- Review
A Review of the Application of Oxalic Acid in Hydrometallurgical Processes
- Muling Sheng,
- Zishuai Liu and
- Yancheng Lv
- + 4 authors
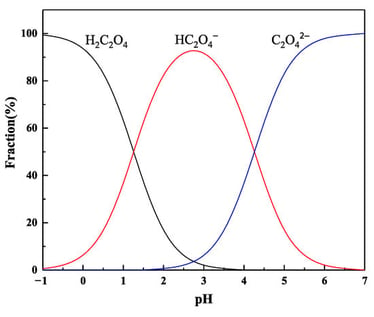
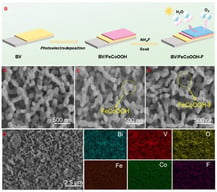
Conventional hydrometallurgical processes typically employ inorganic acids as leaching agents; however, these processes are frequently associated with significant environmental pollution and suffer from poor metal selectivity. Oxalic acid, as a green alternative leaching agent, demonstrates considerable application potential owing to its mild acidity, strong reducing capability, and superior complexing properties. This paper presents a systematic review of recent advances in the application of oxalic acid in hydrometallurgy, encompassing the coordination chemistry between oxalic acid and metal ions, its role as a selective leaching agent, and strategies for handling multicomponent oxalate-rich solutions. Furthermore, the industrial prospects of oxalic acid-based leaching technologies are discussed. Research indicates that oxalic acid exhibits high selectivity and efficient leaching performance for critical metals—including vanadium, lithium, cobalt, nickel, and gallium—from both primary ores and solid secondary resources. The underlying leaching mechanism primarily involves the formation of stable chelation complexes between oxalate anions and high charge-density metal ions, or valence state modulation via reduction, enabling selective dissolution and separation of target metals. In multicomponent oxalate systems, where metals predominantly exist as anionic complexes, established enrichment and purification approaches include anion exchange extraction, as well as precipitation techniques based on valence adjustment and double salt crystallization. To advance the industrial implementation of oxalic acid leaching technologies, further in-depth investigation is required into the recycling mechanisms of oxalic acid and the fundamental reaction pathways governing leaching and metal recovery processes.
12 February 2026