Ingested Polystyrene Micro-Nanoplastics Increase the Absorption of Co-Ingested Arsenic and Boscalid in an In Vitro Triculture Small Intestinal Epithelium Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
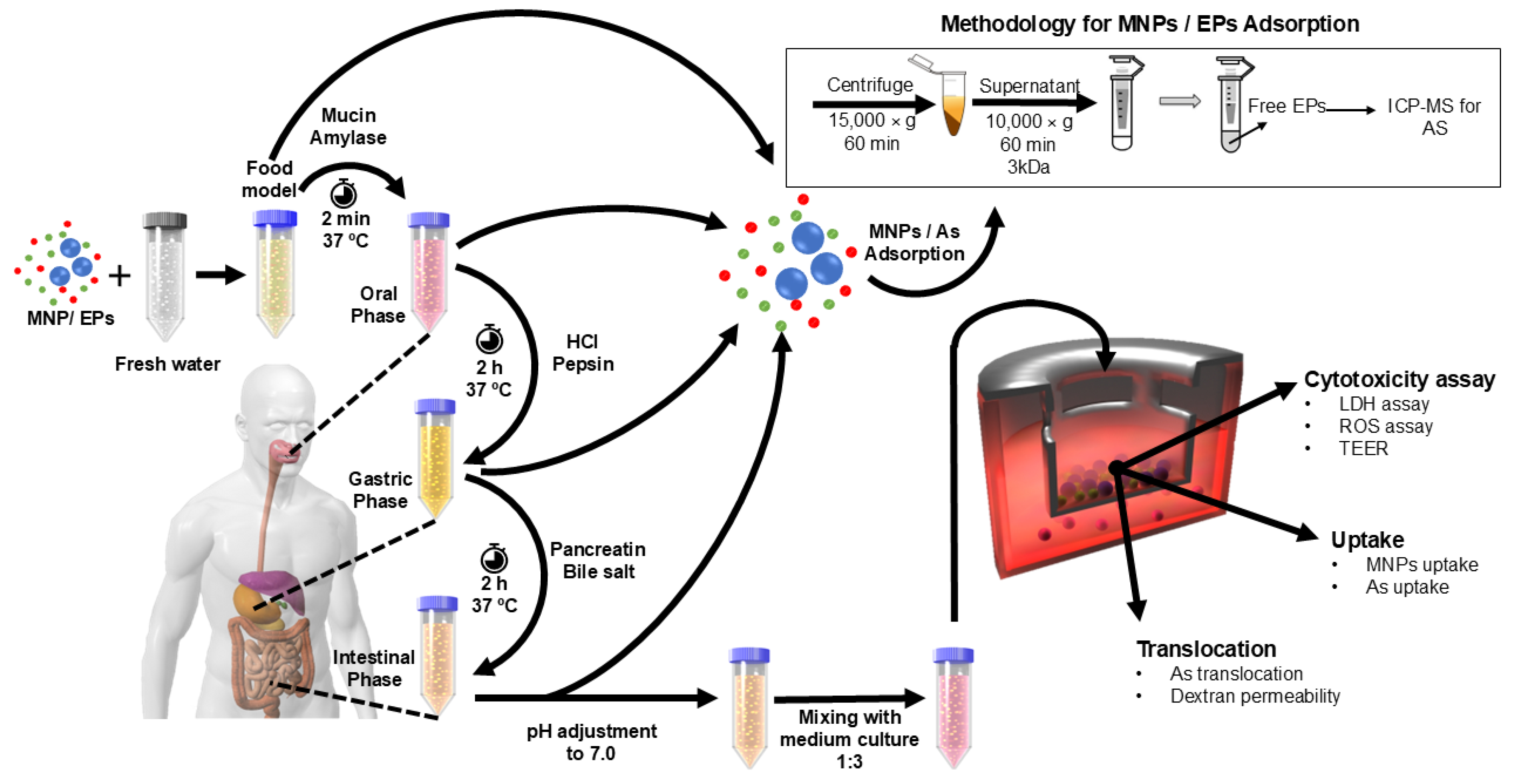
2.1. Preparation of Fresh Water MNP, EP and MNP-EP Test Suspensions/Solutions
2.2. In Vitro Simulated Digestion of MNP, EP and MNP-EP Suspensions/Solutions
2.3. Colloidal Characterization of MNPs
2.4. Assessment of As and Boscalid Sorption by PS MNPs
2.5. Preparation of Triculture Small Intestinal Epithelia Model
2.6. Exposure of Triculture Small Intestinal Model to MNPs and EPs
2.7. Measurement of Trans-Epithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER)
2.8. Cytotoxicity Assessment (LDH Release)
2.9. Measurement of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production
2.10. Dextran Permeability Assessment of Epithelial Barrier Integrity
2.11. Measurement of MNP and EP Uptake
2.12. Measurement of MNP and EP Translocation
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
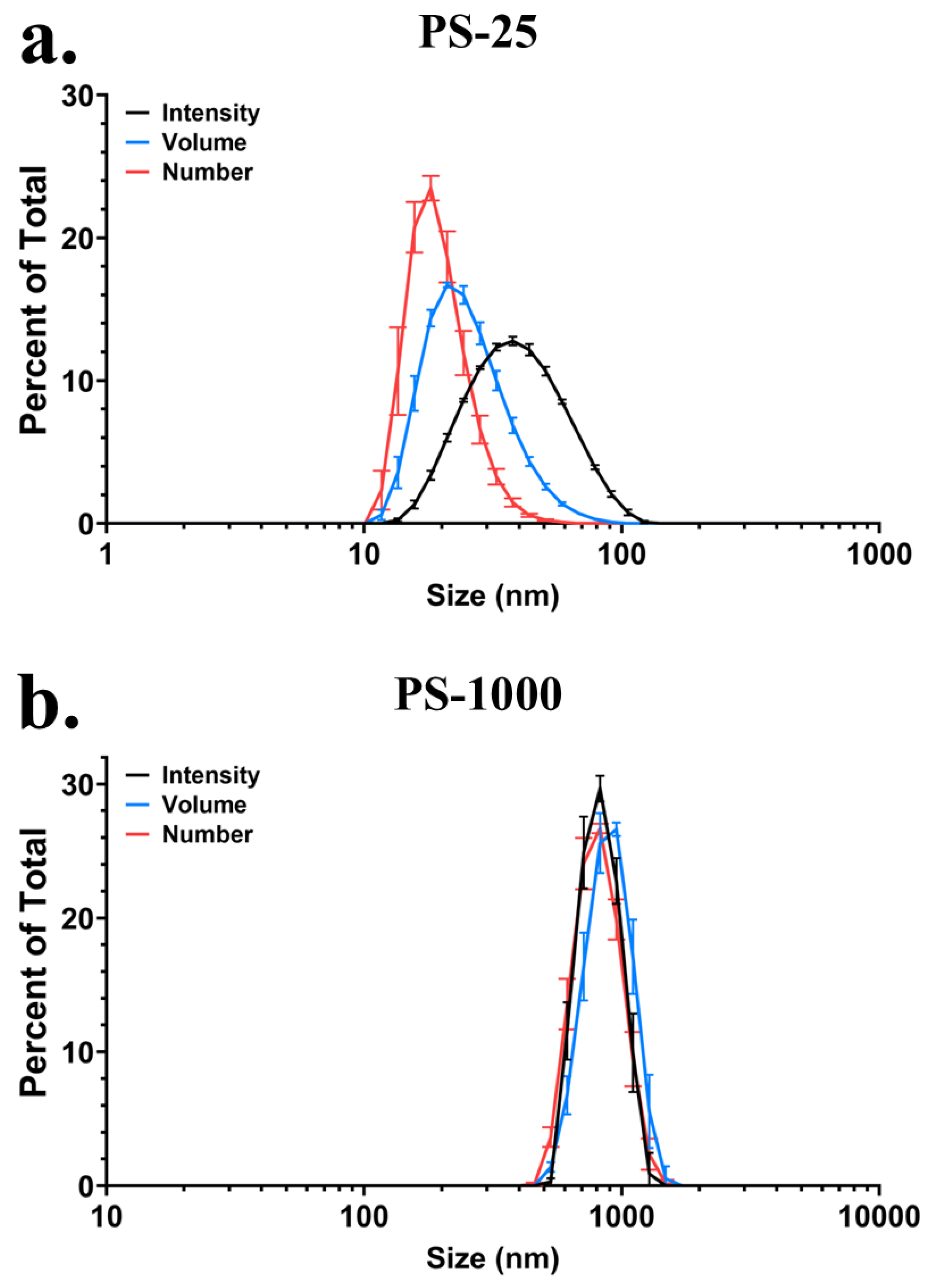
3.1. Colloidal Characterization of PS-25 and PS-1000 in Water
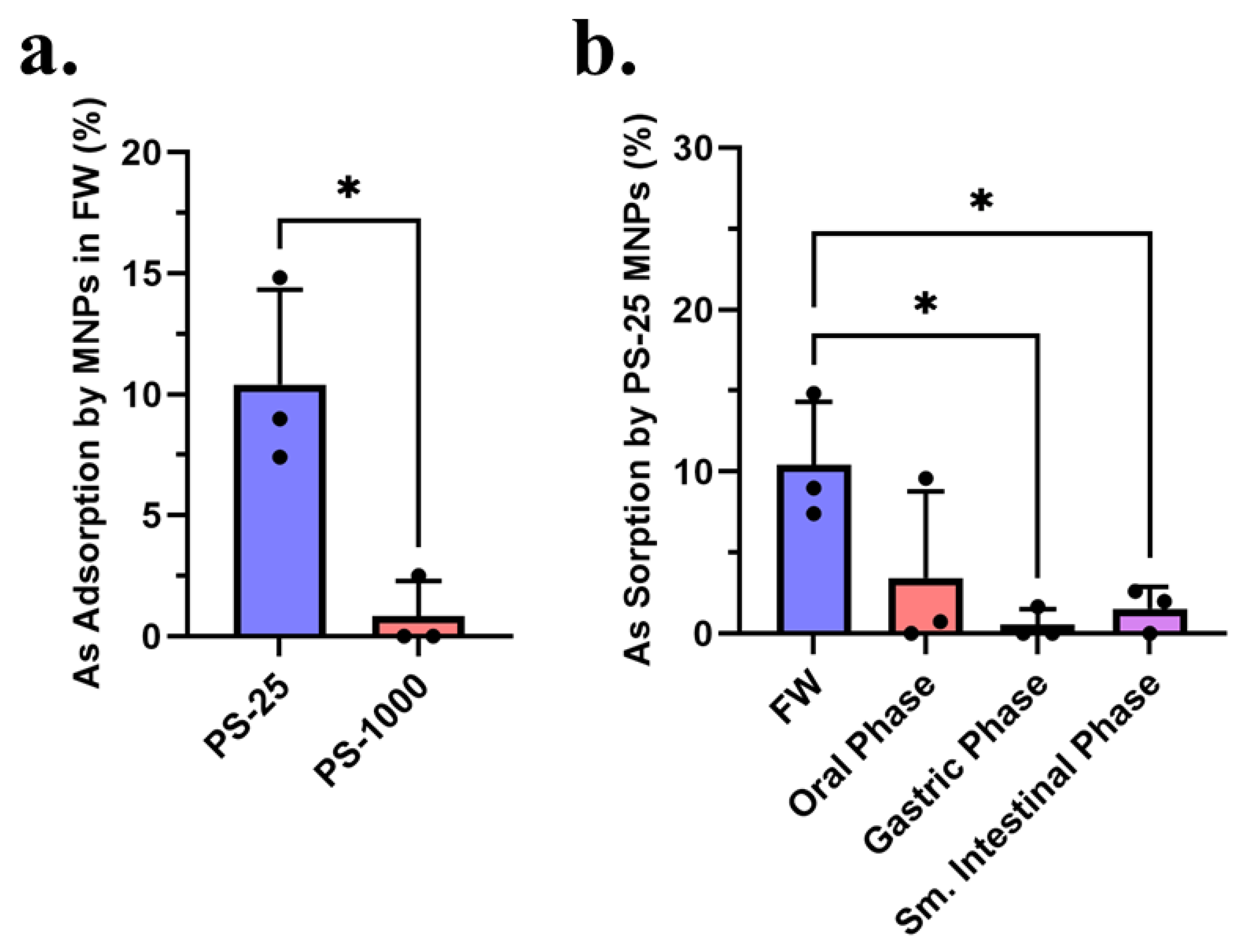
3.2. Sorption of Arsenic and Boscalid by MNPs
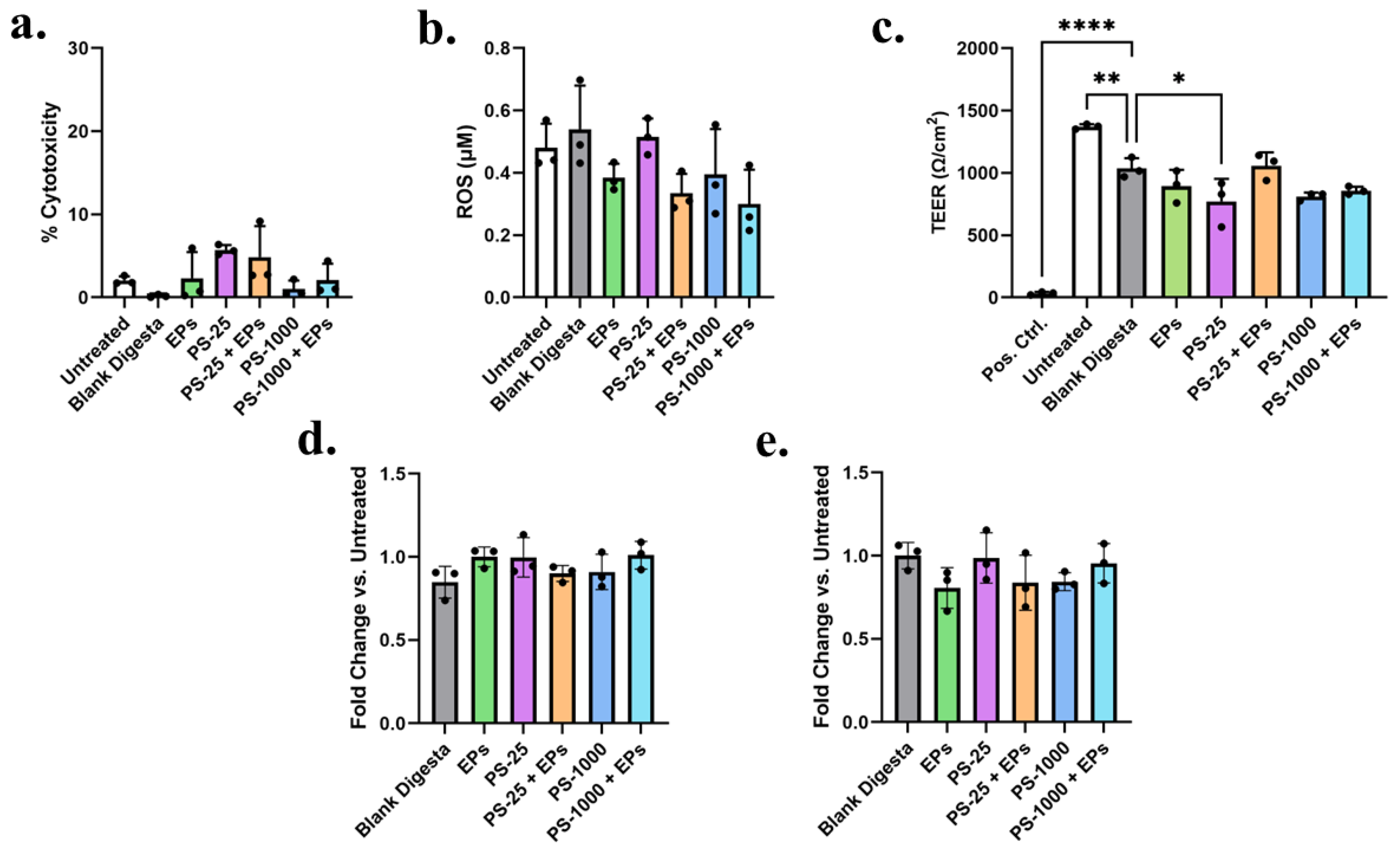
3.3. Assessment of Toxicity In Vitro
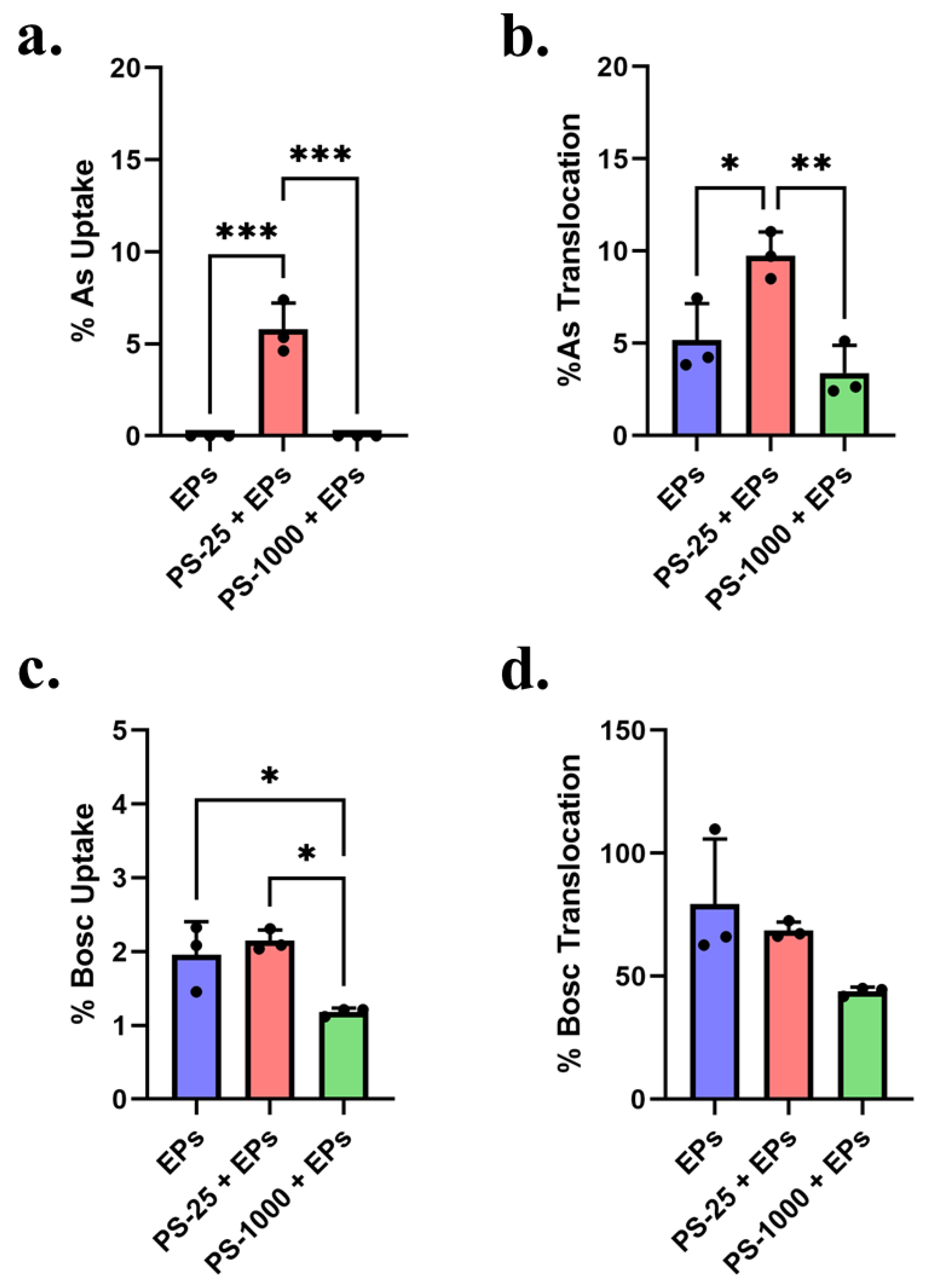
3.4. Effect of MNPs on Uptake and Translocation of Arsenic and Boscalid in the Triculture Model
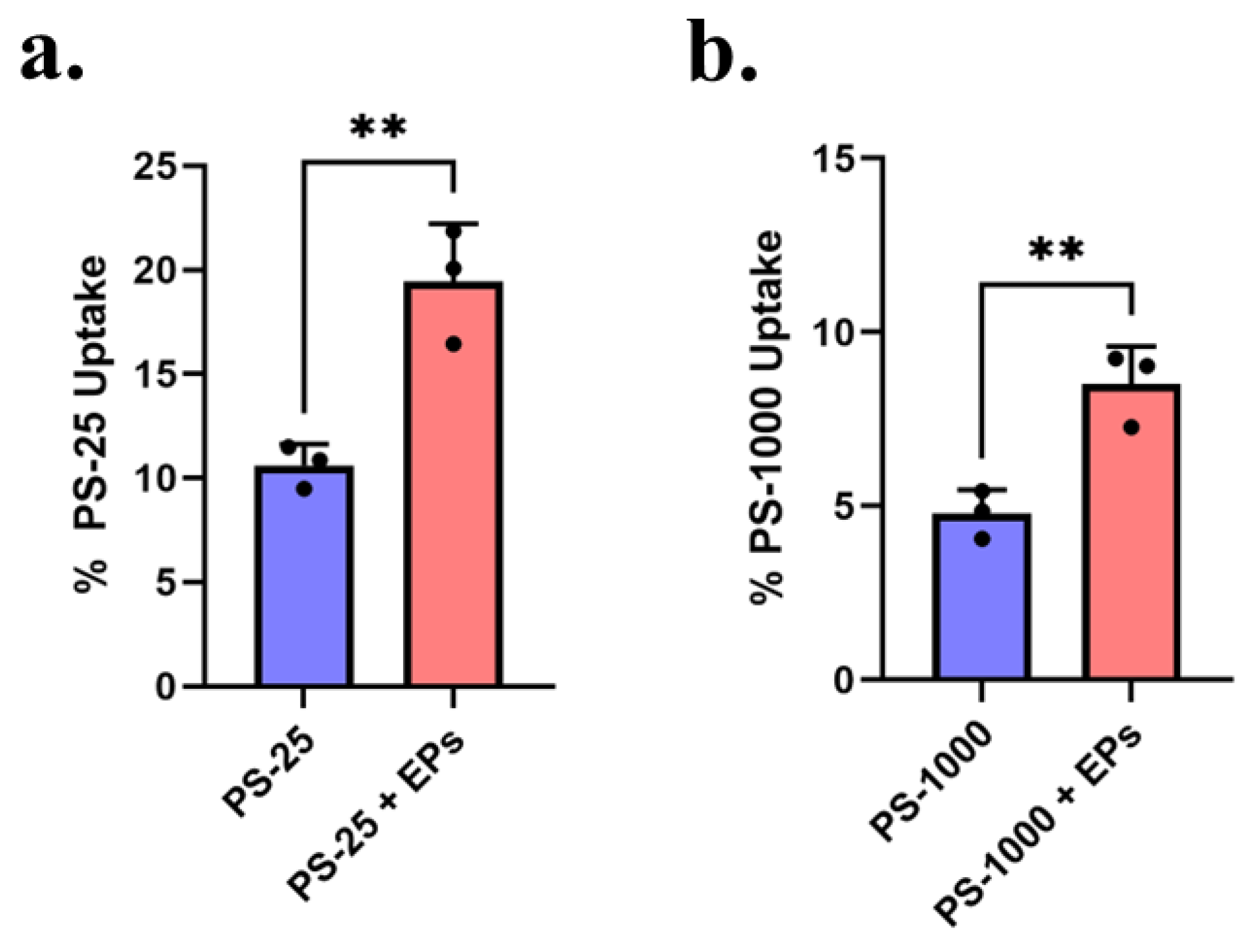
3.5. Effect of EPs on MNP Uptake
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plastics—The Fast Facts 2023 Plastics Europe. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-fast-facts-2023/ (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milbrandt, A.; Coney, K.; Badgett, A.; Beckham, G.T. Quantification and evaluation of plastic waste in the United States. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 183, 106363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; DeLoid, G.M.; Baw, J.; Zarbl, H.; Demokritou, P. Assessment of Ingested Micro- and Nanoplastic (MNP)-Mediated Genotoxicity in an In Vitro Model of the Small Intestinal Epithelium (SIE). Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewert, B.; Plassmann, M.M.; MacLeod, M. Pathways for degradation of plastic polymers floating in the marine environment. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prattichizzo, F.; Ceriello, A.; Pellegrini, V.; La Grotta, R.; Graciotti, L.; Olivieri, F.; Paolisso, P.; D’agostino, B.; Iovino, P.; Balestrieri, M.L.; et al. Micro-nanoplastics and cardiovascular diseases: Evidence and perspectives. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 4099–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donisi, I.; Colloca, A.; Anastasio, C.; Balestrieri, M.L.; D’Onofrio, N. Micro(nano)plastics: An Emerging Burden for Human Health. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 20, 5779–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balali, H.; Morabbi, A.; Karimian, M. Concerning influences of micro/nano plastics on female reproductive health: Focusing on cellular and molecular pathways from animal models to human studies. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2024, 22, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, A.A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahul Hamid, F.; Sanam Bhatti, M.; Anuar, N.; Mohan, P.; Periathamby, A. Worldwide distribution and abundance of microplastic: How dire is the situation? Waste Manag. Res. 2018, 36, 873–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Nag, R.; Cummins, E. Human health concerns regarding microplastics in the aquatic environment—From marine to food systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoganandham, S.T.; Hamid, N.; Junaid, M.; Duan, J.-J.; Pei, D.