-
 A Study on Improving Separation Efficiency Through Weir Curvature Optimization in an FWKO with a Dish-Head Inlet
A Study on Improving Separation Efficiency Through Weir Curvature Optimization in an FWKO with a Dish-Head Inlet -
 Optimizing Natural Organic Matter Removal from Water by UV/H2O2 Advanced Oxidation Using Central Composite Design
Optimizing Natural Organic Matter Removal from Water by UV/H2O2 Advanced Oxidation Using Central Composite Design -
 Phenolic Compounds in Plant-Based Milk Alternatives from the Greek Market
Phenolic Compounds in Plant-Based Milk Alternatives from the Greek Market
Journal Description
Separations
Separations
- formerly Chromatography - is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on separation and purification science and technology in all areas of chemical, biological, physical science, and separation performance, published monthly online by MDPI. The Central European Group of Separation Sciences (CEGSS) is affiliated with Separations and its members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journal: Purification.
Impact Factor:
2.7 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.7 (2024)
Latest Articles
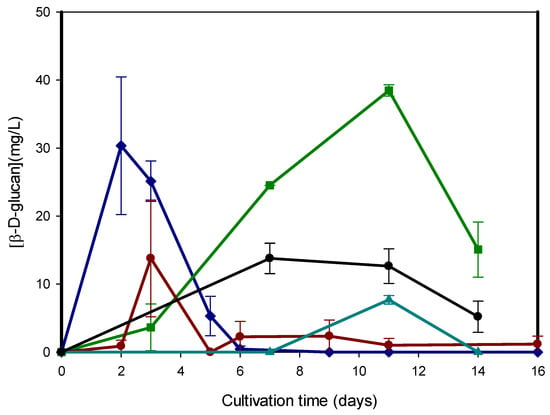
Experimental Planning for Production of β-D-Glucan: Purification and Fluorescence Properties from Basidiomycete Strains
Separations 2025, 12(12), 336; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12120336 (registering DOI) - 7 Dec 2025
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Fruit and coffee industries are responsible for huge quantities of agro-industrial wastes which is of great environmental and public health concern. Therefore, the aim of this work involves the use of such wastes for the production of β-D-glucan from basidiomycete strains which are
[...] Read more.
Fruit and coffee industries are responsible for huge quantities of agro-industrial wastes which is of great environmental and public health concern. Therefore, the aim of this work involves the use of such wastes for the production of β-D-glucan from basidiomycete strains which are powerful biological response modifiers in several clinical disorders. Experimental planning for optimization of several parameters was carried out by a full factorial of two levels of three factors for production of beta-glucans and basidiomycete species, where waste concentration and interaction between species and agro-industrial waste were the most important factors. The best conditions involved a basidiomycete strain of Lentinula edodes in a culture medium containing 400 g/L of waste coffee grounds which revealed the production of extracellular β-glucans (141.16 mg/L) at the 3rd day of fermentation. Intrinsic fluorescence properties of mushroom β-D-glucan were investigated by fluorescence spectroscopy as well as a fluorescence microtiter plate reader exhibiting emission peaks at 492 and 528 nm. Differential chromatographic behavior of β-D-glucan was investigated by immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC) using epoxy-activated Sepharose 6B containing different chelating agents, spacer arms, and metal ions. One-step purification of β-D-glucan was devised using a column of epoxy-activated Sepharose 6B-IDA-Cu (II). FTIR analysis of several β-D-glucans from the chromatographic fractions was carried out to investigate their structural properties.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
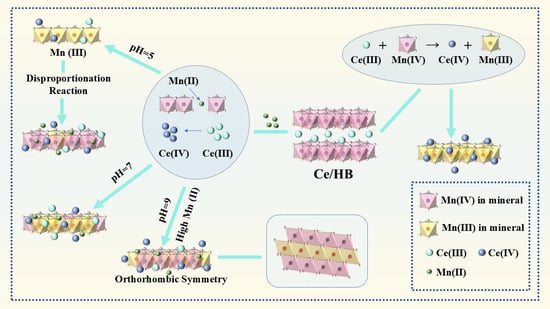
The Influence Mechanism of Mn(II) on the Transformation of Ce-Adsorbed Hexagonal Birnessite
by
Meiqing Chen, Wenjie Dai, Yingying Liu, Guanzheng Zhuang, Yanfu Wei, Zhi Dang and Pingxiao Wu
Separations 2025, 12(12), 335; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12120335 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Birnessite has a strong ability to fix rare-earth elements (REEs), but the transformation process of birnessite and its effects on the migration of these elements are not well understood. This study examines how pH and Mn(II) concentrations influence the transformation of cerium-adsorbed hexagonal
[...] Read more.
Birnessite has a strong ability to fix rare-earth elements (REEs), but the transformation process of birnessite and its effects on the migration of these elements are not well understood. This study examines how pH and Mn(II) concentrations influence the transformation of cerium-adsorbed hexagonal birnessite (Ce/HB) and the behaviors of Ce and Mn. The results show that the effect of Mn(II) on Ce/HB transformation strongly depended on solution pH. At a pH of 5.0, HB initially underwent transformation into feitknechtite, followed by further disproportionation that resulted in the regeneration of HB and Mn(II). Concurrently, redox reactions occur between Mn(IV) in MnO2 (a secondary phase of HB) and Ce(III)/Mn(II), creating a local redox gradient that facilitates partial HB transformation. At pH = 7.0, Mn(II) reduces the crystallinity of transformed products while enhancing the thermodynamic stability of feitknechtite, making it the dominant manganese oxide phase. At pH = 9.0, high-concentration Mn(II) causes lattice distortion in original HB; Ce(III) acts as a structural inducer, promoting mineral transition from hexagonal to orthorhombic symmetry, while excess soluble Mn(II) precipitates new feitknechtite. Additionally, surplus Mn(II) could engage in interfacial redox reactions with high-valent manganese oxides to generate secondary feitknechtite. Ce primarily exists as Ce(IV), forming CeO2 on the mineral surface via oxidation reactions that significantly increase hydroxylation and surface reactivity. This study clarifies the transformation pathways of manganese oxides and the migration and transformation patterns of Ce and Mn in rare-earth-rich mining areas.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Novel Functional Separation Materials for Water Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Adsorption Materials for Carbon Capture: Research Advancements and Prospects
by
Ya Wang, Xiaolong Tang and Honghong Yi
Separations 2025, 12(12), 334; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12120334 - 4 Dec 2025
Abstract
Carbon capture plays a crucial role in mitigating carbon emissions, which is essential for curbing global warming. Owing to its benefits, such as the absence of secondary pollution, operational simplicity, and low energy consumption, adsorption has been widely used in carbon capture. Accordingly,
[...] Read more.
