Journal Description
Geomatics
Geomatics
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on geomatic science published bimonthly online by MDPI. The Federation of Scientific Associations for Territorial and Environmental Information (ASITA) is affiliated with Geomatics and its members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, EBSCO, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Geography, Physical) / CiteScore - Q1 (Earth and Planetary Sciences (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 22.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Companion journal: Remote Sensing.
- Journal Cluster of Geospatial and Earth Sciences: Remote Sensing, Geosciences, Quaternary, Earth, Geographies, Geomatics and Fossil Studies.
Impact Factor:
2.8 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.5 (2024)
Latest Articles
Analytical Assessment of Pre-Trained Prompt-Based Multimodal Deep Learning Models for UAV-Based Object Detection Supporting Environmental Crimes Monitoring
Geomatics 2026, 6(1), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics6010014 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Illegal dumping poses serious risks to ecosystems and human health, requiring effective and timely monitoring strategies. Advances in uncrewed aerial vehicles (UAVs), photogrammetry, and deep learning (DL) have created new opportunities for detecting and characterizing waste objects over large areas. Within the framework
[...] Read more.
Illegal dumping poses serious risks to ecosystems and human health, requiring effective and timely monitoring strategies. Advances in uncrewed aerial vehicles (UAVs), photogrammetry, and deep learning (DL) have created new opportunities for detecting and characterizing waste objects over large areas. Within the framework of the EMERITUS Project, an EU Horizon Europe initiative supporting the fight against environmental crimes, this study evaluates the performance of pre-trained prompt-based multimodal (PBM) DL models integrated into ArcGIS Pro for object detection and segmentation. To test such models, UAV surveys were specially conducted at a semi-controlled test site in northern Italy, producing very high-resolution orthoimages and video frames populated with simulated waste objects such as tyres, barrels, and sand piles. Three PBM models (CLIPSeg, GroundingDINO, and TextSAM) were tested under varying hyperparameters and input conditions, including orthophotos at multiple resolutions and frames extracted from UAV-acquired videos. Results show that model performance is highly dependent on object type and imagery resolution. In contrast, within the limited ranges tested, hyperparameter tuning rarely produced significant improvements. The evaluation of the models was performed using low IoU to generalize across different types of detection models and to focus on the ability of detecting object. When evaluating the models with orthoimagery, CLIPSeg achieved the highest accuracy with F1 scores up to 0.88 for tyres, whereas barrels and ambiguous classes consistently underperformed. Video-derived (oblique) frames generally outperformed orthophotos, reflecting a closer match to model training perspectives. Despite the current limitations in performances highlighted by the tests, PBM models demonstrate strong potential for democratizing GeoAI (Geospatial Artificial Intelligence). These tools effectively enable non-expert users to employ zero-shot classification in UAV-based monitoring workflows targeting environmental crime.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Generalizing Human-Driven Wildfire Ignition Models Across Mediterranean Regions Using Harmonized Remote-Sensing and Machine-Learning Data
by
Nicola Aimane Dimarco, Ibtissam Faraji, Miriam Wahbi, Mustapha Maatouk, Hakim Boulaassal, Otman Yazidi Aalaoui and Omar El Kharki
Geomatics 2026, 6(1), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics6010013 - 1 Feb 2026
Abstract
Wildfires represent a growing environmental and socio-economic threat across Mediterranean landscapes, where prolonged summer droughts and human activity increasingly shape ignition susceptibility. This study presents an open and reproducible modelling framework for comparing the relative influence of anthropogenic and biophysical drivers of wildfire
[...] Read more.
Wildfires represent a growing environmental and socio-economic threat across Mediterranean landscapes, where prolonged summer droughts and human activity increasingly shape ignition susceptibility. This study presents an open and reproducible modelling framework for comparing the relative influence of anthropogenic and biophysical drivers of wildfire ignition susceptibility across selected Mediterranean regions. Using harmonized 500 m predictors derived from global remote-sensing datasets, we integrate vegetation condition, topography, climatic context, and human pressure indicators within a cloud-based Google Earth Engine workflow. Two tree-based machine-learning models (Random Forest and Extreme Gradient Boosting) are trained and evaluated using spatial cross-validation and cross-region transfer experiments. Results consistently highlight the dominant role of anthropogenic pressure in shaping ignition susceptibility across all study areas, with night-time lights and human modification indices contributing to the largest share of model importance. Both models achieve high predictive performance (AUC > 0.90) and retain stable accuracy under cross-region transfer (mean transfer AUC ≈ 0.85), indicating partial generalization of human-driven ignition patterns across Mediterranean landscapes. Beyond predictive performance, the principal contribution of this work lies in its harmonized cross-regional comparison and explicit evaluation of model transferability using open data and scalable cloud processing. The resulting susceptibility maps provide a transparent and operational basis for comparative wildfire risk assessment and prevention planning within comparable Mediterranean contexts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Editorial Board Members’ Collection Series: GeoAI in Disaster)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cross-Learner Spectral Subset Optimisation: PLS–Ensemble Feature Selection with Weighted Borda Count for Grapevine Cultivar Discrimination
by
Kyle Loggenberg, Albert Strever and Zahn Münch
Geomatics 2026, 6(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics6010012 - 28 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The mapping of vineyard cultivars presents a substantial challenge in digital agriculture due to the crop’s high intra-class heterogeneity and low inter-class variability. High-dimensional spectral datasets, such as hyperspectral or spectrometry data, can overcome these difficulties. However, research has yet to fully address
[...] Read more.
