Journal Description
Nitrogen
Nitrogen
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on the whole field of nitrogen research published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access—free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Agricultural and Biological Sciences (miscellaneous))
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer-review and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Journal Cluster of Environmental Science: Sustainability, Land, Clean Technologies, Environments, Nitrogen, Recycling, Urban Science, Safety, Air, Waste and Aerobiology.
Impact Factor:
2.3 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.1 (2024)
Latest Articles
Nitrogen Regulates the Concentration and Accumulation of Macronutrients in Vegetative and Reproductive Organs of Mexican Marigold (Tagetes erecta L.)
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010026 - 27 Feb 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Nitrogen (N) is a key macronutrient that influences the uptake and partitioning of other essential elements in plants. In this research, we evaluated the effect of different N concentrations in the nutrient solution (0, 4.2, 8.4, and 12.6 mg L−1) during
[...] Read more.
Nitrogen (N) is a key macronutrient that influences the uptake and partitioning of other essential elements in plants. In this research, we evaluated the effect of different N concentrations in the nutrient solution (0, 4.2, 8.4, and 12.6 mg L−1) during the flowering stage on the concentration and accumulation of macronutrients in organs of Mexican marigold (Tagetes erecta L.) ‘Inca’. After 40 days of treatment, plants were separated into leaves, flowers, stems, and roots to determine the concentrations of N, P, K, Ca, Mg, and S, as well as their accumulation based on dry biomass. Nitrogen supply significantly affected dry biomass production and its partitioning among organs, promoting biomass allocation to leaves and flowers while reducing relative root biomass at higher N concentrations. Nitrogen concentrations and accumulation increased in leaves, stems, and flowers as N supply increased, whereas an inverse relationship was observed in roots. When applying 8.4 and 12.6 mg N L−1, phosphorus displayed enhanced concentrations in leaves and stems, although root tissues did not change the concentration of this nutrient. When N was supplied at up to 8.4 mg L−1, the concentration of potassium rose in aboveground organs but decreased at the highest dose, while its accumulation in roots was reduced under high N concentrations tested. Calcium exhibited greater accumulation in the aboveground organs, particularly at 12.6 mg N L−1. Magnesium concentration and accumulation increased in aboveground organs with increasing N supply, whereas its accumulation in roots decreased. The highest concentrations of sulfur in leaves and stems were observed at 8.4 mg N L−1, and its accumulation in the aboveground organs tended to stabilize at the highest dose. Effect size analysis (partial ηp2) revealed that N supply explained a large proportion of the variance in macronutrient concentration and accumulation in aerial organs, whereas responses in roots were generally weaker and nutrient specific. Overall, our data indicate that intermediate N levels (8.4 mg L−1) boost a more efficient nutritional balance in the aboveground organs, while the highest dose predominantly enhances Ca and Mg accumulation. Understanding how these plants respond to nitrogen can help improve the quality of Mexican marigold crops and make better use of fertilizers.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Vertical Patterns and Influencing Factors of Soil Stoichiometry on Near-Naturally Restored Lands: A Case Study from the Loess Plateau, China
by
Yugang Guo, Tianyu Hao, Xiang Fan, Jianhao Song, Yankai Feng, Jingyue Xiao, Yuefeng Xu, Chuxin Zhu, Chunjuan Lyu, Zhongke Bai and Xinrui Xu
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010025 - 26 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
China has implemented extensive land restoration programs and now leads the world in artificial forest area. However, such plantations often face degradation, largely due to soil nutrient deficiency. In contrast, near-natural restoration tends to result in better soil quality, ecosystem integrity, and stability.
[...] Read more.
China has implemented extensive land restoration programs and now leads the world in artificial forest area. However, such plantations often face degradation, largely due to soil nutrient deficiency. In contrast, near-natural restoration tends to result in better soil quality, ecosystem integrity, and stability. This study focuses on three near-naturally restored sites on the Loess Plateau—a critical part of China’s National Ecological Security Barrier System, which has undergone substantial ecological restoration in recent decades. Using soil stoichiometry to assess nutrient balance and land sustainability, we investigated two forest types (Betula platyphylla, BP; Larix principis-rupprechtii, LP) and a mixed shrubland (Ostryopsis davidiana and Cotoneaster multiflorus, OD–CM). Soil profiles were sampled at 20 cm intervals from the surface to bedrock. We measured soil carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) contents, along with key environmental factors. The results show the following: (1) The two forest lands exhibited similar C and N levels, which were 1.23–1.26 and 1.40–1.51 times higher, respectively, than those in the shrubland. (2) Lower C/N (BP: 25.05; LP: 23.46) and higher N/P (BP: 4.83; LP: 5.00) in the forest lands indicated lower nitrogen limitation versus the shrubland (C/N: 28.55; N/P: 3.44). (3) Key influencing factors varied across land restoration types, indicating that the vegetation community’s composition mediates nutrient cycling through nutrient uptake and litter input. (4) Relative to plantations in the same region, near-naturally restored lands had 3.47–5.64 times higher C content and 1.51–2.51 times higher N content. Moreover, near-natural communities exhibited higher C/N (21.68–30.56) and C/P (85.92–132.97) compared to plantations (C/N: 8.8–13.1; C/P: 9.16–31.2), reflecting more efficient nitrogen and phosphorus utilization. Thus, near-natural land restoration enhances soil carbon sequestration, nitrogen fixation, and nutrient use efficiency on the Loess Plateau, supporting its promotion as a superior land management strategy for enhancing land sustainability and ecosystem services in this area.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Nitrogen Application and Planting Dates on Growth, Forage Yield and Quality of Maize
by
Asmaa A. Mohamed, Mohamed Allam, Roberto Mancinelli, Emanuele Radicetti and Bahy R. Bakheit
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010024 - 17 Feb 2026
Abstract
Optimizing nitrogen fertilization and planting date is essential for improving forage maize productivity under semi-arid conditions. This study evaluated the effects of nitrogen application rates and planting dates on growth, forage yield, and quality of maize (Zea mays L.) in Upper Egypt.