-S. Micro(nano)plastics in commercial foods: A review of their characterization and potential hazards to human health. Environ. Res. 2023, 236 Pt 2, 116858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, E.; Okuthe, G.E. Plastics and Micro/Nano-Plastics (MNPs) in the Environment: Occurrence, Impact, and Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, J. Micro(nano)plastics in the Human Body: Sources, Occurrences, Fates, and Health Risks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 3065–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; He, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhu, Q.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. Neurotoxicities induced by micro/nanoplastics: A review focusing on the risks of neurological diseases. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 134054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, D.; Manogaran, G.P.; Dharmadurai, D. A systematic review on the impact of micro-nanoplastics on human health: Potential modulation of epigenetic mechanisms and identification of biomarkers. Chemosphere 2024, 363, 142986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, T.; Ghoshal, S.; Tufenkji, N.; Adamowski, J.F.; Bayen, S.; Chen, Q.; Demokritou, P.; Flury, M.; Hüffer, T.; Ivleva, N.P.; et al. Plastics can be used more sustainably in agriculture. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 22, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Wohlleben, W.; De La Torre Roche, R.; White, J.C.; Demokritou, P. Thermal decomposition/incineration of nano-enabled coatings and effects of nanofiller/matrix properties and operational conditions on byproduct release dynamics: Potential environmental health implications. NanoImpact 2019, 13, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, B.; Raffael, B.; Angers-Loustau, A.; Gilliland, D.; Kestens, V.; Petrillo, M.; Rio-Echevarria, I.M.; Van den Eede, G. Review of micro- and nanoplastic contamination in the food chain. Food Addit. Contam.-Part A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2019, 36, 639–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriou, G.A.; Singh, D.; Zhang, F.; Chalbot, M.-C.G.; Spielman-Sun, E.; Hoering, L.; Kavouras, I.G.; Lowry, G.V.; Wohlleben, W.; Demokritou, P. Thermal decomposition of nano-enabled thermoplastics: Possible environmental health and safety implications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 305, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, S.; Rauert, C.; Ribeiro, F.; Okoffo, E.D.; Burrows, S.D.; O’Brien, J.W.; Wang, X.; Wright, S.L.; Thomas, K.V. There’s something in the air: A review of sources, prevalence and behaviour of microplastics in the atmosphere. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setyawati, M.I.; Singh, D.; Krishnan, S.P.R.; Huang, X.; Wang, M.; Jia, S.; Goh, B.H.R.; Ho, C.G.; Yusoff, R.; Kathawala, M.H.; et al. Occupational Inhalation Exposures to Nanoparticles at Six Singapore Printing Centers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2389–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirela, S.V.; Martin, J.; Bello, D.; Demokritou, P. Nanoparticle exposures from nano-enabled toner-based printing equipment and human health: State of science and future research needs. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2017, 47, 683–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccia, P.; Mondellini, S.; Mauro, S.; Zanellato, M.; Parolini, M.; Sturchio, E. Potential Effects of Environmental and Occupational Exposure to Microplastics: An Overview of Air Contamination. Toxics 2024, 12, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; DeLoid, G.M.; Zarbl, H.; Baw, J.; Demokritou, P. Micro- and nanoplastics (MNPs) and their potential toxicological outcomes: State of science, knowledge gaps and research needs. NanoImpact 2023, 32, 100481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Lang, M.; Huang, D.; Yang, C.; Ouyang, Z.; Guo, X. Photo-transformation of microplastics and its toxicity to Caco-2 cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; He, L.; Qu, J.; Zhou, C.; Hong, P.; Sun, S.; Zhao, H.; Liang, Y.; et al. The Complex Toxicity of Tetracycline with Polystyrene Spheres on Gastric Cancer Cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, C.; Domenech, J.; Salazar, M.; Pastor, S.