Abstract
Biologically treated swine farm wastewater still contains high levels of refractory organics, humic substances and antibiotic residues, posing environmental risks and limiting opportunities for water reuse. Wastewater treatment by ozonation alone suffers from low mass transfer efficiency and selective oxidation. To overcome these limitations, a catalytic ozonation process (O3/Fe2+/H2O2) was applied and optimized using Response Surface Methodology (RSM) based on single-factor experiments and Central Composite Design (CCD) for advanced swine farm wastewater treatment. The optimal conditions ([O3] = 25.0 mg/L, [Fe2+] = 25.9 mg/L, [H2O2] = 41.1 mg/L) achieved a COD removal of 44.3%, which was 86.8% higher than that of ozonation alone, and increased TOC removal to 29.5%, indicating effective mineralization. Biodegradability (BOD5/COD) of swine farm wastewater effluent increased from 0.01 to 0.34 after the catalytic ozonation treatment. Humic-like and fulvic-like substances were removed by 93.7% and 95.4%, respectively, and antibiotic degradation was significantly accelerated and enhanced. The synergistic process improved ozone utilization efficiency by 33.1% and removed 53.95% of total phosphorus through Fe3+-mediated coprecipitation. These findings demonstrate that with catalytic ozone decomposition and production of hydroxyl radicals, the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 system effectively integrates enhanced ozone utilization efficiency, radical synergy, and simultaneous pollutant removal, providing a cost-effective and technically feasible strategy for advanced swine farm wastewater treatment and safe reuse.
1. Introduction
Swine farming is one of the most important sectors of global livestock production, with annual pork consumption exceeding 128 million metric tons [1]. Veterinary antibiotics (VAs) are widely administered for disease prevention and control to maintain animal health in high-density rearing systems. Tetracyclines (TCs) and sulfonamides (SAs), owing to their low cost and broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, are among the most extensively used antibiotics in swine production [2]. However, due to limited absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, a substantial proportion of these compounds is excreted unmetabolized, either as parent compounds or metabolites [3]. Research indicates that the excretion rate varies considerably depending on the VA class: sulfonamide antibiotics exhibit excretion rates as high as 90% [4]. This leads to the widespread occurrence of antibiotic residues, classified as emerging contaminants (ECs), in swine farm wastewater. Given that a single pig can generate 4 to 8 L of wastewater daily, the overall wastewater volume is considerable and continues to rise [5]. The complex composition of this wastewater underscores the urgent need for effective treatment strategies.
Among biological treatment technologies, the Anoxic–Oxic (A/O) process is the most commonly applied in swine farms [6]. In practice, although the two-stage A/O process efficiently removes NH3-N, its denitrification performance is often limited by insufficient biodegradable organic carbon. Even after multistage biological treatment, effluents often exhibit high chemical oxygen demand (COD) and coloration [7], primarily due to the presence of recalcitrant humic substances [8], particularly those with particle sizes <0.45 μm, which can enhance the mobility of organic pollutants in soils [9]. Studies have shown that such effluents reduce the soil’s adsorption capacity for antibiotics and increase the risk of leaching and runoff [10]. Therefore, advanced treatment technologies are required to mitigate environmental risks and support safe water reuse.
Integrating advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) with biological treatment provides a promising strategy to improve overall treatment efficiency while minimizing costs. Biological treatment is effective in removing readily biodegradable compounds, thereby reducing the competition for reactive species during subsequent AOPs and facilitating the degradation of refractory compounds. Moreover, AOPs can be applied as an intermediate step to enhance the biodegradability of effluents before biological processes [1]. While individual or combined AOPs, such as Fenton oxidation, ozonation, and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) treatment, have demonstrated effectiveness in removing persistent organics [11], their full-scale application remains limited by operational constraints. Ozonation, although widely used for its strong oxidizing capability and sludge-free operation, suffers from low solubility, limited aqueous stability, and selective oxidation behavior, leading to incomplete degradation of pollutants [12]. Meanwhile, conventional Fenton processes require highly acidic pH (2.8–3.5) and generate excessive sludge, complicating subsequent handling and disposal [13].
To overcome these limitations, catalytic ozonation has attracted increasing attention for its ability to promote ozone decomposition and generate highly reactive hydroxyl radicals (HO•), enhancing the removal efficiency of toxic and refractory pollutants. Homogeneous catalysts such as H2O2 and Fe2+ significantly influence oxidation selectivity, reaction kinetics, and ozone utilization efficiency [14,15]. However, excess H2O2 or Fe2+ can act as HO• scavengers [15], thereby decreasing catalytic efficiency. Therefore, precise optimization of the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 system parameters is critical to ensure energy-efficient and high-performance operation.
Response Surface Methodology (RSM), particularly Central Composite Design (CCD), enables efficient multivariate optimization with minimal experimental runs. CCD allows for the analysis of quadratic interactions and supports the development of predictive models for process performance [16].
In this study, a synergistic O3/Fe2+/H2O2 catalytic ozonation system was investigated to address the persistent limitations in biologically treated swine farm wastewater, such as high concentrations of refractory organics, residual humic substances, and antibiotic contamination. Using RSM-based optimization, the process performance was systematically evaluated, with a focus on COD removal, biodegradability enhancement, and organic substance transformation. The energy efficiency was also assessed. The findings provide a comprehensive basis for applying O3/Fe2+/H2O2 catalytic ozonation in the advanced treatment and safe reuse of swine farm wastewater effluents.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
Ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO4·7H2O), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, 30% w/v), potassium iodide (KI), and sodium thiosulfate (Na2S2O3) were purchased from Xilong Scientific Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China). The antibiotics sulfadiazine (SD, CAS: 68-35-9), sulfamethazine (SMZ, CAS: 57-68-1), tetracycline (TC, CAS: 60-54-8), and oxytetracycline (OTC, CAS: 79-57-2) were obtained from Macklin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Sulfamethoxazole (SMX, CAS: 723-46-6) and sulfamonomethoxine (SMM, CAS: 1220-83-3) were purchased from Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) and Meryer Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), respectively. HPLC-grade methanol (MeOH) was supplied by Sigma-Aldrich (Shanghai, China). Ultrapure water was generated using an HHitech (Shanghai, China) smart S38 water purification system.
Individual antibiotics stock solutions were prepared in ultrapure water at a concentration of 100 mg/L. For the oxidation of antibiotics, before each experiment, the target antibiotic stock solutions were spiked into the biologically treated swine farm wastewater to yield a concentration of 1.0 mg/L for each antibiotic. Considering the background levels of target antibiotics in the wastewater, the actual antibiotics concentrations in the reaction matrix were determined using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS).
2.2. Sample Collection
Swine farm wastewater samples were collected from the treatment facility at a large-scale swine farm in Hainan Province, China. The treatment process at the farm includes solid–liquid separation, upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) fermentation, two-stage anoxic–oxic (A/O) treatment, and physicochemical sedimentation. Key effluent parameters from the two-stage A/O system are provided in Table A1. Effluent from the primary oxic tank (A/O-1) exhibited a COD concentration of 256.03 mg/L and a BOD5/COD ratio of 0.011, indicating low biodegradability. The secondary oxic tank (A/O-2) showed limited removal of COD, NH3-N, TN, and TP. Effluent from the A/O-1 tank was used in all experiments. Samples were transported to the laboratory immediately, stored at 4 °C, and equilibrated to room temperature (25 ± 1 °C) before use.
2.3. Experimental Setup
The schematic diagram of the ozonation system is shown in Figure A1. A custom-fabricated acrylic reactor with an internal diameter of 50 mm, a height of 200 mm, and a working volume of 200 mL was used. A sampling port was positioned 30 mm above the reactor base. Mixing was provided by a magnetic stirrer (Model 85-1, Sile Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). Ozone gas was introduced via a porous stainless-steel diffuser (pore size: 100 μm) installed at the reactor base. Exhaust gas was vented through the reactor top and passed sequentially through two gas-washing bottles, each containing 2% (w/v) KI solution to capture residual ozone.
