Abstract
Nano- (NPs) and microplastics (MPs) are ubiquitous and raising concerns about their toxicity. A popular model for studying acute toxicity is Danio rerio. This study investigated the acute toxicity in FET test of polystyrene nanoparticles (500 nm, nanoPS) at different concentrations (0.01, 0.1, and 0.2 mg/mL), with different surface groups (non-modified, amine, carboxyl) and discuss the toxicological contribution of commercially added compounds. Different behavioural tests were used to investigate the neurotoxicity of nanoPS and sodium azide: coiling assay test, light–dark preference test, and colour preference test. Sodium azide and other preservatives are often present in commercially available NP and MP solutions frequently used in microplastic toxicity tests, but their effects on the results remain largely unknown. In the FET test, nanoPS did not increase mortality or affect the heart rate or body length. A higher hatching rate was observed at 48 hpf. Although nanoPS showed no acute toxicity, behavioural tests revealed subtle neurotoxic effects (changes in colour preference), suggesting a potential impact on neurological function. Additionally, sodium azide exhibited toxicity, indicating that additives may confound toxicity assessments. This highlights the need for careful consideration of preservatives in nanoparticle research to avoid misleading conclusions.
1. Introduction
Danio rerio is a well-known vertebrate model for toxicology studies due to its many advantages, which include a transparent body, rapid development, small size, large number of offspring, and ease of breeding [1]. Currently, there are reliable and standardized protocols for acute toxicity testing for both adults and embryos, such as Fish Acute Toxicity Test (AFT) and Fish Embryo Toxicity Test (FET) [2,3]. The OECD studies have shown its intra- and inter-laboratory reproducibility [4], and numerous studies have shown a correlation between FET and AFT. Micro- (MPs) and nanoplastics (NPs) contamination has become a global concern due to its widespread presence and durability in aquatic ecosystems, posing a growing environmental risk. MPs can accumulate in living organisms and contribute to harmful effects. MPs and NPs are being increasingly tested in the zebrafish model system, both in AFT and FET. Knowledge of the omnipresence of MPs and NPs is already widespread, and new studies on this topic continue to emerge. For instance, the size effect should not be neglected [5]. This drives the desire to understand the potential consequences of plastic presence, especially at the nanoscale and in the environment, including its toxicity.
Studies involving adult zebrafish have shown mostly consistent results: MPs and NPs do not increase mortality or increase it only slightly [6,7,8,9], accumulate in the intestines [7,9,10,11,12], cause damage [9,10,11] and dysbiosis [6,9,10]. Intestinal dysbiosis is associated with various metabolic disorders [10,12]. Recently, an impact on the liver has been reported [13]. A few studies have also indicated behavioural changes after exposure to MPs and NPs [6,14]. The relationships studied include the influence of type (e.g., PE—polyethylene, PP—polypropylene, PVC—polyvinyl chloride, PA—polyamide, PS—polystyrene), concentration, size, and shape (fibres, beads, spheres) of particles. The influence of co-exposure to other compounds and the possibility of transfer between parents and offspring have also been investigated [15]. However, there are still gaps in knowledge; for example, there is no research that takes into account the environmental context.
In the case of embryo research, the results are much more inconsistent. Most studies have concentrated on PS particles, some on PE particles, and very few on other types. In the case of PS, the diameter of the tested particles ranged from several tens of nanometres to several hundred micrometres, and the concentration range was from 0.1 to 100 mg/L. The discrepancies in the tested concentrations [16] are also related to the lack of knowledge about the environmental PS level. The reliable estimation of MP concentrations in fresh and salt waters is biased by the fate, transport, or complex agglomeration patterns of MPs [17].
Individual studies have investigated additional dependencies, such as the effect of the presence of surface groups [18]. In none of the studies on microPS and nanoPS, except those in which microinjection was used [19,20], there was an increase in mortality, severe developmental abnormalities, or changes in heartbeat or hatching rate. However, the absorption of plastic particles on the chorion and their accumulation in various organs has been observed [21,22,23,24,25]. Changes in gene expression [26,27], metabolic profiles, and microbiomes [28]; increased levels of reactive oxygen species) (ROS) [18]; decreased body length [27]; and behavioural changes [24,25,27] have also been observed. There are several possible explanations for the obtained results: (1) microPS and nanoPS cause neurotoxic effects, which are difficult to observe using the FET test; (2) microPS and nanoPS have only a minor impact on zebrafish embryos, leading to alteration in gene expression without any visible signs of toxicity, (3) microPS and nanoPS do not cause toxic effects in zebrafish embryos, and the effects observed in some studies are due to the presence of other substances. In particular, the last hypothesis should be carefully checked as frequently used commercially available MPs and NPs particle solutions contain several added substances. One of the commonly detected antifungal agents is sodium azide (NaN3). In products from the two most commonly used companies (ThermoFisher and Bangs Laboratories), it is present at concentrations < 0.09%. Sodium azide (NaN3) is a colourless crystalline substance. Its toxicity is exhibited in the form of azide after ingestion and in the form of nitrogen oxides produced by combustion. It is used in the production of airbags and as a preservative in laboratory reagents and biological fluids. [29]. The strong toxicity of sodium azide has already been confirmed in rats [30] and is similar to cyanide poisoning [31], with mutagenic effects [32]. For instance, biochemical, immunological, and histological adverse effects have been reported in mice [33]. Finally, NaN3 reaction with hypochlorite in waste treatment plants can cause serious toxicity problems in aquatic environments [34].
Thus, although the aim of this study was to investigate the acute toxicity of model nanoPS (~500 nm) with different functional groups (unmodified, amino- and carboxyl-modified) and at different concentrations, the possible influence of NaN3 was checked. The toxicity of nanoPS depends not only on concentration but also on surface functional groups; different surface charges of NPs result in different mechanisms of toxicity. Usually, positively charged PS with amine groups induce stronger toxicity than negatively charged PS with carboxyl groups, as they are more likely to interact with the cell membrane, although the effects vary between species [35]. In addition to the FET, three different behavioural tests were performed: tail coiling assay, light-dark preference test, and colour preference test. Moreover, owing to the well-known colour preferences of Danio reiro, nanoPS of different colours were introduced to check whether this parameter would have any impact on the effective intake. Behavioural tests allow for the investigation of a given substance’s neurotoxicity, which is not always evident during the FET test [36]. To date, only a few studies have used behavioural tests in studies of NPs and MPs, and they have focused mainly on the light-dark preference test [24,26,27]. An important part of this work is also examining the acute toxicity of sodium azide, which occurs in many commercially available microPS and nanoPS, used in the majority of research. Some studies have found no effect of low concentrations of sodium azide on FET results, but its presence is not considered when determining changes in gene expression and increases in ROS levels. There is also no research on its effects on behavioural test results. Therefore, it cannot be ruled out that it causes their falsification. This paper attempts to fill this knowledge gap.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. NanoPS
Fluorescent (green fluorophore; Ex/Em = 460/500 nm) and colour–dyed (red and blue) polystyrene (PS) nanoplastics, with diameters of 0.472–0.582 nm (1% solid suspension) and densities of 1.05–1.06 g/cm3, were purchased from Lab 261 (Palo Alto, CA, USA). They were suspended in deionised water containing a small amount of surfactant (concentration unknown) and 2 mM sodium azide as an anti-microbial agent. Three types of fluorescently labelled nanoplastics for tracking in larvae bodies were used: without surface groups (PS) and with carboxyl and amine surface groups (PS-COOH and PS-NH2, respectively). Two concentrations were prepared for each type: 0.01 mg/mL and 0.1 mg/mL. PS stained red and blue were used in versions with and without carboxyl surface groups (Red PS, Red PS COOH, Blue PS, and Blue PS COOH, respectively). Three concentrations were prepared for each type: 0.01, 0.1, and 0.2 mg/mL (0.472–0.540 nm range). The concentrations were selected based on a literature review conducted by Bhagat et al. [37].