Carbon capture plays a crucial role in mitigating carbon emissions, which is essential for curbing global warming. Owing to its benefits, such as the absence of secondary pollution, operational simplicity, and low energy consumption, adsorption has been widely used in carbon capture. Accordingly, the design of high-efficiency adsorption materials is critical to achieving superior carbon capture performance. In this review, we systemically outline the adsorption mechanisms, influencing factors, and various adsorption materials, including porous carbon-based material, zeolites, metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), solid amines, and emerging adsorbents (porous liquids and supported ionic liquid phase), along with their recent research progress in carbon capture. Furthermore, we point out the design strategies for enhancing CO2 capture performance and potential research directions in the future.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Fast Analytical Separation of Selected Agricultural Pesticides Using Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
by
Ana Jano, Manuel Badiola, Ana M. Ares, José Bernal, María Teresa Martín, Laura Toribio and Adrián Fuente-Ballesteros
Separations 2025, 12(12), 333; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12120333 - 4 Dec 2025
Abstract
Pesticides are chemical substances widely used to control, prevent, or eliminate pests in agriculture, gardening, and other sectors. However, their use poses risks to human health, and recent regulatory efforts have focused on minimizing exposure and monitoring residue levels. In this study, the
[...] Read more.
Pesticides are chemical substances widely used to control, prevent, or eliminate pests in agriculture, gardening, and other sectors. However, their use poses risks to human health, and recent regulatory efforts have focused on minimizing exposure and monitoring residue levels. In this study, the separation of seven pesticides was investigated using supercritical fluid chromatography coupled to diode-array detection (SFC-DAD). The influence of six different stationary phases and various organic modifiers, as well as additional parameters such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of additives, was systematically evaluated to optimize the chromatographic conditions. The best separation performance was achieved using a LiChrospher® 100 DIOL column with methanol as the organic modifier under a gradient program. Analyses were carried out at a flow rate of 3 mL/min, a column temperature of 35 °C, and a system back pressure of 150 bar, resulting in a total analysis time of approximately 4 min. The optimized method allowed for a faster separation of the selected agricultural pesticides by SFC-DAD compared to conventional chromatographic techniques.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Optimization of Advanced Separation Technologies for the Analysis of Emerging Contaminants)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Study on the Separation Performance of a Baffle Cyclone Clarifier
by
Yulong Zhang, Qiang Liu, Kaiwei Guo, Lanyue Jiang, Anjun Li and Yu Wang
Separations 2025, 12(12), 332; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12120332 - 3 Dec 2025
Abstract
To improve fine particle retention in cyclone clarifiers for mine water treatment, we developed three baffle-structured cyclone clarifiers based on the traditional design: flat-baffle cyclone clarifier, convex-baffle cyclone clarifier, and concave-baffle cyclone clarifier. Using numerical simulation, a comparative analysis was conducted on the
[...] Read more.
To improve fine particle retention in cyclone clarifiers for mine water treatment, we developed three baffle-structured cyclone clarifiers based on the traditional design: flat-baffle cyclone clarifier, convex-baffle cyclone clarifier, and concave-baffle cyclone clarifier. Using numerical simulation, a comparative analysis was conducted on the differences in flow field characteristics and particle separation performance between the traditional cyclone clarifier and the three types of baffle-structured cyclone clarifiers. The convex-baffle cyclone clarifier showed the highest pressure drop. At Section II-II, low tangential velocity minimized internal swirl, while Section I-I exhibited high axial velocity near the wall. The low upward axial velocity in the central region of Section II-II enhanced fine particle settling. The convex baffle also promoted uniform streamlines and efficient space utilization. The concave-baffle cyclone clarifier exhibited a larger flow angle relative to the baffle than the flat-baffle cyclone clarifier, causing stronger impingement and turbulence that transported particles to the overflow outlet. In contrast, the convex-baffle cyclone clarifier’s smaller flow angle yielded weaker impingement and more stable flow, reducing particle escape. Simulations confirmed that baffle-structured cyclone clarifiers improve particle removal. The removal efficiency of the convex-baffle cyclone clarifier reaches 78.19%, representing a 5.22% improvement compared to the traditional cyclone clarifier. Furthermore, the convex-baffle cyclone clarifier demonstrated the most effective removal of 5 μm particles compared with both the flat-baffle and concave-baffle cyclone clarifier.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advances in Separation Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimization of Green Pressurized Liquid Extraction of Phenolic Compounds with Inhibitory Capacity Reactive Oxygen Species from Crescentia alata Using a Box-Behnken Design
by
Paola Ester López-Díaz, Honorio Torres-Aguilar, Rodolfo Solano and Luicita Lagunez-Rivera
Separations 2025, 12(12), 331; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12120331 - 30 Nov 2025
Abstract
Crescentia alata is valued in traditional medicine for its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. However, research on its phytochemical composition and bioactivity is scarce. Phenolic compounds are of pharmacological interest because they reduce oxidative stress and inflammation. This study aimed to optimize the pressurized
[...] Read more.