2.4. Experimental Procedure
Ozonation experiments were conducted in semi-batch mode. High-purity oxygen (≥99.5%) was used as the feed gas for ozone generation. The applied ozone concentration was continuously monitored using an ozone analyzer and adjusted as required. The ozone concentration throughout the manuscript refers to the applied ozone concentration in the inlet gas stream. The ozone concentration in the single-factor experiments was 20 mg/L. In Section 3.3, the ozone concentration was 25 mg/L based on the RSM optimization. Prior to each run, 200 mL of swine farm wastewater was added to the reactor, and FeSO4·7H2O and H2O2 were added to achieve the target concentrations. Ozone gas was then introduced. All experiments were performed at 25 ± 1 °C under constant stirring.
To terminate COD degradation experiments, residual ozone was purged with oxygen [17]. In antibiotic degradation experiments, samples were rapidly withdrawn at specific time intervals and quenched immediately with 0.1 mol/L Na2S2O3 solution to neutralize residual ozone. All experiments were conducted in duplicate.
A central composite design within the response surface methodology framework was applied to optimize the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process for COD removal from swine farm wastewater. The independent variables included O3 concentration (A), Fe2+ concentration (B), and H2O2 concentration (C). Their ranges were determined based on the results of single-factor experiments. COD removal efficiency (Y) served as the response variable. The CCD comprised 8 factorial points (23), 6 axial points, and 3 center points, resulting in a total of 17 experimental runs. The center replicates provided an unbiased estimate of pure experimental error [16]. The experimental data were fitted to a second-order polynomial model (Equation (1)) [18]:
where Y is the predicted COD removal, β0 is the intercept, βi are the linear coefficients, βii are the quadratic coefficients, βij are the interaction coefficients, and Xi are the coded factor levels of the independent variables A, B, and C. The RSM optimization and statistical analysis were performed using Design-Expert 13 software.
Y = β0 + Σ βiXi + Σ βiiXi2 + Σi Σj βijXiXj
Molecular weight (MW) distribution of organic constituents was determined using sequential membrane ultrafiltration. Samples were pre-filtered through 0.45 μm glass fiber membranes and then sequentially passed through ultrafiltration membranes with MW cut-offs of 100, 50, 10, 3, and 1 kDa under 0.2 MPa of high-purity nitrogen pressure. COD in each fraction was measured, and MW distribution was determined by the subtraction method [19].
2.5. Analytical Methods
Standard methods were used for water quality analysis. COD, color, NH3-N, TN, and TP were measured using a multiparameter water quality analyzer (5B-3B V11, Lianhua Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). The color of the treated wastewater was measured as Platinum-Cobalt (Pt-Co) units at a wavelength of 420 nm. BOD5 was determined using the dilution and seeding method. pH was measured using a pH meter (FiveEasy Plus, Mettler Toledo, Zurich, Switzerland). Total organic carbon (TOC) was measured using a TOC analyzer (TOC-L CPH, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). Light absorbance was measured using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (U-T9, Yipu, Shanghai, China). UV254 is mainly caused by electron-rich sites such as aromatic functional groups and conjugated double-bonds in humic substances [20].
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was employed to identify functional groups in organic matter. Samples were filtered (0.45 μm) and freeze-dried before analysis. Spectra data were recorded using an FTIR spectrometer equipped with an attenuated total reflectance (ATR) module (Spotlight 200i, PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA), scanning from 4000 to 400 cm−1 at 4 cm−1 resolution with 32 scans.
Three-dimensional excitation emission matrix (3D-EEM) fluorescence spectra were obtained using a spectrofluorometer (F-7000, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan). Excitation (Ex) and emission (Em) wavelengths were set from 200 to 500 nm and 220 to 550 nm, respectively, with 5 nm step. Slit widths were 5 nm, scan speed was 1200 nm/min, and photomultiplier tube voltage was 400 V. Fluorescence Regional Integration (FRI) was applied to quantify signal intensity [21].
Four sulfonamides (SD, SMZ, SMX, SMM) and two tetracyclines (TC, OTC) were used as representative veterinary antibiotics in this study. Their concentrations were determined using a high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) (LC-40D, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan; Qtrap 6500+, Sciex, Waltham, MA, USA). Chromatographic separation was performed using a Kinetex C18 reversed-phase column (150 mm × 2.1 mm, 1.7 μm, 100 Å; Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA), maintained at 40 °C. Mobile phase flow rate was set at 0.3 mL/min. Samples were filtered through 0.22 μm membranes before injection. The injection volume was 1 μL. Details of the gradient elution program and MS/MS settings are listed in Table A2 and Table A3, respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Single-Factor Experiments and Analysis
Single-factor experiments were conducted to systematically evaluate the individual effects of key operational parameters (ozone flow rate, reaction time, Fe2+ dosage, and H2O2 dosage) on the removal efficiency of organic matter in swine farm wastewater effluent. COD removal was selected as the primary performance indicator, while UV254 absorbance and color removal were used as supplementary metrics. The results of the single-factor experiments provide a basis for selecting rational factor levels for subsequent RSM optimization. Furthermore, the findings offer a strong experimental foundation for developing and analyzing the RSM regression model.
3.1.1. Influence of Ozone Flow Rate and Reaction Time on Organic Matter Removal
The efficiency of ozonation alone is constrained by limited gas–liquid mass transfer and low ozone utilization efficiency. As illustrated in Figure 1, ozonation alone at an ozone concentration of 20 mg/L significantly reduced UV254 absorbance and color, but showed limited COD removal. The rapid color reduction is primarily due to the direct reaction between ozone and chromophoric groups in the swine farm wastewater. However, the modest COD removal implies that only partial transformation of organic pollutants occurred [11]. Increasing the ozone flow rate from 10 to 60 mL/min significantly improved the removal efficiencies of COD, UV254, and color. At all flow rates, the degradation of pollutants exhibited a two-stage kinetic pattern: an initial rapid degradation phase within the first 20 min, followed by a slower stabilization phase between 20 and 40 min. This behavior reflects the preferential reaction of ozone with readily oxidizable compounds containing functional groups such as –OH, –CH3, –OCH3, and C=C bonds [22]. As these moieties are depleted, intermediate products accumulate, resulting in decreased degradation efficiency. Overall, increasing the ozone flow rate from 10 to 60 mL/min enhanced the total COD removal from 13.44% to 22.38% after 40 min. However, beyond 50 mL/min, the removal efficiency plateaued, likely due to the escape of unreacted ozone from the system [23].
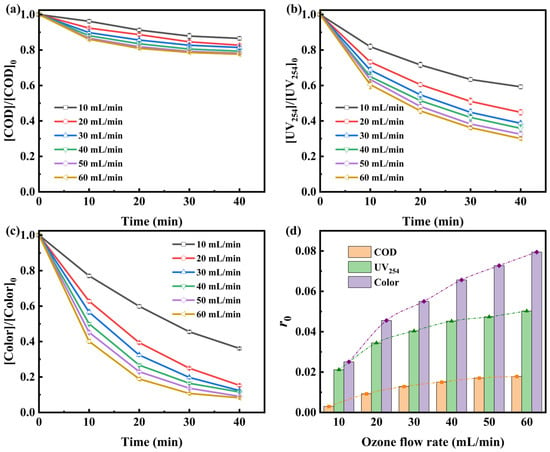
Figure 1.
Removal kinetics of (a) COD, (b) UV254, and (c) color in swine farm wastewater effluent under different ozone flow rates during ozonation alone, and (d) their initial removal rates (r0). [O3] = 20 mg/L.
