Journal Description
Psychology International
Psychology International
- formerly Psych - is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on psychology, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 24.4 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 5.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Journal Cluster of Education and Psychology: Adolescents, Behavioral Sciences, Education Sciences, Journal of Intelligence, Psychology International and Youth.
Latest Articles
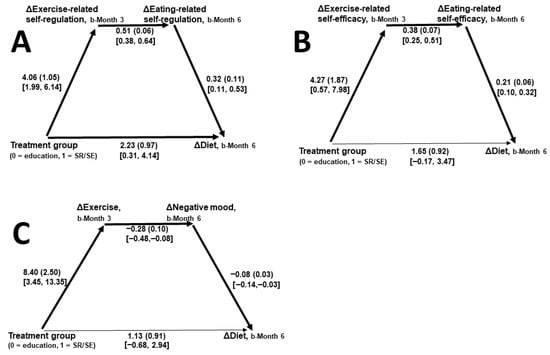
Psychosocial Mechanisms of Exercise–Eating Behavior Change Coaction Processes Within Community-Based Obesity-Reduction Programs
Psychol. Int. 2026, 8(1), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint8010016 - 2 Mar 2026
Abstract
Coaction theory suggests improvement in one health behavior carries over to advancements in other health behaviors. There is evidence of increased exercise leading to improved eating; however, data on its psychosocial mechanisms required to adequately inform behavioral weight-management interventions are lacking. Theory suggests
[...] Read more.
Coaction theory suggests improvement in one health behavior carries over to advancements in other health behaviors. There is evidence of increased exercise leading to improved eating; however, data on its psychosocial mechanisms required to adequately inform behavioral weight-management interventions are lacking. Theory suggests that self-regulation, and the relationship of self-regulation to self-efficacy, promote such carry-over processes. Participants in a community-based obesity program who completed no/minimal weekly exercise at baseline were randomized by participating facility using computer-generated random numbers into 6-month treatments emphasizing either weight loss education (n = 39) or self-regulation/self-efficacy (SR/SE) methods (n = 90). Improvements in exercise outputs, exercise- and eating-related self-regulation and self-efficacy, negative mood, dietary behaviors, and weight were significant overall, and significantly greater in the SR/SE group. Carry-over of increased exercise to improved dietary behaviors was suggested. Paths from the treatment group to dietary changes at 6 and 12 months were significantly mediated by associations of changes in (a) exercise-related self-regulation leading to eating-related self-regulation, (b) exercise-related self-efficacy leading to eating-related self-efficacy, and (c) exercise leading to improved mood. Identified relationships between self-regulation and self-efficacy changes were particularly relevant in the dietary-change context. Weight losses over 6, 12, and 24 months, associated with exercise and dietary changes, were 2.2×–2.7× greater in the SR/SE group than in the weight loss education group (−6.0% vs. −2.6%; −5.6% vs. −2.5%; and −5.1% vs. −1.9%, respectively). Advantages of treatment foci on self-regulatory skills and self-efficacy over typical weight loss education were supported. Clarification of psychosocial mechanisms of the increased exercise → improved eating-behavior relationship, including effects of increased exercise on mood, informed continued advancements in theory-driven obesity treatments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Psychology of Peak Performance in Sport)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessSystematic Review
Psychological Interventions for Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised and Non-Randomised Controlled Trials
by
Claire Adshead, David Sheffield, Dean Fido, Lukasz Lagojda, Ioannis Kyrou, Harpal S. Randeva, Sophie Williams and Chris Kite
Psychol. Int. 2026, 8(1), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint8010015 - 21 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is an endocrine condition affecting 8–13% of reproductive-aged women globally. Psychological features of PCOS are often overlooked despite their association with mental health complications. This systematic review synthesises existing evidence of psychological interventions for women with PCOS. Database searches
[...] Read more.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is an endocrine condition affecting 8–13% of reproductive-aged women globally. Psychological features of PCOS are often overlooked despite their association with mental health complications. This systematic review synthesises existing evidence of psychological interventions for women with PCOS. Database searches returned 4982 articles, of which 20 papers were eligible; 12 studies were meta-analysed. Compared to control, psychological interventions had statistically beneficial effects on change from baseline values for depression, PCOS-specific quality of life, general health, and body image. Significant improvements were found in all PCOS Questionnaire (PCOSQ) domains except acne, yet the importance of these differences in clinical practice was indeterminable. Despite statistical effects, the quality of evidence was judged as low/very-low due to between study heterogeneity, risk of bias, and imprecision in effect estimates. Future studies should focus on rigorously designed, well-reported trials, in order to address the uncertainty around the effectiveness of psychological interventions. The protocol of this systematic review was prospectively registered on the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO: CRD42023472417).