Crescentia alata is valued in traditional medicine for its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. However, research on its phytochemical composition and bioactivity is scarce. Phenolic compounds are of pharmacological interest because they reduce oxidative stress and inflammation. This study aimed to optimize the pressurized liquid extraction of phenolic compounds to enhance the cellular antioxidant activity of the fruit extract. Response Surface Methodology with a Box–Behnken Design was used. Three variables were evaluated at three levels: temperature (25, 37.5, and 50 °C), pressure (10, 30, and 50 bar), and time (10, 20, and 30 min). The effect of these variables was monitored on the total phenolic content, total flavonoid content, and the percentage of inhibition of reactive oxygen species. The optimal extraction conditions were 40.98 °C, 29.52 bar, and 16.89 min, which yielded a TPC of 28.27 mg GAE/g DW, TFC of 19.08 mg QE/g DW, and 72.05% ROS inhibition. This methodology proved to be effective for optimizing the extraction of phenolic compounds and revealed the influence of extraction conditions on their biological activity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Green Extraction of Natural Products for Application in Pharmaceuticals, Foods, Cosmetics and Agriculture)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Horseradish (Armoracia rusticana L.) Processing By-Products as Potential Functional Ingredients in Food Production: A Detailed Insight into Phytochemical Composition and Antioxidant Properties
by
Jovana M. Marković, Ana S. Salević, Danijel D. Milinčić, Uroš M. Gašić, Verica B. Đorđević, Biljana B. Rabrenović, Mirjana B. Pešić, Steva M. Lević, Dragana M. Mihajlović and Viktor A. Nedović
Separations 2025, 12(12), 330; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12120330 - 29 Nov 2025
Abstract
Horseradish (Armoracia rusticana L.) root (HRP) and leaf (HLP) pomaces, by-products of juice production by cold-pressing, were analyzed as a novel potential source of natural antioxidants. Chromatography analysis (UHPLC Q-ToF MS) of the bioactive compounds of pomaces was performed along with spectrophotometric
[...] Read more.
Horseradish (Armoracia rusticana L.) root (HRP) and leaf (HLP) pomaces, by-products of juice production by cold-pressing, were analyzed as a novel potential source of natural antioxidants. Chromatography analysis (UHPLC Q-ToF MS) of the bioactive compounds of pomaces was performed along with spectrophotometric determination of total phenolic content (TPC), total flavonoid content (TFC), total phenolic acid (hydroxycinnamic) content (TPAC), and antioxidant capacity (via 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH•) and 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic-acid) (ABTS•+) radicals’ scavenging activity and ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP)). The concentrations of TPC, TFC, and TPAC differed among the pomaces, significantly favoring HLP. However, both horseradish pomaces (HRP and HLP) contained a considerable amount of various phenolics, with kaempferol and its glucosides dominating. In addition, they exhibit pronounced antioxidant activity, which is confirmed by all three methods used (DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP). These results highlight the potential of valorizing horseradish processing waste as a natural, reliable source of health-promoting bioactive compounds and functional ingredients in food products, thereby fortifying food, preventing oxidation, and prolonging shelf-life. In addition, this study supports endeavors to reduce food waste by providing new insights into the valorization of horseradish pomace, thus contributing to sustainable development and environmental protection.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Natural Product Separation and Characterization of Bioactive Plant Compounds)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Anticoagulant Potential of the Isolate with Green Solvents from Prosthechea karwinskii
by
Anel Karina Bernal-Martínez, Luicita Lagunez-Rivera, Rodolfo Solano, Gabriela Soledad Barragán-Zárate and Jesús Hernández-Juárez
Separations 2025, 12(12), 329; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12120329 - 28 Nov 2025
Abstract
Prosthechea karwinskii is an orchid endemic to Mexico used for medicinal purposes. The objective of this study was to determine the anticoagulant potential ex vivo of the extract isolated using green solvents. Coagulometric assays were performed to evaluate the anticoagulant activity: activated partial
[...] Read more.
Prosthechea karwinskii is an orchid endemic to Mexico used for medicinal purposes. The objective of this study was to determine the anticoagulant potential ex vivo of the extract isolated using green solvents. Coagulometric assays were performed to evaluate the anticoagulant activity: activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), prothrombin time (PT), and thrombin time (TT). For each assay, different concentrations of the extract were evaluated (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.5, 3.5, 4.5, 5.5, 7.5, and 8.5 mg/mL) using platelet-poor plasma from healthy donors. The P. karwinskii leaves extract showed an anticoagulant effect by significantly prolonging (p < 0.05) the APTT and TT from a concentration of 3.5 and 2.5 mg/mL, respectively, compared to basal. The anticoagulant activity was concentration dependent. In addition, the hydroethanolic extract of P. karwinskii leaves inhibited factor XI activity by 86.10 ± 2.3%. The compounds in the extract were identified by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization and quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-ESI-qTOF-MS/MS). The compounds identified were quinic acid, malic acid, succinic acid, L (-)-phenylalanine, guanosine, neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, rutin, kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside, azelaic acid, sebacic acid, pinellic acid, and embelin.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Analysis of Natural Products and Pharmaceuticals)
►▼
Show Figures
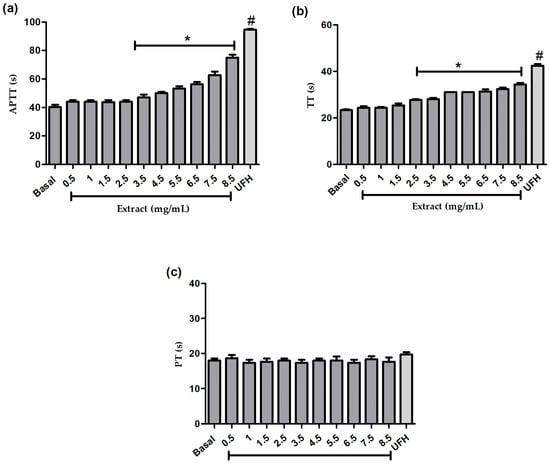
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Reducing Energy Consumption in Reverse Flotation of Iron Ore by Application of Low-Temperature Flotation Reagents: Micro-Flotation, Bench-Scale and Industrial Tests
by
Wenjie Han, Yimin Zhu, Xiuzhen Ma, Jie Liu, Haining Liu and Xiushen Ye
Separations 2025, 12(12), 328; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12120328 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
An eco-friendly flotation process is of great significance to the green and sustainable development of the mining industry. The purpose of this study is to improve the traditional flotation process. Novel reagents, alkyl ether amine (Alkyl carbon chains with a length of 12
[...] Read more.
