Counteracting the Harms of Microplastics on Humans: An Overview from the Perspective of Exposure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Review Methodology
3. Human Exposure to Microplastics
4. Reducing Exposure to Microplastics
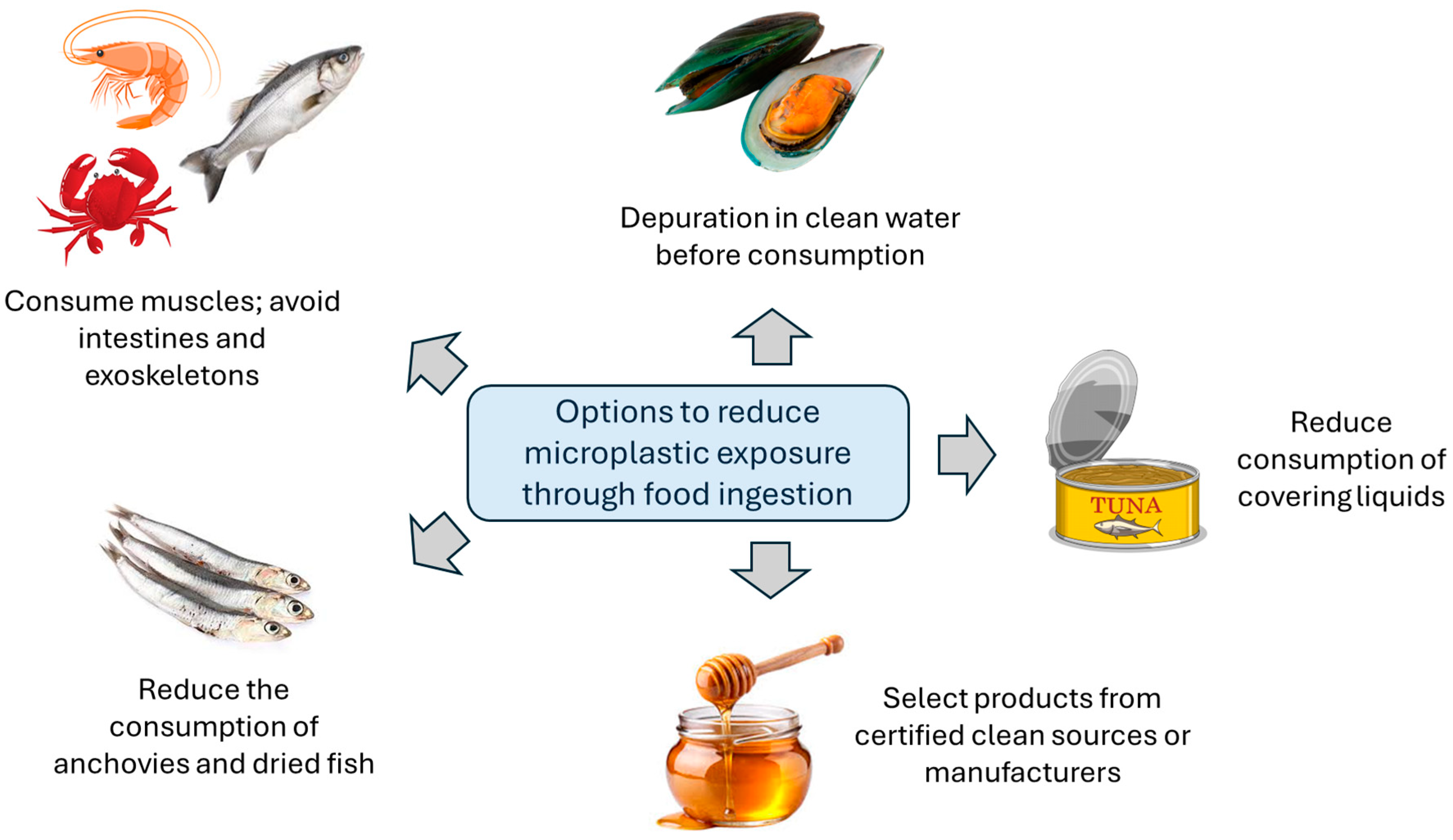
4.1. Reducing Exposure Through Ingestion
4.1.1. Seafood
4.1.2. Other Food Items and Food Packaging
4.1.3. Drinking Water and Beverages
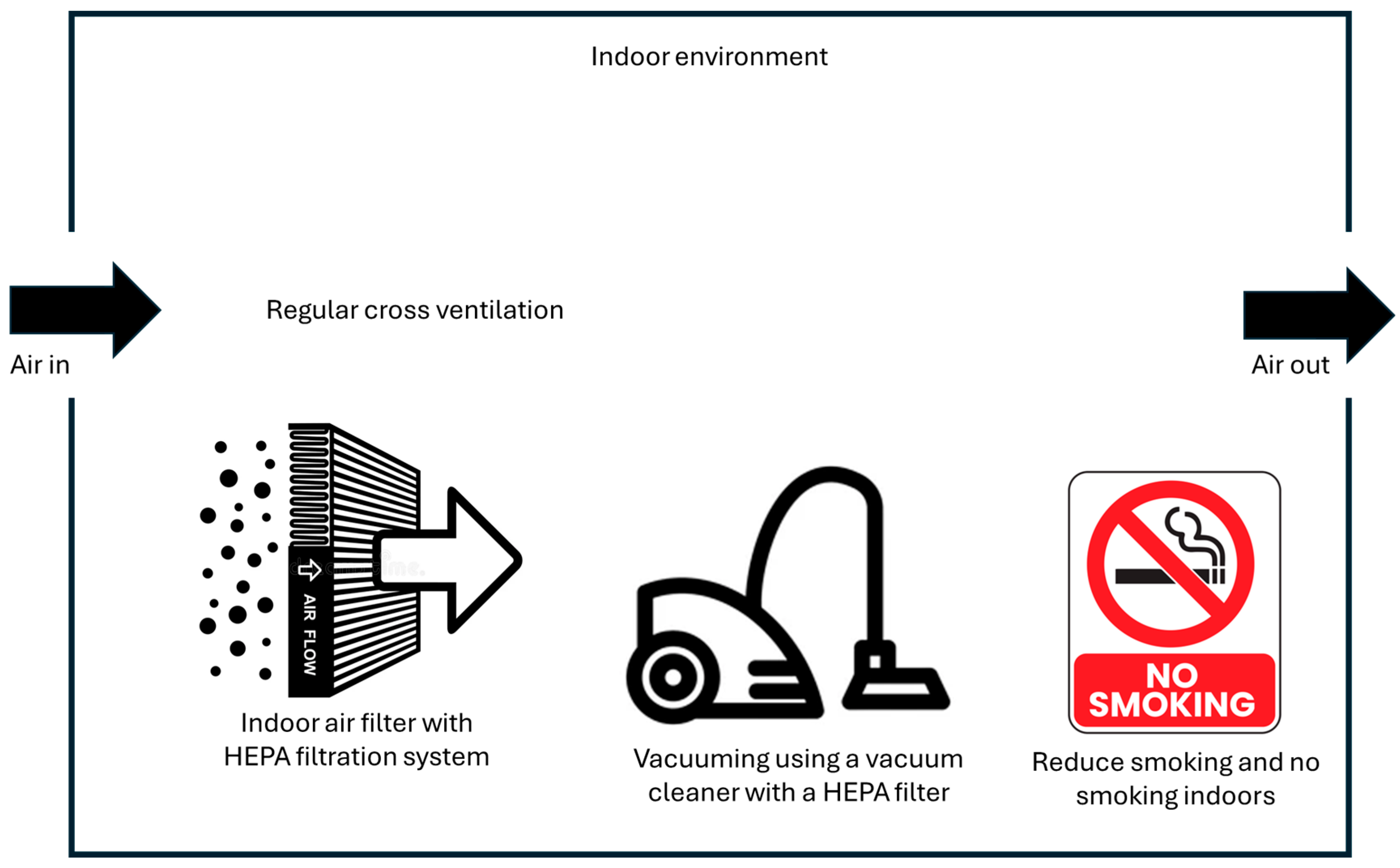
4.2. Reducing Exposure Through Inhalation
4.2.1. Indoor Air Filtering
4.2.2. Reduction or Avoidance of Smoking
4.2.3. Wearing Facemasks
4.3. Reducing Exposure Through Dermal Contact
5. Potential Reduction of Microplastic Toxic Effects Through Antioxidants
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barboza, L.G.A.; Dick Vethaak, A.; Lavorante, B.R.B.O.; Lundebye, A.-K.; Guilhermino, L. Marine microplastic debris: An emerging issue for food security, food safety and human health. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.H.D. Terrestrial and Aquatic Plastisphere: Formation, Characteristics, and Influencing Factors. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, C. Dawn of the plasticene age. New Sci. 2015, 225, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarus, G.M.; Muianga, C.; Hunter, C.M.; Pappas, R.S. A review of data for quantifying human exposures to micro and nanoplastics and potential health risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 144010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.H.D.; Li, R. Aged Microplastics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes: A Review of Aging Effects on Their Interactions. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.H.D. A review of the toxic effects of microplastics based on studies on mammals and mammalian cell lines. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2024, 3, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.H.D. Genotoxicity of Microplastics on Living Organisms: Effects on Chromosomes, DNA and Gene Expression. Environments 2025, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.P.G.L.; Nash, R. Microplastics: Finding a consensus on the definition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Xia, J.; Pan, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Fu, Z. Polystyrene microplastics induce microbiota dysbiosis and inflammation in the gut of adult zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Dhanker, R.; Bhawna; Tomar, A.; Raza, S.; Sharma, A. Fishing Gears and Nets as a Source of Microplastic. In Microplastic Pollution; Shahnawaz, M., Adetunji, C.O., Dar, M.A., Zhu, D., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 127–140. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, K.H.D.; Li, R. The effects of plastisphere on the physicochemical properties of microplastics. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 48, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germanov, E.S.; Marshall, A.D.; Bejder, L.; Fossi, M.C.; Loneragan, N.R. Microplastics: No Small Problem for Filter-Feeding Megafauna. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, C.J.; Hudson, M.D.; Russell, A.E.; Saluveer, M.; Sidaoui-Haddad, G. Microplastics in fish and fishmeal: An emerging environmental challenge? Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowarah, K.; Patchaiyappan, A.; Thirunavukkarasu, C.; Jayakumar, S.; Devipriya, S.P. Quantification of microplastics using Nile Red in two bivalve species Perna viridis and Meretrix meretrix from three estuaries in Pondicherry, India and microplastic uptake by local communities through bivalve diet. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 153, 110982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.S.; Wong, L.C.; Lai, K.P.; Cheung, S.G. The influences of spatial-temporal variability and ecological drivers on microplastic in marine fish in Hong Kong. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Xie, C.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, Z. Accumulation of microplastics in fish guts and gills from a large natural lake: Selective or non-selective? Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, O.A.; Rahman, M.S. An ecotoxicological approach to microplastics on terrestrial and aquatic organisms: A systematic review in assessment, monitoring and biological impact. