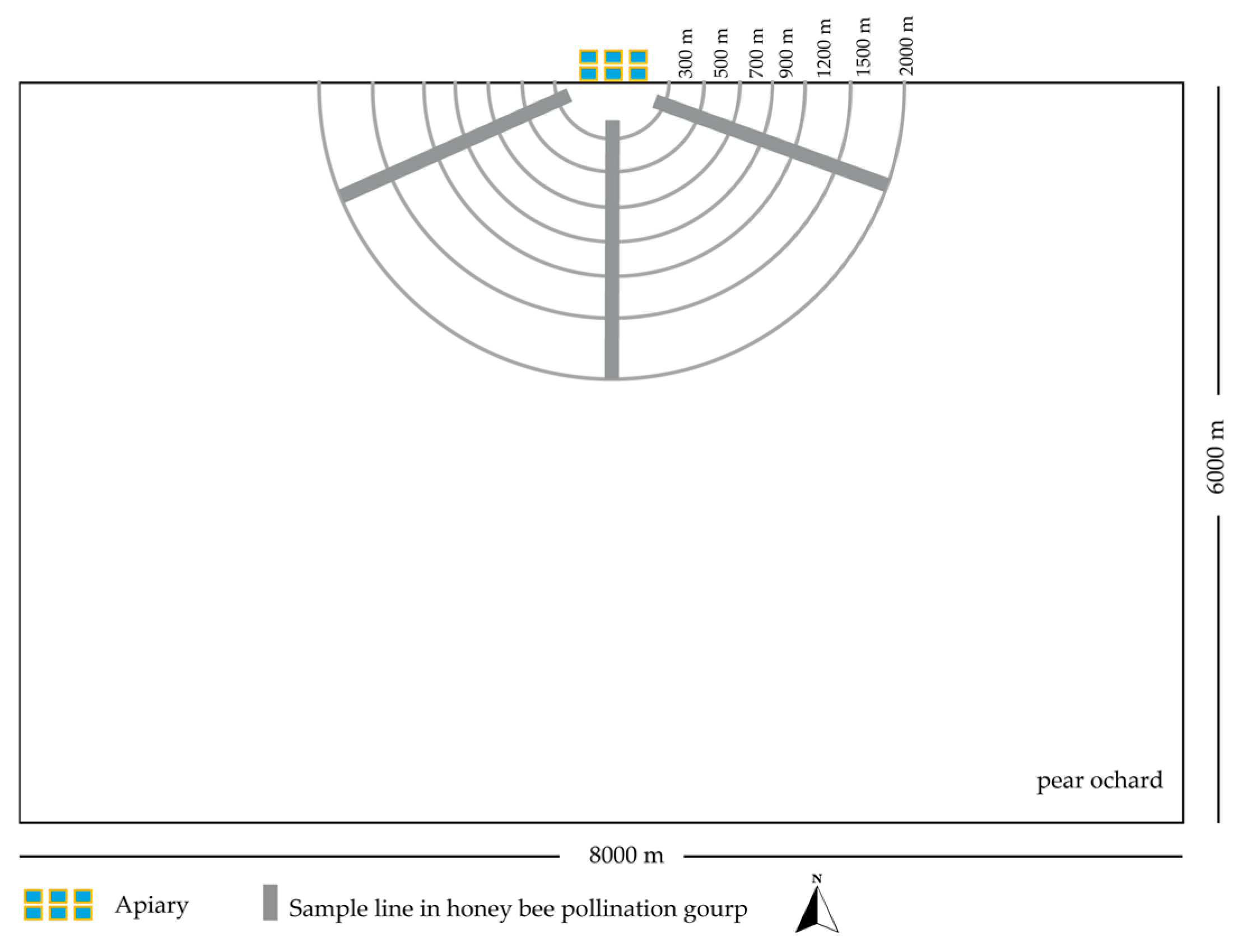
2.3. Comparison of Pollination Effects at Different Pollination Distances
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Different Pollination Methods on the Fruit Set Rate of Xuehua Pears
3.2. Effects of Different Pollination Methods on the Fruit Quality of Xuehua Pears
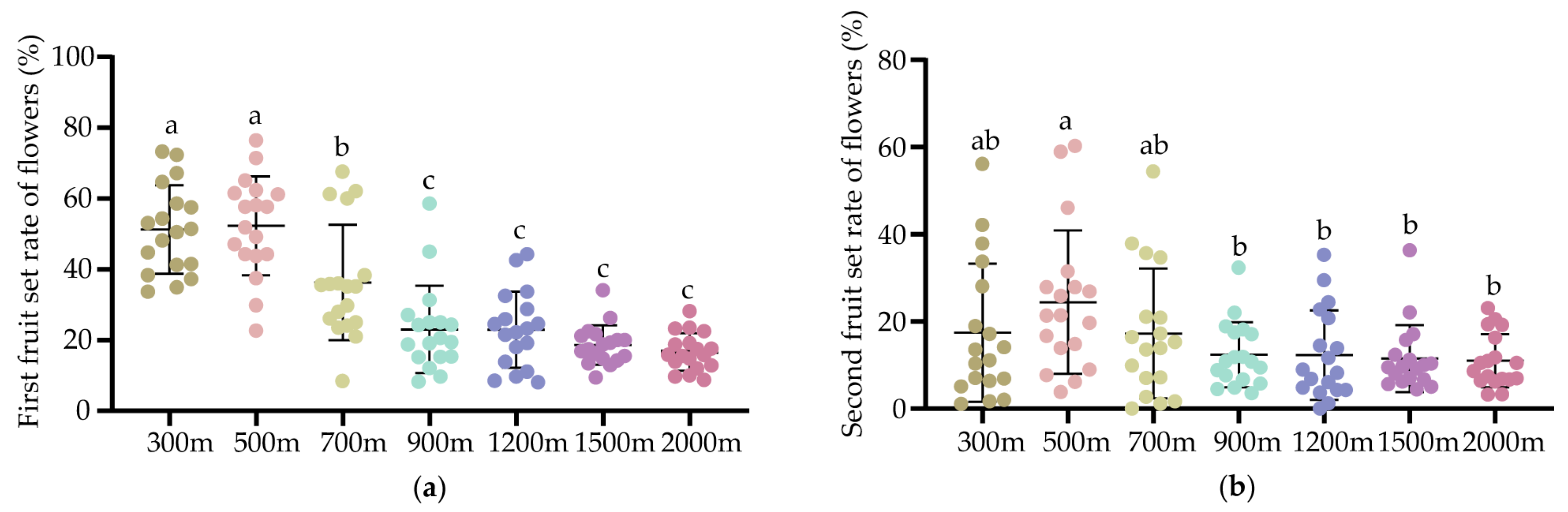
3.3. Effects of Different Distances of Beehives on the Pollination Efficacy for Xuehua Pears
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teng, Y. The pear industry and research in China. Acta Hortic. 2011, 909, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT Report of FAO on the Harvested Area and Yield of Pear. 2023. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#home (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Musacchi, S.; Iglesias, I. Training systems and sustainable orchard management for European pear (Pyrus communis L.) in the Mediterranean area: A review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Chen, C. YOLOv8-Pearpollen: Method for the Lightweight Identification of Pollen Germination Vigor in Pear Trees. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinet, M.; Jacquemart, A.-L. Troubles in pear pollination: Effects of collection and storage method on pollen viability and fruit production. Acta Oecologica 2020, 105, 103558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, C. Pollination services in the North China Plain measured using buckwheat sentinel plants; is there a deficit? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 373, 109129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Wang, X. Design and experiment of pollination wind tunnels: A novel approach for studying artificial pollination in kiwifruits. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 237, 110644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-H.; Pan, Q.-K. An effective knowledge-based evolutionary algorithm for task assignment problem of pollination robots and spraying drones in multi-orchard scenarios. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 279, 127408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, A.; Kimura, T. Cluster-Based Flight Path Construction for Drone-Assisted Pear Pollination Using RGB-D Image Processing. Drones 2025, 9, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Guo, Y. Present situation investigation of bee pollination for pear. Apic. China 2011, 62, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, A.; Anderson, P. Hand pollination effects on the set and development of cherimoya (Annona cherimola) fruit in a humid climate. Sci. Hortic. 1996, 65, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashilingi, S.K.; Zhang, H. Honeybees are far too insufficient to supply optimum pollination services in agricultural systems worldwide. