Journal Description
Journal of Personalized Medicine
Journal of Personalized Medicine
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on personalized medicine, published monthly online by MDPI. The Inter-American Society for Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery (SICCMI), Korean Society of Brain Neuromodulation Therapy (KBNT) and American Board of Precision Medicine (ABOPM) are affiliated with JPM, and their members receive a discount on article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, PubMed, PMC, Embase, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Medicine (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 17.4 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Latest Articles
Trans-Oral Robotic Surgery (TORS) and Postoperative Hemorrhage: An Analysis of Risk Factors
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 201; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050201 - 16 May 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Postoperative hemorrhage is the most common complication after Trans-Oral Robotic Surgery (TORS) described in the literature. The aim of this study is to assess the presence of any risk factors that may impact postoperative bleeding. Methods: This was a retrospective study
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Postoperative hemorrhage is the most common complication after Trans-Oral Robotic Surgery (TORS) described in the literature. The aim of this study is to assess the presence of any risk factors that may impact postoperative bleeding. Methods: This was a retrospective study based on the analysis of patient data. Patients undergoing TORS procedures at the ENT Unit of Forlì Hospital from 2008 to 2022 for OSA (obstructive sleep apnea) or oncological disease and with a minimum follow-up of 30 days were included. The comorbidities analyzed were perioperative anticoagulant/antiplatelet therapy and clinicopathological features concerning the pathology. Total bleeding and severe bleeding (which required management in the operating room) were included. Results: A total of 414 patients (106 oncological TORS and 308 OSA TORS patients) were included. Post-TORS bleeding occurred in 47 cases (11.3%) and severe bleeding in 18 cases (4.3%). The pathology (oncology vs. OSA) treated with TORS did not represent a risk factor (p = 0.466). Antiplatelet intake represented an important risk factor (p = 0.002). Postoperative hemorrhage for oncological TORS occurred in 11.3% patients; of these, 6.6% had severe bleeding. Artery ligation during neck dissection prevented the risk of severe bleeding (p < 0.001). In TORS for OSA, postoperative hemorrhage was found in 11.4% cases, of which 3.6% were major bleeding. Neither the degree of OSA nor the association with other concurrent procedures were risk factors for postoperative bleeding in this study. Conclusions: Patients taking perioperative antiplatelet therapy have an almost 5-fold increased risk of developing postoperative bleeding. The pathology (oncology vs. OSA) does not influence the risk of bleeding. Prophylactic arterial ligation during neck dissection significantly decreases the risk of severe bleeding.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Clinical Medicine, Cell, and Organism Physiology)
Open AccessArticle
From Preliminary Urinalysis to Decision Support: Machine Learning for UTI Prediction in Real-World Laboratory Data
by
Athanasia Sergounioti, Dimitrios Rigas, Vassilios Zoitopoulos and Dimitrios Kalles
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 200; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050200 - 16 May 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are frequently diagnosed empirically, often leading to overtreatment and rising antimicrobial resistance. This study aimed to develop and evaluate machine learning (ML) models that predict urine culture outcomes using routine urinalysis and demographic data, supporting more targeted
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are frequently diagnosed empirically, often leading to overtreatment and rising antimicrobial resistance. This study aimed to develop and evaluate machine learning (ML) models that predict urine culture outcomes using routine urinalysis and demographic data, supporting more targeted empirical antibiotic use. Methods: A real-world dataset comprising 8065 urinalysis records from a hospital laboratory was used to train five ensemble ML models, including random forest, XGBoost (eXtreme gradient boosting), extra trees, voting classifier, and stacking classifier. Models were developed using 10-fold stratified cross-validation and assessed via clinically relevant metrics including specificity, sensitivity, likelihood ratios, and diagnostic odds ratios (DORs). To enhance screening utility, threshold optimization was applied to the best-performing model (XGBoost) using the Youden index. Results: XGBoost and random forest demonstrated the most balanced diagnostic profiles (AUROC: 0.819 and 0.791, respectively), with DORs exceeding 21. The voting and stacking classifiers achieved the highest specificity (>95%) and positive likelihood ratios (>10) but exhibited lower sensitivity. Feature importance analysis identified positive nitrites, white blood cell count, and specific gravity as key predictors. Threshold tuning of XGBoost improved sensitivity from 70.2% to 87.9% and reduced false negatives by 82%, with an associated NPV of 96.4%. The adjusted model reduced overtreatment by 56% compared to empirical prescribing. Conclusions: ML models based on structured urinalysis and demographic data can support clinical decision-making for UTIs. While high-specificity models may reduce unnecessary antibiotic use, sensitivity trade-offs must be considered. Threshold-optimized XGBoost offers a clinically adaptable tool for empirical treatment decisions by improving sensitivity and reducing overtreatment, thus supporting the more personalized and judicious use of antibiotics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in the Use of Machine Learning for Personalized Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures
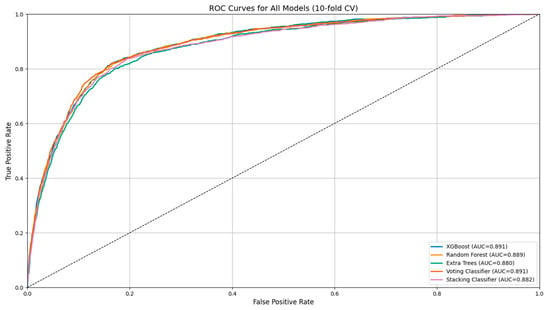
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Clinicopathological Features of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma with NRAS Mutation
by
Andrea Ambrosini-Spaltro, Claudia Rengucci, Laura Capelli, Elisa Chiadini, Chiara Bennati, Angelo Delmonte, Silvia Vecchiarelli, Francesco Limarzi, Sofia Nosseir, Graziana Gallo, Mirca Valli, Paola Ulivi and Daniele Calistri
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 199; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050199 - 16 May 2025
Abstract
(1) Background: NRAS mutations affect fewer than 1% of lung adenocarcinomas. The aim of this study was to describe the clinicopathological features of lung carcinomas with NRAS mutations. (2) Methods: A series of NRAS-mutated lung carcinomas was collected from a molecular
