-
 Peer-Delivered Hepatitis C Testing and Health Screening Provided in a Community Pharmacy Setting: Proof of Concept
Peer-Delivered Hepatitis C Testing and Health Screening Provided in a Community Pharmacy Setting: Proof of Concept -
 Assessing Pharmacy Costs of Intravenous Push Controlled Substance Waste in Hospital-Based Areas: A Multi-Site Study
Assessing Pharmacy Costs of Intravenous Push Controlled Substance Waste in Hospital-Based Areas: A Multi-Site Study -
 Developing a Theoretically Informed Strategy to Enhance Pharmacist-Led Deprescribing in Care Homes for Older People
Developing a Theoretically Informed Strategy to Enhance Pharmacist-Led Deprescribing in Care Homes for Older People -
 Not All U.S. Pharmacists Are Equal: A Full-Time Versus Part-Time Comparison
Not All U.S. Pharmacists Are Equal: A Full-Time Versus Part-Time Comparison
Journal Description
Pharmacy
Pharmacy
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed, and open access journal dealing with pharmacy education and practice, and is published bimonthly online by MDPI. The Academy of Pharmaceutical Sciences (APS) is affiliated with Pharmacy and its members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 22.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: Reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Journal Clusters-Pharmaceutical Science: Scientia Pharmaceutica, Marine Drugs, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Pharmacy, Future Pharmacology, Pharmacoepidemiology, Drugs and Drug Candidates and Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry.
Impact Factor:
1.8 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.0 (2024)
Latest Articles
AI-Enabled Sacramento Public Health (SACPH) App: A Reproducible AI-Based Method for Population-to-Practice Reasoning in Foundational Sciences in Pharmacy Education
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010010 - 16 Jan 2026
Abstract
Foundational biomedical sciences are commonly taught without routine integration of local population health contexts, limiting students’ ability to connect mechanisms to community disease burden and practice responsibilities. In this method paper, we developed and piloted an AI-enabled “Sacramento County Public Health (SACPH)” AI
[...] Read more.
Foundational biomedical sciences are commonly taught without routine integration of local population health contexts, limiting students’ ability to connect mechanisms to community disease burden and practice responsibilities. In this method paper, we developed and piloted an AI-enabled “Sacramento County Public Health (SACPH)” AI workflow and app prototype, a structured, faculty-authored prompt sequence designed to guide population-to-practice reasoning using publicly available data. The workflow was implemented during a TBL session with first-year PharmD students in an immunology course. Using splenectomy and risk of overwhelming post-splenectomy infection (OPSI) as an illustrative use case, students executed a standardized prompt sequence addressing data source identification, coding logic (diagnosis vs. procedure codes), population-level estimation with uncertainty framing, and translation to pharmacist-relevant prevention and counseling implications. Feasibility was defined by conceptual convergence. The validated reasoning workflow was subsequently translated into a prototype, app-style interface using generative design prompts. Across student teams, outputs converged on similar categories, consistent recognition of coding frameworks and verification steps, and directionally similar interpretations of local burden and pharmacist responsibilities. The prototype demonstrated successful externalization of the reasoning workflow into a modular, reproducible artifact. SACPH demonstrates a feasible, reproducible method for using generative AI to integrate foundational science instruction with local population health context and pharmacist practice reasoning, while supporting AI literacy competencies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue AI Use in Pharmacy and Pharmacy Education)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Irisin as a Neuroprotective Agent in Parkinson’s Disease: The Role of Physical Exercise in Modulating Dopaminergic Neurons
by
José Garcia de Brito-Neto, Paulo Leonardo de Góis Morais, José Rodolfo Lopes de Paiva Cavalcanti, Francisco Irochima Pinheiro, Fausto Pierdoná Guzen and Ricardo Ney Cobucci
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010009 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Exercise-induced myokines have emerged as crucial mediators of the beneficial effects of physical activity on neurodegenerative diseases through complex molecular mechanisms involving oxidative stress reduction, neuroinflammation suppression, and synaptic plasticity enhancement. Among these myokines, irisin, encoded by the FNDC5 gene, has gained significant
[...] Read more.
Exercise-induced myokines have emerged as crucial mediators of the beneficial effects of physical activity on neurodegenerative diseases through complex molecular mechanisms involving oxidative stress reduction, neuroinflammation suppression, and synaptic plasticity enhancement. Among these myokines, irisin, encoded by the FNDC5 gene, has gained significant attention as a potential therapeutic target in neurodegenerative conditions due to its ability to cross the blood–brain barrier and exert pleiotropic neuroprotective effects. This review synthesizes current evidence from both preclinical and clinical studies examining the role of exercise-induced irisin in neurodegeneration, with particular emphasis on translational potential and therapeutic applications. A comprehensive search was conducted across PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and EMBASE databases (spanning January 2015 to December 2024) to identify peer-reviewed articles investigating irisin’s neuroprotective mechanisms in neurodegenerative diseases. Ten studies met the inclusion criteria (five rodent/primate model studies and five human clinical investigations), which were analyzed for methodological rigor, intervention protocols, biomarker quantification methods, and reported outcomes. Reviewed studies consistently demonstrated that exercise-induced endogenous irisin elevation correlates with improved cognitive function, reduced neuroinflammatory markers, enhanced synaptic plasticity, and modulation of neurodegenerative pathways, with exogenous irisin administration reproducing several neuroprotective benefits observed with exercise training in animal models. However, substantial heterogeneity exists regarding exercise prescription parameters (intensity, duration, frequency, modality), training-induced irisin quantification methodologies (ELISA versus mass spectrometry), and study designs (ranging from uncontrolled human observations to randomized controlled trials in animal models). Critical appraisal reveals that human studies lack adequate control for confounding variables including baseline physical fitness, comorbidities, concurrent medications, and potential sources of bias, while biochemical studies indicate distinct pharmacokinetics between endogenous training-induced irisin and exogenous bolus dosing, necessitating careful interpretation of therapeutic applicability. The translational potential of irisin as a therapeutic agent or drug target depends on resolving methodological standardization in biomarker measurement, conducting well-designed clinical trials with rigorous control for confounders, and integrating findings from molecular/biochemical studies to elucidate mechanisms linking irisin to disease modification. Future research should prioritize establishing clinical trial frameworks that harmonize exercise prescriptions, employ robust biomarker quantification (mass spectrometry), and stratify participants based on disease stage, comorbidities, and genetic predisposition to clarify irisin’s role as a potential therapeutic intervention in neurodegenerative disease management.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Patient and Physician Perspectives on Pharmacotherapy in Parkinson’s Disease Psychosis: A Mixed-Methods Exploratory Study
by
Olaf Rose, Tobias Hinteregger, Eugen Trinka, Bernhard Iglseder, Johanna Pachmayr and Stephanie Clemens
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010008 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Psychosis is a frequent and disabling non-motor complication of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Clozapine and quetiapine are widely used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease psychosis (PDP). We conducted an exploratory study to compare patient experiences with physician prescribing practices. Patients with PDP hospitalized
[...] Read more.