An eco-friendly flotation process is of great significance to the green and sustainable development of the mining industry. The purpose of this study is to improve the traditional flotation process. Novel reagents, alkyl ether amine (Alkyl carbon chains with a length of 12 are simply referred to as DOEA) as collector and carboxymethyl starch (CMS) as depressant, were used for flotation uAlkyl ether aminender lower temperature, which did not need to heat the tonnage of pulp and reduced the energy consumption. The micro-flotation tests were carried out with three main minerals (quartz, hematite and magnetite) contained in Qidashan (Anshan, China) iron ore at room temperature in winter (18 °C). The bench-scale tests were carried out with flotation feed (mixture of strong magnetic concentrate and weak magnetic concentrate) from the Qidashan flotation workshop at room temperature (18 °C). And the industrial tests were carried out in the flotation workshop of Qidashan Concentrator of Anshan Iron and Steel Co., Ltd. The temperature of the pulp was 17.5~19.7 °C. The results of micro-flotation tests showed that the floatability of the three minerals under the DOEA system decreased in the following order: quartz > hematite > magnetite. The addition of CMS increased the floatability difference between quartz and ferric oxide minerals. DOEA and CMS could effectively separate quartz and ferric oxide minerals at room temperature in winter. The feasibility of the application of DOEA and CMS in Qidashan iron ore was verified by bench-scale tests, and the pulp circulation process was simulated by locked-cycle tests. The results of bench-scale tests showed that under the conditions of CMS dosage 200 g/t, DOEA dosage 150 g/t, and pulp temperature 18 °C, the iron grade of flotation concentrate was 66.54% and iron recovery was 78.37%. The industrial test results showed that the modified flotation process could continuously output qualified iron concentrate without heating the pulp. Compared with the on-site flotation process, it was found that the modified flotation process could save USD 6,460,100 per year. This technology could significantly reduce the energy consumption of iron ore reverse flotation, reduce the carbon emissions generated by heating tons of pulp, and achieve cleaner production.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Separation and Recovery Technology for Mineral Flotation and Solid Waste)
►▼
Show Figures
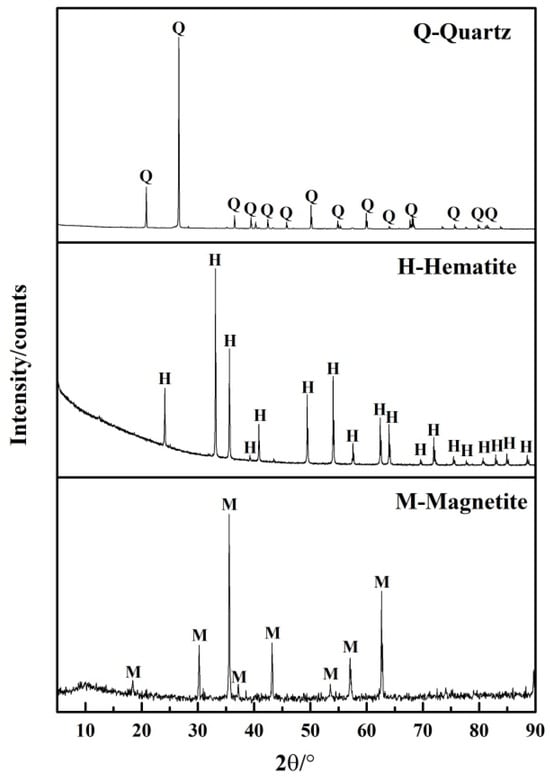
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Cross-Sectional Curve Equation on Flow Field Evolution and Particle Separation in the Spiral Concentrator of the First Turn
by
Shuling Gao, Chunyu Liu, Xiaohong Zhou, Xintong Zhang, Qian Wang and Cong Han
Separations 2025, 12(12), 327; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12120327 - 25 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The flow field evolution in the first turn of the spiral concentrator is decisive for the separation efficiency of solid particles. A laboratory-scale Φ300 mm spiral concentrator was employed as the study subject. The fluid phase was simulated using the RNG k-ε (Renormalization
[...] Read more.
The flow field evolution in the first turn of the spiral concentrator is decisive for the separation efficiency of solid particles. A laboratory-scale Φ300 mm spiral concentrator was employed as the study subject. The fluid phase was simulated using the RNG k-ε (Renormalization Group) turbulence model and the VOF (Volume of Fluid) multiphase model, while the particles were calculated with an Eulerian multi-fluid VOF model that incorporates the Bagnold effect. The influence of the cross-sectional curve equation on the evolution of flow field parameters in the first turn and on the separation behavior of hematite and quartz particles was systematically investigated. The results indicated that the evolution characteristics of fluid parameters, such as the depth of flow film, the tangential velocity of surface flow, the velocity of secondary circulation, and radial flux, were similar. All parameters were observed to undergo an initial decrease or increase, eventually stabilizing as the longitudinal travel progressed. A negative correlation was identified between the index of the cross-sectional curve equation and both the depth of flow film and the tangential velocity of surface flow in the inner half of the trough, whereas an inverse relationship was noted in the outer half. With an increase in the index of the cross-sectional curve equation, the outward circulation velocity in the initial stage and its radial flux in the outer zone were enhanced, while the fluctuations in the evolution of local fluid parameters were suppressed, with more active fluid radial migration observed at the indices of the cross-sectional curve equation of 2.5 and 3. As the flow field evolved, axial separation between hematite and quartz particles was progressively achieved by gravity due to their density difference. In the middle and inner-outer zones, the migration directions of hematite and quartz were observed to become opposite in the later stage of evolution, while the difference in their migration magnitudes was also found to be widened. With an increase in the index of the cross-sectional curve equation, the disparity in the axial separation and movement between hematite and quartz was enhanced, albeit with a diminishing rate of increase. The maximum separation efficiency between hematite and quartz particles was significantly improved with increased longitudinal travel, reaching over 60% by the end of the first turn; higher indices were determined to be more favorable for achieving this performance. Based on the previous research, the variation in separation indices in the third turn was investigated under both independent adjustment of the index of the cross-sectional curve equation and its combined adjustment with the downward bevel angle. Relatively high and stable separation performance was achieved with the indices of the cross-sectional curve equation of 2.5 and 3, where a maximum separation efficiency of 82.02% was obtained, thereby validating the high efficiency and suitability of the selected spiral concentrator profile. This research elucidated the decisive role of the flow field evolution through the first turn in particle separation behavior from the perspective of quantitative description of hydrodynamic parameters, providing beneficial references for the cross-sectional structure design of spirals and the prediction of the separation index of specific feed.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Combination of Phosphoric Acid Extractants P507, P204, or Cyanex272 with LIX984 for Accelerated Extraction of Nickel in Spent Electroless Nickel Plating Baths
by
Rong Zha, Ying Huang, Ling Zhu, Jiali Tan, Zhenfeng Xiong and Baoyan Chi
Separations 2025, 12(12), 326; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12120326 - 22 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Hydroxamic acid extractants, such as LIX984, demonstrate high efficiency in extracting nickel from electron-free nickel waste solutions; however, they suffer from a slow extraction rate. This study investigated the effect of adding 2–5 vol.% of three organophosphate extractants (P507, P204, and Cyanex272) to
[...] Read more.