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: NRAS mutations affect fewer than 1% of lung adenocarcinomas. The aim of this study was to describe the clinicopathological features of lung carcinomas with NRAS mutations. (2) Methods: A series of NRAS-mutated lung carcinomas was collected from a molecular diagnostic unit (from four hospitals). The cases were analyzed with next-generation sequencing. A log-rank test for overall survival (OS) was calculated. (3) Results: NRAS mutations were detected in 14/1948 samples (0.72%) of non-small-cell lung carcinomas from 13 patients (8 males, 5 females). NRAS mutations involved codon 61 in the majority (9/13, 69.2%) of cases. The other NRAS mutations affected codon 12 (2/13, 15.4%), codon 13 (1/13, 7.7%), and codon 142 (1/13, 7.7%). In 7/13 cases, co-alterations in additional genes were also present. Pleomorphic/sarcomatoid features were identified in 3/13 (23.1%) cases, in 2/8 (25.0%) histological specimens, and in 2/5 (40.0%) surgical specimens, respectively. Follow-up data were available in 11/13 cases, with 6 patients deceased. By a log-rank test, patients with NRAS mutations in codon 61 had a better outcome (estimated mean of 32.6 ± 7.1 months) compared to those with other NRAS mutations (estimated mean of 8.7 ± 4.4 months), with a significant difference (p = 0.048 for OS). (4) Conclusions: Lung carcinomas with NRAS mutation may display pleomorphic or sarcomatoid features. Mutations in codon 61 showed a more favorable prognosis than those in other codons.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pathology and Molecular Diagnostics in the Personalized Treatment of Lung Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Shoulder Tendinopathy Induced by Statins: A Case Report and Systematic Review
by
Nicola Manocchio, Carmelo Pirri, Andrea Sorbino, Laura Giordani, Giulia Vita, Concetta Ljoka and Calogero Foti
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 198; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050198 - 15 May 2025
Abstract
Background: Statins are essential for managing cholesterol levels but can induce musculoskeletal side effects, including tendinopathy of the shoulder. Rotator Cuff Disease (RCD) is one of the most common shoulder tendinopathy. The aim of the present study is to report a clinical case
[...] Read more.
Background: Statins are essential for managing cholesterol levels but can induce musculoskeletal side effects, including tendinopathy of the shoulder. Rotator Cuff Disease (RCD) is one of the most common shoulder tendinopathy. The aim of the present study is to report a clinical case of statin-induce RCD after performing a systematic review on the subject. Materials and Methods: We performed a systematic review of the literature and report the case of a 49-year-old man with statin-induced RCD treated with a personalized individual rehabilitation project (IRP) (steroid and HA injections, mesotherapy, and therapeutic exercise) to investigate the relationship between statins and shoulder tendinopathy. The review followed PRISMA guidelines (2020 version), searching PubMed, Web of Science, and SCOPUS. Results: Out of a total of 217 articles, three cohort studies were suitable for our review. Conflicting evidence emerged regarding the association between statins and shoulder tendinopathy from the included papers. The case report describes a patient who experienced RCD after increasing atorvastatin dosage, with symptoms improving after dose reduction and a multimodal personalized IRP. Conclusions: Statins may contribute to tendon injury by altering the extracellular matrix and cell membrane integrity. While tendinopathy and statin relation is still under discussion, clinicians should monitor patients for tendinopathy and consider switching to alternative treatments in case symptoms arise. The case report demonstrated the successful management of statin-induced RCD with a multimodal personalized IRP. Further research is needed to clarify the relationship between statins and shoulder tendinopathy. Early diagnosis and appropriate personalized management are crucial for optimizing patient outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Personalized Therapy and Drug Delivery)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
One-Stop Mitral Valve Transcatheter Edge-to-Edge Repair and Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Mitral Regurgitation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
by
Konstantinos Pamporis, Dimitrios Tsiachris, Konstantinos Grigoriou, Paschalis Karakasis, Ioannis Doundoulakis, Panagiotis Theofilis, Panagiotis Kouvatsos, Athanasios Saplaouras, Athanasios Kordalis, Aikaterini-Eleftheria Karanikola, Panagiotis Antonios Goutis and Konstantinos Tsioufis
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 197; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050197 - 14 May 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Patients with atrial fibrillation and mitral regurgitation (MR) undergoing transcatheter edge-to-edge mitral valve repair (M-TEER) often have concomitant indications for left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO), mandating a more personalized treatment approach. This study aimed to examine the effectiveness and safety of
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Patients with atrial fibrillation and mitral regurgitation (MR) undergoing transcatheter edge-to-edge mitral valve repair (M-TEER) often have concomitant indications for left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO), mandating a more personalized treatment approach. This study aimed to examine the effectiveness and safety of combining M-TEER/LAAO in one procedure. Methods: MEDLINE (PubMed), Scopus, and Cochrane were searched through 21 March 2025 for studies examining M-TEER/LAAO with or without control (M-TEER only). Double-independent study selection, extraction, and quality assessments were performed. Frequentist random-effects models were used to calculate mean differences (MDs) and risk ratios (RRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Results: Seven studies (223 participants) were included. For M-TEER/LAAO, the mean procedural time was 101.6 min (95% CI = [85.06, 118.13]), the mean radiation time was 29.97 min (95% CI = [23.85, 36.09]), the mean length of stay was 5.21 days (95% CI = [3.31, 7.12]), procedural success was achieved in 89.5% of cases (95% CI = [73.4, 96.3], and post-procedure MR > 2+ occurred in 14.8% of cases (95% CI = [3.6, 44.5]). Compared to M-TEER only, patients with M-TEER/LAAO had similar procedural (RR = 0.91, 95% CI = [0.71, 1.17]) and technical success (RR = 1, 95% CI = [0.94, 1.06]) with a similar risk of acute kidney injury (RR = 1, 95% CI = [0.07, 15.12]), bleeding (RR = 0.40, 95% CI = [0.01, 18.06]), and all-cause death (RR = 0.59, 95% CI = [0.22, 1.54]). M-TEER/LAAO was non-significantly associated with in-hospital death (RR = 3, 95% CI = [0.13, 70.23]), stroke (RR = 3, 95% CI = [0.13, 70.23]), and vascular complications (RR = 1.55, 95% CI = [0.43, 5.59]) compared to M-TEER only. Most patients (34.2%, 95% CI = [2.8, 90.4]) received dual antiplatelet therapy at discharge, followed by anticoagulation only (20.2%, 95% CI = [7.5, 44.3]). Conclusions: M-TEER/LAAO can be combined into a single procedure with good peri-procedural outcomes. Safety was also satisfactory; however, some concerns may arise regarding in-hospital death, stroke, and vascular complications. Further research is needed to explore the effectiveness and safety of this combined strategy and elucidate the risk–benefit profile of this personalized treatment approach.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Cardiology and Vascular Health: Pathophysiology, Therapeutics and Epidemiology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Yeast-Produced Human Recombinant Lysosomal β-Hexosaminidase Efficiently Rescues GM2 Ganglioside Accumulation in Tay–Sachs Disease
by
Orhan Kerim Inci, Andrés Felipe Leal, Nurselin Ates, Diego A. Súarez, Angela Johana Espejo-Mojica, Carlos Javier Alméciga-Diaz and Volkan Seyrantepe
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 196; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050196 - 10 May 2025
Abstract
Background: Tay–Sachs disease (TSD) is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder characterized by the accumulation of GM2 ganglioside due to mutations in the HEXA gene, which encodes the α-subunit of β-Hexosaminidase A. This accumulation leads to significant neuropathological effects and premature death in
[...] Read more.
