Journal Description
Journal of Risk and Financial Management
Journal of Risk and Financial Management
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on risk and financial management, published monthly online by MDPI (since Volume 6, Issue 1 - 2013).
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, EconBiz, EconLit, RePEc, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q1 (Business, Management and Accounting (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 18.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 5.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Latest Articles
The Effect of Family Ownership on Overall, Firm-Level, and Market-Level Corporate Transparency
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 127; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020127 (registering DOI) - 7 Feb 2026
Abstract
We examine how family ownership shapes overall corporate transparency by analyzing both firm-level and market-level transparency. Drawing on data from Korean-listed companies between 2001 and 2007, we construct separate indices measuring voluntary disclosure by firms, information quality as assessed by market participants, and
[...] Read more.
We examine how family ownership shapes overall corporate transparency by analyzing both firm-level and market-level transparency. Drawing on data from Korean-listed companies between 2001 and 2007, we construct separate indices measuring voluntary disclosure by firms, information quality as assessed by market participants, and overall transparency combining both dimensions. Our analysis uncovers a striking paradox: while family ownership positively correlates with firm-initiated disclosure efforts, it negatively relates to market participants’ assessment of information quality. These opposing forces result in no significant relationship between family ownership and aggregate transparency. However, when we partition our sample by ownership levels, firms with family stakes below 30% show significantly positive transparency associations, while those above this threshold exhibit no significant relationship. We interpret these patterns as reflecting a genuine commitment by family owners to enhanced disclosure that is systematically discounted by markets, with this skepticism becoming more pronounced as family control intensifies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Economics and Finance)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Predictive Valuation of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Machine Learning Models in Decentralized Finance
by
Athanasios Kranias
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 126; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020126 (registering DOI) - 7 Feb 2026
Abstract
This study examines the pricing dynamics of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) in the secondary market using advanced machine-learning techniques. We construct a large dataset of Ethereum-based NFT transactions initially comprising over 500,000 raw blockchain observations spanning multiple NFT segments, including art, collectibles, gaming, metaverse,
[...] Read more.
This study examines the pricing dynamics of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) in the secondary market using advanced machine-learning techniques. We construct a large dataset of Ethereum-based NFT transactions initially comprising over 500,000 raw blockchain observations spanning multiple NFT segments, including art, collectibles, gaming, metaverse, and utility assets, over the period from November 2018 to March 2023. Following data preprocessing, synchronization across data sources, and the construction of history-dependent features, the analysis focuses on a final analytical sample of approximately 70,000 transactions. To address the challenges of non-fungibility, thin trading, and high price dispersion, we develop an interpretable predictive framework that integrates domain-informed manual feature engineering, automated Deep Feature Synthesis, and dimensionality reduction via Principal Component Analysis. Three non-linear models—Random Forest, XGBoost, and a Multilayer Perceptron—are trained and evaluated using both random and time-aware validation strategies. The results indicate that XGBoost consistently achieves the highest predictive accuracy, both overall and across individual NFT segments, while historical transaction prices emerge as the dominant predictor of future prices. Segment-level analysis reveals substantial heterogeneity in predictability, with art and collectible NFTs exhibiting more stable pricing patterns than gaming and metaverse assets. Overall, the findings highlight strong path dependence and reputation-driven valuation in NFT markets and demonstrate that carefully designed machine-learning models can deliver high predictive performance without sacrificing economic interpretability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Data and Technology: Shaping the Future of Finance, Accounting, and Business Systems Innovation)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Bridging Theoretical Assumptions and Empirical Evidence on Family Firms’ Tax Behavior: A Systematic Review
by
Cledilson Viana, Sérgio Cruz and Ana Dinis
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 125; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020125 - 6 Feb 2026
Abstract
This article provides a systematic review of the theoretical foundations underlying tax behavior in family firms. Drawing on 69 empirical studies indexed in Scopus and Web of Science, the review identifies three core limitations: the insufficient contextualization of socioemotional wealth (SEW) across cultural
[...] Read more.
