- Article
The Effect of Family Ownership on Overall, Firm-Level, and Market-Level Corporate Transparency
- Euikyu Choi,
- Jongmoo Jay Choi and
- Moo Sung Kim
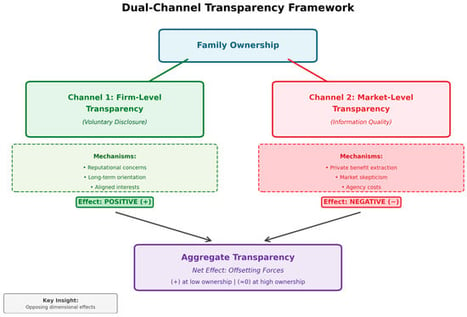
We examine how family ownership shapes overall corporate transparency by analyzing both firm-level and market-level transparency. Drawing on data from Korean-listed companies between 2001 and 2007, we construct separate indices measuring voluntary disclosure by firms, information quality as assessed by market participants, and overall transparency combining both dimensions. Our analysis uncovers a striking paradox: while family ownership positively correlates with firm-initiated disclosure efforts, it negatively relates to market participants’ assessment of information quality. These opposing forces result in no significant relationship between family ownership and aggregate transparency. However, when we partition our sample by ownership levels, firms with family stakes below 30% show significantly positive transparency associations, while those above this threshold exhibit no significant relationship. We interpret these patterns as reflecting a genuine commitment by family owners to enhanced disclosure that is systematically discounted by markets, with this skepticism becoming more pronounced as family control intensifies.
7 February 2026