To further investigate degradation behavior under different ozone flow rates, kinetic models were established for COD, UV254, and color removal (Appendix A). As shown in Figure 1d, the initial removal rate (r0) followed the order: COD < UV254 < color, indicating that UV254 and color were more sensitive to ozone dosage and reaction time than COD. At 50 mL/min ozone flow rate, UV254 and color removal reached 61.73% and 86.39% after 30 min, respectively, whereas COD removal was only 20.78%. These results align with those of Riaño et al. [11], which emphasized ozone’s preferential reactivity with chromophores via 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition, leading to cleavage of conjugated systems and aromatic rings, as evidenced by UV254 reduction [22]. In contrast, recalcitrant compounds with low ozone reactivity require non-selective oxidation by HO• for effective degradation. Therefore, Fe2+ and H2O2 were added to facilitate catalytic ozone decomposition and enhance HO• generation.
Figure 1d shows that r0 of COD increased markedly as ozone flow rate rose from 10 to 50 mL/min. However, beyond 50 mL/min, the rate increment was marginal, suggesting diminishing returns due to mass transfer limitations and kinetic constraints. This trend also implies a potential waste of ozone input and increased operational costs. Most COD, UV254, and color removal occurred within the initial 30 min, consistent with observations by Cortez et al. [24] for landfill leachate treatment, reflecting the preferential oxidation of readily degradable compounds during the early phase of treatment. As the reaction progresses, less reactive intermediates accumulate, hindering further degradation. Additionally, excessive ozone input may lead to saturation of dissolved ozone, further limiting mass transfer efficiency.
Considering removal efficiency, economic feasibility, and ozone utilization, an ozone flow rate of 50 mL/min and a reaction time of 30 min were selected for subsequent RSM experiments. These conditions strike a balance between effective pollutant removal and resource efficiency, laying a solid foundation for catalytic process optimization.
3.1.2. Effect of Fe2+ and H2O2 Dosage on Organic Matter Removal
Fe2+ acts as a homogeneous catalyst in ozonation through two principal mechanisms [25]: (1) initiating chain-reactions that promote ozone decomposition and generate reactive oxygen species, and (2) participating in coordination catalysis by forming complexes with organic compounds.
As shown in Figure 2a, increasing Fe2+ concentration from 0 to 30 mg/L had negligible effects on UV254 and color removal. This observation suggests that direct ozone oxidation dominated the removal of electron-rich chromophores [26], while Fe2+ provided limited enhancement for cleavage of conjugated structures. In contrast, COD removal increased significantly with Fe2+ addition. As Fe2+ concentration increased from 0 to 15 mg/L, COD removal improved from 20.78% to 33.24%, indicating enhanced degradation of refractory organics by HO• produced via Fe2+ catalyzed ozone decomposition. This radical chain reaction is represented by the following mechanism proposed by Sauleda and Brillas [27] (Equations (2) and (3)):
Fe2+ + O3 → FeO2+ + O2
FeO2+ + H2O → Fe3+ + HO• + OH−
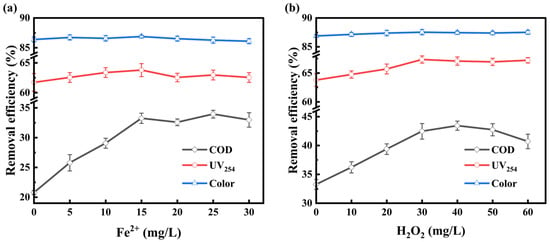
Figure 2.
Effect of Fe2+ (a) and H2O2 (b) concentration on COD, UV254, and color removal. [O3] = 20 mg/L in (a). [O3] = 20 mg/L, [Fe2+] = 15 mg/L in (b).
However, further increasing Fe2+ beyond 15 mg/L (up to 30 mg/L) resulted in a plateau or slight decline in COD removal. This could be due to competitive side reactions occurring under excess Fe2+ conditions (Equation (4)):
FeO2+ + Fe2+ + 2H+ → 2Fe3+ + H2O
Excess Fe2+ consumes FeO2+, intermediates and disrupts the chain generation of HO•. This trend is consistent with findings by Li et al. [28], who reported similar behavior in O3/Fenton treatment of amoxicillin wastewater. To minimize these side reactions and maintain effective radical generation, Fe2+ concentrations were limited to below 30 mg/L in subsequent RSM experiments.
Following Fe2+ optimization, H2O2 was introduced to establish the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 system aiming to enhance radical generation through Fenton-like reactions and overcome the limitations of the Fe2+-O3 combination alone.
Incorporating H2O2 into the Fe2+-catalyzed ozonation system enhanced pollutant degradation by synergistic ozone activation and multiple-pathway radical generation [15]. As shown in Figure 2b, increasing H2O2 from 0 to 40 mg/L improved COD removal from 33.24% to 43.44%. Mechanistically, H2O2 dissociates into HO2− (Equation (5)), which initiates chain reactions with ozone (Equation (6)) [29]. The resulting ozonide radical (O3•−) is protonated to HO3•, which subsequently decomposes to HO• (Equations (7) and (8)) [30]:
H2O2 ⇌ HO2− + H+
HO2− + O3 → HO2• + O3•−
O3•− + H+ ⇌ HO3•
HO3•⇌ HO• + O2
Additionally, H2O2 acts as the key reagent in Fenton reactions, reacting with Fe2+ to generate HO• (Equation (9)) and regenerating Fe2+ via radical-mediated cycles (Equations (10) and (11)) [31]:
Fe2+ + H2O2 → Fe3+ + HO• + OH−
Fe3+ + H2O2 ⇌ Fe–OOH2+ + H+
Fe–OOH2+ → Fe2+ + HO2•
However, when H2O2 dosage exceeded 40 mg/L, COD removal began to decline. This may be due to radical scavenging and quenching reactions initiated by excess H2O2 (Equations (12)–(14)) [32]. These side reactions consume HO• and reduce treatment efficiency.
H2O2 + HO• → HO2• + H2O
HO2• + HO• → O2 + H2O
HO• + HO• → H2O2
COD removal displayed a biphasic response: enhancement at moderate H2O2 dosages followed by inhibition at higher levels, which emphasizes the importance of optimizing the H2O2 concentration. To avoid excessive quenching, H2O2 dosages were restricted to 30–50 mg/L in the subsequent RSM design.
The single-factor results demonstrate that ozone alone is effective in removing UV254 and color but insufficient for COD reduction. Similar findings were reported by Alfonso-Muniozguren et al. [33], who observed that ozone primarily acted as a color-removing agent, with comparable color removal efficiencies across O3, O3/UVC, and O3/UVC/H2O2 processes. By contrast, the combined application of O3, UVC, and H2O2 substantially enhanced the removal of organic pollutants relative to ozone alone. In the present study, the incorporation of Fe2+ and H2O2 significantly improves COD removal through synergistic radical-mediated pathways, offering a promising approach for the degradation of refractory organic pollutants.
3.2. Development and Statistical Analysis of the RSM Optimization Regression Model
3.2.1. RSM Model Construction and Statistical Diagnostics
Based on the preliminary single-factor experiments, the operating ranges and coded levels of the three independent variables for O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process were established (Table 1). The regression analysis produced the following coded polynomial equation (Equation (15)).
COD Removal (%) = 42.19 + 3.47A + 2.93B − 0.63C + 1.06AB + 0.47AC + 0.69BC − 1.50A2 − 3.45B2 − 1.12C2

Table 1.
Coded levels and actual ranges of independent variables for RSM experiments.
In this equation, A, B, and C correspond to the coded ozone, Fe2+, and H2O2 concentrations, respectively. The signs and magnitudes of the coefficients indicate the direction and strength of each parameter’s influence, as well as their interaction effects.