The mapping of vineyard cultivars presents a substantial challenge in digital agriculture due to the crop’s high intra-class heterogeneity and low inter-class variability. High-dimensional spectral datasets, such as hyperspectral or spectrometry data, can overcome these difficulties. However, research has yet to fully address the need for optimal spectral feature subsets tailored for grapevine cultivar discrimination, while few studies have systematically examined waveband subsets that transfer effectively across different learning algorithms. This study sets out to address these gaps by introducing a Partial Least Squares (PLS)-based ensemble feature selection framework with Weighted Borda Count aggregation for cultivar discrimination. Using in-field spectrometry data, collected for six cultivars, and 18 PLS-based feature selection methods spanning filter, wrapper, and hybrid approaches, the PLS–ensemble identified 100 wavebands most relevant for cultivar discrimination, reducing dimensionality by ~95%. The efficacy and transferability of this subset were evaluated using five classification algorithms: Oblique Random Forest (oRF), Multinomial Logistic Regression (Multinom), Support Vector Machine (SVM), Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP), and a 1D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). For oRF, Multinom, SVM, and MLP, the PLS–ensemble subset improved accuracy by 0.3–12% compared with using all wavebands. The subset was not optimal for the 1D-CNN, where accuracy decreased by up to 5.7%. Additionally, this study investigated waveband binning to transform narrow hyperspectral bands into broadband spectral features. Using feature multicollinearity and wavelength position, the 100 selected wavebands were condensed into 10 broadband features, which improved accuracy over both the full dataset and the original subset, delivering gains of 4.5–19.1%. The SVM model with this 10-feature subset outperformed all other models (F1: 1.00; BACC: 0.98; MCC: 0.78; AUC: 0.95).
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Urban Land Cover Mapping Enhanced with LiDAR Canopy Height Data to Quantify Urbanisation in an Arctic City: A Case Study of the City of Tromsø, Norway, 1984–2024
by
Liliia Hebryn-Baidy, Gareth Rees, Sophie Weeks and Vadym Belenok
Geomatics 2026, 6(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics6010011 - 28 Jan 2026
Abstract
Intensifying urbanisation in the Arctic, particularly in spatially constrained coastal and island cities, requires reliable information on long-term land-use/land-cover (LULC) change to assess environmental impacts and support urban planning. However, multi-decadal, high-resolution LULC datasets for Arctic cities remain limited. In this study, we
[...] Read more.
Intensifying urbanisation in the Arctic, particularly in spatially constrained coastal and island cities, requires reliable information on long-term land-use/land-cover (LULC) change to assess environmental impacts and support urban planning. However, multi-decadal, high-resolution LULC datasets for Arctic cities remain limited. In this study, we quantify LULC change on Tromsøya (Tromsø, Norway) from 1984 to 2024 using a Random Forest classifier applied to multispectral satellite imagery from Landsat and PlanetScope, complemented by LiDAR-derived canopy height models (CHM) and building footprints. We mapped LULC change trajectories and examined how these shifts relate to district-level population redistribution using gridded population data. The integration of a LiDAR-derived CHM was found to substantially improve the accuracy of Landsat-based LULC mapping and to represent the dominant source of classification gains, particularly for spectrally similar urban classes such as residential areas, roads, and other paved surfaces. Landsat augmented with CHM was shown to achieve practical equivalence to PlanetScope when the latter was modelled using spectral features only, supporting the feasibility of scalable and cost-effective long-term monitoring of urbanisation in Arctic cities. Based on the best-performing Landsat configuration, the proportions of artificial and green surfaces were estimated, indicating that approximately 20% of green areas were transformed into artificial classes. Spatially, population growth was concentrated in a small number of districts and broadly coincided with hotspots of green-to-artificial conversion The workflow provides a reproducible basis for long-term, district-scale LULC monitoring in small Arctic cities where data constraints limit the consistent use of high-resolution image.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Innovative Approaches in Geospatial Analysis and Modeling of Urban Environments)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
High-Resolution Mapping of Port Dynamics from Open-Access AIS Data in Tokyo Bay
by
Moritz Hütten
Geomatics 2026, 6(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics6010010 - 27 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Knowledge about vessel activity in port areas and around major industrial zones provides insights into economic trends, supports decision-making for shipping and port operators, and contributes to maritime safety. Vessel data from terrestrial receivers of the Automatic Identification System (AIS) have become increasingly
[...] Read more.
