-
 Physico-Mechanical Properties of an Aluminosilicate Refractory Castable Obtained After Chamotte Waste Recycling by Firing Method
Physico-Mechanical Properties of an Aluminosilicate Refractory Castable Obtained After Chamotte Waste Recycling by Firing Method -
 Cellulose-Based Biopolymers from Banana Pseudostem Waste: Innovations for Sustainable Bioplastics
Cellulose-Based Biopolymers from Banana Pseudostem Waste: Innovations for Sustainable Bioplastics -
 Trichoderma harzianum Enzyme Production in Stirred Solid-State Bioreactors as a Strategy for Valorizing Water Hyacinth
Trichoderma harzianum Enzyme Production in Stirred Solid-State Bioreactors as a Strategy for Valorizing Water Hyacinth
Journal Description
Waste
Waste
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on waste management, science and technology, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 24.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Journal Cluster of Environmental Science: Sustainability, Land, Clean Technologies, Environments, Nitrogen, Recycling, Urban Science, Safety, Air, Waste and Aerobiology.
Latest Articles
Evaluation of Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste Leachates and Dairy Wastes Towards Organic-Load Reduction and Optimization of Biomethane Production
Waste 2026, 4(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste4010004 - 31 Jan 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
A rapidly emerging approach within the scientific community involves the utilization of waste streams for renewable energy generation, particularly through biomethane production. A key aspect of this approach lies in the co-digestion of diverse waste streams, which can enhance process efficiency and contribute
[...] Read more.
A rapidly emerging approach within the scientific community involves the utilization of waste streams for renewable energy generation, particularly through biomethane production. A key aspect of this approach lies in the co-digestion of diverse waste streams, which can enhance process efficiency and contribute to a more effective reduction in the organic load. The present study investigates the anaerobic digestion of a mixture of food waste leachates and dairy waste (cheese whey wastewater), with a dual objective: to evaluate the reduction in organic-load efficiency of the mixed substrate and to assess the production of biogas enriched in biomethane content. Three distinct mixing ratios by volume of the two waste streams (25%/75%, 50%/50% and 75%/25%) were subjected to an anaerobic digestion process under the same SIR. The performance of each mixture was assessed in terms of both reduction in organic-load efficiency and biomethane yield, followed by a comparative analysis to identify the optimal mixing ratio. The results indicate that while the organic-load reduction remains consistently effective across all mixing ratios, the biomethane production potential is notably higher for the 25%/75% waste mixture, highlighting it as the most promising configuration for both energy recovery and waste treatment efficiency.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Fine-Fraction Brazilian Residual Kaolin-Filled Coating Mortars
by
Thamires Alves da Silveira, Mirian Dosolina Fusinato, Gustavo Luis Calegaro, Cristian da Conceição Gomes and Rafael de Avila Delucis
Waste 2026, 4(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste4010003 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
This study investigates the use of the fine fraction of Brazilian residual kaolin, a material with no pozzolanic activity according to the modified Chapelle test, as a partial cement replacement in rendering mortars. The kaolin was classified into three granulometric fractions (coarse: 150–300
[...] Read more.
This study investigates the use of the fine fraction of Brazilian residual kaolin, a material with no pozzolanic activity according to the modified Chapelle test, as a partial cement replacement in rendering mortars. The kaolin was classified into three granulometric fractions (coarse: 150–300 µm, intermediate: 75–150 µm, and fine: <75 µm) and incorporated at two filler contents (10% and 20% by weight). Mineralogical and chemical analyses revealed that the fine fractions contained higher proportions of kaolinite and accessory oxides, while medium and coarse fractions were dominated by quartz. Intensity ratios from XRD confirmed greater structural disorder in the fine fraction, which was associated with higher water demand but also improved particle packing and pore refinement. Fresh state tests showed that mortars with fine kaolin maintained higher density and exhibited moderate increases in air content, whereas medium and coarse fractions promoted greater entrainment. In the hardened state, fine kaolin reduced water absorption by immersion and capillary rise, while medium and coarse fractions led to higher porosity. Mechanical tests confirmed these trends: although compressive and flexural strengths decreased with increasing substitution, mortars containing the fine kaolin fraction consistently exhibited more moderate strength losses than those with medium or coarse fractions, reflecting their enhanced packing efficiency and pore refinement. Tensile bond strength results further highlighted the positive contribution of the kaolin additions, as the mixtures with 10% coarse kaolin and 20% fine kaolin achieved adhesion values only about 7% and 4% lower, respectively, than the control mortar after 28 days. All mixtures surpassed the performance requirements of NBR 13281, demonstrating that the incorporation of residual kaolin—even at higher substitution levels—does not compromise adhesion and remains compatible with favorable cohesive failure modes in the mortar layer. Despite the lack of pozzolanic activity, residual kaolin was used due to its filler effect and capacity to enhance particle packing and pore refinement in rendering mortars. A life cycle assessment indicated that the partial substitution of cement with residual kaolin effectively reduces the environmental impacts of mortar production, particularly the global warming potential, when the residue is modeled as a by-product with a negligible environmental burden. This highlights the critical role of methodological choices in assessing the sustainability of industrial waste utilization.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Use of Waste Materials in Construction Industry)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Solar-Assisted Thermochemical Valorization of Agro-Waste to Biofuels: Performance Assessment and Artificial Intelligence Application Review
by
Balakrishnan Varun Kumar, Sassi Rekik, Delmaria Richards and Helmut Yabar
Waste 2026, 4(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste4010002 - 31 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The rapid growth and seasonal availability of agricultural materials, such as straws, stalks, husks, shells, and processing wastes, present both a disposal challenge and an opportunity for renewable fuel production. Solar-assisted thermochemical conversion, such as solar-driven pyrolysis, gasification, and hydrothermal routes, provides a
[...] Read more.
