-
 Accelerated Development of AAV Purification Process Using a High-Throughput and Automated Crossflow System
Accelerated Development of AAV Purification Process Using a High-Throughput and Automated Crossflow System -
 A Chemical Safety Assessment of Lyocell-Based Activated Carbon Fiber with a High Surface Area through the Evaluation of HCl Gas Adsorption and Electrochemical Properties
A Chemical Safety Assessment of Lyocell-Based Activated Carbon Fiber with a High Surface Area through the Evaluation of HCl Gas Adsorption and Electrochemical Properties -
 Isolation of Macrocyclic Trichothecene Mycotoxins from the Lethal Toxic Mushroom Podostroma cornu-damae and Their Cytotoxic Activities
Isolation of Macrocyclic Trichothecene Mycotoxins from the Lethal Toxic Mushroom Podostroma cornu-damae and Their Cytotoxic Activities -
 An LC-MS/MS Method for the Simultaneous Quantification of Insulin, Cortisol, Glucagon-like Peptide 1, Ghrelin, and Osteocalcin
An LC-MS/MS Method for the Simultaneous Quantification of Insulin, Cortisol, Glucagon-like Peptide 1, Ghrelin, and Osteocalcin
Journal Description
Separations
Separations
- formerly Chromatography - is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on separation and purification science and technology in all areas of chemical, biological, physical science, and separation performance published monthly online by MDPI. The Central European Group of Separation Sciences (CEGSS) is affiliated with Separations and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 13.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journal: Purification.
Impact Factor:
2.6 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.7 (2022)
Latest Articles
Aluminum Removal from Rare Earth Chloride Solution through Regulated Hydrolysis via Electrochemical Method
Separations 2024, 11(5), 149; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050149 - 12 May 2024
Abstract
Due to the coexistence of Al3+ and RE3+ and their similar properties, the separation of aluminum from rare earths is difficult. In this study, selective precipitation was used to separate aluminum from rare earth chloride solution via electrochemical regulated hydrolysis. By
[...] Read more.
Due to the coexistence of Al3+ and RE3+ and their similar properties, the separation of aluminum from rare earths is difficult. In this study, selective precipitation was used to separate aluminum from rare earth chloride solution via electrochemical regulated hydrolysis. By controlling the current density and electrolytic time, the rate of hydroxyl ion production was regulated, and the selective separation of rare earth and aluminum was realized according to the different precipitation sequences. By altering the temperature, current density, pH value, and other parameters, the separation performance of aluminum from rare earth in mixed rare earth chloride systems was systematically investigated. The removal rate of aluminum reached 88.35%, and the loss rate of rare earth was only 5.99% under optimized conditions. Compared with traditional neutralization hydrolysis, the new process showed higher efficiency and lower rare earth loss rate. Furthermore, a kinetic analysis of aluminum precipitation revealed that the reaction adhered to pseudo-first order kinetics. Additionally, the precipitate obtained via separation and filtration was amorphous alumina hydroxide with a small amount of rare earth attached. No reagent was consumed for the new process, which was more efficient and cleaner, providing a new idea for removing aluminum impurities from rare earth solutions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Purification Technology)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Study of the Elemental Profiles of Wines from the North-Eastern Coast of the Black Sea
by
Lev A. Oganesyants, Alexandr L. Panasyuk, Dmitriy A. Sviridov, Olesya S. Egorova, Dilyara R. Akbulatova, Mikhail Y. Ganin, Aleksey A. Shilkin and Alexandr A. Il’in
Separations 2024, 11(5), 148; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050148 - 11 May 2024
Abstract
Due to the increasing consumer interest in wines with a controlled place of origin, PGI (Protected Geographical Indication) and PDO (Protected Designation of Origin), the most acute question is how to identify them. One of the most effective ways to confirm the place
[...] Read more.
Due to the increasing consumer interest in wines with a controlled place of origin, PGI (Protected Geographical Indication) and PDO (Protected Designation of Origin), the most acute question is how to identify them. One of the most effective ways to confirm the place of origin of wine in global practice is a comprehensive study of the elemental profile using statistical analysis methods. In the period from 2020 to 2023, 152 grape samples of grapes were collected from various wineries in Crimea and Kuban. The grape must that was obtained from them was fermented in laboratory conditions. The elemental profile was determined in the prepared wines, which included 71 indicators. In the conducted work, it was revealed that wines from Crimea and Kuban differ statistically significantly in the concentration of the elements B, Ca, Cu, Mn, Na, Ni, Re, Si, Sn and U. At the same time, the contents of the elements U, Sn and Re prevail in wines from Crimea, and those of B, Ca, Cu, Mn, Na, Ni and Si prevail in wines from Kuban. At the same time, methods of univariate and multivariate statistics do not allow us to reliably classify wine samples from Crimea and Kuban by their place of origin. In order to reveal the non-linear dependence of the studied indicators in wines on the geographical place of grape growing, the method of a supervised learning Random Forest was used. After training the model on the dataset, the proportion of its correct predictions was 96%. The model used 61 parameters, among which the most important were Ni, Re, Ba, Rb, Na, U, Sb, Zn, Bi, Ag and Ti.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Analytical Methods for Food Quality and Safety Analysis)
Open AccessArticle
Ultrasonic Pretreatment Combined with Microwave-Assisted Hydrodistillation for Extraction of Essential Oil from Melaleuca bracteata ‘Revolution Gold’ Leaves Scales Induced by Cellulase-Inorganic Salt and Its Anti-Fungal Activity
by
Yan Huang, Xiaonan Zhang, Fajian Zeng, Jinmei Chang and Zhiwei Liu
Separations 2024, 11(5), 147; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050147 - 9 May 2024
Abstract
In order to further develop the commercial use of Melaleuca bracteata (F. Muell), this report studied the extraction of essential oil from Melaleuca bracteata (F. Muell) leaves using ultrasonic pretreatment, cellulase-inorganic salt soaked and combined with microwave-assisted hydrodistillation. To optimize the primary contributing
[...] Read more.