This article provides a systematic review of the theoretical foundations underlying tax behavior in family firms. Drawing on 69 empirical studies indexed in Scopus and Web of Science, the review identifies three core limitations: the insufficient contextualization of socioemotional wealth (SEW) across cultural and institutional settings; the weak operationalization of SEW dimensions, often relying on indirect proxies; and the limited examination of the concrete actions firms take to minimize corporate income tax. We propose a research agenda anchored in a multi-layered framework that calls for contextual sensitivity, improved SEW measurement, and stronger empirical grounding in tax minimization mechanisms.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Tax Avoidance and Earnings Management)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Impact of AI and Innovation on MNEs’ Product Market and Financial Performance
by
Shumi Akhtar, Farida Akhtar and Jiongcheng Lu
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 124; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020124 - 6 Feb 2026
Abstract
This study empirically examines how artificial intelligence (AI) adoption and innovation shape product market dynamics and financial performance in multinational enterprises (MNEs) using a global firm sample over 1980–2023. We construct an unbalanced panel dataset by integrating textual analysis, manual verification, and data
[...] Read more.
This study empirically examines how artificial intelligence (AI) adoption and innovation shape product market dynamics and financial performance in multinational enterprises (MNEs) using a global firm sample over 1980–2023. We construct an unbalanced panel dataset by integrating textual analysis, manual verification, and data merged from nine major databases, identifying 411 AI-classified MNEs and a matched 411 non-AI MNEs. Using panel regression models with industry and year fixed effects, we test how AI intensity (the proportion of AI-related products/assets) and R&D—individually and jointly—affect product portfolio breadth and change, market share, industry concentration (HHI), and profitability. The results show that greater AI integration is associated with higher product diversification and a stronger competitive positioning, and that the interaction of AI and R&D is particularly important for explaining market share, concentration, and profitability differences across AI and non-AI MNEs. Overall, the findings highlight the strategic value of aligning AI adoption with innovation investments to strengthen product market outcomes and financial performance in global markets.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Transforming Business and Finance Across Different Sectors)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Property Tax, Local Sales Tax and Business Activity in Nevada: A Spatial Analysis
by
Quan Sun, Minjie Huang, Mehmet Tosun and Hao Sun
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 123; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020123 - 6 Feb 2026
Abstract
This study examines how business activity responds to local taxation, specifically property tax and local sales tax, in Nevada. Using county-level data for the period 1999–2014, we assess the impact of these taxes on various business activity indicators, including employment, annual payroll, the
[...] Read more.
This study examines how business activity responds to local taxation, specifically property tax and local sales tax, in Nevada. Using county-level data for the period 1999–2014, we assess the impact of these taxes on various business activity indicators, including employment, annual payroll, the number of establishments, and the number of small establishments categorized by size. Unlike previous studies that primarily focus on state-level taxation, our research delves into the effects of local tax instruments. By analyzing different components of the property tax (e.g., school district, county, and special district rates) and evaluating the specific effects of local sales tax changes, we provide a nuanced understanding of the local tax–business activity relationship. To address potential policy endogeneity in the sales tax rate, we instrument the sales tax rate using the lagged share of registered Democrats and implement an IV (control-function) spatial Durbin framework, ensuring robust estimates of within-period associations and spatial spillovers. Our analysis is intentionally confined to the 1999–2014 institutional regime, when Nevada businesses were primarily exposed to property and sales taxes. The estimates should, therefore, be interpreted as evidence on how the local tax mix and its components correlate with business activity under this pre-2015 fiscal structure, rather than as a direct forecast for the post-2015 environment shaped by subsequent policy changes and macroeconomic shocks. Across specifications, the IV-identified total effect of the sales tax rate is consistently negative for establishment-related outcomes. Nonetheless, the results remain informative for current debates on the design of local revenue systems because the underlying tax–service bundle and cross-jurisdictional spillover mechanisms continue to be central to local public finance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Real Estate Finance and Risk Management)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
The Impact of Insurtech on Insurance Inclusion: A Systematic Literature Review
by
Farai Borden Mushonga and Syden Mishi
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 122; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020122 - 6 Feb 2026
Abstract
Changing risk dynamics and the demand for more personalized, technology-driven services have spurred innovation in insurance through Insurtech, reshaping how insurance is supplied, purchased, and managed. This paper systematically reviews the impact of Insurtech on insurance inclusion, guided by the PRISMA-P protocol. The
[...] Read more.