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. Nanoplastics as a potential environmental health factor: Effects of polystyrene nanoparticles on human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, M.; Kämpfer, A.A.; Schins, R.P. An inverted in vitro triple culture model of the healthy and inflamed intestine: Adverse effects of polyethylene particles. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, M.; Bredeck, G.; Kämpfer, A.A.M.; Schins, R.P.F. Investigations of acute effects of polystyrene and polyvinyl chloride micro- and nanoplastics in an advanced in vitro triple culture model of the healthy and inflamed intestine. Environ. Res. 2021, 193, 110536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanomi, M.; Salmistraro, N.; Porro, D.; Pinsino, A.; Colangelo, A.M.; Gaglio, D. Polystyrene micro and nano-particles induce metabolic rewiring in normal human colon cells: A risk factor for human health. Chemosphere 2022, 303 Pt 1, 134947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Billey, L.O.; Shelver, W.L. Uptake and toxicity of polystyrene micro/nanoplastics in gastric cells: Effects of particle size and surface functionalization. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLoid, G.M.; Cao, X.; Bitounis, D.; Singh, D.; Llopis, P.M.; Buckley, B.; Demokritou, P. Toxicity, uptake, and nuclear translocation of ingested micro-nanoplastics in an in vitro model of the small intestinal epithelium. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 158, 112609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLoid, G.M.; Cao, X.; Coreas, R.; Bitounis, D.; Singh, D.; Zhong, W.; Demokritou, P. Incineration-Generated Polyethylene Micro-Nanoplastics Increase Triglyceride Lipolysis and Absorption in an In Vitro Small Intestinal Epithelium Model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 12288–12297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ma, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, Y. Systematic toxicity evaluation of polystyrene nanoplastics on mice and molecular mechanism investigation about their internalization into Caco-2 cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L. Size-dependent effects of polystyrene microplastics on cytotoxicity and efflux pump inhibition in human Caco-2 cells. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visalli, G.; Facciolà, A.; Ciarello, M.P.; Marco, G.D.; Maisano, M.; Pietro, A.D. Acute and sub-chronic effects of microplastics (3 and 10 μm) on the human intestinal cells ht-29. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, V.; Böhmert, L.; Lisicki, E.; Block, R.; Cara-Carmona, J.; Pack, L.K.; Selb, R.; Lichtenstein, D.; Voss, L.; Henderson, C.J.; et al. Uptake and effects of orally ingested polystyrene microplastic particles in vitro and in vivo. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 1817–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forte, M.; Iachetta, G.; Tussellino, M.; Carotenuto, R.; Prisco, M.; De Falco, M.; Laforgia, V.; Valiante, S. Polystyrene nanoparticles internalization in human gastric adenocarcinoma cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2016, 31, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domenech, J.; Hernández, A.; Rubio, L.; Marcos, R.; Cortés, C. Interactions of polystyrene nanoplastics with in vitro models of the human intestinal barrier. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 2997–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenech, J.; de Britto, M.; Velázquez, A.; Pastor, S.; Hernández, A.; Marcos, R.; Cortés, C. Long-Term Effects of Polystyrene Nanoplastics in Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, B.; Du, Y.; Li, J.; Tong, X.; Wu, Y.