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 84, 103615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Cao, X.; Fan, Z. Toxicity mechanism of Nylon microplastics on Microcystis aeruginosa through three pathways: Photosynthesis, oxidative stress and energy metabolism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 128094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, C.M.; Vladimirova, V. Preliminary study and first evidence of presence of microplastics in terrestrial herpetofauna from Southwestern Paraguay. Stud. Neotrop. Fauna Environ. 2023, 58, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.-T.; Cai, Y.-F.; Chen, Y.-X.; Yang, Y.-W.; Xing, S.-C.; Liao, X.-D. Occurrence of microplastic in livestock and poultry manure in South China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, A.; Svelato, A.; Santacroce, C.; Catalano, P.; Notarstefano, V.; Carnevali, O.; Papa, F.; Rongioletti, M.C.A.; Baiocco, F.; Draghi, S.; et al. Plasticenta: First evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato-Lourenço, L.F.; Carvalho-Oliveira, R.; Júnior, G.R.; dos Santos Galvão, L.; Ando, R.A.; Mauad, T. Presence of airborne microplastics in human lung tissue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, V.L.S.; Liddle, C.R.; Atherall, C.A.; Chapman, E.; Watkins, M.; Calaminus, S.D.J.; Rotchell, J.M. Microplastics in human blood: Polymer types, concentrations and characterisation using μFTIR. Environ. Int. 2024, 188, 108751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenech, J.; Hernández, A.; Rubio, L.; Marcos, R.; Cortés, C. Interactions of polystyrene nanoplastics with in vitro models of the human intestinal barrier. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 2997–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.H.D.; Li, R.; Li, Z.; Wang, D. Health risk of human exposure to microplastics: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 1155–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.; Wang, W.-X. Human Exposure to Microplastics and Its Associated Health Risks. Environ. Health 2023, 1, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Rehati, P.; Yang, Z.; Cai, Z.; Guo, C.; Li, Y. The potential toxicity of microplastics on human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; You, X.-Y. Recent progress of microplastic toxicity on human exposure base on in vitro and in vivo studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, J.; Ding, L.; Ren, H. Uptake and Accumulation of Polystyrene Microplastics in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) and Toxic Effects in Liver. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4054–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, A.F.; Meyer, D.N.; Petriv, A.-M.V.; Soto, A.L.; Shields, J.N.; Akemann, C.; Baker, B.B.; Tsou, W.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Baker, T.R. Nanoplastics impact the zebrafish (Danio rerio) transcriptome: Associated developmental and neurobehavioral consequences. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Love, D.C.; Rochman, C.M.; Neff, R.A. Microplastics in Seafood and the Implications for Human Health. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Wang, X.; Ren, T.; Wang, J.; Shan, J. Microplastics contamination in food and beverages: Direct exposure to humans. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 2816–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, L.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. Potential adverse health effects of ingested micro- and nanoplastics on humans. Lessons learned from in vivo and in vitro mammalian models. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2020, 23, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walkinshaw, C.; Lindeque, P.K.; Thompson, R.; Tolhurst, T.; Cole, M. Microplastics and seafood: Lower trophic organisms at highest risk of contamination. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eerkes-Medrano, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Aldridge, D.C. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review of the emerging threats, identification of knowledge gaps and prioritisation of research needs. Water Res. 2015, 75, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Mohamed Nor, N.H.; Hermsen, E.; Kooi, M.; Mintenig, S.M.; De France, J. Microplastics in freshwaters and drinking water: Critical review and assessment of data quality. Water Res. 2019, 155, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, K.D.; Covernton, G.A.; Davies, H.L.; Dower, J.F.; Juanes, F.; Dudas, S.E. Human Consumption of Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7068–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, A.I.; Macchia, V.; Sanderson, W.G.; Thompson, R.C.; Henry, T.B. Low levels of microplastics (MP) in wild mussels indicate that MP ingestion by humans is minimal compared to exposure via household fibres fallout during a meal. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Rocher, V.; Saad, M.; Renault, N.; Tassin, B. Microplastic contamination in an urban area: A case study in Greater Paris. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Feng, Q.; Wang, J. Mini-review of microplastics in the atmosphere and their risks to humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Cui, Y.; Brahney, J.; Mahowald, N.M.; Li, Q. Long-distance atmospheric transport of microplastic fibres influenced by their shapes. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, L.C.; Rotchell, J.M.; Bennett, R.T.; Cowen, M.; Tentzeris, V.; Sadofsky, L.R. Detection of microplastics in human lung tissue using μFTIR spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeza-Martínez, C.; Olmos, S.; González-Pleiter, M.; López-Castellanos, J.; García-Pachón, E.; Masiá-Canuto, M.; Hernández-Blasco, L.; Bayo, J. First evidence of microplastics isolated in European citizens’ lower airway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, S.B.; D’Errico, J.N.; Adler, D.S.; Kollontzi, S.; Goedken, M.J.; Fabris, L.; Yurkow, E.J.; Stapleton, P.A. Nanopolystyrene translocation and fetal deposition after acute lung exposure during late-stage pregnancy. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Phoenix, V.R.; Le Roux, G.; Durántez Jiménez, P.; Simonneau, A.; Binet, S.; Galop, D. Atmospheric transport and deposition of microplastics in a remote mountain catchment. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shao, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Feng, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, D. Airborne fiber particles: Types, size and concentration observed in Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Wei, N.; Zong, C.; Li, C.; Jiang, C.; He, Y.; Li, D. To what extent are we really free from airborne microplastics? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianello, A.; Jensen, R.L.; Liu, L.; Vollertsen, J. Simulating human exposure to indoor airborne microplastics using a Breathing Thermal Manikin. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, F.; Zhou, S. Airborne Microplastics: A Review on the Occurrence, Migration and Risks to Humans. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revel, M.; Châtel, A.; Mouneyrac, C. Micro(nano)plastics: A threat to human health? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Stracke, F.; Hansen, S.; Schaefer, U.F. Nanoparticles and their interactions with the dermal barrier. Dermato-Endocrinology 2009, 1, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopinath, P.M.; Saranya, V.; Vijayakumar, S.; Mythili Meera, M.; Ruprekha, S.; Kunal, R.; Pranay, A.; Thomas, J.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Assessment on interactive prospectives of nanoplastics with plasma proteins and the toxicological impacts of virgin, coronated and environmentally released-nanoplastics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, F.; Jannat, S.; Tareq, S.M. Abundance, characteristics and variation of microplastics in different freshwater fish species from Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskuła, P.; Astel, A.M. Microplastics in Commercial Fishes and By-Catch from Selected FAO Major Fishing Areas of the Southern Baltic Sea. Animals 2023, 13, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Soltani, N.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Turner, A.; Hassanaghaei, M. Microplastics in different tissues of fish and prawn from the Musa Estuary, Persian Gulf. Chemosphere 2018, 205, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia-Castañeda, G.; Medina-López, J.A.; Frías-Espericueta, M.G.; Páez-Osuna, F. Farmed stage (age)-dependent accumulation and size of microplastics in Litopenaeus vannamei shrimp reared in a super-intensive controlled system. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 918, 170575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaweera, Y.U.; Hennayaka, H.M.A.I.; Herath, H.M.L.P.B.; Kumara, G.M.P.; Mahagamage, M.G.Y.L.; Rodrigo, U.D.; Manatunga, D.C. A Comprehensive Investigation of Microplastic Contamination and Polymer Toxicity in Farmed Shrimps; L. vannamei and P. monodon. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2025, 236, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atamanalp, M.; Köktürk, M.; Uçar, A.; Duyar, H.A.; Özdemir, S.; Parlak, V.; Esenbuğa, N.; Alak, G. Microplastics in Tissues (Brain, Gill, Muscle and Gastrointestinal) of Mullus barbatus and Alosa immaculata. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 81, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrera, M.C.; Aragona, M.; Porcino, C.; Fazio, F.; Laurà, R.; Levanti, M.; Montalbano, G.; Germanà, G.; Abbate, F.; Germanà, A. Micro and Nano Plastics Distribution in Fish as Model Organisms: Histopathology, Blood Response and Bioaccumulation in Different Organs. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saborowski, R.; Korez, Š.; Riesbeck, S.; Weidung, M.; Bickmeyer, U.; Gutow, L. Shrimp and microplastics: A case study with the Atlantic ditch shrimp Palaemon varians. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 234, 113394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reunura, T.; Prommi, T.O. Detection of microplastics in Litopenaeus vannamei (Penaeidae) and Macrobrachium rosenbergii (Palaemonidae) in cultured pond. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurjar, U.R.; Xavier, M.; Nayak, B.B.; Ramteke, K.; Deshmukhe, G.; Jaiswar, A.K.; Shukla, S.P. Microplastics in shrimps: A study from the trawling grounds of north eastern part of Arabian Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 48494–48504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.S.; Rahman, M.S.; Uddin, M.N.; Sharifuzzaman, S.M.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Sarker, S.; Nawaz Chowdhury, M.S. Microplastic contamination in Penaeid shrimp from the Northern Bay of Bengal. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curren, E.; Leaw, C.P.; Lim, P.T.; Leong, S.C.Y. Evidence of Marine Microplastics in Commercially Harvested Seafood. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 562760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, A.; Moore, F.; Keshavarzi, B.; Soltani, N.; Sorooshian, A. Potentially toxic elements and microplastics in muscle tissues of different marine species from the Persian Gulf: Levels, associated risks, and trophic transfer. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 175, 113283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devriese, L.I.; van der Meulen, M.D.; Maes, T.; Bekaert, K.; Paul-Pont, I.; Frère, L.; Robbens, J.; Vethaak, A.D. Microplastic contamination in brown shrimp (Crangon crangon, Linnaeus 1758) from coastal waters of the Southern North Sea and Channel area. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 98, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, R. Full size microplastics in crab and fish collected from the mangrove wetland of Beibu Gulf: Evidences from Raman Tweezers (1–20 μm) and spectroscopy (20–5000 μm). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunola, S.O.; Reis-Santos, P.; Wootton, N.; Gillanders, B.M. Microplastics in decapod crustaceans sourced from Australian seafood markets. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 179, 113706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Su, L.; Li, H.; Liang, M.; Shi, H. Assessing the relationship between the abundance and properties of microplastics in water and in mussels. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, N.; Porter, A.; Santillo, D.; Simpson, H.; Lloyd-Williams, S.; Lewis, C. Particle characteristics of microplastics contaminating the mussel Mytilus edulis and their surrounding environments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwmeester, H.; Hollman, P.C.H.; Peters, R.J.B. Potential Health Impact of Environmentally Released Micro- and Nanoplastics in the Human Food Production Chain: Experiences from Nanotoxicology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8932–8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lusher, A.L.; Rotchell, J.M.; Deudero, S.; Turra, A.; Bråte, I.L.N.; Sun, C.; Shahadat Hossain, M.; Li, Q.; Kolandhasamy, P.; et al. Using mussel as a global bioindicator of coastal microplastic pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). Presence of microplastics and nanoplastics in food, with particular focus on seafood. EFSA J. 2016, 14, e04501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillo, D.; Miller, K.; Johnston, P. Microplastics as contaminants in commercially important seafood species. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phaoduang, S.; Sutthacheep, M.; Prakopphon, P.; Sriwusait, P.; Yeemin, T. Abundance, composition of microplastics in dried anchovy products from the Western Gulf of Thailand. Ramkhamhaeng Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2021, 4, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, J.; Dristy, E.Y.; Anjumanara; Mondal, P.; Hoque, M.S.; Sumon, K.A.; Hossain, M.A.R.; Shahjahan, M. Dried fish more prone to microplastics contamination over fresh fish—Higher potential of trophic transfer to human body. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 250, 114510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, A.; Golieskardi, A.; Choo, C.K.; Larat, V.; Karbalaei, S.; Salamatinia, B. Microplastic and mesoplastic contamination in canned sardines and sprats. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 1380–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhbarizadeh, R.; Dobaradaran, S.; Nabipour, I.; Tajbakhsh, S.; Darabi, A.H.; Spitz, J. Abundance, composition, and potential intake of microplastics in canned fish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Basantes, M.F.; Nacimba-Aguirre, D.; Conesa, J.A.; Fullana, A. Presence of microplastics in commercial canned tuna. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussien, N.A.; Mohammadein, A.; Tantawy, E.M.; Khattab, Y.; Al Malki, J.S. Investigating microplastics and potentially toxic elements contamination in canned Tuna, Salmon, and Sardine fishes from Taif markets, KSA. Open Life Sci. 2021, 16, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.M.; Almeida, C.M.R.; Guardiola, F.A.; Pereira, R.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Ramos, S. Uncovering microplastics contamination in canned seafood. Food Chem. 2024, 448, 139049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Basantes, M.F.; Conesa, J.A.; Fullana, A. Microplastics in Honey, Beer, Milk and Refreshments in Ecuador as Emerging Contaminants. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Cai, H.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Shi, H. Microplastics in take-out food containers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 122969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadare, O.O.; Wan, B.; Guo, L.-H.; Zhao, L. Microplastics from consumer plastic food containers: Are we consuming it? Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Dai, H.; He, L. Migration testing of microplastics from selected water and food containers by Raman microscopy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 462, 132798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Ying, R.; Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Disposable plastic materials release microplastics and harmful substances in hot water. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.-J.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, T.-L.; Zhu, Y.-Y.; Wang, Z.-J.; Zhou, Z.-S.; Xie, T.-Z.; Luo, X.-D. Migration of (non-) intentionally added substances and microplastics from microwavable plastic food containers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.-L.; Liu, L.-Y.; Guo, J.-L.; Zeng, L.-X.; Guo, Y. Microplastics in take-out food: Are we over taking it? Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedzierski, M.; Lechat, B.; Sire, O.; Le Maguer, G.; Le Tilly, V.; Bruzaud, S. Microplastic contamination of packaged meat: Occurrence and associated risks. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 24, 100489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Jia, P.; He, S.; Dai, H.; Deng, S.; Han, J. Release of microplastics from breastmilk storage bags and assessment of intake by infants: A preliminary study. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Chuah, C.; Amin, M.A.; Khoshyan, A.; Gibson, C.T.; Tang, Y.; Naidu, R.; Fang, C. Assessment of microplastics and nanoplastics released from a chopping board using Raman imaging in combination with three algorithms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, H.; Khan, M.R.H.; Quadir, M.; Rusch, K.A.; Mondal, P.P.; Orr, M.; Xu, E.G.; Iskander, S.M. Cutting Boards: An Overlooked Source of Microplastics in Human Food? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 8225–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymanski, D.; Goldbeck, C.; Humpf, H.-U.; Fürst, P. Analysis of microplastics in water by micro-Raman spectroscopy: Release of plastic particles from different packaging into mineral water. Water Res. 2018, 129, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, S.A.; Welch, V.G.; Neratko, J. Synthetic Polymer Contamination in Bottled Water. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 389699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-J.; Wang, J.; Li, H.-Y.; Zhang, H.-M.; Hua, J.; Zhang, D.L. Microplastic pollution of bottled water in China. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveena, S.M.; Shamsul Ariffin, N.I.; Nafisyah, A.L. Microplastics in Malaysian bottled water brands: Occurrence and potential human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 315, 120494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, L.; Ma, M.; Wu, H.; An, L.; Yang, Z. Occurrence of microplastics in commercially sold bottled water. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 867, 161553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, Y.-T.; Chan, S.M.; Sze, E.T. Quantitative Assessment of Full Size Microplastics in Bottled and Tap Water Samples in Hong Kong. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.; Kerpen, J.; Wolff, S.; Langer, R.; Eschweiler, V. Investigation of microplastics contamination in drinking water of a German city. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 143421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, V.P.; Joseph, A.; Goel, S. Microplastics and other harmful substances released from disposable paper cups into hot water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xu, L.; Yu, K.; Wei, F.; Zhang, M. Release of microplastics from disposable cups in daily use. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, J.-L.; Duan, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, D.; Dong, B.; Mo, M.-Z.; Wang, J.; Zheng, J.-G.; Zhong, H.-N.; et al. Identification and characterisation of microplastics released from plastic-coated paper cups using micro-Raman spectroscopy. Food Control 2023, 153, 109901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzichetti, A.R.P.; Pablos, C.; Álvarez-Fernández, C.; Reynolds, K.; Stanley, S.; Marugán, J. Evaluation of membranes performance for microplastic removal in a simple and low-cost filtration system. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2021, 3, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, A.G.; Liu, Z.; McKie, M.J.; Almuhtaram, H.; Andrews, R.C. Microplastic Removal from Drinking Water Using Point-of-Use Devices. Polymers 2023, 15, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, T.; Wang, J.; Xiao, X.; Lv, J.; Li, Q.; Dai, H.; Liu, X.; Pi, F. Identification and Evaluation of Microplastics from Tea Filter Bags Based on Raman Imaging. Foods 2022, 11, 2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, N.J.H.; Jahedi, F.; Turner, A. Microplastics and nanoplastics in tea: Sources, characteristics and potential impacts. Food Chem. 2025, 466, 142111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaei, G.; García-Rodríguez, A.; Tavakolpournegari, A.; Martín-Pérez, J.; Villacorta, A.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. The release of polylactic acid nanoplastics (PLA-NPLs) from commercial teabags. Obtention, characterization, and hazard effects of true-to-life PLA-NPLs. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 131899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Peng, L.; Fu, J.; Dai, X.; Wang, G. A microscopic survey on microplastics in beverages: The case of beer, mineral water and tea. Analyst 2022, 147, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Shao, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y. Individual Exposure to Microplastics through the Inhalation Route: Comparison of Microplastics in Inhaled Indoor Aerosol and Exhaled Breath Air. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2023, 10, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Ji, X.; Ma, Y.; Lv, B.; Huang, W.; Zhu, X.; Fang, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Dahlgren, R.; et al. Airborne microplastics in indoor and outdoor environments of a coastal city in Eastern China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, E.; Woo, M.; Steele, C.; Sukumaran, S.; Anderson, S. Microplastics Differ Between Indoor and Outdoor Air Masses: Insights from Multiple Microscopy Methodologies. Appl. Spectrosc. 2020, 74, 1079–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Deng, J.; Gao, Y.; Yu, L.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H. Widespread distribution of PET and PC microplastics in dust in urban China and their estimated human exposure. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, C.; Song, J.; Yu, S.; Liao, G.; Zou, P.; Tang, K.H.D.; Wu, C. Airborne microplastics: Occurrence, sources, fate, risks and mitigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacprzak, S.; Tijing, L.D. Microplastics in indoor environment: Sources, mitigation and fate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanzaib, M.; Sharma, S.; Park, D. Microplastics comparison of indoor and outdoor air and ventilation rate effect in outskirts of the Seoul metropolitan city. Emerg. Contam. 