Ecological and Human Health Risks from Potentially Toxic Elements in Environmental Matrices of Kiteezi Landfill, Uganda
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
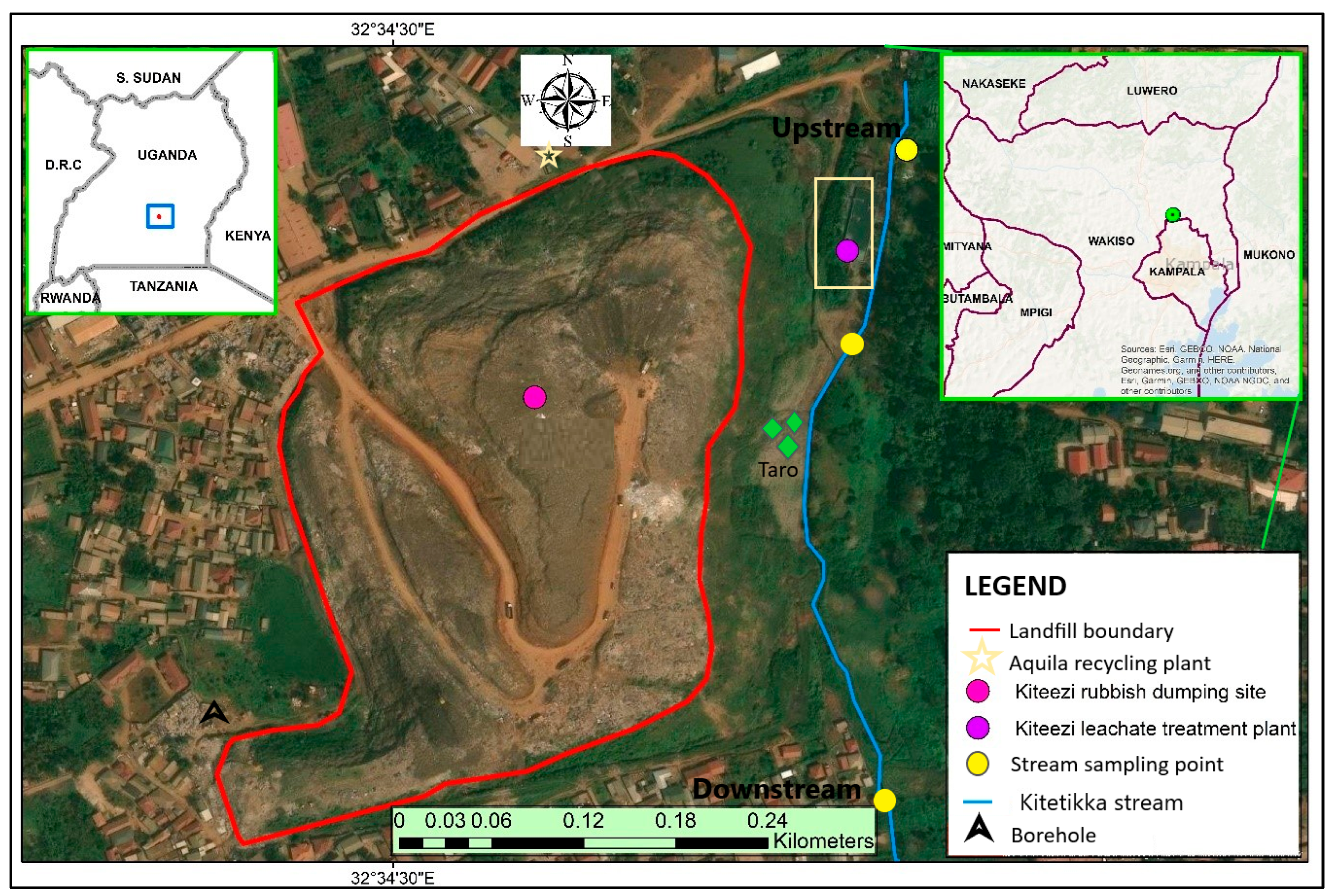
2.1. Description of the Study Area and Reconnaissance Survey
2.2. Sampling of Environmental Matrices
2.3. Determination of Non-Conservable Parameters of Leachate and Water Samples
2.4. Sample Preparation Procedures
2.5. Instrumental Analysis, Quality Assurance, and Quality Control
2.6. Dietary Exposure to PTXEs and the Associated Human Health Risks
2.7. Evaluation of Sediment Pollution Levels
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Temporal Variations in Water and Leachate Chemistry
3.2. Spatiotemporal Distribution of PTXEs in Environmental Matrices of KTLF
3.2.1. Water and Leachates
3.2.2. Superficial Sediments
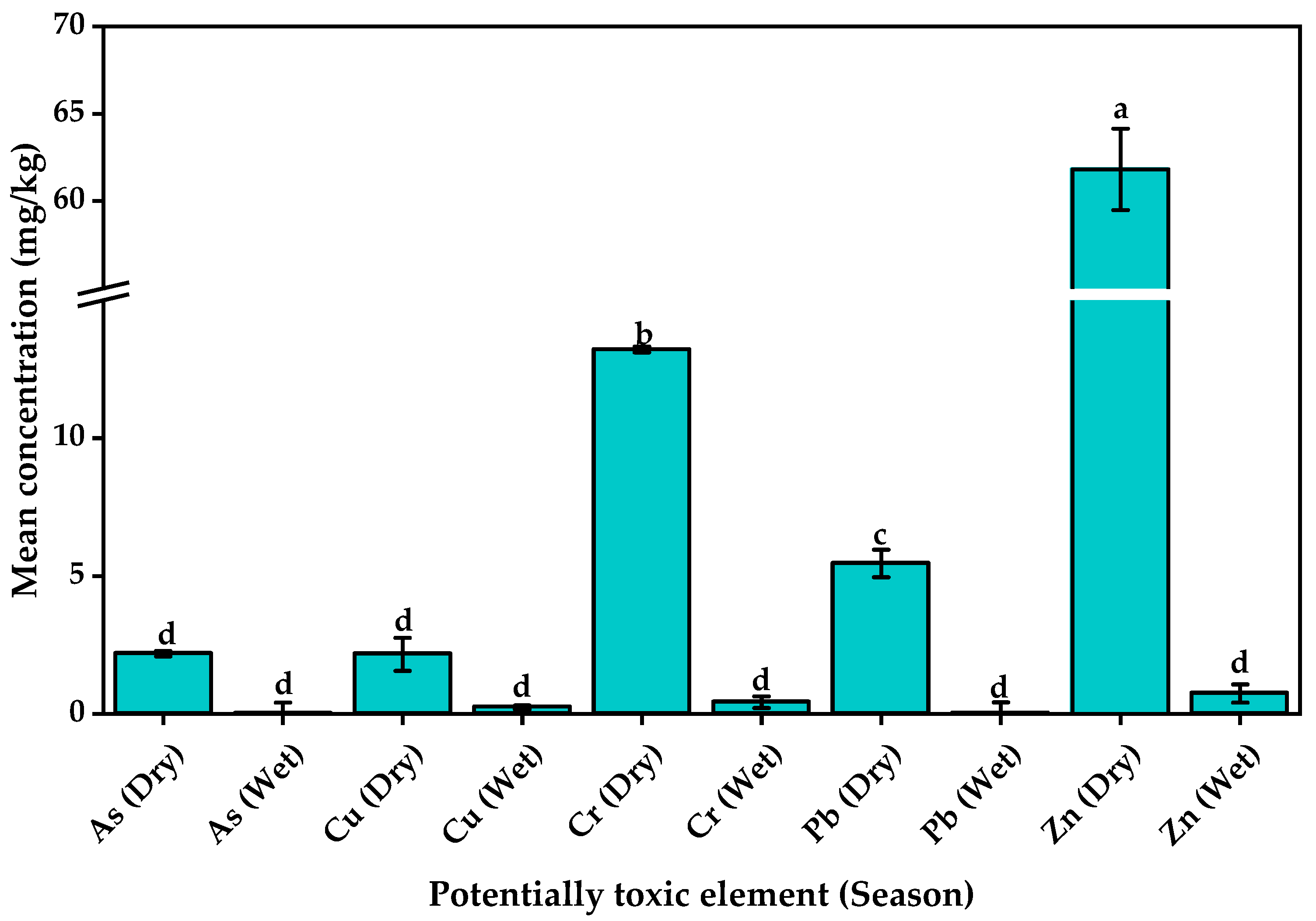
3.2.3. Colocasia esculenta Corms
3.3. Health Risk Assessments from Ingestion of Water and Consumption of C. esculenta
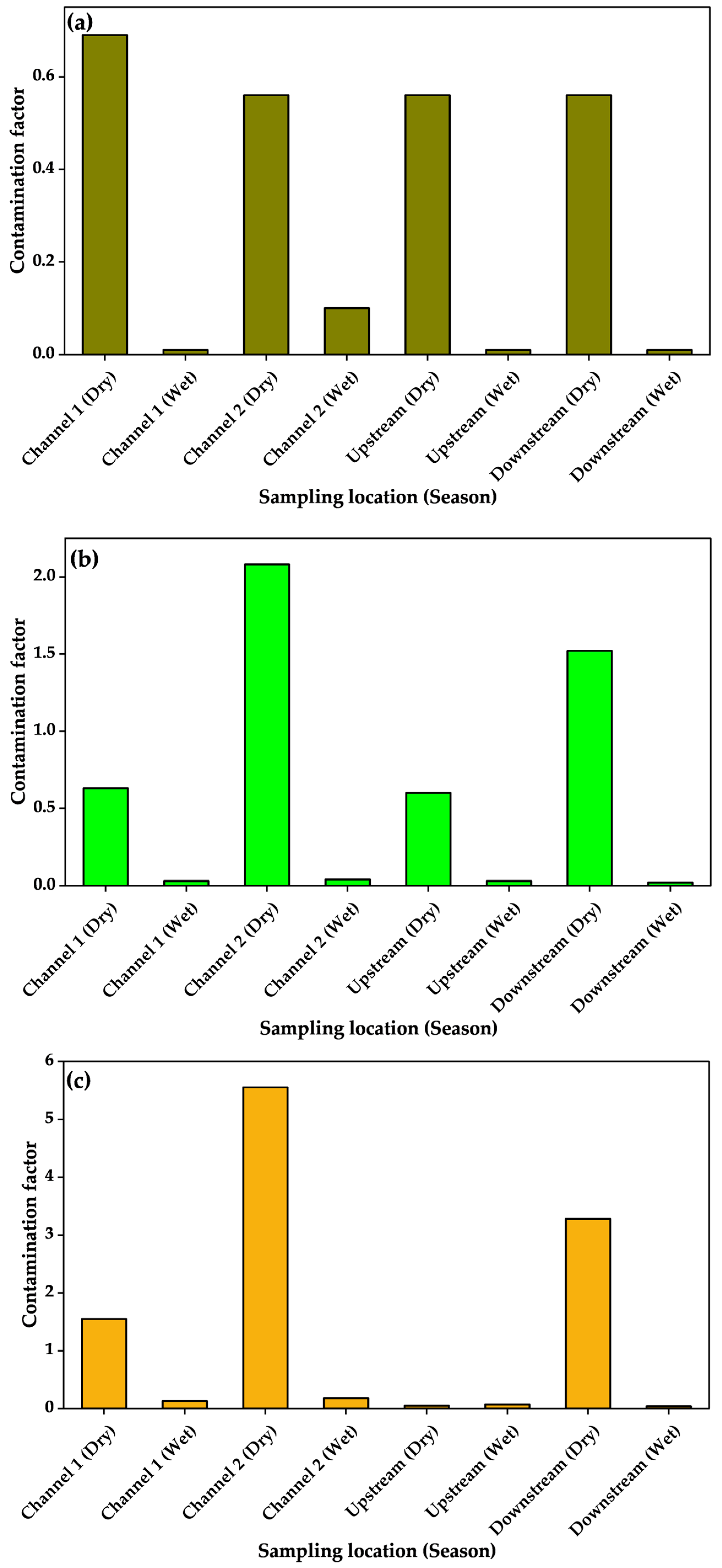
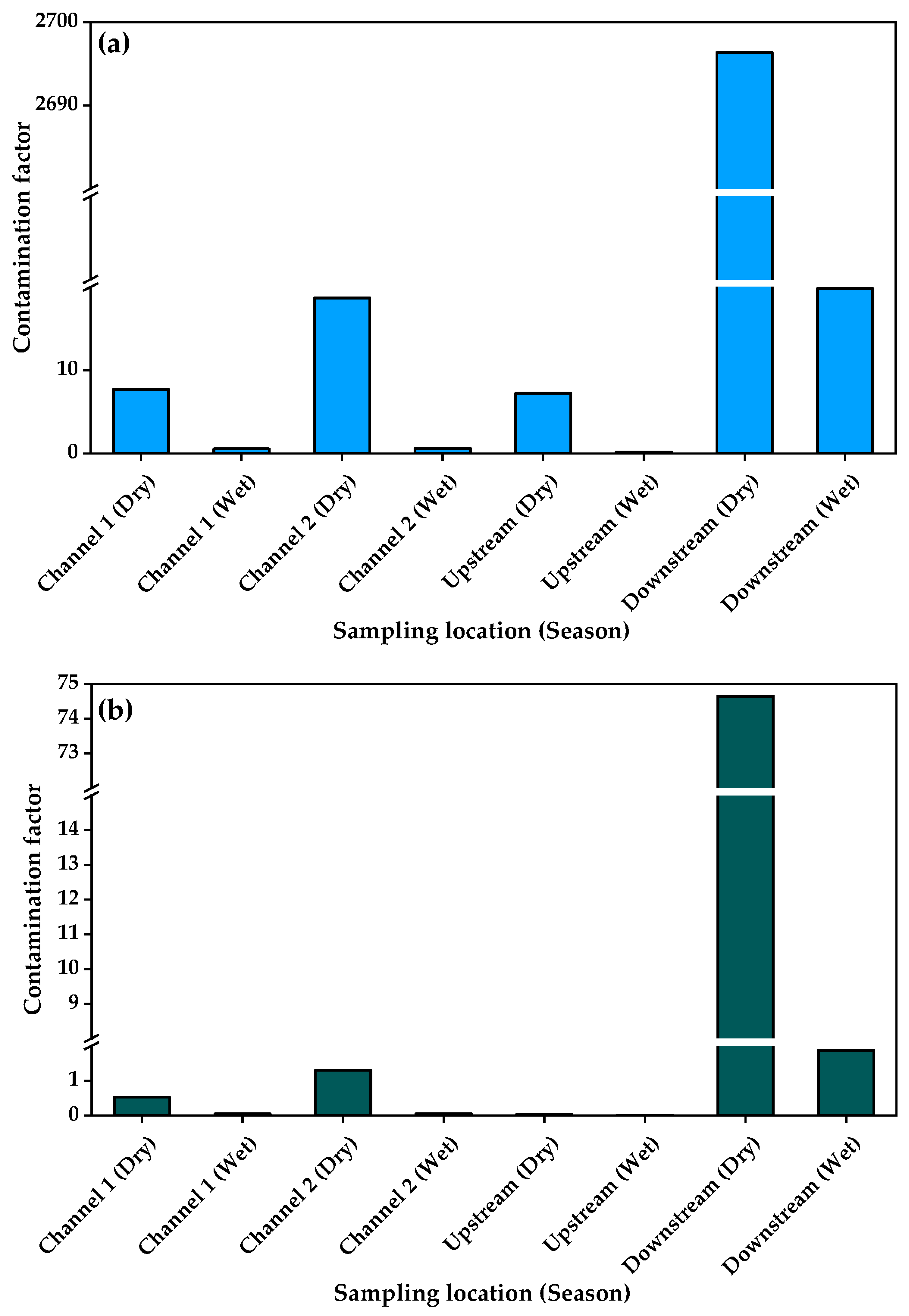
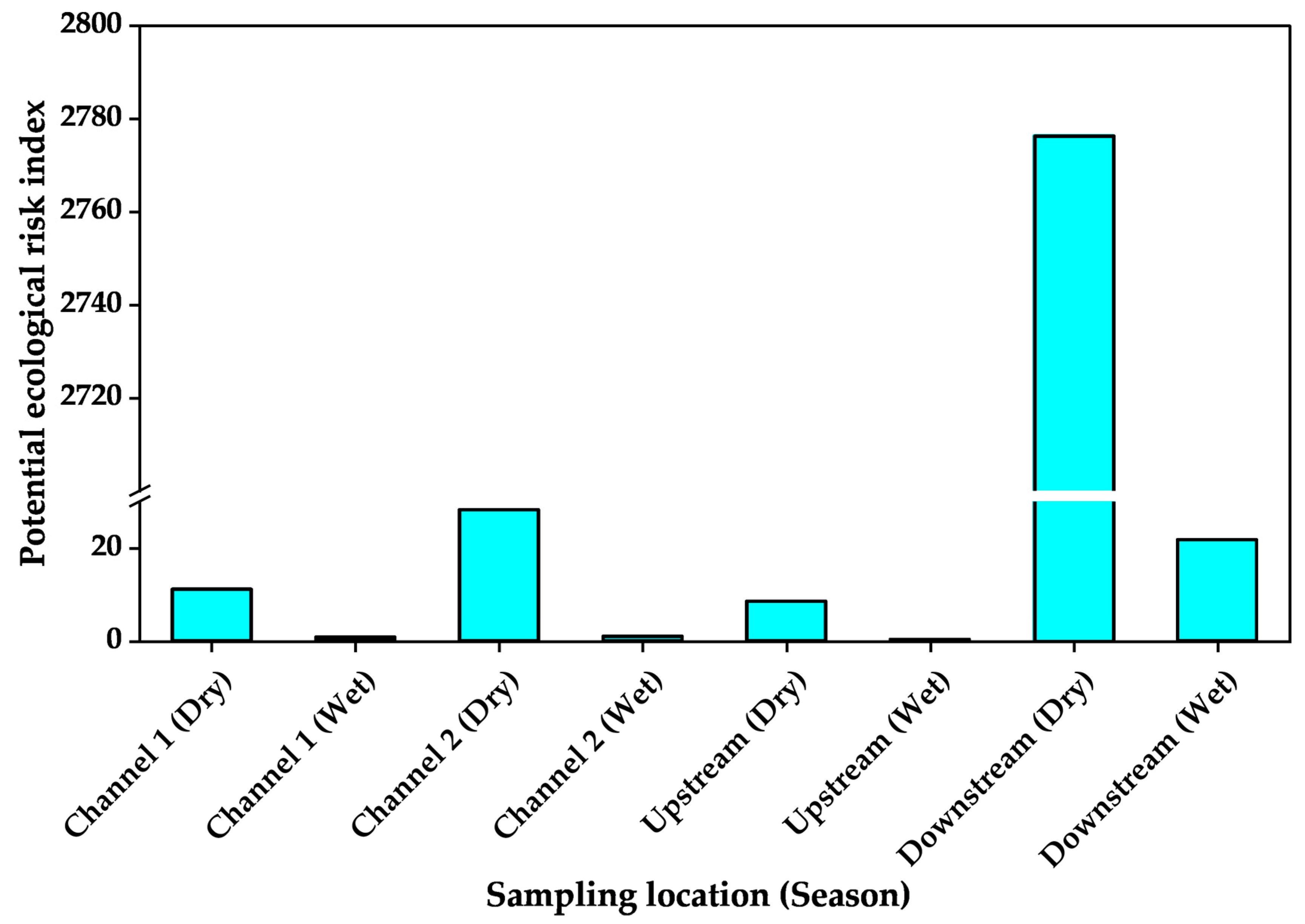
3.4. Heavy Metal Enrichment in Sediments and Associated Ecological Health Risks
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jasińska-Biliczak, A.; Ikwuwunna, E. New directions for the realisationof SDGs given the economic and welfarecosts incurred by air pollution. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1220325. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. The United Nations System: Common Approach Towards a Pollution-Free Planet. Available online: https://unemg.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/UNEP_EMG_UN-system-common-approach-to-Pollution-231122.pdf (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- UNEP. Why Does Air Matter? Available online: https://www.unep.org/topics/air/why-does-air-matter (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Hossain, M.A.; Ferdous, N.; Ferdous, E. Crisis-driven disruptions in global waste management: Impacts, challenges and policy responses amid COVID-19, Russia-Ukraine war, climate change, and colossal food waste. Environ. Chall. 2024, 14, 100807. [Google Scholar]
- Ololade, O.O.; Mavimbela, S.; Oke, S.A.; Makhadi, R. Impact of Leachate from Northern Landfill Site in Bloemfontein on Water and Soil Quality: Implications for Water and Food Security. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryampa, S.; Maheshwari, B.; Sabiiti, E.; Bateganya, N.L.; Bukenya, B. Status of Waste Management in the East African Cities: Understanding the Drivers of Waste Generation, Collection and Disposal and Their Impacts on Kampala City’s Sustainability. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, P.; Ferronato, N.; Torretta, V. Setting priorities to achieve Sustainable Development Goals through appropriate waste management systems in Uganda. Environ. Dev. 2022, 44, 100764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaashikaa, P.R.; Kumar, P.S.; Nhung, T.C.; Hemavathy, R.V.; Jawahar, M.J.; Neshaanthini, J.P.; Rangasamy, G. A review on landfill system for municipal solid wastes: Insight into leachate, gas emissions, environmental and economic analysis. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanga, V.F.; Fabian, C.; Kimbokota, F. Heavy metal pollution in leachates and its impacts on the quality of groundwater resources around Iringa municipal solid waste dumpsite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 8110–8122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hussein, M.; Yoneda, K.; Mohd-Zaki, Z.; Amir, A.; Othman, N. Heavy metals in leachate, impacted soils and natural soils of different landfills in Malaysia: An alarming threat. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryampa, S.; Maheshwari, B.; Sabiiti, E.N.; Bateganya, N.L.; Olobo, C. Understanding the impacts of waste disposal site closure on the livelihood of local communities in africa: A case study of the kiteezi landfill in Kampala, Uganda. World Dev. Perspect. 2022, 25, 100391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryampa, S.; Maheshwari, B.; Sabiiti, E.N.; Bukenya, B.; Namuddu, S. The Impact of Waste Disposal Sites on the Local Water Resources: A Case Study of the Kiteezi landfill, Uganda. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2023, 23, 280–289. [Google Scholar]
- Aliyinza, L. Levels of Heavy Metal Concentration in Leachate, Borehole, and Spring Water in Areas Surrounding Kiteezi Landfill, Wakiso District, Uganda. Master’s Dissertation, Makerere University, Kampala, Uganda, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Asio, L. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of Soils by Leachate from Kiteezi Landfill. Master’s Dissertation, Makerere University, Kampala, Uganda. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10570/13624 (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Mugisa, D.; Banadda, N.; Kiggundu, N.; Asuman, R. Lead uptake of water plants in water stream at Kiteezi landfill site, Kampala (Uganda). Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 9, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwiganga, M.; Kansiime, F. The impact of Mpererwe landfill in Kampala–Uganda, on the surrounding environment. Phys. Chem. Earth 2005, 30, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryampa, S.; Maheshwari, B.; Zamorano, M.; Sabiiti, E.N.; Olobo, C.; Bateganya, N.L. Adaptation of EVIAVE methodology to landfill environmental impact assessment in Uganda—A case study of Kiteezi landfill. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 183, 104310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, L.K.; Asher, D.; Anandaraja, N.; Bopp, R.F.; Merrill, K.; Cullen, M.R.; Luboga, S.; Trasande, L. Childhood lead exposure after the phaseout of leaded gasoline: An ecological study of school-age children in Kampala, Uganda. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadzi, G.Y.; Essumang, D.K.; Ayoko, G.A. Assessment of contamination and potential ecological risks of heavy metals in riverine sediments from gold mining and pristine areas in Ghana. J. Trace Elem. Min. 2024, 7, 100109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakyayita, G.K.; Norrström, A.C.; Kulabako, R.N. Assessment of Levels, Speciation, and Toxicity of Trace Metal Contaminants in Selected Shallow Groundwater Sources, Surface Runoff, Wastewater, and Surface Water from Designated Streams in Lake Victoria Basin, Uganda. J. Environ. Public Health 2019, 2019, 6734017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinobe, J.R.; Niwagaba, C.B.; Gebresenbet, G.; Komakech, A.J.; Vinnerås, B. Mapping out the solid waste generation and collection models: The case of Kampala City. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2015, 65, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Google Maps. Kampala, Uganda. Available online: https://www.google.com/maps/place/Kampala,+Uganda/@0.4117964,32.5732552,765m/data=!3m1!1e3!4m6!3m5!1s0x177dbc0f9d74b39b:0x4538903dd96b6fec!8m2!3d0.3151692!4d32.5816313!16zL20vMGZuZ3k?entry=ttu&g_ep=EgoyMDI1MDIyMy4xIKXMDSoASAFQAw%3D%3D (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Ndibaisa, D. Assessing the Breeding Status of the Grey Crowned Crane (Balearica regulorum) in Kampala Wetlands, Uganda. African Bird Club. Available online: https://www.africanbirdclub.org/sites/default/files/2012_Grey_crowned_Cranes_Kampala_0.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Kyambade, M.; Namatovu, A. Navigating trauma: Mental well-being after Kiteezi landfill collapse and residential displacement in Uganda. Disaster Prev. Manag. 2025, 34, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KCCA. Project Teaser. Kampala Waste Treatment and Disposal PPP. Available online: https://www.kcca.go.ug/uDocs/kampala-waste-treatment-and-disposal-ppp.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Kampala City Council. Environmental Impact Assessment for Proposed Landfill Gas Flaring CDM Project at Mpererwe Landfill Site, Kiteezi, Final Report (November 2008). Available online: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/196551468318878066/pdf/E21450EA0P09801BLIC10AFR1EA1P098012.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Omara, T.; Karungi, S.; Kalukusu, R.; Nakabuye, B.; Kagoya, S.; Musau, B. Mercuric pollution of surface water, superficial sediments, Nile tilapia (Oreochromis nilotica Linnaeus 1758 [Cichlidae]) and yams (Dioscorea alata) in auriferous areas of Namukombe stream, Syanyonja, Busia, Uganda. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimusiima, D.; Byamugisha, D.; Omara, T.; Ntambi, E. Physicochemical and Microbial Quality of Water from the Ugandan Stretch of the Kagera Transboundary River. Limnol. Rev. 2023, 23, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. SW-846 Test Method 9045D: Soil and Waste pH. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-12/documents/9045d.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- EPA. Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion of Siliceous and Organically Based Matrices. Office of Solid Waste, Method 3052-1. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-12/documents/3052.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Nijeje, E.; Senyonjo, A.; Sahan, S.J.; Byamugisha, D.; Ntambi, E. Speciation of Selected Heavy Metals in Bottom Sediments of River Rwizi, Mbarara City, Uganda. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuwamanya, E.; Byamugisha, D.; Nakiguli, C.K.; Angiro, C.; Khanakwa, A.V.; Omara, T.; Ocakacon, S.; Onen, P.; Omoding, D.; Opio, B.; et al. Exposure and Health Risks Posed by Potentially Toxic Elements in Soils of Metal Fabrication Workshops in Mbarara City, Uganda. J. Xenobiot. 2024, 14, 176–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaggwa, A.; Byamugisha, D.; Omara, T.; Ntambi, E. Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements and Their Risks in Water and Sediments of Kitengure Stream, Buhweju Plateau, Uganda. Earth 2024, 5, 743–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opolot, M.; Omara, T.; Adaku, C.; Ntambi, E. Pollution Status, Source Apportionment, Ecological and Human Health Risks of Potentially (Eco)toxic Element-Laden Dusts from Urban Roads, Highways and Pedestrian Bridges in Uganda. Pollutants 2023, 3, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. National centre for environment assessment. In Exposure Factors Handbook; US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ajeh, E.A.; Modi, F.J.; Omoregi, I.P. Health risk estimations and geospatial mapping of trace metals in soil samples around automobile mechanic workshops in Benin city, Nigeria. Toxicol. Rep. 2022, 9, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G. Die Schwermetallbelastung der Sedimenten des Neckars und Seiner Nebenflüsse. Chemiker-Zeitung 1981, 6, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S. The abundance of chemical elements in the continental crust–A new table. Geoch. Cosm. Act. 1964, 28, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickson, O.; Ukundimana, Z.; Wamyil, F.B.; Yusuf, A.A.; Pierre, M.J.; Kagabo, A.S.; Rizinde, T. Quantification and characterization of municipal solid waste at aler dumpsite, Lira City, Uganda: Assessing pollution levels and health risks. Clean. Waste Syst. 2024, 9, 100177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghi, M.H.; Nadimi, H.; Eslami, A.; Bakhtiarvand, S.N.A.; Oghazyan, A.; Setoudeh, S.; Sargolzaei, M.S. Characteristics and pollution indices of leachates from municipal solid waste landfills in Iranian metropolises and their implications for MSW management. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoai, S.T.; Nguyen Lan, H.; Thi Viet, N.T.; Nguyen Hoang, G.; Kawamoto, K. Characterizing Seasonal Variation in Landfill Leachate Using Leachate Pollution Index (LPI) at Nam Son Solid Waste Landfill in Hanoi, Vietnam. Environments 2021, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhambore, N.; Kumar, M.S. Assessing seasonal fluctuations in leachate chemical properties and leachate pollution index as contamination indicators. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsi, A.; Zouboulis, A. A field investigation of the quantity and quality of leachate from a municipal solid waste landfill in a Mediterranean climate (Thessaloniki, Greece). Adv. Environ. Res. 2002, 6, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wdowczyk, A.; Szymańska-Pulikowska, A. Analysis of the possibility of conducting a comprehensive assessment of landfill leachate contamination using physicochemical indicators and toxicity test. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe. 2021, 221, 112434. [Google Scholar]
- Lindamulla, L.; Nanayakkara, N.; Othman, M.; Jinadasa, S.; Herath, G.; Jegatheesan, V. Municipal Solid Waste Landfill Leachate Characteristics and Their Treatment Options in Tropical Countries. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2022, 8, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwisai, R.D.; Areola, O.O.; Segosebe, E.M. Physico-chemical analysis in surface waters around the closed gaborone sanitary landfill in Botswana. Environ. Ecol. Res. 2019, 7, 220–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First and Second Addenda; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/352532/9789240045064-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 25 September 2025).[Green Version]
- Nasir, M.J.; Tufail, M.; Ayaz, T.; Khan, S.; Khan, A.Z.; Lei, M. Groundwater quality assessment and its vulnerability to pollution: A study of district Nowshera, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmi, S.; Baali, F.; Hadji, R.; Brahmi, S.; Hamad, A.; Rahal, O.; Zerrouki, H.; Saadali, B.; Hamed, Y. Assessment of groundwater and soil pollution by leachate using electrical resistivity and induced polarization imaging survey, case of Tebessa municipal landfill, NE Algeria. Arab J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likando, N.M.; Dornack, C.; Hamutoko, J.T. Assessing the physicochemical parameters of leachate from biowaste fractions in a laboratory setting, using the elusion method. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.; Haraguchi, A.; Hassan, M.A.; Othman, M.R.; Wakisaka, M.; Shirai, Y. Measuring organic carbon, nutrients and heavy metals in rivers receiving leachate from controlled and uncontrolled municipal solid waste (MSW) landfills. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2666–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halwani, J.; Halwani, B.; Amine, H.; Kabbara, M.B. Waste Management in Lebanon—Tripoli Case Study; Negm, A., Shareef, N., Eds.; Waste Management in MENA Regions; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 223–239. [Google Scholar]
- Mangimbulude, J.C.; van Breukelen, B.M.; Krave, A.S.; van Straalen, N.M.; Röling, W.F.M. Seasonal dynamics in leachate hydrochemistry and natural attenuation in surface run-off water from a tropical landfill. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; Incorporating the 1st Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241549950 (accessed on 21 September 2025).