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Predictors of Clinical Outcomes in IADC Therapy
by
Fabio D’Antoni and Claudio Lalla
Psychol. Int. 2026, 8(1), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint8010014 - 18 Feb 2026
Abstract
(1) Background: Induced After-Death Communication (IADC) therapy is a brief intervention facilitating grief resolution through a perceived experience of communication with the deceased. Despite growing evidence of its efficacy, little is known about which individual characteristics may influence treatment responsiveness. (2) Methods: This
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: Induced After-Death Communication (IADC) therapy is a brief intervention facilitating grief resolution through a perceived experience of communication with the deceased. Despite growing evidence of its efficacy, little is known about which individual characteristics may influence treatment responsiveness. (2) Methods: This pre–post study investigated psychological predictors of IADC outcomes in 73 bereaved adults. Standardized measures assessed grief severity, alexithymia, dissociation, attachment dimensions, and Big Five personality traits. Changes in grief-related distress and continuing bonds were analyzed using paired-sample t-tests and hierarchical regressions. (3) Results: IADC therapy produced substantial reductions in grief-related distress and enhanced continuing bonds. Dissociation, demographic variables, and most personality traits were unrelated to outcomes. Neuroticism showed a marginally negative association, whereas Openness predicted greater improvement. Alexithymia negatively predicted clinical gains, suggesting that limited emotional awareness may interfere with the therapeutic phase of abreaction and, in turn, limit access to the receptive state. Among attachment dimensions, only Need for Approval significantly predicted poorer outcomes, consistent with performance anxiety and self-evaluative control interfering with spontaneous mental processes. (4) Conclusions: IADC therapy appears highly effective across diverse individual profiles. Screening for alexithymia and Need for Approval may help identify these potential sources of therapeutic failure and be followed by targeted strategies aimed at counteracting their impact and mitigating their effects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Neuropsychology, Clinical Psychology, and Mental Health)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Bienvivance Approach, Emotional Capital and Capacitating Pedagogy: Inner Resource Development for Outer Transformations
by
Bénédicte Gendron
Psychol. Int. 2026, 8(1), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint8010013 - 13 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The present article explores how the development of inner resources can serve as a decisive lever to initiate and sustain individual, organizational, and societal transformations. (1) We first examine the concept of emotional capital, understood as the ability to mobilize emotional competencies defined
[...] Read more.
The present article explores how the development of inner resources can serve as a decisive lever to initiate and sustain individual, organizational, and societal transformations. (1) We first examine the concept of emotional capital, understood as the ability to mobilize emotional competencies defined by models of emotional intelligence, a capital that boosts other forms of capital and enables transformation. (2) We then link this to a capacitating approach, grounded in the work of Sen, which focuses on valuing and expanding human potential. (3) We will introduce the paradigm of bienvivance as an economic and social perspective that ensures a better way of co-vivance, a bienvivance economy; a societal model which proposes to reorient our systems toward a collective dynamic of vitality and meaning, shared living, sustainability, and regeneration. Taken together, these three dimensions pave the way for transformations that connect inner growth with outer change, across educational, organizational, and societal practices. In this article, (4) we will illustrate such a bienvivance approach focused on capacitating pedagogy and emotional capital development via collaborative learning and co-construction of competencies’ student portfolio exercises, as an intrinsic part of development of learners’ lifelong competencies and a lever of potentials’ unlocking, and recognition’s decolonization.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Associations Between Explicit and Implicit Self-Esteem and Attachment in Singles and Partnered Adults
by
Liselotte Visser, Johan Lataster, Ron Pat-El, Jacques Van Lankveld and Nele Jacobs
Psychol. Int. 2026, 8(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint8010012 - 6 Feb 2026
Abstract
Self-esteem and attachment are core constructs in adult relational functioning, yet their interrelations across levels of cognitive processing have remained understudied. This study investigated how explicit and implicit attachment styles relate to self-esteem in individuals seeking a romantic partner (N = 399)
[...] Read more.
Self-esteem and attachment are core constructs in adult relational functioning, yet their interrelations across levels of cognitive processing have remained understudied. This study investigated how explicit and implicit attachment styles relate to self-esteem in individuals seeking a romantic partner (N = 399) and in a partnered sample (N = 108). Participants completed explicit attachment and self-esteem scales, along with three single-target Implicit Association Tests (IATs) assessing implicit self-esteem and avoidant and anxious attachment styles. Regression analyses were conducted using explicit and implicit attachment as predictors of explicit and implicit self-esteem while controlling for covariates. In singles, explicit anxious attachment was negatively associated with explicit self-esteem, while implicit anxious attachment and implicit avoidant attachment were negatively associated with implicit self-esteem. No cross-level associations were found, supporting a parallel-level interpretation in which explicit and implicit variables relate primarily within, rather than across, processing levels. The same regression models applied to the partnered sample showed generally similar trends, although the associations observed in singles for explicit anxious and implicit avoidant attachment were not detected in the partnered group. The inclusion of implicit measures provides new insight into non-conscious relational insecurity, with both implicit anxious and avoidant attachment showing negative associations with implicit self-esteem.