2025, 11, 100408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Lu, W.; Tu, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, M.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Z.; Lin, M.; et al. Evidence of Microplastics in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid among Never-Smokers: A Prospective Case Series. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 2435–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Shi, Y.; Yan, M.; Zhu, H.; Chen, S.; Xu, K.; Wang, L.; Sun, H. Face Mask: As a Source or Protector of Human Exposure to Microplastics and Phthalate Plasticizers? Toxics 2023, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Agullo, A.; Karanasiou, A.; Lacorte, S. Nasal lavage technique reveals regular inhalation exposure of microplastics, not associated from face mask use. Environ. Int. 2023, 178, 108129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Hua, Z.; Guo, Z.; Dong, J.; Tan, Q.; Xie, Y.; Yin, X.; Yan, L.; et al. Assessment of microplastic exposure in nasal lavage fluid and the influence of face masks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Yan, H.; Nan, X.; Sun, H.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, X.; Liu, B. Potential health risks of microplastic fibres release from disposable surgical masks: Impact of repeated wearing and handling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 470, 134219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abafe, O.A.; Harrad, S.; Abdallah, M.A.-E. Novel Insights into the Dermal Bioaccessibility and Human Exposure to Brominated Flame Retardant Additives in Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 10554–10562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoabi, A.; Touitou, E.; Margulis, K. Recent Advances in Nanomaterials for Dermal and Transdermal Applications. Colloids Interfaces 2021, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Xu, E.G.; Du, F.; Li, R.; Liu, J.; Shi, H. Analysis of environmental nanoplastics: Progress and challenges. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 128208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, A.; Combadiere, B.; Hadam, S.; Stieler, K.M.; Lademann, J.; Schaefer, H.; Autran, B.; Sterry, W.; Blume-Peytavi, U. 40 nm, but not 750 or 1500 nm, Nanoparticles Enter Epidermal CD1a+ Cells after Transcutaneous Application on Human Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawalage, N.S.K.; Bellanthudawa, B.K.A. Synthetic polymers in personal care and cosmetics products (PCCPs) as a source of microplastic (MP) pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 182, 113927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos-Aceves, M.A.; Abo-Al-Ela, H.G.; Faggio, C. Physiological and metabolic approach of plastic additive effects: Immune cells responses. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.H.D. Microplastics and Antibiotics in Aquatic Environments: A Review of Their Interactions and Ecotoxicological Implications. Trop. Aquat. Soil Pollut. 2024, 4, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.H.D. Environmental Co-existence of Microplastics and Perfluorochemicals: A Review of Their Interactions. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2023, 13, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.H.D.; Zhou, J. Ecotoxicity of Biodegradable Microplastics and Bio-based Microplastics: A Review of in vitro and in vivo Studies. Environ. Manag. 2024, 75, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, A.E.-D.H.; Hana, M.N.; Hamed, M.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Lee, J.-S.; Soliman, H.A.M. Protective efficacy of dietary natural antioxidants on microplastic particles-induced histopathological lesions in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 24424–24440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Aqeel, M.; Khalid, N.; Irshad, M.K.; Farhat, F.; Nazir, A.; Ma, J.; Akhtar, M.S.; Eldesoky, G.E.; Aljuwayid, A.M.; et al. Glutathione treatment suppresses the adverse effects of microplastics in rice. Chemosphere 2023, 322, 138079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwutayd, K.M.; Aqeel, M.; Khalid, N.; Nawaz, S.; Akhter, N.; Irshad, M.K.; Algopishi, U.B.; Alghanem, S.M.S.; Noman, A. Microplastic Contaminated Root Zone Supplementation With Ascorbic Acid Enhance Photosynthesis, Antioxidant Defense, ROS Scavenging, and Secondary Metabolites in Rice. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2025, 25, 3306–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Seafood | Microplastic Amount | Size (µm) | Tissue/Body Part | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demersal and pelagic fish | 828 total particles across 5 tissues | <100–>1000 | Gills, gut, liver, muscle, skin | [55] |
