- Article
HTD1265 Disrupts GimC-Dependent Cellular Processes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Kaori Itto-Nakama,
- Naoya Hosoyamada and
- Yoshikazu Ohya
- + 8 authors
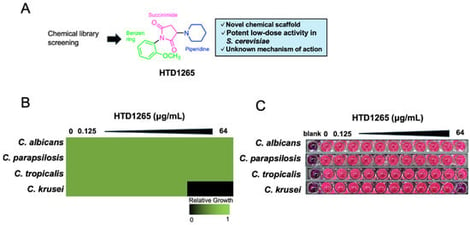
HTD1265 is a newly identified antifungal compound that displays potent activity against Candida krusei, a clinically challenging non-albicans species. To elucidate its mechanism of action, we applied an integrative phenotypic approach combining high-resolution morphological profiling, pathway inference, and genetic validation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Morphological signature extraction revealed a characteristic defect in nuclear positioning upon HTD1265 treatment. Integration of nuclear positioning traits with global morphological similarity highlighted 36 genes enriched for the Gene Ontology term “tubulin complex assembly.” Consistent with this prediction, HTD1265 impaired mitotic spindle elongation without directly inhibiting tubulin polymerization. HTD1265 further induced hallmarks of GimC (prefoldin) deficiency, including aberrant chitin accumulation, actin disorganization, and nuclear mispositioning, and caused hypersensitivity in GimC subunit mutants. These converging observations suggest that HTD1265 exerts antifungal activity by disrupting GimC-dependent cellular processes rather than by directly targeting tubulin. Our findings highlight GimC-dependent cytoskeletal and cell wall regulatory processes as a critical vulnerability for fungal growth and position HTD1265 as a functional tool for dissecting this pathway.
7 February 2026