Full article
Open AccessReview
The Psychology of Working Students: A Scoping Review
by
Gaetana di Biase and Davide Giusino
Psychol. Int. 2026, 8(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint8010011 - 6 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Student employment is an increasingly common feature of higher education, yet psychological research on students who combine paid work and study remains conceptually and methodologically fragmented. This scoping review mapped the extent, range, and nature of empirical evidence on working students’ psychological experiences,
[...] Read more.
Student employment is an increasingly common feature of higher education, yet psychological research on students who combine paid work and study remains conceptually and methodologically fragmented. This scoping review mapped the extent, range, and nature of empirical evidence on working students’ psychological experiences, summarized key psychosocial correlates, and identified gaps for future research. Consistent with PRISMA-ScR guidance, we searched EBSCOhost, Scopus, and Web of Science using tailored Boolean title-field strategies without year limits, screened records against eligibility criteria, and charted and thematically synthesized extracted data. Forty-two peer-reviewed English-language studies were included. Evidence clustered into six recurrent domains, such as work–study interface processes, resources and supports, health, stress and recovery, academic engagement and performance, career development and employability, and identity and social relations. The literature was predominantly quantitative and cross-sectional, with comparatively few intervention studies. Findings suggest that psychological outcomes are frequently examined through, and may be more closely contingent on, the quality of the work–study interface and contextual supports than on employment intensity alone, highlighting the potential value of interventions and institutional/employer practices that enhance role fit, flexibility, and supportive climates, alongside more longitudinal and multi-level research.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Teaching with Purpose: Changes in Motivational Competences Following a Guided Introspective Intervention
by
Irene Díaz-Portales, Patricia Catalá, Sergio Jesús González Castilla, José San Martín López, María Zapata-Cáceres and Cecilia Peñacoba Puente
Psychol. Int. 2026, 8(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint8010010 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
This study examines changes associated with a guided introspective intervention in self-reflection, introspection, and motivational competences among future teachers. Conducted within a Master’s course in Teacher Training, the ten-session program employed the “Casa Vital” framework, a metaphorical and visual model representing personal and
[...] Read more.
This study examines changes associated with a guided introspective intervention in self-reflection, introspection, and motivational competences among future teachers. Conducted within a Master’s course in Teacher Training, the ten-session program employed the “Casa Vital” framework, a metaphorical and visual model representing personal and professional development through structured introspective exercises. Eighty-two participants completed the Self-Reflection and Insight Scale (SRIS-SF) and selected subscales of the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire (MSLQ) in a pre–post quasi-experimental design. Findings reveal significant increases in introspection, intrinsic goal orientation, control of learning beliefs, and self-efficacy for learning and performance (small–moderate effects), while self-reflection, extrinsic goal orientation and task value remained stable. These results suggest that guided introspection enhances motivational competences by promoting self-awareness, value clarification, and alignment of personal and professional goals. The intervention also seems to support autonomy-oriented engagement and purpose-driven decision-making, contributing to the development of reflective and resilient educators. Integrating structured introspective practices into teacher education may strengthen professional identity, psychological flexibility, and internal-driven motivation. The study underscores the practical potential of reflective frameworks such as Casa Vital to foster meaningful, self-determined, and adaptive teaching practices, offering an accessible and scalable approach for enhancing teacher preparation programs. Within the limits of a single-group pre–post design, these findings provide descriptive, theory-consistent indications that introspection may be associated with the cultivation of purposeful, motivated, and competent educators.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Targeting Stress Mindset and Irrational Beliefs to Improve Performance and Reduce Anxiety and Depression Symptoms in Academy Athletes
by
Paul Mansell, Katie Clark, Jordan Brookes, Jason Wright, Samuel Westley, Katherine Sparks and Matthew Slater
Psychol. Int. 2026, 8(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint8010009 - 4 Feb 2026
Abstract
This study aimed to investigate whether a multimodal cognitive behavioural intervention could enhance academy athletes’ stress mindset, self-compassion, and performance, as well as reduce irrational beliefs and symptoms of anxiety and depression. We delivered 6 × 1 h group workshops at five different
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to investigate whether a multimodal cognitive behavioural intervention could enhance academy athletes’ stress mindset, self-compassion, and performance, as well as reduce irrational beliefs and symptoms of anxiety and depression. We delivered 6 × 1 h group workshops at five different football (n = 4) and rugby (n = 1) academies in the United Kingdom. We hypothesised that there would be increases in stress mindset, self-compassion, and perceived performance coupled with decreases in irrational beliefs, anxiety, and depressive symptoms as a result of the intervention, and that such changes would remain evident one month later. Sixty-seven participants (n = 59 males, n = 8 females, Mage = 17.03 years, SD = 2.55) completed assessment at baseline, post-intervention, and at a follow-up. Through paired-sample t-tests, our results demonstrated support for the hypotheses with principally small effect sizes. Findings offer support for the use of a multimodal cognitive behavioural programme in academy athletes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Psychology of Peak Performance in Sport)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessEssay
A Note on Using Scale Sum Scores in Path Analysis
by
Alexander Robitzsch
Psychol. Int. 2026, 8(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint8010008 - 23 Jan 2026
Abstract
Sum scores are widely used in the social sciences, yet their appropriateness remains a topic of considerable debate in the psychometric literature. A recent article by Raykov and Zhang (2025, Struct. Equ. Model.) has cautioned against employing sum scores as predictor variables
[...] Read more.