Psychosis is a frequent and disabling non-motor complication of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Clozapine and quetiapine are widely used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease psychosis (PDP). We conducted an exploratory study to compare patient experiences with physician prescribing practices. Patients with PDP hospitalized at a university center completed semi-structured interviews on perceived efficacy, adverse effects, and daily functioning. Neurologists and geriatricians attending training sessions completed a structured questionnaire on prescribing patterns, attitudes toward clozapine, and perceived treatment burden. Data were analyzed thematically and triangulated across cohorts. Eleven patients (mean age 81 years; nine treated with quetiapine, two with clozapine) were included. Most quetiapine-treated patients reported persistent hallucinations, sedation, dizziness, and reduced autonomy. Fourteen physicians completed the survey and most preferred quetiapine, citing monitoring logistics and agranulocytosis risk as barriers to clozapine. Overall, patient priorities centered on symptom control and independence, whereas physician decisions emphasized feasibility and safety. Facilitating clozapine monitoring and incorporating patient-reported outcomes into routine care may improve patient-centered PDP management.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence-Based Applications to Remove Disruptive Factors from Pharmaceutical Care: A Quantitative Study in Eastern Romania
by
Ionela Daniela Ferțu, Alina Mihaela Elisei, Mariana Lupoae, Alexandra Burlacu, Claudia Simona Ștefan, Luminița Enache, Andrei Vlad Brădeanu, Loredana Sabina Pascu, Iulia Chiscop, Mădălina Nicoleta Matei, Aurel Nechita and Ancuța Iacob
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010007 - 9 Jan 2026
Abstract
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has increasingly contributed to advancements in pharmaceutical practice, particularly by enhancing the pharmacist–patient relationship and improving medication adherence. This quantitative, descriptive, cross-sectional study investigated Eastern Romanian pharmacists’ perception of AI-based applications as effective optimization tools, correlating it with disruptive communication
[...] Read more.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has increasingly contributed to advancements in pharmaceutical practice, particularly by enhancing the pharmacist–patient relationship and improving medication adherence. This quantitative, descriptive, cross-sectional study investigated Eastern Romanian pharmacists’ perception of AI-based applications as effective optimization tools, correlating it with disruptive communication factors. An anonymous and online questionnaire was distributed to community pharmacists, examining sociodemographic characteristics, awareness of disruptive factors, and the perceived usefulness of AI. The sample included 437 respondents: pharmacists (55.6%), mostly female (83.8%), and aged between 25 and 44 (52.6%). Data analysis involved descriptive statistics and independent t-tests. The statistical analysis revealed a significantly positive perception (p < 0.001) of AI on pharmacist–patient communication. Respondents viewed AI as a valuable tool for reducing medication errors and optimizing counseling time, though they maintain a strong emphasis on genuine human interaction. Significant correlations were found between disruptive factors—such as noise and high patient volume—and the quality of communication. Participants also expressed an increased interest in applications like automatic prescription scheduling and the use of chatbots. The study concludes that a balanced implementation of AI technologies is necessary, one that runs parallel with the continuous development of pharmacists’ communication skills. Future research should focus on validating AI’s impact on clinical outcomes and establishing clear ethical guidelines regarding the use of patient data.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue AI Use in Pharmacy and Pharmacy Education)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Epidemiological Assessment of Benzodiazepine Dependence via Pharmacist-Led EMR Review in Pain and Palliative Care Institution
by
Carlos Eduardo Estrada-De La Rosa, Felipe Alexis Avalos-Salgado, Daniel Osmar Suárez-Rico, Martin Zermeño-Ruiz, César Ricardo Cortez-Álvarez and Raymundo Escutia-Gutiérrez
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010006 - 7 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Benzodiazepines (BZDs) are used routinely in cases requiring sedation for anxiety, insomnia, and procedures that require pain management, and daily use of these agents may extend over several months; therefore, monitoring patients is essential to reduce the risk of developing dependence. However,
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Benzodiazepines (BZDs) are used routinely in cases requiring sedation for anxiety, insomnia, and procedures that require pain management, and daily use of these agents may extend over several months; therefore, monitoring patients is essential to reduce the risk of developing dependence. However, the high patient volume in pain and palliative-care settings often limits physicians’ ability to both conduct consultations and perform comprehensive evaluations. In this context, the pharmacist plays a key role in supporting patient care by contributing professional activities that enhance patient well-being, such as conducting systematic reviews of electronic medical records. This pharmacist-led EMR assessment enables the identification of benzodiazepine dependence patterns and supports a more robust epidemiological evaluation within the institution. Methods: A descriptive observational study (January 2022–May 