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Y. Tissue distribution of polystyrene nanoplastics in mice and their entry, transport, and cytotoxicity to GES-1 cells. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, A.P.; Kramer, E.; Hendriksen, P.J.M.; Tromp, P.; Helsper, J.P.F.G.; van der Zande, M.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Bouwmeester, H. Translocation of differently sized and charged polystyrene nanoparticles in in vitro intestinal cell models of increasing complexity. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jani, P.; Halbert, G.W.; Langridge, J.; Florence, A.T. The Uptake and Translocation of Latex Nanospheres and Microspheres after Oral Administration to Rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1989, 41, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jani, P.; McCarthy, D.; Florence, A. Nanosphere and microsphere uptake via Peyer’s patches: Observation of the rate of uptake in the rat after a single oral dose. Int. J. Pharm. 1992, 86, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lemos, B.; Ren, H. Tissue accumulation of microplastics in mice and biomarker responses suggest widespread health risks of exposure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep46687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, J.; Lin, L.; Hu, M.; Jiang, J.; Dai, M.; Wang, B.; et al. Underestimated health risks: Polystyrene micro- and nanoplastics jointly induce intestinal barrier dysfunction by ROS-mediated epithelial cell apoptosis. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2021, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Xu, K.; Yu, L.; Pu, Y.; Xiong, F.; He, Y.; Huang, Q.; Tang, M.; Chen, M.; Yin, L.; et al. Preliminary study on impacts of polystyrene microplastics on the hematological system and gene expression in bone marrow cells of mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 218, 112296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhuan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Meng, L.; Fu, X.; Hou, Y. Polystyrene microplastics induced female reproductive toxicity in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, W.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.-Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Lee, S.-G.; Kim, H.-C.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kwon, M.K.; Hwang, J.-S.; Han, J.E.; et al. Microglial phagocytosis of polystyrene microplastics results in immune alteration and apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Lu, L.; Tu, W.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z. Impacts of polystyrene microplastic on the gut barrier, microbiota and metabolism of mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Ma, T.; Sha, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, X.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Ding, J. Polystyrene microplastics induced male reproductive toxicity in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.J.; Park, J.W.; Lim, Y.; Seo, S.; Hwang, D.Y. In vivo impact assessment of orally administered polystyrene nanoplastics: Biodistribution, toxicity, and inflammatory response in mice. Nanotoxicology 2021, 15, 1180–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cary, C.M.; DeLoid, G.M.; Yang, Z.; Bitounis, D.; Polunas, M.; Goedken, M.J.; Buckley, B.; Cheatham, B.; Stapleton, P.A.; Demokritou, P. Ingested Polystyrene Nanospheres Translocate to Placenta and Fetal Tissues in Pregnant Rats: Potential Health Implications. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Lee, Y.-H.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Chiu, I.-J.; Huang, C.C.-Y.; Chia, Z.-C.; Lee, C.-P.; Lin, Y.-F.; Chiu, H.