[...] Read more.
Optimizing nitrogen fertilization and planting date is essential for improving forage maize productivity under semi-arid conditions. This study evaluated the effects of nitrogen application rates and planting dates on growth, forage yield, and quality of maize (Zea mays L.) in Upper Egypt. A two-year field experiment (2024–2025) was conducted at the Experimental Farm of Assiut University using a strip-plot design arranged in a randomized complete block design with three replications. Four planting dates (15 April, 15 May, 15 June, and 15 July) were assigned horizontally, while three nitrogen rates (167, 238, and 309 kg N ha−1) were applied vertically. Growth traits, fresh and dry forage yield, dry matter percentage, crude protein content, and protein yield were recorded at 60 days after sowing. Results showed that planting date, nitrogen rate, and their interaction significantly affected most measured traits in both seasons. Sowing in mid-May consistently produced the highest plant height, chlorophyll content, fresh and dry forage yield, and protein yield. Increasing nitrogen application enhanced biomass production and forage quality, with the highest values generally recorded at 309 kg N ha−1. The strongest yield response to nitrogen occurred when maize was sown at the optimal planting date, indicating that nitrogen utilization was closely linked to favorable environmental conditions. Phenotypic correlation and multivariate analyses revealed strong associations among vegetative growth traits and forage yield, with a single dominant factor explaining more than 91% of the variation in yield-related traits across seasons. Overall, the results demonstrate that synchronizing planting date with appropriate nitrogen fertilization is critical for maximizing maize forage yield and quality under semi-arid conditions. Mid-May sowing combined with adequate nitrogen supply represents an effective management strategy for forage maize production in Upper Egypt, while further research is needed to optimize nitrogen-use efficiency and long-term sustainability.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Quantification of B-Values and Symbiotic Efficiency of Bradyrhizobium-Inoculated Soybean Varieties Using the δ15N Natural Abundance Method
by
Haimanot Beruk, Tarekegn Yoseph, Georg Cadisch and Tewodros Ayalew
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010023 - 14 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Biological nitrogen fixation (BNF) is crucial for enhancing soybean productivity while reducing reliance on mineral nitrogen fertilizers. The accurate estimation of BNF via the δ15N natural abundance method depends on reliable B-values, which represent plants that derive all their nitrogen from
[...] Read more.
Biological nitrogen fixation (BNF) is crucial for enhancing soybean productivity while reducing reliance on mineral nitrogen fertilizers. The accurate estimation of BNF via the δ15N natural abundance method depends on reliable B-values, which represent plants that derive all their nitrogen from fixation. This study aimed to assess the B-values and symbiotic efficiency of Bradyrhizobium-inoculated soybean varieties using δ15N natural abundance techniques. Eight strains and five soybean varieties were evaluated in sterilized sand culture using a factorial completely randomized design under lath-house conditions. Plants were analyzed for δ15N, shoot N concentration, shoot N content, and symbiotic efficiency (SE). The applied treatments showed highly significant effects with strong interactions, reflecting substantial genotypic variation in symbiotic performance. Strain SD-53 produced the lowest δ15N values (−0.24 to 0.14‰) and the highest SE, with several strain–variety combinations surpassing N-fertilized controls. Shoot N concentration and content ranged from 0.96–3.16% and 9.90–52.73 mg plant−1, respectively, and SE varied from 29.07 to 136.29%. δ15N showed strong negative correlations with SE and plant N traits. The study identified SD-53 as a promising inoculant candidate and generated the first regional soybean B-values (−0.24 to 0.14‰ for each tested variety and a mean of −0.08 ± 0.14‰) for Ethiopia. These values provide an important baseline for %Ndfa calculations and support future field validation and inoculant formulation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessing the Impact of Dietary and Feed Self-Sufficiency Changes on Nitrogen Load and Water Quality in the Kasumigaura Watershed, Japan
by
Nina Hodalova and Koshi Yoshida
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010022 - 12 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In recent years, dietary changes towards reducing animal-based proteins was recognized as a nitrogen pollution-mitigating strategy. This is because producing animal protein generates higher nitrogen emissions compared to its plant-based alternatives. In Japan, there is a switch towards an animal-based diet, potentially leading
[...] Read more.
In recent years, dietary changes towards reducing animal-based proteins was recognized as a nitrogen pollution-mitigating strategy. This is because producing animal protein generates higher nitrogen emissions compared to its plant-based alternatives. In Japan, there is a switch towards an animal-based diet, potentially leading to degraded water quality. While national-scale studies are common, watershed-level scale dietary changes are not researched, even though nitrogen pollution is often localized. This study aims to evaluate whether dietary and feed self-sufficiency changes can reduce nitrogen load and improve water quality in the Kasumigaura watershed. Firstly, nitrogen load was quantified and spatially distributed. Then, the estimated nitrogen concentration was compared with observed data. Finally, the impact of dietary and feed self-sufficiency changes on nitrogen load and water quality was assessed. Results estimated that nitrogen loading for year 2020 was 4403 tons/N/year, correlating with previous research. Results further showed that switch from livestock to legume protein would significantly improve water quality, up to 0.27 mg N/L. On the other hand, increasing feed self-sufficiency would negatively affect the water quality, up to 0.32 mg N/L. The results emphasize the importance of dietary patterns in mitigating nitrogen pollution. This method can be generalized on other watersheds.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Preceding Crops and Fertilization Strategies on Wheat Performance and Disease Dynamics
by
Alina Șimon, Ovidiu Adrian Ceclan, Felicia Chețan, Alin Popa, Marius Bărdaș, Laura Șopterean and Ana-Maria Vălean
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010021 - 9 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Mineral fertilization is crucial for maximizing wheat yield, ensuring optimal nitrogen and phosphorus supply according to plant development, pedoclimatic conditions, and previous crops, with a balanced N:P ratio being decisive for productivity. This study, conducted at ARDS Turda during 2020/2021–2024/2025, evaluated the long-term
[...] Read more.