The rapid growth and seasonal availability of agricultural materials, such as straws, stalks, husks, shells, and processing wastes, present both a disposal challenge and an opportunity for renewable fuel production. Solar-assisted thermochemical conversion, such as solar-driven pyrolysis, gasification, and hydrothermal routes, provides a pathway to produce bio-oils, syngas, and upgraded chars with substantially reduced fossil energy inputs compared to conventional thermal systems. Recent experimental research and plant-level techno-economic studies suggest that integrating concentrated solar thermal (CSP) collectors, falling particle receivers, or solar microwave hybrid heating with thermochemical reactors can reduce fossil auxiliary energy demand and enhance life-cycle greenhouse gas (GHG) performance. The primary challenges are operational intermittency and the capital costs of solar collectors. Alongside, machine learning (ML) and AI tools (surrogate models, Bayesian optimization, physics-informed neural networks) are accelerating feedstock screening, process control, and multi-objective optimization, significantly reducing experimental burden and improving the predictability of yields and emissions. This review presents recent experimental, modeling, and techno-economic literature to propose a unified classification of feedstocks, solar-integration modes, and AI roles. It reveals urgent research needs for standardized AI-ready datasets, long-term field demonstrations with thermal storage (e.g., integrating PCM), hybrid physics-ML models for interpretability, and region-specific TEA/LCA frameworks, which are most strongly recommended. Data’s reporting metrics and a reproducible dataset template are provided to accelerate translation from laboratory research to farm-level deployment.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Waste Separation Behavioral Intention Among Residents After the Abolition of the Zero-COVID Policy: A Case Study of Shanghai, China
by
Xinrui Li, Takehiko Murayama, Shigeo Nishikizawa and Kultip Suwanteep
Waste 2026, 4(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste4010001 - 27 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In recent years, China has made strong national commitments to waste reduction and circular economy, including the implementation of mandatory municipal solid waste separation policies and the rollout of zero-waste city initiatives. These efforts represent a strategic shift toward systemic environmental governance. However,
[...] Read more.
In recent years, China has made strong national commitments to waste reduction and circular economy, including the implementation of mandatory municipal solid waste separation policies and the rollout of zero-waste city initiatives. These efforts represent a strategic shift toward systemic environmental governance. However, the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic in early 2020—and the subsequent implementation of the country’s stringent zero-COVID policy—led to an abrupt disruption of these programs. Under this policy, strict lockdowns, quarantine of both confirmed and suspected cases, and city-wide containment became top priorities, sidelining environmental initiatives such as waste separation and sustainable waste infrastructure development. This study investigates how Chinese residents’ motivations for waste separation evolved across three key phases: pre-pandemic, during the zero-COVID enforcement period, and post-pandemic recovery. Grounded in the Theory of Planned Behavior and pro-environmental behavior theory, we developed an extended model incorporating pandemic-related social, psychological, and policy variables. Based on 526 valid questionnaire responses collected in late 2023 in Shanghai, we conducted structural equation modeling and repeated-measures analysis. Findings reveal a significant shift from externally driven compliance—reliant on governmental enforcement and service provision—to internally motivated behavior based on environmental values and personal efficacy. This transition was most evident after the pandemic, suggesting the potential for sustained pro-environmental habits despite weakened policy enforcement. Our findings underscore the importance of strengthening internal drivers in environmental governance, especially under conditions where policy continuity is vulnerable to systemic shocks such as public health emergencies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sustainable Valorization of Juice Industry Wastes: A Life Cycle Assessment Case Study
by
Fotini Drosou, Tryfon Kekes, Athanasios Kardamanidis and Magdalini Krokida
Waste 2025, 3(4), 42; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3040042 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
The juice industry generates substantial quantities of solid waste and wastewater. Consequently, efforts have focused on their treatment and valorization to obtain high-value-added products. Traditionally, these wastes are managed through landfill disposal and treatment in municipal wastewater facilities, respectively. In the present work,
[...] Read more.
The juice industry generates substantial quantities of solid waste and wastewater. Consequently, efforts have focused on their treatment and valorization to obtain high-value-added products. Traditionally, these wastes are managed through landfill disposal and treatment in municipal wastewater facilities, respectively. In the present work, two alternative scenarios for the valorization of orange juice waste were developed and assessed in comparison to the conventional approach by performing a Life Cycle Assessment (LCA). Scenario 1 involved hydro-distillation of solid waste for essential oil recovery, followed by anaerobic digestion for biogas and fertilizer production, with wastewater treated via membrane filtration and chlorination. In Scenario 2, solvent-free microwave extraction (SFME) was employed for essential oil recovery, followed by anaerobic digestion. Wastewater was treated in a membrane bioreactor followed by ultraviolet treatment. According to the results, Scenario 1 achieved a 36% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions due to the beneficial effects of biogas and fertilizer production, despite its high energy demands. Scenario 2 exhibited the best environmental performance due to lower energy demands and higher extraction efficiency compared to Scenario 1, with reductions of 46% in greenhouse gas emissions and 48% in resource depletion. Overall, the findings highlight the potential of integrating innovative, energy-efficient technologies for the sustainable valorization of juice industry waste, offering measurable environmental advantages for industrial-scale implementation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Agri-Food Wastes and Biomass Valorization—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Integrated Framework to Assess Advanced Phosphorus Recycling as a Sustainable Alternative to Sewage Sludge in Agricultural Soils
by
Juan Serrano-Gomez, Henrique Rasera Raniro, Ludwig Hermann, Manuel Pulido-Velazquez and Matthias Zessner
Waste 2025, 3(4), 41; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3040041 - 27 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Advanced phosphorus (P) recycling from wastewater is critical for improving nutrient circularity and reducing soil pollution associated with the direct application of sewage sludge in agriculture. However, few studies evaluate the long-term environmental and economic trade-offs between recycled P products and raw sewage
[...] Read more.