Changing risk dynamics and the demand for more personalized, technology-driven services have spurred innovation in insurance through Insurtech, reshaping how insurance is supplied, purchased, and managed. This paper systematically reviews the impact of Insurtech on insurance inclusion, guided by the PRISMA-P protocol. The review finds strong evidence that Insurtech enhances insurance inclusion by lowering transaction costs, improving accessibility, and broadening market participation. These effects are most visible in short-term insurance, where digital platforms and tailored products reach previously underserved populations. Beyond this primary finding, the review highlights how insurance inclusion is conceptualized and measured in the literature. Quantitative measures typically include penetration rates, density, and the proportion of households with insurance coverage, while broader indices account for availability, usage, and accessibility of insurance services. Qualitative approaches often emphasize mismatches between the products offered and those needed, particularly for vulnerable groups. Similarly, studies of Insurtech adopt both demand-side indicators (such as product uptake and coverage per user) and supply-side measures (including patents, capital inflows, and innovation outputs). These insights suggest that fostering Insurtech development, while addressing regulatory, access, and equity concerns, can significantly improve insurance inclusion and narrow protection gaps.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue InsurTech Development and Insurance Inclusion)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Limits to Arbitrage and Speculative Bubbles in Emerging Stock Markets: Evidence from Gold-Backed Certificates
by
Turgay Yavuzarslan, Bülent Çelebi and Selman Aslan
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 121; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020121 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
This study examines the pricing efficiency of the Mint Gold Certificate (ALTINS1) traded on Borsa Istanbul and its relationship with the underlying asset (gram gold), focusing on the structural break identified in the data. Analyses conducted using Mann–Kendall trend analysis, the Pettitt structural
[...] Read more.
This study examines the pricing efficiency of the Mint Gold Certificate (ALTINS1) traded on Borsa Istanbul and its relationship with the underlying asset (gram gold), focusing on the structural break identified in the data. Analyses conducted using Mann–Kendall trend analysis, the Pettitt structural break test, Rolling Window regression, and the Threshold Error Correction Model (Threshold ECM) reveal that certificate prices have systematically decoupled from the underlying asset, creating a persistent premium exceeding 16%. The findings indicate that the risk structure of the certificate has diverged from the underlying asset, the market has become desensitized to high premium levels (asymmetric threshold effect), and prices move independently of fundamental value through a speculative feedback loop (Granger causality). The study argues that the root cause of this anomaly lies in the “Limits to Arbitrage” problem stemming from supply constraints and short-sale bans, offering new evidence on the pricing efficiency of financial innovations in emerging markets.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Behavioral Factors and Risk-Taking in Financial Markets)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Do Carbon Exchanges Make a Difference to Carbon Disclosure and Performance? Evidence from Indonesia
by
Ayu Oktaviani, Syahrial Shaddiq and Novika Rosari
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 120; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020120 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
The presence of the Indonesia Carbon Exchange (ICE) puts pressure on management to carry out its active role in reducing the potential of climate change through business strategies such as disclosure and improving carbon performance. This study seeks to prove the significant difference
[...] Read more.
The presence of the Indonesia Carbon Exchange (ICE) puts pressure on management to carry out its active role in reducing the potential of climate change through business strategies such as disclosure and improving carbon performance. This study seeks to prove the significant difference in carbon disclosure and performance after the launch of the ICE, as well as to review the profound differences in the increase in carbon disclosure and performance in the high and low-polluting sectors in the population of companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange for the 2022 and 2024 periods. The two research models used in formulating the results are the Wilcoxon test and the Difference-in-Differences model. The results of this study indicate a significant difference in carbon disclosure and performance after the launch of ICE, which illustrates the changing dynamics of environmental regulations encouraging companies to improve transparency and corporate carbon performance in an effort to maintain their legitimacy. This study shows that there was no significant difference in the comprehensiveness of carbon disclosure or the improvement in carbon performance between high- and low-polluting sectors after the launch of ICE.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Carbon Accounting, Climate Reporting, and Sustainable Finance)
Open AccessReview
The Sovereign Wealth Fund Paradox: Evolution, Challenges, and Unresolved Issues
by
David M. Kemme
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 119; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020119 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
Sovereign wealth funds enhance the international movement of capital and often facilitate economic development in domestic and host countries. However, the lack of transparency and accountability of SWFs varies, and state ownership gives rise to suspicions and realizations of political motivations, unfair commercial
[...] Read more.