The statistical diagnostics in Figure A2 demonstrated the model’s robustness. The normal probability plot of residuals (Figure A2a) displayed an approximately linear distribution, indicating that residuals were normally distributed. The predicted vs. actual values plot (Figure A2b) showed close clustering around the 45° line, confirming high predictive accuracy for COD removal. Analysis of variance (ANOVA, Table 2) confirmed the model’s high statistical significance (F = 152.66, p < 0.0001), with a non-significant lack-of-fit (F = 1.84, p = 0.3881), indicating an adequate model fit. The model demonstrated strong statistical performance, with R2 = 0.9949, R2adj = 0.9884, and R2pred = 0.9654. The small difference between R2adj and R2pred (<0.03) suggests the model’s robustness. An adequate precision value of 38.2956 (>4) indicated a strong signal-to-noise ratio, validating the model’s reliability for navigating the design space.

Table 2.
Analysis of variance for the RSM model.
Residual plots (Figure A2c,d) exhibited random scatter around the zero baseline without noticeable patterns, further supporting the assumptions of residual independence and homoscedasticity. Collectively, these results confirm that the developed quadratic model is statistically sound and suitable for predicting and optimizing COD removal in the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process.
3.2.2. Parameter Analysis in the CCD Model
Pareto analysis (Figure 3) was employed to quantify the relative contributions of each regression term to COD removal efficiency [34]. Contribution percentages were calculated from the squared regression coefficients of each term.
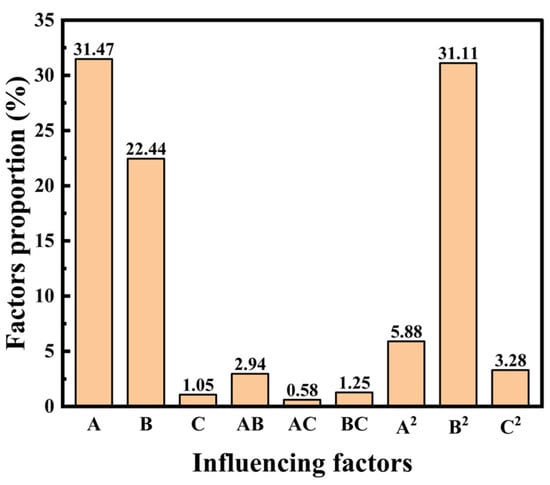
Figure 3.
Results of the Pareto analysis.
The results identified ozone concentration (A) and Fe2+ concentration (B) as the dominant factors, contributing 31.47% and 22.44% to COD removal, respectively. The pronounced effect of Fe2+ may be attributed to its dual role in catalyzing HO• production and facilitating chemical coagulation, thereby enhancing the removal of both dissolved organic pollutants and colloidal particles [35]. The quadratic term of Fe2+ concentration (B2) accounted for 31.11% of the total variation. At low Fe2+ concentrations, the linear term is dominant, enhancing COD removal. However, beyond a critical threshold, the quadratic term becomes more influential, and removal efficiency declines due to the scavenging of HO• by excess Fe2+.
In contrast, H2O2 concentration (C) contributed only 1.05%, and its quadratic term (C2) contributed 3.28%. This relatively low impact aligns with the findings of Yuan et al. [36] and may be explained by analytical interference during COD determination. The residual H2O2 reacts with potassium dichromate (Equation (16)), generating a positive bias in COD measurement [37]. Such interference could mask part of the catalytic contribution of H2O2, thereby underestimating its role in COD removal within the statistical model.
K2Cr2O7 + 3H2O2 + 4H2SO4 → K2SO4 + Cr2(SO4)3 + 7H2O + 3O2
Overall, the Pareto analysis underscores that ozone dosage and Fe2+ dosage are the primary levers for optimizing COD removal in the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process, while H2O2 acts mainly as a supplementary oxidant rather than a dominant factor. This insight is critical for fine-tuning reagent ratios to achieve maximum treatment efficiency with minimal chemical consumption.
3.2.3. Response Surfaces and Optimization Results
The three-dimensional response surface plots (Figure 4) illustrate the multivariate interactions influencing COD removal efficiency in the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 system. Each contour line represents a set of combinations of two experimental variables, while the third variable is fixed at its central level. The optimal operating region is located within the innermost elliptical contour, where predicted COD removal is maximized. When strong interaction effects exist between variables, the contour plots exhibit an elliptical distribution, with higher eccentricity indicating a greater magnitude of interaction.
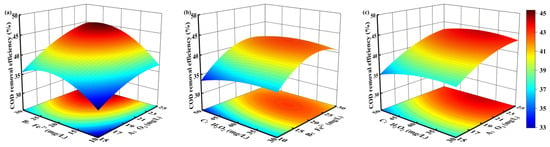
Figure 4.
Analysis of parameter interactions in model response surface plots: (a) O3 vs. Fe2+; (b) Fe2+ vs. H2O2; (c) O3 vs. H2O2.
Overall, the Pareto analysis underscores that ozone dosage and Fe2+ dosage are the primary levers for optimizing COD removal in the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process, while H2O2 acts mainly as a supplementary oxidant rather than a dominant factor. This insight is critical for fine-tuning reagent ratios to achieve maximum treatment efficiency with minimal chemical consumption. The O3-Fe2+ response surface (Figure 4a) revealed strong synergistic effects. COD removal increased sharply at moderate ozone concentrations in the presence of Fe2+, but plateaued at higher ozone levels, likely due to ozone solubility limits and mass transfer constraints [38]. This pattern indicates that while Fe2+ significantly enhances ozone utilization and HO• production, excessive ozone input does not proportionally improve removal efficiency. The Fe2+-H2O2 response surface (Figure 4b) displayed weaker interaction, likely due to suboptimal pH conditions that hinder the classic Fenton reaction pathway [39]. Nonetheless, the combination of Fe2+ and H2O2 still contributed to HO• generation via Fenton-like mechanisms, albeit with diminishing returns at high concentrations. The O3-H2O2 surface exhibited minimal interaction (Figure 4c), consistent with Pareto analysis results. This suggests that H2O2 acts more as a bridging or supplementary agent rather than a dominant contributor to COD removal in this system.
Based on the quadratic RSM model, the predicted optimal conditions for COD removal were [O3] = 25.0 mg/L, [Fe2+] = 25.9 mg/L, and [H2O2] = 41.1 mg/L.
Under these optimal conditions, the model predicted a COD removal efficiency of 45.32%. Triplicate validation experiments yielded an average COD removal of 44.28%, with only a 2.3% deviation from the predicted value. This close agreement demonstrates the predictive reliability and robustness of the RSM model for process optimization.
3.3. Treatment Efficiency of Organic Pollutants by O3/Fe2+/H2O2 Process Under Optimized Conditions
Effluents with comparable COD concentrations can differ markedly in the composition, structure, and treatability of their organic constituents. Therefore, relying solely on COD as a performance indicator may obscure important changes in pollutant characteristics and biodegradability. To address this limitation, the performance of the optimized O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process ([O3]: 25.0 mg/L, [Fe2+]: 25.9 mg/L, [H2O2]: 41.1 mg/L) was systematically evaluated using molecular weight distribution, FTIR, UV-Vis spectroscopy, 3D-EEM fluorescence, and antibiotic degradation as key analytical endpoints. For comparison, the same evaluations were performed for ozonation alone ([O3] = 25.0 mg/L).
3.3.1. Molecular Weight Distribution and Biodegradability Enhancement
As shown in Figure 5a-b, both ozonation alone and the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process shifted the MW profile of dissolved organics toward lower MW fractions. In the raw effluent, approximately 68.27% of COD was distributed among the >100 kDa, 50–100 kDa, 10–50 kDa, 3–10 kDa, and 1–3 kDa fractions. Ozonation alone removed 62.09%, 35.97%, 29.93%, 61.24%, and 49.91% of these fractions, respectively. In comparison, the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process achieved higher removal with 72.55%, 64.75%, 51.70%, 83.71%, and 74.69%, indicating a superior capacity to break down macromolecular pollutants. The pronounced increase in the <1 kDa fraction confirmed the fragmentation of larger molecules into low MW intermediates, attributable to the synergistic action of direct ozonation and HO•-mediated oxidation [40].