Advanced phosphorus (P) recycling from wastewater is critical for improving nutrient circularity and reducing soil pollution associated with the direct application of sewage sludge in agriculture. However, few studies evaluate the long-term environmental and economic trade-offs between recycled P products and raw sewage sludge application. This study compares struvite, vivianite, and dicalcium phosphate (CaP) as P alternatives to sludge to mitigate heavy metal accumulation in Spanish agricultural soils. Using data from 27,835 plots, heavy metal accumulation was simulated over 50- and 100-year fertilisation scenarios. The results indicate that continuous sludge application leads to widespread exceedances of zinc, copper, and cadmium, especially in alkaline soils, whereas substitution with recycled products can substantially reduce these risks. Vivianite balances P recycling and costs, CaP offers the best environmental performance but with higher investment, and struvite suits smaller regions prioritising environmental safety. Economic analysis favours advanced recycling over sludge, especially considering externalities such as soil remediation costs. Despite limitations, our findings emphasise the importance of integrating environmental externalities into economic assessments and the value of advanced P recycling for sustainable soil management.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Adoption of Solid Waste Compost in Paddy Farming: Insights from Sri Lanka’s Organic Farming Policy
by
Chamila Jeewanee Fernando and Aramaki Toshiya
Waste 2025, 3(4), 40; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3040040 - 20 Nov 2025
Abstract
The utilization of Solid Waste Compost (SWC) as an organic fertilizer (OF) in agriculture has garnered significant attention in recent years due to growing concerns about worsening waste management issues. This empirical study investigates paddy farmers’ perceptions of SWC under Sri Lanka’s organic
[...] Read more.
The utilization of Solid Waste Compost (SWC) as an organic fertilizer (OF) in agriculture has garnered significant attention in recent years due to growing concerns about worsening waste management issues. This empirical study investigates paddy farmers’ perceptions of SWC under Sri Lanka’s organic farming policy and uniquely addresses its underexploited potential as an organic fertilizer. Data were collected from 254 respondents in the Attanagalla Divisional Secretariat Division via a structured questionnaire. Nine key performance indicators were established to evaluate SWC against other organic fertilizers considered for the study. Findings revealed that meeting the ‘required quantity’ OF was the most challenging aspect (91%) for organic paddy cultivation, while only 14.2% of paddy farmers were able to utilize SWC for paddy fields due to limited availability. Farmers appreciated SWC as the most effective in balancing pest–predator interactions, even surpassing straw; however, its availability lagged compared to alternatives such as straw. Farmers expressed a higher likelihood of adopting SWC if it met government certification standards. The findings conclude that, while increasing production of SWC could enhance its role as an organic fertilizer in paddy farming, achieving its quality standards for paddy farming through government standard certification is crucial for successful implementation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advances in Organic Solid Waste and Wastewater Management)
Open AccessSystematic Review
From Trash to Treasure: Systematic Evaluation of Potential and Efficiency of Waste-to-Energy Incineration for Electricity Generation
by
Nontobeko Gloria Maphuhla and Opeoluwa Oyehan Oyedeji
Waste 2025, 3(4), 39; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3040039 - 17 Nov 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
The massive production of municipal solid waste presents a significant global challenge for sustainable urban development and maintaining citizens’ quality of life, requiring effective management and disposal strategies. Waste-to-energy incineration technology has become increasingly important as a solution that simultaneously addresses the growing
[...] Read more.