Sovereign wealth funds enhance the international movement of capital and often facilitate economic development in domestic and host countries. However, the lack of transparency and accountability of SWFs varies, and state ownership gives rise to suspicions and realizations of political motivations, unfair commercial advantages, opportunities for corruption, and national security threats, thereby challenging the liberal economic order. This paper provides an overview and identifies major concerns and policy options associated with SWFs. Defining SWFs, measuring their size and transparency, domestic, cultural, and political origins, and policies for oversight and mitigation of geopolitical risk are discussed. The goals and behavior of SWFs are too diverse to draw broad, general conclusions. The growth in the number of funds and assets under management has increased their diversity, but the essential defining characteristic is that they are state-owned financial investment vehicles not subject to the hard budget constraints or regulations of comparable private sector, market-oriented entities. Transparency varies, with democratic country SWFs more transparent and less problematic than those of autocracies. SWFs have evolved into unbounded state-owned entities ushering in a new era of financial statecraft. Policies to guide their behavior and enforcement mechanisms are host-country specific and highly variable. An often-discussed international regulatory framework to mitigate geopolitical risk has not emerged and is not likely.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Globalization and Economic Integration)
Open AccessArticle
Examining the Role of Accountant’s Knowledge of Forensic Accounting, Corporate Governance Policies and Fraud Awareness Training in Preventing Fraud: A Survey of Indian Corporates
by
Rakhi P. Sangale, Dipak Santram Vakrani, Suresh B. Pathare and Jewel Kumar Roy
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 118; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020118 - 4 Feb 2026
Abstract
Corporate fraud remains a persistent problem that highlights the need for improved internal control and governance. Research on corporate governance (CG) and forensic accounting (FA) has been largely performed as separate studies. Little has been done to look at how accountants’ knowledge and
[...] Read more.
Corporate fraud remains a persistent problem that highlights the need for improved internal control and governance. Research on corporate governance (CG) and forensic accounting (FA) has been largely performed as separate studies. Little has been done to look at how accountants’ knowledge and the specific training of accountants in fraud awareness for their company’s leaders affect preventing fraud (FP). The study surveyed 150 accountants in India from April 2023 to May 2024. The results are based on Chi-Square testing and binary logistic regression. The study investigated how companies in India incorporate CG policy understanding and FG use for KMP and boards and how these factors affect FP. The findings indicate that understanding CG, using FA, and having specific training on fraud awareness for KMPs and boards of directors are all significant factors in reducing the occurrence of fraud. In addition, general employee training has no impact on FP. The theories of agency, stakeholder, and fraud triangle were combined to create one model to provide guidance to both organizations and regulators on how to institutionalize FG and to improve transparency in governance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Economics and Finance)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Measuring the Spillover Effects from the Stock Market Volatility in Selected Major Economies to the Stock Market Volatility in the United Kingdom
by
Minko Markovski, Salman Almutawa and Jayendira P. Sankar
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 117; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020117 - 4 Feb 2026
Abstract
This study investigates volatility spillovers from the stock markets of the United States, Germany, China, and Japan to the UK stock market using daily data from major benchmark indices (FTSE 100, S&P 500, DAX, Shanghai Composite, and Nikkei 225) and Brent crude oil
[...] Read more.
This study investigates volatility spillovers from the stock markets of the United States, Germany, China, and Japan to the UK stock market using daily data from major benchmark indices (FTSE 100, S&P 500, DAX, Shanghai Composite, and Nikkei 225) and Brent crude oil prices. Using a novel two-stage bootstrap framework, we first model time-varying conditional volatilities with GARCH-family models and compare them with long-memory FIGARCH specifications to account for persistent volatility dynamics. These volatilities are then incorporated into a VAR-X model, treating Brent crude oil price volatility as an endogenous or exogenous variable in robustness checks. To overcome limitations of traditional VARs, bootstrap-corrected GIRFs are employed to trace dynamic, order-invariant impacts across key sub-periods: the global financial crisis, Brexit, COVID-19, and the Ukraine war. We also benchmark our results against the Diebold–Yilmaz connectedness index and conduct rigorous out-of-sample forecasting and Value-at-Risk backtesting. Results reveal heterogeneous spillovers: US and German shocks trigger strong, immediate, and persistent UK market volatility, reflecting deep integration; Chinese shocks are delayed and gradual, while Japanese shocks are muted or short-lived. Spillover intensity is time-varying, peaking during global crises. Our model outperforms standard benchmarks in out-of-sample volatility forecasting and risk management applications. The study offers critical insights for investors seeking international diversification and for policymakers aiming to manage systemic risk in an interconnected global financial system.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Economics and Finance)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Internal Capital Markets and Macroprudential Policy Lessons from the 2007–2009 Crisis
by
Nilufer Ozdemir
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 116; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020116 - 4 Feb 2026
Abstract
Financial regulation assumes that parent firms reliably support distressed subsidiaries during crises. We test this assumption with evidence from the 2007–2009 financial crisis and find that parent support was selective rather than reliable. Using novel measures of sibling distress and granular parent-affiliate funding
[...] Read more.