Knowledge about vessel activity in port areas and around major industrial zones provides insights into economic trends, supports decision-making for shipping and port operators, and contributes to maritime safety. Vessel data from terrestrial receivers of the Automatic Identification System (AIS) have become increasingly openly available, and we demonstrate that such data can be used to infer port activities at high resolution and with precision comparable to official statistics. We analyze open-access AIS data from a three-month period in 2024 for Tokyo Bay, located in Japan’s most densely populated urban region. Accounting for uneven data coverage, we reconstruct vessel activity in Tokyo Bay at ~30 m resolution and identify 161 active berths across seven major port areas in the bay. During the analysis period, we find an average of

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Forecasting Sea-Level Trends over the Persian Gulf from Multi-Mission Satellite Altimetry Using Machine Learning
by
Hamzah Tahir, Ami Hassan Md Din, Thulfiqar S. Hussein and Zaid H. Jabbar
Geomatics 2026, 6(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics6010009 - 23 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
One of the most significant impacts of climate change is sea-level rise, which is increasingly threatening to the coastal setting, infrastructure, and socioeconomic systems. Since a change at the sea level is spatially non-uniform and highly modulated by local oceanographic and climatic events,
[...] Read more.
One of the most significant impacts of climate change is sea-level rise, which is increasingly threatening to the coastal setting, infrastructure, and socioeconomic systems. Since a change at the sea level is spatially non-uniform and highly modulated by local oceanographic and climatic events, local or regional-scale measurements are necessary—especially in semi-enclosed basins. This paper examines the long-term variability of sea levels throughout the Persian Gulf and illustrates a strong spatial variance of the trends over the past and the future. Using three decades of satellite-derived observations, regional sea-level trends were estimated from monthly sea-level anomaly (SLA) data, which were also used to generate future projections to 2100. The analysis shows that the rate of sea-level rise along the UAE–Oman stretch is 3.88 mm year−1 and that of the Strait of Hormuz is 5.23 mm year−1, with a mean of 4.44 mm year−1 in the basin. Statistical forecasts of sea-level change were projected by a statistical forecasting scheme with high predictive ability with the optimal configuration of an average of 0.0391 m, an RMSE of 0.0492 m, and an R2 of 0.80 when independent validation was conducted. It is estimated that by 2100, the average rise of the sea level in the Persian Gulf is about 0.30–0.40 m, and the peak rise in sea level is at the Strait of Hormuz. Since these projections are based on statistical extrapolation rather than physics-based climate models, they are interpreted within the uncertainty envelope defined by IPCC AR6 scenarios. This study presents a unique, regionally resolved viewpoint on sea-level rise that is relevant to coastal risk management and adaptation planning in semi-enclosed marine basins by connecting robust statistical performance with physically interpretable regional patterns.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Remote Sensing-Based Mapping of Forest Above-Ground Biomass and Its Relationship with Bioclimatic Factors in the Atacora Mountain Chain (Togo) Using Google Earth Engine
by
Demirel Maza-esso Bawa, Fousséni Folega, Kueshi Semanou Dahan, Cristian Constantin Stoleriu, Bilouktime Badjaré, Jasmina Šinžar-Sekulić, Huaguo Huang, Wala Kperkouma and Batawila Komlan
Geomatics 2026, 6(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics6010008 - 22 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Accurate estimation of above-ground biomass (AGB) is vital for carbon accounting, biodiversity conservation, and sustainable forest management, especially in tropical regions under strong anthropogenic pressure. This study estimated and mapped AGB in the Atacora Mountain Chain, Togo, using a multi-source remote sensing approach
[...] Read more.
Accurate estimation of above-ground biomass (AGB) is vital for carbon accounting, biodiversity conservation, and sustainable forest management, especially in tropical regions under strong anthropogenic pressure. This study estimated and mapped AGB in the Atacora Mountain Chain, Togo, using a multi-source remote sensing approach within Google Earth Engine (GEE). Field data from 421 plots of the 2021 National Forest Inventory were combined with Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar, Sentinel-2 multispectral imagery, bioclimatic variables from WorldClim, and topographic data. A Random Forest regression model evaluated the predictive capacity of different variable combinations. The best model, integrating SAR, optical, and climatic variables (S1S2allBio), achieved R2 = 0.90, MAE = 13.42 Mg/ha, and RMSE = 22.54 Mg/ha, outperforming models without climate data. Dense forests stored the highest biomass (124.2 Mg/ha), while tree/shrub savannas had the lowest (25.38 Mg/ha). Spatially, ~60% of the area had biomass ≤ 50 Mg/ha. Precipitation correlated positively with AGB (r = 0.55), whereas temperature showed negative correlations. This work demonstrates the effectiveness of integrating multi-sensor satellite data with climatic predictors for accurate biomass mapping in complex tropical landscapes. The approach supports national forest monitoring, REDD+ programs, and ecosystem restoration, contributing to SDGs 13, 15, and 12 and offering a scalable method for other tropical regions.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
The Spherical Harmonic Representation of the Geoid
by
Robert Tenzer, Wenjin Chen, Shengwang Yu and Zhengfeng Jin
Geomatics 2026, 6(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics6010007 - 21 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Global Gravitational Models (GGMs) describe the Earth’s external gravitational field by a set of spherical harmonic (Stokes) coefficients. These coefficients are routinely used to compute the geoid model, while disregarding the upper continental crustal (i.e., topographic) masses above the geoid. Strictly speaking, however,
[...] Read more.