Hydroxamic acid extractants, such as LIX984, demonstrate high efficiency in extracting nickel from electron-free nickel waste solutions; however, they suffer from a slow extraction rate. This study investigated the effect of adding 2–5 vol.% of three organophosphate extractants (P507, P204, and Cyanex272) to LIX984. The results show that incorporating 2–5 vol.% of P507 or Cyanex272 significantly improves both extraction efficiency and kinetics. The addition of organophosphate extractants increased the extraction rate by 1.5–10 times, indicating a direct correlation between the extractant content and the acceleration of the extraction process, with higher concentrations yielding faster extraction. Compared to the use of LIX984 alone, where nickel extraction efficiency was only 46%, the addition of 5 vol.% P507 increased efficiency to over 99%, with a substantial improvement in extraction rate. Similarly, 2 vol.% P204 achieved a nickel removal efficiency of 99.8%. In non-electroplating waste solutions (pH 4–6), selective removal of iron and zinc impurities was achieved by first adding 2–5 vol.% P204 or P507, followed by adjusting the pH to 6–7 and using a mixture of organophosphate extractants. The spent electroless nickel plating baths were then treated with LIX984 combined with organophosphoric acid extractants, yielding nickel salt solutions of higher purity. Thus, P507, P204, and Cyanex272 serve as effective promoters for the hydroxamic acid extractant LIX984, resulting in both enhanced nickel extraction efficiency and faster extraction kinetics.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Gas Disturbance Model and Industrial Application of the BH Packing
by
Qunsheng Li, Huifang Zhang, Qiulian Chang, Kehan Wang and Yuxin Zhang
Separations 2025, 12(12), 325; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12120325 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
This study presents the development and comprehensive evaluation of a novel structured packing, termed ‘BH’ packing (derived from Beijing University of Chemical Technology), alongside the introduction of an innovative gas disturbance model and its successful industrial implementation. Addressing inherent limitations of traditional structured
[...] Read more.
This study presents the development and comprehensive evaluation of a novel structured packing, termed ‘BH’ packing (derived from Beijing University of Chemical Technology), alongside the introduction of an innovative gas disturbance model and its successful industrial implementation. Addressing inherent limitations of traditional structured packings—such as liquid film aging and high mass transfer resistance in straight corrugated channels—the BH packing incorporates a uniquely designed alternating-angle corrugation (45°–30°–45°). This structural innovation actively disrupts the liquid film, intensifies gas–liquid interaction, and significantly enhances mass transfer efficiency. Experimental assessments demonstrate that the BH-250 packing outperforms conventional corrugated plate packings in gas distribution uniformity. Furthermore, the newly developed gas disturbance model can accurately capture the gas mixing dynamics within the packed bed. Its prediction results are more accurate than those of traditional mixing tank models, especially in regions near the tower wall. In industrial practice, the application of BH packing has led to remarkable improvements in product purity: methanol purity reached 99.95%, hexafluorobutene achieved 6N grade, and dichlorosilane impurities were reduced to parts per trillion (ppt) levels. These outcomes underscore the substantial contribution of BH packing to advancing separation efficiency and product quality in high-purity chemical production.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Novel Solvents and Methods in Distillation Process)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Composition- and Temperature-Dependent Solubility of Sinomenine Hydrochloride in Ethanol–Water Mixtures
by
Yuxin Bian, Honggen Wu and Wenlong Li
Separations 2025, 12(12), 324; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12120324 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
Sinomenine Hydrochloride is a bioactive alkaloid extracted from the root and stem of the medicinal plant sinomenium acutum, and is widely used to treat rheumatoid arthritis. Relevant studies were consulted, and the solubility data of Sinomenine Hydrochloride in ethanol–water mixed solvent have not
[...] Read more.