Financial regulation assumes that parent firms reliably support distressed subsidiaries during crises. We test this assumption with evidence from the 2007–2009 financial crisis and find that parent support was selective rather than reliable. Using novel measures of sibling distress and granular parent-affiliate funding flows, our findings reveal that capital allocation within bank holding companies (BHCs) disproportionately favored stronger affiliates. The results show that BHCs channeled capital toward more liquid and resilient subsidiaries while limiting support to weaker ones. Profitable parents became increasingly selective under stress, and nonbank subsidiaries emerged as critical internal liquidity providers when external markets froze. This selective reallocation highlights a gap between regulatory doctrine and actual behavior: intra-group capital allocation mechanisms can amplify systemic stress rather than mitigate it. By examining overlooked internal market dynamics during this major financial crisis, the study offers insights for strengthening financial stability against future systemic shocks. Assessing parent firm strength alone appears insufficient. Effective crisis prevention requires supervisory frameworks that monitor sibling fragility across conglomerates, evaluate the liquidity roles of nonbank affiliates, and stress test intra-group capital flows.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Financial Markets and Institutions and Financial Crises)
Open AccessArticle
Do Shiller Macro and Micro Narratives Characterize the S&P 500 Index Returns? New Insights
by
Anastasios G. Malliaris and Mary Malliaris
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 115; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020115 - 4 Feb 2026
Abstract
We propose two narratives to analyze monthly returns for the S&P 500 Index. The first narrative emphasizes variables that represent the macroeconomy: Fed Funds Effective Rate, Real M2, 10-Year T-Note minus 2-Year T-Note, Shiller Housing Index, industrial production, and 1-Year Expected Inflation. The
[...] Read more.
We propose two narratives to analyze monthly returns for the S&P 500 Index. The first narrative emphasizes variables that represent the macroeconomy: Fed Funds Effective Rate, Real M2, 10-Year T-Note minus 2-Year T-Note, Shiller Housing Index, industrial production, and 1-Year Expected Inflation. The second narrative focuses on microeconomic fundamentals that include earnings, CBOE Volatility, consumer sentiment, interest rates, global price of copper, and the Dollar Index. We perform a methodology of 348 rolling regressions for each narrative, each with a sample of 60 monthly observations, and estimate the significance of the independent variables considered. We conclude that the microeconomic narrative with its indicators tied to stock market activities correlates with monthly returns more closely than macro fundamentals do. The new insight from this paper is that it is beneficial to employ both narratives as complementary rather than as competitive.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Editorial Board Members’ Collection Series: Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Diversity at the Top: How Ethnic Composition of Management Influences Corporate Performance in U.S. Companies
by
Silvia-Andreea Peliu
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 114; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020114 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
This paper aims to investigate the impact of ethnic diversity among employees and managers on firm performance, focusing on return on assets and return on equity. The analysis is conducted on a sample of 391 U.S. companies over a five-year period, 2020–2024. The
[...] Read more.