Sum scores are widely used in the social sciences, yet their appropriateness remains a topic of considerable debate in the psychometric literature. A recent article by Raykov and Zhang (2025, Struct. Equ. Model.) has cautioned against employing sum scores as predictor variables in subsequent analyses, as this practice may lead to biased estimates of regression coefficients. As an alternative, structural equation modeling (SEM) based on a unidimensional factor model—where the latent factor replaces the sum score—has been advocated. The present article argues that reliability adjustments can also be implemented without resorting to SEM, using reliability-corrected regression models designed for measurement error correction. Furthermore, it is demonstrated that the SEM approach becomes inferior to measurement error correction methods when the assumption of a unidimensional measurement model is violated or when design-based reliability indices, such as Cronbach’s alpha, are preferred over model-based alternatives like McDonald’s omega. The article concludes that a fully integrated SEM approach, combining both measurement and structural components, is advantageous over measurement error correction approaches with reliability adjustment only under specific and limited conditions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Psychometrics and Educational Measurement)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cognitively Processing Covert Aggression from a Target’s Perspective
by
Stace Kent, Peter J. Jordan and Ashlea C. Troth
Psychol. Int. 2026, 8(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint8010007 - 21 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This article sets out to investigate how individuals process their experiences of covert aggression in their workplace. Covert aggression is operationalized within this article as behaviors that are subversive, mal-intended behaviors which attempt to undermine an individual’s confidence within the social milieu of
[...] Read more.
This article sets out to investigate how individuals process their experiences of covert aggression in their workplace. Covert aggression is operationalized within this article as behaviors that are subversive, mal-intended behaviors which attempt to undermine an individual’s confidence within the social milieu of their workplace and their capabilities and knowledge within the context of their job role. Using the critical incident technique embedded in a semi-structured interview format, the findings pointed to the targets of covert aggression undergoing a process of realizing they are experiencing covert aggression, sensemaking of why this is happening to them, self-monitoring their behaviors and responses around the aggressor, and creating scripts as a way to manage their working relationship with their aggressor. This cognitive process that we unveil in this article establishes a baseline for further investigations into the experiences of being targeted by covert aggression.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Emotional Congruence in Childhood: The Influence of Music and Color on Cognitive Processing
by
Aurélie Simoës-Perlant, Sarah Benintendi-Medjaoued and Camille Gramaje
Psychol. Int. 2026, 8(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint8010006 - 15 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Emotions are known to influence cognitive processes, yet the nature of this influence remains debated, particularly during childhood. According to the emotional congruence model, information congruent with an individual’s affective state is processed more efficiently than incongruent information. While this effect has been
[...] Read more.