2025) using electronic medical records and prescription data was conducted. Consecutive adults with an active BZD prescription and a documented BDEPQ-MX (Benzodiazepine Dependence Questionnaire, Mexican version) were included. Outcomes were BDEPQ-MX categories (No dependence; Pleasurable effects; Perceived need; Dependence) and a binary endpoint was stablished as “any dependence” (either scored in Perceived need or Dependence category) vs. No dependence (either scored as No dependence or Pleasurable effects categories). Group comparisons used χ2, Student’s t, and one-way ANOVA. A logistic regression modeled any dependence; a general linear model (GLM) examined the BDEPQ-MX total score. Results: Of 181 complete cases, BDEPQ-MX categories were No dependence 33.2% (60/181), Pleasurable effects 7.2% (13/181), Perceived need 17.1% (31/181), and Dependence 42.5% (77/181); hence, 59.7% met “any dependence.” Women comprised 67.4% overall. Compared with No dependence, the any-dependence group had higher comorbidity (83.3% vs. 65.8%, p = 0.006) and markedly greater duration of BZD use (months) (22.6 ± 11.5 vs. 5.9 ± 4.9, p < 0.001), with no difference in daily dose (p = 0.6). Benzodiazepine medications shifted toward alprazolam in dependence (38.9% vs. 20.5%, p = 0.009) and away from clonazepam (43.5% vs. 58.9%, p = 0.042). In the adjusted model, the male sex was associated with lower odds of any dependence (aOR 0.29, 95% CI 0.11–0.76; p = 0.013), while the duration of BZD use (per month) increased the odds (aOR 1.32, 1.20–1.45; p < 0.001). In the GLM, the duration showed the largest effect on BDEPQ-MX total (F = 203.26; p < 0.001; partial η2 = 0.545). Conclusions: In this outpatient pain and palliative-care population, benzodiazepine-related dependence phenomena were common: 59.7% of patients met the criteria for dependence based on the pharmacist-led EMR review. The involvement of the pharmacist was essential, as this systematic evaluation would have been difficult to perform within routine medical consultations. The pharmacist’s contribution enabled a detailed epidemiological characterization, revealing that the exposure duration—more than daily dose—was the principal, modifiable correlate of dependence, and that alprazolam was disproportionately represented in the higher-dependence categories. These findings underscore the value of pharmacist-supported surveillance to identify and measure BZD dependance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmacists’ Roles in the Identification, Prevention and Treatment of Substance Use Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Structured Medication Review and Shared Decision-Making in Patients with Mild Intellectual Disabilities Who Use Psychotropic Medication
by
Gerda de Kuijper, Josien Jonker and Rien Hoge
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010005 - 6 Jan 2026
Abstract
People with intellectual disabilities frequently use psychotropic and other medications, sometimes inappropriately. To promote shared decision-making, they require accessible information about their medication. This study combined data from two similar intervention studies, conducted in two different settings, to assess the appropriateness of medication
[...] Read more.
People with intellectual disabilities frequently use psychotropic and other medications, sometimes inappropriately. To promote shared decision-making, they require accessible information about their medication. This study combined data from two similar intervention studies, conducted in two different settings, to assess the appropriateness of medication use and the shared decision-making process among adults with mild intellectual disabilities who used psychotropic medication. The intervention consisted of a structured, multidisciplinary medication review, including the provision of accessible psychotropic medication leaflets, and a discussion of the pharmacotherapeutic treatment plan with the patient by either a pharmacist or physician, depending on the setting. Outcomes included medication use, pharmacotherapeutic problems, implementation of recommendations, and perceived shared decision-making, measured with the Shared Decision-Making Questionnaire Q9. The 15 included participants used an average of nearly seven medications, which were mainly neurotropic, gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, and respiratory agents. On average, two pharmacotherapeutic problems were identified; the most common were overtreatment, side effects, and administration difficulties. Recommendations often involved dose reduction or tapering, and about 75% were fully or partially implemented. Both participants and clinicians reported high satisfaction with shared decision-making. Multidisciplinary, structured medication reviews, incorporating accessible medication leaflets, may enhance appropriate medication use and shared decision-making, but more research is needed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacy Practice and Practice-Based Research)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Beyond Addiction: Burden of Polypharmacy and Risk in Frail Patients with Substance Use Disorder
by
L. Goretti Santiago Gutiérrez, Daida Alberto Armas, Verónica Hernández García, Juan Ramón Santana Ayala, Roberto García Sánchez, Soraya Paz Montelongo, Ángel J. Gutiérrez, Arturo Hardisson de la Torre and Carmen Rubio Armendáriz
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010004 - 1 Jan 2026
Abstract
Substance use disorder (SUD) is a chronic and clinically complex condition, frequently complicated by significant organic and psychiatric comorbidities. Most patients are polymedicated and require opioid substitution programs (OSPs). This complexity is further exacerbated by drug–drug interactions, therapeutic duplication, and fragmentation of the
[...] Read more.