This paper aims to investigate the impact of ethnic diversity among employees and managers on firm performance, focusing on return on assets and return on equity. The analysis is conducted on a sample of 391 U.S. companies over a five-year period, 2020–2024. The quantitative framework includes a wide range of indicators related to financial performance, ethnic diversity among employees, ethnic categories of managers, and other control variables. The research methodology employs the ordinary least squares (OLS) method to highlight these effects, using fixed-effects and random-effects regression models, both linear and nonlinear. By estimating the regression models, the empirical results support the hypotheses established in the current state of the literature, indicating that ethnic diversity affects firm performance in a mixed manner, with both positive and negative effects on ROA and ROE. These findings are particularly relevant for practitioners, given the need to integrate minority representation into performance assessment, risk evaluation, and decision-making processes. Furthermore, regarding the female component within firms, this dimension contributes to the promotion of sustainability and a sound ESG-oriented approach. Consequently, social factors such as ethnicity can influence companies’ financial performance and shape how firms are perceived by investors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Trends and Innovations in Corporate Finance and Governance)
Open AccessArticle
Exploring Gender Diversity, Board Heterogeneity, and Corporate Risk Outcomes: Evidence from STOXX600 Firms
by
Nicoleta Tiloiu
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 113; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020113 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
This study examines the evolving role of board heterogeneity, including gender diversity, board attributes, and governance practices, in shaping corporate risk outcomes. In mature governance settings, corporate risk management emerges from the interaction between board structure, independence, leadership arrangements, and boardroom composition, such
[...] Read more.
This study examines the evolving role of board heterogeneity, including gender diversity, board attributes, and governance practices, in shaping corporate risk outcomes. In mature governance settings, corporate risk management emerges from the interaction between board structure, independence, leadership arrangements, and boardroom composition, such that gender diversity in isolation may no longer fully capture board effectiveness. We argue that while gender diversity remains relevant, its explanatory power operates in conjunction with other board characteristics that condition the quality of decision-making in already well-functioning boards. Using multiple regression estimations on a sample of STOXX600 firms, our main outcomes show that in mature European boards gender diversity (1) improves the operational efficiency, conditional by model specification, (2) increase debts level to finance growth, thereby enabling more rapid expansion than would otherwise be possible, without pushing to extensive borrowing, while reduce leverage starting 33% (3) prevents corporate failure starting 40% women on board (4) gender-diverse boards increase liquidity when critical mass is met (33%). Overall, the findings suggest that gender-diverse boards contribute to a reconfiguration of firms’ risk exposure across operational, financial, liquidity, and failure dimensions, rather than a uniform reduction in risk.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Trends and Innovations in Corporate Finance and Governance)
Open AccessArticle
Climate Performance and Firm Valuation: A Meta-Analysis of Tobin’s Q in the Post-IPCC AR6 Era
by
Akanksha Akanksha and Thirupathi Manickam
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 112; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020112 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
This study examines whether corporate climate performance is reflected in firm valuation by synthesising recent empirical evidence, using Tobin’s Q as a forward-looking indicator of market expectations. Employing a random-effects meta-analysis of 30 peer-reviewed studies published between 2020 and 2025 across multiple industries
[...] Read more.
This study examines whether corporate climate performance is reflected in firm valuation by synthesising recent empirical evidence, using Tobin’s Q as a forward-looking indicator of market expectations. Employing a random-effects meta-analysis of 30 peer-reviewed studies published between 2020 and 2025 across multiple industries and regions, the findings reveal a modest yet statistically significant positive association between stronger climate performance and higher market valuations, suggesting that investors increasingly incorporate climate-related information into firm pricing. Contrary to prevailing assumptions in the literature, proactive climate strategies, such as emissions-reduction initiatives, do not systematically generate greater valuation benefits than disclosure-oriented approaches; both exhibit comparable positive effects. Similarly, valuation outcomes do not differ materially between self-reported and externally verified climate data. Meta-regression analysis identifies data source as the only statistically significant moderator, although its influence remains nuanced. Overall, the results indicate that climate performance enhances firm valuation in a context-dependent manner, challenging the view that only proactive strategies or externally verified data are uniquely rewarded by financial markets. The study contributes to the sustainable and corporate finance literature by clarifying how capital markets price climate-related corporate behaviour under heterogeneous strategic responses.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Trends and Innovations in Corporate Finance and Governance)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Reimagining Value-Added Tax Reform Through Digital Rebates and Advanced Simulation for Inclusive Fiscal Policy
by
Vinodh K. Natarajan, Jayendira P. Sankar and Lamin Jarju
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 111; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020111 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
This paper examines the regressive nature of the value-added tax and proposes an integrated framework combining a uniform value-added tax rate with progressive, digitally administered rebates. The model was performed using household- and firm-level microsimulations with Monte Carlo methods. It demonstrates that equity
[...] Read more.
