- Article
LC-ESI-MS/MS Analysis of Echium asperrimum from the Algerian Aurès Region: Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, Cholinesterase Inhibitory, and Antiproliferative Activities
- Amina Guetteche,
- Hamza Fadel and
- Luca Rastrelli
- + 12 authors
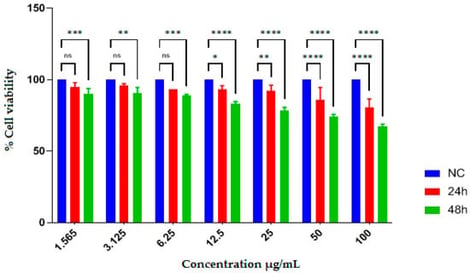
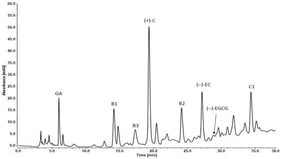
The aim of the present study was to characterize the phenolic profile of hydroethanolic (EAEE) and ethyl acetate (EAAE) extracts of Echium asperrimum and to evaluate their antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-Alzheimer-related (cholinesterase inhibitory) activity, and antiproliferative activities. The DPPH radical scavenging activity of EAEE and EAAE showed IC50 values of 32.53 ± 1.25 and 97.85 ± 2.31 µg/mL, respectively. In addition, both extracts exhibited phosphomolybdenum reduction capacity, with A0.50 values of 61.60 ± 2.97 µg/mL for EAEE and 23.20 ± 1.55 µg/mL for EAAE. Acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibition assays revealed IC50 values comparable to the reference compound galantamine. Both extracts also showed antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial strains. LC-ESI-MS/MS analysis indicated that p-coumaric acid (5.12 mg/g), vanillic acid (11.6 mg/g), hydroxybenzaldehyde (3.82 mg/g), and gentisic acid (1.66 mg/g) were the major phenolic constituents of EAAE, whereas p-coumaric acid (0.13 mg/g), salicylic acid (0.141 mg/g), sinapic acid (0.20 mg/g), and trans-ferulic acid (0.20 mg/g) predominated in EAEE. Furthermore, EAAE exhibited dose-dependent antiproliferative activity at concentrations of 50 and 100 µg/mL, with an IC50 value of 83.09 ± 6.50 µg/mL. Taken together, these findings suggest that E. asperrimum represents a promising source of bioactive compounds with potential relevance for future pharmaceutical and nutraceutical research.
7 February 2026