Mineral fertilization is crucial for maximizing wheat yield, ensuring optimal nitrogen and phosphorus supply according to plant development, pedoclimatic conditions, and previous crops, with a balanced N:P ratio being decisive for productivity. This study, conducted at ARDS Turda during 2020/2021–2024/2025, evaluated the long-term effects of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization on the yield, grain protein content, and foliar disease incidence of winter wheat grown after maize and soybean. The experimental design was polyfactory, in randomized blocks, including 25 variants and 6 repetitions, according to the uninterrupted protocol used since 1967, winter wheat being cultivated after maize for grain and soybean. Phosphorus (0–160 kg P2O5 ha−1) was applied in autumn, while nitrogen (0–160 kg N ha−1 after maize and 0–120 kg N ha−1 after soybean) was split 50% in autumn and 50% in spring. Results indicate that wheat yield is strongly influenced by nitrogen–phosphorus interactions and climatic conditions, with nitrogen increasing yield by 450–2700 kg·ha−1 and maximum yields of 7600–7828 kg·ha−1 achieved at N120 with higher phosphorus rates. Grain protein content (14.96%) was high at N120 dose, while foliar disease incidence and severity were low at minimal fertilization and rose with intensified mineral nutrition.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Landscape Determinants of Nitrogen Leaching Risk: Mechanisms, Impacts, and Mitigation Strategies
by
Bonface O. Manono, Jacinta M. Kimiti and Damaris K. Musyoka
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010020 - 5 Feb 2026
Cited by 1
Abstract
Nitrogen leaching from land and farms is a major global issue that pollutes water, damages ecosystems, and accelerates climate change. This review synthesizes evidence from the literature on how interactions among landscape characteristics, sources of nitrogen input, and temporal dynamics shape leaching vulnerability.
[...] Read more.
Nitrogen leaching from land and farms is a major global issue that pollutes water, damages ecosystems, and accelerates climate change. This review synthesizes evidence from the literature on how interactions among landscape characteristics, sources of nitrogen input, and temporal dynamics shape leaching vulnerability. It identifies conditions under which nitrogen is most likely to be transported through soil systems into aquatic environments. This review reveals that leaching vulnerability is strongly conditioned by soil hydraulic properties and topographic position. Coarse-textured upland soils exhibit substantially greater nitrate mobilization than finer-textured, hydrologically buffered lowland soils. Fertilizer formulation and application timing further modulate loss potential, with late-season mineral nitrogen inputs disproportionately contributing to subsurface export relative to demand-synchronized applications. Most of the nitrogen leaching occurs outside the active growing period, when vegetative uptake is suppressed and drainage intensity is highest. Farmers can lower nitrate runoff by using targeted fertilization, cover crops, and nitrification inhibitors, while landscape-scale features like controlled drainage and vegetative buffers provide additional downstream filtration. The effectiveness of regulatory approaches is amplified when aligned with economic incentives and regionally calibrated nutrient thresholds. Advances in high-resolution observation platforms and process-based predictive tools offer new capacity for anticipatory management, although widespread deployment is limited by financial and institutional constraints. Collectively, these insights support the development of more targeted and sustainable nitrogen management strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nitrogen Uptake and Loss in Agroecosystems)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Abundance of Indigenous Soybean-Nodulating Rhizobia in Relation to Soil Properties and Cropping Patterns in a Midland Agro-Ecology of Southern Ethiopia
by
Haimanot Beruk and Tewodros Ayalew
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010019 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Estimating indigenous rhizobial populations is crucial for understanding soil rhizobia abundance, determining the potential need for inoculation, and evaluating the performance of introduced inoculant strains. However, in southern Ethiopia, information on the population abundance of soybean-nodulating rhizobia is limited. To address this gap,
[...] Read more.
Estimating indigenous rhizobial populations is crucial for understanding soil rhizobia abundance, determining the potential need for inoculation, and evaluating the performance of introduced inoculant strains. However, in southern Ethiopia, information on the population abundance of soybean-nodulating rhizobia is limited. To address this gap, the present study was conducted to evaluate the population abundance of indigenous soybean-nodulating rhizobia and to assess the influence of cropping history and soil properties on rhizobial abundance. The study was conducted across five sites suitable for soybean cultivation in southern Ethiopia: Arsi-Negelle, Boricha, Dore, Hawassa, and Wondo Genet. The study sites represented a range of cropping systems, including sole maize, sole tobacco, sole haricot bean, maize–potato intercropping, and crop rotation. Composite soil samples were collected from a depth of 0–20 cm, and rhizobial abundance was determined using the most probable number (MPN) technique. Indigenous rhizobial populations ranged from 0 to 1.7 × 101 cells g−1 of dry soil. Overall, the population levels were low, suggesting that inoculation with effective rhizobial strains would likely improve nodulation and biological nitrogen fixation. Relatively higher rhizobial population densities were observed at Arsi-Negelle under haricot bean cropping history. Statistically significant positive correlations were found between rhizobial abundance and cation exchange capacity, organic carbon, and organic matter. In general, native rhizobial populations across all study locations were below levels considered sufficient to support effective soybean nodulation and nitrogen fixation, indicating the need for inoculation to enhance soybean productivity in the study areas.