This paper examines the regressive nature of the value-added tax and proposes an integrated framework combining a uniform value-added tax rate with progressive, digitally administered rebates. The model was performed using household- and firm-level microsimulations with Monte Carlo methods. It demonstrates that equity can be reached without revenue neutrality being undermined. Simulation results for a calibrated 2024–2025 economy show the proposed rebate structure reduces the effective tax burden on the lowest income quintile from 13.5% to 5.4% of income, delivering a net cash benefit of USD 786.88 and a welfare gain of 6.10%. The policy is projected to generate a robust average VAT revenue of USD 17.44 million, with a 97.8% probability of a positive fiscal impact, while reducing the poverty rate by 2.6% and lowering inequality (Gini coefficient of utility to 0.199). The outcomes present a welfare gain for the poor, a small firm-level effect, and a decrease in poverty and inequality. The results suggest a feasible policy route towards a more equitable tax system, thus promoting indirectly to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), specifically SDG 8 (decent work and economic growth) and SDG 10 (reduced inequalities).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Business and Entrepreneurship)
►▼
Show Figures
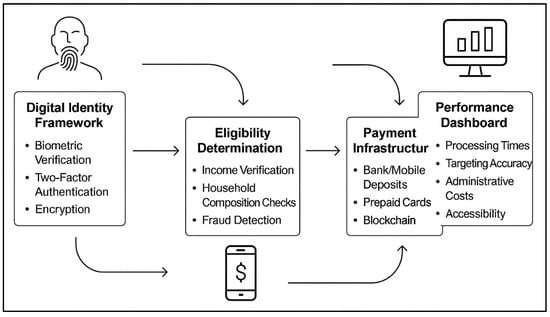
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
From Pricing to Integration: A PRISMA-Guided Systematic Review of ESG Integration and Risk Modelling in European Banking
by
Evanthia K. Zervoudi, Rafael Hadjimarcou and Apostolos G. Christopoulos
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 110; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020110 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
This paper conducts a PRISMA-guided systematic review of the empirical literature on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) risk integration in European banking. Using evidence systematically retrieved from Scopus, ScienceDirect, IDEAS/RePEc, and SSRN, the review synthesizes 51 peer-reviewed and working studies published between 2020
[...] Read more.
This paper conducts a PRISMA-guided systematic review of the empirical literature on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) risk integration in European banking. Using evidence systematically retrieved from Scopus, ScienceDirect, IDEAS/RePEc, and SSRN, the review synthesizes 51 peer-reviewed and working studies published between 2020 and 2025, reflecting the recent and rapidly evolving nature of this research field. The analysis classifies the literature into three domains—pricing and allocation, monitoring and stress testing, and governance and management control systems—and evaluates whether ESG variables operate as first-order drivers within production credit-risk models. The results indicate that while ESG signals are increasingly incorporated into pricing decisions, stress-testing exercises, and governance frameworks, no study provides verifiable evidence of full model-level integration within Probability of Default (PD) or Loss Given Default (LGD) models. The contribution of this review lies in systematically identifying the structural, data-related, and supervisory constraints that sustain this integration gap and in proposing a roadmap that distinguishes incremental ESG sensitivity from genuine prudential model embedding. Overall, the findings clarify that ESG responsiveness in European banking is substantial, yet integration into core risk models remains limited.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Banking and Finance)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Equity at the Top: Board Diversity and Executive Remuneration in South Africa
by
Gretha Steenkamp, Mareli Dippenaar, Tamzin de Lange, Jenna Frade and Cara Jordaan
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 109; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020109 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
For listed companies, board diversity is often associated with improved decision-making, sustainability and financial performance. However, prior studies have neglected the interplay between board diversity and executive remuneration, especially in developing countries, over extended time horizons, and at the level of individual executives.
[...] Read more.
