Mechanical Performance and Durability of Concretes with Partial Replacement of Natural Aggregates by Construction and Demolition Waste
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
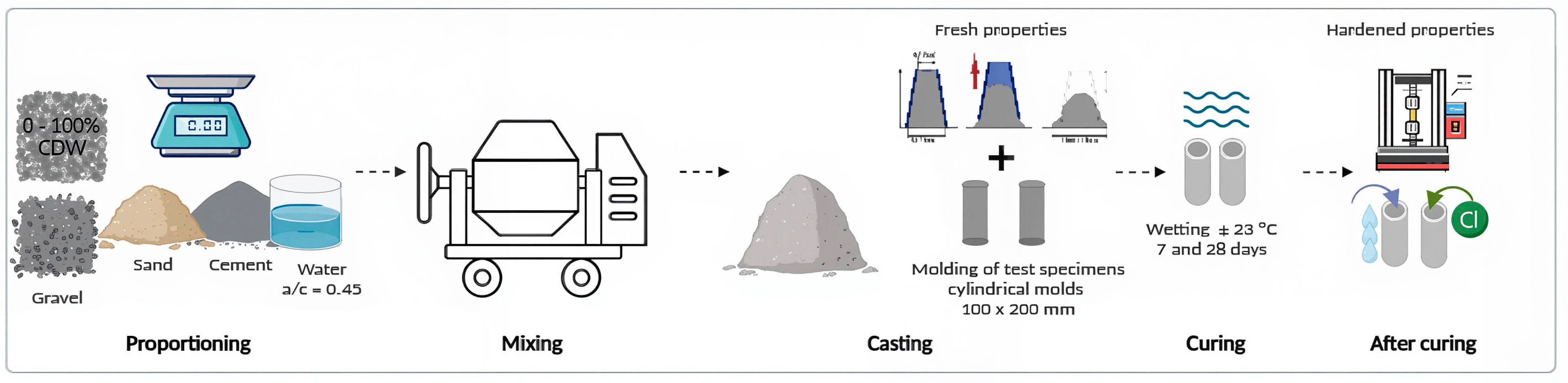
2.2. Concrete Mix Proportioning and Production
2.3. Fresh-State Testing
2.4. Compressive Strength
2.5. Water Absorption by Immersion and Capillarity
2.6. Chloride Ion Penetration
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Properties of Natural and Recycled Aggregates
3.2. Fresh-State Properties of the Concretes
3.3. Compressive Strength at 7 and 28 Days
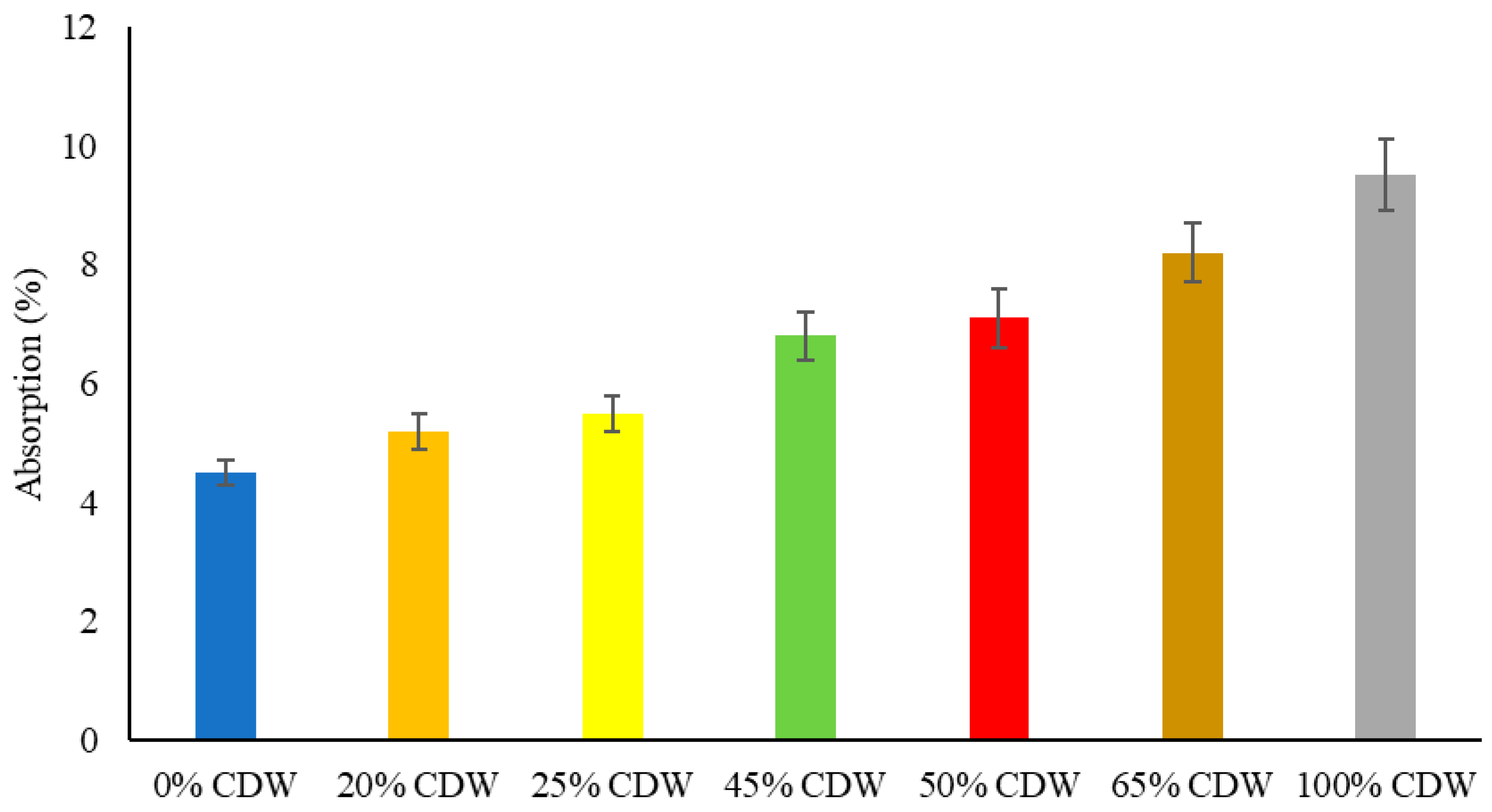
3.4. Water Absorption
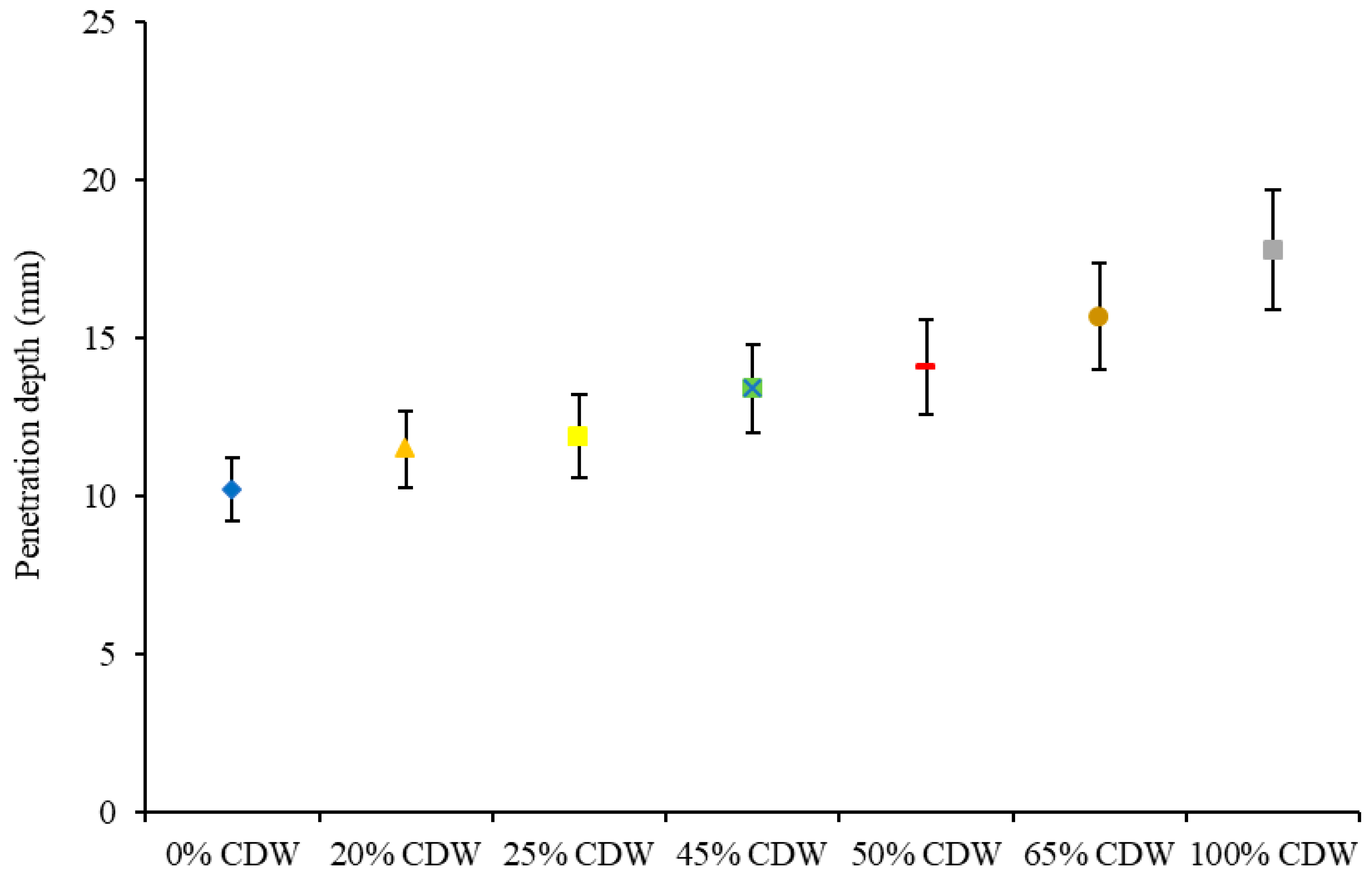
3.5. Chloride Penetration
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silva, R.V.; De Brito, J.; Dhir, R.K. Properties and Composition of Recycled Aggregates from Construction and Demolition Waste Suitable for Concrete Production. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 65, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Alimi, W.; Assaggaf, R.; Salami, B.A.; Oladapo, E.A. An Overview of Factors Influencing the Properties of Concrete Incorporating Construction and Demolition Wastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 367, 130307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, H.S.; Pachiappan, T.; Avudaiappan, S.; Maureira-Carsalade, N.; Roco-Videla, Á.; Guindos, P.; Parra, P.F. A Comprehensive Review on Recycling of Construction Demolition Waste in Concrete. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, A.; Sarmah, A.K. Construction and Demolition Waste Generation and Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete: A Global Perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 186, 262–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussat, N.; Dujet, C.; Méhu, J. Choosing a Sustainable Demolition Waste Management Strategy Using Multicriteria Decision Analysis. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, A.; de Brito, J. Influence of Construction and Demolition Waste Management on the Environmental Impact of Buildings. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Su, J.; Wu, B. A Hybrid Bayesian Model Updating and Non-Dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm Framework for Intelligent Mix Design of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 161, 112071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, X.-Y. Mesoscale Modeling of Recycled Aggregate Concrete under Uniaxial Compression and Tension Using Discrete Element Method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Fang, G.-H.; Kurda, R.; Sabuj, A.R.; Zhao, X.-Y. An Agile, Intelligent and Scalable Framework for Mix Design Optimization of Green Concrete Incorporating Recycled Aggregates from Precast Rejects. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso, F.L. Concreto: Material Construtivo Mais Consumido No Mundo, 53rd ed.; IBRACON: São Paulo, Brazil, 2009; Volume XXXVII. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Aguiar, J.; Wan, X.; Wang, Y.; Cunha, S.; Jia, Z. Application of Aggregates from Construction and Demolition Wastes in Concrete: Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Ma, Z.; Sui, T.; Akbarnezhad, A.; Duan, Z. Mechanical Properties of Concrete Mixed with Recycled Powder Produced from Construction and Demolition Waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 720–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarimehr, D.; Eslami, A.; Nasiri, A.; Rahai, M.; Karakouzian, M. Performance Study of Sustainable Concrete Containing Recycled Aggregates from Non-Selected Construction and Demolition Waste. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z. Micro-Properties and Mechanical Behavior of High-Ductility Engineered Geopolymer Composites (EGC) with Recycled Concrete and Paste Powder as Green Precursor. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 152, 105672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.A.; El-sayed, A.A.; Aboraya, A.M.; Fathy, I.N.; Abouelnour, M.A.; Tayeh, B.A.; Nabil, I.M. Investigating the Effects of Granite, Marble, Granodiorite, and Ceramic Waste Powders on the Physical, Mechanical, and Radiation Shielding Performance of Sustainable Concrete. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2025, 216, 111274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Thaickavil, N.N.; Wilson, P.M. Strength and Durability of Concrete Containing Recycled Concrete Aggregates. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 19, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattouh, M.S.; Abouelnour, M.A.; Mahmoud, A.A.; Fathy, I.N.; El Sayed, A.F.; Elhameed, S.A.; Nabil, I.M. Impact of Modified Aggregate Gradation on the Workability, Mechanical, Microstructural and Radiation Shielding Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 18428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez del Bosque, I.F.; Van den Heede, P.; De Belie, N.; Sánchez de Rojas, M.I.; Medina, C. Carbonation of Concrete with Construction and Demolition Waste Based Recycled Aggregates and Cement with Recycled Content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 234, 117336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABNT NBR:16697; Portland Cement—Requirements. Brazilian Association of Technical Standards (ABNT): São Paulo, Brazil, 2018; pp. 1–9.