Full article
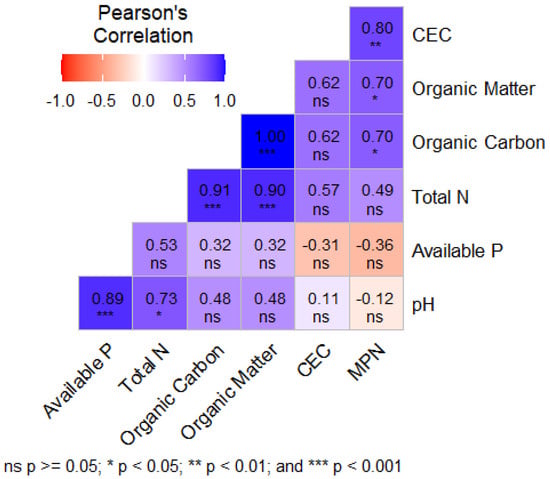
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Integrating Milk Protein Hydrolysate and Plasma-Activated Water as Alternative Nitrogen Inputs for Growth, Nutrition, and Postharvest Quality of Hydroponic Cos Lettuce Under Low Nutrient Supply
by
Aryanis Mutia Zahra, Apiradee Uthairatanakij, Natta Laohakunjit, Pongphen Jitareerat, Nattapon Kaisangsri and Arak Tira-Umphon
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010018 - 1 Feb 2026
Abstract
The application of plasma-activated water and biostimulants offers a sustainable approach to supporting plant growth under reduced-nutrient conditions by supplying bioavailable nitrogen. This study investigated the growth and postharvest performance of hydroponically grown cos lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) supplied with three Hoagland-based
[...] Read more.
The application of plasma-activated water and biostimulants offers a sustainable approach to supporting plant growth under reduced-nutrient conditions by supplying bioavailable nitrogen. This study investigated the growth and postharvest performance of hydroponically grown cos lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) supplied with three Hoagland-based nutrient treatments: half-strength solution prepared with tap water (HS), half-strength solution with plasma-activated water (HS+PAW), and half-strength solution with plasma-activated water containing 1 mL L−1 milk protein hydrolysate (HS+PAW+MPH). Plants treated with PAW, particularly those in the HS+PAW+MPH, exhibited increases in growth, biomass accumulation, and mineral composition, with reduced nitrate content compared to controls. At harvest, lettuce under HS+PAW+MPH exhibited nearly double fresh yield and enhanced dry matter, protein, lipid, phenolic, and flavonoid profiles as well as increased antioxidant capacity, indicating improved nitrogen utilization and nutritional quality under reduced nutrient input. Postharvest quality was evaluated by packing samples in polypropylene bags and storing them at 10 ± 1 °C and 95–98% relative humidity for 21 days. The HS+PAW+MPH treatment substantially suppressed respiration and production of ethylene, limited weight loss and color change, and better preserved pigments, bioactive compounds, and antioxidant stability compared to HS and HS+PAW, indicating HS+PAW+MPH as a sustainable nutrient management approach for hydroponic systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovative Nitrogen Management Strategies in Aquaponics, Hydroponics, Soilless, and Soil-Based Crop Systems for Sustainable Agriculture)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Validation of the Overseer Cropping Model for Estimating Nitrate Leaching Losses in Precision Agriculture
by
Raveendrakumaran Bawatharani, Miles Grafton and Paramsothy Jeyakumar
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010017 - 29 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The Overseer model is widely used in New Zealand as a precision-agriculture-related tool for estimating nitrate (NO3−) leaching losses in agricultural systems. This study evaluated the accuracy of the Overseer model in predicting nitrate (NO3−) leaching through
[...] Read more.
The Overseer model is widely used in New Zealand as a precision-agriculture-related tool for estimating nitrate (NO3−) leaching losses in agricultural systems. This study evaluated the accuracy of the Overseer model in predicting nitrate (NO3−) leaching through a two-year lysimeter experiment conducted at Woodhaven Gardens, New Zealand, under beetroot and pak choi cultivation. Seven distinct nitrogen (N) fertilizer treatments were applied to assess model performance. In year 1, Overseer overestimated NO3− leaching by an average of 45.2 kg N/ha (15.7%), and in year 2, the model overestimated by 35.2 kg N/ha (43.5%). A sensitivity analysis highlighted soil texture, impeded layer depth and crop residue incorporation as key drivers of leaching variability, underscoring the need for improved model calibration. Overseer performed reasonably well under lysimeter conditions, with a strong linear relationship (Pearson’s correlation coefficient r = 0.89, p < 0.0001) between measured and predicted values and explaining 77% of the variance (R2 = 0.77) in the observed data. The model predicted a baseline leaching loss of 39.4 kg N/ha/year even when measured losses were zero. Overseer demonstrates moderate reliability in predicting NO3− leaching under vegetable cropping systems but exhibits notable limitations in handling crop-specific N dynamics, soil hydrology, and fertilizer timing.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Coupling Effects of Water and Nitrogen on the Morphological Plasticity and Photosynthetic Physiology of Piptanthus nepalensis Seedlings: Implications for Ecological Restoration on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau
by
Yanying Han, Minghang Hu, Wenqiang Huang, Zheng Wu, Lingchen Tong, Shaobing Zhang and Yanhui Ye
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010016 - 29 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Water and nitrogen supply are key factors limiting the establishment of alpine plant seedlings and the efficiency of ecological restoration on the Tibetan Plateau. As an endemic shrub to Tibet, the morphological and physiological response mechanisms of Piptanthus nepalensis (Hook.) D. Don to
[...] Read more.
