Abstract
Nitrous oxide (N2O), a potent greenhouse gas, is an important environmental concern associated with biological nitrogen removal in wastewater treatment plants. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox), recognized as an advanced carbon-neutral nitrogen removal technology, requires a continuous supply of nitrite, which also serves as a key precursor for N2O generation. However, the regulation of the carbon-to-nitrogen (C/N) ratio to minimize N2O emission in mainstream anammox systems remains insufficiently understood. In this study, we evaluated the long-term nitrogen removal performance and N2O emission potential of an oxygen-limited anammox biofilm reactor treating synthetic municipal wastewater with a typical C/N range of 4.0–6.0. Experimental results demonstrated that the highest nitrogen removal efficiency (95.3%), achieved through coupled anammox and denitrification, and the lowest N2O emission factor (0.73%) occurred at a C/N ratio of 5.0. As the C/N ratio increased from 4.0 to 5.0, N2O emissions decreased progressively, but rose slightly when the ratio was further increased to 6.0. High-throughput sequencing revealed that microbial community composition and the abundance of key functional taxa were significantly influenced by the C/N ratio. At a C/N ratio of 5.0, proliferation of anammox bacteria and the disappearance of Acinetobacter populations appeared to contribute to the significant reduction in N2O emission. Furthermore, gene annotation analysis indicated higher abundances of anammox-associated genes (hzs, hdh) and N2O reductase gene (nosZ) at this ratio compared with others. Overall, this study identifies a C/N-dependent strategy for mitigating N2O emissions in mainstream anammox systems and provides new insights into advancing carbon-neutral wastewater treatment.
1. Introduction
Water pollution has become an inevitable challenge in urban development [1]. Excessive discharge of carbon- and nitrogen-containing compounds into aquatic environments not only drives eutrophication but also threatens aquatic ecosystems and human health. Conventional biological nitrogen removal (BNR) processes, which rely on nitrification and denitrification, have been widely used in municipal wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) [2]. However, these processes are major sources of nitrous oxide (N2O), a potent greenhouse gas with a global warming potential approximately 300 times that of CO2 and 21 times that of CH4, contributing to both ozone depletion and climate change [3]. Recent estimates indicate that N2O emissions from BNR in WWTPs have been steadily increasing, reaching 108 Mt CO2-equivalent and accounting for 3.4% of global N2O emissions [4]. Consequently, the wastewater treatment sector faces pressing challenges in enhancing treatment efficiency, reducing pollutant discharge, and simultaneously lowering its carbon footprint.
Anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox), in which NH4+-N is directly converted to N2 in the presence of nitrite by anammox bacteria under anaerobic conditions, has emerged as a promising autotrophic nitrogen removal pathway. This process offers several advantages, including high nitrogen removal efficiency, reduced aeration energy savings, and the elimination of external carbon requirements [5]. The application of anammox for mainstream municipal wastewater treatment thus presents a potential pathway toward sustainable nitrogen management in WWTPs. Nevertheless, the provision of nitrite, via partial nitrification or partial denitrification, as a precursor step for anammox [6] may lead to N2O accumulation as an intermediate, even though anammox itself does not generate N2O.
The carbon-to-nitrogen (C/N) ratio is a critical parameter that strongly influences both nitrogen removal performance and N2O emission in mainstream anammox systems [7]. Pijuan et al. [8] reported that the addition of COD suppressed anammox activity, which recovered once COD was no longer supplied. For pure anammox cultures, the optimal C/N ratio is generally below 0.5. However, in one-stage mixed-culture systems, higher C/N ratios can enhance anoxic microenvironments within biomass aggregates, thereby supporting anammox activity. Overall, N2O emissions tend to be greater at lower C/N ratios than at higher ones. For instance, insufficient C/N ratios below 3.0 during denitrification can cause incomplete denitrification, substantially increasing N2O emissions in systems coupling anammox with heterotrophic denitrification [9]. Similarly, Zhou et al. [10] observed that the N2O emission factor reached 2.22% in a mainstream anammox-based reactor at a C/N ratio of 2.5. By contrast, Sun et al. [7] identified an optimal C/N ratio of 2.1 in a partial denitrification–anammox system, while elevated C/N values (2.4–3.0) led to higher N2O emissions.
Previous studies have primarily investigated N2O emission characteristics under low C/N conditions in municipal wastewater. However, the C/N (COD/TN) ratio of municipal wastewater in most regions of China typically ranges between 4.0 and 6.0 [11]. N2O emission potential under these moderate C/N conditions has not been comprehensively assessed. Moreover, studies specifically aimed at optimizing C/N ratios to simultaneously enhance nitrogen removal and minimize carbon emissions remain scarce. In this study, we systematically investigated the long-term effect of different C/N ratios (4.0–6.0) on nitrogen removal performance and N2O emission dynamics in an oxygen-limited anammox sequencing batch biofilm reactor (SBBR) treating synthetic domestic wastewater (influent ammonia nitrogen concentration is 50 mg/L). In addition, nitrogen transformation pathways and N2O emission patterns were analyzed across different C/N conditions. Finally, microbial community dynamics and nitrogen metabolic gene profiles were examined using 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing. Collectively, this work provides preliminary evidence for developing C/N-optimized strategies to reduce the N2O emission footprint in mainstream anammox-based nitrogen removal processes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
A lab-scale sequencing batch biofilm reactor (SBBR) with an effective working volume of 5 L was employed (Figure 1). The reactor operated on two 12 h cycles per day, each consisting of 2 min influent feeding, 700 min reaction, 15 min settling, and 3 min effluent discharge, with an exchange ratio of 50%. During the reaction phase, a bottom-mounted aeration disk supplied stable low-oxygen aeration, regulated by an air compressor and a mass flow controller to precisely maintain dissolved oxygen (DO) levels. To support the co-culture of anammox bacteria and denitrifiers, the DO concentration was controlled at 0.8–1.0 mg/L [12]. The reactor was maintained at 30 ± 1 °C and agitated at 200 rpm using a thermostatic magnetic stirrer. A gas collection port located at the top of the sealed reactor was used to capture N2O emissions.