Substance use disorder (SUD) is a chronic and clinically complex condition, frequently complicated by significant organic and psychiatric comorbidities. Most patients are polymedicated and require opioid substitution programs (OSPs). This complexity is further exacerbated by drug–drug interactions, therapeutic duplication, and fragmentation of the healthcare system. This retrospective observational study analyses the prevalence of polypharmacy and associated pharmacotherapeutic risks in a cohort of 1050 patients with SUD treated at Drug Care Units (DCUs) in Tenerife (Canary Islands, Spain). Prescriptions were dominated by methadone (62%), antidepressants, and antipsychotics, often in combination with benzodiazepines. Significant polypharmacy (>10 active prescriptions) was observed in 2.3% of patients, while 8.1% received 6–10 medications and 37.2% were using 2–5 medications. Women showed a higher pharmacological burden, with 3.5% experiencing significant polypharmacy (>10 different prescriptions) compared with 1.1% of men. Overall, 31% of patients received antidepressants, 31% were treated with antipsychotics—frequently with concurrent use of multiple agents—and 6.4% received opioids outside the OSP. Therapeutic duplication was observed in 15.6% of patients for psycholeptics, 14.2% for psychoanaleptics, and 3.2% for antiepileptics. Additionally, 25.2% of patients reported self-medication, predominantly with benzodiazepines. These findings underscore the need for integrated pharmaceutical care programs incorporating individualized therapeutic review and deprescribing strategies to enhance the safety and efficacy of SUD treatment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacy Practice and Practice-Based Research)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
“Let’s Talk Stigma”: A Pharmacy-Based Program for Opioid Use Disorder Anti-Stigma Education in Pennsylvania
by
Joni C. Carroll, Sophia M. C. Herbert, Kim C. Coley, Thai Q. Nguyen, Melissa A. Somma McGivney, Kelsey L. Hake, Jennifer Padden Elliott and Elizabeth Bunk Barton
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010003 - 24 Dec 2025
Abstract
Opioid overdoses in the United States remain a significant public health concern. Opioid use disorder (OUD) is stigmatized, exacerbating negative health outcomes. Reducing stigma in healthcare, including in pharmacies, is critical. The “Let’s Talk Stigma” program was collaboratively developed with two schools of
[...] Read more.
Opioid overdoses in the United States remain a significant public health concern. Opioid use disorder (OUD) is stigmatized, exacerbating negative health outcomes. Reducing stigma in healthcare, including in pharmacies, is critical. The “Let’s Talk Stigma” program was collaboratively developed with two schools of pharmacy, a local health department, and individuals with lived drug use experience. It aimed to reduce OUD-related stigma among pharmacists, pharmacy technicians, student pharmacists, and other allied health professionals. The program included six core components: a podcast, continuing education, a standardized curriculum for student pharmacists, training for pharmacy technicians and medical assistants, pharmacy outreach by student pharmacists, and partnerships with chain pharmacies. The anti-stigma podcast reached a global audience with nearly 22,000 listens, while local sessions engaged over 5000 individuals. These initiatives were integrated into Doctor of Pharmacy curricula, with student pharmacists distributing stigma-reduction kits in local pharmacies. A mixed-methods approach, incorporating qualitative data from participant reflections and quantitative data from surveys, podcast analytics, and attendance records, was used for program evaluation. Participants reported increased awareness of stigma, improved attitudes, and greater professional responsibility to reduce stigma. The program successfully leveraged partnerships, flexible delivery methods, and inclusion of people with lived drug use experience in its design.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmacists’ Roles in the Identification, Prevention and Treatment of Substance Use Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Drug Manipulation in Pediatric Care: A Scoping Review of a Widespread Practice Signaling Systemic Gaps in Pharmaceutical Provision
by
Charlotte Vermehren, Laura Giraldi, Sarah Al-Rubai, Ida M. Heerfordt, Yasmine Merimi, Rene Mathiasen, Anette Müllertz, Jon Trærup Andersen, Susanne Kaae and Christina Gade
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010002 - 24 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Pediatric patients often receive medicines manipulated from adult formulations due to a lack of age-appropriate products. While such practices are clinically routine, they may reflect deeper systemic deficiencies in pediatric pharmacotherapy. Objective: This scoping review aimed to map the prevalence, definitions, and
[...] Read more.
Background: Pediatric patients often receive medicines manipulated from adult formulations due to a lack of age-appropriate products. While such practices are clinically routine, they may reflect deeper systemic deficiencies in pediatric pharmacotherapy. Objective: This scoping review aimed to map the prevalence, definitions, and types of pediatric drug manipulation and to conceptualize manipulation as an indicator of structural gaps in formulation science, regulation, and access. Methods: A systematic search of PubMed (January 2014–July 2024) included 10 studies reporting the frequency of drug manipulation in children aged ≤18 years. Eligible studies were synthesized narratively according to PRISMA-ScR guidelines. Results: Ten studies from nine countries were included, reporting manipulation frequencies ranging from 6.4% to 62% of all drug administrations and up to 60% at the patient level. Manipulated formulations most commonly included oral solid doses, altered through dispersing, splitting, or crushing. Definitions and methodologies varied considerably. The findings revealed five recurring structural gaps: limited pediatric formulations, inconsistent regulatory implementation, lack of standardized definitions and guidance, insufficient evidence on manipulation safety, and inequitable access across regions. Conclusion: Manipulation of finished dosage forms for use in children is a widespread, measurable phenomenon reflecting systemic inadequacies in formulation development, regulation, and access. Recognizing manipulation as a structural indicator may guide policy, innovation, and equitable pediatric pharmacotherapy worldwide.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluating the Accuracy and Educational Potential of Generative AI Models in Pharmacy Education: A Comparative Analysis of ChatGPT and Gemini Across Bloom’s Taxonomy
by
Tuan Tran, Uyen Le and Victor Phan
Pharmacy 2026, 14(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy14010001 - 23 Dec 2025
Abstract
This study evaluated the accuracy and educational potential of three generative AI models, ChatGPT 3.5, ChatGPT 4o, and Gemini 2.5, by addressing pharmacy-related content across three key areas: biostatistics, pharmaceutical calculations, and therapeutics. A total of 120 exam-style questions, categorized by Bloom’s Taxonomy
[...] Read more.
