Plant Latex Proteases in Hemostasis: Beyond Thrombin-like Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
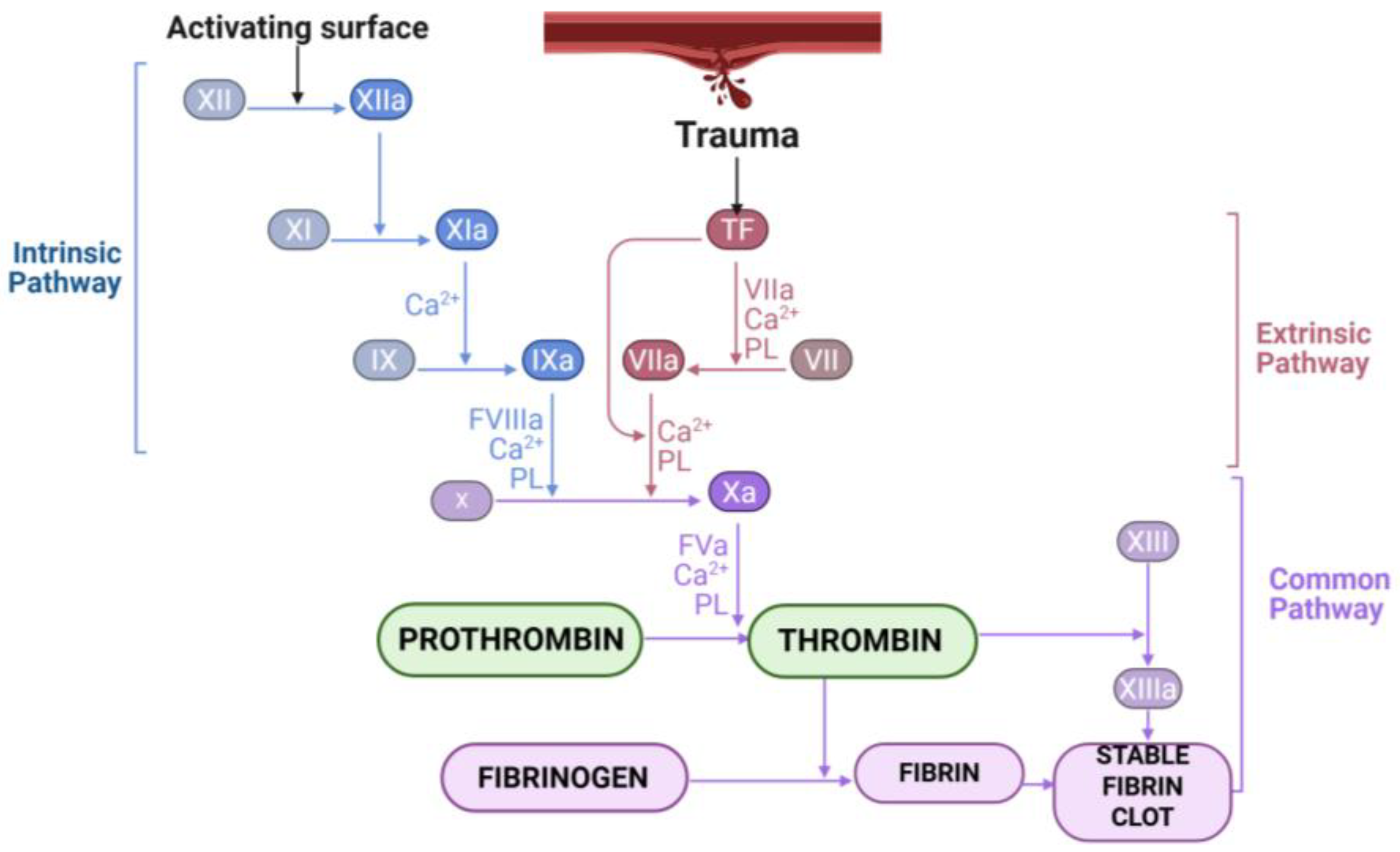
2. Overview of the Blood Coagulation Cascade
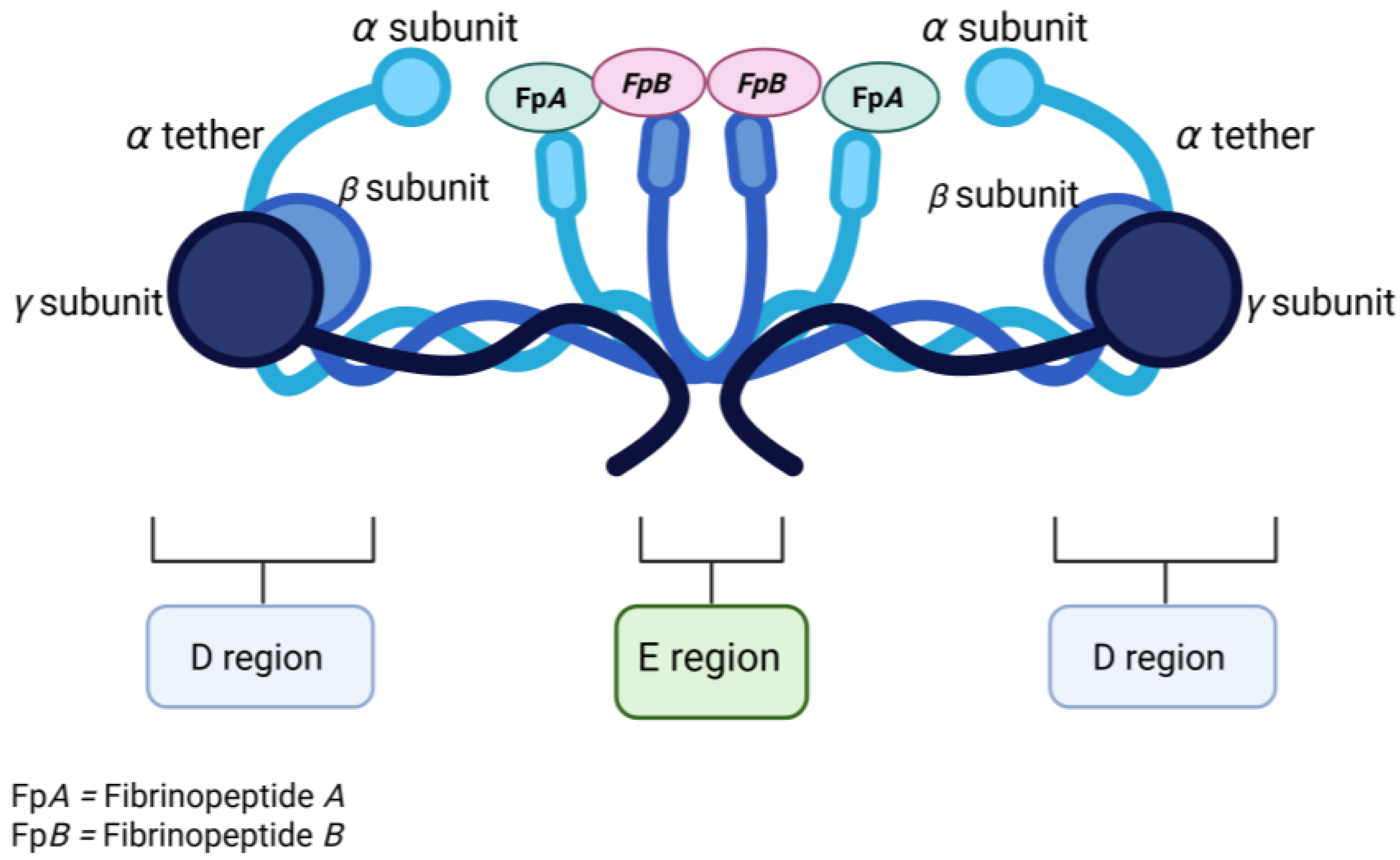
2.1. Thrombin and Fibrinogen
2.2. Role of Thrombin in Fibrinogen–Fibrin Transformation
3. Exogenous Hemostatic Factors
4. Thrombin-like Enzymes
Thrombin-like Enzymes Structural Properties
5. Plant Latex Proteases
5.1. Latex Proteases: Hemostatic Activities and Analysis
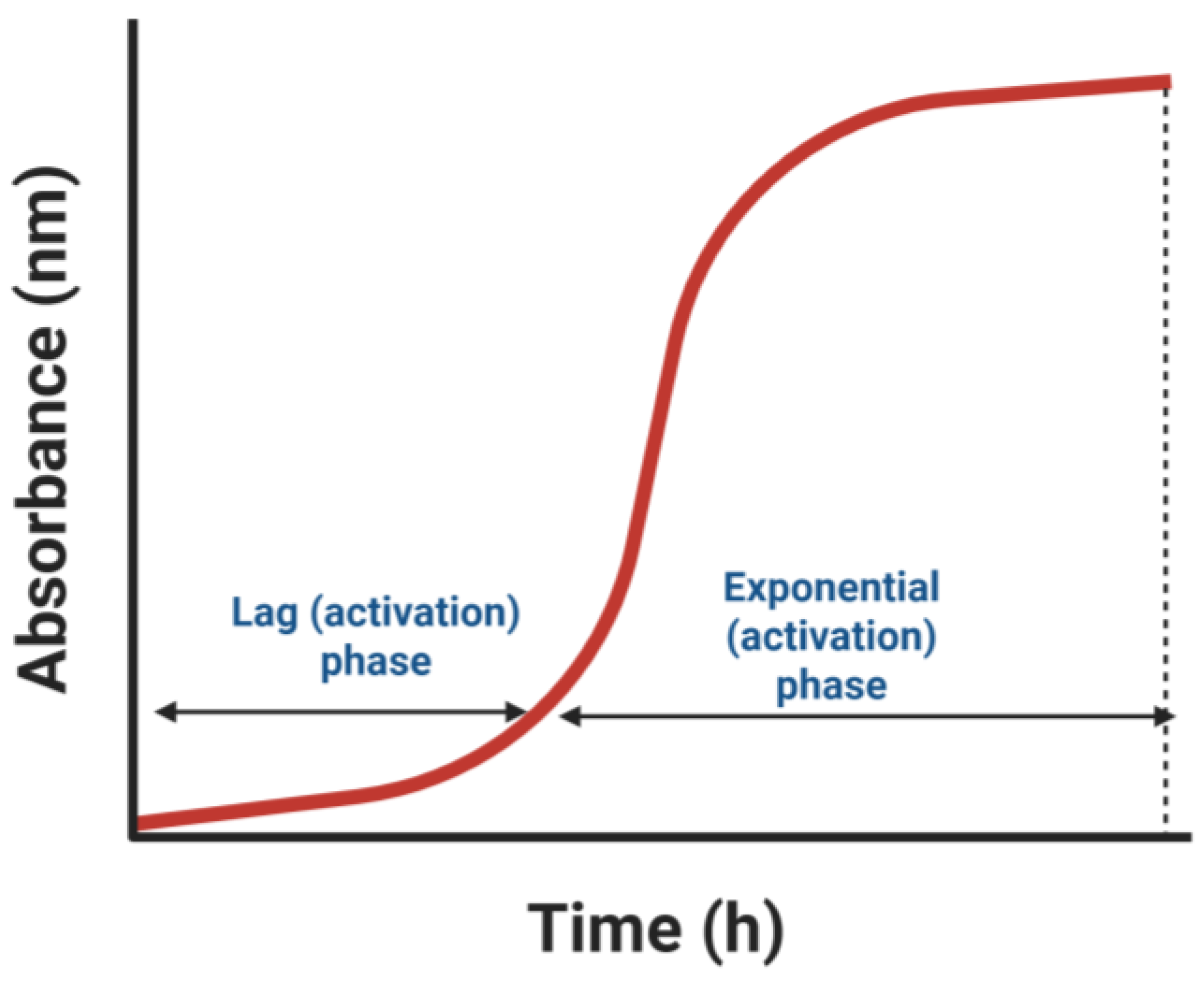
5.1.1. In Vitro Hemostatic Assays
5.1.2. Electrophoretic Analysis and Fibrinogenolytic Activity
6. Thrombin-like Activity of Plant Latex
7. Beyond Thrombin-like Activity: Multifunctionality in Plant Latex
8. Future Perspective and Research Opportunities
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bordoloi, C.; Kumar, S.; Barbhuiya, A.M.; Kushari, S.; Kalita, J.M.; Sahu, B.P.; Laloo, D. Herbal Medicine Used for Wound Healing by the Tribes of the North Eastern States of India: A Comprehensive Review. J. Herb. Med. 2023, 41, 100697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urs, A.P.; Manjuprasanna, V.N.; Rudresha, G.V.; Hiremath, V.; Sharanappa, P.; Rajaiah, R.; Vishwanath, B.S. Molecular Cell Research Thrombin-like Serine Protease, Antiquorin from Euphorbia Antiquorum Latex Induces Platelet Aggregation via PAR1-Akt/P38 Signaling Axis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2021, 1868, 118925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusuma, C.G.; Gubbiveeranna, V.; Sumachirayu, C.K.; Bhavana, S.; Ravikumar, H.; Nagaraju, S. Thrombin- and Plasmin-like and Platelet-Aggregation-Inducing Activities of Plumeria alba L. Latex: Action of Cysteine Protease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 273, 114000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaprasad, H.V.; Rajesh, R.; Nanda, B.L.; Dharmappa, K.K.; Vishwanath, B.S. Thrombin like Activity of Asclepias curassavica L. Latex: Action of Cysteine Proteases. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 123, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seon, G.M.; Lee, M.H.; Kwon, B.-J.; Kim, M.S.; Koo, M.-A.; Kim, D.; Seomun, Y.; Kim, J.-T.; Park, J.-C. Functional Improvement of Hemostatic Dressing by Addition of Recombinant Batroxobin. Acta Biomater. 