- Schack, T.; Strybny, B.; Haist, M. Improving the Early Age Strength of Eco-Efficient Mortar with Low Clinker Content Considering Binder Granulometry and Chemical Additives. Materials 2024, 17, 4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABNT NBR:15900; 1—Water for Mixing Concrete—Part 1: Requirements. Brazilian Association of Technical Standards (ABNT): São Paulo, Brazil, 2009.
- ABNT NBR: 15116; Recycled Aggregates for Uses in Mortar and Concrete—Requirements and Test Methods. Brazilian Association of Technical Standards (ABNT): São Paulo, Brazil, 2021; pp. 1–20.
- Helene, P.; Terzian, P. Manual de Dosagem e Controle de Concreto; Editoria Pini: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1993; ISBN 8572660070. [Google Scholar]
- ABNT NBR: 8953; Concrete for Structural Use—Density, Strength and Consistence Classification. Brazilian Association of Technical Standards (ABNT): São Paulo, Brazil, 2015.
- ABNT NBR: 5738; Concrete—Procedure for Molding and Curing Concrete Test Specimens. Brazilian Association of Technical Standards (ABNT): São Paulo, Brazil, 2015.
- NM AMDN NM 67; Hormigón—Determinación de la Consistencia Mediante el Asentamiento del Tronco de Cono. Brazilian Association of Technical Standards (ABNT): São Paulo, Brazil, 1998.
- Carasek, H.; Araújo, R.C.; Cascudo, O.; Angelim, R. Parâmetros Da Areia Que Influenciam a Consistência e a Densidade de Massa Das Argamassas de Revestimento. Matéria (Rio Janeiro) 2016, 21, 714–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABNT NBR 5739:2018; Concreto—Ensaio de Compressão de Corpos de Prova Cilíndricos. Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2018.
- ABNT NBR: 6118; Projeto de Estruturas de Concreto. Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2024.
- ABNT NBR: 9778; Argamassa e Concreto Endurecidos—Determinação Da Absorção de Água, Índice de Vazios e Massa Específica. Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2009.
- ASTM C1202-19; Test Method for Electrical Indication of Concretes Ability to Resist Chloride Ion Penetration. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019.
- Kou, S.C.; Poon, C.S. Enhancing the Durability Properties of Concrete Prepared with Coarse Recycled Aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 35, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.S.; Shui, Z.H.; Lam, L.; Fok, H.; Kou, S.C. Influence of Moisture States of Natural and Recycled Aggregates on the Slump and Compressive Strength of Concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Cunha, S.; Aguiar, J.; Shi, C. Enhancing the Durability of Concrete with Construction and Demolition Waste Aggregate through Its Functionalization with Phase Change Materials (Paraffin). Cem. Concr. Compos. 2025, 162, 106135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, C.; Zhu, W.; Howind, T.; Isabel, M.; Rojas, S. De Influence of Mixed Recycled Aggregate on the Physical e Mechanical Properties of Recycled Concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 68, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Bao, J.; Gu, F.; Lu, J.; Ma, Z.; Hou, S.; Duan, Z. Determining the Importance of Recycled Aggregate Characteristics Affecting the Elastic Modulus of Concrete by Modeled Recycled Aggregate Concrete: Experiment and Numerical Simulation. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2025, 162, 106118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brito, J.; Saikia, N. Recycled Aggregate in Concrete; Green Energy and Technology; Springer London: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4471-4539-4. [Google Scholar]
- McNeil, K.; Kang, T.H.K. Recycled Concrete Aggregates: A Review. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2013, 7, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, Y.R.; Abadel, A.A.; Mayhoub, O.A.; Kohail, M. Effect of Using Available Metakaoline and Nano Materials on the Behavior of Reactive Powder Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Zhao, W.; Ye, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C. Measurement of Water Absorption of Recycled Aggregate. Materials 2022, 15, 5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, R.K.; de Brito, J.; Silva, R.V.; Lye, C.Q. Sustainable Construction Materials; Recycled Aggregates: Garland, TX, USA, 2019; ISBN 9780081009857. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, P.; Ding, X.; Xue, S.