The massive production of municipal solid waste presents a significant global challenge for sustainable urban development and maintaining citizens’ quality of life, requiring effective management and disposal strategies. Waste-to-energy incineration technology has become increasingly important as a solution that simultaneously addresses the growing volumes of municipal solid waste and rising energy needs worldwide. This comprehensive review examines the research findings on the effectiveness of incineration as a waste-to-energy conversion method. The primary goal was to conduct a thorough systematic review assessing WtE incineration effectiveness across several key areas: energy recovery efficiency, waste volume reduction capabilities, environmental impact, and economic feasibility. A comprehensive literature search was conducted across ScienceDirect and additional pertinent databases, utilizing appropriate search terms in accordance with the PRISMA framework. A total of 431 studies were systematically identified, published between 2015 and 2025, and only 25 relevant studies were included in this review. Researchers collected data focusing on energy recovery percentages, volume reduction rates, emission reductions, and economic performance metrics. The findings revealed that every study included in the analysis showed positive results for WtE incineration across various performance measures. This research discovered the feasibility of generating electrical power from garbage through WtE incineration processes. The projected energy yields, ranging from gigawatt-hours to kilowatt-hours, were quantified for several nations, including Mexico (11,681.64 GWh), Cambodia (1625.81 GWh), Bangladesh (187.04 GWh), South Africa (6944 GWh), Iran (17,678 GWh), Nigeria (10,000 GWh), Indonesia (2487 MWh), Algeria (11.6 MWh), China (2316.52 MWh), Iraq (203.917 MWh), Uganda (774 kWh), and Pakistan (675 kWh). Energy recovery efficiency demonstrated a wide range from 30% to 92.75%, with waste volume reduction consistently reaching 90–95% levels, significantly prolonging landfill operational lifespans. From an environmental perspective, technology achieved greenhouse gas emission reductions ranging from 30% to 87%. This dual-purpose approach makes it an attractive, sustainable solution for both waste management and renewable energy production. By adopting this approach, cities can address waste and energy issues while boosting economic growth and job creation. However, it also involves substantial costs, technical difficulties, and environmental hazards that necessitate meticulous oversight.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Recent Advances in Municipal Solid Waste Management and Technology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Proliferation of Plastic Packaging and Its Environmental Impacts at the Commune of Agoè-Nyivé 4 in Togo
by
Ibrahim Batcham, Djiwonou Koffi Adjalo, Koko Zébéto Houedakor, Komlan Kounon Etienne Tede and Kossiwa Zinsou-Klassou
Waste 2025, 3(4), 38; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3040038 - 3 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The overconsumption of plastic packaging has alarming repercussions on the environment, notably through waste accumulation in public spaces and clogged drains. This study identifies factors driving plastic proliferation, analyzes their impacts, and proposes strategies for sustainable waste management. A cross-sectional design combined document
[...] Read more.
The overconsumption of plastic packaging has alarming repercussions on the environment, notably through waste accumulation in public spaces and clogged drains. This study identifies factors driving plastic proliferation, analyzes their impacts, and proposes strategies for sustainable waste management. A cross-sectional design combined document review, field observations, and interviews with 156 households and 24 informants. Descriptive statistics characterized consumption patterns and service access. Impacts were assessed through litter hotspots, blocked drains, flood-prone points, and reported health risks. Households used five to six plastic bags daily, while collection coverage remained below 50%, sustaining persistent leakage. Findings reveal excessive reliance on plastics, shaped by technical, social, and institutional gaps, including weak segregation and limited pre-collection. Agoè-Nyivé 4, a fast-growing peri-urban commune within Greater Lomé, faces limited services but high consumption, making it a relevant case for rapidly growing municipalities. Yet the population often adopts counterproductive practices, hampering responsible waste management. A policy mix is outlined: expanding pre-collection and door-to-door services, integrating informal collectors, and targeted community sensitization. Without urgent interventions, plastic leakage will intensify environmental degradation, flooding, and health risks. The study recommends integrated policy measures to curb single-use dependence and foster a local circular economy.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Cellulose-Based Biopolymers from Banana Pseudostem Waste: Innovations for Sustainable Bioplastics
by
Alice Waithaka, Sofia Plakantonaki, Kyriaki Kiskira, Ann W. Mburu, Ioannis Chronis, Georgios Zakynthinos, John Githaiga and Georgios Priniotakis
Waste 2025, 3(4), 37; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3040037 - 25 Oct 2025
Cited by 3
Abstract
Plastic materials are widely used for packaging due to their versatility and availability. Global production, mainly from petrochemicals, is estimated at 380 million tons, increasing annually by 4%. Packaging plastics have the shortest lifespan and contribute significantly to environmental pollution. Current production, use,
[...] Read more.
Plastic materials are widely used for packaging due to their versatility and availability. Global production, mainly from petrochemicals, is estimated at 380 million tons, increasing annually by 4%. Packaging plastics have the shortest lifespan and contribute significantly to environmental pollution. Current production, use, and disposal of these plastics harm the environment, hu-mans, and ecosystems. Microplastics, (plastics particles ranging from 1 µm to 5 mm) formed through degradation, accumulate in ecosystems and the human body, including the brain. Bioplastics and biodegradable polymers from biological sources are a sustainable alternative; however, most production still relies on food crops, raising concerns about food security and sustainability. Utilizing organic wastes reduces production costs, lessens pressure on food systems, and supports waste management efforts. Cellulose, an abundant natural polymer, offers strong potential due to biodegradability, availability, and mechanical properties. This review explores extracting cellulose from banana pseudostem waste for packaging, high-lighting extraction and conversion methods and characterization via FTIR, TGA, SEM, XRD, and mechanical testing. FTIR confirmed the effective removal of lignin and hemicellulose, XRD revealed increased crystallinity corresponding to Type I cellulose, SEM showed a roughened fiber surface after alkaline treatment, and TGA indicated high thermal stability up to 250 °C. The goal is eco-friendly packaging by promoting agrowaste use. Further research should improve performance and scalability of cellulose-based bioplastics to meet industry needs and compete effectively with conventional plastics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Agri-Food Wastes and Biomass Valorization—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
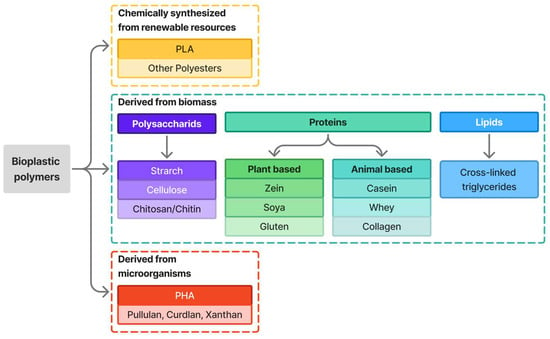
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Life Cycle Assessment of Reconditioned Guardrail Beams
by
Daniel Mattos, Joaquim C. G. Esteves da Silva and Luis Pinto da Silva
Waste 2025, 3(4), 36; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3040036 - 22 Oct 2025
Abstract
Steel consumption in the construction sector is one of the main contributors to global greenhouse gas emissions. Therefore, developing processes for the reuse of steel-based products with lower environmental impacts is essential for the sustainability of the construction sector. One example is the
[...] Read more.
