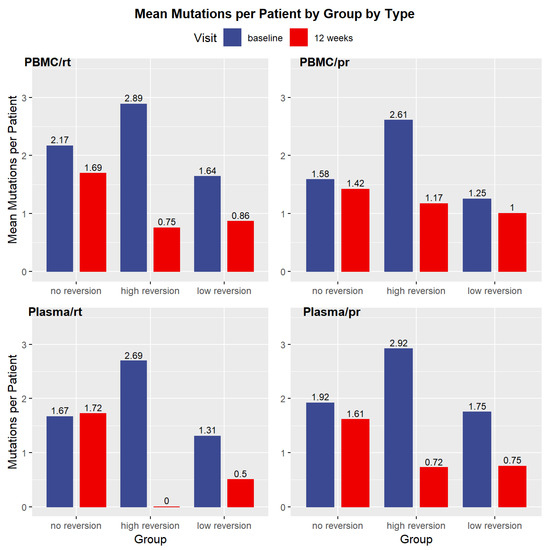
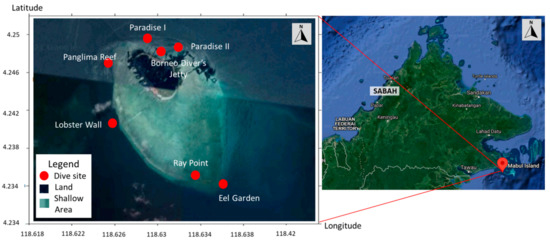
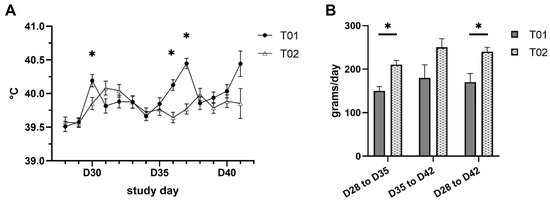
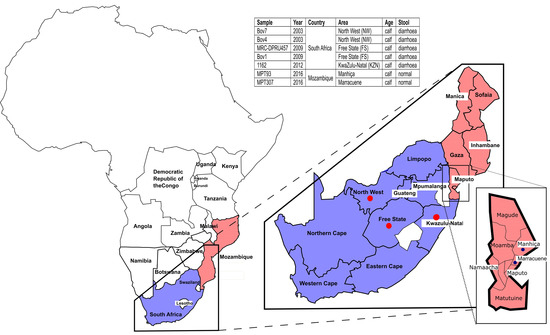
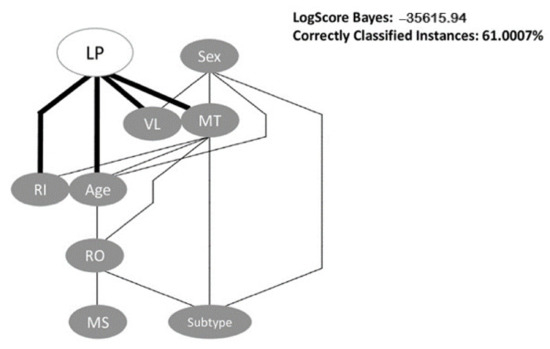
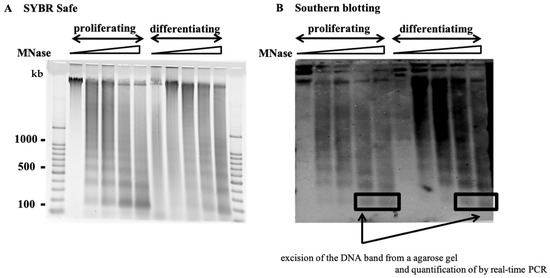
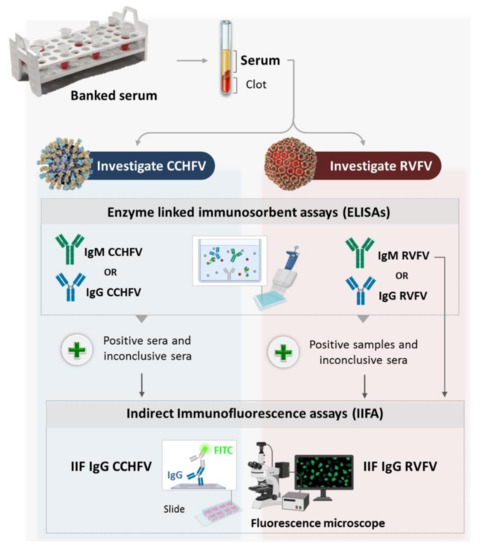
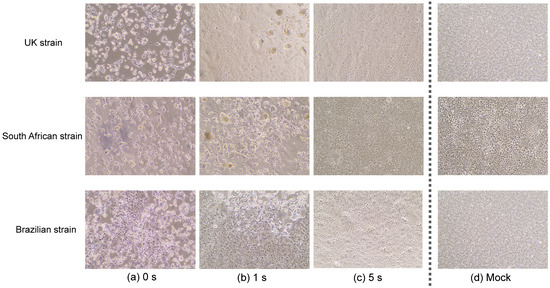
Feature Papers in Viral Pathogens
A topical collection in Pathogens (ISSN 2076-0817). This collection belongs to the section "Viral Pathogens".
Submission Status: Closed | Viewed by 403998Editor
Interests: filoviruses; emerging viruses; aerobiology; animal model development; medical countermeasures to hazard group 4 viruses; survival and inactivation of hazard group 4 viruses
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
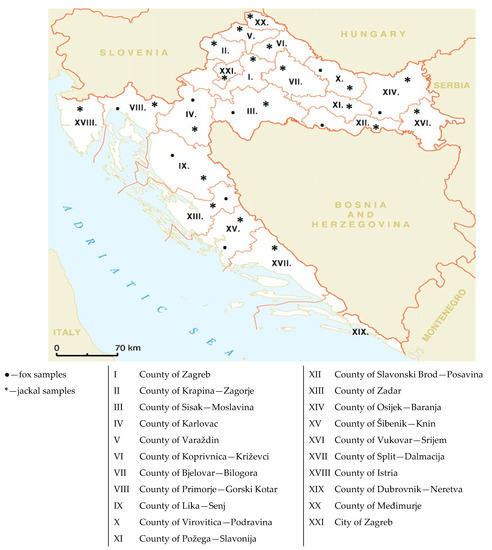
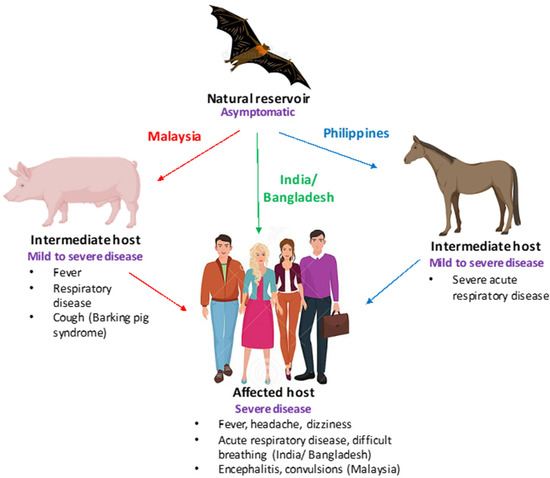
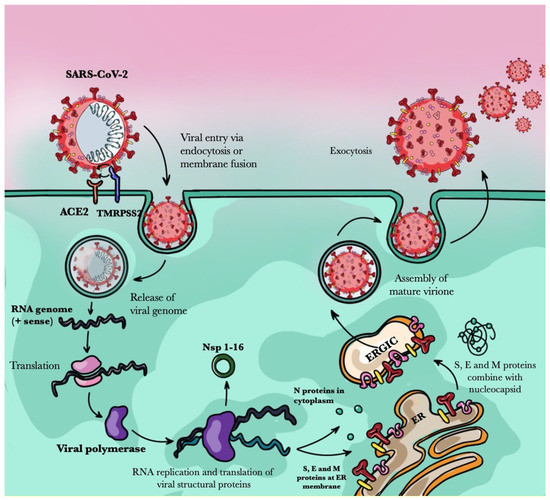
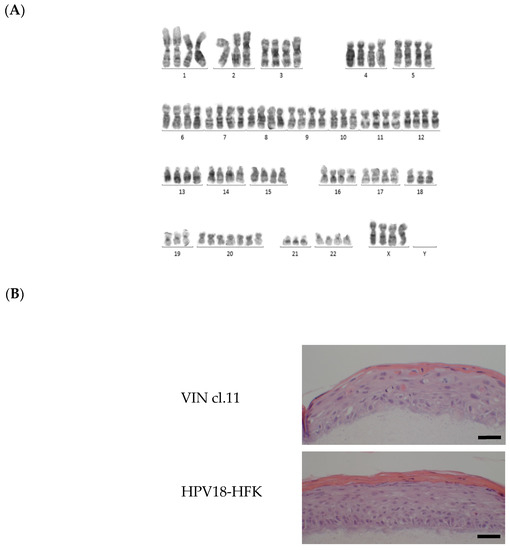
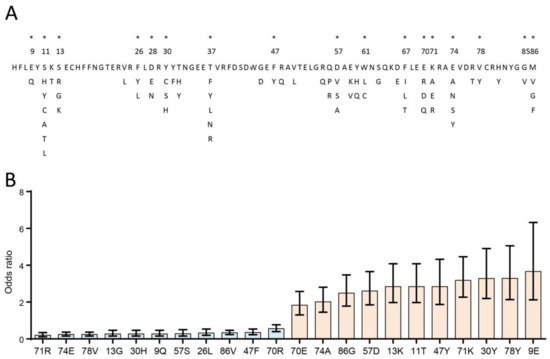