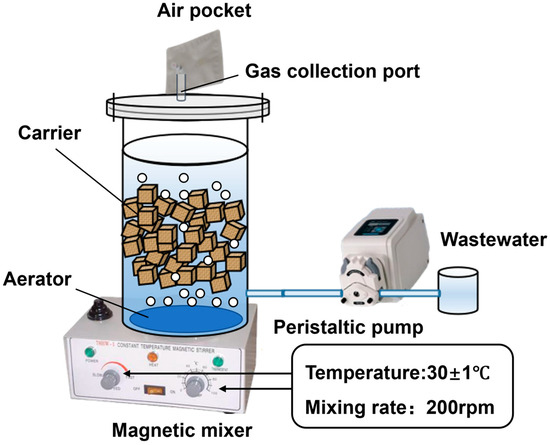
Figure 1.
SBBR system.
2.2. Seed Sludge and Wastewater
Anammox biomass (approximately 5.5 g VSS/L), cultivated in a high-strength ammonium wastewater treatment system for nearly 1.5 years [13], was used as an inoculum for the SBBR. The reactor was supplied with synthetic municipal wastewater containing an influent total nitrogen concentration of 50 mg/L. Glucose, NH4Cl, and KH2PO4 served as the carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus sources, respectively. Each liter of wastewater contained 0.53 g NaHCO3, 0.04 g KH2PO4, and 1 mL/L of a trace element solution. The trace element solution consisted of (per liter): 5 g EDTA, 1.5 g FeCl3, 0.17 g Na2SeO3, 0.12 g MnSO4, 0.06 g Na2MoO4, 0.03 g CuSO4, 0.015 g H3BO4, 0.19 g NiCl2·6H2O, 0.15 g CoCl2·6H2O, and 0.12 g ZnSO4·7H2O.
2.3. Operating Condition
To investigate the effect of the C/N ratio on the N2O emissions in SBBR, four C/N ratios (4.0, 4.5, 5.0, and 6.0) were tested. The influent pH was maintained at 7.0 ± 0.2 using 1.0 M HCl or NaOH. The organic loading rate (OLR) and food-to-microorganism (F/M) ratio were 0.20–0.30 kg COD/(m3·d) and 0.036–0.054 kg COD/(kg MLVSS·d), respectively. The operating conditions for each phase (P1–P4) are summarized in Table 1. The total experimental period was 115 days.

Table 1.
Operating conditions in the whole experiment.
2.4. Chemical Analysis
Effluent samples were first filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane filter, after which 1 mL of 2 M H2SO4 was added to inhibit microbial activity. COD, ammonia-nitrogen (NH4+-N), nitrite-nitrogen (NO2−-N), and nitrate-nitrogen (NO3−-N) were analyzed using Lange cuvette test kits (HACH DR1900, HACH Company, Loveland, CO, USA). Total nitrogen (TN) was calculated as the sum of these nitrogen species. The pH was monitored with a portable pH meter (FE20, Mettler-Toledo Instruments Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China).
2.5. N2O Sampling and Determination
2.5.1. Gaseous N2O Sampling
The headspace of the reactor was continuously flushed with nitrogen gas (N2) at a low flow rate of 30 mL/min to promote mixing and enable gas collection. The outlet gas flow rate (Q) was quantified using a wet gas flow meter. Gas samples were withdrawn with a gas-tight syringe and transferred to 100 mL gas sampling bags for subsequent analysis.
2.5.2. Dissolved N2O Sampling
Dissolved N2O concentrations were determined by the headspace equilibrium method. A 30 mL aliquot of reactor supernatant was mixed with an equal volume of N2 in a gas-tight syringe. The mixture was shaken for 5 min and allowed to equilibrate for 1 h before the gas-phase concentration was measured. Dissolved N2O concentrations were then calculated according to Equation (1):
where CN2O represents the dissolved N2O concentration (mg/L), ω N2O,dis is the headspace concentration (mg/L), and β is Ostwald’s solubility coefficient of N2O (0.538 at 30 °C) [14].
2.5.3. N2O Measurement
Gas-phase N2O concentrations were determined using gas chromatography (GC) equipped with an electron capture detector (ECD) (GC3410, Beifen–Ruili Analytical Instrument Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). High-purity nitrogen gas (≥99.999%) was used as the carrier at a flow rate of 30 mL/min. The injector, detector, and column temperatures were maintained at 200 °C, 280 °C, and 80 °C, respectively. All gas samples were analyzed within 24 h, and each measurement was performed in triplicate; mean values were used for subsequent analysis.
2.5.4. N2O Calculation
The daily production, production rate, and emission factor of N2O were calculated according to Equations (2)–(5) following established methods [15,16]:
where
N2O production (mg N2O/d) = MN2O,dis,end-MN2O,dis,begin + ∑(CN2O,gas × Qair × ∆t)
N2O production rate (g N2O-N/(L·min)) = (CN2O,dis,n+1-CN2O,dis,n + CN2O,gas,n)/∆t
N2O emission factor (%) = MN2O Production × 100/TN load
TN load (mg TN/d) = [TN]inf × V/HRT
- MN2O,dis,begin and MN2O,dis,end represent the amount of dissolved N2O at the beginning and end of the cycle (mg).
- Qair is the reactor gas flow rate (L/min).
- ∆t is the time interval (min).
- CN2O,gas, CN2O,dis, denote N2O concentrations in the off-gas and solution (mg/L), while CN2O,gas,n, and CN2O,dis,n indicate concentrations at the sampling intervals.
- MN2O production is the daily N2O production (mg/d).
- TN load is the influent total nitrogen loading (mg/d).
- [TN]inf is the influent TN concentration (mg/L).