In order to further develop the commercial use of Melaleuca bracteata (F. Muell), this report studied the extraction of essential oil from Melaleuca bracteata (F. Muell) leaves using ultrasonic pretreatment, cellulase-inorganic salt soaked and combined with microwave-assisted hydrodistillation. To optimize the primary contributing parameters, the Box–Behnken design (BBD) was applied. The optimum yield of essential oil was 9.61 mL/kg DW at a microwave power of 510.77 W, lithium chloride dose of 63.56 μmol, and microwave irradiation period of 46.97 min. The essential oil included a total of 41 compounds, and methyl eugenol (76.53%) and methyl cinnamate (12.62%) were the main compounds. The inhibitory impact was notable when the essential oil concentration was 1.6 mg/mL. Therefore, it has the potential to replace chemical pesticides. When the concentration of the essential oil solution was 1.6 mg/mL, the three pathogenic species of fungus (Pseudocercospora psidii, Colletotrichum eriobotryae, and Colletotrichum siamense) were greatly affected; at this dose, the fungus was unable to develop and its growth diameter was 0 mm. Additionally, the fungus’s inhibition rate reached 100%.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Discovery of Bioactive Compounds from Natural Organisms and Their Molecular Mechanisms against Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimizing Operational Parameters for Lithium Hydroxide Production via Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis
by
Guoxiang Wei, Mengmeng Wang, Chenxiao Lin, Chuan Xu and Jie Gao
Separations 2024, 11(5), 146; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050146 - 9 May 2024
Abstract
Traditional lithium hydroxide production techniques, like lithium sulfate and lithium carbonate causticizing methods, suffer from drawbacks including high specific energy consumption, time-consuming processes, and low recovery rates. The conversion of lithium chloride to lithium hydroxide using bipolar membrane electrodialysis is straightforward; however, the
[...] Read more.
Traditional lithium hydroxide production techniques, like lithium sulfate and lithium carbonate causticizing methods, suffer from drawbacks including high specific energy consumption, time-consuming processes, and low recovery rates. The conversion of lithium chloride to lithium hydroxide using bipolar membrane electrodialysis is straightforward; however, the influence of operational parameters on bipolar membrane electrodialysis performance have not been investigated. Herein, the impact of the current density (20 mA/cm2~80 mA/cm2), feed concentration (0.5 M~2.5 M), initial feed pH (2.5, 3.5 and 4.5), and the volume ratio of the feed and base solution (1:1, 2:1 and 3:1) on the current efficiency and specific energy consumption in the bipolar membrane electrodialysis was systematically investigated. The bipolar membrane electrodialysis process showed promising results under optimal conditions with a current density of 50 mA/cm2 and an initial lithium chloride concentration of 1.5 M. This process achieved a current efficiency of 75.86% with a specific energy consumption of 3.65 kwh/kg lithium hydroxide while also demonstrating a lithium hydroxide recovery rate exceeding 90% with a purity of about 95%. This work will provide valuable guidance for hands on implementation of bipolar membrane electrodialysis technology in the production of LiOH.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Purification Technology)
►▼
Show Figures
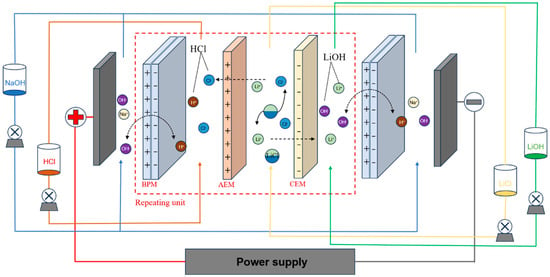
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Flavonoids from Fagopyrum tataricum Bran
by
Zhou Xu, Xiaomei Da, Jipeng Qu and Shiming Xiao
Separations 2024, 11(5), 145; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050145 - 8 May 2024
Abstract
In this study, eleven kinds of flavonoids were identified from F. tataricum bran (FTB) by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS, and HPLC-DAD analysis revealed that four compounds, including rutin, quercetin, kaempferol, and nicotiflorin, were the most significant components. Subsequently, natural deep eutectic solvent-based ultrasound-assisted extraction (NADES-UAE) was
[...] Read more.
In this study, eleven kinds of flavonoids were identified from F. tataricum bran (FTB) by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS, and HPLC-DAD analysis revealed that four compounds, including rutin, quercetin, kaempferol, and nicotiflorin, were the most significant components. Subsequently, natural deep eutectic solvent-based ultrasound-assisted extraction (NADES-UAE) was employed to extract flavonoids from FTB. Among the six kinds of NADES prepared, choline chloride–ethylene glycol (ChCl-EG) was identified as a promising candidate for extracting flavonoids due to its superior extraction performance. The extraction conditions were statistically investigated using response surface methodology conducted by Box-Behnken design (BBD). The optimal operational conditions were as follows: ultrasonic time 268 s, ultrasonic temperature 76 °C, and liquid–solid ratio 43 mL/g, which resulted in a high total flavonoid yield of 40.29 mg/g. Afterwards, the efficient extraction mechanism of NADES-UAE was comprehensively explored through FT-IR spectra, COSMO model, and microstructural analysis. In conclusion, NADES-UAE extraction is considered a green, efficient, and sustainable method for FTB flavonoids.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Extraction and Analysis of Chemical Compositions of Natural Products and Plants)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Degradation of Levofloxacin by Electroactivated Sodium Persulfate on Carbon Cloth Cathode Modified with Cerium-Based Metal Organic Frameworks (Ce-MOF) Derivatives
by
Xinbiao Mao, Mingyu Ou, Wenjun Zhao, Shuangting Yu and Hao Xu
Separations 2024, 11(5), 144; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050144 - 7 May 2024
Abstract
Levofloxacin (LFX), which is difficult to degrade effectively due to its molecular stability, has become an problem that needs to be solved urgently. The advanced oxidation technology of persulfate has received increasing attention from researchers. In this study, a Ce-MOF derivative (Ce-MOF-T) was
[...] Read more.