Background: Tay–Sachs disease (TSD) is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder characterized by the accumulation of GM2 ganglioside due to mutations in the HEXA gene, which encodes the α-subunit of β-Hexosaminidase A. This accumulation leads to significant neuropathological effects and premature death in affected individuals. No effective treatments exist, but enzyme replacement therapies are under investigation. In our previous work, we demonstrated the internalization and efficacy of human recombinant lysosomal β-hexosaminidase A (rhHex-A), produced in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris, in reducing lipids and lysosomal mass levels in fibroblasts and neural stem cells derived from patient-induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). In this study, we further evaluated the potential of rhHex-A to prevent GM2 accumulation using fibroblast and neuroglia cells from a TSD patient alongside a relevant mouse model. Methods: Fibroblasts and neuroglial cell lines derived from a murine model and TSD patients were treated with 100 nM rhHexA for 72 h. After treatment, cells were stained by anti-GM2 (targeting GM2 ganglioside; KM966) and anti-LAMP1 (lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1) colocalization staining and incubated with 50 nM LysoTracker Red DND-99 to label lysosomes. In addition, GM2AP and HEXB expression were analyzed to assess whether rhHex-A treatment affected the levels of enzymes involved in GM2 ganglioside degradation. Results: Immunofluorescence staining for LysoTracker and colocalization studies of GM2 and Lamp1 indicated reduced lysosomal mass and GM2 levels. Notably, rhHex-A treatment also affected the expression of the HEXB gene, which is involved in GM2 ganglioside metabolism, highlighting a potential regulatory interaction within the metabolic pathway. Conclusions: Here, we report that rhHex-A produced in yeast can efficiently degrade GM2 ganglioside and rescue lysosomal accumulation in TSD cells.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Inborn Errors of Metabolism: From Pathomechanisms to Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Methodologies for the Emulation of Biomarker-Guided Trials Using Observational Data: A Systematic Review
by
Faye D. Baldwin, Rukun K. S. Khalaf, Ruwanthi Kolamunnage-Dona and Andrea L. Jorgensen
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 195; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050195 - 10 May 2025
Abstract
Background: Target trial emulation involves the application of design principles from randomised controlled trials (RCTs) to observational data, and is particularly useful in situations where an RCT would be unfeasible. Biomarker-guided trials, which incorporate biomarkers within their design to either guide treatment
[...] Read more.
Background: Target trial emulation involves the application of design principles from randomised controlled trials (RCTs) to observational data, and is particularly useful in situations where an RCT would be unfeasible. Biomarker-guided trials, which incorporate biomarkers within their design to either guide treatment and/or determine eligibility, are often unfeasible in practice due to sample size requirements or ethical concerns. Here, we undertake a systematic review of methodologies used in target trial emulations, comparing treatment effectiveness, critically appraising them, and considering their applicability to the emulation of biomarker-guided trials. Methods: A comprehensive search strategy was developed to identify studies reporting on methods for target trial emulation comparing the effectiveness of treatments using observational data, and applied to the following bibliographic databases: PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Ovid MEDLINE. A narrative description of methods identified in the review was undertaken alongside a critique of their relative strengths and limitations. Results: We identified a total of 59 papers: 47 emulating a target trial (‘application’ studies), and 12 detailing methods to emulate a target trial (‘methods’ studies). A total of 25 papers were identified as emulating a biomarker-guided trial (42%). While all papers reported methods to adjust for baseline confounding, 40% of application papers did not specify methods to adjust for time-varying confounding. Conclusions: This systematic review has identified a range of methods used to control for baseline, time-varying, and residual/unmeasured confounding within target trial emulation and provides a guide for researchers interested in emulation of biomarker-guided trials.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Disease Biomarker)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Accuracy of ChatGPT-4o in Interpreting Chest and Abdominal X-Ray Images
by
Pietro G. Lacaita, Malik Galijasevic, Michael Swoboda, Leonhard Gruber, Yannick Scharll, Fabian Barbieri, Gerlig Widmann and Gudrun M. Feuchtner