Global Gravitational Models (GGMs) describe the Earth’s external gravitational field by a set of spherical harmonic (Stokes) coefficients. These coefficients are routinely used to compute the geoid model, while disregarding the upper continental crustal (i.e., topographic) masses above the geoid. Strictly speaking, however, these coefficients can describe only gravity field quantities at (or above) the Earth’s surface to satisfy Laplace’s equation. Consequently, the GGM coefficients cannot be used to define the geoid surface rigorously without accounting for the internal convergence domain and the gravitational effect of topographic masses. In most technical and scientific applications, the computation of the geoid model directly from the GGM coefficients has been accepted under the assumption that errors due to disregarding the internal convergence domain (inside the topographic masses) are typically less than a few centimeters (i.e., at the level of global geoid model uncertainties). In this study, we demonstrate that these errors reach several decimeters and even meters, with maxima in Tibet and Himalayas exceeding ~4 m. Moreover, relatively large errors, reaching decimeters, are already detected in regions with a moderately elevated topography. In scientific applications requiring a high accuracy, such errors cannot be ignored. Instead, GGM coefficients describing the Earth’s external gravitational field have to be corrected for the effect of (topographic) masses distributed above the geoid surface to obtain spherical harmonic coefficients that explicitly define the geoid globally. The explicit definition of the global geoid model in the spectral domain is derived in this study and used to compile spherical harmonic coefficients of the geoid up to degree/order 2160 from the EIGEN-6C4 global gravitational model.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessing Historical Shoreline Change and Forecasting Future Trends Along Monrovia’s Coastline, Liberia
by
Titus Karderic Williams, Tarik Belrhaba, Abdelahq Aangri, Youssef Fannassi, Zhour Ennouali, John C. L. Mayson, George K. Fahnbulleh, Aıcha Benmohammadi and Ali Masria
Geomatics 2026, 6(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics6010006 - 21 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Coastal settlements worldwide face increasing threats from erosion, and the Monrovia coastline in Liberia is no exception. This study investigates shoreline dynamics along a 20.5 km stretch of Monrovia’s coast, which is characterized by low-lying elevations, gentle slopes, and sandy beaches. Using Landsat
[...] Read more.
Coastal settlements worldwide face increasing threats from erosion, and the Monrovia coastline in Liberia is no exception. This study investigates shoreline dynamics along a 20.5 km stretch of Monrovia’s coast, which is characterized by low-lying elevations, gentle slopes, and sandy beaches. Using Landsat satellite imagery (1986–2025), supported by Sentinel-2 MSI and qualitative validation drone data, we analyzed historical shoreline change with remote sensing and GIS techniques. Shorelines were extracted using a band-ratio thresholding method and quantified with the Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS 5.0), applying end-point rate (EPR), linear regression rate (LRR), and net shoreline movement (NSM). Exploratory projections for 2036 and 2046 were generated using a Kalman Filter model integrated into DSAS. Results show maximum historical erosion rates of up to 3.8 m/yr and accretion rates of up to 5.9 m/yr, with shoreline retreat reaching 150 m and advance up to 194 m. Erosion hotspots are projected for Hotel Africa, Westpoint, New Kru Town, and the JFK–ELWA corridor, while areas near the St. Paul and Mesurado estuaries are expected to accrete. These findings confirm historical trends and suggest that Monrovia will continue to face significant shoreline change, with implications for natural habitats, infrastructure, land loss, and population displacement.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
A Validated Framework for Regional Sea-Level Risk on U.S. Coasts: Coupling Satellite Altimetry with Unsupervised Time-Series Clustering and Socioeconomic Exposure
by
Swarnabha Roy, Cristhian Roman-Vicharra, Hailiang Hu, Souryendu Das, Zhewen Hu and Stavros Kalafatis
Geomatics 2026, 6(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics6010005 - 19 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study presents a validated framework to quantify regional sea-level risk on U.S. coasts by (i) extracting trends and seasonality from satellite altimetry (ADT, GMSL), (ii) learning regional dynamical regimes via PCA-embedded KMeans on gridded ADT time series, and (iii) coupling these regimes
[...] Read more.
This study presents a validated framework to quantify regional sea-level risk on U.S. coasts by (i) extracting trends and seasonality from satellite altimetry (ADT, GMSL), (ii) learning regional dynamical regimes via PCA-embedded KMeans on gridded ADT time series, and (iii) coupling these regimes with socioeconomic exposure (population, income, ocean-sector employment/GDP) and wetland submersion scoring. Relative to linear and ARIMA/SARIMA baselines, a sinusoid+trend fit and an LSTM forecaster reduce out-of-sample error (MAE/RMSE) across the North Atlantic, North Pacific, and Gulf of Mexico. The clustering separates high-variability coastal segments, and an interpretable submersion score integrates elevation quantiles and land cover to produce ranked adaptation priorities. Overall, the framework converts heterogeneous physical signals into decision-ready coastal risk tiers to support targeted defenses, zoning, and conservation planning.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Evaluating Neural Radiance Fields for Image-Based 3D Reconstruction: A Comparative Study with SfM-MVS
by
Alessia Giaquinto, Giampaolo Ferraioli and Silvio Del Pizzo
Geomatics 2026, 6(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics6010004 - 10 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Recent advances in image-based 3D reconstruction have seen a shift from traditional photogrammetric techniques to learning-based methods, with Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) emerging as a powerful alternative. This study evaluates NeRF (via Nerfstudio) for accurate 3D reconstruction, comparing its performance to the widely
[...] Read more.