- V is the influent wastewater volume (L).
- HRT is the hydraulic retention time (d).
2.6. Metagenomic Analysis
Biofilm samples were collected on Days 19, 56, 78, 115, and 138, for high-throughput sequencing to characterize the microbial community structures. Before processing, the samples were freeze-dried and subsequently crushed. Genomic DNA was extracted using the E.Z.N.A.™ Mag-Bind Soil DNA Kit (OMEGA, M5635-02, Norcross, GA, USA) following the manufacturer’s protocol (http://omegabiotek.com/product/soil-dna-extraction-kit-e-z-n-a-soil-dna-kit/) URL (accessed on 3 October 2025). The V3–V4 hypervariable regions of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene were amplified via polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using primers 341F (5′-CCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG-3′) and 805R (5′-GACTACHVGGGTATCTAATCC-3′). The extracted DNA was quantified with a Qubit 3.0 fluorometer using the Qubit DNA Assay Kit (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA). An equal amount of DNA (10 ng per sample) was pooled and subjected to Illumina MiSeq high-throughput sequencing (Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). Sequence reads were clustered into operational taxonomic units (OTUs) at a 97% similarity threshold. Functional annotation of nitrogen metabolism-related genes was predicted using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database (https://www.kegg.jp/) URL (accessed on 3 October 2025).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nitrogen Removal and N2O Emissions
Figure 2 illustrates the long-term dynamics of nitrogen species (NH4+-N, NO2−-N, NO3−-N), and nitrogen removal efficiencies under varying C/N ratios in a mainstream anammox system. At a C/N ratio of 4.0, the effluent NH4+-N concentration gradually decreased and stabilized at 1.1 mg/L. However, the effluent NO3−-N concentration remained relatively high, exceeding 3.0 mg/L on most days. This suggested that the thin biofilm formed on the carrier surface under low C/N conditions restricted the development of anaerobic micro-zones [17], thereby reducing anammox activity. When the C/N ratio increased to 4.5, the higher influent COD concentration initially caused the effluent NH4+-N concentration to rise sharply to 6.2 mg/L. Subsequently, the NH4+-N concentration declined to below 1.0 mg/L, resulting in an average ammonia removal efficiency (ARE) of 98.2%. The complete conversion of influent NH4+-N also yielded an average nitrogen removal efficiency (NRE) of 93.4%. These results can be attributed to the proliferation of heterotrophic bacteria on the biofilm surface, which created anaerobic conditions within the biofilm and enhanced the activity of anaerobic microorganisms, including anammox bacteria and denitrifiers [13]. Further increasing the C/N ratio to 5.0 enhanced ARE and NRE to 99.0% and 95.3%, respectively. The higher influent COD promoted rapid oxygen consumption and the establishment of more micro-anoxic layers within the thickened biofilm. This provided favorable conditions for anammox activity, thereby improving nitrogen removal without inhibition from organic matter. However, when the C/N ratio was increased further to 6.0, both ARE and NRE declined at steady state. This decline was likely due to the excessive availability of organic carbon, which stimulated the overgrowth of heterotrophic bacteria. These organisms outcompeted autotrophic bacteria such as nitrifiers and anammox, thereby suppressing overall nitrogen removal performance.
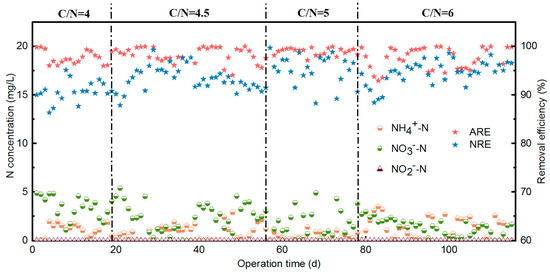
Figure 2.
Overall nitrogen removal performance during the whole experiment (30 °C; pH 7.0; DO 0.8 mg/L).
Table 2 presents the effluent nitrogen concentrations, nitrogen removal efficiency (NRE), and nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions of the system. When the C/N ratio increased from 4.0 to 5.0, effluent NH4+-N remained at a relatively low level. A consistently high ammonium removal efficiency (ARE) could be sustained across different C/N ratios, provided that aeration was sufficient. In general, however, effluent nitrate concentrations declined progressively as the C/N ratio increased. A relatively high influent COD enhanced denitrification without exerting inhibitory effects on autotrophic bacteria in the anammox reactor. This effect can be attributed to the gradual thickening of heterotrophic bacterial biofilms on the carrier surface, which expanded the anaerobic microzones within the biofilm and thereby promoted synergistic interactions between anammox and denitrification [18]. Consequently, this led to an improvement of ~5% in NRE. At the highest C/N ratio tested (6.0), heterotrophic bacteria became predominant over autotrophic bacteria, leading to reductions in both ARE and NRE. These results highlight that optimizing the C/N ratio is critical to balancing the activities of nitrifiers, anammox bacteria, and denitrifiers, thereby achieving efficient nitrogen removal within a single reactor [19].

Table 2.
Effluent nitrogen, nitrogen removal and N2O emission under different C/N conditions.
With respect to N2O emissions, the system exhibited an overall pattern of initial decline followed by a slight increase as the C/N ratio increased. Specifically, N2O emissions decreased from 0.46 mg to 0.37 mg as the C/N ratio rose from 4.0 to 5.0, accompanied by a reduction in the N2O emission factor from 0.92% to 0.73%. This suggests that a moderate increase in the C/N ratio enhanced the contribution of anammox to nitrogen removal by enlarging the anoxic microenvironment, thereby leading to a gradual reduction in N2O release. However, when the C/N ratio was further increased from 5.0 to 6.0, N2O emissions rose slightly from 0.37 mg to 0.38 mg, with the corresponding emission factor increasing from 0.73% to 0.76%. This trend indicates that higher C/N ratios promote greater N2O production as a byproduct of intensified denitrification, while concurrently suppressing anammox activity [20].