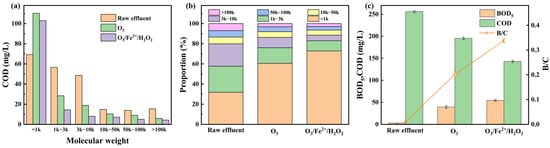
Figure 5.
(a) Molecular weight distribution of organic matter, (b) proportional changes in MW fractions, and (c) evolution of biodegradability in swine farm wastewater effluent before and after treatment.
Biodegradability trends further demonstrated the effectiveness of the combined process (Figure 5c). The raw effluent showed a low BOD5/COD ratio (0.01), reflecting poor biodegradability. Ozonation alone increased the BOD5/COD ratio to 0.20, whereas the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process achieved a significantly higher BOD5/COD ratio of 0.34, indicating transformation of refractory compounds into more biodegradable intermediates. This finding highlights the potential of the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process to enhance the efficiency of downstream biological treatment.
3.3.2. FTIR and UV-Vis Analyses
FTIR spectra (Figure 6a) revealed that the raw swine farm wastewater effluent contained multiple peaks of phenols/alcohols O–H, amine N–H stretching (3600–3400 cm−1), amide I C=O stretching in proteins (~1640 cm−1), lipid-associated bands (~1380 cm−1), polysaccharides or aromatics C–O stretching (1000–1200 cm−1) [41], ester C–O–C bending (885 and 948 cm−1) [42], N–H bending in primary amines (833 cm−1) [43], and aldehyde/ketone C–C=O (550–650 cm−1) [44]. Ozonation alone intensified several oxygenated functional group peaks, reflecting the accumulation of low-MW, less aromatic intermediates [23], consistent with partial oxidation and transformation of chromophores rather than complete mineralization. In contrast, the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process showed weaker residual peaks, demonstrating a superior capability in achieving pollutant mineralization via hydroxyl radical oxidation [36]. This conclusion was further confirmed by the TOC analysis results. Specifically, ozonation alone achieved a TOC removal of 8.5%, whereas the combined system demonstrated a TOC removal efficiency of 29.5%.
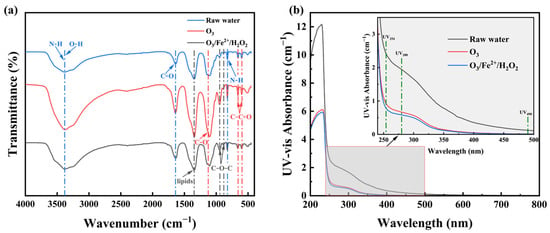
Figure 6.
(a) FTIR spectra and (b) UV-Vis spectra of swine farm wastewater effluent before and after treatment.
UV-Vis analysis (Figure 6b and Table 3) supported these observations. The integrated absorbance between 226 and 400 nm (A226–400), associated with aromatic chromophores [45], decreased significantly under both treatments, with greater reductions for O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process. Decolorization efficiency, indicated by E490 [36], reached 90.01% for ozonation alone and 93.16% for O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process. Absorbance reductions at 280 nm and 254 nm, associated with aromatic and phenolic π-π transitions [44], were also higher for the combined process (70.08% and 67.55%) than for ozonation alone (65.74% and 61.71%). Increase in absorbance ratios (E240/E420, E250/E365, and E300/E400) indicated a decrease in aromaticity, consistent with breakdown of large molecules into smaller, less conjugated molecules [46].

Table 3.
Characteristic UV-Vis absorbance in swine farm wastewater before and after treatment.
3.3.3. D-EEM Analysis
Based on established fluorescence region classifications [21], the 3D-EEM spectra were segmented into five regions corresponding to specific fluorophore components.
As shown in Figure 7a, the raw swine farm wastewater effluent contained two major fluorescence peaks: humic-like (Ex/Em = 325/410 nm) and fulvic-like (245/425 nm) substances. Notably, no signal was observed within the tryptophan-like region, suggesting that readily biodegradable proteins had already been removed during the preceding A/O-1 biological treatment stage [7]. This result aligns with the findings of Liu et al. [8], who reported that A/O processes effectively degrade tryptophan-like substances but exhibiting limited removal of humic fractions. Ozonation alone (Figure 7b) substantially reduced fluorescence intensity, while the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process (Figure 7c) nearly eliminated these peaks, indicating more thorough degradation of complex recalcitrant DOM.
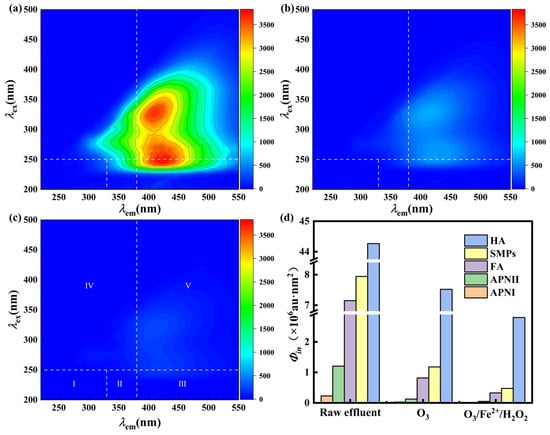
Figure 7.
3D-EEM fluorescence spectra of (a) Raw swine farm wastewater effluent, (b) O3-treated swine farm wastewater effluent, (c) O3/Fe2+/H2O2-treated swine farm wastewater effluent, and (d) intensity of five fluorescent components before and after treatment (I: tryptophan-like aromatic proteins, II: tyrosine-like proteins, III: fulvic acid-like substances, IV: soluble microbial byproducts, V: humic acid-like substances).
FRI analysis (Figure 7d) was conducted to further quantify transformations of individual components. Ozonation alone treatment removed 83.01% of HA and 88.57% of FA, while the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process further enhanced the removal to 93.68% and 95.42%, respectively. The total fluorescence reduction by O3/Fe2+/H2O2 was 62.1% higher than that by ozonation alone, confirming a more effective conversion of DOM to biodegradable forms.
3.3.4. Antibiotic Degradation
The degradation kinetics of four sulfonamides and two tetracyclines in swine farm wastewater effluent are illustrated in Figure 8. Across all compounds, the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process achieved significantly higher removal efficiencies compared to ozonation alone. Antibiotics within the same category exhibited comparable degradation kinetics. Sulfonamides exhibited pseudo-first-order kinetics (R2 > 0.98) under both treatment processes. With ozonation alone, over 90% removal was achieved within 5 min, primarily due to ozone’s electrophilic attack on amino groups, aromatic rings, and unsaturated bonds [47]. The O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process enhanced the apparent rate constants. Degradation followed a biphasic profile, characterized by an initial rapid removal phase (0–0.5 min), dominated by the HO• from Fe2+/H2O2 catalyzed ozone decomposition, followed by a slower phase over the next 5.5 min. This kinetic transition reflects the rapid consumption of reactive oxidants by antibiotics, resulting in a steady-state process governed by residual ozone [48]. Compared to ozone alone, HO• facilitates non-selective oxidation by hydrogen abstraction from electron-deficient moieties, initiating radical-mediated chain reactions and enhancing sulfonamide degradation [49].
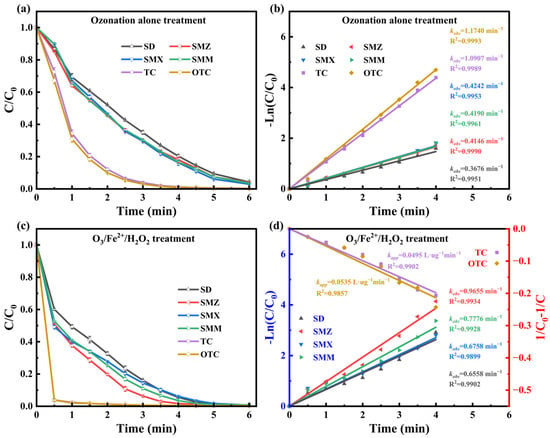
Figure 8.