Water and nitrogen supply are key factors limiting the establishment of alpine plant seedlings and the efficiency of ecological restoration on the Tibetan Plateau. As an endemic shrub to Tibet, the morphological and physiological response mechanisms of Piptanthus nepalensis (Hook.) D. Don to coupled water and nitrogen stress remain poorly understood. This study employed a pot experiment with a completely randomized two-factor design, incorporating five water gradients (0–100% field capacity, FC) and five nitrogen levels (0–4 g·plant−1 urea). The aim was to elucidate the regulatory mechanisms of water/nitrogen coupling on Piptanthus nepalensis growth, physiology, and morphogenesis. The results indicated the following: (1) A significant water/nitrogen coupling effect was observed, with optimal water/nitrogen combinations producing pronounced synergistic effects. Principal component analysis (PCA) revealed that the first two axes cumulatively explained 99.32% of the morphological variation. The W3N3 treatment (40–60% FC water + 2 g·plant−1 nitrogen) exhibited optimal growth traits and maximum leaf elongation, establishing the optimal water and fertilizer management threshold for this species. (2) Confronted with two starkly contrasting stresses—drought (W4, W5) and waterlogging (W1)—plants adopted convergent “conservative” morphological adaptation strategies (significantly reduced leaf length and width) to lower metabolic expenditure. (3) Photosynthetic physiological analysis revealed that under extreme water deficiency (W5) or waterlogging (W1) stress, intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci) paradoxically increased, indicating a shift in photosynthetic suppression mechanisms from stomatal limitation to non-stomatal limitation (metabolic injury). (4) The Mantel Test confirmed that photosynthetic physiological traits significantly drove morphological trait variation (p < 0.001), establishing a close feedback loop between “physiological function and morphological structure”. Conclusions: Moderate water deficit (40–60% FC) combined with moderate nitrogen fertilization (2 g·plant−1) effectively alleviates non-stomatal limitation and releases morphological constraints, thereby promoting rapid growth in Piptanthus nepalensis. This study reveals the phenotypic plasticity and convergent adaptation mechanisms of Piptanthus nepalensis under water/nitrogen co-stress, providing precise water and fertilizer management guidelines for vegetation restoration in degraded ecosystems of Tibet.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Non-Destructive Estimation of Nitrogen and Crude Protein in Mombasa Grass Using Morphometry, Colorimetry, and Spectrophotometry
by
Rafael M. Amaral, Berman E. Espino, Floridalma E. M. Francisco, Oswaldo Navarrete and Carlomagno S. Castro
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010015 - 29 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Estimating nitrogen (N) and the corresponding crude protein (CP) content in forage crops is essential for optimizing fertilization and livestock nutrition. However, standard methods such as the Dumas and Kjeldahl techniques are destructive, costly, and impractical for field use in certain regions of
[...] Read more.
Estimating nitrogen (N) and the corresponding crude protein (CP) content in forage crops is essential for optimizing fertilization and livestock nutrition. However, standard methods such as the Dumas and Kjeldahl techniques are destructive, costly, and impractical for field use in certain regions of developing countries. This study evaluated four non-destructive approaches—morphometric measurements, Pantone® color scales, smartphone-based RGB analysis (ColorDetector app), and SPAD chlorophyll readings—for predicting N and CP in Megathyrsus maximus (Mombasa grass). A total of 120 samples were collected under three nitrogen fertilization levels and assessed using linear mixed-effects models with cross-validation. Morphometric variables showed poor performance (R2 < 0.01), indicating low correlation with nutrient content. Pantone-based RGB models provided slightly better predictions (R2 ≈ 0.30) but were limited by subjectivity and discrete data. SPAD-based models demonstrated moderate predictive accuracy (R2 ≈ 0.53; RMSE ≈ 0.46%). The highest accuracy was achieved with smartphone-derived RGB data, where full RGB models reached R2 = 0.60 and RMSE = 0.45%. Based on these results, a practical green color scale was developed from RGB values to support real-time, in-field nitrogen and crude protein assessment. This study highlights smartphone imaging as a scalable, low-cost, and accurate tool for non-destructive estimation of nitrogen and crude protein in tropical forages, offering an accessible alternative to laboratory methods for producers and field technicians.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessing the Performance of Bio-Based Nitrogen Fertilisers Under Salinity and Drought Stress in Spinach: A Preliminary Trial
by
Amrita Saju, Ivona Sigurnjak and Erik Meers
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010014 - 16 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Recently, the EU approved RENURE-criteria materials to be used as substitutes for synthetic N fertilisers. Several studies have been performed on the agronomic efficacy and potential environmental impacts of different bio-based fertilisers (BBFs) from biomass recovery, including the RENURE-criteria materials. But information is
[...] Read more.
Recently, the EU approved RENURE-criteria materials to be used as substitutes for synthetic N fertilisers. Several studies have been performed on the agronomic efficacy and potential environmental impacts of different bio-based fertilisers (BBFs) from biomass recovery, including the RENURE-criteria materials. But information is lacking about their effectiveness under abiotic stress conditions like salinity and drought. The predictions for climate change-induced increased drought and soil salinisation for the European soils have also increased, making it inevitable to understand BBF performance in these impending situations. Two RENURE-criteria top-priority materials (ammonium nitrate (AN) and ammonium sulphate (AS) and another commercially used BBF—an evaporator concentrate (CaE)) were evaluated in a pot trial growing spinach under salinity and drought stress with a reference ‘no stress’ condition to examine crop growth, nutrient uptake, and nitrogen fertiliser replacement value (NFRV). Agronomically, BBFs performed at par with the synthetic fertiliser (SF) under unstressed and salt-stressed conditions, whereas, under drought stress, BBFs outperformed the SF treatment. AS exhibited the highest yield and nutrient uptake, displaying an NFRV of 3.1 and 1.8 under no-stress and salt-stress conditions, respectively. Salt stress did not negatively impact the crops grown in this trial, potentially due to the higher potassium content in the system, which alleviated the possible negative impacts of high sodium. This study delves into the agronomic response, without evaluating crop physiological changes, and, hence, should be taken as a preliminary step into further investigation of observed elemental interactions (that could be potentially driving stress mitigation) while also examining the crop physiology during the duration of stress.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Nitrogen Dynamics and Use Efficiency in Pasture-Based Grazing Systems: A Synthesis of Ecological and Ruminant Nutrition Perspectives
by
Bashiri Iddy Muzzo
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010013 - 15 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Pasture-based ruminant systems link nitrogen (N) nutrition with ecosystem N cycling. Grazing ruminants convert fibrous forages into milk and meat but excrete 65 to 80% of ingested N, creating excreta hotspots that drive ammonia volatilization, nitrate leaching, and nitrous oxide (N2O)
[...] Read more.