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 194; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050194 - 10 May 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Large language models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT, have emerged as potential clinical support tools to enhance precision in personalized patient care, but their reliability in radiological image interpretation remains uncertain. The primary aim of our study was to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Large language models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT, have emerged as potential clinical support tools to enhance precision in personalized patient care, but their reliability in radiological image interpretation remains uncertain. The primary aim of our study was to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of ChatGPT-4o in interpreting chest X-rays (CXRs) and abdominal X-rays (AXRs) by comparing its performance to expert radiology findings, whilst secondary aims were diagnostic confidence and patient safety. Methods: A total of 500 X-rays, including 257 CXR (51.4%) and 243 AXR (48.5%), were analyzed. Diagnoses made by ChatGPT-4o were compared to expert interpretations. Confidence scores (1–4) were assigned and responses were evaluated for patient safety. Results: ChatGPT-4o correctly identified 345 of 500 (69%) pathologies (95% CI: 64.81–72.9). For AXRs 175 of 243 (72.02%) pathologies were correctly diagnosed (95% CI: 66.06–77.28), while for CXRs 170 of 257 (66.15%) were accurate (95% CI: 60.16–71.66). The highest detection rates among CXRs were observed for pulmonary edema, tumor, pneumonia, pleural effusion, cardiomegaly, and emphysema, and lower rates were observed for pneumothorax, rib fractures, and enlarged mediastinum. AXR performance was highest for intestinal obstruction and foreign bodies, and weaker for pneumoperitoneum, renal calculi, and diverticulitis. Confidence scores were higher for AXRs (mean 3.45 ± 1.1) than CXRs (mean 2.48 ± 1.45). All responses (100%) were considered to be safe for the patient. Interobserver agreement was high (kappa = 0.920), and reliability (second prompt) was moderate (kappa = 0.750). Conclusions: ChatGPT-4o demonstrated moderate accuracy for the interpretation of X-rays, being higher for AXRs compared to CXRs. Improvements are required for its use as efficient clinical support tool.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Methodology, Drug and Device Discovery)
►▼
Show Figures
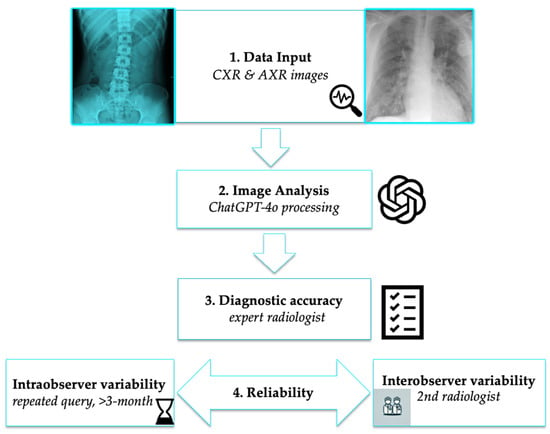
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Study on the Epidemiological Characteristics, Treatment Patterns, and Factors Influencing the Timeliness of Treatment in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) in Stages III and IV: Experience of a Mexican Hospital
by
Victor Manuel Oyervides Juarez, Daneli Ruiz Sanchez, Alejandro De Leon Cruz, Luis Angel Ceceñas Falcon, Marco Mendez Saenz, Carlos Alfredo Gomez de la Cruz, Mario Alberto Campos Coy, Juan Manuel Sánchez Castillo, Oscar Vidal Gutierrez, Joaquin Manzo Merino, Silvia Peralonso Bombin, Yuridia Evangelina Rodríguez Rosales, Gabriela Lugo Martinez, Jimena Maria Iglesias, Sebastian Medina Gonzalez and Claudia Catalina Beltran Rodriguez
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 193; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050193 - 9 May 2025
Abstract
Objective: In Mexico, head and neck cancers pose a significant health burden. GLOBOCAN reported approximately 3183 new cases and 1636 deaths in 2020. Despite being the sixth leading cause of cancer incidence and mortality worldwide, data on epidemiology and treatment patterns in Mexico
[...] Read more.
Objective: In Mexico, head and neck cancers pose a significant health burden. GLOBOCAN reported approximately 3183 new cases and 1636 deaths in 2020. Despite being the sixth leading cause of cancer incidence and mortality worldwide, data on epidemiology and treatment patterns in Mexico remain limited. This study aimed to characterize the profile, clinical features, and management of patients with Stage III–IVB head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) in a real-world setting. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed a database of 187 patients with Stage III, IVA, or IVB HNSCC treated at the University Hospital Dr. José Eleuterio González. Demographics, disease characteristics, and treatment patterns were summarized as frequencies and percentages. Exploratory endpoints included clinical outcomes and recurrence types. Results: The cohort was 82.9% male (n = 155). The most frequent tumor sites were the oral cavity (36.9%) and larynx (36.9%), with 55% (n = 103) diagnosed at stage IVA. Of 75 cases tested for p16, 35.3% (n = 36) were positive. The median time from symptom onset to diagnosis was 166.5 days (95% CI: 123.4–197.8) and from diagnosis to treatment 42 days (95% CI: 31.6–50.4). Initial treatments included surgery (36.4%), chemoradiotherapy (24.6%), induction chemotherapy (19.8%), supportive care (11.2%), and radiotherapy (8%). Locoregional control was achieved in 42.8% of patients, with an overall recurrence rate of 2.8%. Conclusions: This study provides real-world insights into the epidemiology and management of locally advanced HNSCC in Mexico, outlining the patient journey from initial symptoms to treatment and underscoring the need for more individualized therapeutic strategies based on molecular profiling and clinical characteristics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Epidemiology)
►▼
Show Figures
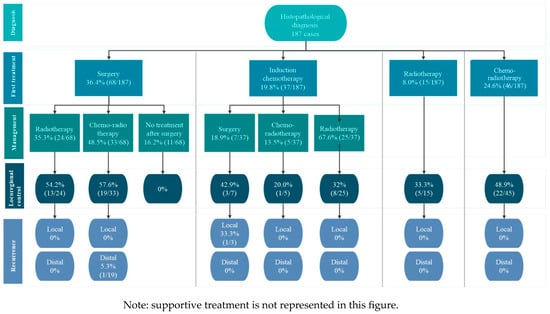
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Three in a Bed: Can Partner Support Improve CPAP Adherence? A Systematic Review and Intervention Recommendations
by
Giada Rapelli, Carola Caloni, Francesca Cattaneo, Marco Redaelli, Roberto Cattivelli, Giulia Landi, Eliana Tossani, Silvana Grandi, Gianluca Castelnuovo and Giada Pietrabissa
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 192; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050192 - 8 May 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is the standard approach for treating obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS), but patient adherence is often low due to various influencing factors. Recently, researchers have increasingly begun to explore the influence of partner support on adherence
[...] Read more.