Steel consumption in the construction sector is one of the main contributors to global greenhouse gas emissions. Therefore, developing processes for the reuse of steel-based products with lower environmental impacts is essential for the sustainability of the construction sector. One example is the reuse of metal road guardrail beams on highways. This study investigated the environmental sustainability of a reconditioning process for such beams, instead of using new guardrails. The environmental impacts of the process were studied and compared with the impacts of the traditional production process using a Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) approach. This study revealed that most of the impacts of the reconditioning process derive from the use of electricity. The comparison with the traditional beam production process revealed that when primary raw materials are replaced by reused raw materials, the environmental impacts associated with the production process decrease significantly. Of the 19 impact indicators assessed, 18 were lower, and 17 had a drop of more than 90 percent compared to the traditional production process. The results indicate that the reconditioning process has the potential to significantly reduce environmental impacts by avoiding the consumption and transportation of primary raw materials, which were identified as the main sources of impacts in the traditional production process, as well as minimizing waste generation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Use of Waste Materials in Construction Industry)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Physico-Mechanical Properties of an Aluminosilicate Refractory Castable Obtained After Chamotte Waste Recycling by Firing Method
by
Leonel Díaz-Tato, Jesús Fernando López-Perales, Yadira González-Carranza, José Eulalio Contreras de León and Edén Amaral Rodríguez-Castellanos
Waste 2025, 3(4), 35; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3040035 - 17 Oct 2025
Cited by 4
Abstract
Developing sustainable ceramic formulations that integrate industrial by-products addresses the high energy and raw material demands of refractory manufacturing while advancing circular economy goals. This study investigates the recycling of chamotte waste from rejected fired electrical porcelain as a partial substitute (5 and
[...] Read more.
Developing sustainable ceramic formulations that integrate industrial by-products addresses the high energy and raw material demands of refractory manufacturing while advancing circular economy goals. This study investigates the recycling of chamotte waste from rejected fired electrical porcelain as a partial substitute (5 and 10 wt.%) for flint clay in aluminosilicate refractory castables. Samples were fired at 110, 815, 1050, and 1400 °C and evaluated for bulk density, apparent porosity, cold crushing strength, and flexural strength. Microstructural and mineralogical changes were analyzed by SEM and XRD. Incorporating 10 wt.% chamotte waste fostered an in situ mullite-reinforced microstructure, enhancing mechanical strength (58 MPa—CCS, 18.8 MPa—MOR) and lowering porosity (24.4%), demonstrating chamotte’s dual role as recycled raw material and reinforcement phase for densification and durability. These properties matched or surpassed those of the conventional formulation, with strength improvements of up to 44%. The findings demonstrate that high-temperature industrial waste can be effectively valorized in advanced refractories, reducing reliance on virgin raw materials, diverting waste from landfills, and promoting industrial symbiosis within the ceramics and metallurgical sectors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Circular Economy in Interdisciplinary Perspective: Valorization of Raw Materials, Sustainable Products, and Pro-Ecological Industrial Developments)
►▼
Show Figures
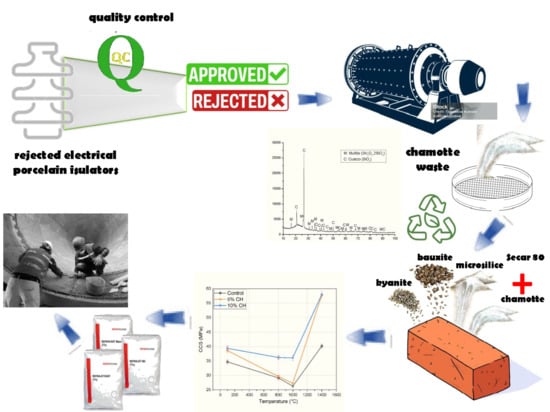
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Impact on the Rheological Properties and Amino Acid Compositions of the Industrial Evaporation of Waste Vinasse in the Production of Nutritional Supplements for Livestock
by
Nayeli Gutiérrez-Casiano, Cesar Antonio Ortíz-Sánchez, Karla Díaz-Castellanos, Luis Antonio Velázquez-Herrera, Solmaría Mandi Pérez-Guzmán and Eduardo Hernández-Aguilar
Waste 2025, 3(4), 34; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3040034 - 2 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Vinasse a byproduct of ethanol manufacturing, is a challenge for ethanol producers which possesses a high organic content that presents a considerable environmental threat. This complicates its management and treatment utilizing standard technologies like anaerobic digestion. This residue contains a substantial quantity of
[...] Read more.