2017, 48, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D. Hematology Products from Snake Venoms. Thromb. Res. 2025, 245, 109215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Masood, R.; Ali, I.; Ullah, K.; Ali, H.; Akbar, H.; Betzel, C. Thrombin-like Enzymes from Snake Venom: Structural Characterization and Mechanism of Action. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 788–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.D.; Stack, S.; Markl, F.S. Thrombin-like serine proteinases in reptile venoms. In Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 351–362. [Google Scholar]
- Vu, T.T.; Stafford, A.R.; Leslie, B.A.; Kim, P.Y.; Fredenburgh, J.C.; Weitz, J.I. Batroxobin Binds Fibrin with Higher Affinity and Promotes Clot Expansion to a Greater Extent than Thrombin*. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 16862–16871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, G.W. Snake Venoms in Diagnostic Hemostasis and Thrombosis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2021, 48, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivaprasad, H.V.; Rajaiah, R.; Frey, B.M.; Frey, F.J.; Vishwanath, B.S. ‘Pergularain e I’—A Plant Cysteine Protease with Thrombin-like Activity from Pergularia Extensa Latex. Thromb. Res. 2010, 125, e100–e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivaprasad, H.V.; Riyaz, M.; Venkatesh Kumar, R.; Dharmappa, K.K.; Tarannum, S.; Siddesha, J.M.; Rajesh, R.; Vishwanath, B.S. Cysteine Proteases from the Asclepiadaceae Plants Latex Exhibited Thrombin and Plasmin like Activities. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2009, 28, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, M.B.; El-Badry, M.O.; Kandil, E.I.; Borai, I.H.; Fahmy, A.S. A Contradictory Action of Procoagulant Ficin by a Fibrinolytic Serine Protease from Egyptian Ficus Carica Latex. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 27, e00492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osoniyi, O.; Onajobi, F. Coagulant and Anticoagulant Activities in Jatropha Curcas Latex. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 89, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macfarlane, R.G. An Enzyme Cascade in the Blood Clotting Mechanism, and Its Function as a Biochemical Amplifier. Nature 1964, 202, 498–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrier, C.; Shima, M.; Hoffman, M.; Pradel, L. Blood Reviews The Central Role of Thrombin in Bleeding Disorders. Blood Rev. 2019, 38, 100582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, M.; Monroe, D.M., III. A Cell-Based Model of Hemostasis. Thromb. Haemost. 