Exposure concentrations were prepared by diluting the stock solution with E3 egg water. E3 was prepared by dissolving 4.7 mM NaCl, 0.17 mM KCl, 0.32 mM CaCl2, and 0.38 mM MgCl2 in 1 litre ultrapure water. The pH was adjusted to 6.9–7.5 using NaOH. All reagents were purchased from Sigma–Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
Fluorescent and colour–dyed nanoPS were used for toxicity studies. Fluorescently labelled nanoplastics were also used to image the distribution of NPs on the surface and inside embryos and for behavioural studies. Colour-dyed nanoplastics (0.474–0.582 nm) were primarily used for behavioural studies. The aim of using blue and red nanoPS was to check whether the colour of nanoplastics would affect the colour preferences of zebrafish—whether the larvae would prefer to stay in the zone with a colour similar to the nanoPS or avoid it.
2.2. Zebrafish Husbandry
Adult zebrafish, reared in the Experimental Medicine Center, Medical University of Lublin facility, were maintained at 28.5 °C on a 14:10 h light/dark cycle under standard aquaculture conditions. Fertilised zebrafish eggs were obtained from AB wild—type zebrafish via natural spawning. Embryos were reared in embryo medium E3 in an incubator at 28.5 °C. All experiments were performed in accordance with the National Institute of Health Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and the European Community Council Directive for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of 22 September 2010 (2010/63/EU). For experiments involving larvae up to 5 dpf, approval from the Local Ethical Commission was not required.
For the experiments, properly developed eggs were selected and collected under a stereomicroscope (Stemi 508, Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH, Oberkochen, Germany) at approximately 4 hpf.
2.3. Experimental Set-Up
2.3.1. FET
Two different sets of experiments were carried out for fluorescent and colour—dyed PS nanoplastics. The experiments using fluorescent nanoPS were conducted in two replicates; nanoPS and nanoPS-NH2 were on one plate, and nanoPS-COOH on the other (hence the separate negative control). Experiments using colour-dyed PS were conducted on four different plates, each type, and colour on a separate plate.
The FET test was performed based on the OECD Guideline Test no. 236 (OECD, 2013) with few modifications. For nanoPS toxicity tests, a simplified assay was used because it was unclear whether nanoPS would have any toxic effect on zebrafish embryos. Embryos (4 hpf) were randomly divided into test and control groups and placed in different concentrations and types of nanoPS solutions or E3 in 6–well plates. For fluorescent nanoPS, two test groups were used: 0.01 and 0.1 mg/mL, while for colour–dyed nanoPS, an additional 0.2 mg/mL group was used. For fluorescent nanoPS, each group consisted of 20 eggs, while for colour–dyed nanoPS, each group consisted of 30 eggs.
To confirm that sodium azide did not affect nanoPS toxicity, a FET test was performed. Sodium azide (Sigma–Aldrich Cas No. 26,628-2-8) was dissolved in E3, and test concentrations were prepared (2, 10, 50, 250, 500, and 1000 μM). Embryos (4 hpf) were randomly divided into test concentrations and control solution (E3) and placed individually in 96-well plates. A total of 24 eggs were used per concentration. The experiment was performed in a blinded manner. The exposure conditions in all tests were semi-static. During the experiments, morphological changes were observed daily, and toxicological endpoints were checked (coagulation, lack of tail detachment, lack of somites formation, lack of heartbeat). Dead larvae were removed from plates. At the end of each test, after additional assays (e.g., behavioural tests or imaging), the embryos were sacrificed using high doses of tricaine. Heartbeats per minute were counted for 10–15 randomly selected larvae on the last day of the experiment that had previously been anaesthetised with a safe level of tricaine (0.006%-as was determined in a separate assay (Figure S1)). Then, pictures (magnification 3.2×) were captured using a stereomicroscope (Stereo Discovery V8, Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH, Germany). Before imaging larvae were immobilized in agarose (1.5% solution). To assess potential vasotoxicity, the transgenic zebrafish line (Flil: EGFP) was used, where the fish express an enhanced green fluorescence protein (EGFP) under the control of an endothelial-specific promoter (fli1). The exposure to the substance lasted from 4 hpf to 96 hpf.
2.3.2. Behavioural Tests
In the case of fluorescent nanoPS, the experiments were conducted on larvae at 96 hpf because they were used primarily to investigate the accumulation of nanoPS, and at this stage, pigmentation is not fully developed, making imaging easier. Experiments with colour–dyed nanoPS were conducted on larvae at 120 hpf because their behaviour endpoints are more stable due to the formation of the swim bladder.
Three types of behavioural tests were performed: the tail coiling assay (performed at 24 hpf, only for sodium azide toxicity evaluation), the light-dark preference test (performed at 96/120 hpf), and the colour–preference test (performed at 120 hpf). For the tail coiling assay, embryos (4 hpf) were randomly divided into test concentrations and control solution (E3) and placed on 6-well plates. Four concentrations, that is, 2, 10, 50, and 100 μM, with 20 eggs per concentration, were used. The light–dark preference test and the colour–preference test were performed after the acute toxicity tests were completed. Before those tests, embryos were transferred to a fresh E3 medium. In the light–dark preference test, sodium azide was tested at three concentrations: 2, 10, and 50 μM (24 larvae per concentration). Fluorescent nanoPS was applied at 0.01 and 0.1 mg/mL (18 larvae per concentration), while color-dyed nanoPS was tested at 0.01, 0.1, and 0.2 mg/mL (18 larvae per concentration). In the coulor–preference test, coulor–dyed nanoPS were tested at a concentration of 0.1 mg/mL (12 larvae), while sodium azide was tested at concentrations 2, 10, and 50 μM (18 larvae per concentration).