This study evaluated the accuracy and educational potential of three generative AI models, ChatGPT 3.5, ChatGPT 4o, and Gemini 2.5, by addressing pharmacy-related content across three key areas: biostatistics, pharmaceutical calculations, and therapeutics. A total of 120 exam-style questions, categorized by Bloom’s Taxonomy levels (Remember, Understand, Apply, and Analyze), were administered to each model. Overall, the AI models achieved a combined accuracy rate of 77.5%, with ChatGPT 4o consistently outperforming ChatGPT 3.5 and Gemini 2.5. The highest accuracy was observed in therapeutics (83.3%), followed by biostatistics (81.7%) and calculations (67.5%). Performance was strongest at lower Bloom levels, reflecting proficiency in recall and conceptual understanding, but declined at higher levels requiring analytical reasoning. These findings suggest that generative AI tools can serve as effective supplementary aids for pharmacy education, particularly for conceptual learning and review. However, their limitations in quantitative and higher-order reasoning highlight the need for guided use and faculty oversight. Future research should expand to additional subject areas and assess longitudinal learning outcomes to better understand AI’s role in improving critical thinking and professional competence among pharmacy students.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The AI Revolution in Pharmacy Practice and Education)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Intrathecal Drug Delivery Systems for Chronic Pain Management: A Narrative Review of Pharmacologic Agents, Clinical Applications, and Considerations
by
Milan Patel, Alison J. Deng, Madelyn Reilly, Mariam Morcus, Alyssa McKenzie, Lukas Henjum, Alan D. Kaye and Alaa Abd-Elsayed
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 185; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060185 - 16 Dec 2025
Abstract
This narrative review seeks to delve into the different on and off-label medications commonly used with intrathecal drug delivery systems (IDDS) and their clinical applications specifically in pain management settings. This review utilizes a variety of studies including reviews, retrospective chart analyses, and
[...] Read more.
This narrative review seeks to delve into the different on and off-label medications commonly used with intrathecal drug delivery systems (IDDS) and their clinical applications specifically in pain management settings. This review utilizes a variety of studies including reviews, retrospective chart analyses, and more to analyze the current effectiveness of various pharmacological agents on reducing chronic pain through IDDS. The initial results of intrathecal delivery of these medications have provided benefit in pain reduction and overall patient satisfaction; however, this review will seek to analyze the current data and understanding and suggest areas of strength and improvement within the field and our current understanding.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Prevalence of Potentially Inappropriate Medications in Drug Dispensing Data of Older Adults Living in Northwest Italy
by
Lucrezia Greta Armando, Jacopo Luboz, Abdoulaye Diarassouba, Gianluca Miglio and Clara Cena
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 184; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060184 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The increasing use of multiple medications among older adults raises concerns about potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs), which are associated with adverse health outcomes and increased healthcare costs. This study aimed to assess the prevalence and types of PIMs dispensed to older adults living
[...] Read more.
The increasing use of multiple medications among older adults raises concerns about potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs), which are associated with adverse health outcomes and increased healthcare costs. This study aimed to assess the prevalence and types of PIMs dispensed to older adults living in Northwest Italy using real-world pharmacy claims data. An observational, retrospective analysis was conducted on anonymized drug dispensing datasets from two local health authorities, covering individuals aged 65 years or older between 2018 and 2021. PIMs were identified according to the 2019 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria, focusing on drugs that are inappropriate or should be used with caution in older adults or have anticholinergic properties. Over half of older adults who received medications during the study period were dispensed at least one PIM, with stable or slight increased prevalence over time with no differences by sex or region. Proton-pump inhibitors used for more than 8 weeks and paroxetine were the most common PIMs, while furosemide and sulfonylureas were also frequently reported PIMs. These findings indicate a persistently high burden of inappropriate prescribing in older adults and highlight the need for coordinated deprescribing interventions and prescriber education to promote safer, evidence-based pharmacotherapy in aging populations.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
Pharmacy Students’ Perspectives on Integrating Generative AI into Pharmacy Education
by
Kaitlin M. Alexander, Eli O. Jorgensen, Casey Rowe and Khoa Nguyen
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 183; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060183 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
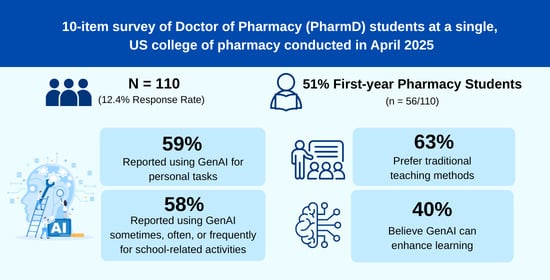
Objective: This study aims to evaluate pharmacy students’ perceptions regarding the integration of generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) into pharmacy curricula, providing evidence to inform future curriculum development. Methods: A cross-sectional survey of Doctor of Pharmacy (PharmD) students at a single U.S. College of
[...] Read more.
Objective: This study aims to evaluate pharmacy students’ perceptions regarding the integration of generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) into pharmacy curricula, providing evidence to inform future curriculum development. Methods: A cross-sectional survey of Doctor of Pharmacy (PharmD) students at a single U.S. College of Pharmacy was conducted in April 2025. Students from all four professional years (P1–P4) were invited to participate. The 10-item survey assessed four domains: (1) General GenAI Use, (2) Knowledge and Experience with GenAI Tools, (3) Learning Preferences with GenAI, and (4) Perspectives on GenAI in the curriculum. Results: A total of 110 students responded (response rate = 12.4%). Most were P1 students (56/110, 50.9%). Many reported using GenAI tools for personal (65/110, 59.1%) and school-related purposes (64/110, 58.1%) sometimes, often, or frequently. ChatGPT was the most used tool. While 40% (40/99) agreed or strongly agreed that GenAI could enhance their learning, 62.6% (62/99) preferred traditional teaching methods. Open-ended responses (n = 25) reflected a mix of positive, neutral, and negative views on GenAI in education. Conclusions: Many pharmacy students in this cohort reported using GenAI tools and demonstrated a basic understanding of GenAI functions, yet students also reported that they preferred traditional learning methods and expressed mixed views on incorporating GenAI into teaching. These findings provide valuable insights for faculty and schools of pharmacy as they develop strategies to integrate GenAI into pharmacy education.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue AI Use in Pharmacy and Pharmacy Education)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Impacts of Outsourcing Medication Repackaging in Nursing Homes: Quality and Areas of Pharmacy–Nursing Collaboration
by
Thomas Schmid, Falk Hoffmann, Michael Dörks and Kathrin Jobski
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 182; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060182 - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
The task of repackaging resident’s medication into medication organizers is increasingly outsourced from nursing homes to pharmacies, presenting an opportunity to redefine the interaction between nursing and pharmaceutical staff. This study investigated whether outsourcing medication repackaging changes the quality and subjects of collaboration
[...] Read more.