Pasture-based ruminant systems link nitrogen (N) nutrition with ecosystem N cycling. Grazing ruminants convert fibrous forages into milk and meat but excrete 65 to 80% of ingested N, creating excreta hotspots that drive ammonia volatilization, nitrate leaching, and nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions. This review synthesizes ecological and ruminant nutrition evidence on N flows, emphasizing microbial processes, biological N2 fixation, plant diversity, and urine patch biogeochemistry, and evaluates strategies to improve N use efficiency (NUE). We examine rumen N metabolism in relation to microbial protein synthesis, urea recycling, and dietary factors including crude protein concentration, energy supply, forage composition, and plant secondary compounds that modulate protein degradability and microbial N capture, thereby influencing N partitioning among animal products, urine, and feces, as reflected in milk and blood urea N. We also examine how grazing patterns and excreta distribution, assessed with sensor technologies, modify N flows. Evidence indicates that integrated management combining dietary manipulation, forage diversity, targeted grazing, and decision tools can increase farm-gate NUE from 20–25% to over 30% while sustaining performance. Framing these processes within the global N cycle positions pasture-based ruminant systems as critical leverage points for aligning ruminant production with environmental and climate sustainability goals.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Impact of Soil Tillage Systems and Fertilization Strategies on Winter Wheat Yield Under the Variable Weather Conditions of the Transylvanian Plain
by
Felicia Chețan, Cornel Chețan, Alina Șimon, Ovidiu Adrian Ceclan, Diana Hirișcău, Raluca Rezi, Alin Popa, Marius Bărdaș, Camelia Urdă, Roxana Elena Călugăr, Paula Ioana Moraru and Teodor Rusu
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010012 - 15 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Agronomic systems that can guarantee consistent and sufficient crop yields must be developed and implemented in order to address the problems presented by climate change, especially the increase in average annual temperatures and the unequal distribution of precipitation. Over the course of five
[...] Read more.
Agronomic systems that can guarantee consistent and sufficient crop yields must be developed and implemented in order to address the problems presented by climate change, especially the increase in average annual temperatures and the unequal distribution of precipitation. Over the course of five successive growing seasons (2019–2024), a Poly-Factorial field experiment was carried out at the Agricultural Research and Development Station (ARDS) Turda, Romania, which is situated in the hilly region of the Transylvanian Plain. The study investigated the combined effects of soil tillage system (conventional tillage—CS; no-tillage—NT) and fertilization strategies (N48P48K48 at sowing vs. N48P48K48 at sowing + N40.5CaO10.5MgO7 applied in early spring at the growth resumption) on the quantitative and qualitative performance of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Results showed a modest yield difference of 206 kg ha−1 between the two tillage systems, favoring conventional tillage. However, the application of additional early-spring fertilization resulted in a significant average yield increase of 338 kg ha−1. Yield variability across the five years ranged from 262 to 1797 kg ha−1, highlighting the strong influence of climatic conditions on crop performance and emphasizing the need for adaptive management practices under changing environmental conditions.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Nitrogen-Enriched Nanobiochar Enhances Spinach Growth via Improved Nitrogen Retention and Uptake Mechanisms
by
Kashaf, Sumera Anwar, Fahad Shafiq, Abida Kausar, Shahbaz Khan, Muhammad Ashraf and Syed Ahmed Shah
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010011 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The increasing demand for sustainable agriculture requires innovative strategies to enhance nitrogen use efficiency while minimizing environmental losses associated with conventional fertilizers. This study aimed to develop and compare ammonium chloride- and ammonium nitrate-modified nanobiochar as controlled-release nitrogen carriers and to elucidate their
[...] Read more.
The increasing demand for sustainable agriculture requires innovative strategies to enhance nitrogen use efficiency while minimizing environmental losses associated with conventional fertilizers. This study aimed to develop and compare ammonium chloride- and ammonium nitrate-modified nanobiochar as controlled-release nitrogen carriers and to elucidate their effects on nitrogen retention, soil properties, and physiological nitrogen utilization in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Nitrogen-modified nanobiochar was synthesized using ammonium chloride (NB-AC) and ammonium nitrate (NB-AN) at three nitrogen rates (0.03, 0.06, and 0.12 g N g−1 NB) and applied to soil at 1% (w/w). Soil properties, nutrient dynamics, and plant growth and physiological traits were analyzed after 15 and 30 days. Nitrogen modification significantly improved soil nitrogen retention and nutrient availability compared with unmodified nanobiochar. The highest nitrogen loading treatments (NB-AC3 and NB-AN3) notably improved spinach growth, photosynthetic efficiency, pigment content, nitrogen metabolism enzymatic activities, and accumulation of key metabolites (soluble sugars, flavonoids). Nitrogen-release assessments indicated a pronounced controlled-release with reduced nitrogen leaching and greater retention, particularly under NB-AN3. Overall, this study demonstrates that nitrogen-modified nanobiochar functions as an effective nitrogen carrier that enhances nitrogen utilization and growth. These findings provide mechanistic insights into its potential as a sustainable alternative to conventional nitrogen fertilizers.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
From Waste to Wealth: Integrating Fecal Sludge-Based Co-Compost with Chemical Fertilizer to Enhance Nutrient Status and Carbon Storage in Paddy Soils
by
Sabina Yeasmin, Md. Sabbir Hosen, Zaren Subah Betto, Md. Kutub Uddin, Md. Parvez Anwar, Md. Masud Rana, A. K. M. Mominul Islam, Tahsina Sharmin Hoque and Sirinapa Chungopast
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010010 - 7 Jan 2026
Abstract
This study evaluated the effects of applying fecal sludge-based co-compost (CC) integrated with chemical fertilizers on soil nutrient status, organic carbon (OC) storage, and economic returns in paddy soils. Ten integrated nutrient management (INM) treatments were tested, i.e., BRRI recommended dose of fertilizer
[...] Read more.
