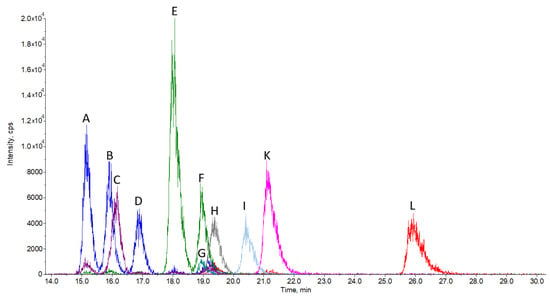
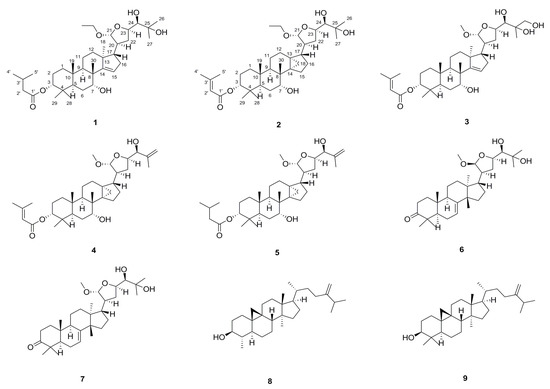
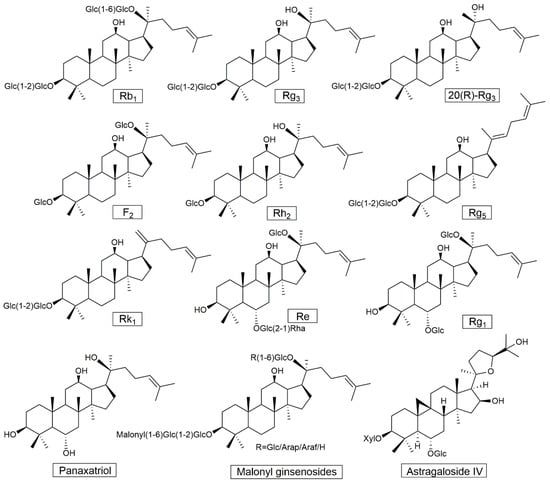
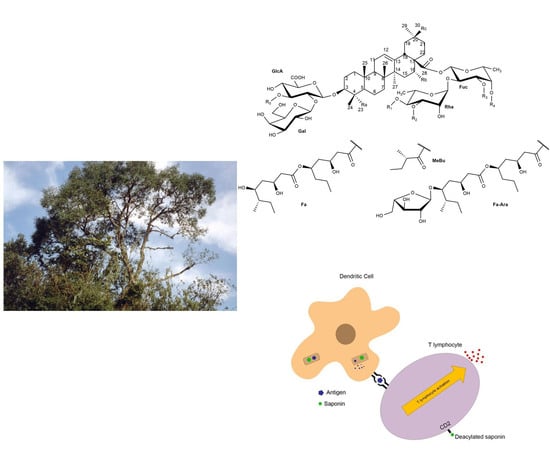
Triterpenes and Triterpenoids
A topical collection in Molecules (ISSN 1420-3049). This collection belongs to the section "Natural Products Chemistry".
Submission Status: ClosedEditors
Interests: biomedical applications; electrospinning; nanofibers; hybrid materials; marine biopolymers
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: isolation; structure elucidation; marine natural products; marine biopolymers; marine-derived microorganisms
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
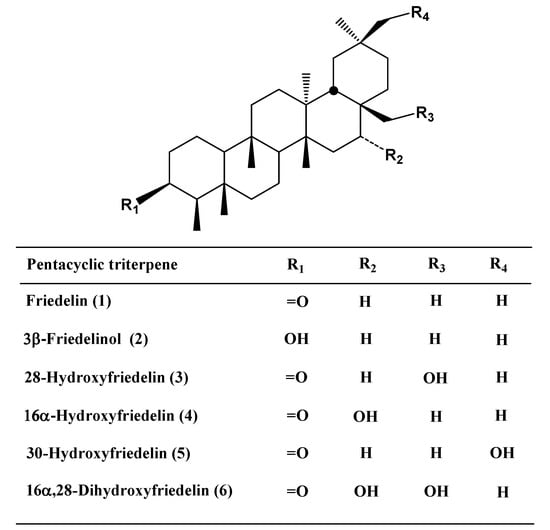
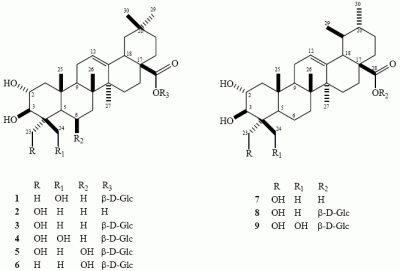
Triterpenes, constituting one of the classes of higher terpenes, show a widespread occurrence in nature and can be found in almost all terrestrial and marine organisms. Nevertheless, most of the bioactive triterpenes have been detected in higher plants.
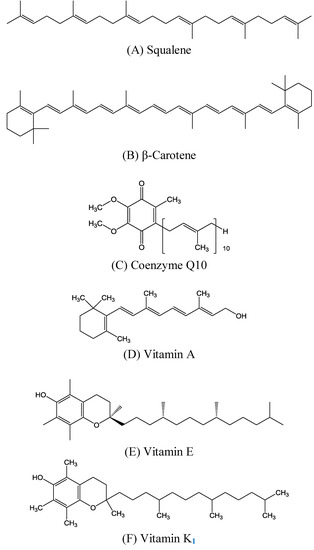
Triterpenes are naturally occurring alkenes included in the broad and structurally diverse group of triterpenoids, which also include natural degradation products, oxidation, and hydrogenation products. Taking into consideration the architecture of the carbon skeleton, triterpenes may be divided into linear and cyclic ones, mainly including tetracyclic and pentacyclic carbocycles.
Due to their relatively complex and diverse structures, triterpenoids frequently exhibit a wide range of biological activities, such as cytotoxic, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative, anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, and would healing activity.
The continuous investigations of natural sources and biotransformation studies on known metabolites are constantly revealing new triterpenoids that might display even more promising properties. Taking together the current knowledge, triterpenes are considered a promising class of molecules for the development of new drugs.
Prof. Dr. Vassilios Roussis
Dr. Efstathia Ioannou
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Molecules is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- isolation and structure elucidation of triterpenes and triterpenoids
- pharmacological activity
- medicinal chemistry
- biotransformation studies
Related Special Issue
- Triterpenes and Triterpenoids 2013 in Molecules (36 articles - displayed below)