Emotions are known to influence cognitive processes, yet the nature of this influence remains debated, particularly during childhood. According to the emotional congruence model, information congruent with an individual’s affective state is processed more efficiently than incongruent information. While this effect has been widely studied in adults, evidence in children is still limited. The present research investigates the influence of emotional congruence on selective attention in typically developing children from preschool to fifth grade, using a dual emotional induction paradigm based on music and color. In Study 1, classical music excerpts were used to induce pleasant or unpleasant emotional states and to validate the effectiveness of musical induction across age groups. In Study 2, this musical induction was combined with emotionally valenced color cues (yellow vs. gray) embedded in a visual search task to examine their impact on attentional performance. Results from Study 1 confirmed that music effectively modulated children’s emotional valence, although this effect was weaker in younger participants. In Study 2, attentional performance improved significantly when the task was presented on a yellow background, regardless of the valence of the previously induced musical emotion. No robust emotional congruence effect between music and color was observed, although performance was highest in the joyful music–yellow color condition. Overall, these findings suggest that perceptual emotional cues embedded in the task context, particularly positive color cues, exert a stronger and more persistent influence on children’s selective attention than transient affective states induced by music. This study contributes to developmental models of emotion–cognition interaction by highlighting asymmetrical valence effects and the predominant role of perceptual emotional signals in childhood attention.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Expecting Less and Getting It: The Role of Rejection Sensitivity in Feedback-Seeking and Supervisory Relationships
by
Emily Bosk, Alicia Mendez, Tareq Hardan, Abigail Williams-Butler, Thomas Mackie and Michael MacKenzie
Psychol. Int. 2026, 8(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint8010005 - 9 Jan 2026
Abstract
While there is extensive literature on the strengths of different supervisory models, we have limited understanding of how the relational capacity of front-line staff may impact how they receive and seek feedback from their supervisor. This study examines how mental health providers’ and
[...] Read more.
While there is extensive literature on the strengths of different supervisory models, we have limited understanding of how the relational capacity of front-line staff may impact how they receive and seek feedback from their supervisor. This study examines how mental health providers’ and front-line staff’s own rejection sensitivity may be associated with the supervisory relationship and the ways in which job feedback is sought and received in community-based mental health settings. Cross-sectional survey data were collected from 156 front-line staff of three mental health agencies. Staff were administered an original survey using validated measures related to supervision, feedback, and relational capacities. We found staff with a higher rejection sensitivity (RS) were less likely to actively seek feedback about their performance; and, when feedback was received, were more likely to rate its quality as poor. Staff with a higher RS were more likely to perceive their supervisor and their relationship negatively. This is the first study to examine whether workers’ relational capacities, as expressed through a higher RS, influence their perceptions of supervision and quality of feedback and their feedback-seeking behaviors. These findings build theory related to the important role that staff relational capacities play in influencing organizational dynamics and support.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Self-Esteem and Eating Attitudes in Emerging Adulthood: The Mediating Role of Social Physique Anxiety and the Moderating Role of Gender
by
Chrysi Mouatsou and Katerina Koutra
Psychol. Int. 2026, 8(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint8010004 - 9 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Emerging adulthood is a critical time for the development of disordered eating attitudes. Low self-esteem is a known risk factor for unhealthy eating attitudes, but the mechanisms behind this link are not fully understood. This study examined the relationship between self-esteem and eating
[...] Read more.
Emerging adulthood is a critical time for the development of disordered eating attitudes. Low self-esteem is a known risk factor for unhealthy eating attitudes, but the mechanisms behind this link are not fully understood. This study examined the relationship between self-esteem and eating attitudes in emerging adults, focusing on the mediating role of social physique anxiety and the moderating role of gender. The sample included 495 university students (68.9% women, mean age = 20.94 years, SD = 1.97). Self-esteem, social physique anxiety, and eating attitudes were assessed using the Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale, Social Physique Anxiety Scale, and Eating Attitudes Test-26, respectively. Mediation and moderation mediation analyses were conducted using PROCESS macro. Women reported lower self-esteem, higher levels of social physique anxiety, and more frequent disordered eating behaviors. Mediation analysis indicated that social physique anxiety fully mediated the relationship between self-esteem and eating attitudes (path c’: b = 0.05, 95% CI [−0.12, 0.21]; indirect effect: b = −0.44, 95% CI [−0.57, −0.32]). Moderated mediation revealed that the indirect effect of low self-esteem on maladaptive eating attitudes through social physique anxiety was stronger among women (index of moderated mediation: b = 0.28, 95% CI [0.07, 0.51]). These findings indicate that low self-esteem can heighten body-related distress in social settings, increasing vulnerability to disordered eating, especially among women. By providing a better understanding of the mechanisms linking self-esteem and eating attitudes in emerging adults, the findings can inform the development of interventions targeting self-perception and body-related concerns, especially among women, to reduce the risk of eating disorders and promote healthier eating attitudes.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Digital Coercive Control, Institutional Trust, and Help-Seeking Among Women Experiencing Violence: Evidence from Greece and the UK
by
Stefanos Balaskas and Ioanna Yfantidou
Psychol. Int. 2026, 8(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint8010003 - 8 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Violence against women remains prevalent, yet many survivors do not engage with services even where health infrastructure exists. This study investigated the role of institution-facing resources, Institutional Trust (ITR) and Procedural Justice (PJ), and the role of interpersonal resources, Social Support Provided (SSP),
[...] Read more.