Recent advances in image-based 3D reconstruction have seen a shift from traditional photogrammetric techniques to learning-based methods, with Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) emerging as a powerful alternative. This study evaluates NeRF (via Nerfstudio) for accurate 3D reconstruction, comparing its performance to the widely used SfM-MVS pipeline implemented in Agisoft Metashape Professional (v. 2.2.1). This work considers a diverse set of datasets with varying object scales, capture methods (including drone imagery), and lighting conditions. Several assessment analyses were conducted, including evaluation of accuracy, completeness, planarity, and density of the reconstructed point clouds. Special attention was given to the influence of shadows and surface flatness on the fidelity of reconstruction. Results show that, despite not being initially designed for metric accuracy, NeRF demonstrates promising spatial consistency, producing reconstructions in some cases comparable to those of conventional methods when provided with precise camera poses. These findings suggest that NeRF may serve as a viable tool for 3D modelling in controlled settings. The applicability of the approach to more diverse and challenging scenarios remains to be explored, with particular attention to optimizing the reconstruction pipeline in terms of pose estimation, point cloud density, and robustness to varying lighting conditions.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of Temporal Changes in the Floating Vegetation and Algae Surface of the Water Bodies of Kis-Balaton Based on Aerial Image Classification and Meteorological Data
by
Kristóf Kozma-Bognár, Angéla Anda, Ariel Tóth, Veronika Kozma-Bognár and József Berke
Geomatics 2026, 6(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics6010003 - 3 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Climate change and related weather extremes are increasingly having an impact on all aspects of life. The main objective of the research was to analyze the impact of the most important meteorological elements and the image data of various water bodies of the
[...] Read more.
Climate change and related weather extremes are increasingly having an impact on all aspects of life. The main objective of the research was to analyze the impact of the most important meteorological elements and the image data of various water bodies of the Kis-Balaton wetland, Hungary. The primary question was which meteorological elements have a positive or negative influence on vegetational surface cover. Drones have facilitated the visual surveying and monitoring of challenging-to-reach water bodies in the area, including a lake and multiple channels. The individual channels had different flow conditions. Aerial surveys were conducted monthly, based on pre-prepared flight plans. Images captured by a Mavic 3 drone flying at an altitude of 150 m and equipped with a multispectral sensor were processed. The time-series images were aligned and assembled into orthophotos. The image details relevant to the research were segregated and classified using Maximum Likelihood classification algorithm. The reliability of the image data used was checked by Shannon entropy and spectral fractal dimension measurements. The results of the classification were compared with the meteorological data collected by a QLC-50 automatic climate station of Keszthely. The investigations revealed that the surface cover of the examined water bodies was different in the two years but showed a kind of periodicity during the year. In those periods, where photosynthetic organisms multiplied in a higher proportion in the water body, higher monthly average air temperatures and higher monthly global solar radiation sums were observed.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Low-Cost Panoramic Photogrammetry: A Case Study on Flat Textures and Poor Lighting Conditions
by
Ondrej Benko, Marek Fraštia, Marián Marčiš and Adrián Filip
Geomatics 2026, 6(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics6010002 - 3 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The article addresses the issue of panoramic photogrammetry for the reconstruction of interior spaces. Such environments often present challenges, including poor lighting conditions and surfaces with variable texture for photogrammetric scanning. In this case study, we reconstruct the interior spaces of the historical
[...] Read more.
The article addresses the issue of panoramic photogrammetry for the reconstruction of interior spaces. Such environments often present challenges, including poor lighting conditions and surfaces with variable texture for photogrammetric scanning. In this case study, we reconstruct the interior spaces of the historical house of Samuel Mikovíni, which represents these unfavorable conditions. The 3D reconstruction of interior spaces is performed using the Ricoh Theta Z1 spherical camera (Ricoh Company, Ltd.; Tokyo, Japan) in six variants, each employing a different number of images and different camera networks. Scale is introduced into the reconstructions based on significant dimensions measured with a measuring tape. A comparison is carried out using a point cloud obtained from terrestrial laser scanning and difference point clouds are generated for each variant. Based on the results, reconstructions produced from a reduced number of spherical images can serve as a basic source for simple documentation with accuracy up to 0.15 m. When the number of spherical images is increased and images from different height levels are included, the reconstruction accuracy improves markedly, achieving positional accuracy of up to 0.05 m, even in areas affected by poor lighting conditions or low-texture surfaces. The results confirm that for interior reconstruction, a higher number of images not only increases the density of the reconstructed point cloud but also enhances its positional accuracy.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Developing a Predictive Model for Gender-Based Violence in Urban Areas Using Open Data
by
Sandra Hernandez-Zetina, Angel Martin-Furones, Alvaro Verdu-Candela, Carlos Martinez-Montes and Ana Belen Anquela-Julian
Geomatics 2026, 6(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics6010001 - 20 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Gender-based violence (GBV) in urban contexts is a complex, multifactorial phenomenon shaped by socioeconomic, territorial, and contextual factors. This study aims to develop a predictive model for GBV-related crimes in Valencia (Spain), using open geospatial data and advanced machine learning techniques to support
[...] Read more.