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 335, 108003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sun, M. High pollination deficit and strong dependence on honeybees in Pollination of Korla Fragrant Pear, Pyrus sinkiangensis. Plants 2022, 11, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zisovich, A.; Goldway, M. Adding bumblebees (Bombus terrestris L., Hymenoptera: Apidae) to pear orchards increases seed number per fruit, fruit set, fruit size and yield. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedek, P.; Ruff, J. Flower constancy of honeybees (Apis mellifera L.) to blooming pear plantations. Int. J. Hortic. Sci. 2000, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hünicken, P.L.; Morales, C.L. Insect pollination, more than plant nutrition, determines yield quantity and quality in apple and pear. Neotrop. Entomol. 2020, 49, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Pollination Effects of Pear Trees by Honeybee and Its Influencing Factors. Asian Agric. Res. 2023, 15, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.A.; Tanveer, M. Declining abundance of pollinating insects drives falls in loquat (Eriobotrya japonica) fruit yields in the Pothwar region of Pakistan. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 339, 108138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, H.; Martin, T.R. Starvation affects vitellogenin production but not vitellogenin mRNA levels in the lubber grasshopper, Romalea microptera. J. Insect Physiol. 2005, 51, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.W.; Zhang, W. Variation law and comprehensive evaluation of fruit quality of Korla fragrant pear from different production areas during growth period. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2022, 13, 6032–6041. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.P.; Wang, J.Z. Analysis of Fruit Quality and Aromatic Components of Plum New Variety “Jinhong” in Different Harvest Times. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2015, 27, 88–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Li, J.F. Establishment of a method for rapid determination of fructose content based on anthraquinone sulfate colorimetric method. Heilongjiang Sci. 2017, 8, 82–85. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Klein, A.-M.; Vaissière, B.E. Importance of pollinators in changing landscapes for world crops. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, K.; Tonaka, N. Related polymorphic F-box protein genes between haplotypes clustering in the BAC contig sequences around the S-RNase of Japanese pear. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 1887–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z. A comprehensive review of autonomous flower pollination techniques: Progress, challenges, and future directions. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 237, 110577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinet, M.; Jacquemart, A.