Violence against women remains prevalent, yet many survivors do not engage with services even where health infrastructure exists. This study investigated the role of institution-facing resources, Institutional Trust (ITR) and Procedural Justice (PJ), and the role of interpersonal resources, Social Support Provided (SSP), in women’s formal care-seeking intentions, as mediated by Psychological Distress (PSS) and General Self-Efficacy (GSE). An online survey was administered to women in Greece (n = 392) and the United Kingdom (n = 328), yielding a sample of 718. To compare the structural paths in the model across the two countries, measurement invariance was first explored, while the model was estimated through multi-group structural equation modeling. Across the pooled sample, PJ and GSE predicted HSB firmly, while ITR had no direct link to the construct. SSP did not directly predict HSB, but was linked to GSE in all models. The results of the interaction and group-difference models showed PJ and SSP had a slight indirect effect through GSE, while distress-based pathways were weaker and context-dependent. Multi-group models revealed significant cross-national differences: the direct effect of ITR and PSS on GSE was stronger in the United Kingdom than in Greece. The direct effect of PJ/GSE and SSP/GSE also had a stronger impact in Greece than in the United Kingdom. Overall, the results indicate that the willingness of women to seek help is less driven by their trust in institutions and more driven by their expectations of fairness in provider interaction and their perceived personal capability, where social support plays a role as the antecedent increasing women’s Perceived Self-Efficacy. The implications include prioritizing procedurally just practices, designing interventions that enhance self-efficacy for system navigation, and mobilizing informal networks as partners in the help-seeking process.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Startle Habituation and Vagally Mediated Heart Rate Variability Influence the Use of Emotion Regulation Strategies
by
Xiao Yang, Fang Fang and Angela Ximena Babb
Psychol. Int. 2026, 8(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint8010002 - 7 Jan 2026
Abstract
Emotion regulation refers to the processes through which people modulate their emotional experiences and expressions, and difficulties in these processes underpin many forms of psychopathology. According to the process model, emotion regulation encompasses five classes of strategies, commonly grouped into antecedent-focused strategies (e.g.,
[...] Read more.
Emotion regulation refers to the processes through which people modulate their emotional experiences and expressions, and difficulties in these processes underpin many forms of psychopathology. According to the process model, emotion regulation encompasses five classes of strategies, commonly grouped into antecedent-focused strategies (e.g., cognitive reappraisal) and response-focused strategies (e.g., expressive suppression). These strategies involve both explicit and implicit processes, which can be objectively assessed using physiological indices. The present study examined the effects of startle habituation and vagally mediated heart rate variability (vmHRV) on the use of cognitive appraisal and suppression. Forty-nine college-aged participants were recruited, and their resting heart rate variability (HRV) and response habituation to an auditory startle-eliciting stimulus were measured. Emotion regulation strategies were assessed by a self-report questionnaire. Multiple regressions were used to analyze the effects of startle habituation, vmHRV, and their interaction on emotion regulation strategies. Results indicated that, although suppression was not associated with any physiological indices in the regression models, cognitive reappraisal was predicted by both vmHRV and startle habituation. Notably, vmHRV and startle habituation interacted such that the positive association between vmHRV and cognitive reappraisal emerged only among individuals who exhibited slow startle habituation. These findings have practical implications for the prevention and treatment of psychopathology, as well as for promoting more adaptive emotion regulation in daily life.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Neuropsychology, Clinical Psychology, and Mental Health)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of LSD and Psilocybin on Heart Rate in Patients Receiving Psychedelic Treatment for Depressive and Anxiety Disorders: A Retrospective Observational Study
by
Mylène Cheng, Tatiana Aboulafia-Brakha, Albert Buchard, Raya Boyanova Anastasova, Lea Girani, Anna Breitenmoser, Sylvie Alaux, Cedric Mabilais, Caroline Amberger, Federico Seragnoli, Leonice Furtado, Gabriel Thorens, Daniele Zullino and Louise Penzenstadler
Psychol. Int. 2026, 8(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint8010001 - 19 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Classic psychedelics such as lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) and psilocybin induce mild cardiovascular activation in addition to their psychological effects. While these effects are well described in healthy adults, little is known about their dynamics in clinical populations undergoing psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy. This retrospective,
[...] Read more.