- Okafor, O.C.; Obaze, W.O. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contents of Surface Water Around Waste Dumpsites in Ebonyi, Enugu and Anambra States, Southeastern Nigeria. Environ. Forensics 2025, 46, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, F.; Tareq, S.M. Impact of landfill leachate contamination on surface and groundwater of Bangladesh: A systematic review and possible public health risks assessment. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adu, J.T.; Aneke, F.I. Evaluation of heavy metal contamination in landfills from e-waste disposal and its potential as a pollution source for surface water bodies. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 104431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vongdala, N.; Tran, H.-D.; Xuan, T.D.; Teschke, R.; Khanh, T.D. Heavy Metal Accumulation in Water, Soil, and Plants of Municipal Solid Waste Landfill in Vientiane, Laos. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 22. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA. Guidelines for Water Reuse. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2019-08/documents/2012-guidelines-water-reuse.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Hosseini Beinabaj, S.M.; Heydariyan, H.; Mohammad Aleii, H.; Hosseinzadeh, A. Concentration of heavy metals in leachate, soil, and plants in Tehran’s landfill: Investigation of the effect of landfill age on the intensity of pollution. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Mostafa, M.G. Occurrence, Source, and Mobilization of Iron, Manganese, and Arsenic Pollution in Shallow Aquifer. Geofluids 2023, 2023, 628095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turekian, K.K.; Wedepohl, K.H. Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geo. Soc. Am. Bull. 1961, 72, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Sediment Quality Guidelines; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- MacDonald, D.D.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Berger, T. Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 39, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnejais, L.H.; Martin, W.R.; Signell, R.P.; Bothner, M.H. Role of Sediment Resuspension in the Remobilization of Particulate-Phase Metals from Coastal Sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2282–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruchuwararak, P.; Intamat, S.; Tengjaroenkul, B.; Neeratanaphan, L. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in local edible plants near a municipal landfill and the related human health risk assessment. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2019, 25, 1760–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulistyowati, L.; Nurhasanah, N.; Riani, E.; Cordova, M.R. Heavy metals concentration in the sediment of the aquaticenvironment caused by the leachate discharge from a landfill. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2023, 9, 323–336. [Google Scholar]
- FAO/WHO. Codex Alimentarius—General Standards for Contaminants and Toxins in Food. Schedule 1 Maximum and Guideline Levels for Contaminants and Toxins in Food; Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme; Reference CX/FAC 02/16; Codex Committee: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- JECFA. Codex General Standard for Contaminants and Toxins in Food and Feeds. In Proceedings of the 64th Meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), JECFA/64/CAC/RCP 49-2001, Rome, Italy, 8–17 February 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Oluyemi, E.A.; Feuyit, G.; Oyekunle, J.A.O.; Ogunfowokan, A.O. Seasonal variations in heavy metal concentrations in soil and some selected crops at a landfill in Nigeria. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 2, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Kundu, G.K.; Biswas, M.; Annana, R.P.; Rahman, A.F.M.H. Unveiling Taro’s (Colocasia esculenta) potential as a source of antioxidants and nutritional elements: Industrial impact on quantitative risk assessment of potentially toxic metals accumulation. Appl. Food Res. 2024, 4, 100586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergedus, A.; Kristl, J.; Ivancic, A.; Sober, A.; Sustar, V.; Krizan, T.; Lebot, V. Variation of mineral composition in different parts of taro (Colocasia esculenta) corms. Food Chem. 2015, 170, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobbinah, F.N.Y.; Kyei, S.K.; Azanu, S.; Kabange, R.S. Bioaccumulation Factor and Health Hazards of Heavy Metals in Taro in the Atiwa East Municipality, Ghana. Available online: https://www.ssrn.com/abstract=5117863 (accessed on 21 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Uwamariya, V.; Wamalwa, L.N.; Anyango, J.; Nduko, J.M.; Indieka, A.S. Variation and correlation of corm trace elements, anti-nutrients and sensory attributes of taro crisps. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 100, 103896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongi, R.; Chove, L. Heavy Metal Contamination in Cocoyam Crops and Soils in Countries around the Lake Victoria Basin (Tanzania, Uganda and Kenya). TAJAS 2020, 19, 148–160. [Google Scholar]