This study evaluated the effects of applying fecal sludge-based co-compost (CC) integrated with chemical fertilizers on soil nutrient status, organic carbon (OC) storage, and economic returns in paddy soils. Ten integrated nutrient management (INM) treatments were tested, i.e., BRRI recommended dose of fertilizer (RDF), CC 5.0 t ha−1, RDF + CC 2.0 t ha−1, RDF + CC 1.5 t ha−1, RDF + CC 1.0 t ha−1, RDF + CC 0.5 t ha−1, 75% RDF + CC 2.0 t ha−1, 75% RDF + CC 1.5 t ha−1, 75% RDF + CC 1.0 t ha−1, and 75% RDF + CC 0.5 t ha−1. Two rice varieties were cultivated over two consecutive seasons—winter rice (boro) and monsoon rice (aman)—in the experimental field. Soil samples (0–15 cm) were collected before and after the seasons and fractionated into labile particulate organic matter (>53 µm) and stable mineral-associated organic matter (<53 µm). Bulk soils and CC were analyzed for OC, nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), sulfur (S), and heavy metals, while the fractions were analyzed for OC and N. Across both seasons, 75% RDF combined with 2.0 t ha−1 or 1.5 t ha−1 of CC consistently showed the highest OC, total N, and soil C stock, with moderate P, K, and S levels. Sole RDF produced the lowest OC and N. Among fractions, stable OC was the highest in the 75% RDF + 2.0 t ha−1 CC treatment, statistically similar to 75% RDF + 1.5 t ha−1 CC, and the lowest under RDF alone. Economically, sole RDF yielded the highest profit, while full RDF + CC achieved competitive returns. Reduced RDF + CC treatments (75% RDF + 1.5 or 2.0 t ha−1 CC) offered slightly lower returns but improved soil sustainability indicators. Overall, applying 75% RDF + 1.5 t ha−1 CC provided the most cost-effective balance of nutrient enrichment, soil C stock, and profitability. This CC-based INM approach reduces chemical fertilizer dependency, enhances soil health, and promotes sustainable waste management, supporting environmentally resilient rice production.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nitrogen Uptake and Loss in Agroecosystems)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimizing Nitrogen Management Across Sowing Methods and Water Regimes for Wheat Production on the Loess Plateau
by
Jiangyu Chang, Pengli Yuan, Zhongze Si, Yuqi Niu, Hafeez Noor, Yongkang Ren, Linghong Li, Pengcheng Ding, Aixia Ren and Min Sun
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010009 - 6 Jan 2026
Abstract
Sustainable nitrogen (N) management is critical for enhancing wheat production in the water-limited environment of China’s Loess Plateau. This study investigated the effects of four N rates (0, 120, 180, and 240 kg N ha−1) and two sowing methods, furrow sowing
[...] Read more.
Sustainable nitrogen (N) management is critical for enhancing wheat production in the water-limited environment of China’s Loess Plateau. This study investigated the effects of four N rates (0, 120, 180, and 240 kg N ha−1) and two sowing methods, furrow sowing (FS) and drill sowing (DS), on wheat yield, grain quality, and water-use efficiency (WUE). Results indicated that N application significantly improved all metrics. The optimal N rate for yield was 180 kg N ha−1 (N180), producing yields equivalent to the higher 240 kg N ha−1 rate (N240). Compared to the N0 control, the N240 treatment under FS in 2022–23 increased grain yield by 25.4% and WUE by 11.9%, while under DS it increased yield by 23.6% and WUE by 11.1%. However, in the following year (2023–24), the greatest benefits under FS came from N180, which increased yield by 19.3% and WUE by 11.5% over the control. Higher N rates markedly elevated grain quality: N240 resulted in the highest steamed bread score and concentration of volatile compounds. Nitrogen application also intensified soil water use, particularly before anthesis. In 2022–23, the highest N240 reduced soil water at maturity by 16.6% (FS) and 15.9% (DS) and increased total water consumption by up to 7.8% compared to N0. Yield was strongly correlated with soil water depletion in the 0–200 cm layer during the reproductive period. While N240 optimized quality, the N180 rate combined with improved sowing methods (FS or DS) provided the best balance, drill sowing was crucial agronomic practice for enhancing nitrogen-use efficiency (NUE), achieving high yield, superior WUE, and acceptable quality. We therefore recommend an N rate of 180 kg ha−1 with improved sowing as a sustainable practice for dryland wheat production on the Loess Plateau.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nitrogen Management in Plant Cultivation)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Nitrogen Sources on Physiological Processes and Morphological Development of Yellow Passion Fruit Seedlings
by
Gilmara da Silva Rangel, Thais de Souza Pastor, Vinicius Rodrigues Ferreira, Tayná de Oliveira Costa, Regiane Carla Bolzan Carvalho, Murilo de Oliveira Souza, Ana Paula Candido Gabriel Berilli and Savio da Silva Berilli
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010008 - 5 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Nitrogen is the nutrient most required by plants and plays a central role in agricultural productivity due to its involvement in essential nutrients. This study evaluated the effects of different nitrogen sources on the physiological and morphological development of yellow passion fruit (
[...] Read more.