Classic psychedelics such as lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) and psilocybin induce mild cardiovascular activation in addition to their psychological effects. While these effects are well described in healthy adults, little is known about their dynamics in clinical populations undergoing psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy. This retrospective, observational, single-center study analyzed routinely collected data from 30 patients (mean age = 51.56 ± 12.19 years; 15/30 female) treated under compassionate use for treatment-resistant depression or anxiety disorders. Participants received either LSD (100–200 mcg) or psilocybin (15–30 mg) in supervised outpatient sessions. Heart rate and self-rated anxiety (VAS 0–100) were recorded at seven intervals from 30 to 300 min post-administration. Linear mixed models examined heart rate trajectories over time × substance, controlling for age and, in a second model, perceived anxiety. Linear mixed models revealed no significant main effect of time (F(6, 77.25) = 0.76, p = 0.60) or substance (F(1, 30.82) = 0.66, p = 0.42), but a significant time × substance interaction (F(6, 77.25) = 3.03, p = 0.01). LSD was associated with a delayed but sustained increase in heart rate peaking at 3–4 h, whereas psilocybin showed an earlier decline. These patterns persisted after adjustment for age and anxiety, and anxiety did not significantly modify the relationship between time and substance. No serious cardiovascular adverse events occurred. These preliminary findings suggest that LSD and psilocybin may produce distinct temporal patterns of cardiovascular activation in clinical settings. However, interpretation should be cautious due to the retrospective design, small sample size, and dose imbalance between substances.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
During the COVID-19 Pandemic, the Gap in Career Awareness Between Urban and Rural Students Widened
by
Keisuke Kokubun
Psychol. Int. 2025, 7(4), 103; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint7040103 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
Numerous studies have examined the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on university students’ attitudes. However, little is known about how their career awareness changed and how such changes differed between urban and rural areas. This study analyzed psychological data collected through a questionnaire
[...] Read more.
Numerous studies have examined the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on university students’ attitudes. However, little is known about how their career awareness changed and how such changes differed between urban and rural areas. This study analyzed psychological data collected through a questionnaire survey conducted from 9 November 2020, to 19 January 2021, among 516 first- to fourth-year students enrolled in social science faculties in Japan. The analysis compared changes in career awareness by university location. The results indicated that, during the pandemic, urban students placed greater emphasis on self-worth, while rural students placed greater emphasis on working conditions, suggesting a possible widening gap between the two groups. Furthermore, logistic multiple regression and path analyses revealed that, among rural students, greater concern for working conditions was associated with a stronger focus on interpersonal relationships, which in turn enhanced their preference for local employment. In addition, valuing interpersonal relationships was linked to a stronger focus on social recognition, which may foster more intrinsic aspects of career awareness.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Neuropsychology, Clinical Psychology, and Mental Health)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Drinking Motives, Mental Health, and Adolescent Alcohol Use Among Croatian Adolescents
by
Roberta Matković and Josipa Glavaš
Psychol. Int. 2025, 7(4), 102; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint7040102 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
Adolescence is a critical period during which alcohol is the most commonly used substance worldwide, and such use has detrimental effects on neurobiological, psychosocial, and physiological development. Despite substantial international evidence, little is known about the concurrent influence of drinking motives and internalizing
[...] Read more.
Adolescence is a critical period during which alcohol is the most commonly used substance worldwide, and such use has detrimental effects on neurobiological, psychosocial, and physiological development. Despite substantial international evidence, little is known about the concurrent influence of drinking motives and internalizing symptoms on adolescent alcohol use, particularly in the Croatian context, where adolescent drinking rates remain high. A cross-sectional study using a survey questionnaire was conducted in 2024 in Split-Dalmatia County, Croatia. The final stratified cluster sample comprised 925 students (58.8% of the planned sample), with a mean age of 15.41 years. Using hierarchical regression analysis, the results showed that the final model, which included both drinking motives and mental health indicators, explained 39.6% of the variance in alcohol use, 37.2% of the variance in binge drinking, and 31.8% of the variance in alcohol intoxication. Male sex was consistently associated with all three outcomes, whereas age was positively associated with alcohol use and binge drinking. Drinking motives contributed the largest proportion of the explained variance. Furthermore, lower levels of loneliness and higher levels of anxiety were associated with more frequent alcohol use, while lower stress and higher anxiety were associated with more frequent intoxication. Drinking motives are stronger predictors of adolescent alcohol use and risky drinking patterns than internalizing symptoms whose predictive strength was generally small. Prevention programs should address aspects of drinking motives in addition to promoting mental health.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Perceptions of Interest/Enjoyment, Perceived Competence, and Value/Usefulness Among Young Soccer Players in an 11-Week Soccer Training Program: A Randomized Controlled Trial