Levofloxacin (LFX), which is difficult to degrade effectively due to its molecular stability, has become an problem that needs to be solved urgently. The advanced oxidation technology of persulfate has received increasing attention from researchers. In this study, a Ce-MOF derivative (Ce-MOF-T) was prepared by hydrothermal synthesis and calcination, which synergistically responded to electroactivation to generate sulfate radicals for the efficient degradation of LFX. It has been proven that electrical activation and the Ce-MOF derivatives work together to generate sulfate radicals and effectively degrade LFX. Ce-MOF-550-modified carbon cloth was used as the cathode and a platinum electrode as the anode, the concentration of LFX was 20 mg·L−1, the loading of Ce-MOF-550 was 15 mg, pH = 5, the concentration of sodium persulfate (PMS) was 0.3 g·L−1, the current density was 100 A·m−2, and the degradation rate was 82.05% after 1 h of reaction and 95% after 3 h of reaction. After five cycle tests, the degradation rate was still higher than 75.00%, indicating that the material had good stability. In addition, the degradation of LFX was consistent with a quasi-primary kinetic reaction with apparent rate constants of 2.26 × 10−2 min−1.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Applications of Electrochemistry in Water and Wastewater Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures
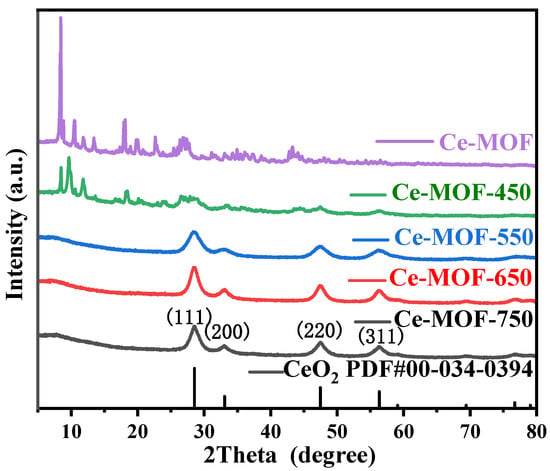
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Achievements in Preparation of Cyclodextrin–Based Porous Materials for Removal of Pollutants
by
Kaiyue Bao, Anyun Zhang, Yiyao Cao and Lei Xu
Separations 2024, 11(5), 143; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050143 - 7 May 2024
Abstract
Cyclodextrin–based porous materials have been widely applied in removing various organic pollutants from water environments, due to their unique physical and chemical properties, like the size–matching effect and hydrophobic interaction. Large numbers of hydroxyl groups in its external structure give cyclodextrin a high
[...] Read more.
Cyclodextrin–based porous materials have been widely applied in removing various organic pollutants from water environments, due to their unique physical and chemical properties, like the size–matching effect and hydrophobic interaction. Large numbers of hydroxyl groups in its external structure give cyclodextrin a high solubility in water, but the existence of these hydroxyl groups also endows cyclodextrin with the ability to be chemically modified with various functional groups to reduce its solubility in water and, meanwhile, to develop some novel functionalized cyclodextrin–based porous materials for selective removal of the target organic pollutants. This review focuses on the recent development in the synthesis of cyclodextrin–based porous materials (crosslinked cyclodextrin polymers and immobilized cyclodextrins), as well as highlighting their applications and mechanisms in the removal of dyes, endocrine disruptors, and mixed pollutants from water. Finally, the challenges and future perspectives in related research fields are discussed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Adsorption and Remediation of Emerging Pollutants from Water and Soil)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Efficient Separation of Re (VII) and Mo (VI) by Extraction Using E-1006–Ammonium Sulfate Aqueous Two-Phase System
by
Linlin Fan, Wenhui Li, Zilong Dai, Min Zhou and Yunren Qiu
Separations 2024, 11(5), 142; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050142 - 7 May 2024
Abstract
Aqueous two-phase extraction (APTE) stands out as an environmentally friendly technique for the separation of metal ions. The separation of Re (VII) and Mo (VI) in an aqueous solution was investigated using a novel aqueous two-phase system (ATPS) consisting of isodecanol polyoxyethylene ether
[...] Read more.
Aqueous two-phase extraction (APTE) stands out as an environmentally friendly technique for the separation of metal ions. The separation of Re (VII) and Mo (VI) in an aqueous solution was investigated using a novel aqueous two-phase system (ATPS) consisting of isodecanol polyoxyethylene ether (E-1006), ammonium sulfate, and water. A phase diagram of this system was developed, and the effects of pH, temperature, extraction time, the concentrations of E-1006 and (NH4)2SO4, and metal ions on the separation of Re (VII) and Mo (VI) were examined. The results show that at pH 7.0, Mo (VI) had almost transformed into the (NH4)2SO4-rich phase, while Re (VI) was extracted into the E-1006-rich phase. The increase in temperature induces a transition of Mo (VI) to the salt-rich phase, which is unfavorable for the extraction of Re (VII). The increase in the concentrations of E-1006 and (NH4)2SO4 has a positive effect on the separation of rhenium and molybdenum. Overall, the ATPS consisting of 200 g/L of E-1006, 200 g/L of (NH4)2SO4, and water yields an extraction efficiency of 97.2% for Re and a high separation factor of 2700 for Re (VII) and Mo (VI) from a mixture of 0.1 g/L of Re (VII) and 5 g/L of Mo (VI) at pH 7.0 and 323.15 K. Separation studies of the simulated leaching solution show that the extraction efficiency for Re (VI) is 99.1% and the separation factor of Re (VII) and Mo (VI) is 5100.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advanced Processes and Technologies for Wastewater: Collection, Treatment, and Resource)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Decoding the Volatile Profile of White Romanian Fetească Wines
by
Fulvia-Ancuța Manolache, Denisa-Eglantina Duță, Gabriela Daniela Criveanu-Stamatie, Teodora-Alexandra Iordache and Maria-Cristina Todașcă
Separations 2024, 11(5), 141; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050141 - 3 May 2024
Abstract
The wine’s volatilome, most of the time, defines not only its aroma, but also, its major attributes. In the case of wines, the authentication process has become imperative, in light of increased production of alcoholic beverages; consequently, reliable analytical methods have served for
[...] Read more.