Vinasse a byproduct of ethanol manufacturing, is a challenge for ethanol producers which possesses a high organic content that presents a considerable environmental threat. This complicates its management and treatment utilizing standard technologies like anaerobic digestion. This residue contains a substantial quantity of dead and lysed yeast cells, which can function as a protein source for livestock’s nutritional needs. The application of multi-effect evaporation enhances the characteristics of this residue by increasing protein concentration, reducing volume, and minimizing water content. This study examines the impact of the five-effect evaporation procedure on vinasse waste, focusing on its rheological properties and the concentrations of proteins, amino acids, RNA, and DNA. This study aims to assess the thermal impacts linked to the evaporation process. The findings of the one-way statistical analysis demonstrate that the five evaporation effects are relevant in the utilization of waste as feed for livestock. The substance has a viscosity of 0.933 Pa s, comprising 6.3 g/100 g of crude protein, 4.08 g/100 g of amino acids, 0.1158 g/L of DNA, and 0.1031 g/L of RNA.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Industrial Food Waste Screening in Emilia-Romagna and the Conceptual Design of a Novel Process for Biomethane Production
by
Antonio Conversano, Samuele Alemanno, Davide Sogni and Daniele Di Bona
Waste 2025, 3(4), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3040033 - 30 Sep 2025
Abstract
The REPowerEU plan is aimed at a target of 35 bcm of biomethane annually by 2030, up from 4 bcm in 2023, requiring about EUR 37 billion in investment. Food waste is identified as a key feedstock, characterized by discrete homogeneity, although its
[...] Read more.
The REPowerEU plan is aimed at a target of 35 bcm of biomethane annually by 2030, up from 4 bcm in 2023, requiring about EUR 37 billion in investment. Food waste is identified as a key feedstock, characterized by discrete homogeneity, although its availability may vary seasonally. In Italy, the Emilia-Romagna region generates approximately 450 kt/y of industrial waste from the food and beverage sector, primarily originating from meat processing (NACE 10.1), fruit and vegetable processing (NACE 10.3), and the manufacture of vegetable and animal oils and fats (NACE 10.4). Of this amount, food and beverage processing waste (EWC 02) accounts for about 302 kt from NACE 10 (food, year 2019) and 14 kt from NACE 11 (beverage, year 2019). This study provides a comprehensive screening of waste streams generated by the local food and beverage industry in Emilia-Romagna, evaluating the number of enterprises, their value added, and recorded waste production. The screening led to the identification of suitable streams for further valorization strategies: a total of ~93 kt/y was selected for the preliminary conceptual design of an integrated process combining anaerobic digestion with hydrothermal treatment, aimed at supporting national biomethane production targets while maximizing material recovery through hydrochar production. Preliminary estimations indicate that the proposed process may achieve a biochemical methane potential of approximately 0.23 Nm3/kgVS, along with a hydrochar yield of about 130 kg/twaste.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Trends in Liquid and Solid Effluent Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mechanical Performance and Durability of Concretes with Partial Replacement of Natural Aggregates by Construction and Demolition Waste
by
Thamires Alves da Silveira, Rafaella dos Passos Nörnberg, Marcelo Subtil Santi, Renata Rabassa Morales, Alessandra Buss Tessaro, Hebert Luis Rosseto, Rafael de Avila Delucis and Guilherme Hoehr Trindade
Waste 2025, 3(4), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3040032 - 30 Sep 2025
Abstract
This study investigated the mechanical performance and durability of concretes produced with varying proportions of recycled coarse aggregate from construction and demolition waste (CDW), ranging from 0% to 100% replacement of natural coarse aggregate, using recycled aggregates derived from crushed concrete and mortar
[...] Read more.
This study investigated the mechanical performance and durability of concretes produced with varying proportions of recycled coarse aggregate from construction and demolition waste (CDW), ranging from 0% to 100% replacement of natural coarse aggregate, using recycled aggregates derived from crushed concrete and mortar debris, characterized by lower density and high water absorption (~9%) compared to natural aggregates. A key contribution of this research lies in the inclusion of intermediate replacement levels (20%, 25%, 45%, 50%, and 65%), which are less explored in the literature and allow a more refined identification of performance thresholds. Fresh-state parameters (slump), axial compressive strength (7 and 28 days), total immersion water absorption, sorptivity, and chloride ion penetration depth (after 90 days of immersion in a 3.5% NaCl solution) were evaluated. The results indicate that, up to 50% CDW content, the concrete maintains slump (≥94 mm), characteristic strength (≥37.2 MPa at 28 days), and chloride penetration (≤14.1 mm) within the limits for moderate exposure conditions, in accordance with ABNT: NBR 6118. Water absorption doubled from 4.5% (0% CDW) to 9.5% (100% CDW), reflecting the higher porosity and adhered mortar on the recycled aggregate, which necessitates adjustments to the water–cement ratio and SSD pre-conditioning to preserve workability and minimize sorptivity. Concretes with more than 65% CDW exhibited chloride penetration depths exceeding 15 mm, potentially compromising durability without additional mitigation. The judicious incorporation of CDW, combined with optimized mix design practices and the use of supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs), demonstrates technical viability for reducing environmental impacts without significantly impairing the structural performance or service life of the concrete.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Use of Waste Materials in Construction Industry)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Characterisation and Fertiliser Potential of Mechanically Dewatered Faecal Sludge from Anaerobic Digestion
by
Dennis Ofori-Amanfo, Eugene Appiah-Effah, Barbara Gyapong-Korsah, Esi Awuah, Helen M. K. Essandoh, Miriam Appiah-Brempong and Issahaku Ahmed
Waste 2025, 3(4), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3040031 - 29 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
While mechanical dewatering is widely used in faecal sludge treatment, the agricultural potential of mechanically dewatered faecal sludge (MDFS) combined with anaerobic digestion (AD) remains underexplored, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa where nutrient recovery is critical for food security. This study provides the first
[...] Read more.