The task of repackaging resident’s medication into medication organizers is increasingly outsourced from nursing homes to pharmacies, presenting an opportunity to redefine the interaction between nursing and pharmaceutical staff. This study investigated whether outsourcing medication repackaging changes the quality and subjects of collaboration between the two professions. A cross-sectional survey was developed targeting heads of nursing in German nursing homes. A simple random sample of 1415 nursing homes was contacted by phone. Respondents participated either by phone or by online survey. Quality of collaboration was measured using Kenaszchuk’s Interprofessional Collaboration Scale (ICS) with its subscales Communication, Accommodation and Isolation. Topics of interaction were ascertained using items along a medication management phase model. Differences in response frequencies were analyzed using Fisher’s exact test. A total of 268 nursing homes participated (response: 18.9%). Of these, 132 (49.3%) had outsourced repackaging. Respondents at nursing homes with in-house medication repackaging rated the subscale Accommodation more favorably (p = 0.008), while Communication and Isolation showed no difference. Of the 13 individual ICS items, “passing on information” (Communication) was rated better by respondents at homes with outsourced repackaging (p = 0.019) and “consideration of convenience” (Accommodation) more favorably by respondents at homes with in-house repackaging (p = 0.042). Nursing staff at homes with outsourced medication repackaging interacted with pharmaceutical staff more frequently on medication changes (p < 0.001), but less frequently on tablet splitting (p = 0.035). In conclusion, outsourcing medication repackaging has a limited impact on the quality of interprofessional collaboration between the two professions but may have the potential to reduce ambiguities regarding splitting tablets.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacy Practice and Practice-Based Research)
►▼
Show Figures
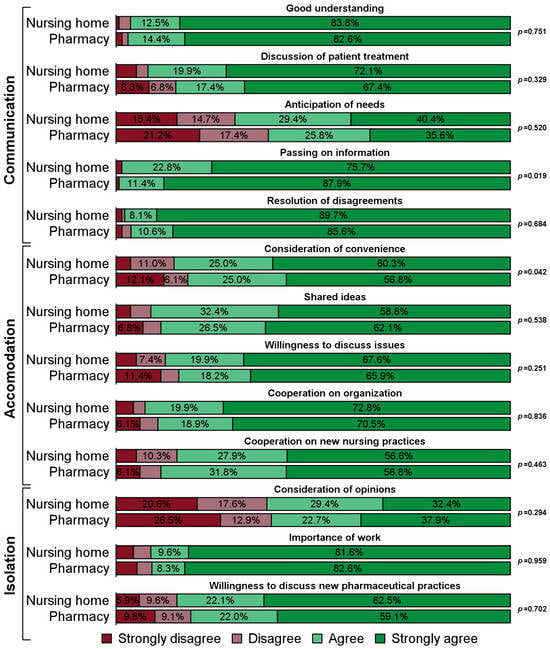
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Benzodiazepine (BZD) Use and Patient Safety: Opportunities for Community Pharmacy Involvement in the Management of Drug Interactions
by
Juan Ramón Santana Ayala, Daida Alberto Armas, Veronica Hernández García, Armando Aguirre-Jaime, Ángel J. Gutiérrez, Soraya Paz-Montelongo, Arturo Hardisson de la Torre and Carmen Rubio Armendáriz
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 181; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060181 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
Introduction: During pharmaceutical care, community pharmacists play a crucial role by carrying out interventions aimed at preventing, detecting, and resolving drug-related problems (DRPs) and negative outcomes associated with medication (NOM), simultaneously enhancing patients’ knowledge about their treatments. The chronic use of Benzodiazepines (BZDs)
[...] Read more.
Introduction: During pharmaceutical care, community pharmacists play a crucial role by carrying out interventions aimed at preventing, detecting, and resolving drug-related problems (DRPs) and negative outcomes associated with medication (NOM), simultaneously enhancing patients’ knowledge about their treatments. The chronic use of Benzodiazepines (BZDs) is known to be associated with risks such as tolerance, dependence, and cognitive impairment. Furthermore, the combined use of BZDs with other medications or alcohol may expose patients to significant drug interactions. Objectives: This study aimed to characterize and describe the clinical profile of patients using BZDs, to evaluate the extent of polypharmacy and potential drug interactions, to investigate their level of knowledge regarding BZD treatment, and ultimately, to propose evidence-based interventions from the community pharmacy to contribute to improving patient safety and minimizing risks associated with BZD use. Method: A cross-sectional, descriptive study was conducted in a single community pharmacy in Gran Canaria (Canary Islands, Spain). The study population comprised 125 adult patients with active BZD prescriptions. Data collection was performed through pharmacist–patient structured interviews using a questionnaire that included sociodemographic, clinical, and BZD knowledge variables. Results: Lormetazepam and alprazolam were the BZDs most frequently prescribed and dispensed. Potential drug interactions with other medications were detected in 38.4% of BZD users. Notably, 61.5% of patients using BZDs also reported the concurrent use of opioid analgesics, with tramadol being the most common opioid (48.1% of BZD users were also treated with tramadol). Statistically significant differences were observed between patients with and without BZD and other drug interactions in several adverse outcome variables, including the risk of falls (p = 0.003), cognitive impairment (p = 0.047), and urinary incontinence (p = 0.016). Existing BZD dependence is detected in 25% and 22.1% of cases, respectively. Patients’ knowledge of their BZD treatment revealed critical gaps, which are identified as a challenge and a clear opportunity for intervention through pharmaceutical care services. Conclusions: The findings underscore the essential and proactive role of community pharmacists in identifying and managing drug interactions, as well as in supporting deprescribing strategies through collaborative and interprofessional care models.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacy Practice and Practice-Based Research)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessPerspective
Advances in Drug and Vaccine Delivery for Low- and Middle-Income Healthcare Programs—The Case for Replacing Multi-Dose Vials with Prefilled Single-Dose Delivery Systems
by
Darin Zehrung and Michael J. Free
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 180; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060180 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The transition toward wide-scale use of single-dose administration systems such as prefilled syringes has primarily occurred in high-income countries due to economic considerations. This has resulted in a disparity of access to such technologies in low- and middle-income countries, which continue to utilize
[...] Read more.