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, T. Influence of the Incorporation of Recycled Coarse Aggregate on Water Absorption and Chloride Penetration into Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 239, 117845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, W.; Fan, Y.; Huang, X. An Overview of Study on Recycled Aggregate Concrete in China (1996–2011). Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 31, 364–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuki, N.; Miyazato, S.; Yodsudjai, W. Influence of Recycled Aggregate on Interfacial Transition Zone, Strength, Chloride Penetration and Carbonation of Concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2003, 15, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicula, L.M.; Corbu, O.; Iliescu, M.; Sandu, A.V.; Hegyi, A. Study on the Durability of Road Concrete with Blast Furnace Slag Affected by the Corrosion Initiated by Chloride. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.S.; Yang, C.C. Using RCPT Determine the Migration Coefficient to Assess the Durability of Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 167, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Oxide | Content (%) |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 21.4 ± 0.3 |
| Al2O3 | 5.1 ± 0.2 |
| Fe2O3 | 3.1 ± 0.2 |
| CaO | 63.5 ± 0.5 |
| MgO | 2.2 ± 0.1 |
| SO3 | 2.8 ± 0.2 |
| K2O | 0.7 ± 0.1 |
| Mix Proportion | Cement (kg/m3) | Sand (kg/m3) | Gravel (kg/m3) | Natural CDW (kg/m3) | Recycled Water (kg/m3) | Water/Cement Ratio (w/c) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% CDW | 420 | 740 | 1050 | 0 | 189 | 0.45 |
| 20% CDW | 420 | 740 | 840 | 210 | 189 | 0.45 |
| 25% CDW | 420 | 740 | 788 | 262 | 189 | 0.45 |
| 45% CDW | 420 | 740 | 578 | 472 | 189 | 0.45 |
| 50% CDW | 420 | 740 | 525 | 525 | 189 | 0.45 |
| 65% CDW | 420 | 740 | 368 | 682 | 189 | 0.45 |
| 100% CDW | 420 | 740 | 0 | 1050 | 189 | 0.45 |
| Property | Natural Sand | Natural Aggregate (0) | Natural Aggregate (1) | Recycled Fine Aggregate | Recycled Coarse Aggregate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific mass (g/cm3) | 2.60 ± 0.01 | 2.64 ± 0.02 | 2.75 ± 0.02 | 2.46 ± 0.02 | 2.16 ± 0.03 |
| Water absorption (%) | 1.29 ± 0.05 | 1.70 ± 0.08 | 1.25 ± 0.07 | 9.31 ± 0.15 | 9.00 ± 0.20 |
| Fineness Modulus (Sand) | 2.40 ± 0.05 | — | — | 2.30 ± 0.05 | — |
| Mix Proportion | Slump (mm) | Standard Deviation (mm) | Cohesion Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% CDW | 115 | ±5 | Good cohesion, no segregation |
| 20% CDW | 108 | ±6 | Slight exudation |
| 25% CDW | 105 | ±5 | Good cohesion, little exudation |
| 45% CDW | 98 | ±7 | Moderate exudation |
| 50% CDW | 94 | ±6 | Pronounced exudation |
| 65% CDW | 91 | ±5 | Incipient segregation |
| 100% CDW | 85 | ±7 | Clearly visible segregation and exudation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silveira, T.A.d.; Nörnberg, R.d.P.; Santi, M.S.; Morales, R.R.; Tessaro, A.B.; Rosseto, H.L.; Delucis, R.d.A.; Trindade, G.H. Mechanical Performance and Durability of Concretes with Partial Replacement of Natural Aggregates by Construction and Demolition Waste. Waste 2025, 3, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3040032
Silveira TAd, Nörnberg RdP, Santi MS, Morales RR, Tessaro AB, Rosseto HL, Delucis RdA, Trindade GH. Mechanical Performance and Durability of Concretes with Partial Replacement of Natural Aggregates by Construction and Demolition Waste. Waste. 2025; 3(4):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3040032
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilveira, Thamires Alves da, Rafaella dos Passos Nörnberg, Marcelo Subtil Santi, Renata Rabassa Morales, Alessandra Buss Tessaro, Hebert Luis Rosseto, Rafael de Avila Delucis, and Guilherme Hoehr Trindade. 2025. "Mechanical Performance and Durability of Concretes with Partial Replacement of Natural Aggregates by Construction and Demolition Waste" Waste 3, no. 4: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3040032
APA StyleSilveira, T. A. d., Nörnberg, R. d. P., Santi, M. S., Morales, R. R., Tessaro, A. B., Rosseto, H. L., Delucis, R. d. A., & Trindade, G. H. (2025). Mechanical Performance and Durability of Concretes with Partial Replacement of Natural Aggregates by Construction and Demolition Waste. Waste, 3(4), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste3040032