The wine’s volatilome, most of the time, defines not only its aroma, but also, its major attributes. In the case of wines, the authentication process has become imperative, in light of increased production of alcoholic beverages; consequently, reliable analytical methods have served for it. Therefore, the goal of this research was to establish the global volatile profile of traditional Romanian white wines from Fetească varieties (Fetească albă, Fetească regală) in order to identify its unique characteristics by means of a headspace solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography analysis (HS-SPME/GC-MS) and e-Nose devoted techniques. Statistics was also employed aimed at differentiating the analyzed wine by varietal groups. Consequently, 23 volatile compounds were detected and quantified in 39 Fetească white wine samples originating from various production areas (Muntenia, Oltenia, Transylvania, Banat and Dobrogea), then further classified according to their odor thresholds in five aromatic classes (floral, fruity, sweet, lactic (cheesy) and other). In addition, statistics (Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Hieratical Clustering Analysis (HCA)) were used aiming to differentiate the analyzed varietal groups. The outcomes have pointed out the existence of distinct clusters connected with ethyl esters or alcohol composition and production year, depending on each examined variety.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advances in Analysis of Food and Beverages)
►▼
Show Figures
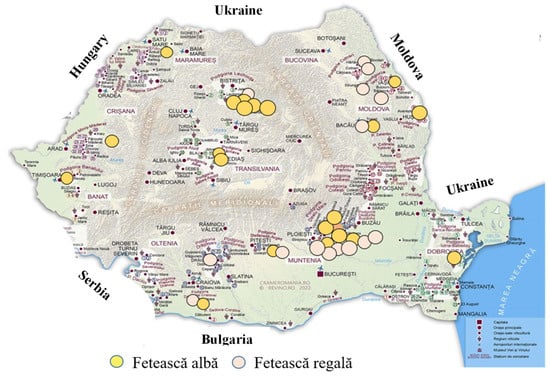
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development and Validation of an LC-MS/MS Method for the Determination of Plasma and Red Blood Cell Omega Fatty Acids: A Useful Diagnostic Tool
by
Lénárd Farczádi, Minodora Dobreanu, Adina Huțanu and Silvia Imre
Separations 2024, 11(5), 140; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050140 - 1 May 2024
Abstract
Background: LC-MS is an ever-increasingly used methodology for clinical applications. Due to the superior selectivity and sensitivity, in certain situations, it can offer an advantage or be the only option for diagnostics and biomonitoring applications. Methods: A high selectivity sensitive LC-MS/MS method was
[...] Read more.
Background: LC-MS is an ever-increasingly used methodology for clinical applications. Due to the superior selectivity and sensitivity, in certain situations, it can offer an advantage or be the only option for diagnostics and biomonitoring applications. Methods: A high selectivity sensitive LC-MS/MS method was developed for direct quantification of free plasma polyunsaturated fatty acids as well as conjugated membrane polyunsaturated fatty acids, using isocratic reverse phase elution. A quick and simple sample purification method was used in order to ensure high-throughput analysis of biological samples. The method was validated with regard to selectivity, sensitivity, linearity, accuracy, precision, carryover, and recovery, as well as other relevant parameters. Results and Conclusions: The method was developed and validated with respect to all relevant parameters and was successfully used in a number of clinical diagnostics and biomonitoring applications. The simple sample purification process allowed for an easy learning curve for analysts and other users, while ensuring a low chance of systematic or random errors and thus reliable results usable in a clinical setting.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Analysis and Bioanalysis of Pharmaceuticals: Sample Preparation and Chromatography)
►▼
Show Figures
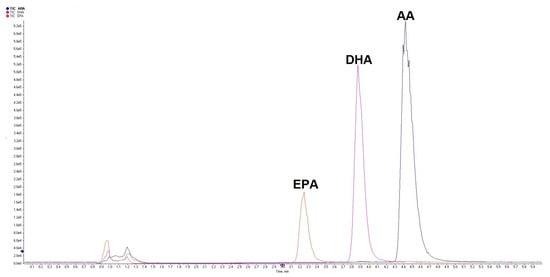
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Fertilizers’ Impact on Grassland in Northeastern Romania
by
Otilia A. Culicov, Doina Tarcau, Inga Zinicovscaia, Octavian G. Duliu, Mihai Stavarache and Vasile Vintu
Separations 2024, 11(5), 139; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050139 - 1 May 2024
Abstract
In order to obtain more data concerning the influence of fertilizers (organic and mineral) on different forage plants in the northeastern Romanian grassland, the mass fractions of 14 essential, enzymatic, or toxic elements were determined by instrumental neutron activation analysis together with the
[...] Read more.
In order to obtain more data concerning the influence of fertilizers (organic and mineral) on different forage plants in the northeastern Romanian grassland, the mass fractions of 14 essential, enzymatic, or toxic elements were determined by instrumental neutron activation analysis together with the amount of crude proteins, ash, fibers, as well as fat ether extract. The final results showed a significant variance in the content of analyzed elements on organic as well as on mineral fertilized experimental plots. At the same time, increased content of crude protein and fat ether extract was evident in fertilized grasses for all applied fertilizers, while other global indicators such as neutral and acid fibers of sulfuric lignin content decreased, suggesting significantly higher nutritional values for fertilized forage plants.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Determination of Potentially Toxic Elements in Food, Beverage and Medicinal Plants by Analytical Methods and Separation Technologies)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Phosphate Recovery Mechanism from Low P-Containing Wastewaters via CaP Crystallization Using Apatite as Seed: Seed Adsorption, Surface-Induced Crystallization, or Ion Clusters Aggregation?
by
Xiaobao Nie, Yinan Li, Junli Wan, Shuai Ouyang, Zhengbo Wang, Guoqi Wang and Heng Jiang
Separations 2024, 11(5), 138; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050138 - 30 Apr 2024
Abstract
Low P-containing wastewaters (LPWs) exhibit huge P recovery potential, considering their larger volume. P recovery via CaP crystallization using apatite as seed is documented as being potentially well suited for LPWs. However, its responsible mechanisms remain a subject for debate. Taking hydroxyapatite (HAP)
[...] Read more.