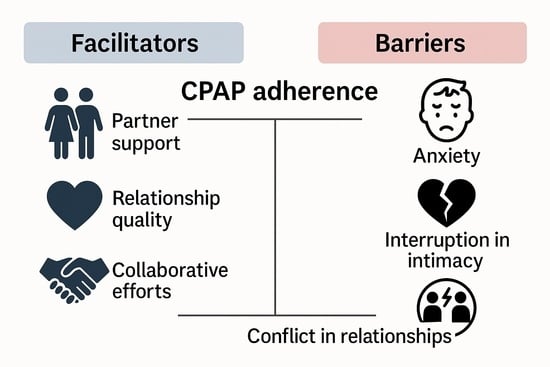
Background/Objectives: Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is the standard approach for treating obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS), but patient adherence is often low due to various influencing factors. Recently, researchers have increasingly begun to explore the influence of partner support on adherence to CPAP therapy. This systematic review seeks to consolidate current evidence regarding the impact of partner support on CPAP adherence in individuals with OSAS. Methods: A comprehensive literature search was carried out across PubMed, Scopus, Medline, PsycINFO, and Web of Science databases under PRISMA guidelines. Stringent inclusion criteria were used, and at least two independent reviewers screened all studies. The mixed methods appraisal tool (MMAT) was used to assess selected articles for quality. Data relevant to the review’s objectives were extracted and presented through narrative synthesis. The review protocol was preregistered (Prospero CRD420251016574). Results: Nine studies met the inclusion criteria. Findings highlighted the significant influence of adherence to CPAP. Partner support, relationship quality, and collaborative efforts emerged as facilitators of adherence, with partnered individuals exhibiting higher adherence to CPAP use. However, barriers such as anxiety, interruption in intimacy, and conflict in relationships were also identified. Conclusions: To the best of our knowledge, this is the first systematic review to synthesize evidence on the partner’s role in CPAP adherence and inform clinicians on the importance of providing personalized care based on biopsychosocial characteristics of patients; for example, assessing the partner support in the management of the illness. Furthermore, the findings emphasize the need for further research—particularly randomized controlled trials and dyadic designs—to deepen understanding of how partner dynamics influence effects of CPAP treatment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Personalized Therapy and Drug Delivery)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
From Consultation to Collaboration: A Patient-Centered Approach to Shingles Pain and Postherpetic Neuralgia Management
by
Yin-Tse Wu, Hsuan-Chih Lao, Sheng-Chin Kao, Ying-Chun Lin, Ying-Wei Yang, Ying-Hsin Li and Yi-Jun Chen
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 191; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050191 - 8 May 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Herpes zoster (shingles), caused by reactivation of the varicella zoster virus, often leads to acute pain that may progress to postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). Current evidence is insufficient to determine the optimal interventional treatment for these conditions. This study aimed to evaluate
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Herpes zoster (shingles), caused by reactivation of the varicella zoster virus, often leads to acute pain that may progress to postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). Current evidence is insufficient to determine the optimal interventional treatment for these conditions. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of shared decision-making (SDM) forms developed by MacKay Memorial Hospital (MMH) in reducing patient anxiety and improving personalized care. Method: Between 1 August 2022 and 30 August 2024, we retrospectively reviewed SDM records of patients with shingles pain and PHN who were referred to the pain clinic for interventional treatment due to unresolved pain. The SDM forms were developed, reviewed, and authorized by the MMH Committee of Medical Quality and Safety. We analyzed the chosen interventions, anxiety levels, pain intensity, and patient preferences regarding treatment selection. Results: A total of 51 individuals (36 with shingles pain, 15 with PHN) were included in this cohort study. Most patients with acute or chronic zoster pain opted for subcutaneous steroid injections. Anxiety scores significantly decreased following SDM intervention, from 5.0 (IQR: 3.5–5.0) to 3.0 (IQR: 2.0–3.0) in shingles patients and from 5.0 (IQR: 4.0–5.0) to 2.0 (IQR: 2.0–3.0) in PHN patients. Pain intensity, measured using the numerical rating scale (NRS), also improved markedly after interventional pain management, with scores reducing from 8.0 (IQR: 6.0–9.0) to 3.0 (IQR: 1.0–6.5) in shingles patients and from 5.0 (IQR: 4.0–8.0) to 2.0 (IQR: 1.0–3.0) in PHN patients. Shingles patients expressed greater concern about the risks of interventional therapy complications, whereas PHN patients prioritized cost, complication rates, treatment frequency, and continuity of care. Additionally, SDM forms received high scores for promoting patient participation and knowledge, indicating that they improved their understanding of their condition and treatment options. Conclusions: SDM significantly improved patient comprehension, reduced anxiety, facilitated informed treatment decisions, and strengthened doctor–patient communication for those with shingles pain and PHN.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue How to Undertake Personalized Assessments and Cures for Pain)
►▼
Show Figures
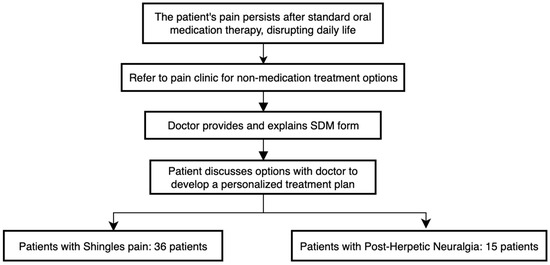
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Tissue Preservation and Access: Modern Innovation in Biobanking Moving Forwards a Personalized Treatment
by
Chiara Tessari, Saima Jalil Imran, Nukhba Akbar and Gino Gerosa
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 190; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050190 - 7 May 2025
Abstract
Tissue substitution and graft transplantation are currently the best treatment options for patients suffering from severe heart diseases. However, the limited availability of donors and the restricted durability of tissues applied in cardiovascular treatments result in a constraint on applicability and a suboptimal
[...] Read more.