Sinomenine Hydrochloride is a bioactive alkaloid extracted from the root and stem of the medicinal plant sinomenium acutum, and is widely used to treat rheumatoid arthritis. Relevant studies were consulted, and the solubility data of Sinomenine Hydrochloride in ethanol–water mixed solvent have not been reported. It is essential to choose a proper solvent in the process of crystallization that has a significant influence on the purity and productivity. Therefore, it is necessary to determine the solubility of Sinomenine Hydrochloride under the conditions of different ratios of ethanol–water mixed solvent and temperature. In this study, the solubility of Sinomenine Hydrochloride in ethanol–water mixed solvent was determined using high-performance liquid chromatography within the temperature range of 283.15 K–308.15 K. At the same time, the CNIBS/R-K model, Modified Apelblat model, Yaws model, and Apelblat–Jouyban–Acree model were used to fit the solubility data, and the relevant thermodynamic parameters were calculated using the Van’t Hoff model. The results showed that the solubility of Sinomenine Hydrochloride was higher in pure water than in pure ethanol. Moreover, with the increase in the mass fraction of ethanol in the mixed solvent, the solubility of Sinomenine Hydrochloride showed a trend of increasing first and then decreasing. When the ethanol–water ratio was 5:5, the solubility of the compound reached the maximum. In addition, experimental data showed that the solubility of Sinomenine Hydrochloride was affected by temperature. In the experimental temperature range, the solubility increased with the increase in temperature. Among these four solubility models, the CNIBS/R-K model had the best fitting effect; the maximum RAD and RMSD were 4.622 × 10−3 and 4.079 × 10−3, respectively. The thermodynamic model fitting results showed that the predicted values were in good agreement with the experimental data, and the thermodynamic parameters ΔHd, ΔSd, and ΔGd were all positive values. This indicated that the dissolution of Sinomenine Hydrochloride in the ethanol–water mixture was a non-spontaneous and endothermic process. A proper ratio of ethanol–water and temperature improved the solubility of Sinomenine Hydrochloride. The data determined in this study can provide basic data for the industrial purification of Sinomenine Hydrochloride.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sample Preparation and Chromatographic Analysis of Environmental Samples)
►▼
Show Figures
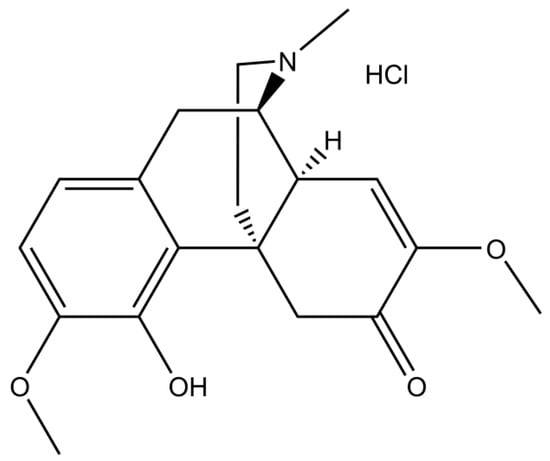
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
UHPLC-QTOF-MS/MS Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Environmental, Morphological, and Taxonomic Drivers of Chemical Diversity in Neotropical Banisteriopsis and Stigmaphyllon
by
Jaqueline Munise Guimarães da Silva, Grazielle Jesus dos Santos, Rafael Felipe de Almeida and Maria Luiza Zeraik
Separations 2025, 12(11), 323; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12110323 - 20 Nov 2025
Abstract
Banisteriopsis and Stigmaphyllon are among the most species-rich liana genera in the Neotropical Malpighiaceae family, known for their diverse chemical and biological activities. However, metabolomic information correlating these genera with their biome of occurrence, humidity levels, and plant habit (liana vs. shrub) remains
[...] Read more.
Banisteriopsis and Stigmaphyllon are among the most species-rich liana genera in the Neotropical Malpighiaceae family, known for their diverse chemical and biological activities. However, metabolomic information correlating these genera with their biome of occurrence, humidity levels, and plant habit (liana vs. shrub) remains limited. This study explored in detail the metabolomic profiles of 15 species (29 specimens) of Banisteriopsis and 26 species (35 specimens) of Stigmaphyllon using Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA). Leaf extracts obtained with ethanol/water (4:1, v/v) were analyzed by Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography coupled to Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (UHPLC-QTOF-MS/MS). Comparative analyses were performed at the genus level and across biome, humidity, and plant habit variables. The UHPLC-MS/MS profiling enabled the annotation of compounds, including previously unreported metabolites identified in B. quadriglandula and S. saxicola. Shared metabolites between the two genera were also characterized. PLS-DA revealed discriminant metabolites associated with the different comparative parameters, notably glucose (plant habit), coumaroyl hexoside, myricetin-3-galactoside, quercetin (genus), and quercetin-3-O-robinobioside (environment). With 95% confidence, our results demonstrate that environmental and morphological factors significantly influence metabolite biosynthesis in Banisteriopsis and Stigmaphyllon, providing valuable insights for future phytochemical and ecological research in the Neotropics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Natural Product Separation and Characterization of Bioactive Plant Compounds)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Dye Removal Efficiency Through Sustainable Adsorbent Production from Corncobs (Zea mays L. ssp. amilacea)
by
Rosmery Godoy Bautista, Rubén Alfredo Palomino Infante, Cipriano Mendoza Rojas, Kirianova Godoy Bautista, Juan Carlos Woolcott Hurtado, Ulises Roman-Concha and Héctor Luis Gómez Ramírez
Separations 2025, 12(11), 322; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12110322 - 20 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Active surface materials such as activated carbon are used in the removal of contaminants and dyes in effluents. The primary objective of this study was to convert starchy corncobs into valuable activated carbon, capable of efficiently adsorbing dyes, and to comprehensively analyze the
[...] Read more.
Active surface materials such as activated carbon are used in the removal of contaminants and dyes in effluents. The primary objective of this study was to convert starchy corncobs into valuable activated carbon, capable of efficiently adsorbing dyes, and to comprehensively analyze the resulting material’s physical and structural properties. To achieve this purpose, a 23 factorial design was employed to create optimized activated carbon for effective methylene blue dye adsorption. The factors considered were carbonization temperatures, carbonization times, and H3PO4 activating agent concentrations. This design yielded eight types of activated carbon, namely B-85%, D-85%, M-85%, L-85%, A-45%, S-45%, P-45% and X-45%, observing that the increase in temperature and carbonization time had negative effects on the adsorption capacity, while the increase in the percentage of activating agent had positive effects. The variant labeled as A-45% displayed the highest cationic methylene blue dye removal efficiency, boasting a remarkable adsorption capacity of 99.93%. This result almost reached the performance of commercial activated carbon, which exhibited a similar methylene blue dye removal efficiency (99.94%), while the removal efficiency of the anionic dye nigrosin was 95.24%. X-ray diffraction analysis of activated carbon A-45% indicated a slightly crystalline amorphous structure. Moreover, surface area analysis utilizing the BET method revealed that this material possessed a micromesoporous nature, mainly consisting of cylindrical micropores, resulting in an impressive surface area of 306,493 m2/g. FTIR analysis revealed the presence of functional groups, including O-H, C=C, C-O, C-X, and P=O, which create a highly polar surface that enhances the chemisorption of cationic molecules like methylene blue. These findings demonstrate the potential application of the synthesized activated carbon in industrial effluent treatment processes.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Comparison and Validation of QuEChERS Extraction Methods Coupled with UHPLC/Orbitrap HR-MS for the Determination of Antibiotics and Related Compounds in Fish and Fish Feed
by
Kleopatra Miserli, Vasiliki Boti, Dimitra Hela, Triantafyllos Albanis and Ioannis Konstantinou
Separations 2025, 12(11), 321; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12110321 - 18 Nov 2025
Abstract
The widespread presence of pharmaceutical active compounds (PhACs) in aquatic environments raises significant environmental and public health concerns, particularly through their accumulation in marine biota and potential transfer to humans via seafood. In aquaculture, fish feed is essential for production but may also
[...] Read more.