2001, 85, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, D.M.; Hoffman, M. What Does It Take to Make the Perfect Clot? Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, J.T.B.; Zanardelli, S.; Chion, C.K.N.K.; Lane, D.A. The Central Role of Thrombin in Hemostasis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinov, R.I.; Pieters, M.; Lange-Loots, Z.D.; Weisel, J.D. Fibrinogen and fibrin. In Macromolecular Protein Complexes III: Structure and Function; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 471–501. [Google Scholar]
- Weisel, J.W.; Litvinov, R.I. Fibrin Formation, Structure and Properties. In Fibrous Proteins: Structures and Mechanisms; Parry, D.A.D., Squire, J.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 405–456. ISBN 9783319496740. [Google Scholar]
- Protopopova, A.D.; Barinov, N.A.; Zavyalova, E.G.; Kopylov, A.M.; Sergienko, V.I. Visualization of Fibrinogen a C Regions and Their Arrangement during Fibrin Network Formation by High-Resolution AFM. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, L.; Huang, L.; Cardinalli, B.; Profumo, A.; Gorkun, O.V.; Lord, S.T. Substitution of the Human AC Region with the Analogous Chicken Domain Generates a Fibrinogen with Severely Impaired Lateral Aggregation: Fibrin Monomers Assemble into Protofibrils but Protofibrils Do Not Assemble into Fibers. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 9066–9075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomback, B. Fibrinogen and Fibrin Transformation. In Fibrinolytics and Antifibrinolytics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1978; pp. 49–79. [Google Scholar]
- Kattula, S.; Byrnes, J.R.; Wolberg, A.S. Fibrinogen and Fibrin in Hemostasis and Thrombosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, e13–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomb, B.; Bark, N. Fibrinopeptides and Fibrin Gel Structure. Biophys. Chem. 2004, 112, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Mochalkin, I.; Doolittle, R.F. A Model of Fibrin Formation Based on Crystal Structures of Fibrinogen and Fibrin Fragments Complexed with Synthetic Peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 14146–14161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornalik, F. Toxins affecting blood coagulation and fibrinolysis. In Handbook of Toxinology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 683–760. [Google Scholar]