Nitrogen is the nutrient most required by plants and plays a central role in agricultural productivity due to its involvement in essential nutrients. This study evaluated the effects of different nitrogen sources on the physiological and morphological development of yellow passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims) seedlings. The experiment followed a randomized block design with six treatments (water, urea, ammonium sulfate, potassium nitrate, calcium nitrate, and magnesium nitrate), six replicates per treatment, and two plants per plot. An equal amount of nitrogen was supplied to all treatments, while the urea treatment excluded the additional macronutrients present in the other fertilizers (S, K, Ca, and Mg), allowing us to assess whether the benefits were exclusively attributable to the nitrogen source. The results indicated that ammonium sulfate and calcium nitrate promoted better root system development, while ammonium sulfate also improved shoot growth and physiological characteristics. Multivariate analysis revealed that CP1 explained most of the variability between treatments, highlighting the contribution of these sources compared to the control. Overall, fertilization with ammonium sulfate produced the best results, indicating that it is a more efficient nitrogen source for seedling development.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Interaction Between Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae and Pseudomonas alkylphenolica Enhances Faba Bean Growth and Resilience to Water Deficit Under Nitrogen-Fixing Conditions
by
Mohamed Tamoudjout, Hamid Msaad, Soukaina Lahmaoui, Ahmed El Moukhtari, Cherki Ghoulam and Mohamed Farissi
Nitrogen 2026, 7(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen7010007 - 1 Jan 2026
Cited by 1
Abstract
Water deficit is a major constraint limiting the growth and yield of faba bean (Vicia faba L.). A pot experiment was conducted under controlled conditions to evaluate the effect of inoculation with Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae BIHB 1148 (strain F14) and Pseudomonas
[...] Read more.
Water deficit is a major constraint limiting the growth and yield of faba bean (Vicia faba L.). A pot experiment was conducted under controlled conditions to evaluate the effect of inoculation with Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae BIHB 1148 (strain F14) and Pseudomonas alkylphenolica PF9 (strain L13) on faba bean drought resilience. Two irrigation regimes were applied: well-watered (80% of field capacity) versus water-stressed (40% of field capacity). Strain F14 was used to ensure effective biological nitrogen fixation, while strain L13 was applied in co-inoculation to evaluate its biostimulatory effects. The control plants received nitrogen in its chemical form. Results indicated that water deficit significantly (p < 0.001) reduced plant growth, nodulation, and photosynthesis-related parameters, and increased hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, which are key markers of oxidative stress. However, co-inoculation with strains F14 and L13 significantly enhanced shoot and root biomass, as well as most agro-morphological traits. It also stimulated (p < 0.05) the antioxidant activities of superoxide dismutase (3-fold), guaiacol peroxidase (12%), and catalase (104%), and increased proline content (119%), which led to lower levels of MDA (54% decrease) and H2O2 (55% decrease), improved membrane stability, water status, and enhanced photosynthesis. Overall, co-inoculation of faba bean with Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae BIHB 1148 and Pseudomonas alkylphenolica PF9 offers a promising and sustainable approach to improve plant resilience under water deficit.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Microbial Interactions with Plants: Advancing Nitrogen Fixation, Uptake, and Utilization)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
6 November 2025
MDPI Launches the Michele Parrinello Award for Pioneering Contributions in Computational Physical Science
MDPI Launches the Michele Parrinello Award for Pioneering Contributions in Computational Physical Science

28 February 2026
MDPI INSIGHTS: The CEO’s Letter #32 - MDPI China and Thailand, China Science Daily, 1,000 Partnerships, R2R
MDPI INSIGHTS: The CEO’s Letter #32 - MDPI China and Thailand, China Science Daily, 1,000 Partnerships, R2R

Topics
Topic in
Agronomy, Crops, Land, Plants, Atmosphere, Nitrogen, Agriculture, Methane
Multi-Objective Optimization of Staple Crop Production for Yield, Carbon Sequestration, and Greenhouse Gas Mitigation
Topic Editors: Qiang Xu, Wei Yang, Ziyin Shang, Peng ZhangDeadline: 31 October 2026
Topic in
Agriculture, Agronomy, Environments, IJMS, Nitrogen, Plants
Ammonium Biology: From Molecular Response to Fertilization
Topic Editors: Dongwei Di, Soichi Kojima, Byoung Ryong Jeong, Monika SkowrońskaDeadline: 31 December 2026
Topic in
Agriculture, Agronomy, Horticulturae, Nitrogen, Plants, Biology
Precision Water and Fertilizer Management Technologies and Equipment for Sustainable Agriculture
Topic Editors: Jiandong Wang, Jian Zheng, Wenyi Dong, Haitao WangDeadline: 31 May 2027
Topic in
Agriculture, Crops, Nitrogen, Plants, Agronomy
High-Efficiency Utilization of Water-Fertilizer Resources and Green Production of Crops, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Peng Zhang, Xianqing Hou, Wenyi Dong, Peng WuDeadline: 30 June 2027

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Nitrogen
Nitrogen Management in Plant Cultivation
Guest Editors: Nasratullah Habibi, Francisco PadillaDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
Nitrogen
Nitrogen Cycling and Microbial Community Shifts in Soil Ecosystems
Guest Editors: Hanqing Wu, Quan Zhang, Xiantao Fang, Haifei ChenDeadline: 15 April 2026
Special Issue in
Nitrogen
Innovative Nitrogen Management Strategies in Aquaponics, Hydroponics, Soilless, and Soil-Based Crop Systems for Sustainable Agriculture
Guest Editors: Abdel Razzaq Altawaha, Abdulkadir BayirDeadline: 15 June 2026
Special Issue in
Nitrogen
Nitrogen–Carbon Interactions in Global Biogeochemistry
Guest Editors: Wenliang Ju, Dengke Ma, Yong ZhangDeadline: 30 June 2026