Low P-containing wastewaters (LPWs) exhibit huge P recovery potential, considering their larger volume. P recovery via CaP crystallization using apatite as seed is documented as being potentially well suited for LPWs. However, its responsible mechanisms remain a subject for debate. Taking hydroxyapatite (HAP) as the seed of LPWs, this paper conducted HAP adsorption/dissolution experiments, titration experiments, and P recovery experiments to distinguish the primary responsible mechanism. Results showed that it was HAP dissolution, not P adsorption, that occurred when the initial P concentration was no higher than 5 mg/L, ruling out adsorption mechanism of P recovery from LPWs using HAP as the seed. Significant OH− consumption and rapid P recovery occurred simultaneously within the first 60 s in titration experiments, suggesting CaP crystallization should be responsible for P recovery. Moreover, the continuous increase in P recovery efficiency with seed dosages observed in P recovery experiments seemed to follow well the mechanism of pre-nucleation ion clusters (PNCs) aggregation. During PNCs aggregation, P aggregates with Ca2+ quickly, generating CaP PNCs; then, CaP PNCs aggregate with seed particles, followed by CaP PNCs fusion, and ultimately transform into fines attached to the seed surface. PNCs’ aggregation mechanism was further supported by a comparison of seed SEM images before and after P recovery, since denser and smaller rod-shaped fines were observed on the seed surface after P recovery. This study suggests that PNCs’ aggregation is the dominant mechanism responsible for the recovery of P from LPWs via CaP crystallization using HAP as the seed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Environmental Separations)
►▼
Show Figures
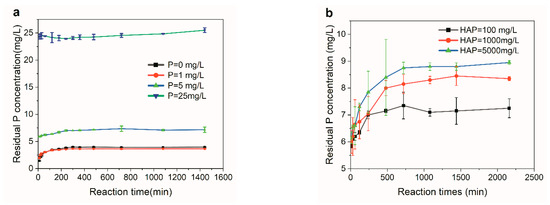
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Formation Mechanism of Deposits in Rotary Kiln during Steelmaking Dust Carbothermic Recycling
by
Xiaobo Min, Luyu Huang, Maixin Yu, Yunyan Wang, Yong Ke, Cong Peng, Xu Yan, Qingyu Huang and Yun Li
Separations 2024, 11(5), 137; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050137 - 29 Apr 2024
Abstract
Rotary kiln has been widely used in hazardous waste treatment because of its strong adaptability to raw materials, high productivity, and simple processing technology. However, the formation of deposits reduces its performance period and profitability. This study characterized the deposit mineralogy and thermodynamically
[...] Read more.
Rotary kiln has been widely used in hazardous waste treatment because of its strong adaptability to raw materials, high productivity, and simple processing technology. However, the formation of deposits reduces its performance period and profitability. This study characterized the deposit mineralogy and thermodynamically and experimentally investigated its formation mechanism. The results show that the main phases of the deposit are magnetite, monolithic iron, olivine, and yellow feldspar. They indicate that the deposit formation process was accompanied by the participation of alkaline and iron oxides. The intermediate product Ca2SiO4 can promote the generation of low melting point phases, such as CaFeSiO4 and Ca2Al2SiO7, which are the main phases of deposit materials. Additionally, the reduction intermediate product FeO facilitated the generation of a liquid ferrous mixture (Fe3O4-FeO and Fe3O4-FeO-Fe mixture), which in turn further promoted the growth of the initial deposit phase. The solid deposit formed and attached to the kiln inner wall, along with a decrease in temperature. These results are expected to provide an idea or approach for fundamentally solving the problem of deposits in the rotary kiln.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Separation Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
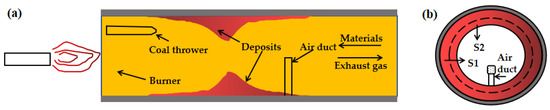
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Multiplex Detection of Seven Staphylococcal Enterotoxins Using Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Combined with a Novel Capture Molecule
by
Jing Lv, Tingting Liu, Xinyu Fang, Songyang Han, Lina Dong, Jiaxin Li, Jing Wang, Jinglin Wang, Shan Gao, Lin Kang and Wenwen Xin
Separations 2024, 11(5), 136; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050136 - 29 Apr 2024
Abstract
Food poisoning caused by Staphylococcal enterotoxins (SEs) is prevalent globally, making efficient detection of these toxins very important. Traditionally, liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry required immunosorbent enrichment by magnetic bead-coupled antibodies obtained by animal-specific immunization. However, this method is time-consuming and costly. In this study,
[...] Read more.