The transition toward wide-scale use of single-dose administration systems such as prefilled syringes has primarily occurred in high-income countries due to economic considerations. This has resulted in a disparity of access to such technologies in low- and middle-income countries, which continue to utilize multi-dose vial-based presentations and syringes for parenteral delivery. Single-dose innovations currently available or in the product development pipeline represent the promise of enhanced access globally and the potential for public health impact. This perspective article discusses the reported benefits of pre-filled single-dose delivery systems compared to multi-dose vials, as well as the higher standards of infection control regulations and practices that resulted in the increasing use of and benefit from single-dose administration systems in high-income countries. We evaluated how these benefits and standards could enhance health initiatives in low- and middle-income countries. Finally, we explored the potential for making pre-filled single-dose delivery methods both accessible and affordable in low- and middle-income countries.
Full article
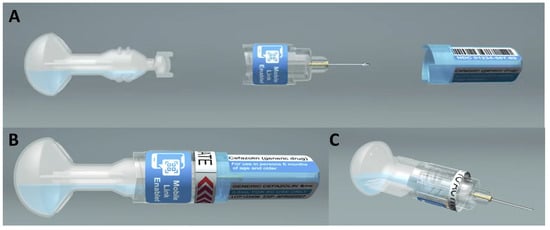
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Drug Repurposing for Inclusion of COVID-19-Related Indication: Field Study of the European Medicines Agency’s Response to the Pandemic
by
Antonio Ivanov, Violeta Getova-Kolarova and Ines Hababa-Ivanova
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 179; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060179 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
As one of the biggest challenges for healthcare in the 21st century, COVID-19 placed a sustained and intense demand on the European Medicines Agency’s resources and required constant adaptation and mobilization of different regulatory processes. In this situation, drug repurposing appeared as a
[...] Read more.
As one of the biggest challenges for healthcare in the 21st century, COVID-19 placed a sustained and intense demand on the European Medicines Agency’s resources and required constant adaptation and mobilization of different regulatory processes. In this situation, drug repurposing appeared as a promising potential approach in quickly emerging health crises due to its main advantage of reducing the time and cost for addition of new indications since it uses products proven to be of high quality, safe, and effective. We performed an analysis of European Public Assessment Reports for medicinal products authorized for the SARS-CoV-2 infection by the European Medicines Agency, showing a total of eight products with this indication, three (37.5%) of which used repurposing as a mechanism for development (remdesivir, tocilizumab, and anakinra). The application of this mechanism by these medicines highlights the importance of the life cycle stage at which repositioning is undertaken, which resulted in different volumes of data submitted in the respective European Public Assessment Reports. The participation of organizations other than the marketing authorization holder in key stages in the drug development process of repurposed products was once again confirmed, which emphasizes the need to regulate this interaction.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Drug Repurposing: Strengthening Outcomes of Existing Pharmaceuticals to Shift Emerging Health Challenges)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mining of Adverse Event Signals Associated with Fluticasone Furoate/Umeclidinium/Vilanterol Triple Therapy: A Post-Marketing Analysis Based on FAERS
by
Jiajun Chen, Ying Qiao, Gaoxing Qiao, Xiaocan Jia and Jicun Zhu
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 178; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060178 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a major global health burden. The fluticasone furoate (FF)/umeclidinium (UMEC)/vilanterol (VI) triple therapy provides new treatment, but its long-term real-world safety lacks evidence. A post-marketing analysis used the FAERS database to identify adverse event (AE) signals for
[...] Read more.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a major global health burden. The fluticasone furoate (FF)/umeclidinium (UMEC)/vilanterol (VI) triple therapy provides new treatment, but its long-term real-world safety lacks evidence. A post-marketing analysis used the FAERS database to identify adverse event (AE) signals for FF/UMEC/VI. Disproportionality methods including reporting odds ratio (ROR), proportional reporting ratio (PRR), information component (IC), and empirical Bayesian geometric mean (EBGM), were applied to detect AE signals, focusing on reports from third quarter (Q3) 2019 to Q3 2024. Among 16,238 reports listing FF/UMEC/VI as primary suspect, significant AE signals occurred in ‘injury, poisoning and procedural complications’ (n = 9067, ROR 2.46, PRR 2.08, IC 1.06, EBGM 2.08), and ‘respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders’ (n = 6567, ROR 4.87, PRR 4.15, IC 2.05, EBGM 4.13). A total of 196 significantly disproportionate preferred terms (PTs) were identified, including previously undocumented AEs such as chronic eosinophilic rhinosinusitis, dysphonia, and vocal cord dysfunction. This post-marketing safety study revealed significant signals for dysphonia and vocal cord dysfunction associated with FF/UMEC/VI, suggesting that clinicians should remain vigilant for these events.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Telepharmacy Consultations (TPCs) in Local Pharmacies—A Bi-Centric Survey of Customer Opinions
by
Nathalie Floch, Philipp Harand, Chris Graichen and Thilo Bertsche
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 177; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060177 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Telepharmacy consultations (TPCs) became a routine element of pharmacy operations. However, there is limited data available on local pharmacy customer feedback related to TPC. Methods: A customer survey was developed seeking feedback on TPC. The pharmacy customers were invited to
[...] Read more.