by
Knut Skjesol, Svein Olav Ulstad, Arne Sørensen and Pål Lagestad
Psychol. Int. 2025, 7(4), 101; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint7040101 - 17 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: In this study, we aimed to examine the changes in players’ interest/enjoyment, perceived competence, and value/usefulness through an 11-week soccer training program, using a randomized experimental study. Methods: Overall, 175 children aged 9–12 years applied to join the soccer training
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: In this study, we aimed to examine the changes in players’ interest/enjoyment, perceived competence, and value/usefulness through an 11-week soccer training program, using a randomized experimental study. Methods: Overall, 175 children aged 9–12 years applied to join the soccer training program at a free soccer school. Of the 175 applicants, 100 were randomly chosen to participate in the soccer training program in the intervention group (IG), whereas the other 75 children were in the control group (CG). Both groups completed a questionnaire with validated items related to interest/enjoyment, perceived competence, and value/usefulness before (pre-test) and after (post-test) the soccer training program. Results: The main finding was that participation in the 11-session soccer training program did not affect the children’s perceived competence, interest/enjoyment, or value/usefulness in a positive or negative direction compared to the CG. Another main finding was a significant decrease in interest/enjoyment from pre-test to post-test in both the control group and the intervention group. Also, the control group had higher values of perceived competence than the intervention group at both pre-test and post-test. However, the effect sizes are very small in both groups, and the practical relevance is small. Conclusions: This study demonstrated that participation at the 11-session soccer training program did not affect the children’s perceived competence, interest/enjoyment, and value/usefulness in a positive or negative direction compared to the CG. Future studies should include longer intervention periods with more weekly and overall training sessions.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Online Group-Based Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) for Stroke Survivors: A Study of Fidelity of Delivery Within the Wellbeing After Stroke (WAterS) Study
by
Hannah Foote, Audrey Bowen, Sarah Cotterill and Emma Patchwood
Psychol. Int. 2025, 7(4), 100; https://doi.org/10.3390/psycholint7040100 - 17 Dec 2025
Abstract
Stroke survivors often experience psychological difficulties, yet specialist provision is limited. The Wellbeing After Stroke (WAterS) study co-developed a nine-week, online Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) group programme designed to be delivered by non-specialist practitioners using structured, script-informed session clinical protocols. This study
[...] Read more.
Stroke survivors often experience psychological difficulties, yet specialist provision is limited. The Wellbeing After Stroke (WAterS) study co-developed a nine-week, online Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) group programme designed to be delivered by non-specialist practitioners using structured, script-informed session clinical protocols. This study explored whether fidelity of delivery could be assessed, both to the clinical protocol (what was delivered) and to ACT therapeutic processes (how it was delivered). Eight practitioners were trained, and four delivered the intervention to three groups of four stroke survivors. Fidelity was assessed using a bespoke WAterS checklist, completed by practitioners after each session, and the ACT-Fidelity Measure (ACT-FM), completed by researchers rating a sub-set of recorded sessions. Practitioners delivered 92–100% of planned content, indicating high fidelity to protocol. ACT-FM ratings suggested some consistency with ACT processes, though there was variability across practitioners. These findings provide preliminary, proof-of-principle evidence that non-specialists can deliver a structured ACT-based group intervention with fidelity to protocol, and that both self-completed and observer-rated methods can feasibly assess fidelity. However, the small sample size means these results should be considered exploratory. The study highlights the potential value of these methods for informing training and fidelity assessment in future research.
Full article
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
IJERPH, Behavioral Sciences, Sexes, Social Sciences, Psychology International
Social, Structural and Behavioral Interventions for HIV Prevention
Topic Editors: Greg Rebchook, Susan Kegeles, Sophia Zamudio-HaasDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topic in
Social Sciences, Societies, Laws, World, Psychology International, IJCS
Motivated Social Cognition in Individuals, Organizations, and Societies
Topic Editors: Andrew S. Franks, Hajime OtaniDeadline: 31 October 2027
Topic in
Social Sciences, Societies, Psychology International
Parent–Child Bonds and the Psychology of Development
Topic Editors: Renata Tambelli, Francesca FavieriDeadline: 30 November 2027

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Psychology International
Digitally Assisted Interventions in Special Education for Promoting Psychological Health, and Well-Being
Guest Editor: Eleni MitseaDeadline: 30 June 2026
Special Issue in
Psychology International
Psychology and the Olympic Games
Guest Editors: Antonio Hernández-Mendo, Verónica Morales-Sánchez, Rafael Enrique Reigal Garrido, Regina Brandao, Sidonio SerpaDeadline: 30 June 2026
Special Issue in
Psychology International
The Psychology of Peak Performance in Sport
Guest Editors: Yair Galily, Gershon TenenbaumDeadline: 31 December 2026