-L. Cultivar placement affects pollination efficiency and fruit production in European pear (Pyrus communis) orchards. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 91, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decourtye, A.; Alaux, C. Toward the protection of bees and pollination under global change: Present and future perspectives in a challenging applied science. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2019, 35, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; He, M. Optimization of Application Parameters for UAV-Based Liquid Pollination in Pear Orchards: A Yield and Cost Perspective. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurz, A.; Grass, I. Hand pollination of global crops–a systematic review. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2021, 56, 299–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komlatskiy, G.; Makarova, T. Pollination by bees in industrial crop production. BIO Web Conf. 2023, 66, 12001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-M.; Gu, C. Characteristic of pollen tube that grew into self style in pear cultivar and parent assignment for cross-pollination. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 216, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, S.A.; Elshafiey, E.H. Overview of bee pollination and its economic value for crop production. Insects 2021, 12, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winfree, R.; Williams, N.M. Wild bee pollinators provide the majority of crop visitation across land-use gradients in New Jersey and Pennsylvania, USA. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 45, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatt, B.K.; Holzschuh, A. Bee pollination improves crop quality, shelf life and commercial value. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20132440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xin, L.; Lu, H.; Chen, X. How Much Area of a Pear Orchard Can One Honey Bee Colony Pollinate? Agriculture 2025, 15, 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212302
Qu X, Zhang X, Wang R, Wang Y, Cheng Q, Xu Y, Xin L, Lu H, Chen X. How Much Area of a Pear Orchard Can One Honey Bee Colony Pollinate? Agriculture. 2025; 15(21):2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212302
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Xinying, Xinru Zhang, Rongshen Wang, Yuesen Wang, Qingfang Cheng, Yaxiong Xu, Lingjun Xin, Hanbing Lu, and Xiao Chen. 2025. "How Much Area of a Pear Orchard Can One Honey Bee Colony Pollinate?" Agriculture 15, no. 21: 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212302
APA StyleQu, X., Zhang, X., Wang, R., Wang, Y., Cheng, Q., Xu, Y., Xin, L., Lu, H., & Chen, X. (2025). How Much Area of a Pear Orchard Can One Honey Bee Colony Pollinate? Agriculture, 15(21), 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212302