Tissue substitution and graft transplantation are currently the best treatment options for patients suffering from severe heart diseases. However, the limited availability of donors and the restricted durability of tissues applied in cardiovascular treatments result in a constraint on applicability and a suboptimal therapeutic approach that is still not fully resolved. There are multiple ways to preserve heart tissue grafts, and the choice of method is solely dependent upon the nature and complexity of the tissue and the length of storage. The conventional cold storage method provides the base to nearly all of the preservation protocols for short- and long-term storage. Short-term storage methods frequently rely on designing preserving solutions to protect the graft against warm and cold ischemia at the temperature above freezing point. As ice-nucleation is the major notorious phenomenon during graft preservation, the modern era of research is focusing on developing ice-free preservation techniques, termed vitrification. However, despite the promising outcomes of vitrification, there are several recognized hurdles required to be overcome to build a biobank of heart grafts for an extended period of time. Besides tissue deterioration due to extreme cold temperature, there is another extreme phenomenon of tissue rejection mainly caused by the presence of cellular antigens. The modern approach of decellularization has the potential to minimize the chances of tissue rejection by removing the cells and providing a structural support and sustained biochemical signal via keeping the extracellular matrix of the graft intact. In conclusion, both nano-warming and decellularization are the leading approaches that have great potential to store the graft tissue in its optimal form via keeping its viability safe for a longer time and extending its applicability. This review article outlines a variety of approaches for the preservation and bioengineering of tissue to fulfill the need for the availability of on-shelf long-lasting grafts both in clinical and laboratory setups.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Updates on Heart Valve Diseases: Personalized Treatment and Management)
►▼
Show Figures
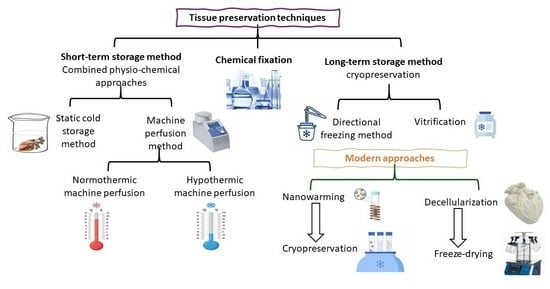
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Real-Life Treatment Intervals and Morphological Outcomes Following the Switch to Faricimab Therapy in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration
by
Katrin Löw, Vasilena Sitnilska, Yuhe Tang, Jeany Q. Lammert, Tim U. Krohne and Lebriz Altay
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 189; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050189 - 6 May 2025
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the efficacy of faricimab in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) that did not respond to other VEGF inhibitors. Methods: This retrospective study included the eyes of patients diagnosed with nAMD who had been switched to faricimab
[...] Read more.
Objectives: To evaluate the efficacy of faricimab in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) that did not respond to other VEGF inhibitors. Methods: This retrospective study included the eyes of patients diagnosed with nAMD who had been switched to faricimab treatment due to the persistence of intraretinal fluid (IRF) and/or subretinal fluid (SRF), despite monthly anti-VEGF treatment with aflibercept, bevacizumab, or ranibizumab using the treat and extend regimen, and who had received at least three faricimab injections following the switch. Best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) measurement and optical coherence tomography (OCT) analysis were performed at each visit, and the OCT results were graded by two independent readers. Results: We included 41 eyes of 39 patients (21 male, 18 female) with a mean age of 80.5 ± 8.1 years. The median duration of anti-VEGF treatment prior to the switch to faricimab was 5.0 years, with a median of 53 injections. Complete resolution of IRF and SRF was observed after the first dose of faricimab in 12 eyes (29.3%) and after the third dose in 15 eyes (36.6%). Twenty-eight eyes reached a follow-up time after a switch of at least 12 months, with a median of 10 faricimab injections. Of these 28 eyes, 10 eyes (35.7%) exhibited complete IRF/SRF resolution; treatment intervals were extended beyond 4 weeks in 21 eyes (80.7%), and 8 eyes (28.6%) presented complete IRF/SRF resolution under extended treatment intervals at month 12. Central retinal thickness after 12 months was reduced from a median of 368.0 µm to 297.5 µm (p < 0.001), and the BCVA remained stable (p = 0.057). No adverse events were reported throughout the entire treatment period. Conclusions: In nAMD patients with poor anti-VEGF treatment response, complete and fast fluid resolution and the extension of treatment intervals can be reached by switching to faricimab, even after years of prior unsuccessful therapy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Personalized Medicine in Retinal Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
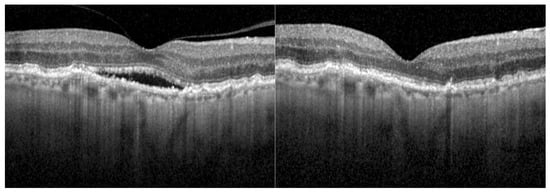
Figure 1
Open AccessCorrection
Correction: Zieliński, G.; Gawda, P. Analysis of the Use of Sample Size and Effect Size Calculations in a Temporomandibular Disorders Randomised Controlled Trial—Short Narrative Review. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 655
by
Grzegorz Zieliński and Piotr Gawda
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 188; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050188 - 6 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In the original publication [...]
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Antibiotic-Mixed Cement Filling for Chronic Osteomyelitis
by
Seung-Hwan Park, Young Rak Choi, Inyong Jeong and Ho Seong Lee
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 187; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050187 - 6 May 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Traditional treatment for chronic osteomyelitis is temporary implantation of antibiotic-impregnated cement beads, followed by bone grafting after the infection is controlled. In this way, a staged operation is needed, and undergoing repetitive general anesthesia is a burden. Moreover, damage to the soft