At lower C/N ratios (4.0–4.5), insufficient organic carbon results in thin heterotrophic biofilms and limited oxygen consumption, thereby maintaining relatively high dissolved oxygen (DO) concentrations within the biofilm. This condition restricts the ecological niches available for anammox and denitrifying bacteria, leading to lower total nitrogen (TN) removal and greater N2O accumulation. By contrast, a C/N ratio of 5.0 provides optimal carbon availability, supporting moderate heterotrophic growth that rapidly consumes oxygen in the outer biofilm layer and establishes a stable anoxic microenvironment. These conditions enrich both anammox bacteria and denitrifiers, thereby improving TN removal while reducing the N2O emission factor. At a C/N ratio of 6.0, however, excess carbon promotes excessive biofilm thickening and shifts the microbial balance towards denitrifiers, while simultaneously inhibiting anammox activity. Consequently, TN removal efficiency declines and N2O emissions increase slightly due to weakened anammox performance. Overall, these findings demonstrate that regulation of the C/N ratio governs heterotrophic metabolism, shapes stratified anoxic and anaerobic microenvironments within biofilms, and dynamically modulates the functional interactions between anammox and denitrifying communities, ultimately determining nitrogen removal efficiency and the extent of N2O release.
3.2. Nitrogen Conversion Characteristics in Typical Cycle
Figure 3 illustrates nitrogen species transformations during typical operational cycles under varying C/N ratios. The pattern of nitrogen conversion was strongly influenced by the C/N ratio. At a C/N ratio of 4.0, the initial NH4+-N concentration was 28.0 mg/L at the start of the cycle. As the reaction progressed, NH4+-N concentration gradually decreased, reaching near-complete removal (2.5 mg/L) by 480 min and declining further to 0.5 mg/L by the end of the cycle. The NO3−-N concentration displayed a characteristic “V-shaped” trend: within the first 300 min, NO3−-N was almost completely removed. Concurrently, NO2−-N accumulated during the initial 60 min, suggesting that partial denitrification occurred with influent organic carbon serving as the electron donor. Subsequently, residual ammonia and accumulated nitrite were removed via anammox over an extended period, leading to the production of a small fraction of nitrate. When the influent C/N ratio increased to 4.5 and 5.0, NH4+-N was removed at an accelerated rate, while nitrate and nitrite concentrations decreased more rapidly. This trend indicates enhanced anammox activity, likely supported by the stable formation of micro-anaerobic zones within the carrier interiors. Moreover, denitrification also became more pronounced as the C/N ratio increased, and the combined stimulation of denitrification and anammox resulted in progressively faster nitrogen conversion rates and higher overall nitrogen removal efficiency. However, when the C/N ratio was further elevated to 6.0, the rate of ammonia oxidation slowed, leaving 1.1 mg/L of ammonia in the effluent at the end of the cycle. The higher organic carbon load promoted the growth of heterotrophic bacteria, which outcompeted autotrophic bacteria such as anammox and nitrifiers. This shift reduced anammox activity while enhancing denitrification, leading to a slight decline in total nitrogen removal performance compared with the C/N ratio of 5.0.
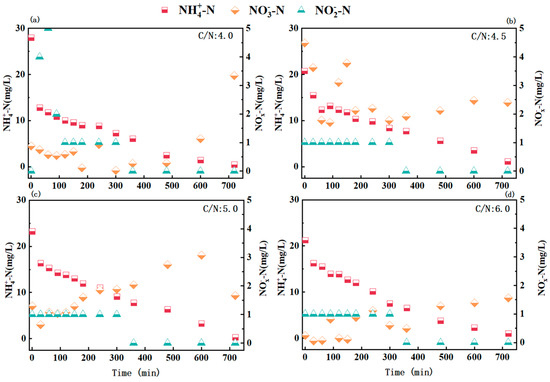
Figure 3.
Nitrogen variation in the typical cycle at different C/N (30 °C; pH 7.0; DO 0.8 mg/L) ratios: (a) C/N:4.0; (b) C/N:4.5; (c) C/N:5.0; (d) C/N:6.0.
3.3. N2O Emission Behaviors in Typical Cycle
Figure 4 presents the N2O emission profiles during typical operational cycles under different C/N ratios. The temporal patterns of N2O release were generally consistent across all C/N conditions and followed three distinct stages, consistent with previous reports [10,21]. In the initial stage, N2O concentrations increased rapidly to a peak. This was followed by a prolonged stabilization phase (100–500 min), during which N2O levels remained relatively high. Finally, N2O concentrations declined sharply, approaching near depletion by the end of the cycle. Notably, as the influent C/N ratio increased, the concentration of dissolved N2O progressively surpassed that of gaseous N2O. This trend suggests that higher C/N ratios promoted N2O accumulation in the liquid phase, likely due to incomplete denitrification, while simultaneously reducing the amount released as gas.
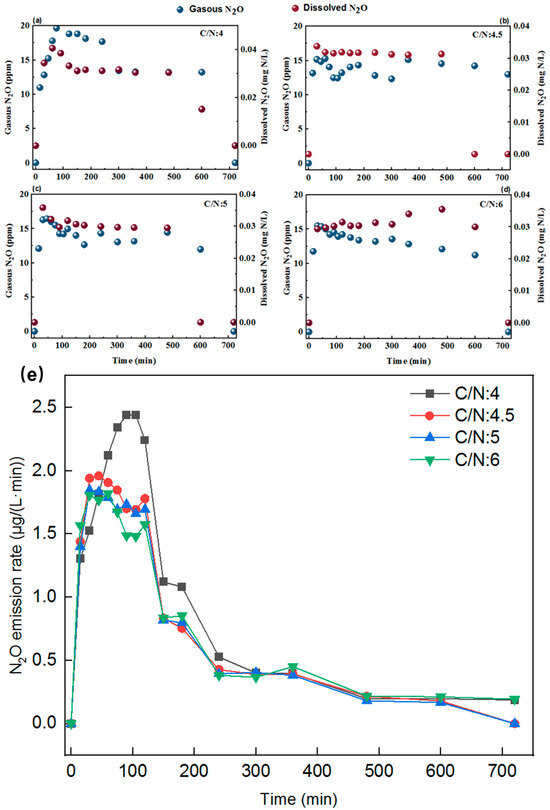
Figure 4.