During the tail coiling assay, 6–well plates were placed under a stereomicroscope, and then the behaviour of the embryos in each well (n = 18–20) was recorded for 5 min using a digital microscope (Discovery Artisan 512, Levenhuk, Tampa, FL, USA). In the light-dark preference test, 24-well plates (one larvae per well; n = 24 − sodium azide; n = 18 − nanoPS) were placed in the observation chamber (DanioVision Observation Chamber, Noldus Information Technology, Wageningen, The Netherlands) at 28 °C. After 10 min of adaptation to light, the position of the embryo was tracked three times for 5 min in light and then for 5 min in darkness. The test was slightly modified for colour–dyed nanoPS–instead of 10 min acclimatization in light, there was 10 min acclimatization in dark. The main purpose of modifying the protocol was to assess thigmotaxis—that is, to evaluate whether exposure to microplastics influences anxiety-related behavior in zebrafish. This step was crucial for accurately interpreting results from the subsequent behavioral test, namely colour preference, as it was necessary to determine whether any observed changes in colour choice could be attributed to an anxiogenic effect of microplastics. To clearly observe thigmotaxis, the behavioral test protocol was adjusted to begin with a dark adaptation phase instead of light. This change aimed to stabilize baseline locomotor activity and minimize variability caused by light-induced stimulation during thigmotaxis assessment. In the colour preference test, 6-well plates with a bottom divided into two colour zones (using strips of coloured film-Figure S2) (one larvae per well; n = 18 − sodium azide; n = 12 − colour − dyed nanoPS) were placed in an observation chamber at 28 °C. The larvae were placed in the middle of the plate to allow it to make its own choice. The position of the embryo was monitored for 5 min. One variant was selected (blue-red) based on a pilot experiment in which the innate preference for selected colors was determined (Figure S3).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis was performed using the GraphPad Prism 8 software. For all tests, with the exception of the light-dark preference test and the colour-preference test, a one-way variance analysis (ANOVA) was performed, and if the normal distribution condition was not met, the Kruskal-Wallis test was performed. Then, the post-hoc tests, respectively, Dunnett and Dunn, were performed. For the light-dark preference, a two-way variance analysis (ANOVA) was performed, and a Sidack post hoc method was used. The Wilcoxon test was performed for the colour-preference test. As a level of statistical significance, p = 0.05 was selected in each case. Default settings were used for each test. Results are given as mean ± standard deviation (SD). To determine the LC50 for sodium azide, a sigmoid curve was matched to the data using a four-parameter nonlinear regression analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Sodium Azide
3.1.1. Sodium Azide Toxicity in FET
Table 1 briefly summarizes the most important observations made during the FET test at four different time points (based on hpf). Figure 1 shows representative pictures of 96 hpf larvae after the end of FET.

Table 1.
Key observations throughout the duration of the FET test for different concentrations of sodium azide.

Figure 1.
Representative pictures of Danio rerio at 96 hpf exposed to different concentrations of sodium azide (magnification: 3.2×). Pictures of larvae exposed to 2, 10, and 50 μM sodium azide are not shown, as they are not different from the control.
The two highest concentrations of sodium azide tested (1000 and 500 μM) caused 100% mortality. At a concentration of 500 μM, no tail detachment, pigmentation (Figure 1), or development of the blood system was observed; death occurred almost immediately. At a concentration of 1000 μM, tail detachment and partial pigmentation were observed (Figure 1), and death occurred later than at 500 μM. At a concentration of 250 μM, developmental delay and the appearance of abnormalities, such as pericardial and yolk oedema and blood clots, were observed. Mortality was partial. Delayed hatching was observed at 50 μM, with no other abnormalities. Embryo development at 10 and 2 μM concentrations was normal and comparable to that of the control group. The survival rate in the negative control was higher than 95%.
The LC50 at 96 hpf was determined to be 264 μM (Figure 2).
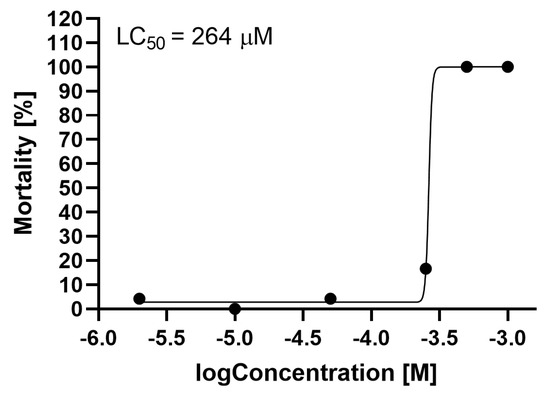
Figure 2.
Mortality of Danio rerio at 96 hpf, depending on the concentration of sodium azide. LC50 was determined using four parameters and nonlinear regression analysis.
As shown in Figure 3, sodium azide caused a statistically significant decrease in heart rate at a concentration of 250 μM. In addition, the heart rate at this concentration was highly diverse, which was due to the fact that this concentration was very close to the LC50, and some larvae were near death.
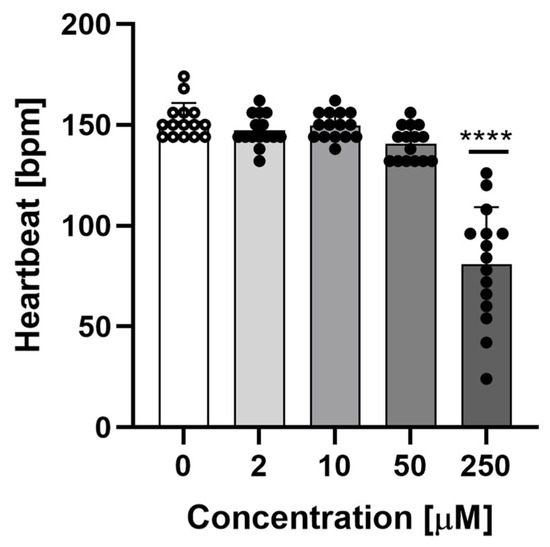
Figure 3.
Heartbeats per minute of 96 hpf Danio rerio at different concentrations of sodium azide. Data are shown as mean ± SD; n = 15; **** p < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA, post-hoc Dunnett test.
The length of larvae exposed to different non–lethal sodium azide concentrations (2, 10, and 50 μM) was compared to that of the negative control. No significant differences were observed between any of the treatments and the control (Figure S4). Sodium azide did not affect the length.
In a separate experiment, the influence of non–lethal sodium azide concentrations on angiogenesis inhibition at 120 hpf was investigated by measuring the distance between vessels in the tail (methodology proposed by Delov et al. (2014) [38]). No significant differences were observed (Figure S5).
Sodium azide concentrations present in test concentrations of nanoPS (0.01, 0.1, and 0.2 mg/mL) of 2, 20, and 40 μM did not cause severe developmental abnormalities, body length, or heart rate changes. 40 μM may cause delayed hatching in 48 hpf larvae.
3.1.2. Sodium Azide Toxicity in Behavioural Tests
Figure 4 shows the results of the tail coiling assay for Danio rerio embryos at 24 hpf. A concentration of 50 μM sodium azide caused a decrease in overall activity, length, and number of single movements.
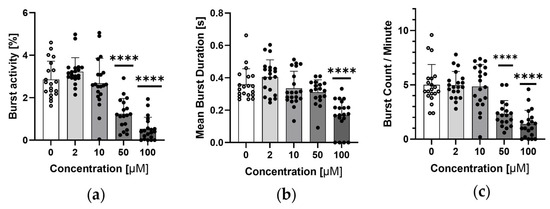
Figure 4.
Tail coiling assay results for 24 hpf Danio rerio embryos. (a) Embryo activity as a percentage of time when they were moving at different concentrations of sodium azide, (b) mean burst duration of single embryo movement at different concentrations of sodium azide and (c) number of single embryo movements per minute at different concentrations of sodium azide. Data are shown as mean ± SD; n = 18–20; **** p < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA; post-hoc Dunnett test.