-W. The Kidney-Related Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics on Human Kidney Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells HK-2 and Male C57BL/6 Mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 57003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Chen, R.; Wang, M.; Bai, R.; Cui, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, C.; Chen, C. Perturbation of gut microbiota plays an important role in micro/nanoplastics-induced gut barrier dysfunction. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 8806–8816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wan, Z.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Polystyrene microplastics induce gut microbiota dysbiosis and hepatic lipid metabolism disorder in mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Yuan, G.-H.; Jiang, B.-R.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Lv, H.-J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.-L.; Wu, Q.; Li, L. Effects of microplastics (MPs) and tributyltin (TBT) alone and in combination on bile acids and gut microbiota crosstalk in mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Shi, M.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Cai, D.; Xiao, F. Keap1-Nrf2 pathway up-regulation via hydrogen sulfide mitigates polystyrene microplastics induced-hepatotoxic effects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Peng, C.; Cui, G.; Shao, H.; Du, Z. Activation of pyroptosis and ferroptosis is involved in the hepatotoxicity induced by polystyrene microplastics in mice. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Yin, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yue, R.; Xiong, X. Polystyrene microplastics-triggered mitophagy and oxidative burst via activation of PERK pathway. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Q.; Wei, J.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Polystyrene microplastics cause cardiac fibrosis by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and promoting cardiomyocyte apoptosis in rats. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, N.; Zhu, S.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Yao, J.; Zhang, L. The impact of polystyrene microplastics on cardiomyocytes pyroptosis through NLRP3/Caspase-1 signaling pathway and oxidative stress in Wistar rats. Environ. Toxicol. 2021, 36, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Xie, J.; Han, Q.; Chen, M. Comparing the effects of polystyrene microplastics exposure on reproduction and fertility in male and female mice. Toxicology 2022, 465, 153059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Lei, Z.; Cui, L.; Hou, Y.; Yang, L.; An, R.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L. Polystyrene microplastics lead to pyroptosis and apoptosis of ovarian granulosa cells via NLRP3/Caspase-1 signaling pathway in rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 212, 112012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, R.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Xu, F.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L. Polystyrene microplastics cause granulosa cells apoptosis and fibrosis in ovary through oxidative stress in rats. Toxicology 2021, 449, 152665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadi, A.; Kessabi, K.; Boughammoura, S.; Ben Rhouma, M.; Mlouka, R.; Banni, M.; Messaoudi, I. Exposure to microplastics leads to a defective ovarian function and change in cytoskeleton protein expression in rat. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 34594–34606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, B.; Wang, F.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z. Reproductive toxicity of polystyrene microplastics: In vivo experimental study on testicular toxicity in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Yan, M.; Pan, C.; Liu, Z.; Sha, X.; Jiang, C.; Li, L.; Pan, M.; Li, D.; Han, X.; et al. Chronic exposure to polystyrene microplastics induced male reproductive toxicity and decreased testosterone levels via the LH-mediated LHR/cAMP/PKA/StAR pathway. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Deng, T.; Duan, J.; Xie, J.; Yuan, J.; Chen, M. Exposure to polystyrene microplastics causes reproductive toxicity through oxidative stress and activation of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Yu, H.; Yang, L.; Sun, Y.; Xu, N.; Wang, N.; Lei, Z.; Hou, J.; Jin, Y.; et al. Polystyrene microplastics induce blood–testis barrier disruption regulated by the MAPK-Nrf2 signaling pathway in rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 47921–47931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, H.A.; van Velzen, M.J.; Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campen, M.; Nihart, A.; Garcia, M.; Liu, R.; Olewine, M.; Castillo, E.; Bleske, B.; Scott, J.; Howard, T.; Gonzalez-Estrella, J.; et al. Bioaccumulation of Microplastics in Decedent Human Brains Assessed by Pyrolysis Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Res. Sq. 2024, 3, 4345687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, A.; Svelato, A.; Santacroce, C.; Catalano, P.; Notarstefano, V.; Carnevali, O.; Papa, F.; Rongioletti, M.C.A.; Baiocco, F.; Draghi, S.; et al. Plasticenta: First evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.A.; Liu, R.; Nihart, A.; El Hayek, E.; Castillo, E.; Barrozo, E.R.; Suter, M.A.; Bleske, B.; Scott, J.; Forsythe, K.; et al. Quantitation and identification of microplastics accumulation in human placental specimens using pyrolysis gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Toxicol. Sci. 2024, 199, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marfella, R.; Prattichizzo, F.; Sardu, C.; Fulgenzi, G.; Graciotti, L.; Spadoni, T.; D’Onofrio, N.; Scisciola, L.; Grotta, R.L.; Frigé, C.; et al. Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Atheromas and Cardiovascular Events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 900–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-C.; Bao, L.-J.; Liu, L.-Y.; Shi, L.; Tao, S.; Zeng, E.Y. Impact of Polymer Colonization on the Fate of Organic Contaminants in Sediment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10555–10561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Li, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, F.; Cao, W.; Zheng, L. Study on the capability and characteristics of heavy metals enriched on microplastics in marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 144, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.E.; Pearce, C.I.; Sanguinet, K.A.; Hu, D.; Chrisler, W.B.; Kim, Y.-M.; Wang, Z.; Flury, M. Polystyrene nano- and microplastic accumulation at Arabidopsis and wheat root cap cells, but no evidence for uptake into roots. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 1942–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, R.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, F. Uptake and translocation of nano/microplastics by rice seedlings: Evidence from a hydroponic experiment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Wen, X.; Huang, D.; Du, C.; Deng, R.; Zhou, Z.; Tao, J.; Li, R.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; et al. Interactions between microplastics/nanoplastics and vascular plants. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 117999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Wu, J.; Zeb, A.; Zheng, S.; Ma, T.; Peng, F.; Tang, J.; Liu, W. Do polystyrene nanoplastics affect the toxicity of cadmium to wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)? Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liao, Y.; Yang, W.; Jiang, X.; Li, M. Enhanced microalgal toxicity due to polystyrene nanoplastics and cadmium co-exposure: From the perspective of physiological and metabolomic profiles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 427, 127937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Gao, M.; Qiu, W.; Song, Z. Uptake of microplastics by carrots in presence of As (III): Combined toxic effects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, D.Q.; Nekrassova, O.; Compton, R.G. Analytical methods for inorganic arsenic in water: A review. Talanta 2004, 64, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, P.; Zhao, F.-J. Toxic Metals and Metalloids in Food: Current Status, Health Risks, and Mitigation Strategies. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2024, 11, 468–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomova, K.; Jenisova, Z.; Feszterova, M.; Baros, S.; Liska, J.; Hudecova, D.; Rhodes, C.J.; Valko, M. Arsenic: Toxicity, oxidative stress and human disease. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2011, 31, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffetta, P.; Sambati, L.; Sassano, M. Systematic review of studies on exposure to arsenic in drinking water and cognitive and neurobehavioral effects. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2024, 54, 174–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, F.; Chen, Y.; Yunus, M.; Olopade, C.; Segers, S.; Slavkovich, V.; Argos, M.; Hasan, R.; Ahmed, A.; Islam, T.; et al. Arsenic Exposure and Impaired Lung Function. Findings from a Large Population-based Prospective Cohort Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, B.K.; Suzuki, K.T. Arsenic round the world: A review. Talanta 2002, 58, 201–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurin, M.-C.; Bostanian, N.J. Short-term contact toxicity of seven fungicides on Anystis baccarum. Phytoparasitica 2007, 35, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostanian, N.J.; Thistlewood, H.M.A.; Hardman, J.M.; Racette, G. Toxicity of six novel fungicides and sulphur to Galendromus occidentalis (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2009, 47, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angioni, A.; Dedola, F.; Garau, V.L.; Schirra, M.; Caboni, P. Fate of Iprovalicarb, Indoxacarb, and Boscalid Residues in Grapes and Wine by GC–ITMS Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 6806–6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandstrom, M.W.; Nowell, L.H.; Mahler, B.J.; Van Metre, P.C. New-generation pesticides are prevalent in California’s Central Coast streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.; Cui, F.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Qi, S.; Wang, C. Mechanisms of developmental toxicity in zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio) induced by boscalid. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Meng, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhou, L.; Su, M.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liao, X.; Cao, Z.; Lu, H. Characterization of boscalid-induced oxidative stress and neurodevelopmental toxicity in zebrafish embryos. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Qi, S.; Wang, Z.; Magnuson, J.T.; Volz, D.C.; Schlenk, D.; Jiang, J.; Wang, C. Environmentally relevant concentrations of boscalid exposure affects the neurobehavioral response of zebrafish by disrupting visual and nervous systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Qi, S.; Zhang, J.; Duan, M.; Schlenk, D.; Jiang, J.; Wang, C. Exposure to Boscalid Induces Reproductive Toxicity of Zebrafish by Gender-Specific Alterations in Steroidogenesis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14275–14287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, W.; Bousfield, D.; Kettle, J. Application of Nano-Fibrillated Cellulose As a Paper Surface Treatment for Inkjet Printing. In Proceedings of the Paper Conference and Trade Show, Paper Con, Austin, TX, USA, 1–4 May 2011; pp. 2222–2233. Available online: http://www.tappi.org/content/events/11papercon/documents/212.517.pdf (accessed on 16 August 2015).