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Traditional treatment for chronic osteomyelitis is temporary implantation of antibiotic-impregnated cement beads, followed by bone grafting after the infection is controlled. In this way, a staged operation is needed, and undergoing repetitive general anesthesia is a burden. Moreover, damage to the soft tissue at the surgical site due to several incisions is a concern. This study was conducted to investigate the outcomes of one-stage antibiotic-mixed cement blocks, instead of beads, used as a primary salvage procedure to treat chronic osteomyelitis of the foot, ankle, and lower leg. Methods: Twenty patients with chronic osteomyelitis of the leg and foot were included. They underwent complete debridement of the infected bone, and antibiotic-mixed cement fillings were placed into the defected bone space. Full-weight-bearing activities were allowed immediately after surgery. Results: For 16 of the 18 patients, infection was controlled after one-time surgery. Repeat antibiotic cement-filling surgery was necessary for two patients. Two-staged surgery with continuous irrigation and cement filling was necessary for one large tibial lesion. Conversion into arthrodesis of the metatarsophalangeal joint was necessary for metatarsal head infection. Conclusions: One-stage surgery with complete debridement and antibiotic-mixed cement filling is a simple and effective procedure for treating intractable chronic osteomyelitis, which makes full-weight-bearing walking possible immediately after surgery.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Clinical Medicine, Cell, and Organism Physiology)
►▼
Show Figures
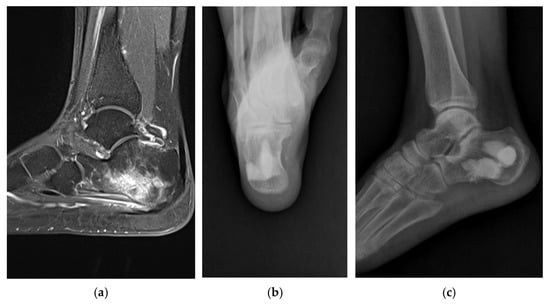
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Accuracy of Patient-Specific Osteosynthesis in Bimaxillary Surgery: Comparative Feasibility Analysis of Four- and Two-Miniplate Fixation
by
Hylke van der Wel, Haye Glas, Johan Jansma and Rutger Schepers
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 186; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050186 - 4 May 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Patient-specific osteosynthesis (PSO) plates, in combination with virtual surgical planning (VSP), have significantly improved the accuracy of orthognathic surgery. This study aimed to compare the surgical accuracy of two-plate versus four-plate fixation methods in Le Fort I osteotomies using PSO. Methods
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Patient-specific osteosynthesis (PSO) plates, in combination with virtual surgical planning (VSP), have significantly improved the accuracy of orthognathic surgery. This study aimed to compare the surgical accuracy of two-plate versus four-plate fixation methods in Le Fort I osteotomies using PSO. Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted on 21 patients who underwent maxilla-first bimaxillary surgery at a single centre in 2024. Eight patients received two-plate fixation, while thirteen received four-plate fixation. All surgeries were planned using VSP. Postoperative cone beam computed tomography scans were used to assess the accuracy of maxillary positioning by comparing the planned versus achieved outcomes in terms of translation and rotation. Results: Both fixation methods yielded comparable results in maxillary positioning, with no significant differences observed between the two groups regarding translational or rotational deviations. The two-plate PSO approach demonstrated practical benefits, including reduced material usage and the potential for smaller surgical incisions, without compromising surgical accuracy. Conclusions: Two-plate PSO fixation is a viable alternative to the traditional four-plate method for Le Fort I osteotomies, offering similar accuracy with potential procedural advantages. While these findings support broader clinical adoption, further research is warranted to confirm the results in larger cohorts and to investigate biomechanical considerations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Personalized Therapy and Drug Delivery)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prevalence of Actionable Exposures to Pharmacogenetic Medications Among Solid Organ Transplant Recipients in a Population-Scale Biobank
by
Alaa Radwan, Kimberly M. Deininger, Amrut V. Ambardekar, Heather D. Anderson, Nicholas Rafaels, Laura M. Saba, The Colorado Center for Personalized Medicine and Christina L. Aquilante
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 185; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050185 - 2 May 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Solid organ transplant (SOT) recipients are exposed to multiple medications, many of which have pharmacogenetic (PGx) prescribing recommendations. This study leveraged data from a population-scale biobank and an enterprise data warehouse to determine the prevalence of actionable exposures to PGx medications
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Solid organ transplant (SOT) recipients are exposed to multiple medications, many of which have pharmacogenetic (PGx) prescribing recommendations. This study leveraged data from a population-scale biobank and an enterprise data warehouse to determine the prevalence of actionable exposures to PGx medications among kidney, heart, and lung transplant recipients during the first six months post-transplant. Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of adult SOT patients with genetic data available from the Colorado Center for Personalized Medicine (CCPM) biobank and clinical data from Health Data Compass (HDC). We evaluated 29 variants in 13 pharmacogenes and 42 Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) level A or B medications (i.e., sufficient evidence to recommend at least one prescribing action based on genetics). The primary outcome was actionable exposure to a PGx medication (i.e., actionable phenotype and a prescription for an affected PGx medication). Results: The study included 358 patients. All patients were prescribed at least one PGx medication, and 49.4% had at least one actionable exposure to a PGx medication during the first six months post-transplant. The frequency of actionable exposure was highest for tacrolimus (15.4%), followed by proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) (15.1%) and statins (12.8%). Statin actionable exposures significantly differed by transplant type, likely due to variations in prescribing patterns and actionable phenotypes for individual statins. Conclusions: Our findings highlight the potential clinical utility of PGx testing among SOT patients. Further studies are needed to address the impact on clinical outcomes and the optimal timing of PGx testing in the SOT population.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacogenetics)
►▼
Show Figures
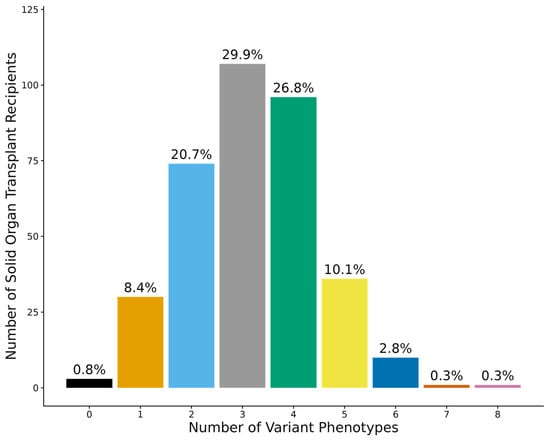
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Temporary Mechanical Support in Cardiogenic Shock Secondary to Heart Failure: An Evolving Paradigm
by
Nandini Nair, Dongping Du and Balakrishnan Mahesh
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 184; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050184 - 2 May 2025
Abstract
Cardiogenic shock can be defined as a state of circulatory collapse resulting in hypoperfusion and end-organ dysfunction. It carries a large burden of mortality, but management strategies are driven by expert consensus rather than adequately powered randomized clinical trials. The goal of this
[...] Read more.