Variation in the N2O concentration profile in the typical cycle at different C/N (30 °C; pH 7.0; DO 0.8 mg/L) ratios: (a) C/N:4.0; (b) C/N:4.5; (c) C/N:5.0; (d) C/N:6.0. (e) Profile of N2O emission rate in the typical cycle at different C/N ratios.
At a C/N ratio of 4.0 (Figure 4a), gaseous N2O concentration gradually increased during the initial phase, peaking at 20.7 ppm at 90 min, while dissolved N2O concentration reached its maximum of 0.04 mg/L at 60 min. Subsequently, both gaseous and dissolved N2O concentrations declined, reaching 13.4 mg/L and 0.03 mg/L, respectively, by 300 min. By the end of the cycle (480 min), concentrations of both gaseous and dissolved N2O decreased to zero. When the influent C/N ratio was increased to 4.5 (Figure 4b), the peak in gaseous N2O emissions occurred earlier, at 60 min, which was shorter than at a C/N ratio of 4.0. In contrast, the dissolved N2O concentration increased compared with that at a C/N ratio of 4.0. Nevertheless, the total N2O emission (0.39 mg) remained lower than that observed at a C/N ratio of 4.0. At a C/N ratio of 5.0 (Figure 4c), N2O emission peaks occurred earlier, with gaseous N2O reaching 16.2 mg/L at 45 min and dissolved N2O reaching 19.04 μg/L at 30 min. The subsequent decline in N2O followed trends similar to those observed under the previous C/N conditions. Notably, dissolved N2O decreased to 0 mg/L by 600 min, coinciding with the near-complete nitrogen conversion shown in Figure 3. Under these conditions, the system exhibited the lowest total N2O emissions (0.37 mg), indicating optimal nitrogen removal efficiency with minimal N2O release. When the C/N ratio was further increased to 6.0 (Figure 4d), gaseous N2O emissions continued to decrease, whereas dissolved N2O concentrations increased compared with those at a C/N ratio of 5.0. This phenomenon may be attributed to the inhibition of nitrification and anammox processes, coupled with enhanced denitrification under elevated organic carbon conditions.
Figure 4e illustrates N2O emission rates under different C/N conditions. At the lowest C/N ratio of 4.0, the emission rate was the highest (2.44 µg/(L·min)) primarily due to incomplete denitrification. In contrast, higher C/N ratios of 4.5, 5.0, and 6.0 resulted in lower peak emission rates (1.96, 1.85, and 1.82 µg/(L·min), respectively), suggesting reduced N2O generation through NH2OH oxidation and heterotrophic denitrification pathways [22,23] as the C/N ratio increased.
3.4. Microbial Community Dynamics
Figure 5 presents a heatmap illustrating the microbial community composition at the genus level under different C/N ratios. The corresponding relative abundances of bacterial genera at varying C/N ratios are summarized in Table A1. Three well-known anammox genera, Candidatus Kuenenia, Candidatus Anammoxoglobus, and Candidatus Brocadia, were successfully detected in the system. In particular, the relative abundance of Candidatus Kuenenia was 0.34%, 0.61%, 1.33%, and 0.57% at C/N ratios of 4.0, 4.5, 5.0, and 6.0, respectively, indicating its dominant role in shaping the anammox community structure. Notably, the highest relative abundance of anammox bacteria occurred at a C/N ratio of 5.0. This enrichment pattern was strongly associated with the observed variation in nitrogen removal efficiency (Figure 2). These findings suggest that an optimal C/N ratio promotes the stable development of anoxic and anaerobic microenvironments within the biofilm, while simultaneously minimizing interspecific inhibition or competition from heterotrophic denitrifiers, thereby enhancing the enrichment of anammox bacteria. Furthermore, Armatimonadetes_gp5 and Pirellula were frequently detected in association with anammox bacteria in anammox-based reactors [24,25]. Additionally, certain aerobic heterotrophic bacteria, such as Gp4, Subdivision3_genera_incertae_sedis, Defluviimonas, and Thauera, exhibited specialized denitrification capabilities, reducing NO3−-N to NO2−-N [26,27]. These key synergistic microorganisms play a critical role in maintaining the stability and nitrogen removal performance of the anammox biofilm reactor.
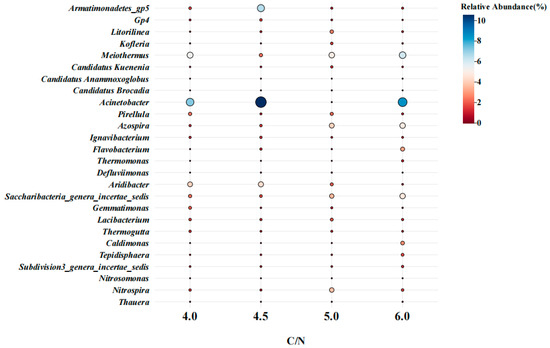
Figure 5.
Changes in the relative abundance of bacterial genera at different C/N (30 °C; pH 7.0; DO 0.8 mg/L) ratios.
Nitrospira, a nitrite-oxidizing bacterium (NOB), was detected in the system, with its highest relative abundance (3.76%) observed at a C/N ratio of 5.0. In contrast, Nitrosomonas, an ammonia-oxidizing bacterium (AOB), was scarcely detected. This suggests that complete ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (comammox) rather than canonical NOB may be responsible for ammonia removal in the oxygen-limited, low-ammonium reactor. Indeed, the co-existence of comammox and anammox has frequently been reported in single reactors due to their similar physiological traits [28,29].