- DeLoid, G.M.; Wang, Y.; Kapronezai, K.; Lorente, L.R.; Zhang, R.; Pyrgiotakis, G.; Konduru, N.V.; Ericsson, M.; White, J.C.; De La Torre-Roche, R.; et al. An integrated methodology for assessing the impact of food matrix and gastrointestinal effects on the biokinetics and cellular toxicity of ingested engineered nanomaterials. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2017, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van-der Veen, I.; Van Mourik, L.M.; Van-Velzen, M.J.M.; Groenewoud, Q.R.; Leslie, H.A. Final Plastic Particles in Livestock Feed, Milk, Meat and Blood A Pilot Study. In Environment & Health; Plastic Soup Foundation: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dessì, C.; Okoffo, E.D.; O’brien, J.W.; Gallen, M.; Samanipour, S.; Kaserzon, S.; Rauert, C.; Wang, X.; Thomas, K.V. Plastics contamination of store-bought rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, F.; Okoffo, E.D.; O’brien, J.W.; Fraissinet-Tachet, S.; O’brien, S.; Gallen, M.; Samanipour, S.; Kaserzon, S.; Mueller, J.F.; Galloway, T.; et al. Quantitative Analysis of Selected Plastics in High-Commercial-Value Australian Seafood by Pyrolysis Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9408–9417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, A.; Øysæd, K.B.; Palmas, L.; Skogerbø, G. Application of GCMS-pyrolysis to estimate the levels of microplastics in a drinking water supply system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Ou, Q.; Jiao, M.; Liu, G.; van der Hoek, J.P. Identification and Quantification of Nanoplastics in Surface Water and Groundwater by Pyrolysis Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 4988–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, S.; Shanker, U. Shikha Arsenic Contamination of Groundwater: A Review of Sources, Prevalence, Health Risks, and Strategies for Mitigation. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 304524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- eCFR :: 40 CFR 180.589—Boscalid; Tolerances for Residues. Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-40/chapter-I/subchapter-E/part-180/subpart-C/section-180.589 (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- DeLoid, G.M.; Cohen, J.M.; Pyrgiotakis, G.; Demokritou, P. Preparation, characterization, and in vitro dosimetry of dispersed, engineered nanomaterials. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; DeLoid, G.M.; Bitounis, D.; De La Torre-Roche, R.; White, J.C.; Zhang, Z.; Ho, C.G.; Ng, K.W.; Eitzer, B.D.; Demokritou, P. Co-exposure to the food additives SiO2 (E551) or TiO2 (E171) and the pesticide boscalid increases cytotoxicity and bioavailability of the pesticide in a tri-culture small intestinal epithelium model: Potential health implications. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 2786–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Kim, S.-H.; Bae, S.; Im, M.-H. Monitoring of Pesticide Residues in Chili Peppers Using International Pesticide Monitoring Data for Safety Management. Toxics 2024, 12, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatayud, M.; Gimeno, J.; Vélez, D.; Devesa, V.; Montoro, R. Characterization of the intestinal absorption of arsenate, monomethylarsonic acid, and dimethylarsinic acid using the Caco-2 cell line. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2010, 23, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calatayud, M.; Barrios, J.A.; Vélez, D.; Devesa, V. In vitro study of transporters involved in intestinal absorption of inorganic arsenic. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Khare, S.; DeLoid, G.M.; Gokulan, K.; Demokritou, P. Co-exposure to boscalid and TiO2 (E171) or SiO2 (E551) downregulates cell junction gene expression in small intestinal epithelium cellular model and increases pesticide translocation. NanoImpact 2021, 22, 100306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tienpont, B.; David, F.; Vanwalleghem, F.; Sandra, P. Pyrolysis-capillary gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the determination of polyvinyl chloride traces in solid environmental samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 911, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, Z.; Kintzi, A.; Muñoz, K.; Schaumann, G.E. A simple method for the selective quantification of polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene plastic debris in soil by pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2020, 147, 104803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLoid, G.M.; Yang, Z.; Bazina, L.; Kharaghani, D.; Sadrieh, F.; Demokritou, P. Mechanisms of ingested polystyrene micro-nanoplastics (MNPs) uptake and translocation in an in vitro tri-culture small intestinal epithelium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 473, 134706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Treatment Groups | As (µg/L) | Bosc (mg/L) | PS25C (mg/mL) | PS1KC (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank Ctrl | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| EPs | 100 | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| PS-25 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| PS-1000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| PS-25/EPs | 100 | 10 | 1 | 0 |
| PS-1000/EPs | 100 | 10 | 0 | 1 |
| Particle | dH (nm) | PdI | ζ (mV) | σ (mS cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS-25 | 33.02 ± 0.01 | 0.151 ± 0.013 | −66.8 ± 1.8 | 0.0414 ± 0.0004 |
| PS-1000 | 849.17 ± 16.91 | 0.199 ± 0.006 | −41.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0164 ± 0.0000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kharaghani, D.; DeLoid, G.M.; Bui, T.H.; Zuverza-Mena, N.; Tamez, C.; Musante, C.; White, J.C.; Demokritou, P. Ingested Polystyrene Micro-Nanoplastics Increase the Absorption of Co-Ingested Arsenic and Boscalid in an In Vitro Triculture Small Intestinal Epithelium Model. Microplastics 2025, 4, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4010004
Kharaghani D, DeLoid GM, Bui TH, Zuverza-Mena N, Tamez C, Musante C, White JC, Demokritou P. Ingested Polystyrene Micro-Nanoplastics Increase the Absorption of Co-Ingested Arsenic and Boscalid in an In Vitro Triculture Small Intestinal Epithelium Model. Microplastics. 2025; 4(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleKharaghani, Davood, Glen M. DeLoid, Trung Huu Bui, Nubia Zuverza-Mena, Carlos Tamez, Craig Musante, Jason C. White, and Philip Demokritou. 2025. "Ingested Polystyrene Micro-Nanoplastics Increase the Absorption of Co-Ingested Arsenic and Boscalid in an In Vitro Triculture Small Intestinal Epithelium Model" Microplastics 4, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4010004
APA StyleKharaghani, D., DeLoid, G. M., Bui, T. H., Zuverza-Mena, N., Tamez, C., Musante, C., White, J. C., & Demokritou, P. (2025). Ingested Polystyrene Micro-Nanoplastics Increase the Absorption of Co-Ingested Arsenic and Boscalid in an In Vitro Triculture Small Intestinal Epithelium Model. Microplastics, 4(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4010004