While mechanical dewatering is widely used in faecal sludge treatment, the agricultural potential of mechanically dewatered faecal sludge (MDFS) combined with anaerobic digestion (AD) remains underexplored, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa where nutrient recovery is critical for food security. This study provides the first comprehensive characterisation of MDFS from Ghana’s largest treatment facility and evaluates anaerobic digestion effectiveness for agricultural application. Over six months, 182 composite MDFS samples from Lavender Hill Faecal Treatment Plant were analysed for physicochemical properties, nutrients, heavy metals, and microbial contaminants before and after AD treatment. MDFS demonstrated exceptional nutrient density, with total nitrogen (2141.05 mg/kg), phosphorus (190.08 mg/kg), and potassium (4434.88 mg/kg) concentrations comparable to commercial organic fertilisers. AD achieved significant pathogen reduction, decreasing total coliforms from 148,808.70 to 493.33 cfu/100 g (p < 0.001) and Ascaris lumbricoides eggs from 12.08 to 3.33 eggs/L, while maintaining nutrient integrity and keeping heavy metals within safe agricultural limits. Statistical modelling revealed a significant correlation between treatment duration and pathogen reduction efficiency. Despite substantial improvements, treated MDFS still exceeded some regulatory thresholds, indicating a need for complementary post-treatment strategies. This research establishes AD as an effective primary treatment for converting MDFS into a nutrient-rich organic fertiliser, supporting circular economy principles in urban sanitation systems and providing a sustainable pathway for agricultural nutrient recovery in resource-constrained settings.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Trichoderma harzianum Enzyme Production in Stirred Solid-State Bioreactors as a Strategy for Valorizing Water Hyacinth
by
Nohemi López-Ramírez, Ernesto Favela-Torres, Tania Volke-Sepúlveda and Fernando Méndez-González
Waste 2025, 3(4), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3040030 - 25 Sep 2025
Abstract
Water hyacinth is an invasive weed that can valorize through the production of hydrolytic enzymes via solid-state culture. This study explores the application of Trichoderma harzianum in producing xylanases and endoglucanases on water hyacinth beds. Laboratory-scale packed-bed column bioreactors (PBCBs) with a capacity
[...] Read more.
Water hyacinth is an invasive weed that can valorize through the production of hydrolytic enzymes via solid-state culture. This study explores the application of Trichoderma harzianum in producing xylanases and endoglucanases on water hyacinth beds. Laboratory-scale packed-bed column bioreactors (PBCBs) with a capacity of 8 grams of dry mass (gdm) were used to evaluate the effects of temperature (28–36 °C) and initial moisture content (65–80%) on microbial growth and enzyme production. High yields of biomass and enzymes were produced at 30 °C. Moreover, xylanase activity was enhanced in cultures with a moisture content of 65% (~71.24 U/gdm), and endoglucanase activity at 75–80% moisture (~20.13 U/gdm). The operational conditions identified for xylanase production were applied to 6 L bench-scale cross-flow internally stirred bioreactors, packed to 40% capacity with 450 gdm. Two stirring regimes were tested: intermittent and continuous. The results showed that continuous stirring promotes both microbial growth and xylanase activity. In fact, xylanase activity in continuous stirring conditions was comparable to that achieved in PBCBs. Consequently, continuous stirring enables a 56-fold increase in bioreactor capacity without compromising xylanase production. The approaches developed in this study can support the design of large-scale bioprocesses for the valorization of water hyacinth.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Circular Economy in Interdisciplinary Perspective: Valorization of Raw Materials, Sustainable Products, and Pro-Ecological Industrial Developments)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Transforming Waste to Water Filters: A Mini-Review of Ceramic Membranes from Upcycled Materials
by
Asma Nouira, Mabrouk Ben Hamden, Mouna Sayehi and Imene Bekri-Abbes
Waste 2025, 3(3), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3030029 - 8 Sep 2025
Cited by 2
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The escalating global water crisis, coupled with the unsustainable accumulation of industrial and urban waste, demands innovative solutions that align with circular economy principles. This review explores the transformative potential of waste-derived ceramic membranes as a sustainable strategy for water purification, simultaneously addressing
[...] Read more.
The escalating global water crisis, coupled with the unsustainable accumulation of industrial and urban waste, demands innovative solutions that align with circular economy principles. This review explores the transformative potential of waste-derived ceramic membranes as a sustainable strategy for water purification, simultaneously addressing waste valorization and clean water scarcity. Ceramic membranes, traditionally fabricated from high-purity inorganic materials, are renowned for their superior chemical resistance, thermal stability, and durability. Recent advances demonstrate that industrial byproducts, such as red mud, coal fly ash, blast furnace slag, coal gangue, and kiln roller waste, can be effectively repurposed into cost-effective, high-performance filtration materials. This paper critically examines fabrication techniques, material properties, and performance metrics of waste-derived ceramic membranes. By transforming industrial waste into functional filtration materials, this approach not only mitigates environmental pollution but also contributes to sustainable water security.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Energy Efficiency and Waste Reduction Through Maintenance Optimization: A Case Study in the Pharmaceutical Industry
by
Nuno Soares Domingues and João Patrício
Waste 2025, 3(3), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3030028 - 21 Aug 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The global rise in population, increased life expectancy, and heightened international mobility have escalated disease prevalence and pharmaceutical demand. This growth intensifies energy consumption and chemical waste production within the pharmaceutical industry, challenging environmental sustainability and operational efficiency. Chromatography, a vital analytical technique
[...] Read more.