| Tiger prawn (P. semisulcatus) | 7–21 microplastics in muscle | <100–>1000 | Muscle | [55] |
| White leg shrimp (L. vannamei) | 1211 total microplastics; 193 ± 76.6 microplastics/g in gut | 15–4686 | Gut, gills, exoskeleton | [56] |
| L. vannamei | 4.99 items/g | 100–250 | Exoskeleton | [57] |
| P. monodon | 1.87 items/g | 500–1000 | Exoskeleton | [57] |
| Red mullet and Black sea shad | 40% in gut, 7% in brain; 168 total microplastics for red mullet, 264 for black sea shad | 50–200 | Gut, gills, brain, muscle | [58] |
| Atlantic ditch shrimp | Experimentally ingested microbeads (200–2 × 1013 items/mL suspension) | 0.1–9.9 | Gut | [60] |
| Freshwater prawns | ~33 microplastics per individual; ~32 microplastics/g in gut | <250–5000 | Gut | [61] |
| Crab (P. pelagicus) | 1.04 items/g in muscle | <100–500 mainly | Muscle | [65] |
| Green tiger prawn | 0.62 items/g | <100–500 mainly | Muscle | [65] |
| Jinga shrimp | 0.45 items/g | <100–500 mainly | Muscle | [65] |
| Hilsa shad | 0.33 items/g | <100–500 mainly | Muscle | [65] |
| Bartail flathead | 0.11 items/g | <100–500 mainly | Muscle | [65] |
| Crabs (mangrove wetland) | 1.224–7.790 items/individual | 1–5000 | Whole body | [67] |
| Fish (mangrove wetland) | 1.779–8.610 items/individual | 1–5000 | Whole body | [67] |
| Prawns (Australia) | 0.8 ± 0.1 items/individual | 38–1000 mainly | Whole body | [68] |
| Crabs (Australia) | 1.6 ± 0.1 items/individual | 38–1000 | Whole body | [68] |
| Mussels (China) | 2–11 items/g; 4–57 items/individual | 5–5000 | Whole body | [72] |
| Mussels (Belgium) | 3–5 fibers/10 g | 200–1500 | Whole body | [71] |
| Dried anchovies | 0.47–3.18 items/g | 109–1006 | Whole body | [75] |
| Dried ribbonfish | 46 items/g | <500–5000 | Whole body | [76] |
| Fresh ribbonfish | 6.41 (gills), 6.20 (gut), 1.2 (muscle) items/g | <500–5000 | Gills, gut, muscle | [76] |
| Dried hairfin anchovy | 2.17 items/g | <500–5000 | Whole body | [76] |
| Fresh hairfin anchovy | 0.06 items/g | <500–5000 | Whole body | [76] |
| Canned sardines/sprats | 1–3 items per brand (only 4/20 brands positive) | >149 | Edible parts | [77] |
| Canned tuna (Iran) | 0.05–0.22 items/g | <50–5000 | Muscle | [78] |
| Canned tuna (Ecuador) | 4.4–6.9 items/g | 1–50 | Muscle | [79] |
| Canned liquid (oil/water) | 0.006–6 items/mL | 1–50 | Liquid surrounding seafood | [79] |
| Source | Microplastic Level (Particles/L) | Size (µm) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bottled water (Germany) | Disposable: 14; Refillable: 118; Cartons: ~12 | 5–20 mainly | [93] |
| Bottled water (global samples) | >100 µm: 10.4; Total (6.5–100 µm): 325 | 6.5–>100 | [94] |
| Bottled water (China) | 2–23 particles per bottle | >25 | [95] |
| Bottled water (Malaysia) | 8–22; Average: 11.7 | 100–300 mainly | [96] |
| Bottled vs. tap water (China) | Bottled: 72.3; Tap: 49.7 | 10–50 mainly | [97] |
| Bottled water (Hong Kong) | ≥50 µm: 8–50; <50 µm: 1570–17,817 | <50 and ≥50 | [98] |
| Tap water (Germany) | 0 (no microplastics found) | N/A | [99] |
| Paper cups (hot water, 100 mL) | ~25,000 particles per cup (~250,000/L) | ~1 | [100] |
| Disposable cups | Polystyrene: 838–5215; Polyethylene-paper: 675–5984; Polypropylene: 781–4951 | <20 Mainly | [101] |
| Paper cups (5 brands) | 1.29 × 106 | 1–60 | [102] |
| Tea filter bags | Not quantified (up to 94% released MPs) | 620–840 | [105] |
| Plastic tea bags | 105–106 | <0.22–150 | [106] |
| Compostable PLA tea bags | ~107 particles per bag | 0.1595–0.3951 | [107] |
| Loose tea leaves | ~200–500 particles/g | Not specified | [108] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, K.H.D. Counteracting the Harms of Microplastics on Humans: An Overview from the Perspective of Exposure. Microplastics 2025, 4, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030047
Tang KHD. Counteracting the Harms of Microplastics on Humans: An Overview from the Perspective of Exposure. Microplastics. 2025; 4(3):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030047
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Kuok Ho Daniel. 2025. "Counteracting the Harms of Microplastics on Humans: An Overview from the Perspective of Exposure" Microplastics 4, no. 3: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030047
APA StyleTang, K. H. D. (2025). Counteracting the Harms of Microplastics on Humans: An Overview from the Perspective of Exposure. Microplastics, 4(3), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030047