- Essumang, D.; Dodoo, D.K.; Obiri, S.; Yaney, J.Y. Arsenic, Cadmium, and Mercury in Cocoyam (Xanthosoma sagititolium) and Watercocoyam (Colocasia esculenta) in Tarkwa a Mining Community. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 79, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjei-Mensah, R.; Ofori, H.; Tortoe, C.; Torgbor, J.P.N.; Aryee, D.; Kofi, F.S. Effect of home processing methods on the levels of heavy metal contaminants in four food crops grown in and around two mining towns in Ghana. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 8, 1830–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omara, T.; Nteziyaremye, P.; Akaganyira, S.; Opio, D.W.; Karanja, L.N.; Nyangena, D.M.; Kiptui, B.J.; Ogwang, R.; Epiaka, S.M.; Jepchirchir, A.; et al. Physicochemical quality of water and health risks associated with consumption of African lung fish (Protopterus annectens) from Nyabarongo and Nyabugogo rivers, Rwanda. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol. Mar. Res. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.Y.; Shen, D.S.; Wang, H.T.; Lu, W.J.; Zhao, Y. Heavy metal source analysis in municipal solid waste (MSW): Case study on Cu and Zn. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, Y.M.; Lion, L.W.; Shuler, M.L.; Ghiorse, W.C. Effect of oxide formation mechanisms on lead adsorption by biogenic manganese (hydr)oxides, iron (hydr)oxides, and their mixtures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.M.; Mohana, A.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Rahman, M.; Naidu, R.; Rahman, M.M. A Comprehensive Review of the Current Progress of Chromium Removal Methods from Aqueous Solution. Toxics 2023, 11, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutehenda, D.R.; Adaku, C.; Omara, T.; Angiro, C.; Ntambi, E. Enrichment, Bioaccumulation and Health Risks of Trace Metals in Soils and Leafy Vegetables Grown on the Banks of the Ugandan Lifeline River, River Rwizi. World 2024, 5, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Matrices | Season | pH | Electrical Conductivity (μS/cm) | Temperature (°C) | Oxidation–Reduction Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water (Borehole) | Dry | 5.33 ± 0.10 a | 233.8 ± 1.2 a | 24.6 ± 2.4 a | 78.5 ± 0.5 a |
| Wet | 5.30 ± 0.04 a | 213.0 ± 17.0 a | 23.8 ± 4.7 a | 78.5 ± 4.9 a | |
| Water (Upstream) | Dry | 6.76 ± 0.02 b | 225.0 ± 14.1 a | 24.3 ± 1.3 a | −4.0 ± 2.8 b |
| Wet | 6.91 ± 0.01 b | 195.0 ± 7.1 a | 20.6 ± 0.4 a | −13.5 ± 0.7 b | |
| Water (Downstream) | Dry | 8.20 ± 0.10 c | 11,650.0 ± 338.1 b | 24.3 ± 1.0 a | −92.0 ± 1.4 c |
| Wet | 8.50 ± 0.10 c,d | 8550.0 ± 3111.3 b,c | 23.9 ± 4.5 a | −110.0 ± 4.2 d | |
| Leachate (Clarifier) | Dry | 9.30 ± 0.05 e | 10,046.7 ± 321.5 b,c | 23.9 ± 0.4 a | −158.5 ± 0.7 e |
| Wet | 9.50 ± 0.09 e | 7240.0 ± 183.8 b,c | 24.1 ± 4.6 a | −168.0 ± 5.7 e | |
| Leachate (Channel 1) | Dry | 8.10 ± 0.16 d | 28,966.7 ± 907.4 d | 24.2 ± 0.8 a | −87.0 ± 1.4 c |
| Wet | 8.60 ± 0.11 c,d | 26,400.0 ± 424.3 d | 23.7 ± 4.2 a | −110.0 ± 4.2 d | |
| Leachate (Channel 2) | Dry | 8.49 ± 0.03 c,d | 27,133.3 ± 1050.4 d | 24.0 ± 1.2 a | −106.5 ± 0.7 d |
| Wet | 8.65 ± 0.07 c,d | 22,450.0 ± 353.6 e | 23.8 ± 4.4 a | −113.0 ± 4.2 d |
| Source | Season | As | Cu | Cr | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Borehole | Dry | 0.010 ± 0.009 a | 0.007 ± 0.004 a | 0.008 ± 0.002 a | 0.021 ± 0.003 a | 0.210 ± 0.043 a |
| Wet | 0.037 ± 0.027 b | 0.018 ± 0.002 a | <0.001 | 0.005 ± 0.003 b | 0.002 ± 0.001 b | |
| Upstream | Dry | 0.009 ± 0.001 a | 0.003 ± 0.001 b | 0.007 ± 0.003 a | 0.028 ± 0.010 a | 0.023 ± 0.015 c |
| Wet | 0.040 ± 0.038 b | 0.115 ± 0.067 c | <0.001 | 0.051 ± 0.031 c | 0.003 ± 0.002 b | |
| Downstream | Dry | 0.001 ± 0.050 c | 0.048 ± 0.019 d | 0.072 ± 0.012 b | 0.175 ± 0.115 d | 0.663 ± 0.328 d |
| Wet | 0.022 ± 0.008 a | 0.025 ± 0.014 e | <0.001 | 0.015 ± 0.011 a | 0.001 ± 0.020 b | |
| WHO limits [55] | 0.01 | 2.0 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 3.0 |
| Source | Season | As | Cu | Cr | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clarifier | Dry | 0.011 ± 0.010 a | 0.016 ± 0.002 a | 0.040 ± 0.001 a | 0.009 ± 0.001 a | 0.184 ± 0.032 a |
| Wet | 0.123 ± 0.103 b | 0.035 ± 0.022 a | <0.001 | 0.032 ± 0.030 b | 0.004 ± 0.003 b | |
| Channel 1 | Dry | 0.001 ± 0.010 c | 0.101 ± 0.015 b | 0.172 ± 0.012 b | 0.092 ± 0.017 c | 0.778 ± 0.263 c |