Antibiotic degradation under ozonation (a,b) and O3/Fe2+/H2O2 (c,d) processes: (a) concentration profiles under ozonation alone, (b) reaction kinetics under ozonation alone, (c) concentration profiles under O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process, (d) reaction kinetics under O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process (the left Y-axis represents the pseudo-first-order kinetics for SD, SMZ, SMX, and SMM, while the right Y-axis represents the pseudo-second-order kinetics for TC and OTC).
Tetracyclines also exhibited pseudo-first-order kinetics under ozonation (R2 > 0.99) in the ozonation alone process, with the apparent degradation rate constant almost three times that of sulfonamides. This enhanced reactivity is attributed to the presence of multiple oxidation-prone moieties, including tertiary amines, phenolic hydroxyls, and conjugated enones [47]. Under the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process, tetracycline degradation accelerated markedly, with ~96% removal within 0.5 min, and the reaction kinetics shifted from pseudo-first-order to pseudo-second-order, reflecting a dual pathway. In addition to HO• oxidation, the rapid formation of Fe2+-tetracycline complexes, particularly via coordination with phenolic-diketone sites in the rings without amino substitution, facilitated interfacial electron transfer and molecular breakdown [50]. The enhanced antibiotic removal capacity of the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 advanced oxidation process highlights its strong potential for mitigating emerging antibiotic contaminants in engineered wastewater treatment systems.
In summary, the optimized O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process outperformed ozonation alone in terms of MW reduction, biodegradability enhancement, DOM degradation, and antibiotic removal, demonstrating its strong potential for treating biologically refractory swine farm wastewater.
3.4. Analysis of Energy Efficiency
The performance of ozone-based advanced oxidation processes in wastewater treatment is fundamentally governed by the ozone utilization efficiency [51]. Given the high energy input required for ozone generation, improving the ozone utilization efficiency not only enhances pollutant degradation but also reduces operational costs and environmental impact.
3.4.1. Ozone Utilization Efficiency Analysis
Ozone utilization efficiency was calculated using Equation (17) [52]:
where QG is the ozone gas flow rate (mL/min), VL is the liquid sample volume (mL), [O3G,i] and [O3G,O] represent inlet and outlet gas-phase ozone concentrations (mg/L), and t is the reaction time (min).
As shown in Figure 9, the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process exhibited markedly improved ozone utilization efficiency compared to ozonation alone, owing to enhanced gas–liquid mass transfer and catalytic decomposition of ozone into radicals. In ozonation alone, utilization efficiency declined from 69.12% to 44.64% over 30 min, reflecting ozone mass transfer limitations and slower reaction kinetics as easily oxidizable compounds were depleted. This trend aligns with Ratnawati et al. [53], who reported rapid ozone dissolution during the initial stage, followed by stabilization at equilibrium. Overall, the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 system maintained higher overall ozone utilization and a more gradual decline in efficiency compared with ozone alone. This may be attributed to sustained HO• production from catalytic ozone decomposition. The continuous oxidation of refractory organics by HO• depletes dissolved ozone, maintaining a concentration gradient across the gas–liquid interface. This gradient enhances ozone mass transfer from gas to liquid phase while minimizing ozone loss via gas stripping.
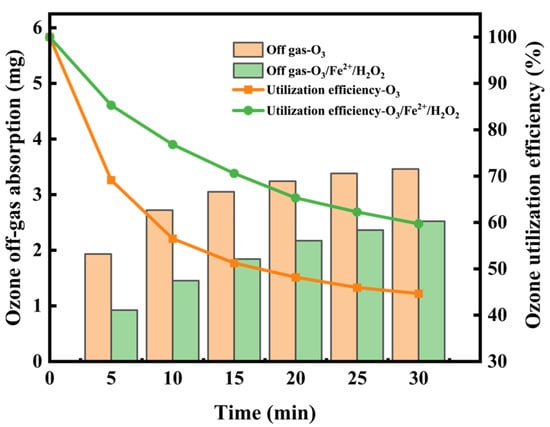
Figure 9.
Temporal variations in off-gas ozone concentration and ozone utilization efficiency in O3 and O3/Fe2+/H2O2 processes.
3.4.2. Economic Assessment
The main economic constraint for catalytic ozonation is the electrical energy demand for ozone generation. Therefore, the normalized ozone consumption per unit COD removal (Equation (18)) [54] is a critical cost-effectiveness metric:
where A is the normalized ozone consumption (mg O3/mg COD), ΔCO3 is the ozone concentration difference between the inlet and outlet (mg/L), Q is the ozone flow rate (mL/min), t is the treatment time (min), ΔCCOD is the reduction in COD (mg/L), and V is the sample volume (mL).
Over a 30 min treatment, the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process achieved a significantly lower ozone consumption value (1.16 mg O3/mg COD removal) compared to ozonation alone (1.62 mg O3/mg COD removal), representing a 28.4% reduction.
Additionally, the combined process removed 53.95% of total phosphorus (TP) through Fe3+-mediated flocculation and coprecipitation [55]. This simultaneous removal of organics and phosphorus can reduce the chemical demand in downstream treatment, thereby further enhancing cost-effectiveness and operational sustainability for large scale wastewater treatment applications.
4. Conclusions
This study optimized a synergistic O3/Fe2+/H2O2 catalytic oxidation process using RSM for advanced treatment of swine farm wastewater effluent. Multidimensional characterization and comprehensive evaluation were conducted to understand the treatment performance and cost-effectiveness.
Under the optimal conditions ([O3] = 25.0 mg/L, [Fe2+] = 25.9 mg/L, and [H2O2] = 41.1 mg/L), the COD removal was 44.28%, which was 86.75% higher than that of ozonation alone. BOD5/COD of the swine farm wastewater effluent reached 0.338 after the treatment, reflecting markedly enhanced biodegradability after treatment. Notably, 93.68% of humic acid-like and 95.42% of fulvic acid-like substances were removed, demonstrating efficient breakdown of recalcitrant DOM. The degradation of commonly used antibiotics SAs and TCs by the catalytic ozonation process was higher than that of ozonation alone, driven by HO• oxidation and the formation of Fe–antibiotic complexation. A 33.1% improvement in ozone utilization efficiency compared to ozonation alone confirmed higher energy efficiency. Additionally, 53.95% of TP was removed via Fe3+-mediated flocculation and coprecipitation, potentially reducing chemical costs in downstream treatment.