Viral pathogens infect all types of life forms, from human, animals, and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Examples of common human diseases caused by viruses include the common cold, influenza, chickenpox, and cold sores. Many serious diseases such as rabies, Ebola virus disease, AIDS (HIV), avian influenza, and SARS are caused by viruses, and current global COVID-19 pandemic is caused by SARS-CoV-2. Animals are usually the “natural host” for viruses that infect humans (Viral Zoonoses) and may also be carriers of viruses originating from environmental contamination. Livestock, Companion animals, mammals, Fish, et al. are all susceptible to serious viral infections. Among pathogens, plant viruses are economically important because they are responsible for more than half of the emerging infectious diseases in plants. Plant viruses are a continuous threat to agricultural crops and cause significant economic losses in crop yields worldwide. Bacteriophages are a common and diverse group of viruses and are the most abundant biological entity in aquatic environments. Bacteriophages can be used to treat some bacterial infections. The current discovery and research of viral pathogens are essential for the in-depth exploration of various viral diseases.
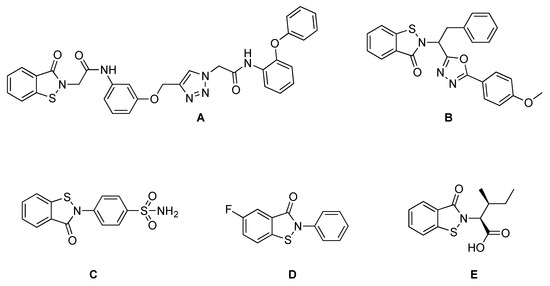
This Topical Collection "Feature Papers in Viral Pathogens" welcomes contributions that include original research and review papers, covering all aspects of viral pathogens and host-virus interactions. This includes the latest findings in viral pathogenesis, viral transformation, viral transmission, genome structure and evolution, host defense, host immune responses, vaccines, antiviral drugs, antiviral therapy, emerging viruses, et al. We look forward to your contribution.
Dr. Anna Honko
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Pathogens is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2200 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- virus
- viral pathogens
- host-virus interaction
- pathogenesis
- immune responses
- vaccines
- epidemiology
- diagnosis
- transmission
- antiviral