| Wet | 0.057 ± 0.032 d | 0.082 ± 0.056 b | <0.001 | 0.090 ± 0.070 c | 0.016 ± 0.014 d | |
| Channel 2 | Dry | 0.003 ± 0.002 c | 0.091 ± 0.001 b | 0.112 ± 0.025 c | 0.099 ± 0.031 c | 0.919 ± 0.661 e |
| Wet | 0.126 ± 0.046 b | 0.097 ± 0.040 b | <0.001 | 0.082 ± 0.021 c | 0.003 ± 0.002 b |
| Source | Season | As | Cu | Cr | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Channel 1 | Dry | 0.125 ± 0.025 a | 19.176 ± 18.133 a | 18.857 ± 17.645 a | 17.104 ± 16.394 a | 37.279 ± 36.029 a |
| Wet | 0.001 ± 0.040 b | 1.407 ± 0.233 b | 1.013 ± 0.182 b | 1.421 ± 0.239 b | 3.606 ± 0.473 b | |
| Channel 2 | Dry | 0.100 ± 0.001 a | 46.705 ± 6.410 c | 62.543 ± 20.907 c | 61.099 ± 23.713 c | 90.803 ± 30.060 c |
| Wet | 0.018 ± 0.011 c | 1.489 ± 0.321 b | 1.276 ± 0.121 b | 1.998 ± 0.499 d | 3.294 ± 0.688 b | |
| Upstream | Dry | 0.100 ± 0.060 a | 18.093 ± 16.206 a | 18.024 ± 19.067 a | 0.537 ± 0.197 a | 2.923 ± 30.324 b |
| Wet | 0.001 ± 0.020 b | 0.423 ± 0.077 b | 1.038 ± 0.163 b | 0.812 ± 0.207 a | 0.879 ± 0.179 d | |
| Downstream | Dry | 0.100 ± 0.033 a | 6740.858 ± 612.219 d | 45.71 ± 4.025 c | 36.078 ± 9.411 e | 5225.724 ± 322.895 e |
| Wet | 0.001 ± 0.019 b | 49.500 ± 11.892 e | 0.522 ± 0.229 b | 0.483 ± 0.024 a | 131.500 ± 39.955 f | |
| Overall range | 0.001–0.125 | 0.423–6740.858 | 0.522–62.543 | 0.483–61.099 | 0.879–5225.724 | |
| Average shale value [63] | 13 | 45 | 90 | 20 | 95 | |
| Toxicity reference value [64] | 8.2 | 16 | 26 | 31 | 110 | |
| Threshold effect concentration [65] | 9.79 | 31.6 | 43.4 | 35.8 | 121 | |
| Probable Effect Concentration [65] | 33.0 | 149 | 111 | 128 | 459 | |
| Location | As | Cu | Cr | Pb | Zn | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kiteezi landfill, Uganda | 0.001–2.187 | 0.237–2.167 | 0.423–13.223 | 0.018–5.462 | 0.741–61.822 | Current study |
| Atiwa East, Ghana | 0.43–1.89 | 12.78–25.12 | 9.11–16.45 | 2.14–6.33 | – | Cobbinah et al. [74] |
| Industrial areas, Bangladesh | – | 4.43–266.67 | 1.80–19.33 | BDL–6.33 | 3.8–146.67 | Kundu et al. [72] |
| Kenya | BDL–0.19 | – | 3.02–3.90 | 1.05–1.08 | 8.1 –11.3 | Uwamariya et al. [75] |
| Lake Victoria Basin (Tanzania, Uganda, Kenya) | BDL–3.5 | 3.0–7.5 | BDL–6.0 | – | Mongi and Chove [76] | |
| Tarkwa, Ghana | 366 and 401 | – | – | – | – | Essumang et al. [77] |
| Kade, Ghana | 0.012–0.019 | – | – | – | – | Adjei-Mensah et al. [78] |
| Maximum allowed concentration | 1.4 | 40 | 2.3 | 5 | 60 | [69,70] |
| Sampling Point | Season | As | Cu | Cr | Pb | Zn | PLI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF | Igeo | CF | Igeo | CF | Igeo | CF | Igeo | CF | Igeo | |||
| Channel 1 | Dry | 0.07 | −4.4 | 1.5 | 0.03 | 0.3 | −2.3 | 0.3 | −2.3 | 0.5 | −1.5 | 0.40 |
| Wet | 0.001 | −11.4 | 0.1 | −3.7 | 0.02 | −6.5 | 0.03 | −5.9 | 0.1 | −4.9 | 0.02 | |
| Channel 2 | Dry | 0.1 | −4.8 | 3.7 | 1.3 | 1.0 | −0.5 | 1.1 | −0.4 | 1.3 | −0.2 | 0.80 |
| Wet | 0.01 | −7.2 | 0.1 | −3.7 | 0.02 | −6.1 | 0.04 | −5.4 | 0.1 | −5.0 | 0.03 | |
| Upstream | Dry | 0.1 | −4.8 | 1.5 | −0.1 | 0.3 | −2.3 | 0.01 | −7.3 | 0.04 | −5.2 | 0.10 |
| Wet | 0.001 | −11.4 | 0.03 | −5.5 | 0.02 | −6.4 | 0.01 | −6.7 | 0.01 | −6.9 | 0.01 | |
| Downstream | Dry | 0.1 | −4.8 | 539.3 | 8.5 | 0.8 | −1.0 | 0.7 | −1.2 | 74.7 | 5.6 | 4.07 |
| Wet | 0.001 | −11.4 | 4.0 | 1.4 | 0.01 | −7.4 | 0.01 | −7.4 | 1.9 | 0.3 | 0.05 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ebbu, E.; Nalumansi, I.; Kiganda, I.; Nakiguli, C.K.; Onen, P.; Ocakacon, S.; Adaku, C.; Omara, T.; Ntambi, E. Ecological and Human Health Risks from Potentially Toxic Elements in Environmental Matrices of Kiteezi Landfill, Uganda. J. Xenobiot. 2025, 15, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15060185
Ebbu E, Nalumansi I, Kiganda I, Nakiguli CK, Onen P, Ocakacon S, Adaku C, Omara T, Ntambi E. Ecological and Human Health Risks from Potentially Toxic Elements in Environmental Matrices of Kiteezi Landfill, Uganda. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2025; 15(6):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15060185
Chicago/Turabian StyleEbbu, Emmanuel, Irene Nalumansi, Ivan Kiganda, Caroline Kiwanuka Nakiguli, Patrick Onen, Simon Ocakacon, Christopher Adaku, Timothy Omara, and Emmanuel Ntambi. 2025. "Ecological and Human Health Risks from Potentially Toxic Elements in Environmental Matrices of Kiteezi Landfill, Uganda" Journal of Xenobiotics 15, no. 6: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15060185
APA StyleEbbu, E., Nalumansi, I., Kiganda, I., Nakiguli, C. K., Onen, P., Ocakacon, S., Adaku, C., Omara, T., & Ntambi, E. (2025). Ecological and Human Health Risks from Potentially Toxic Elements in Environmental Matrices of Kiteezi Landfill, Uganda. Journal of Xenobiotics, 15(6), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15060185










