- Review
The Impact of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals on Embryonic Recurrent Implantation Failure: A Narrative Review
- Anastasios Potiris,
- Panagiotis Antsaklis and
- Charalampos Theofanakis
- + 9 authors
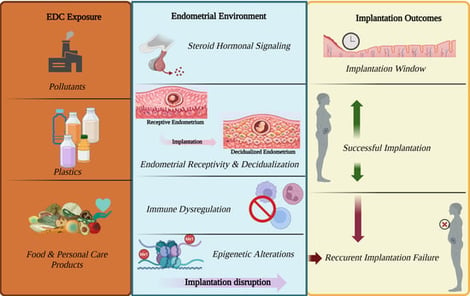
A significant and persistent issue in assisted reproduction is recurrent implantation failure (RIF), which is often observed even after the transfer of embryos of high morphological and/or genetic quality. Accumulating data suggest that exposure to chemicals with endocrine-disrupting effects (EDCs) may be associated with adverse implantation outcomes. Many environmentally widespread substances have the potential to interfere with the regulation of the endocrine system, affecting critical mechanisms involved in implantation, such as endometrial receptivity, steroid hormone receptor signaling, immune tolerance at the maternal–fetal interface, and the epigenetic regulation of genes that are essential for successful implantation. Experimental studies have shown that exposure to EDCs can alter gene expression in the endometrium, inflammatory pathways, and the dynamics of early embryonic development, while clinical and epidemiological data have associated increased levels of EDCs in the body with lower implantation rates in assisted reproductive technology (ART) cycles. This narrative review examines the implications of these findings in reproductive medicine, summarizes recent experimental and clinical data, and highlights the molecular mechanisms linking exposure to endocrine disruptors with recurrent implantation failure. Recognizing environmental chemical exposure as a potentially modifiable risk factor may offer new perspectives for the prevention of RIF and the development of more personalized therapeutic strategies.
8 February 2026