- Article
Mobile Phone Craving in Spain: Associations with Impulsivity, Anxiety, Gaming Problem, and Gambling Severity
- Jose de-Sola,
- Joan I. Mestre-Pintó and
- Fernando Rodríguez de Fonseca
- + 4 authors
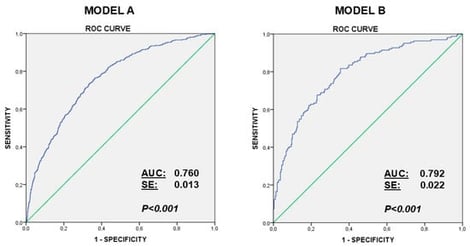
Craving for mobile phone use is increasingly discussed as a relevant feature of problematic engagement with digital technologies. This population-based study of 1601 Spanish adults examined psychological factors (impulsivity traits and affective symptoms) and behavioral correlates linked to mobile phone craving. Primary outcome: Mobile phone craving scale (MPACS). Secondary analyses: Associations between craving and impulsivity, anxiety, depression, Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD), gambling severity, and alcohol use. Craving measured with the MPACS was most common among younger participants (16–35 years old) and strongly related to greater daily phone use, heightened impulsivity, especially urgency and sensation seeking, and higher levels of anxiety and depressive symptoms. Among individuals who use their phones for gaming or gambling (n = 463), craving was strongly associated with IGD and gambling severity, suggesting that mobile phones may amplify involvement in these behaviors. Exploratory factor analyses consistently revealed four underlying dimensions—Reactive Impulsivity, Cognitive Impulsivity, Negative Emotions, and Addictive Behaviors—each contributing differently depending on craving intensity. Logistic regression analyses showed that anxiety, impulsivity, phone-use duration, and IGD scores independently predicted high craving levels. Overall, the findings highlight mobile phone craving as a clinically meaningful, multidimensional construct tied to emotional dysregulation and behavioral addiction. Assessing craving may help identify individuals at heightened risk for problematic technology use and related psychological difficulties.
6 February 2026