In conclusion, the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 process overcomes the limitations of ozonation alone in terms of selective oxidation, mass transfer inefficiency, and economic constraints. In practical terms, this integrated process offers a robust and energy-efficient strategy for advanced swine farm wastewater treatment, supporting safe effluent reuse and contributing to the mitigation of agricultural non-point-source pollution and the protection of soil and aquatic environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Y. and R.Q.; methodology, H.Y. and K.T.; software, H.Y. and Z.T.H.; validation, H.Y.; formal analysis, H.Y., K.T. and J.L.; investigation, H.Y., K.T. and L.D.; resources, H.Y. and K.T.; data curation, H.Y., J.L. and L.D.; writing—original draft preparation, H.Y. and K.T.; writing—review and editing, Z.T.H., D.W. and R.Q.; supervision, R.Q.; project administration, R.Q. and D.W.; funding acquisition, R.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Key Laboratory of Agro-Forestry Environmental Processes and Ecological Regulation of Hainan Province (AFEPRR202501), National Natural Science Foundation of China (22150410342), and Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province, grant number (624MS038).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Acknowledgments
During the preparation of this study, the author(s) used [Design-Expert 13] for the purposes of RSM optimization. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| RSM | Response Surface Methodology |
| CCD | Central Composite Design |
| VAs | Veterinary antibiotics |
| TCs | Tetracyclines |
| SAs | Sulfonamides |
| ECs | Emerging Contaminants |
| A/O | Anoxic–Oxic |
| AOPs | Advanced Oxidation Processes |
| MW | Molecular weight |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared |
| UV-Vis | Ultraviolet-Visible |
| 3D-EEM | Three-dimensional excitation emission matrix |
| FRI | Fluorescence Regional Integration |
Appendix A
To identify an appropriate operational range, the independent effects of ozone flow rate and reaction time on pollutant removal were evaluated. Given the complexity of the wastewater matrix and the formation of intermediate products, cubic polynomial regression models (Y = A + B1x + B2x2 + B3x3) were fitted to the removal data as a function of reaction time (t), yielding high correlation coefficients (R2 > 0.9800). The B1 coefficient was used to calculate the initial removal rate (r0) within the 40 min reaction period. This systematic evaluation also serves to reduce potential bias in RSM modeling caused by mass transfer limitations, and provides a theoretical basis for ozone parameters in the O3/Fe2+/H2O2 combined process.

Table A1.
Water quality parameters of the effluent from the two-stage A/O process of swine farm wastewater.
Table A1.
Water quality parameters of the effluent from the two-stage A/O process of swine farm wastewater.
| Parameter | A/O-1 Effluent | A/O-2 Effluent |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.18 ± 0.06 | 6.07 ± 0.07 |
| TOC (mg/L) | 71.60 ± 0.71 | 68.35 ± 0.78 |
| COD (mg/L) | 256.03 ± 2.29 | 238.10 ± 2.71 |
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 2.88 ± 0.34 | 1.93 ± 0.4 |
| UV254 | 2.43 ± 0.03 | 2.47 ± 0.04 |
| NH3-N (mg/L) | 5.13 ± 0.08 | 4.95 ± 0.10 |
| TN (mg/L) | 361.06 ± 6.56 | 342.12 ± 7.55 |
| TP (mg/L) | 95.20 ± 0.71 | 94.61 ± 0.69 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 38.63 ± 0.84 | 27.37 ± 0.69 |
| Color (PCU) | 635 ± 5 | 625 ± 5 |
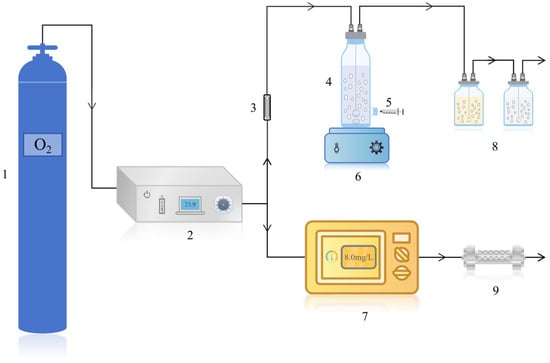
Figure A1.
Schematic diagram of the ozone reactor. (1. Oxygen cylinder 2. Ozone generator 3. Gas flowmeter 4. Reactor 5. Sampler 6. Magnetic stirrer 7. Ozone monitor 8. KI absorption solution 9. Tail gas absorber).

Table A2.
Gradient elution method in this study.
Table A2.
Gradient elution method in this study.
| Time | Command | value | Mobile phase |
|---|---|---|---|
| Start | B. Conc | 10% | Phase A: Ultra-pure Water (UPW) with 0.1% formic acid Phase B: methanol |
| 4.5 min | B. Conc | 10% | |
| 6.5 min | B. Conc | 95% | |
| 6.6 min | B. Conc | 95% |

Table A3.
Mass transition parameters for six antibiotics in LC-MS/MS analysis.
Table A3.
Mass transition parameters for six antibiotics in LC-MS/MS analysis.
| Antibiotics | Q1 Mass | Q3 Mass | DP (V) | CE (V) | Detection Method | Linearity (R2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD | 251.1 | 156 | 40 | 22 | MRM+ | 0.9989 |
| 92 | 38 | |||||
| SMM | 281.1 | 156 | 75 | 25 | MRM+ | 0.9961 |
| 126.1 | 30 | |||||
| SMX | 254.1 | 156 | 65 | 22 | MRM+ | 0.9956 |
| 108 | 36 | |||||
| SMZ | 279.11 | 186.1 | 60 | 23 | MRM+ | 0.9967 |
| 156 | 27 | |||||
| TC | 445.1 | 410.2 | 80 | 24 | MRM+ | 0.9975 |
| 427.1 | 19 | |||||
| OTC | 461.2 | 426.2 | 80 | 25 | MRM+ | 0.9912 |
| 443.2 | 17 |
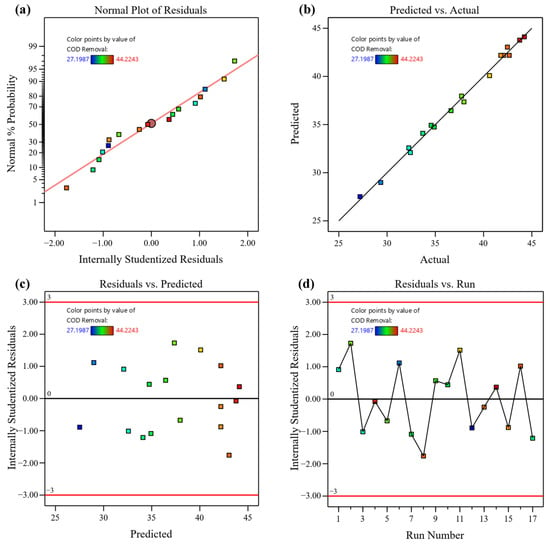
Figure A2.
(a) Normal probability plot of residuals; (b) Predicted vs. actual values; (c) Residuals vs. predicted values; (d) Residuals vs. run order.