In the microbial community, aerobic and facultative heterotrophic bacteria overwhelmingly dominated across the four C/N ratios, largely due to the abundant presence of organic matter. The relative abundances of both denitrifying and heterotrophic bacteria gradually increased with rising C/N ratios. Several high-abundance microorganisms, including Acinetobacter, Azospira, and Lacibacterium, are known for their ability to degrade organic matter and perform aerobic denitrification [30]. In particular, the relative abundance of Acinetobacter reached 7.22%, 10.57%, and 8.55% at C/N ratios of 4.0, 4.5, and 6.0, respectively, whereas it was only 0.06% at a C/N ratio of 5.0. Previous studies have shown that a significant enrichment of Acinetobacter may lead to the accumulation of N2O via aerobic denitrification under low-oxygen conditions, primarily due to the absence of N2O reductase [31]. In addition, several other aerobic or facultative heterotrophic genera, such as Ignavibacterium, Subdivision3_genera_incertae_sedis, Gemmatimonas, Tepidisphaera, and Litorilinea, were also detected. These microorganisms play pivotal roles in the biodegradation of organic matter, thereby protecting anammox bacteria from organic inhibition. Taken together, the enrichment of anammox bacteria and the sharp decline of Acinetobacter at a C/N ratio of 5.0 appear to be key factors contributing to the reduction of N2O emission.
Figure 6 illustrates the relative abundances of key functional bacterial groups under varying C/N ratios. Notably, the abundance of heterotrophic bacteria exceeded that of autotrophic bacteria in the presence of organic matter. The relative abundance of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria (AnAOB) initially increased with rising C/N ratios, reaching a maximum of 1.5% at a C/N ratio of 5.0, and subsequently declined at higher ratios. Among nitrifiers, AOB were scarcely detected, whereas NOB, including comammox bacteria, were prevalent within the biofilms. NOB and comammox bacteria exhibited a trend similar to AnAOB, with their relative abundance peaking at a C/N ratio of 5.0. Previous studies have indicated that comammox bacteria, rather than conventional AOB or NOB, contribute minimally to N2O emissions due to their complete ammonia-oxidation gene pathway [32,33]. In contrast, the relative abundances of denitrifying heterotrophic bacteria (DHB) and non-denitrifying heterotrophic bacteria (NDHB) did not display clear correlations with the C/N ratio, although they consistently dominated the microbial community structure. At a C/N ratio of 5.0, the moderately lower abundance of heterotrophic bacteria facilitated the stable immobilization and establishment of AnAOB within the biofilm microbial community. Under this condition, the combination of relatively low denitrifiers with sufficient AnAOB and comammox bacteria likely minimized N2O emissions while maintaining efficient nitrogen removal.
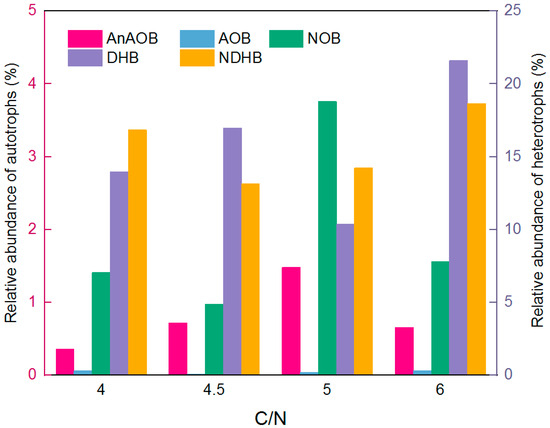
Figure 6.
Relative abundance of functional bacteria (30 °C; pH 7.0; DO 0.8 mg/L).
3.5. Functional Genes Generation Revealed via KEGG
Figure 7 presents a heatmap illustrating the variations in functional gene abundance under different C/N ratios. The abundance of anammox-associated functional genes (hzs and hdh) [34] was consistently much higher than that of other nitrogen conversion genes. At a C/N ratio of 5.0, the relative abundance of hzs and hdh reached its maximum, coinciding with the highest nitrogen removal efficiency. As the C/N ratio increased, the total abundance of denitrification genes (nar, nap, nir, nor, and nos) gradually increased. This pattern supports the conclusion that anammox was the dominant pathway, coupled with denitrification in the oxygen-limited SBBR. Within the nitrification process, the nitrite oxidoreductase (nxr) accounted for more than 70% of the total nitrification enzymes, suggesting the potential occurrence of comammox in the system. Biofilm reactors are known to effectively cultivate and enrich comammox, enabling them to play a leading role in nitrification [35,36]. Because of their complete nitrifying enzyme systems, comammox bacteria can significantly reduce N2O emissions compared to canonical ammonia oxidizers [37,38]. Moreover, the abundance of the key enzyme Nos, which catalyzed the reduction of N2O to N2 [39], increased with higher C/N ratios, indicating that its activity was influenced by C/N conditions. At the optimal C/N ratio of 5.0, the nos enzyme was at its peak, suggesting that more N2O was completely converted into N2. Consequently, N2O emissions were effectively reduced under these conditions. In summary, an optimal C/N ratio promotes a synergistic interaction among anammox, comammox, and denitrification functional genes, thereby enhancing nitrogen removal efficiency while minimizing greenhouse gas emissions.
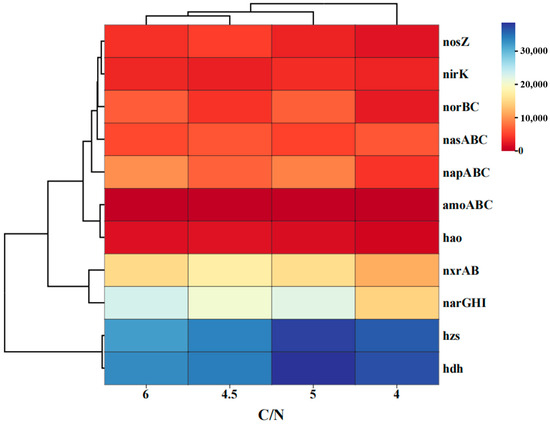
Figure 7.