Gender-based violence (GBV) in urban contexts is a complex, multifactorial phenomenon shaped by socioeconomic, territorial, and contextual factors. This study aims to develop a predictive model for GBV-related crimes in Valencia (Spain), using open geospatial data and advanced machine learning techniques to support the identification of high-risk areas and guide targeted interventions. A 25 m grid was generated to homogenize crime data and independent variables, including socioeconomic indicators, urban services, real estate information, and traffic intensity. Multiple models were tested—Multiple Linear Regression (MLR), Decision Tree (DT), and Random Forest (RF). Linear models were found to be insufficient for explaining GBV patterns (R2 ≈ 0.45), while RF and DT achieved high predictive accuracy (R2 ≈ 0.97 and 0.95, respectively. The variables with the greatest influence were traffic intensity, average monthly income, unemployment rate, and proximity to nightlife venues. To enhance the interpretability of the most accurate models, we applied SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) to quantify the contribution of each predictor and elucidate the direction and magnitude of their effects on model predictions. These findings demonstrate the utility of geospatial ML techniques in understanding the spatial dynamics of GBV and in supporting urban safety policies. While the current model focuses on static spatial predictors and does not explicitly model temporal dynamics or spatial autocorrelation, future research will integrate these aspects, along with participatory data, and test the model’s applicability in other cities to enhance its robustness and generalizability.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Multisource Mapping of Lagoon Bathymetry for Hydrodynamic Models and Decision-Support Spatial Tools: The Case of the Gambier Islands in French Polynesia
by
Serge Andréfouët, Oriane Bruyère and Thomas Trophime
Geomatics 2025, 5(4), 81; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics5040081 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
Precise lagoon bathymetry remains scarcely available for most tropical islands despite its importance for navigation, resource assessment, spatial planning, and numerical hydrodynamic modeling. Hydrodynamic models are increasingly used for instance to understand the ecological connectivity between marine populations of interest. Island remoteness and
[...] Read more.
Precise lagoon bathymetry remains scarcely available for most tropical islands despite its importance for navigation, resource assessment, spatial planning, and numerical hydrodynamic modeling. Hydrodynamic models are increasingly used for instance to understand the ecological connectivity between marine populations of interest. Island remoteness and shallow waters complicate in situ bathymetric surveys, which are substantially costly. A multisource strategy using historical point sounding, multibeam surveys and well calibrated satellite-derived bathymetry (SDB) can offer the possibility to map entirely extensive and geomorphologically complex lagoons. The process is illustrated here for the rugose complex lagoon of Gambier Islands in French Polynesia. The targeted bathymetry product was designed to be used in priority for numerical larval dispersal modeling at 100 m spatial resolution. Spatial gaps in in situ data were filed with Sentinel-2 satellite images processed with the Iterative Multi-Band Ratio method that provided an accurate bathymetric model (1.42 m Mean Absolute Error in the 0–15 m depth range). Processing was optimized here, considering the specifications and the constraints related to the targeted hydrodynamic modeling application. In the near future, a similar product, possibly at higher spatial resolution, could improve spatial planning zoning scenarios and resource-restocking programs. For tropical island countries and for French Polynesia, in particular, the needs for lagoon hydrodynamic models remain high and solutions could benefit from such multisource coverage to fill the bathymetry gaps.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Ocean Mapping and Hydrospatial Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Integrated Remote Sensing and Machine Learning Approach to Assess the Impact of Soil Salinity on Rice Yield in Northeastern Thailand
by
Jurawan Nontapon, Neti Srihanu, Niwat Bhumiphan, Nopanom Kaewhanam, Anongrit Kangrang, Umesh Bhurtyal, Niraj KC, Siwa Kaewplang and Alfredo Huete
Geomatics 2025, 5(4), 80; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics5040080 - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The Northeast region of Thailand covers approximately 16.89 million hectares, with about 6.17 million hectares of seasonal rice cultivation and 2.85 million hectares affected by soil salinity—a major constraint to agricultural productivity in this region. This study develops an integrated data fusion framework
[...] Read more.