- Yeon, B.; Sik, K.; Yong, K.; Joo, H.; Rae, B. Anti-Fibrinolytic Activity of a Metalloprotease Inhibitor from Bumblebee (Bombus ignitus) Venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C 2021, 245, 109042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Gao, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, Y.; Han, Y.; Meng, P.; Chen, W.; Lu, Q. Expression and Purification Expression and Characterization of a Fibrinogenolytic Enzyme from Horse Fly Salivary Gland. Protein Expr. Purif. 2017, 129, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sik, K.; Yeon, B.; Joo, H.; Soo, Y.; Rae, B. Secapin, a Bee Venom Peptide, Exhibits Anti- Fi Brinolytic, Anti-Elastolytic, and Anti-Microbial Activities. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 63, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Kopparapu, N.; Li, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zheng, P.X. Biochemical Characterization of a Novel Fibrinolytic Enzyme from Cordyceps Militaris. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 94, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, D.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yu, X. Fibrinolytic Evaluation of Compounds Isolated from a Marine Fungus Stachybotrys Longispora FG216. Chin. J. Chem. 2016, 34, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anusree, M.; Swapna, K.; Aguilar, C.N.; Sabu, A. Optimization of Process Parameters for the Enhanced Production of Fibrinolytic Enzyme by a Newly Isolated Marine Bacterium. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2020, 11, 100436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzkar, N.; Jahromi, S.T.; Fabio, V. Marine Microbial Fibrinolytic Enzymes: An Overview of Source, Production, Biochemical Properties and Thrombolytic Activity. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjuprasanna, V.N.; Urs, A.P.; Rudresha, G.V.; Milan Gowda, M.D.; Jayachandra, K.; Hiremath, V.; Rajaiah, R.; Vishwanath, B.S. Drupin, a Thrombin-like Protease Prompts Platelet Activation and Aggregation through Protease—Activated Receptors. J. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 122, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uday, P.; Maheshwari, M.; Sharanappa, P.; Nafeesa, Z.; Kameshwar, V.H.; Priya, B.S.; Nanjunda Swamy, S. Exploring Hemostatic and Thrombolytic Potential of Heynein—A Cysteine Protease from Ervatamia Heyneana Latex. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 199, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, E.F.; Flores-Ortiz, R.J.; Alvarenga, V.G.; Eble, J.A. Direct Fibrinolytic Snake Venom Metalloproteinases Affecting Hemostasis: Structural, Biochemical Features and Therapeutic Potential. Toxins 2017, 9, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyama, E.; Takahashi, H. Structures and Functions of Snake Venom Metalloproteinases (SVMP) from Protobothrops Venom Collected in Japan. Molecules 2017, 22, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Fujimura, Y.; Titani, K. Snake Venom Proteases Affecting Hemostasis and Thrombosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1477, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackessy, S. Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, H.C.; Zingali, R.B.; Albuquerque, M.G.; Pujol-Luz, M.; Rodrigues, C.R. Snake Venom Thrombin-like Enzymes: From Reptilase to Now. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradniwat, P.; Rojnuckarin, P. Snake Venom Thrombin-like Enzymes. Toxin Rev. 2014, 33, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, R.M.; Cho, Y.K. Metalloproteases Affecting Blood Coagulation, Fibrinolysis and Platelet Aggregation from Snake Venoms: Definition and Nomenclature of Interaction Sites. Toxins 2016, 8, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, H.C.; Silva, D.M.; Craik, C.; Zingali, R.B. Structural Features of a Snake Venom Thrombin-like Enzyme: Thrombin and Trypsin on a Single Catalytic Platform? Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 2001, 1547, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, D.; Verma, S.K. In Silico Study of Iron, Zinc and Copper Binding Proteins of Pseudomonas syringae pv. lapsa: Emphasis on Secreted Metalloproteins. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Dixit, R.; Pandey, K.C. Cysteine Proteases: Modes of Activation and Future Prospects as Pharmacological Targets. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedstrom, L. Serine Protease Mechanism and Specificity. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4501–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siti-Balqis, Z.; Rosma, A.; Kim-Teck, L.; Ismail, M.N. Artocarpus Altilis Latex Polypeptides: An Insight into Its Fibrino(Geno)Lytic Activity. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.K.; Bindhu, O.S. Plant latex: A rich source of haemostatic proteases. In Herbal Medicine in India; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 143–153. [Google Scholar]
