A New Saponin from Tea Seed Pomace (Camellia oleifera Abel) and Its Protective Effect on PC12 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
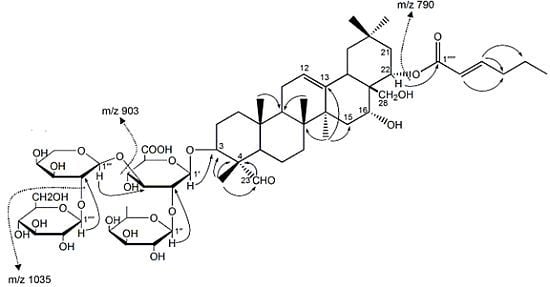
2. Results and Discussion
| No. | δC | δH | No. | δC | δH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 39.8 | 2.55 (m) | 3-O-GlcA | ||
| 2 | 26.1 | 1.53 (m) | GlcA-1′ | 105.3 | 4.41(d, 6.0) |
| 3 | 86.6 | 3.92 (m) | GlcA-2′ | 78.7 | 3.8(m) |
| 4 | 56.8 | GlcA-3′ | 84.3 | 3.71(m) | |
| 5 | 49.1 | 1.37 (m) | GlcA-4′ | 71.1 | 3.86(m) |
| 6 | 21.7 | 0.96 (m) | GlcA-5′ | 77.4 | 3.57(m) |
| 7 | 33.7 | 1.29 (m) | GlcA-6′ | 172.6 | |
| 8 | 42.6 | 2′-O-Gal | |||
| 9 | 48.4 | 1.11 (m) | Gal-1′′ | 103.2 | 5.05(d, 6.0) |
| 10 | 37.5 | Gal-2′′ | 74.0 | 3.76(m) | |
| 11 | 25.1 | 1.99 (m) | Gal-3′′ | 75.3 | 3.76(m) |
| 12 | 124.8 | 5.39 (br s) | Gal-4′′ | 71.4 | 3.55(m) |
| 13 | 144.5 | Gal-5′′ | 76.7 | 3.68(m) | |
| 14 | 41.7 | Gal-6′′ | 62.9 | 3.82(m) | |
| 15 | 35.6 | 1.65(m) | 3′-O-Ara | ||
| 16 | 71 | 4.11(br s) | Ara-1′′′ | 102.1 | 4.54(d, 6.0) |
| 17 | 45.8 | Ara-2′′′ | 83.7 | 3.89(m) | |