The Northeast region of Thailand covers approximately 16.89 million hectares, with about 6.17 million hectares of seasonal rice cultivation and 2.85 million hectares affected by soil salinity—a major constraint to agricultural productivity in this region. This study develops an integrated data fusion framework combining multi-temporal Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 imagery to train machine learning (ML) models for the prediction of rice yield and soil salinity, allowing for an analysis of their relationship. The field data comprised 380 rice yield and 625 soil electrical conductivity (EC) samples collected in 2023. Three ML models—Random Forest (RF), Classification and Regression Trees (CART), and Support Vector Regression (SVR)—were applied for variable reduction and optimal predictor selection. RF achieved the highest accuracy for yield prediction (R2 = 0.86, RMSE = 0.19 t ha−1) and salinity estimation (R2 = 0.93, RMSE = 0.87 dS/m) when using fused Landsat–Sentinel data. Spatial analysis of 5000 matched points showed a strong negative relationship between seedling stage EC and yield (R2 = 0.71), with yields declining sharply above 5 dS/m and remaining below 1.5 t ha−1 beyond 15 dS/m. These results demonstrate the potential of multi-sensor fusion and ensemble ML approaches for precise soil salinity monitoring and sustainable rice production.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
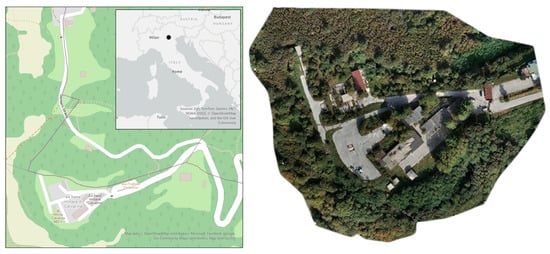
Autonomous BIM-Aware UAV Path Planning for Construction Inspection
by
Nagham Amer Abdulateef, Zainab N. Jasim, Haider Ali Hasan, Bashar Alsadik and Yousif Hussein Khalaf
Geomatics 2025, 5(4), 79; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics5040079 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Accurate 3D reconstructions of architecture, engineering, and construction AEC structures using UAV photogrammetry are often hindered by occlusions, excessive image overlaps, or insufficient coverage, leading to inefficient flight paths and extended mission durations. This work presents a BIM-aware, autonomous UAV trajectory generation framework
[...] Read more.
Accurate 3D reconstructions of architecture, engineering, and construction AEC structures using UAV photogrammetry are often hindered by occlusions, excessive image overlaps, or insufficient coverage, leading to inefficient flight paths and extended mission durations. This work presents a BIM-aware, autonomous UAV trajectory generation framework wherein a compact, geometrically valid viewpoint network is first derived as a foundation for path planning. The network is optimized via Integer Linear Programming (ILP) to ensure coverage of IFC-modeled components while penalizing poor stereo geometry, GSD, and triangulation uncertainty. The resulting minimal network is then sequenced into a global path using a TSP solver and partitioned into battery-feasible epochs for operation on active construction sites. Evaluated on two synthetic and one real-world case study, the method produces autonomous UAV trajectories that are 31–63% more compact in camera usage, 17–35% shorter in path length, and 28–50% faster in execution time, without compromising coverage or reconstruction quality. The proposed integration of BIM modeling, ILP optimization, TSP sequencing, and endurance-aware partitioning enables the framework for digital-twin updates and QA/QC monitoring, accordingly, offering a unified, geometry-adaptive solution for autonomous UAV inspection and remote sensing.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Structural Change in Romanian Land Use and Land Cover (1990–2018): A Multi-Index Analysis Integrating Kolmogorov Complexity, Fractal Analysis, and GLCM Texture Measures
by
Ion Andronache and Ana-Maria Ciobotaru
Geomatics 2025, 5(4), 78; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics5040078 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Monitoring land use and land cover (LULC) transformations is essential for understanding socio-ecological dynamics. This study assesses structural shifts in Romania’s landscapes between 1990 and 2018 by integrating algorithmic complexity, fractal analysis, and Grey-Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) texture analysis. Multi-year maps were used
[...] Read more.
Monitoring land use and land cover (LULC) transformations is essential for understanding socio-ecological dynamics. This study assesses structural shifts in Romania’s landscapes between 1990 and 2018 by integrating algorithmic complexity, fractal analysis, and Grey-Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) texture analysis. Multi-year maps were used to compute Kolmogorov complexity, fractal measures, and 15 GLCM metrics. The measures were compiled into a unified matrix, and temporal trajectories were explored with principal component analysis and k-means clustering to identify inflection points. Informational complexity and Higuchi 2D decline over time, while homogeneity and angular second moment rise, indicating greater local uniformity. A structural transition around 2006 separates an early heterogeneous regime from a more ordered state; 2012 appears as a turning point when several indices reach extreme values. Strong correlations between fractal and texture measures imply that geometric and radiometric complexity co-evolve, whereas large-scale fractal dimensions remain nearly stable. The multi-index approach provides a replicable framework for identifying critical transitions in LULC. It can support landscape monitoring, and future work should integrate finer temporal data and socio-economic drivers.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Hybrid Data Collection for Traffic Accident Site Documentation
by
Zdeněk Svatý, Pavel Vrtal, Tomáš Kohout, Luboš Nouzovský and Karel Kocián
Geomatics 2025, 5(4), 77; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics5040077 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study examines the possibilities of using hybrid data collection methods based on photogrammetric and LiDAR imaging for documenting traffic accident sites. The evaluation was performed with an iPhone 15 Pro and a viDoc GNSS receiver. Comparative measurements were made against instruments with
[...] Read more.