The widespread presence of pharmaceutical active compounds (PhACs) in aquatic environments raises significant environmental and public health concerns, particularly through their accumulation in marine biota and potential transfer to humans via seafood. In aquaculture, fish feed is essential for production but may also act as a pathway for contaminants in the marine environment. This study aimed to develop and validate an analytical method for the extraction and quantification of 14 antibiotics and ethoxyquin antioxidant in fish tissue and feed. Two QuEChERS-based extraction protocols were compared: the AOAC 2007.01 method (Method A) using Z-Sep+ as clean-up, and the original QuEChERS method (Method B) employing Enhanced Matrix Removal (EMR)-lipid. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with Orbitrap mass spectrometry using electrospray ionization in positive and negative mode was applied for identification and quantification. Validation included assessment of recovery, linearity, precision, limits of detection and quantification, uncertainty, matrix effects, and process efficiency. Both methods showed good linearity (R2 > 0.9899) and precision (<19.7%). Method B achieved superior recoveries for most analytes in both fish tissue (70–110%) and feed (69–119%), with lower uncertainties (<18.4%) compared to Method A. Overall, the original QuEChERS method demonstrated better analytical performance, supporting its application as a green, robust tool for monitoring emerging contaminants in aquaculture products.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Optimization of Advanced Separation Technologies for the Analysis of Emerging Contaminants)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Multi-Parameter Synergistic Effects on Fine Coal Slurry Sedimentation in High-Gravity Fields: A CFD Study
by
Lingyun Liu, Huikuan Pan, Wei Ge and Chuilei Kong
Separations 2025, 12(11), 320; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12110320 - 16 Nov 2025
Abstract
This study addresses the technical challenges of conventional coal slurry sedimentation equipment in handling fine coal particles, such as poor settling performance and strong dependence on chemical reagents, by designing a novel high-gravity sedimentation and dewatering device. Solid–liquid centrifugal separation was simulated on
[...] Read more.
This study addresses the technical challenges of conventional coal slurry sedimentation equipment in handling fine coal particles, such as poor settling performance and strong dependence on chemical reagents, by designing a novel high-gravity sedimentation and dewatering device. Solid–liquid centrifugal separation was simulated on the CFD-Fluent platform using the Eulerian–Eulerian method, with the solid volume fraction and effective deposition thickness adopted as key indicators of particle settling performance. The settling behavior and flow field characteristics of particles with different sizes (0.045–0.5 mm) were elucidated under varying centrifugal radii (400–800 mm) and rotational speeds (400–1200 r·min−1), thereby providing a solid theoretical foundation for the parameter optimization of centrifugal settling processes for fine particles. The results indicate that increasing the centrifugal radius and rotational speed strengthens the centrifugal field effect, markedly enhancing the dynamic pressure gradient and interphase slip velocity. Under high-speed (ω = 1200 r·min−1) and large-radius (R = 800 mm) conditions, the dynamic pressure of fine particles (0.045 mm) reached 7.52 MPa with a radial velocity of 0.79 m·s−1, effectively compensating for the settling disadvantage of fine particles, promoting solid–liquid separation, and ensuring the stable deposition of coal particles. Meanwhile, as particle size increases, a distinct deposition thickness can be formed under different operating conditions, demonstrating that particle size is the dominant factor governing deposition behavior. The study elucidates the intrinsic mechanism of how multiple parameters—rotational speed, centrifugal radius, and coal particle size—synergistically influence particle deposition characteristics. By regulating these parameters to accommodate different particle sizes, the findings provide valuable insights for the parameter optimization of centrifugal settling processes for fine particles.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Solid Waste Recycling and Strategic Metal Extraction)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Solid-Phase Extraction Combined with Digital Image Colorimetry for the Analysis of Lead in Water Samples
by
Wenying Wu, Zhen Ma, Xu Jing and Xinyuan Bi
Separations 2025, 12(11), 319; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12110319 - 15 Nov 2025
Abstract
In this study, we developed a rapid method for determining lead(II) by integrating solid-phase extraction with digital image colorimetry to reduce the time and labor required for the analysis of lead(II) in water samples. The solid-phase extraction column was packed with cellulose as
[...] Read more.
In this study, we developed a rapid method for determining lead(II) by integrating solid-phase extraction with digital image colorimetry to reduce the time and labor required for the analysis of lead(II) in water samples. The solid-phase extraction column was packed with cellulose as a bio-based adsorbent, which facilitated adsorption and enrichment of lead(II) during sample loading. The elution step, which is time-consuming and solvent-intensive, was eliminated from the procedure. An aqueous solution of sodium rhodizonate was added to react with lead(II), forming a red–brown complex. The color intensity was quantified using a smartphone-based digital image colorimetry. The method showed good linearity in the range of 0.01–0.8 mg L−1 with R2 > 0.99. In tap, river, and spring water, the recovery was 93.5% to 97.5% with a relative standard deviation of 1.7–4.8%. Five complementary greenness assessment tools confirmed the environmental friendliness of the method. This rapid pretreatment and detection technique can be applied to analyzing lead(II) in aqueous samples.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Research on Novel Separation Media and Separation/Analysis Technologies)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Numerical Analysis and Experimental Study on the Classification of Fine Particles Using a Hydrocyclone with Multiple Vortex Finders
by
Feng Li, Guodong Huang, Chaoqi Zou, Yuting Fu, Jiawei Li, Baocong Ma, Yanchao Wang and Chenglei Zhang
Separations 2025, 12(11), 318; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12110318 - 15 Nov 2025
Abstract
Ultrafine particles, as raw materials for various industries such as construction and environmental protection, are currently obtained through repeated ball milling and multiple classifications, but classification efficiency remains at a low level. Based on the principle of hydrocyclone classification, this paper designs a
[...] Read more.