References
- Domingues, E.; Fernandes, E.; Gomes, J.; Martins, R.C. Advanced oxidation processes perspective regarding swine wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D.; Liu, Y.; Shan, X.; Nghiem, L.D.; Nguyen, L.N. Removal process of antibiotics during anaerobic treatment of swine wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Kakarla, D.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Megharaj, M.; Yoon, Y.-E.; Lee, Y.B. Veterinary antibiotics (VAs) contamination as a global agro-ecological issue: A critical view. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 257, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling-Sørensen, B.; Jensen, J.; Tjørnelund, J.; Montforts, M. Worst-case estimations of predicted environmental soil concentrations (PEC) of selected veterinary antibiotics and residues used in Danish agriculture. In Pharmaceuticals in the Environment: Sources, Fate, Effects and Risks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 143–157. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Li, A.; Zhang, H.; Gao, S.; Li, S.; Cai, J.; Yan, R.; Xing, Z. The potential and sustainable strategy for swine wastewater treatment: Resource recovery. Chemosphere 2023, 336, 139235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Xing, S.; Li, S.; Niu, Y.; Li, C.; Huang, T.; Liao, X. Potential regulation of small RNAs on bacterial function activities in pig farm wastewater treatment plants. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 91, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, D.; Zeng, W.; Yang, J. Removal of refractory organics from piggery bio-treatment effluent by the catalytic ozonation process with piggery biogas residue biochar as the catalyst. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhong, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, B. Dissolved organic matter characterization of swine wastewater with step-feed two-stage anoxic/oxic (A/O/A/O) process by using EEM-PARAFAC. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aust, M.-O.; Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Eckhardt, K.-U.; Leinweber, P. Composition of organic matter in particle size fractionated pig slurry. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5736–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhardt, M.; Stamm, C. Depth distribution of sulfonamide antibiotics in pore water of an undisturbed loamy grassland soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaño, B.; Coca, M.; García-González, M.C. Evaluation of Fenton method and ozone-based processes for colour and organic matter removal from biologically pre-treated swine manure. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bai, Z. Fe-based catalysts for heterogeneous catalytic ozonation of emerging contaminants in water and wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 312, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Lai, C.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Zhang, C.; Qin, L.; Hu, L.; Zhou, C.; Xiong, W. Metal-organic frameworks for highly efficient heterogeneous Fenton-like catalysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 368, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, L.; Cheng, X.; Wang, X. The application and reaction mechanism of catalytic ozonation in water treatment. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2012, 2, 2161-0525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekhate, C.V.; Srivastava, J. Recent advances in ozone-based advanced oxidation processes for treatment of wastewater-A review. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2020, 3, 100031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.K.; Meena, H.; Chakraborty, S.; Meikap, B. Application of response surface methodology (RSM) for optimization of leaching parameters for ash reduction from low-grade coal. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2018, 28, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Han, C.; Wang, P.; Guo, S.; Yan, G.; Li, Q.X. Investigation on Titanium Silicalite ETS-4 Catalyzed Ozonation for Chemicals in Wastewater, Exemplified With 4-Chlorophenol. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 2016, 44, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; How, Z.T.; Benally, C.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, H.; El-Din, M.G. Removal of colloidal impurities by thermal softening-coagulation-flocculation-sedimentation in steam assisted gravity drainage (SAGD) produced water: Performance, interaction effects and mechanism study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 313, 123484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulekgurgen, E.; Doğruel, S.; Karahan, Ö.; Orhon, D. Size distribution of wastewater COD fractions as an index for biodegradability. Water Res. 2006, 40, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, F.J.; Schlenger, P.; García-Valverde, M. Monitoring changes in the structure and properties of humic substances following ozonation using UV–Vis, FTIR and 1H NMR techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenheer, J.A.; Booksh, K. Fluorescence excitation− emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvares, A.; Diaper, C.; Parsons, S. Partial oxidation by ozone to remove recalcitrance from wastewaters-a review. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Qiu, B.; Sun, D. Degradation of refractory organics from biologically treated incineration leachate by VUV/O3. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 370, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, S.; Teixeira, P.; Oliveira, R.; Mota, M. Evaluation of Fenton and ozone-based advanced oxidation processes as mature landfill leachate pre-treatments. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawrocki, J.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. The efficiency and mechanisms of catalytic ozonation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 99, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; He, X.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Van Hulle, S.W. Comparison of macro and micro-pollutants abatement from biotreated landfill leachate by single ozonation, O3/H2O2, and catalytic ozonation processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauleda, R.; Brillas, E. Mineralization of aniline and 4-chlorophenol in acidic solution by ozonation catalyzed with Fe2+ and UVA light. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2001, 29, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zeng, Z.; Li, Y.; Arowo, M.; Chen, J.; Meng, H.; Shao, L. Treatment of amoxicillin by O3/Fenton process in a rotating packed bed. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 150, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staehelin, J.; Hoigne, J. Decomposition of ozone in water: Rate of initiation by hydroxide ions and hydrogen peroxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1982, 16, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhler, R.; Staehelin, J.; Hoigne, J. Ozone Decomposition in Water Studied by Pulse Radiolysis 1. HO2/O2-and HO3/O3-as Intermediates-Correction. J. Phys. Chem. 1984, 88, 5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamarro, E.; Marco, A.; Esplugas, S. Use of Fenton reagent to improve organic chemical biodegradability. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruganandham, M.; Swaminathan, M. Decolourisation of Reactive Orange 4 by Fenton and photo-Fenton oxidation technology. Dye. Pigment. 2004, 63, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso-Muniozguren, P.; Gomes, A.I.; Saroj, D.; Vilar, V.J.; Lee, J. The role of ozone combined with UVC/H2O2 process for the tertiary treatment of a real slaughterhouse wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 289, 112480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelalak, R.; Alizadeh, R.; Ghareshabani, E.; Heidari, Z. Degradation of sulfonamide antibiotics using ozone-based advanced oxidation process: Experimental, modeling, transformation mechanism and DFT study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canizares, P.; Paz, R.; Sáez, C.; Rodrigo, M.A. Costs of the electrochemical oxidation of wastewaters: A comparison with ozonation and Fenton oxidation processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Xia, Y.; Wu, X.; He, C.; Qin, Y.; He, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; He, X. Efficient advanced treatment of coking wastewater using O3/H2O2/Fe-shavings process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.; Sohn, K.; Lee, K. Hydrogen peroxide interference in chemical oxygen demand during ozone based advanced oxidation of anaerobically digested livestock wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 8, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, C.; Roche, P.; Joret, J.-C.; Paillard, H. Comparison of the effect of ozone, ozone-hydrogen peroxide system and catalytic ozone on the biodegradable organic matter of a fulvic acid solution. Water Res. 1997, 31, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, G.; Wang, P. A review on Fenton-like processes for organic wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 762–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Gu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, A. Improved oxidation of refractory organics in concentrated leachate by a Fe2+-enhanced O3/H2O2 process. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 35797–35806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Chen, L.; Jiang, T. Characterization and modeling of the soluble microbial products in membrane bioreactor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 76, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Han, J. Polyvinyl Alcohol–Citric Acid: A New Material for Green and Efficient Removal of Cationic Dye Wastewater. Polymers 2023, 15, 4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; He, X.; Zhang, H.; Deng, Y.; Chen, L.; Jiang, J. Characterization of dissolved organic matter extracted from fermentation effluent of swine manure slurry using spectroscopic techniques and parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC). Microchem. J. 2012, 102, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; He, X.; Pan, H. Spectroscopic study on transformations of dissolved organic matter in coal-to-liquids wastewater under integrated chemical oxidation and biological treatment process. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 70, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xi, B.; Yu, H.; Ma, W.; He, X. The structure and origin of dissolved organic matter studied by UV-vis spectroscopy and fluorescence spectroscopy in lake in arid and semi-arid region. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, A.; Gu, Z.; Li, Q. Enhanced degradation of refractory organics in concentrated landfill leachate by Fe0/H2O2 coupled with microwave irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Gunten, U. Ozonation of drinking water: Part I. Oxidation kinetics and product formation. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1443–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, W.; Qiang, Z.; Pan, X.; Chen, M. Removal of veterinary antibiotics from sequencing batch reactor (SBR) pretreated swine wastewater by Fenton’s reagent. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4392–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, M.; Xing, S.; Zhu, C.; Sheng, L.; Lu, K.; Gao, N. Kinetics of ozonation of typical sulfonamides in water. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2011, 24, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Lin, Y.; Feng, M.; Dai, Y.; Dai, Z.; Duan, X.; Dewil, R.; Guan, X. Unexpected tetracycline antibiotics degradation in the Fenton process under near-neutral pH conditions: Performance and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 495, 138858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Payan, V.; Herrera-Lopez, E.J.; Navarro-Laboulais, J.; Lopez-Lopez, A. Parametric sensitivity analysis and ozone mass transfer modeling in a gas–liquid reactor for advanced water treatment. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, S.; Teixeira, P.; Oliveira, R.; Mota, M. Ozonation as polishing treatment of mature landfill leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnawati, R.; Kusumaningtyas, D.A.; Suseno, P.; Prasetyaningrum, A. Mass transfer coefficient of ozone in a bubble column. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 156, 02015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Sheng, M.; Li, Y.; Xue, W.; Li, K.; Cao, G. A hybrid process of Fe-based catalytic ozonation and biodegradation for the treatment of industrial wastewater reverse osmosis concentrate. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Dong, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, G.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, B. Advanced oxidation removal of hypophosphite by O3/H2O2 combined with sequential Fe (II) catalytic process. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).