Figure 5 shows the total distance moved by the embryo in the light-dark preference test during dark periods for different sodium azide concentrations. A concentration of 50 μM sodium azide decreased the overall activity during the dark period.
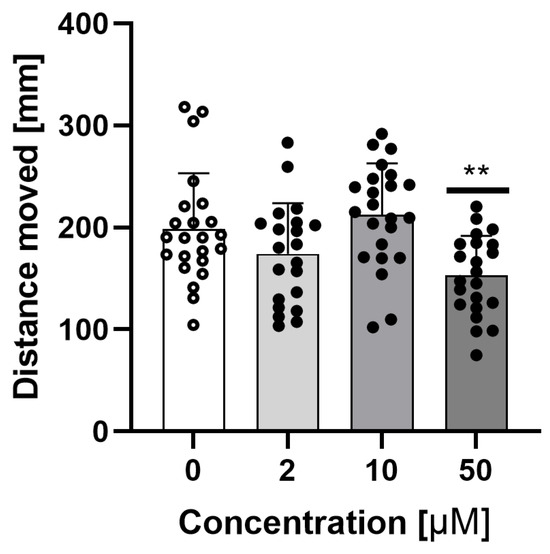
Figure 5.
Total distance moved by embryo at 96 hpf in light–dark preference test during dark periods for different, non–lethal sodium azide concentrations. Data are shown as mean ± SD; n = 21–23; ** p < 0.01; one-way ANOVA, post-hoc Dunnett test.
Figure 6 shows the colour preference results. The larvae in the negative control group had a natural preference for the colour blue. The presence of sodium azide did not cause any changes.
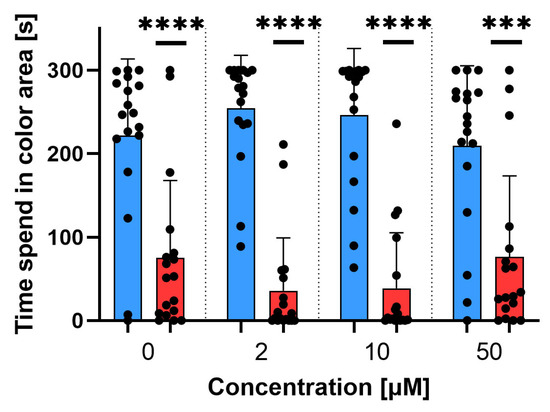
Figure 6.
Colour–preference test for Danio rerio at 120 hpf. Comparison between time spent in blue and red areas for different non–lethal sodium azide concentrations. Data are shown as mean ± SD; n = 18; t-test Wilcoxon test, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001.
Behavioural test results indicate the neurotoxicity of sodium azide, which is visible even at low concentrations. A concentration of 50 μM caused hypoactivity at 24 hpf, higher weakness, and an associated decrease in overall activity and the number of single movements. It also reduced larval activity during the dark period. Sodium azide does not disrupt the preference for colours.
The presented results are important for interpreting the behavioural test results for microPS and nanoPS.
3.2. Nanopolystyrene
3.2.1. Nanopolystyrene Toxicity in FET
During the experiments, no increase in mortality or developmental abnormalities compared to the negative controls was observed. All embryos developed normally. The only difference between the treatments was the hatching rate at 48 hpf. Figure 7 and Figure 8 show the hatching rates for fluorescent and colour–dyed nanoplastics, respectively.
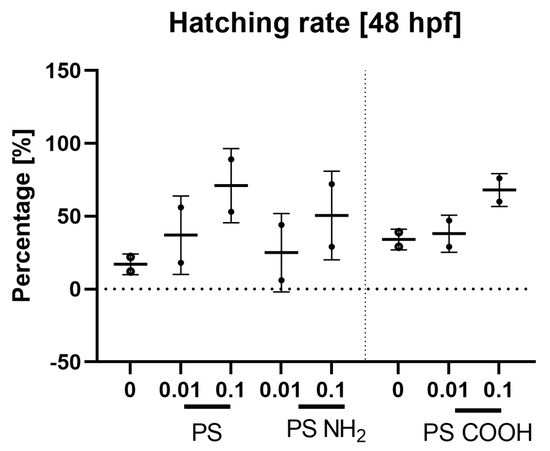
Figure 7.
Hatching rate at 48 hpf for larvae exposed to different concentrations [mg/mL] of fluorescent NanoPS. Data are shown as mean ± SD; n = 2 for all.
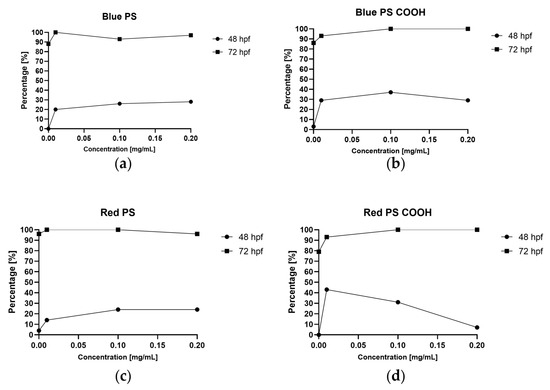
Figure 8.
Hatching rate at 48 and 72 hpf for larvae exposed to different concentrations of (a) blue PS, (b) blue PS with carboxyl groups, (c) red PS, and (d) red PS with carboxyl groups.
The hatching rate at 48 hpf was higher in the PS treatment group than in the negative control group. In most cases (excluding experiments using red PS with carboxyl groups), the hatching rate was higher at 0.1 mg/mL than at 0.01 mg/mL and higher (plain PS) or lower (PS with carboxyl groups) at 0.2 mg/mL than at 0.1 mg/mL. As the experiments were not carried out in replicates, statistical significance could not be determined. However, there was a visible trend in which the presence of nanoPS increased the hatching rate.
Figure 9 shows the images of embryos exposed to different concentrations and types of nanoPS at different time points. The nanoPS adsorbed on the surface of the chorion and filled the digestive tract of the hatched embryos. To better show this, pictures under a confocal microscope were taken (Figure S6). NanoPS diffused from the gastrointestinal tract to the yolk sac but did not enter the cardiovascular system.
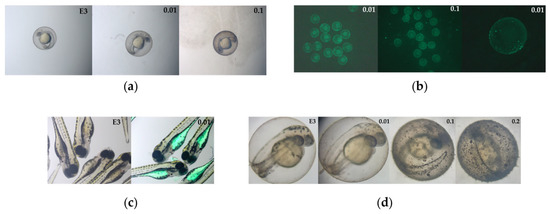
Figure 9.
Representative pictures of Danio rerio embryos exposed to different concentrations of PS: (a) Pictures of embryos at 24 hpf exposed to fluorescent NanoPS, with negative control (magnification: 3.2×), (b) Pictures of embryos at 24 hpf exposed to fluorescent NanoPS in blue light; autoexposition 220 ms (magnification: 1.6× and 3.2×), (c) Pictures of larvae at 96 hpf exposed to fluorescent NanoPS, with negative control, (d) Pictures of larvae at 48 hpf exposed to colour–dyed NanoPS, with negative control (magnification: 9×).