- Siritapetawee, J.; Khunkaewla, P.; Thumanu, K. Chemico-Biological Interactions Roles of a Protease from Euphorbia Resinifera Latex in Human Anticoagulant and Antithrombotic Activities. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 329, 109223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.K.; Rajagopalan, A.; Tanimu, H.; Omana, B. Purification, Characterization and Fibrino (Geno) Lytic Activity of Cysteine Protease from Tabernaemontana Divaricata Latex. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijkriengkraikul, N.; Nuchprayoon, I. Study of Optimum Condition for Rapid Preparation of Thrombin Using Russell’s Viper Venom Factor X Activator. Open Biotechnol. J. 2018, 12, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momot, A.P. The Dynamics of the Hemostatic Parameters in Physiological Pregnancy and After Delivery. Hematol. Blood Transfus. Disord. 2016, 3, 10-18411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, W.E.; Flax, S.D.; Harris, N.S. Coagulation Testing in the Core Laboratory. Lab. Med. 2017, 48, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventakesha, S.H.; Rajaiah, R.; Vishwanath, B.S. Hemostatic Interference of Plant Latex. SM J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 1, 1002. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, M.V.; Viana, C.A.; Silva, A.F.B.; Freitas, C.D.T.; Figueiredo, I.S.T.; Oliveira, R.S.B.; Alencar, N.M.N.; Lima-Filho, J.V.M.; Kumar, V.L. Proteins Derived from Latex of C. Procera Maintain Coagulation Homeostasis in Septic Mice and Exhibit Thrombin- and Plasmin-like Activities. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Pharmacol. 2012, 385, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, N.-S.; Kim, S.-H. Two Fibrin Zymography Methods for Analysis of Plasminogen Activators on Gels. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 281, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, B.; Brazón, J. Aqueous Extract from Brownea Grandiceps Flowers with Effect on Coagulation and Fibrinolytic System. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 160, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, I., Jr.; Lazar, I., Sr. Gel Analyzer 23.1.1: Freeware 1D Gel Electrophoresis Image Analysis Software. Available online: http://www.gelanalyzer.com (accessed on 20 February 2021).