Cardiogenic shock can be defined as a state of circulatory collapse resulting in hypoperfusion and end-organ dysfunction. It carries a large burden of mortality, but management strategies are driven by expert consensus rather than adequately powered randomized clinical trials. The goal of this review is to highlight the differences in presentation and outcomes in cardiogenic shock depending on the etiology, such as acute myocardial infarction (AMI) versus acute-on-chronic heart failure (HF), gender-based differences in treatment strategies and outcomes and the need for more precise risk stratification and modeling to improve the efficiency of treatment delivery in a personalized fashion. PubMed and Google Scholar were used to search the literature for this qualitative review. The differences in gender and etiology of cardiogenic shock are not consistent in all studies in the exiting literature. There is a need for identification of novel risk factors that define the different phenotypes that present with similar hemodynamic and biomarker profiles. There is an urgent need to devise a methodology to understand and differentiate the different cardiogenic shock phenotypes and their trajectories. Better risk prediction models should be generated to help deliver well-tailored treatment, paving the way to the efficient delivery of personalized medicine.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Perspectives of Critical Care Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Frontal Sinus Inverted Papilloma: A Systematic Review
by
Maxime Fieux, Valentin Favier, Andre Sousa Machado, Mikail Nourredine, Caroline Giroudon, Florent Carsuzaa, Paresh P. Naik and the yo-IFOS Group
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 183; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050183 - 2 May 2025
Abstract
Background: Frontal sinus inverted papilloma (IP) is a particularly rare form of IP and its management is challenging, with a high rate of recurrence. Objectives: Our aim was to evaluate the recurrence rate of frontal sinus IP after surgery and compare
[...] Read more.
Background: Frontal sinus inverted papilloma (IP) is a particularly rare form of IP and its management is challenging, with a high rate of recurrence. Objectives: Our aim was to evaluate the recurrence rate of frontal sinus IP after surgery and compare this rate according to the surgical modality (purely endoscopic sinus surgery vs. a combined/open approach). Design: A systematic review without meta-analysis conducted by a working group of the Young Otolaryngologists of the International Federation of Otorhinolaryngological Societies (yo-IFOS). Data Sources and Methods: A systematic analysis of the literature was performed and reported following the criteria laid down in the SWiM guidelines. The review was registered on Prospero, a dedicated software was used for screening (Covidence), and R (v.4.2.2) was used for statistical analysis. Eligible articles were studies reporting at least five cases of frontal sinus IP surgically treated. Results: A total of 2925 studies were identified based on the MeSH equation, and 39 studies were included (n = 642 patients). Among the studies included, the recurrence rate was 18.4% (118/642) with a mean time to recurrence of 25.6 (±11.7) months. The difference between surgical modalities was not statistically significant in terms of recurrence rate (14.7% vs. 16.5%; p = 0.675). Conclusions: The recurrence rate of frontal sinus IP is not different between surgical modalities. However, it does not reduce the need for a tailored therapeutic strategy, as other factors also need to be considered (time to recurrence, complications, quality of life) when choosing the most appropriate approach.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Personalized Medicine for Otolaryngology (ENT))
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Association of MMP-8 -799C/T Polymorphism with Peri-Implantitis: A Cross-Sectional Study
by
Ioannis Fragkioudakis, Christine Kottaridi, Aikaterini-Elisavet Doufexi, Konstantinos Papadimitriou, Leonidas Batas and Dimitra Sakellari
J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15(5), 182; https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050182 - 1 May 2025
Abstract
Purpose: This study explored the relationship between matrix metalloproteinase−8 (MMP−8) gene polymorphisms (−799C/T, −381A/G, and +17C/G) and peri-implantitis, examining clinical parameters including the probing depth (PD), clinical attachment level (CAL), and bleeding on probing (BOP). Methods: This cross-sectional study involved 120
[...] Read more.
Purpose: This study explored the relationship between matrix metalloproteinase−8 (MMP−8) gene polymorphisms (−799C/T, −381A/G, and +17C/G) and peri-implantitis, examining clinical parameters including the probing depth (PD), clinical attachment level (CAL), and bleeding on probing (BOP). Methods: This cross-sectional study involved 120 participants categorized into peri-implantitis and healthy implant groups according to the 2018 classification criteria for periodontal and peri-implant diseases. Saliva samples were analyzed for MMP−8 polymorphisms using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Sanger sequencing. Statistical analyses were conducted to evaluate genotype- and allele-specific risks and their associations with clinical parameters. Results: Among the 95 samples analyzed, the −799C/T polymorphism was significantly associated with peri-implantitis, with T allele carriers having a higher diagnosis rate (odds ratio: 3.04, p = 0.010). Although T allele carriers exhibited higher mean values for the probing depth (PD), clinical attachment level (CAL), and bleeding on probing (BOP), these differences were not statistically significant across genotypes. No associations were found between the −381A/G and +17C/G polymorphisms and peri-implantitis clinical parameters. Conclusions: The −799C/T polymorphism, specifically the T allele, is strongly linked to peri-implantitis, indicating its potential as a genetic marker for disease susceptibility. Further research is required to investigate the role of MMP-8 polymorphisms in peri-implant diseases and to advance the development of personalized diagnostic tools.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Mechanisms of Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- JPM Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Diagnostics, JCTO, JCM, JPM, Tomography
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and OCT Angiography – Recent Advances
Topic Editors: Sumit Randhir Singh, Jay ChhablaniDeadline: 26 May 2025
Topic in
JCM, JPM, JVD, Diagnostics, Cancers
Diagnosis, Management, and Prognostic Assessment of Chronic Disease
Topic Editors: Xiude Fan, Enfa Zhao, Yang Xia, Shanshan Shao, Tatsunori Miyata, Dongxing XieDeadline: 5 July 2025
Topic in
JCM, Diagnostics, JPM, Brain Sciences, JVD
Diagnosis and Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke
Topic Editors: Hyo Suk Nam, Byung Moon Kim, Tae-jin Song, Minho HanDeadline: 20 September 2025
Topic in
Antibiotics, JPM, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Medicines
Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Modelling in Drug Discovery and Development
Topic Editors: Inaki F. Troconiz, Victor Mangas Sanjuán, Maria Garcia-Cremades MiraDeadline: 31 October 2025
Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
JPM
Breast Cancer: Current Trends and Future Challenges in Evaluation and Treatment
Guest Editors: Stefano Spinaci, Giulia FerrarazzoDeadline: 20 May 2025
Special Issue in
JPM
Personalized Therapeutics and Drug Development of Liver Disease
Guest Editors: Cristina Muzica, Irina GirleanuDeadline: 20 May 2025
Special Issue in
JPM
Sex and Gender-Related Issues in the Era of Personalized Medicine
Guest Editors: Davide Bizzoca, Anna Maria Moretti, Biagio MorettiDeadline: 22 May 2025
Special Issue in
JPM
Innovations in Personalized Diagnosis and Treatment for Cystic Fibrosis
Guest Editor: Martina GentzschDeadline: 22 May 2025