The heart rate was measured at 96 hpf (larvae exposed to fluorescent nanoPS) or 120 hpf (larvae exposed to colour–dyed NPs). NanoPS did not cause any significant changes in heart rate (Figures S7 and S8). The length of the larvae was compared to that of the negative control group. No significant differences were observed between any of the treatments and the control (Figures S9 and S10). NanoPS did not affect the length.
3.2.2. Nanopolystyrene Toxicity in Behavioural Tests
In the light–dark preference test for fluorescent nanoPS, there were no differences between treatments and the negative control in the total distance moved by larvae during the dark periods (Figure S11). Figure 10 shows the results of the light-dark preference test for colour–dyed nanoPS.
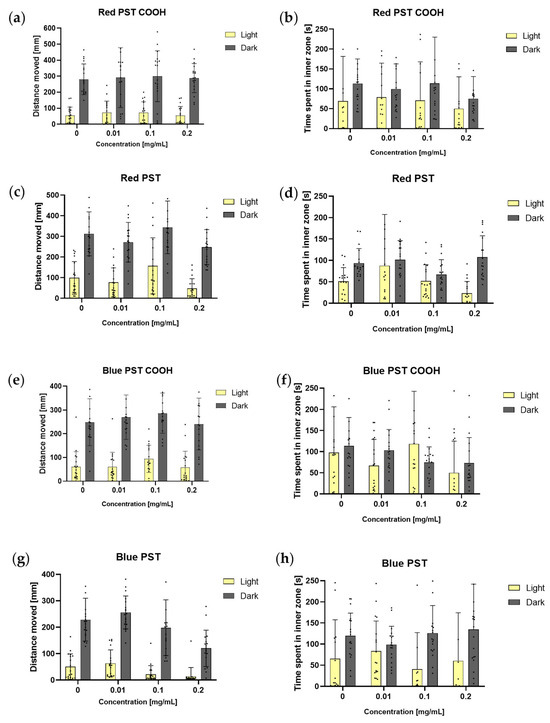
Figure 10.
Total distance moved and total time spent in the inner zone by larvae (n = 18) at 120 hpf in dark and light periods in the light–dark preference test for different types and concentrations of colour-dyed nanoPS. Data are shown as mean ± SD; two–way ANOVA; post–hoc Sidak (a) total distance moved for red PS with carboxyl groups, (b) time spent in inner zone for red PS with carboxyl groups, (c) total distance moved for red PS, (d) time spent in inner zone for red PS, (e) total distance moved for blue PS with carboxyl groups, (f) time spent in inner zone for blue PS with carboxyl groups, (g) total distance moved for blue PS, (h) time spent in inner zone for blue PS.
In each variant tested, the larvae were more active in the dark than in the light (p < 0.0001). In most cases, the larvae spent a comparable amount of time in the inner zone of the well. For red and blue nanoPS with carboxyl groups, no statistically significant differences were observed between the treatments. The larvae were more active during the dark periods and spent a comparable amount of time in the inner zone of the well. For red, non-modified nanoPS, there were no statistically significant differences between the test treatments and the negative control. However, larvae exposed to 0.1 mg/mL of nanoPS were significantly more active in the light than larvae exposed to 0.2 mg/mL of nanoPS (p < 0.05). Larvae exposed to 0.2 mg/mL spent more time in the inner zone of the well in the dark than in the light (p< 0.001). For blue, non–modified nanoPS, there were also no statistically significant differences between the test treatments and the negative control. However, larvae exposed to 0.01 and 0.1 mg/mL of nanoPS were significantly more active in the dark (p < 0.0001 and p < 0.05, respectively) than embryos exposed to 0.2 mg/mL of nanoPS. The larvae spent comparable amounts of time in the inner zone of the well throughout the experiment.
NanoPS with carboxyl groups did not cause any changes in the light–dark preference test. Non–modified nanoPS caused only slight changes, none of which were statistically significant compared to the negative control.
Figure 11 shows the colour preference results. For the colour–dyed nanoPS, in the blue-red variant test, the blue colour preference was maintained only for blue PS with carboxyl surface groups, while for the rest, it disappeared.
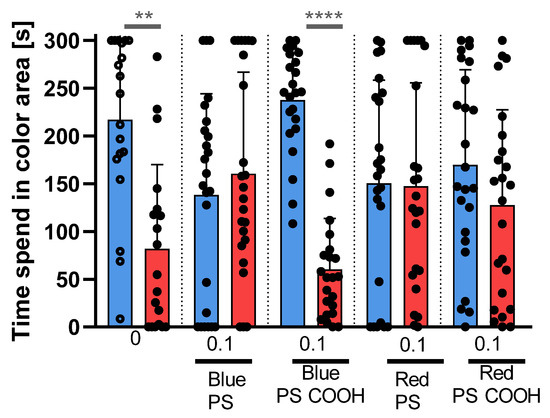
Figure 11.
Colour–preference test for Danio rerio. Comparison between time spent in blue and red areas for different types of colour–dyed nanoPS. Data are shown as mean ± SD; n = 12; Wilcoxon test, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001.
Behavioural test results indicated no or only slight neurotoxicity of the tested nanoPS.
4. Discussion
NanoPS is the most commonly studied nanoplastic in the zebrafish embryo model system. The results of this study showed no increase in mortality or serious developmental abnormalities. However, more subtle effects were observed. This suggests a low acute toxicity of nanoPS but slight neurotoxicity. The findings of this study are consistent with the literature, which reports normal development with slight changes (e.g., in gene expression or behaviour) [18,24,26,27,28]. After exposure to nanoPS, no increase in mortality or changes in heart rate or body length were observed. The only observed change from the negative control was the hatching rate; for each type of nanoPS tested, the hatching rate at 48 hpf was higher. Normally, the higher the concentration (except for red nanoPS-COOH), the higher the hatching rate. This may be related to the adsorption of NanoPS to the chorion (even visible under a stereomicroscope) and the resulting hypoxic conditions. One study showed SEM images of chorions after exposure to different sizes of NanoPS-500 nm particles, which were mostly adsorbed on the chorions. Only a few pores were entered [39]. The results of this study are consistent with this observation. Although the chorionic pores in zebrafish embryos can reach up to 500 nm in diameter, the chorion still serves as an effective barrier against nanoparticles. Due to their strong affinity for the embryonic chorion, likely driven by the high lipophilicity of plastics [40], nanoparticles do not penetrate the chorion but instead adhere tightly to its surface, potentially causing physical or biological effects. After hatching, fluorescent particles were observed to accumulate in the yolk sac and digestive tract of zebrafish larvae through oral uptake. Further research is needed to determine whether distribution to other organs occurs in humans. Previous studies have demonstrated that particles 50 nm or smaller can be absorbed into embryos, while those 250 nm or larger cannot penetrate body tissues [23].
In most commercially available nanoPS solutions, additives are present in the form of surfactants (e.g., Tween, SDS) and preservatives, most often sodium azide. In most studies, it is assumed that these additives do not affect the toxicity of nanoPS. Few studies have examined the effects of sodium azide on mortality, hatching, and heart rate [22]. However, no studies have shown that these preservatives and additives do not affect behavioural test results, gene expression changes, or other subtle effects. This study examined the acute toxicity of sodium azide and its influence on the results of behavioural tests.