Food poisoning caused by Staphylococcal enterotoxins (SEs) is prevalent globally, making efficient detection of these toxins very important. Traditionally, liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry required immunosorbent enrichment by magnetic bead-coupled antibodies obtained by animal-specific immunization. However, this method is time-consuming and costly. In this study, two recombinant protein capture molecules were designed based on the principle of toxins binding to Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHCII) and T cell receptor (TCR) molecules. The two capture molecules are called MHCII and MHCII-D10. The design of the MHCII and TCR-D10 was achieved through searching for the binding site protein sequence of Staphylococcal enterotoxins in the relevant literature, and MHCII-D10 was to link MHCII sequence with TCR-D10 sequence using linker (G4S)3 linking peptide. These capture molecules were shown to effectively bind to seven types of toxins and to capture SEs in various matrices. The digestion time, ratio, and temperature were further optimized, reducing the overall digestion time to just 2 h. The specificity, linearity, sensitivity, precision (RSD%), and recovery of the two methods were verified by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. When the MHCII and MHCII-D10 captured the toxins, the limit of quantification (LOD) in the 1 × PBS, plasma, and milk matrices ranged from 1.5625 to 100 fmol/µL, with the recovery rate ranging from 18.4% to 96%. The design of these capture molecules eliminates the need for animal-specific immunization, simplifying the pre-detection process and avoiding ethical concerns. This development holds significant promise for clinical diagnosis and reference.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Application of Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry and Related Techniques)
►▼
Show Figures
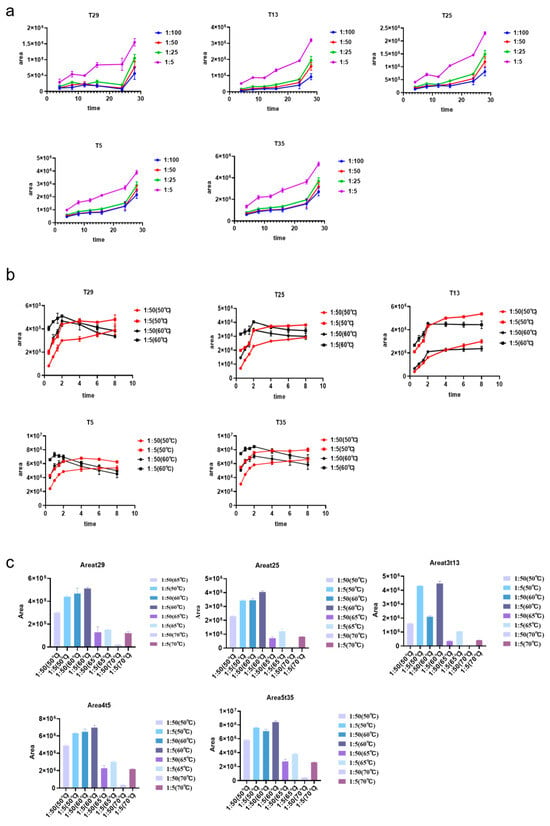
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring Varied (Green) Extraction Methods to Optimize Galia Melon Peel Antioxidant Potential
by
Vassileios Dimtsas, Anastasia Douma, Dimitra Soukia, Theodoros Chatzimitakos, Vassilis Athanasiadis, Konstantina Kotsou, Eleni Bozinou and Stavros I. Lalas
Separations 2024, 11(5), 135; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050135 - 28 Apr 2024
Abstract
Cucumis melo L. (C. melo), commonly known as the melon, is a widely cultivated tropical fruit associated with nutritional benefits and bioactive properties. With global production reaching 40 million tons annually, the fruit processing industry generates significant waste, primarily peels, totaling
[...] Read more.
Cucumis melo L. (C. melo), commonly known as the melon, is a widely cultivated tropical fruit associated with nutritional benefits and bioactive properties. With global production reaching 40 million tons annually, the fruit processing industry generates significant waste, primarily peels, totaling 8 to 20 million tons yearly. These organic by-products are rich in bioactive compounds such as antioxidants, offering health benefits such as a reduced risk of cancer and cardiovascular diseases, as well as of diabetes and neurogenerative diseases, offering an opportunity for sustainable utilization. C. melo by-products have demonstrated various health benefits, including anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antioxidant properties, attributed mainly to polyphenols. Recognizing the potential of melon waste, this study systematically explored different extraction methods, including stirring (ST), ultrasound (US), and pulsed electric field (PEF) methods, while considering factors such as extraction time, temperature, and solvent composition. The primary goal was to identify the most effective extraction procedures and optimal conditions for maximizing the yield of total polyphenols and antioxidant capacity (using the FRAP and DPPH methods) from C. melo peel by-products. According to the results, the optimum conditions include ST as the extraction method, an ethanolic solvent with a strength of 50%, a 150 min extraction duration, and an 80 °C extraction temperature. The maximum values of total polyphenols that can be observed are 3.75 mg gallic acid equivalents (GAE)/g of dry weight (dw) and 25.77 μmol ascorbic acid equivalents (AAE)/g dw and 34.44 μmol AAE/g dw from FRAP and DPPH antioxidant assays, respectively. The polyphenols identified were the following: gallic acid, neochlorogenic acid, catechin, chlorogenic acid, epicatechin, and kaempferol. By securing the maximum isolation of bioactive content and antioxidant activity, the research will contribute to sustainable waste management by reducing waste and developing value-added products.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Purification Technology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pomegranate Juice Clarification Using Ultrafiltration: Influence of the Type of Variety and Degree of Ripeness
by
Asunción M. Hidalgo, José A. Macario, Marta Abellán-Baeza, Teresa Sánchez-Moya, Rubén López-Nicolás and Fulgencio Marín-Iniesta
Separations 2024, 11(5), 134; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050134 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
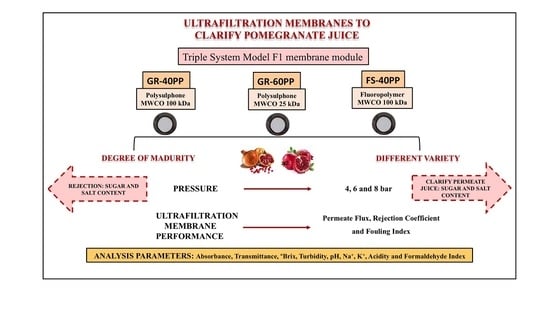
Fruit consumption guarantees the supply of most of the necessary nutrients for a complete and balanced diet, as it is a relevant source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. In particular, pomegranate has very interesting medicinal properties, such as an anti-inflammatory effect and the
[...] Read more.