Heatmap of functional gene abundance in nitrogen conversion functional genes (30 °C; pH 7.0; DO 0.8 mg/L).
4. Conclusions
In the mainstream anammox SBBR system, both nitrogen removal efficiency and N2O emission were investigated under varying C/N ratios from 4.0 to 6.0. At a C/N ratio of 5.0, average ARE reached 99.0%, and NRE reached 95.3%, representing the highest values across all tested conditions. At the same ratio, overall N2O emissions were minimized (0.37 mg), with an N2O emission factor of only 0.73%. This C/N ratio facilitated faster ammonia oxidation rates and resulted in lower effluent nitrate and nitrite concentrations, which accelerated both the formation and subsequent disappearance of N2O peaks. Moreover, the highest relative abundance of anammox bacteria (Candidatus Kuenenia) and key functional genes (nosZ, hzs, and hdh) was observed at the optimal C/N ratio. These findings demonstrate that C/N optimization simultaneously enhances nitrogen removal efficiency while minimizing the N2O emission footprint. In the determination of N2O emissions, the measured dissolved N2O concentration strongly depends on the solubility coefficient of N2O, thereby influencing the accuracy of the final quantification. To address this limitation, in situ N2O microelectrodes will be employed in future work to monitor real-time dissolved N2O concentrations and obtain more precise gas emission data. For influents with C/N ratios higher than 6.0, we will continue to examine their effect on nitrogen removal and N2O emission to refine and extend the current findings across a broader C/N range. Furthermore, the microbial mechanisms underlying N2O emission reduction will be explored in depth through metagenomic and metatranscriptomic analyses.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Z.; methodology, X.C.; data curation, X.C.; writing—original draft preparation, D.D.; writing—review and editing, X.Z.; supervision, X.Z.; funding acquisition, X.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Open Fund Program of Key Laboratory of Songliao Aquatic Environment, Ministry of Education, Jilin Jianzhu University (No. JLJUSLKF042024007), Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province (No. 202403021221049) and Shanxi Province Patent Transformation Plan Funding Project (No. 202401011).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Relative abundance of bacterial genera at different C/N.
Table A1.
Relative abundance of bacterial genera at different C/N.
| Genus | Relative Abundance (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/N = 4.0 | C/N = 4.5 | C/N = 5.0 | C/N = 6.0 | |
| Armatimonadetes_gp5 | 1.65 | 6.59 | 1.09 | 1.05 |
| Gp4 | 0.8 | 1.54 | 0.73 | 0.34 |
| Litorilinea | 0.34 | 0.93 | 2.63 | 0.84 |
| Kofleria | 0.2 | 0.2 | 1.54 | 0.46 |
| Meiothermus | 5.37 | 2.4 | 4.98 | 6.1 |
| Candidatus Kuenenia | 0.34 | 0.61 | 1.33 | 0.57 |
| Candidatus Anammoxoglobus | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.06 |
| Candidatus Brocadia | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.03 |
| Acinetobacter | 7.22 | 10.57 | 0.06 | 8.55 |
| Pirellula | 2.36 | 0.98 | 2.22 | 1.03 |
| Azospira | 1.2 | 1.5 | 4.18 | 4.88 |
| Ignavibacterium | 1.18 | 1.38 | 0.75 | 0.86 |
| Flavobacterium | 0.11 | 1.24 | 0.25 | 3.2 |
| Thermomonas | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 1.17 |
| Defluviimonas | 0 | 0.24 | 0.33 | 0.09 |
| Aridibacter | 4.16 | 4.46 | 2.08 | 0.69 |
| Saccharibacteria_genera_incertae_sedis | 2.33 | 1.76 | 3.6 | 4.78 |
| Gemmatimonas | 1.99 | 0.52 | 1.02 | 0.39 |
| Lacibacterium | 1.54 | 1.21 | 1.94 | 1.19 |
| Thermogutta | 1.35 | 0.8 | 1.02 | 0.82 |
| Caldimonas | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 2.84 |
| Tepidisphaera | 0.35 | 0.6 | 0.53 | 1.83 |
| Subdivision3_genera_incertae_sedis | 0.68 | 0.79 | 0.71 | 1.31 |
| Nitrosomonas | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| Nitrospira | 1.41 | 0.98 | 3.76 | 1.56 |
| Thauera | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.21 |
References
- Saxena, V. Water quality, air pollution, and climate change: Investigating the environmental impacts of industrialization and urbanization. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2025, 236, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Houweling, D.; Dold, P. Biological nutrient removal in municipal wastewater treatment: New directions in sustainability. J. Environ. Eng. 2012, 138, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonchyk, M.; Peterson, M.P.; Zhang, L.; Hurynovich, V.; He, Y. Greenhouse gases emissions and global climate change: Examining the influence of CO2, CH4, and N2O. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 935, 173359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edenhofer, O. Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kartal, B.; Kuenen, J.V.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Sewage treatment with anammox. Science 2010, 328, 702–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Ji, B.; Liu, Y. Towards mainstream deammonification of municipal wastewater: Partial nitrification-anammox versus partial denitrification-anammox. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Cao, J.; Xu, R.; Zhang, T.; Luo, J.; Xue, Z.; Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Zhou, H. Influence of C/N ratio and ammonia on nitrogen removal and N2O emissions from one-stage partial denitrification coupled with anammox. Chemosphere 2023, 341, 140035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijuan, M.; Ribera-Guardia, A.; Balcázar, J.L.; Micó, M.M.; Torre, T.D.L. Effect of COD on mainstream anammox: Evaluation of process performance, granule morphology and nitrous oxide production. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, G.; Wang, R. Drivers of nitrous oxide accumulation in denitrification biofilters with low carbon:nitrogen ratios. Water Res. 2016, 106, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Song, J.; Wang, G.; Yin, Z.; Cao, X.; Gao, J. Unravelling nitrogen removal and nitrous oxide emission from mainstream integrated nitrification-partial denitrification-anammox for low carbon/nitrogen domestic wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, B.; Tian, Z.; Song, Y.; Yu, H.; Xiang, L.; Wang, S.; Sun, C. Johannesburg-sulfur autotrophic denitrification system treatment of municipal wastewater with a low COD/TN ratio: Performance, material balance and bacterial community. Desalin Water Treat. 