The global rise in population, increased life expectancy, and heightened international mobility have escalated disease prevalence and pharmaceutical demand. This growth intensifies energy consumption and chemical waste production within the pharmaceutical industry, challenging environmental sustainability and operational efficiency. Chromatography, a vital analytical technique for ensuring product quality and regulatory compliance, can also contribute to material waste and energy inefficiencies if not properly maintained and optimized. This study applies Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to chromatographic equipment maintenance within Hovione’s Engineering and Maintenance Department, aiming to identify and mitigate failure risks. By integrating environmental metrics derived from Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) into the FMEA framework, a hybrid risk evaluation tool was developed that prioritizes both equipment reliability and sustainability performance. The findings demonstrate how this integrated approach reduces unplanned downtime, lowers solvent waste, and improves energy efficiency. Additionally, the study proposes a conceptual dashboard to support proactive, sustainability-driven asset management in pharmaceutical laboratories. By bridging reliability engineering and environmental sustainability, this research offers a strategic model for optimizing resource use, minimizing chemical waste, and enhancing long-term operational resilience in regulated pharmaceutical environments.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Role of E-Waste in Sustainable Mineral Resource Management
by
Dina Mohamed, Adham Fayad, Abdel-Mohsen O. Mohamed and Moza T. Al Nahyan
Waste 2025, 3(3), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3030027 - 19 Aug 2025
Cited by 3
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper analyses the role of electronic waste (E-waste) as a secondary source of critical and precious minerals, addressing the challenges and opportunities in transitioning towards a circular economy (CE) for electronics. The surging global demand for these essential materials, driven by technological
[...] Read more.
This paper analyses the role of electronic waste (E-waste) as a secondary source of critical and precious minerals, addressing the challenges and opportunities in transitioning towards a circular economy (CE) for electronics. The surging global demand for these essential materials, driven by technological advancements and renewable energy infrastructure, necessitates alternative supply strategies due to the depletion of natural reserves and the environmental degradation associated with primary mining. E-waste contains a rich concentration of valuable metals, such as gold, silver, and platinum, making its recovery a promising solution aligned with CE principles, which can mitigate environmental impacts and ensure long-term material availability. This paper examines the environmental, economic, and technological aspects of E-waste recovery, focusing on core processes such as physical and mechanical separation, pyrometallurgical, hydrometallurgical, bio-metallurgical, and electrochemical techniques. It explores innovative strategies to improve material recovery efficiency and sustainability, with consideration of evolving regulatory frameworks, technological advancements, and stakeholder engagement. The analysis highlights that e-waste, particularly printed circuit boards, can contain 40–800 times more gold than mined ore, with 1000–3000 g of gold per tonne compared to 5–10 g per tonne in traditional ores. Recovery costs using advanced E-waste recycling technologies range between $10,000–$20,000 USD per kilogram of gold, significantly lower than the $30,000–$50,000 USD per kilogram in primary mining. Globally, over 50 million tonnes of E-waste are generated annually, yet less than 20% is formally recycled. Efficient recycling methods can recover up to 95% of base and precious metals under optimized conditions. The paper argues that E-waste recycling presents a viable pathway to conserve critical raw materials, reduce environmental degradation, and enhance circular economic resilience. However, it also emphasizes persistent challenges—including high initial investment, technological limitations in developing regions, and regulatory fragmentation—that must be addressed for scalable adoption.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Energies, Materials, Recycling, Sustainability, Waste
Circular Economy in Interdisciplinary Perspective: Valorization of Raw Materials, Sustainable Products, and Pro-Ecological Industrial Developments
Topic Editors: Krzysztof Pielichowski, Piotr Duda, Michał Łach, Tomasz Mariusz Majka, Tomasz Zdeb, Giovanni De FeoDeadline: 30 March 2026
Topic in
Catalysts, Energies, Processes, Sustainability, Waste, Water, Molecules, Nanomaterials
New Research on Waste Treatment, Disposal and Valorization
Topic Editors: Antonella Angelini, Carlo PastoreDeadline: 30 April 2026
Topic in
Microorganisms, Pollutants, Processes, Sustainability, Recycling, Waste, Microbiology Research
The Role of Microorganisms in Waste Treatment
Topic Editors: Zuotao Zhang, Tan Chen, Bing ZhangDeadline: 31 May 2026
Topic in
Energies, Pollutants, Recycling, Sustainability, Toxics, Waste
Recent Advances in Municipal Solid Waste Management and Technology
Topic Editors: Chengyun Zhou, Wenjun Wang, Binbin ShaoDeadline: 30 June 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Waste
The Role of Recycling in Reducing Microplastic Pollution in Textile Industry
Guest Editors: Maria Râpă, Carmen GaidauDeadline: 30 April 2026
Special Issue in
Waste
Feature Papers in Treatment of Waste Materials Using Metallurgical Unit Operations
Guest Editor: Srecko StopicDeadline: 31 May 2026
Special Issue in
Waste
Advances in Waste Bioprocessing and Fermentation Technologies
Guest Editors: José Agustín Tapia Hernández, Francisco Rodríguez-FélixDeadline: 30 September 2026
Special Issue in
Waste
Towards a Circular Economy: Value-Added Products from Waste
Guest Editor: Catherine MulliganDeadline: 30 November 2026