LC50 was determined at 264 μM of sodium azide–one order of magnitude higher than the value reported in a previous study on acute toxicity in zebrafish embryos [41]. Concentrations that occurred in nanoPS test solutions (2, 20, and 40 μM) caused no changes in mortality, abnormalities, body length, hatching success and time, or heart rate. The light–dark test results showed no changes compared to the negative control.
Behavioural tests, mainly light–dark preference tests, are used in nanoPS studies. In the light-dark preference test, larvae show a strong increase in locomotor activity when the lights are off and a sudden reduction when the lights are on again [42]. Deviations from this behaviour suggest changes in the nervous system. Researchers using 1 mg/L 500 nm NanoPS found no effect on the total distance travelled in the light-dark test, with an increase in the turning angle [24]. Other researchers found a significant decrease in the distance travelled in the darkness, for 1 mg/L 50 nm [27] and 3 mg/L 25 nm nanoPS [25]. In previous studies, using 1 mg/L and 0.1 mg/L of 1 μm PS MPs, researchers also found a significant decrease in the total distance travelled in the dark, which was greater for the lower concentration [26]. A significant increase in embryo activity during the dark was also observed for 0.5 mg/L 25 nanoPS [25]. Depending on the concentration and size, polystyrene exposure resulted in decreased activity during the dark period. In this study, 10 and 100 mg/L of 500 nm nanoPS did not influence the results of the light–dark preference test. These results are consistent with those of other studies that used particles of this size but at lower concentrations [24]. The other three studies used particles smaller than 25 nm [25], 50 nm [27], and larger than 1 μm [26]. In these studies, there was a significant change in the distance travelled in the dark after exposure to NPs, suggesting a disturbance within the nervous system. Thigmotaxis was analysed during the same light and dark cycles. This behaviour reflects the tendency of the larvae to remain in the outer zone of the arena. It is a well-recognised indicator of anxiety in both animals and humans; when fish experience greater anxiety, they are more likely to swim along the edges of the tank [43]. In the conducted studies, no effect of nanoparticles on thigmotaxis was observed, indicating that their presence did not influence the larval tendency to remain in the outer zone of the arena or alter anxiety-related behaviours. Since only a few studies have applied the light–dark test to nanoPS toxicity studies, it is difficult to draw any conclusions; it is possible that both very small and very large polystyrene (PS) particles affect zebrafish larval behavior, while particles of intermediate size have little or no impact. However, this hypothesis remains unproven.
The tail coiling assay involves the analysis of spontaneous tail movements in embryos at an early stage of development. The spinal cord is responsible for the formation of these movements [44]. This method is still under development and does not have a standardised protocol. Nevertheless, it represents a promising method for rapid hazard assessment and screening of neurotoxic substances [45] and potentially for studying their mechanisms of action [46,47]. The tail coiling assay is rarely used in NP and MP studies. One study using 25 nm nanoPS showed a statistically significant increase in burst counts per minute (for 0.5 and 3 mg/L), while the mean burst duration decreased, indicating that PS caused hyperactivity [25].
There is a growing body of research investigating how micro- and nanoplastics (MPs and NPs) affect zebrafish behaviour, including their responses to visual stimuli and colour preference. However, direct studies on colour preference for coloured nanoplastics remain rare. The colour preference test is the least methodologically developed. It is based on a choice between colours. The number of colours, as well as their placement (bottom, sides, or top of the plate), varies greatly in the literature, which further complicates the interpretation of the results. Most studies have indicated a strong blue colour preference in zebrafish larvae [48,49,50]. In the present study, a choice between two colours was evaluated: blue and red, based on a pilot experiment that identified which colours zebrafish prefer (Figure S3). The results show that for colour–dyed nanoPS, the blue preference is maintained only for blue PS with carboxyl surface groups, while for the rest (red-dyed nanoPS), it disappeared—larvae similarly preferred both blue and red. This may suggest that prolonged exposure to red plastic particles led the larvae to become accustomed to the colour, which could explain the lack of a clear colour preference observed during the test. One study closely related to this topic investigated the effects of polystyrene nanoparticles on zebrafish larvae, showing that exposure disrupted their natural colour preferences (blue vs. yellow). Although the research did not directly assess the attraction or avoidance of the coloured particles, the observed impairment in visual preference was likely due to neurochemical disturbances [51]. A study on Psalidodon eigenmanniorum (freshwater fish) demonstrated that microplastic colour significantly affected ingestion rates, with yellow and blue fragments being consumed most often and white fragments being generally avoided. This finding suggests that colour can influence feeding behaviour, and similar mechanisms may exist in zebrafish. Although the precise role of plastic colour in feeding choices is still uncertain, species-specific visual perception likely contributes to why some colours attract certain fish and repel others [52].
5. Conclusions
NanoPS has low acute toxicity in the tested time and concentration ranges; it does not increase mortality, cause serious developmental abnormalities, or change heart rate. This may have caused a higher hatching rate at 48 hpf, probably due to hypotaxis caused by the adsorption of particles on the chorion. This can be classified as the mechanical effect of adsorbed particles. As observed in the behavioural tests, sodium azide in the test solution increased neurotoxicity. For nanoPS, there were no significant differences between exposure concentrations (0.01, 0.1, and 0.2 mg/mL), surface groups (non–modified, amine, or carboxyl), or type (fluorescently labelled or colour–dyed) of nanoPS. Subtle effects were detected through behavioural tests, particularly in terms of colour preference. This suggests that while nanoPS may not be highly toxic, its potential impact on neurological function warrants further investigation. This does not exclude the different effects of long-lasting exposure.