| 18 | 41.8 | 2.56 (m) | Ara-3′′′ | 71.5 | 3.69(m) |
| 19 | 42.7 | 2.26 (m) | Ara-4′′′ | 67.8 | 4(dd, 12.0, 6.0) |
| 20 | 32.5 | Ara-5′′′ | 64.9 | 3.26(m) | |
| 21 | 43.0 | 2.27 (m) | 2′′′-O-Glc | ||
| 22 | 73.9 | 5.45(dd, 6.0, 3.0) | Glc-1′′′′ | 108.1 | 4.54(d, 6.0) |
| 23 | 211.2 | 9.48 (br s) | Glc-2′′′′ | 75.4 | 3.53(m) |
| 24 | 11.3 | 1.21(s) | Glc-3′′′′ | 76.5 | 3.32(m) |
| 25 | 17.7 | 0.96 (s) | Glc-4′′′′ | 71.6 | 3.64(m) |
| 26 | 16.9 | 1.07 (s) | Glc-5′′′′ | 78.4 | 3.69(m) |
| 27 | 28.2 | 1.54 (s) | Glc-6′′′′ | 63.1 | 3.77(m) |
| 28 | 63.1 | 3.72 (br s) | 22-O-(cis-2-Hexenoyl) | ||
| 29 | 34.1 | 0.95 (s) | 1′′′′′ | 168.8 | |
| 30 | 25.7 | 1.08 (s) | 2′′′′′ | 121.9 | 5.85(dt, 12.0, 1.6) |
| 3′′′′′ | 151.4 | 6.29(dt, 12.0, 4.0) | |||
| 4′′′′′ | 32.4 | 2.66(m) | |||
| 5′′′′′ | 23.8 | 1.51(m) | |||
| 6′′′′′ | 14.4 | 0.99(t, 8.0) | |||
3. Experimental
3.1. General
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
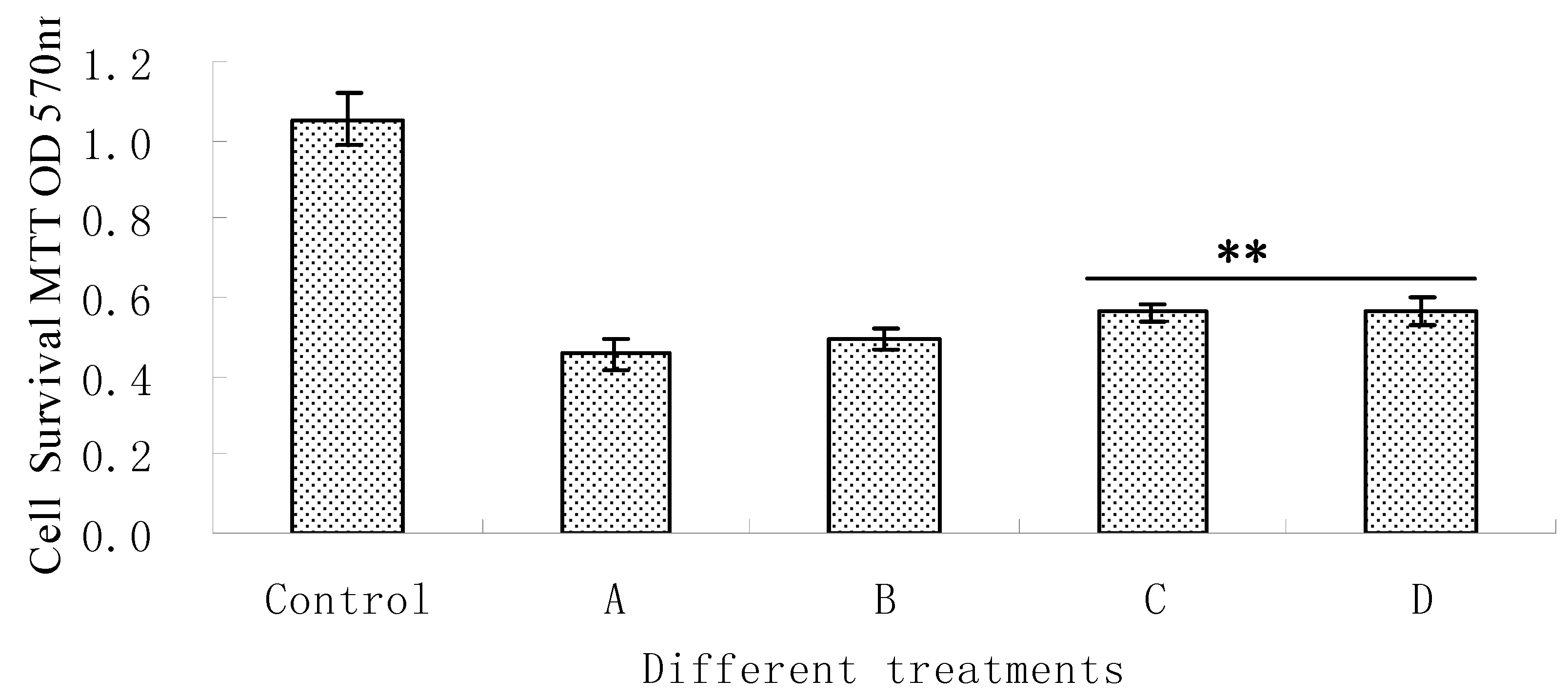
3.4. Measurement of Cell Viability
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
- Samples Availability: Not available.