This study examines the possibilities of using hybrid data collection methods based on photogrammetric and LiDAR imaging for documenting traffic accident sites. The evaluation was performed with an iPhone 15 Pro and a viDoc GNSS receiver. Comparative measurements were made against instruments with higher accuracy. The test scenarios included measuring errors along a 25 m line and scanning a larger traffic area. Measurements were conducted under limiting conditions on a homogeneous surface without terrain irregularities or objects. The results show that although hybrid scanning cannot fully replace traditional surveying instruments, it provides accurate results for documenting traffic accident sites. The analysis additionally revealed an almost linear spread of errors on homogeneous asphalt surfaces. Moreover, it was confirmed that the use of a GNSS receiver and control points has a significant impact on the quality of the data. Such a comprehensive assessment of surface homogeneity has not been tested yet. To achieve accuracy, it is recommended to use a scanning mode based on at least 90% image overlap with RTK GNSS. The relative error rate on a linear section ranged from 0.5 to 1.0%, which corresponds to an error of up to 5 cm over a 5 m section. When evaluating a larger area using hybrid data collection, 93.38% of the points had an error below 10 cm, with a mean deviation of 6.2 cm. These findings expand current knowledge and define practical device settings and operational limits for the use of hybrid mobile scanning.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of Shoreline Dynamics and Beach Profile Evolution over More than a Decade: Satellite Image Characterization and Machine Learning Modeling
by
Dalia A. Moreno-Egel, Alfonso Arrieta-Pastrana and Oscar E. Coronado-Hernández
Geomatics 2025, 5(4), 76; https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics5040076 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study presents a detailed analysis of the morphological evolution of beaches in the Bocagrande sector of Cartagena de Indias, Colombia, over more than a decade, based on periodic monitoring of six beach profiles. The beaches in this area are in bays constrained
[...] Read more.
This study presents a detailed analysis of the morphological evolution of beaches in the Bocagrande sector of Cartagena de Indias, Colombia, over more than a decade, based on periodic monitoring of six beach profiles. The beaches in this area are in bays constrained by headlands and promontories located at both ends of each bay. Changes in shoreline position, dry beach widths, and the surf zone were evaluated using aerial photographs, orthophotos, satellite imagery, and field data, together with sediment size determined through granulometric analysis. The results indicate that the beaches exhibit characteristics of wave-dominated, exposed systems, with sediments classified as fine sand that tend to increase in grain size toward the northern sector of the bay. A cyclical variation in the shoreline was observed, with average retreats and advances ranging from 5 to 10 m, depending on the climatic season. Dry beach widths ranged from 10 to 90 m, decreasing toward the north. Differences in morphology between profiles and shoreline variation are attributed to the climatic season, profile location within the bay, and proximity to a coastal structure and its particular type. Beach profiles were fitted to conceptual equilibrium profile models using traditional equations, which yielded a coefficient of determination of 0.76; when machine learning algorithms were applied, this value improved to 0.99. This study provides an important baseline for future morphological assessments and coastal management efforts in the city and places with similar characteristics, particularly considering ongoing shoreline protection projects.
Full article
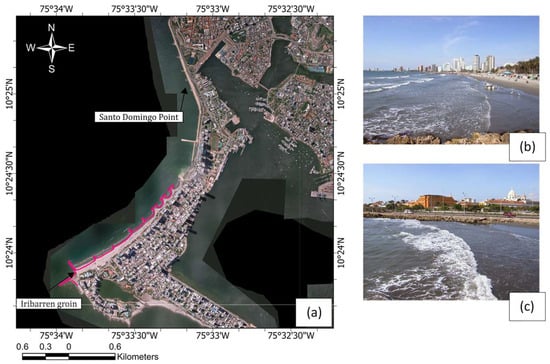
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Geomatics Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Electronics, Geomatics, Energies, Sensors, Drones
Navigation and Positioning System: Opportunities and Obstacles
Topic Editors: Kamil Maciuk, Paulina Lewińska, Artur KrawczykDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
Atmosphere, Geomatics, Hydrology, Remote Sensing, Water, Climate
Advances in Hydrological Remote Sensing
Topic Editors: Hailong Liu, Liangliang JiangDeadline: 30 April 2026
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Drones, Geomatics, Heritage, IJGI, Remote Sensing, Sensors
3D Documentation of Natural and Cultural Heritage
Topic Editors: Lorenzo Teppati Losè, Elisabetta Colucci, Arnadi Dhestaratri MurtiyosoDeadline: 31 August 2026
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Geomatics, IJGI, Remote Sensing, Smart Cities
The Geography of Digital Twin: Concepts, Architectures, Modeling, AI and Applications
Topic Editors: Chaowei Yang, Daniel Q. Duffy, Xiao Huang, Lingbo LiuDeadline: 20 September 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Geomatics
Editorial Board Members’ Collection Series: GeoAI in Disaster
Guest Editor: Suchi GopalDeadline: 20 April 2026
Special Issue in
Geomatics
Advances and Innovations in Geomatics: Celebrating a New Chapter—First Impact Factor and CiteScore Received
Guest Editors: Enrico Corrado Borgogno Mondino, Caterina BallettiDeadline: 15 June 2026
Special Issue in
Geomatics
Innovative Remote Sensing Approaches: 3D Reconstruction, UAV Photogrammetry, and BIM in Cultural Heritage and Infrastructure
Guest Editors: Lidia M. Ortega Alvarado, María Ramos GalanDeadline: 30 September 2026