Fruit consumption guarantees the supply of most of the necessary nutrients for a complete and balanced diet, as it is a relevant source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. In particular, pomegranate has very interesting medicinal properties, such as an anti-inflammatory effect and the protection of the cardiovascular system, among others. During pomegranate juice production, it appears cloudy and must be clarified to remove suspended solids such as colloids and high-molecular weight tannins. The membrane clarification process is a cost-effective alternative to the conventional methods, resulting in a high-quality product. In this work, the clarification of pomegranate juice using the Triple System Model F1 membrane module was carried out for the Mollar and Wonderful varieties with early and late maturity. Three ultrafiltration membranes with different molecular weight cut-off and different chemical compositions were used. The rejection coefficient and permeate flux (which represent the selectivity of the membranes and the process efficiency, respectively) were measured. GR-40PP showed the best results in terms of membrane selectivity and process efficiency, achieving adequate physicochemical juice parameters. Regarding the comparison of the maturity degree, in general terms, the Mollar variety showed better results. Ripe pomegranates showed greater selectivity, while the process efficiency was higher for the early samples.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Analysis of Natural Products and Pharmaceuticals)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Phthalates: The Main Issue in Quality Control in the Beverage Industry
by
Alessia Iannone, Cristina Di Fiore, Fabiana Carriera, Pasquale Avino and Virgilio Stillittano
Separations 2024, 11(5), 133; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050133 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Phthalate esters (PAEs) are a group of chemicals used to improve the flexibility and durability of plastics. The chemical properties and the resistance to high temperatures promote their degradation and release into the environment. Food and beverages can be contaminated by PAEs through
[...] Read more.
Phthalate esters (PAEs) are a group of chemicals used to improve the flexibility and durability of plastics. The chemical properties and the resistance to high temperatures promote their degradation and release into the environment. Food and beverages can be contaminated by PAEs through the migration from packaging material because they are not covalently bound to plastic and also via different kinds of environmental sources or during processing. For instance, alcoholic drinks in plastic containers are a particular risk, since the ethanol contained provides a good solubility for PAEs. According to its role as an endocrine disruptor compound and its adverse effects on the liver, kidney, and reproductive and respiratory systems, the International Agency on Research Cancer (IARC) classified di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) as a possible human carcinogen. For this reason, to control human exposure to PAEs, many countries prohibited their use in food as non-food substances. For example, in Europe, the Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/2005 restricts the use of DEHP, dibutyl phthalate (DBP), benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP), and diisobutyl phthalate (DiBP) to a concentration equal to or below 0.1 by weight in plasticizers in articles used by consumers or in indoor areas. There are reports from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that some beverages (and food as well), particularly fruit juices, contain high levels of phthalates. In some cases, the deliberate adulteration of soft drinks with phthalate esters has been reported. This paper would like to show the difficulties of performing PAE analysis in beverage matrices, in particular alcoholic beverages, as well as the main solutions provided for quality control in the industrial branches.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Analysis of Food and Beverages)
►▼
Show Figures
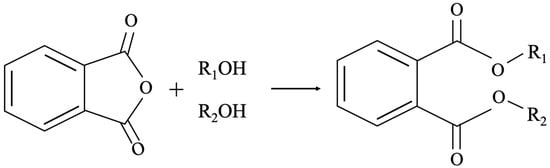
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Metabolite Profiling and Molecular Network Shows Kinkeloids as Promoting of Collagen Synthesis from Combretum micranthum
by
Souhila Messaili, Doha Haggouch, Mikaela Bignard, Pierre-Eric Campos, Emilie Destandau and Eldra Delannay
Separations 2024, 11(5), 132; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050132 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Combretum micranthum, a plant native to Africa, has a well-documented traditional use in the treatment of various ailments such as fever, diabetes, and malaria. Its pharmaceutical benefits include nephroprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties, which were proven. In addition, its potential for
[...] Read more.
Combretum micranthum, a plant native to Africa, has a well-documented traditional use in the treatment of various ailments such as fever, diabetes, and malaria. Its pharmaceutical benefits include nephroprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties, which were proven. In addition, its potential for cosmetic applications is being explored due to its depigmenting, anti-inflammatory, and UV-damage-repairing properties. This article investigates the molecular composition and new cosmetically relevant biological activity of C. micranthum and enriched fractions to begin the establishment of the structure–activity relationship. Firstly, an extract of C. micranthum was prepared and selected for its overall biological response and then fractionated to obtain simplified molecular fractions. One fraction was particularly enriched in kinkeloids, a specific family of compounds to this species. All the fractions and the crude extract were then tested on biological targets to evaluate and compare their cosmetic activities. Molecular networks were constructed from the UHPLC-MS/HRMS data to better characterize the extract and fractions and to highlight structure–activity relationships. This study highlights the metabolic profiling of a butylene glycol extract of C. micranthum, showing its main chemical families and revealing that the kinkeloids, identified by HRMS and NMR, promote an increase in collagen I synthesis, an interesting cosmetic activity neither previously described for these compounds and neither for C. micranthum extract.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Bioactive Compounds from Natural Sources: Extraction, Characterization, Evaluation and Application)
►▼
Show Figures
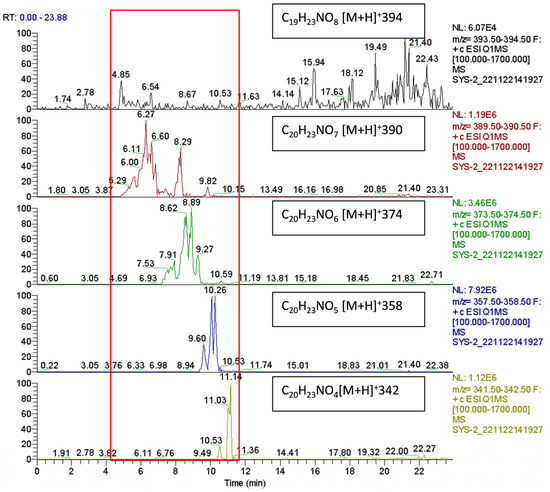
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Kinetic Analysis of Triclosan Degradation under UV-C and Simulated Solar Irradiation
by
Lázaro Adrián González-Fernández, Myriam Chems, Nahum Andrés Medellín-Castillo, Ventura Castillo-Ramos, Manuel Sánchez-Polo, Javier E. Vilasó-Cadre and Raúl Ocampo-Pérez
Separations 2024, 11(5), 131; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050131 - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
This research delves deeply into the intricate degradation kinetics of triclosan, employing two distinct methodologies: UV and simulated solar irradiation. Through a comprehensive comparative analysis, the study endeavors to elucidate the efficacy of these techniques, aiming to shed light on their respective methodological
[...] Read more.