References
- Chen, Y.F.; Yang, C.H.; Chang, M.S.; Ciou, Y.P.; Huang, Y.C. Foam properties and detergent abilities of the saponins from Camellia oleifera. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 4417–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaicharoenpong, C.; Petsom, A. Quantitative thin layer chromatographic analysis of the saponins in tea seed meal. Phytochem. Anal. 2009, 20, 253–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; He, M.; Chen, H.; Shao, L.; Liu, D.; Luo, Y.; Dai, Y. Protective effects of sasanquasaponin on injury of endothelial cells induced by anoxia and reoxygenation in vitro. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 101, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Shao, L.; He, M.; Chen, H.; Liu, D.; Luo, Y.; Dai, Y. Inhibitory effects of sasanquasaponin on over-expression of ICAM-1 and on enhancement of capillary permeability induced by burns in rats. Burns 2005, 31, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, T.; Li, N.; Nagatomo, A.; Matsuda, H.; Li, X.; Yoshikawa, M. Triterpene saponins with gastroprotective effects from tea seed (the seeds of Camellia sinensis). J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Morikawa, T.; Nakamura, S.; Li, N.; Li, X.; Matsuda, H. Bioactive saponins and glycosides. XXV. Acylated oleanane-type triterpene saponins from the seeds of tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa, T.; Matsuda, H.; Li, N.; Li, X.; Yoshikawa, M. Bioactive Saponins and glycosides- Part 29- Acylated oleanane-type triterpene saponins: Theasaponins A(6), A(7), and B-5, from the seeds of Camellia sinensis. Helv. Chim. Acta 2007, 90, 2342–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, I.; Hori, K.; Motozawa, T.; Murakami, T.; Yoshikawa, M. Structures of new acylated oleanene-type triterpene oligoglycosides, theasaponins E1 and E2, from the seeds of tea plant, Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 46, 1901–1906. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Morikawa, T.; Li, N.; Nagatomo, A.; Li, X.; Matsuda, H. Bioactive saponins and glycosides. XXIII. Triterpene saponins with gastroprotective effect from the seeds of Camellia sinensis - Theasaponins E-3, E-4, E-5, E-6, and E-7. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 53, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar]
- Attele, A.S.; Wu, J.A.; Yuan, C.S. Ginseng pharmacology: Multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 58, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.C.; Lin, T.C.; Yang, C.W.; Lin, C.L.; Chen, G.F.; Huang, J.W. Bioactive saponin from tea seed pomace with inhibitory effects against Rhizoctonia solani. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2010, 58, 8618–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Morikawa, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Kato, Y.; Nagatomo, A.; Matsuda, H. Floratheasaponins A-C, acylated oleanane-type triterpene oligoglycosides with anti-hyperlipidemic activities from flowers of the tea plant (Camellia sinensis). J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1360–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, H.; Nakamura, S.; Fujimoto, K.; Moriuchi, R.; Kimura, Y.; Ikoma, N.; Hata, Y.; Muraoka, O.; Yoshikawa, M. Medicinal flowers. XXXI. Acylated oleanane-type triterpene saponins, sasanquasaponins I-V, with antiallergic activity from the flower buds of Camellia sasanqua. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1617–1621. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Z.; Yin, D.; Wang, W.; Zeng, G.; Liu, D.; Chen, H.; Huang, Q.; He, M. Cardioprotective effect of sasanquasaponin preconditioning via bradykinin-NO pathway in isolated rat heart. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.; Babu, U.; Garg, H. A triterpene glycoside from Scrophularia koelzii. Phytochemistry 1997, 45, 1717–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Murakami, T.; Yoshizumi, S.; Murakami, N.; Yamahara, J.; Matsuda, H. Bioactive saponins and glycosides. V. Acylated polyhydroxyolean-12-ene triterpene oligoglycosides, camelliasaponins A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, and C2, from the seeds of Camellia japonica L.: structures and inhibitory activity on alcohol absorption. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1996, 44, 1899–1907. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Li, N.; Ma, Z.Z.; Tu, P.F. Comparison of the chemical constituents of aged Pu-erh Tea, ripened Pu-erh Tea, and other teas using HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS(n). J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2011, 59, 8754–8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.S.; Tzou, B.C.; Liu, Y.P.; Tsai, M.J.; Shyue, S.K.; Tzeng, S.F. Inhibition of cadmium-induced oxidative injury in rat primary astrocytes by the addition of antioxidants and the reduction of intracellular calcium. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 103, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.-F.; Han, Y.-Y.; Bao, G.-H.; Ling, T.-J.; Zhang, L.; Gao, L.-P.; Xia, T. A New Saponin from Tea Seed Pomace (Camellia oleifera Abel) and Its Protective Effect on PC12 Cells. Molecules 2012, 17, 11721-11728. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171011721
Zhang X-F, Han Y-Y, Bao G-H, Ling T-J, Zhang L, Gao L-P, Xia T. A New Saponin from Tea Seed Pomace (Camellia oleifera Abel) and Its Protective Effect on PC12 Cells. Molecules. 2012; 17(10):11721-11728. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171011721
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xin-Fu, Ying-Ying Han, Guan-Hu Bao, Tie-Jun Ling, Liang Zhang, Li-Ping Gao, and Tao Xia. 2012. "A New Saponin from Tea Seed Pomace (Camellia oleifera Abel) and Its Protective Effect on PC12 Cells" Molecules 17, no. 10: 11721-11728. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171011721
APA StyleZhang, X.-F., Han, Y.-Y., Bao, G.-H., Ling, T.-J., Zhang, L., Gao, L.-P., & Xia, T. (2012). A New Saponin from Tea Seed Pomace (Camellia oleifera Abel) and Its Protective Effect on PC12 Cells. Molecules, 17(10), 11721-11728. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171011721