Ultrafine particles, as raw materials for various industries such as construction and environmental protection, are currently obtained through repeated ball milling and multiple classifications, but classification efficiency remains at a low level. Based on the principle of hydrocyclone classification, this paper designs a hydrocyclone with a triple-vortex finder structure that can achieve finer particle size distributions without altering the main structure of the hydrocyclone. The classification performance of the triple-vortex finder hydrocyclone is investigated through numerical analysis and experimental methods, with numerical comparisons made to single-vortex finder and double-vortex finder structures. The results indicate that with an increase in the number of vortex finders, the static pressure and tangential velocity gradually decrease, reducing the likelihood of tangential vortex formation while meeting classification requirements. The axial velocity in the triple-vortex finder structure is significantly reduced, which extends the residence time within the hydrocyclone and facilitates sufficient particle classification. As the number of vortex finders increases, the zero-velocity envelope surface (LZVV) gradually migrates inward, enlarging the external swirling classification space. Through numerical and experimental analyses, it is found that the triple-vortex finder hydrocyclone exhibits the highest classification efficiency, the strongest cutting ability, and the best classification accuracy. Compared to the single-vortex finder structure, the cutting particle size of the triple-vortex finder hydrocyclone decreases by 2.5 µm, and the content of fine particles in the underflow is reduced by 4.36 percentage points, effectively decreasing the fine particle content in the underflow. The quality efficiency improves by 18.85 percentage points compared to the single-vortex finder, while the quantity efficiency shows no significant decline. The obtained data provide a theoretical foundation and data support for the structural design of the new hydrocyclone.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advances in Separation Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Comprehensive Analytical Workflow for the Quantification of Carotenoid Presence in Chicken Egg Yolks
by
Eleni D. Myrtsi, Dionysios T. Pavlopoulos, Vasilios Iliopoulos, Sofia D. Koulocheri and Serkos A. Haroutounian
Separations 2025, 12(11), 317; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12110317 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
Chicken egg is included among the main components of the human diet as an important source of nutrients, such as proteins, lipids, vitamins, minerals and carotenoids. The latter are terpenoid pigments present in egg yolks, providing their color and playing a vital role
[...] Read more.
Chicken egg is included among the main components of the human diet as an important source of nutrients, such as proteins, lipids, vitamins, minerals and carotenoids. The latter are terpenoid pigments present in egg yolks, providing their color and playing a vital role because of their significant bioactivities. The carotenoid content of egg yolk varies considerably since it is strongly influenced by the respective laying hens’ farming and feeding procedures, and there is therefore a need to establish an efficient method for their assessment. The absence of such a method prompted us to develop a novel procedure consisting of the extraction, saponification and quantitative assessment of contained carotenoids. For this purpose, the optimal conditions for the extraction of carotenoids from egg yolks were defined, along with the optimal saponification conditions of carotenoids, with respect to reaction duration and pH influence on the extract’s contents of lutein and zeaxanthin. The carotenoid content of extracts was determined using a novel, developed herein LC-MS/MS method that allows the accurate, fast and simultaneous quantitation of the 11 most abundant carotenoids in egg yolks. The method accuracy and reliability were validated for six different parameters determined for each analyte. The novel procedure was applied for the assessment of the carotenoid content of ten egg yolks of diverse origin, indicating the bioactive carotenoids lutein and retinol as the most abundant, while lesser amounts of the remaining natural and synthetic carotenoids were found and there was no trace of fucoxanthin or astaxanthin molecules. The results herein revealed a variation in the carotenoid content of chicken eggs that depended on the diet and farming method of egg-laying hens.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovative Adsorption Materials and Extraction Technology for Food Sample Detection)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Separations Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Analytica, Foods, Molecules, Processes, Separations
Progress in Analytical Chemistry in Materials and Food and Environmental Samples
Topic Editors: Gavino Sanna, Domenica Tonelli, Oscar Núñez, Stefan TsakovskiDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Clean Technol., IJERPH, Membranes, Microorganisms, Water, Separations
Sustainable Development of Clean Water and Sanitation
Topic Editors: Rajendra Prasad Singh, Chris Zevenbergen, Dafang FuDeadline: 15 March 2026
Topic in
Analytica, Foods, Molecules, Processes, Separations, Chemosensors
Application of Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry and Related Techniques, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Chao Kang, Ronald BeckettDeadline: 30 April 2026
Topic in
ChemEngineering, Materials, Molecules, Nanomaterials, Separations
Porous Materials for Energy and Environment Applications, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Yi-Nan Wu, Fei KeDeadline: 31 May 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Separations
Recovery of Precious Metals and Metal Nanoparticles from Electronic and Industrial Waste
Guest Editors: Dimosthenis Giokas, Manolis ManosDeadline: 10 December 2025
Special Issue in
Separations
Chromatographic Methods for Environment, Biota and Food Contaminants Analysis
Guest Editors: Melinda Haydee Kovács, Emőke Dalma KovácsDeadline: 10 December 2025
Special Issue in
Separations
Removal of Organic Pollutants from Aqueous Systems
Guest Editor: Li YanDeadline: 10 December 2025
Special Issue in
Separations
Mineral Processing and Separation: Research, Innovation and Production
Guest Editor: Jiangang KuDeadline: 10 December 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Separations
CEGSS Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow
Collection Editors: Bogusław Buszewski, Erwin Rosenberg
Topical Collection in
Separations
Recent Trends in the Separation of Natural Products and Pharmaceuticals
Collection Editors: Paraskevas D. Tzanavaras, Susanne Wiedmer
Topical Collection in
Separations
Synthetic Membrane Separation Science and Technology
Collection Editors: Mohamed Khayet, Elena Guillen Burrieza
Topical Collection in
Separations
Feature Paper Collection in Section 'Environmental Separations'
Collection Editors: Maria Elizabeth Tiritan, Cláudia Maria Rosa Ribeiro