This research delves deeply into the intricate degradation kinetics of triclosan, employing two distinct methodologies: UV and simulated solar irradiation. Through a comprehensive comparative analysis, the study endeavors to elucidate the efficacy of these techniques, aiming to shed light on their respective methodological strengths and limitations. The study compares the efficacy of UV and simulated solar irradiation techniques for triclosan degradation, revealing that both methods exhibit effectiveness in degrading triclosan, with variations observed in degradation rates and byproduct formation. Through a detailed examination of the kinetics of triclosan degradation, the study reveals the intricate pathways and mechanisms involved in the photodegradation process. Results highlight the influence of irradiance levels and residence times on degradation efficiency. The research identifies optimal conditions for triclosan degradation, emphasizing the importance of residence time and irradiance levels. Results show that a residence time of 4 h and an irradiance level of 450 W m−2 maximize degradation efficiency. Analysis of degradation byproducts provides insights into the transformation pathways of triclosan under UV and simulated solar irradiation, indicating the formation of 2,4-dichlorophenol, quinone, and hydroquinone as primary byproducts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Application of Biosorbents in Environmental Purification)
►▼
Show Figures
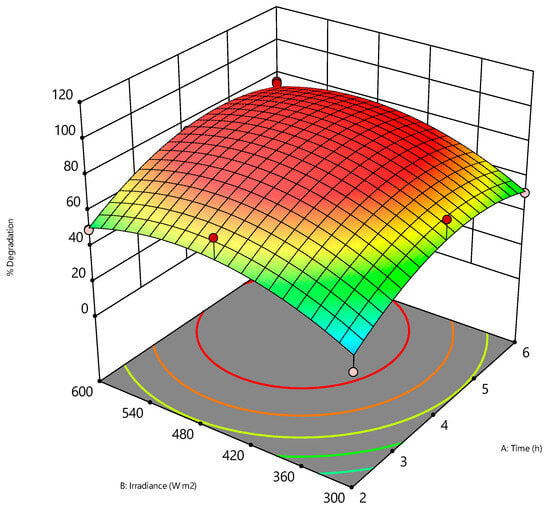
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Application of Magnetic Separation Technology in Resource Utilization and Environmental Treatment
by
Jiangang Ku, Kunpeng Wang, Qian Wang and Zhongyun Lei
Separations 2024, 11(5), 130; https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050130 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
Magnetic separation technology is a physical separation method that uses the differences in magnetism between matter to separate them from each other by different motion behaviors in a non-uniform magnetic field. It is highly efficient, green, and environmentally friendly, with little change in
[...] Read more.
Magnetic separation technology is a physical separation method that uses the differences in magnetism between matter to separate them from each other by different motion behaviors in a non-uniform magnetic field. It is highly efficient, green, and environmentally friendly, with little change in the physical and chemical properties of raw materials. Magnetic separation technology is commonly used in the field of mineral processing engineering for magnetite, hematite, titanite, and other magnetic ferrous metal oxide minerals. This paper summarizes the application of magnetic separation technology for resource utilization and environmental treatment in different fields, such as non-metal decomposition, valuable metal recovery, use of magnetic carrier chemical separation, biomedical targeted magnetic separation, and use of magnetic species separation in water and wastewater treatment. We seek to review the application and potential of magnetic separation technology in various fields, emphasize their key role, and explore possible directions for their future development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Application of Magnetic Separation Technology in Green Production)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Separations Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Energies, Molecules, Nanomaterials, Separations, Sustainability
Carbon Capture Science & Technology (CCST)
Topic Editors: Zilong Liu, Meixia Shan, Yakang JinDeadline: 15 May 2024
Topic in
Beverages, Fermentation, Foods, Molecules, Separations
Advances in Analysis of Flavors and Fragrances: Chemistry, Properties and Applications in Food Quality Improvement
Topic Editors: Ana Leahu, Marìa Soledad Prats Moya, Cristina GhineaDeadline: 31 May 2024
Topic in
Catalysts, Nanomaterials, Separations, Sustainability, Water
Novel Advanced Oxidation Processes for Wastewater Treatment
Topic Editors: Yuwei Pan, Xiang Li, Yizhen Zhang, Xuedong Du, Jingju Cai, Lu Gan, Qi Zhang, Jun JiangDeadline: 30 June 2024
Topic in
Analytica, Antioxidants, Biomedicines, Nutrients, Separations
Discovery of Bioactive Compounds from Natural Organisms and Their Molecular Mechanisms against Diseases
Topic Editors: Jun Dang, Tengfei Ji, Xinxin ZhangDeadline: 31 July 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Separations
Separation Methods in Mineral Industry
Guest Editors: Haishen Jiang, Yadong Zhang, Ligang TangDeadline: 20 May 2024
Special Issue in
Separations
Research on the Application of Mass Spectrometry in Environmental Analysis Integrated with Contributions from Italian 5th MS-Enviday
Guest Editors: Fulvio Magni, Donatella Caruso, Salvatore Barreca, Giuliana BiancoDeadline: 30 May 2024
Special Issue in
Separations
Separation, Beneficiation, and Purification of Carbonaceous Minerals and Materials
Guest Editors: Xiangning Bu, Yangshuai Qiu, Yuran ChenDeadline: 20 June 2024
Special Issue in
Separations
Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Separation and Purification
Guest Editors: Yang Cheng, Zhen YanDeadline: 30 June 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Separations
Feature Paper Collection in Section 'Materials in Separation Science'
Collection Editors: Dimosthenis Giokas, Manolis Manos
Topical Collection in
Separations
Recent Trends in the Separation of Natural Products and Pharmaceuticals
Collection Editors: Paraskevas D. Tzanavaras, Susanne Wiedmer
Topical Collection in
Separations
Synthetic Membrane Separation Science and Technology
Collection Editors: Mohamed Khayet, Elena Guillen Burrieza
Topical Collection in
Separations
State of the Art in Separation Science
Collection Editor: Victoria Samanidou