2017, 59, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.J.; Kumar, M.; Wang, C.C.; Lin, J.G. Development of simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification (SNAD) process in a sequential batch reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5514–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. A novel single-stage process integrating simultaneous COD oxidation, partial nitritation-denitritation and anammox (SCONDA) for treating ammonia-rich organic wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 254, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabel, R.; Schultz, B. Solubility of Nitrous Oxide in Water, 20–80 °C. Anesthesiology 1973, 38, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, G.; Capodici, M.; Cosenza, A.; Di Trapani, D.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Nitrous oxide emission in a University of Cape Town membrane bioreactor: The effect of carbon to nitrogen ratio. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, Y.; Lant, P.; Yuan, Z. The confounding effect of nitrite on N2O production by an enriched ammonia-oxidizing culture. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7186–7194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmer, C.; Tromm, C.; Hippen, A.; Rosenwinkel, K.H.; Seyfried, C.F.; Kunst, S. Single stage biological nitrogen removal by nitritation and anaerobic ammonium oxidation in biofilm systems. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Huang, S.; Bian, W.; Liang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Ma, X.; Li, J. Enhanced nitrogen removal of the simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification (SNAD) biofilm reactor for treating mainstream wastewater under low dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 283, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, J. Microbial characteristics and nitrogen removal of simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification (SNAD) process treating low C/N ratio sewage. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hai, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, X. Insights into deterioration and reactivation of a mainstream anammox biofilm reactor response to C/N ratio. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 320, 115780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Rathnayake, R.M.; Zhang, L.; Ishii, S.; Kindaichi, T.; Satoh, H.; Okabe, S. Source identification of nitrous oxide emission pathways from a single-stage nitritation-anammox granular reactor. Water Res. 2016, 102, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampschreur, M.J.; Temmink, H.; Kleerebezem, R.; Jetten, M.S.; van Loosdrecht, M.C. Nitrous oxide emission during wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4093–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massara, T.M.; Malamis, S.; Guisasola, A.; Baeza, J.A.; Noutsopoulos, C.; Katsou, E. A review on nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions during biological nutrient removal from municipal wastewater and sludge reject water. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596, 106–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Jiang, B.; Tang, X.; Liu, S. Metagenomic insights into functional traits variation and coupling effects on the anammox community during reactor start-up. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, L.; Chen, S.; Zhao, X. Analysis of the partial nitrification/anammox performance and microbial structure of low C/N wastewater by A2/O process. Water. 2023, 15, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Lian, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Tian, S. Effects of low-intensity ultrasound on nitrite accumulation and microbial characteristics during partial nitrification. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, R.; Peng, Y.; Ji, J.; Shi, L.; Gao, R.; Li, X. Partial denitrification providing nitrite: Opportunities of extending application for anammox. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 105001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottshall, E.Y.; Bryson, S.J.; Cogert, K.I.; Landreau, M.; Sedlacek, C.J.; Stahl, D.A.; Winkler, M. Sustained nitrogen loss in a symbiotic association of Comammox Nitrospira and Anammox bacteria. Water Res. 2021, 202, 117426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilardi, K.; Cotto, I.; Bachmann, M.; Parsons, M.; Klaus, S.; Wilson, C. Co-occurrence and cooperation between comammox and anammox bacteria in a full-scale attached growth municipal wastewater treatment process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 5013–5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Li, X.; Fan, W.; Wang, J. Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification by a novel Acinetobacter sp. ND7 isolated from municipal activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roothans, N.; Gabriëls, M.; Abeel, T.; Pabst, M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.; Laureni, M. Aerobic denitrification as an N2O source from microbial communities. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrae116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Wu, D.; Sun, D.; Zhao, M.; Wang, M.; Wen, T. N2O and NOy production by the comammox bacterium Nitrospira inopinata in comparison with canonical ammonia oxidizers. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, W.; Liu, G. Enhancing the relative abundance of comammox nitrospira in ammonia oxidizer community decreases N2O emission in nitrification exponentially. Chemosphere 2024, 356, 141883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Che, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xia, Y.; Luo, R.; Cheng, S.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, T. High-quality bacterial genomes of a partial-nitritation/anammox system by an iterative hybrid assembly method. Microbiome 2020, 8, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Yang, W.; Hu, J.; Jia, Z.; Hu, B. Biofilm: A strategy for the dominance of comammox Nitrospira. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, G.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y. Deciphering the concurrence of comammox, partial denitrification and anammox in a single low-oxygen mainstream nitrogen removal reactor. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kits, K.D.; Jung, M.Y.; Vierheilig, J.; Pjevac, P.; Sedlacek, C.J.; Liu, S.; Herbold, C.; Stein, L.Y.; Richter, A.; Wissel, H.; et al. Low yield and abiotic origin of N2O formed by the complete nitrifier Nitrospira inopinata. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Fang, F.; Liu, G. Efficient nitrification and low-level N2O emission in a weakly acidic bioreactor at low dissolved-oxygen levels are due to comammox. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 87, e00154-21. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Koch, K.; Wells, G.F.; Zheng, M.; Yuan, Z.; Ye, L. Insights into nitrous oxide mitigation strategies in wastewater treatment and challenges for wider implementation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 7208–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).