Background: Telepharmacy consultations (TPCs) became a routine element of pharmacy operations. However, there is limited data available on local pharmacy customer feedback related to TPC. Methods: A customer survey was developed seeking feedback on TPC. The pharmacy customers were invited to complete the survey in two local pharmacies in Germany. The survey and corresponding informed consent form were approved by the Ethics Committee. Results: In total, 178 pharmacy customers were enrolled (median age 41–50 years). From those, 37% agreed when asked whether they were generally interested in TPC. A total of 37% had the nearest pharmacy 5–15 min from their home. A total of 42% visited their pharmacy quarterly. A total of 36% used technical devices in median 1–2 h per days. A total of 33% classified their own digital skills at least as sufficient. A total of 59% would use their smartphone as a potential device for TPC. A total of 83% rated it as (slightly) important that the pharmacist providing TPC can be heard clearly. A total of 76% each (strongly) agreed that an argument for TPC would include limited mobility or pandemic/quarantine. A total of 33% (strongly) agreed that a key argument against TPC were technical requirements. A total of 75% considered situations of immobility to be the most important future perspective for TPC. Conclusions: Many pharmacy customers see TPC as an opportunity, e.g., in cases of limited mobility or during pandemic or quarantine. However, the use of appropriate technology can be a limiting factor.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacy Practice and Practice-Based Research)
►▼
Show Figures
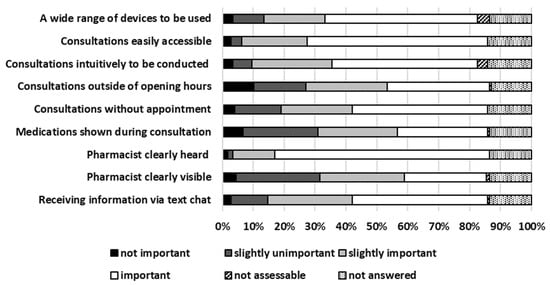
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Large Language Models for Drug-Related Adverse Events in Oncology Pharmacy: Detection, Grading, and Actioning
by
Md Muntasir Zitu, Ashish Manne, Yuxi Zhu, Wasimul Bari Rahat and Samar Binkheder
Pharmacy 2025, 13(6), 176; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy13060176 - 3 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Preventable medication harm in oncology is often driven by drug-related adverse events (AEs) that trigger order changes such as holds, dose reductions, delays, rechallenges, and enhanced monitoring. Much of the evidence needed to make these decisions lives in unstructured clinical texts, where large
[...] Read more.
Preventable medication harm in oncology is often driven by drug-related adverse events (AEs) that trigger order changes such as holds, dose reductions, delays, rechallenges, and enhanced monitoring. Much of the evidence needed to make these decisions lives in unstructured clinical texts, where large language models (LLMs), a type of artificial intelligence (AI), now offer extraction and reasoning capabilities. In this narrative review, we synthesize empirical studies evaluating LLMs and related NLP systems applied to clinical text for oncology AEs, focusing on three decision-linked tasks: (i) AE detection from clinical documentation, (ii) Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) grade assignment, and (iii) grade-aligned actions. We also consider how these findings can inform pharmacist-facing recommendations for order-level safety. We conducted a narrative review of English-language studies indexed in PubMed, Ovid MEDLINE, and Embase. Eligible studies used LLMs on clinical narratives and/or authoritative guidance as model inputs or reference standards; non-text modalities and non-empirical articles were excluded. Nineteen studies met inclusion criteria. LLMs showed the potential to detect oncology AEs from routine notes and often outperformed diagnosis codes for surveillance and cohort construction. CTCAE grading was feasible but less stable than detection; performance improved when outputs were constrained to CTCAE terms/grades, temporally anchored, and aggregated at the patient level. Direct evaluation of grade-aligned actions was uncommon; most studies reported proxies (e.g., steroid initiation or drug discontinuation) rather than formal grade-to-action correctness. While prospective, real-world impact reporting remained sparse, several studies quantified scale advantages and time savings, supporting an initial role as high-recall triage with pharmacist adjudication. Overall, the evidence supports near-term, pharmacist-in-the-loop use of AI for AE surveillance and review, with CTCAE-structured, citation-backed outputs delivered into the pharmacist’s electronic health record order-verification workspace as reviewable artifacts. Future work must standardize reporting and CTCAE/version usage, and measure grade-to-action correctness prospectively, to advance toward order-level decision support.
Full article

Graphical abstract

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Pharmacy Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
JCM, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Pharmacy, Healthcare
Optimization of Drug Utilization and Medication Adherence
Topic Editors: Enrica Menditto, Sara Mucherino, Ignacio Aznar-LouDeadline: 30 October 2026
Topic in
Biomedicines, Future Pharmacology, Pharmacy, IJMS, Biomolecules, Genes
Prospects of Multi-Target Agonists in Metabolic and Epigenetic Medicine
Topic Editors: Riham Abouleisa, Yanming LiDeadline: 30 November 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Pharmacy
The Evolving Role of the Pharmacist in Improving Vaccination Uptake
Guest Editor: Mary BushellDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
Pharmacy
Advancing Pharmacy Education: Integrating Science and Clinical Practice
Guest Editors: Ryoichi Fujiwara, Frank YuDeadline: 15 April 2026
Special Issue in
Pharmacy
Pharmacist Workforce Challenges and Solutions: Perspectives from Research and Practice
Guest Editors: Ioana Popovici, Manuel J. CarvajalDeadline: 30 April 2026
Special Issue in
Pharmacy
Drug Repurposing: Strengthening Outcomes of Existing Pharmaceuticals to Shift Emerging Health Challenges
Guest Editors: Ilko Getov, Hristina LebanovaDeadline: 30 April 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Pharmacy
New Insights into Pharmacy Teaching and Learning during COVID-19
Collection Editors: Darko Modun, Ana Seselja Perisin







