- Review
Dietary Patterns Influence Chronic Disease Risk and Health Outcomes in Older Adults: A Narrative Review
- Jordan A. Gunning,
- Madeline F. Converse and
- Behzad Gudarzi
- + 2 authors
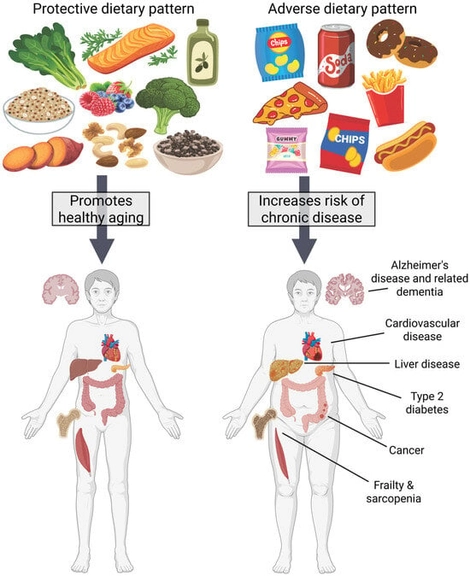
The global population is aging rapidly and the prevalence of age-related noncommunicable diseases is increasing. Favorable dietary patterns have the power to reduce the risk or progression of various age-related chronic diseases, including obesity, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, several types of cancer, and some neurodegenerative diseases. In contrast, adverse dietary patterns may contribute to the onset or progression of many chronic diseases or their risk factors. A diet rich in wholesome, nutrient-dense, minimally processed foods, such as a Mediterranean-style diet, may promote health and prevent disease through its abundance of antioxidants, fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and micronutrients. Conversely, a diet high in nutrient-poor and ultra-processed foods may accelerate disease onset and progression by promoting inflammation and affecting metabolic pathways adversely. This narrative review summarizes the literature from clinical trials and large population-based studies on protective dietary patterns and adverse dietary patterns that influence risk of cardiovascular disease and related risk factors, cancer, Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias, type 2 diabetes, frailty, and liver disease.
13 December 2025