Sodium azide exhibited toxicity, indicating that its presence in the studied materials may confound the findings. This underscores the importance of carefully considering additives in nanoparticle research, as they can contribute to the observed effects and potentially lead to misleading conclusions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microplastics4030045/s1, Figure S1: Hearbeat per minute of 96 hpf larvae (n = 15) for different concentration of tricaine. Data are shown as mean ± SD; **—p < 0.01, ****—p < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA; post-hoc Dunnett test; Figure S2: Plates used in the colour-preference test. Larvae are initially placed in the center of a well; Figure S3: Innate colour preference for zebrafish larvae at 120 hpf for different variants. Data are shown as mean ± SD; n = 19–41; Wilcoxon test, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01; Figure S4: Length of larvae exposed to different, non-lethal concentrations of sodium azide. Data are shown as mean ± SD; one-way ANOVA; post-hoc Dunnett test; Figure S5: Identification of vasotoxicity at 120 hpf for different, non–lethal concentrations of sodium azide with comparison to negative control: (a) Blood vessels of control Tg(fli1:EGFP) with measured trunk width (red) and vessel length (purple) (magnification: 8×), (b) Relative intersegmental vessel (ISV), calculated as trunk width to vessel length ratio, for different concentrations of sodium azide. Data are shown as mean ± SD; one-way ANOVA; post–hoc Dunnett test; Figure S6: Pictures of zebrafish larvae at 96 hpf taken under a confocal microscope (magnification: 200×), for 0.1 mg/mL NanoPS with different surface groups (non-modified, amine, carboxyl) compared to negative control (E3); Figure S7: Hearbeat per minute of 96 hpf larvae (n = 16) for different concentration and type of fluorescent NanoPS. Data are shown as mean ± SD; one-way ANOVA; post-hoc Dunnett test; Figure S8: Hearbeat per minute of 120 hpf larvae (n = 16) for different concentration and type of colour-dyed NanoPS. Data are shown as mean ± SD; one-way ANOVA; post-hoc Dunnett test. (a) blue PS, (b) blue PS with carboxyl groups, (c) red PS, (d) red PS with carboxyl groups; Figure S9: Length of zebrafish (n = 7–16) at 96 hpf for different concentration and type of fluorescent NanoPS. Data are shown as mean ± SD; one-way ANOVA; post-hoc Dunnett test; Figure S10: Length of larvae (n = 7–16) at 120 hpf for different concentration and type of colour-dyed NanoPS. Data are shown as mean ± SD; one-way ANOVA; post-hoc Dunnett test; * p < 0.05. (a) blue PS, (b) blue PS with carboxyl groups, (c) red PS, (d) red PS with carboxyl groups; Figure S11: Total distance moved by larvae in dark periods in light-dark preference test, for different types and concentrations of NanoPS. Data are shown as mean ± SD; one-way ANOVA; post-hoc Dunnett test.
Author Contributions
W.K. 80%, Ł.K. 15%, A.D. 5%. Conceptualisation, A.D. and Ł.K.; methodology, A.D. and Ł.K.; software, Ł.K.; validation, Ł.K.; formal analysis, W.K. and Ł.K.; investigation, W.K., and Ł.K.; resources, A.D. and Ł.K.; data curation, W.K., and Ł.K.; writing—original draft preparation, W.K.; writing—review and editing, A.D. and Ł.K.; visualisation, W.K.; supervision, A.D. and Ł.K.; project administration, A.D.; funding acquisition, A.D. and Ł.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by PBmb210 Medical University of Lublin.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study because according to the EU Directive 2010/63/EU on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes, the Directive applies only to live non-human vertebrate animals from the stage at which they are capable of independent feeding. In the case of zebrafish (Danio rerio), this stage has been widely recognized to occur at 5 days post-fertilization (dpf). Scientific publications support this developmental benchmark. Additionally, the SCHEER Opinion prepared as scientific guidance for the Directive explicitly states that zebrafish larvae reach the relevant level of maturity at 5 dpf. Therefore, experiments conducted on zebrafish embryos prior to this stage do not fall within the scope of the Directive and are exempt from ethical review.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Jakub Semeniuk for his valuable assistance in conducting the experiments. This research was partially supported by IDUB grants from the University of Warsaw internal funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AFT | Acute Fish Toxicity Test |
| FET | Fish Embryo Toxicity Test |
| hpf | Hours post-fertilization |
| MP | microplastic |
| NP | nanoplastic |
| OECD | Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development |
| PA | Polyamide |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| PVC | Polyvinyl chloride |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
References
- Kurach, Ł.; Chłopaś-Konowałek, A.; Budzyńska, B.; Zawadzki, M.; Szpot, P.; Boguszewska-Czubara, A. Etazene induces developmental toxicity in vivo Danio rerio and in silico studies of new synthetic opioid derivative. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. 203: Fish, Acute Toxicity Test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals; OCED Publishing: Paris, France, 1992; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. 236: Fish embryo acute toxicity (FET) test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals; OCED Publishing: Paris, France, 2013; Volume 2, pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Busquet, F.; Strecker, R.; Rawlings, J.M.; Belanger, S.E.; Braunbeck, T.; Carr, G.J.; Cenijn, P.; Fochtman, P.; Gourmelon, A.; Hübler, N.; et al. OECD validation study to assess intra- and inter-laboratory reproducibility of the zebrafish embryo toxicity test for acute aquatic toxicity testing. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 69, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oger, M.J.L.; Vermeulen, O.; Lambert, J.; Madanu, T.L.; Kestemont, P.; Cornet, V. Down to size: Exploring the influence of plastic particle Dimensions on physiological and nervous responses in early-stage zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 351, 124094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, C.W.; Ching-Fong Yeung, K.; Chan, K.M. Acute toxic effects of polyethylene microplastic on adult zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, R.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wolosker, M.B.; Zhu, Q.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y. Accumulation of different shapes of microplastics initiates intestinal injury and gut microbiota dysbiosis in the gut of zebrafish. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainieri, S.; Conlledo, N.; Larsen, B.K.; Granby, K.; Barranco, A. Combined effects of microplastics and chemical contaminants on the organ toxicity of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Res. 2018, 162, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Wu, S.; Lu, S.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Fu, Z.; Shi, H.; Raley-Susman, K.M.; He, D. Microplastic particles cause intestinal damage and other adverse effects in zebrafish Danio rerio and nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, R.; Sheng, C.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, H.; Lemos, B. Microplastics induce intestinal inflammation, oxidative stress, and disorders of metabolome and microbiome in zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Xia, J.; Pan, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Fu, Z. Polystyrene microplastics induce microbiota dysbiosis and inflammation in the gut of adult zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Bao, Z.; Wan, Z.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Polystyrene microplastic exposure disturbs hepatic glycolipid metabolism at the physiological, biochemical, and transcriptomic levels in adult zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Ommati, M.M.; Chen, D.; Chen, W.; Han, L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, S.; Sun, P. Hepatotoxic effects of environmentally relevant concentrations of polystyrene microplastics on senescent Zebrafish (Danio rerio): Patterns of stress response and metabolomic alterations. Aquat. Toxicol. 2025, 279, 107252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasamma, S.; Audira, G.; Siregar, P.; Malhotra, N.; Lai, Y.-H.; Liang, S.-T.; Chen, J.-R.; Chen, K.H.-C.; Hsiao, C.-D. Nanoplastics Cause Neurobehavioral Impairments, Reproductive and Oxidative Damages, and Biomarker Responses in Zebrafish: Throwing up Alarms of Wide Spread Health Risk of Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, J.A.; Trevisan, R.; Massarsky, A.; Kozal, J.S.; Levin, E.D.; Di Giulio, R.T. Maternal transfer of nanoplastics to offspring in zebrafish (Danio rerio): A case study with nanopolystyrene. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, R.; Mortimer, M.; Richter, J.; Rani-Borges, B.; Yu, Z.; Heinlaan, M.; Lin, S.; Ivask, A. Hazard of polystyrene micro-and nanospheres to selected aquatic and terrestrial organisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 158560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ompala, C.; Renault, J.