- Van Truong, L.; Paulsen, B.S.; Bac, V.H. A Novel Serine Protease from Pseuderanthemum Latifolium B. Hansen: Characterization and Fibrino(Geno)Lytic Activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 2640–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siritapetawee, J.; Teamtisong, K.; Limphirat, W.; Charoenwattanasatien, R.; Attarataya, J.; Mothong, N. Identification and Characterization of a Protease (EuRP-61) from Euphorbia Resinifera Latex. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.C.; Barker, T.H. Fibrin-Based Biomaterials: Modulation of Macroscopic Properties through Rational Design at the Molecular Level. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1502–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denson, K.W.E. Coagulant and Anticoagulant Action of Snake Venoms. Toxicon 1969, 7, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajesh, R.; Shivaprasad, H.V.; Raghavendra Gowda, C.D.; Nataraju, A.; Dhananjaya, B.L.; Vishwanath, B.S. Comparative Study on Plant Latex Proteases and Their Involvement in Hemostasis: A Special Emphasis on Clot Inducing and Dissolving Properties. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doolittle, R.F. Clotting of Mammalian Fibrinogens by Papain: A Re-Examination. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 6687–6694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Litvinov, R.I.; Gorkun, O.V.; Galanakis, D.K.; Yakovlev, S.; Medved, L.; Shuman, H.; Weisel, J.W. Polymerization of Fibrin: Direct Observation and Quantification of Individual B:B Knob-Hole Interactions. Blood 2006, 109, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvinov, R.I.; Yakovlev, S.; Tsurupa, G.; Gorkun, O.V.; Medved, L.; Weisel, J.W. Direct Evidence for Specific Interactions of the Fibrinogen AC-Domains with the Central E Region and with Each Other. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 9133–9142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiti, F.; Calamai, M.; Taddei, N.; Stefani, M.; Ramponi, G.; Dobson, C.M. Studies of the Aggregation of Mutant Proteins in Vitro Provide Insights into the Genetics of Amyloid Diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16419–16426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, C.M. Principles of Protein Folding, Misfolding and Aggregation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 15, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Selvaraja, L.-K.; Zulfigar, S.-B. Plant Latex Proteases in Hemostasis: Beyond Thrombin-like Activity. Appl. Biosci. 2025, 4, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci4030037
Selvaraja L-K, Zulfigar S-B. Plant Latex Proteases in Hemostasis: Beyond Thrombin-like Activity. Applied Biosciences. 2025; 4(3):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci4030037
Chicago/Turabian StyleSelvaraja, Linesh-Kumar, and Siti-Balqis Zulfigar. 2025. "Plant Latex Proteases in Hemostasis: Beyond Thrombin-like Activity" Applied Biosciences 4, no. 3: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci4030037
APA StyleSelvaraja, L.-K., & Zulfigar, S.-B. (2025). Plant Latex Proteases in Hemostasis: Beyond Thrombin-like Activity. Applied Biosciences, 4(3), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci4030037








