- Article
Recycling of Medical Waste in the Circular Economy: LCA Analysis of the Production of Bone Allografts from Femoral Heads Used in Dental Implantology
- Szidonia Krisztina Veress,
- Bálint Botond Bögözi and
- Melinda Székely
- + 2 authors
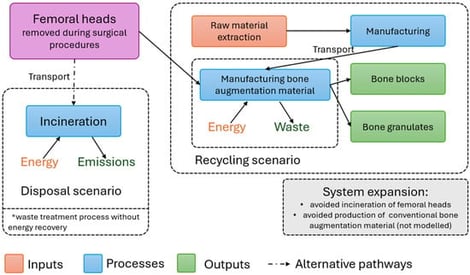
Background/Objectives: Bone grafting is fundamental in oral implantology in order to achieve appropriate esthetic and functional results. One of the options for bone grafting is the use of allografts, which can be produced using femoral heads removed during orthopedic surgeries in accordance with the principles of the circular economy. The aim of this study is to examine the environmental impacts of the production of cancellous block and granulates of bone graft materials produced in this way. Methods: The cradle-to-gate life cycle assessment was performed at the Petz Aladár University Teaching Hospital Tissue Bank Department, Győr, Hungary, with the system boundaries defined and the bone graft material produced during a production process defined as a functional unit. The environmental impacts were determined with the OpenLCA v2.5.0. software, using the ReCiPe v1.03 2016 midpoint (H) and endpoint (H) assessment methods. Results: During the production process, 500 g of bone graft material is produced in both forms, packaged as 1 g. The carbon footprint of the production of the cancellous bone block was 88,972 kgCO2-Eq, while that of the bone granulates was 100,033 kgCO2-Eq, to which the chemicals used for the degreasing and deantigenization of the bone tissue contributed the most. Within the impact categories, the material resources of metals–minerals, terrestrial ecotoxicity and climate change contributed the most to the environmental impacts. Within most impact categories, electricity was the most significant influencing factor. Conclusions: The environmental impact of the production of bone substitute granulates is greater than that of the bone block, to which the packaging of the products contributes primarily.
6 February 2026