-P.; Taché, O.; Cournède, É.; Devineau, S.; Chivas-Joly, C. Stability and dispersibility of microplastics in experimental exposure medium and their dimensional characterization by SMLS, SAXS, Raman microscopy, and SEM. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 134083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shi, H.; Xie, B.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Zhao, Y. Microplastics as Both a Sink and a Source of Bisphenol A in the Marine Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10188–10196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sökmen, T.Ö.; Sulukan, E.; Türkoğlu, M.; Baran, A.; Özkaraca, M.; Ceyhun, S.B. Polystyrene nanoplastics (20 nm) are able to bioaccumulate and cause oxidative DNA damages in the brain tissue of zebrafish embryo (Danio rerio). NeuroToxicology 2020, 77, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneman, W.J.; Spaink, H.P.; Brun, N.R.; Bosker, T.; Vijver, M.G. Pathway analysis of systemic transcriptome responses to injected polystyrene particles in zebrafish larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 190, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zu, B.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Mei, X. Desorption of bisphenol A from microplastics under simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1195964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.A.; Kozal, J.S.; Jayasundara, N.; Massarsky, A.; Trevisan, R.; Geitner, N.; Wiesner, M.; Levin, E.D.; Di Giulio, R.T. Uptake, tissue distribution, and toxicity of polystyrene nanoparticles in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 194, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Pomeren, M.; Brun, N.R.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Vijver, M.G. Exploring uptake and biodistribution of polystyrene (nano)particles in zebrafish embryos at different developmental stages. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 190, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parenti, C.C.; Ghilardi, A.; Della Torre, C.; Magni, S.; Del Giacco, L.; Binelli, A. Evaluation of the infiltration of polystyrene nanobeads in zebrafish embryo tissues after short-term exposure and the related biochemical and behavioural effects. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Ruiz, M.; de Alba González, M.; Morales, M.; Martin-Folgar, R.; González, M.C.; Cañas-Portilla, A.I.; De la Vieja, A. Neurotoxicity and endocrine disruption caused by polystyrene nanoparticles in zebrafish embryo. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, L.; Cheng, J. Exposure to microplastics decreases swimming competence in larval zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 176, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Gundlach, M.; Yang, S.; Jiang, J.; Velki, M.; Yin, D.; Hollert, H. Quantitative investigation of the mechanisms of microplastics and nanoplastics toward zebrafish larvae locomotor activity. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhou, J.; Shen, M.; Wang, X.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Effects of polystyrene microplastics on the composition of the microbiome and metabolism in larval zebrafish. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Lamm, S.H. Human Health Effects of Sodium Azide Exposure: A Literature Review and Analysis. Int. J. Toxicol. 2003, 22, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faqi, A.S.; Richards, D.; Hauswirth, J.W.; Schroeder, R. Maternal and developmental toxicity study of sodium azide in rats. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 52, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, L.L.; Garrett, K.K.; Bae, Y.; Frawley, K.L.; Totoni, S.C.; Peterson, J. A Potential Antidote for Both Azide and Cyanide Poisonings. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2024, 388, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.A.; Starkey, J.R.; Kleinhofs, A. Toxicity and mutagenicity of sodium azide in mammalian cell cultures. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. 1980, 77, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shenawy, N.S.; AL-Harbi, M.S.; Hamza, R.Z. Effect of vitamin E and selenium separately and in combination on biochemical, immunological and histological changes induced by sodium azide in male mice. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 67, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betterton, E.A.; Lowry, J.; Ingamells, R.; Venner, B. Kinetics and mechanism of the reaction of sodium azide with hypochlorite in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Cheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Duan, Z.; Cui, W.; Shi, Y.; Qin, L. Influence of Functional Group Modification on the Toxicity of Nanoplastics. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 800782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klüver, N.; König, M.; Ortmann, J.; Massei, R.; Paschke, A.; Kühne, R.; Scholz, S. Fish Embryo Toxicity Test: Identification of Compounds with Weak Toxicity and Analysis of Behavioral Effects To Improve Prediction of Acute Toxicity for Neurotoxic Compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7002–7011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, J.; Zang, L.; Nishimura, N.; Shimada, Y. Zebrafish: An emerging model to study microplastic and nanoplastic toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delov, V.; Muth-Köhne, E.; Schäfers, C.; Fenske, M. Transgenic fluorescent zebrafish Tg(fli1:EGFP)y1 for the identification of vasotoxicity within the zFET. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 150, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Cho, H.-J.; Kim, E.; Huh, Y.H.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, B.; Kang, T.; Lee, J.-S.; Jeong, J. Bioaccumulation of polystyrene nanoplastics and their effect on the toxicity of Au ions in zebrafish embryos. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 3173–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Duan, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Gong, Z.; Wang, L. Barrier function of zebrafish embryonic chorions against microplastics and nanoplastics and its impact on embryo development. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; van Mil, H.G.J.; Richardson, M.K. Large-Scale Assessment of the Zebrafish Embryo as a Possible Predictive Model in Toxicity Testing. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, S.; Rodenburg, F.; Schaaf, M.J.M.; Tudorache, C. Detailed Analysis of Zebrafish Larval Behaviour in the Light Dark Challenge Assay Shows That Diel Hatching Time Determines Individual Variation. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 827282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciąg, M.; Michalak, A.; Skalicka-Woźniak, K.; Zykubek, M.; Ciszewski, A.; Budzyńska, B. Zebrafish and mouse models for anxiety evaluation—A comparative study with xanthotoxin as a model compound. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 165, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saint-Amant, L.; Drapeau, P. Time course of the development of motor behaviors in the zebrafish embryo. J. Neurobiol. 1998, 37, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacchetti, I.; Cristiano, W.; Kevin, D.D.; Carere, M.; Mancini, L. Coiling tail activity in zebrafish embryo: A protocol for an early warning system of neurotoxic substances. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2022, 8427–8434. [Google Scholar]
- Zindler, F.; Beedgen, F.; Brandt, D.; Steiner, M.; Stengel, D.; Baumann, L.; Braunbeck, T. Analysis of tail coiling activity of zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos allows for the differentiation of neurotoxicants with different modes of action. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 186, 109754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Hellfeld, R.; Gade, C.; Baumann, L.; Leist, M.; Braunbeck, T. The sensitivity of the zebrafish embryo coiling assay for the detection of neurotoxicity by compounds with diverse modes of action. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 75281–75299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, B.W.M.M.; Moeskops, M.; Veenvliet, A.R.J. Color Preference in Danio rerio: Effects of Age and Anxiolytic Treatments. Zebrafish 2016, 13, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Ryu, J.-H.; Choi, T.-I.; Bae, Y.-K.; Lee, S.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, C.-H. Innate Color Preference of Zebrafish and Its Use in Behavioral Analyses. Mol. Cells 2016, 39, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siregar, P.; Juniardi, S.; Audira, G.; Lai, Y.-H.; Huang, J.-C.; Chen, K.H.-C.; Chen, J.-R.; Hsiao, C.-D. Method Standardization for Conducting Innate Color Preference Studies in Different Zebrafish Strains. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.-S.; Son, Y.; Kim, S.S.; Shin, D.-S.; Lim, S.H.; Yang, J.Y.; Jeong, H.N.; Lee, B.H.; Bae, M.A. Size-Dependent Effects of Polystyrene Nanoparticles (PS-NPs) on Behaviors and Endogenous Neurochemicals in Zebrafish Larvae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos, J.M.; Tesitore, G.; de Mello, F.T. Does color play a predominant role in the intake of microplastics fragments by freshwater fish: An experimental approach with Psalidodon eigenmanniorum. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 49457–49464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).