For listed companies, board diversity is often associated with improved decision-making, sustainability and financial performance. However, prior studies have neglected the interplay between board diversity and executive remuneration, especially in developing countries, over extended time horizons, and at the level of individual executives. This study addressed this gap by examining the evolution of board diversity and executive remuneration in South African listed companies from 2002 to 2017. Specifically, it investigated trends in board diversity and the determinants of executive remuneration, with particular attention to gender and ethnic pay gaps. Descriptive and regression analyses were conducted on a dataset comprising 8835 executive-level observations. Findings reveal a steady increase in female and non-white executive representation, possibly to align with societal expectations and remain legitimate. However, persistent gender and ethnic pay gaps were also noted, which might indicate that white and/or male executives are more entrenched and able to extract additional remuneration in line with the managerial power theory. The study contributes to the literature by documenting long-term trends in diversity and remuneration, providing empirical evidence on the influence of demographic attributes on remuneration outcomes, and offering insights for regulators, investors and non-executive directors seeking to advance equity and effective governance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Research on Corporate Governance and Financial Reporting)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Financial Risk Management of Digital Services Companies Using Integrated Entropy-Weight TOPSIS Model
by
Weng Siew Lam, Weng Hoe Lam and Pei Fun Lee
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2026, 19(2), 108; https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm19020108 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
Digital services companies help in the digitalization and transformation of the industry in driving Malaysia by advancing the economy of the country. However, digital services companies often face financial risks in terms of liquidity, solvency, efficiency, profitability, and operational risks. These risks increase
[...] Read more.
Digital services companies help in the digitalization and transformation of the industry in driving Malaysia by advancing the economy of the country. However, digital services companies often face financial risks in terms of liquidity, solvency, efficiency, profitability, and operational risks. These risks increase the chances of failure and financial volatility, which put the companies at a serious disadvantage. This paper proposes an integrated Entropy-Weight TOPSIS model to analyze the financial risks of the listed digital services companies within Malaysia. The entropy method helps to prevent subjective weights by reflecting on information obtained from the financial reports of the companies. This study also provides an analysis to show possible improvements for the companies. The interest coverage ratio (ICR), which measures the capability to settle interest on debt, shows the highest weight followed by the basic indicator approach (BIA) and return on asset (ROA) based on the entropy weighting method. In addition, CLOUDPT, ITMAX, and MSNIAGA are ranked as the top three digital services companies that give the highest relative closeness to the ideal solution. The results help the risk managers to identify the criteria that caused the greatest financial risk in digital services companies to formulate targeted strategies to improve the companies’ financial health.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue AI and Emerging Technologies in Governance, Risk and Earnings Management)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal MenuJournal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Economies, IJFS, JRFM, Risks, Sustainability
Insurance and Risk Management Advances in the 4A Era—AI, Aging, Abruptions, and Adoptions
Topic Editors: Xiaojun Shi, Lingyan Suo, Feng Gao, Baorui DuDeadline: 30 May 2026
Topic in
Economies, JRFM, Risks, Sustainability
The Future of Global Finance and Business: Trends, Policies and Market Evolution
Topic Editors: John Malindretos, Giuliana Andreopoulos, Eleftherios Thalassinos, Ana Cristina SiqueiraDeadline: 31 July 2026
Topic in
Economies, IJFS, Sustainability, Businesses, JRFM
Sustainable and Green Finance
Topic Editors: Otilia Manta, Maria PalazzoDeadline: 31 October 2026
Topic in
Clean Technol., Economies, FinTech, JRFM, Sustainability
Green Technology Innovation and Economic Growth
Topic Editors: David (Xuefeng) Shao, Miaomiao Tao, Selena ShengDeadline: 31 December 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
JRFM
Investment Strategies and Market Dynamics
Guest Editors: Wayne Y. Lee, Craig G. RennieDeadline: 28 February 2026
Special Issue in
JRFM
Innovative Approaches to Financial Modeling and Decision-Making
Guest Editors: Gordon H. Dash, Nina Kajiji, Bruno Kamdem, Helper ZhouDeadline: 28 February 2026
Special Issue in
JRFM
Green Finance and Corporate Strategy: Challenges and Opportunities
Guest Editor: Lewis LiuDeadline: 28 February 2026
Special Issue in
JRFM
Applied Public Finance and Fiscal Analysis
Guest Editors: Andrey Zahariev, Borislav Dimitrov BorisovDeadline: 28 February 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
JRFM
Quantitative Advances and Risks in Asian Financial Markets
Collection Editors: Svetlozar (Zari) Rachev, Shigeyuki Hamori, Yasushi Hamao, Shuangzhe Liu, Ali Jaffri








