- Article
In Vivo Passive Sampling Implantation in Fish for Monitoring of PAHs: Calibration and Kinetics
- Jhon Fredy Narváez Valderrama,
- Juan José García Londoño and
- Jorge L. Gallego
- + 2 authors
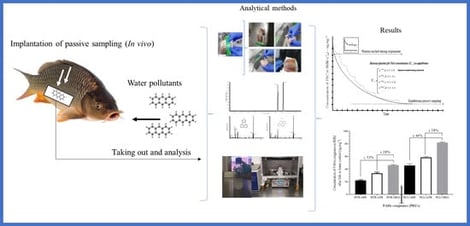
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) can enter water bodies and bioaccumulate in fish, leading to biomagnification; therefore, their monitoring is necessary. Passive sampling is easy to handle and shows potential for this purpose. However, studies in vivo are scarce, and kinetic parameters governing analyte partitioning between tissue and samplers remain poorly characterized. In this study, the silicone rubber membranes (SRMs) were exposed to fish fillet from common carp (Cyprinus carpio) to determine bioaccumulation parameters based on dissipation modelling using performance reference compounds (PRCs). The SRM was implanted in vivo in fish, and the dissipated PRCs were measured and applied to a mono-compartmental model. The results in fish fillet showed a pseudo-first kinetic order, and the plateau was attained at a time > 30 h. However, the equilibrium may not be ensured because of the low lipid fraction (fl) in fish (4.5%), which could lead to a local saturation of the tissue in contact with the SRM. The ratio between elimination and uptake constants (Ke/Ku) showed faster PAHs–SRM sorption than PAHs-fish tissue sorption (200 times); thus, fish with low fl will lead to faster SRM sorption. By contrast, in fish with higher fl, the long-term exposures will be necessary. The percentage of released deuterated PAHs from SRM during in vivo fish exposure was 1.6 times higher than that observed in the fish fillet, indicating an active clearance process. Therefore, during implantation, the rate of clearance and the fl should be considered to ensure detectable levels for applying the integrative equation based on dissipation modelling.
10 February 2026