Abstract
This study assesses De Lone and McLean’s Information System (D&M IS) Success Model concerning DAS throughout small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in Saudi Arabia (SA). The present work mainly sought to evaluate the impact of information quality (IQ), system quality (SysQ), service quality (SrvQ) serving, system utilization, and user satisfaction (Usat) on the usage of the Digital Accounting System (DAS), which is posited to ultimately improve the quality of sustainable decision-making. The research utilized a quantitative methodology, employing a self-administered questionnaire to collect data from 328 decision-makers who are knowledgeable about actual DAS usage by SMEs in SA. Subsequent to gathering data, validation was conducted via Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) by utilizing smart-PLS software. The findings indicate that SysQ and IQ significantly influenced system utilization, although SrvQ did not. DAS was determined to significantly influence user happiness. Moreover, system utilization and user satisfaction positively influenced DAS, thereby affecting the sustainability of decision-making and reflecting the overall benefits of DAS. This work enhances the current IS literature by identifying the characteristics that affect the net advantages of DAS, with the suggested model evaluated in SMEs in SA utilizing DAS. This study serves as a reference to elucidate the significance of DAS and offers consequences, limitations, and prospects for further research.
1. Introduction
The proper functioning of every business depends on its accounting department. Even nonprofit organizations are governed by decisions made based on financial data (Al-Okaily et al., 2022a; Al-Hattami et al., 2025; Morshed & Khrais, 2025). As the technological revolution of the last few decades has reshaped the global landscape, it was inevitable that it would extend to everyday vocations and transactions. Technological developments and inventions have transformed the execution of numerous jobs in the accounting profession, leading to a continuous revolution (Mujalli et al., 2024; Smith, 2015). Initially, automation sought to alleviate the burden on accountants by employing technology to execute repetitive operations, thus allowing them to focus on more complex issues, resulting in a significant enhancement of their productivity (Al-Okaily et al., 2022b; Al-Hattami et al., 2025; Mujalli & Almgrashi, 2020). Historically, accountants have relied on paper and calculators to keep track of transactions and ensure the accuracy of ledgers. Currently, the focus is on employing innovative accounting ISs and techniques that have significantly enhanced the efficiency of the accounting profession (Schmitz & Leoni, 2019).
Traditionally, DAS has been referred to as a system a firm employs for gathering and processing its financial data and information. This information is then utilized by decision-makers to enhance the performance of the organization (Al-Hattami et al., 2025; Dagiliene & Šutiene, 2019). Nonetheless, there are a number of ways in which modern DASs diverge from their predecessors. One such difference is that software is currently concerned with Big Data, and this has opened up new possibilities for data mining (Balios, 2021; Lutfi et al., 2022b). Moreover, the present and future digital transformation movements are being propelled by the effects of blockchain technology and the Internet of Things (IoT) (Arief, 2024; Sandner et al., 2020). For instance, blockchain may enhance both transparency and safety by offering a shared ledger (Diedrich, 2016; Schmitz & Leoni, 2019).
Due to the aforementioned technology improvements that are occurring across various domains, such as accounting, the concept of business intelligence (BI) has garnered increased recognition in the academic literature (Al-Okaily et al., 2022a; Niu et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2020). BI refers to computerized techniques for converting data into information (Pirttimäki et al., 2006), which is ultimately utilized to improve the decision-making that is performed by an organization (Dagiliene & Šutiene, 2019; Lutfi et al., 2022e). The concept of BI includes DASs (Al-Okaily et al., 2022a; Klisarova-Belcheva et al., 2017; Rikhardsson & Yigitbasioglu, 2018), which is the primary emphasis of our study. Although the correlation between investment in BI and business value remains ambiguous (Krishnamoorthi & Mathew, 2018), the BI market is projected to exhibit a substantial and increasing share of the market (Niu et al., 2021; Qasim & Kharbat, 2020; Rane et al., 2024).
The information produced by these platforms enhances organizational success. Nevertheless, if this information is not effectively utilized in decision-making, it will exert only a minimal impact on a company’s overall performance (Al-Hattami et al., 2024, 2025; Jasim & Ibrahim, 2023; Lutfi et al., 2022e, 2022d; Saad, 2023). Up until this point, the connection between DASs and company success has remained a mystery, leaving a vacuum for scholars in the area of ISs, which includes accounting software (Al-Hattami et al., 2024). Moreover, contemporary firms must assess the advantages and disadvantages of DASs in order to validate investment and record their impact on the entity’s value (Al-Hattami et al., 2025). Consequently, the value of an organization can be directly correlated with the quality of the procedures taken for making decisions. Research (Al-Okaily et al., 2022a; Al-Hattami et al., 2024) reports that high-performing businesses employ rigorous analysis methods for making decisions at double the frequency of their lower-performing counterparts. These studies are employed to build strategies and facilitate daily procedures for making decisions.
In contrast, organizations may not consistently realize the anticipated advantages of digital systems if they disregard the factors that affect the utilization of the information they generate (Al-Okaily et al., 2022b). To achieve successful ISs, businesses have to succeed in both the technological implementation and cultivation of a conducive atmosphere for information utilization, particularly with attitudes towards information in procedures for making decisions (Popovič et al., 2012).
Over the years, business and government enterprises in Saudi Arabia have implemented measures to utilize DASs for improving operational capabilities and efficiencies. The rapid increase in DAS users has compelled the Saudi government to allocate funds and measures to address resource shortages in firms (Mohamed, 2025). Despite this attempt, companies in Saudi Arabia and other developing countries continue to grapple with fully leveraging DASs, especially with reference to their application in business analytics as well as decision support. It is for this reason that the decision-making modules and the related execution costs are complex. Consequently, decision-makers have leveraged their real-time information capabilities to assess and analyze functional data, resulting in favorable decision-making outcomes (Al-Hattami et al., 2025; Mohamed, 2025). Utilizing DASs for optimal information flow facilitates sound management decision-making, ultimately resulting in the attainment of the organization’s objectives and goals (Lutfi et al., 2022e; Monteiro & Cepêda, 2021; Mujalli et al., 2024).
Based on the above, the present study ascertains and evaluates the influence of DASs on the sustainability of management decision-making, as the sequential assessment of their effects on sustainability remains contentious, despite research existing on DASs (Al-Okaily et al., 2022a; Al-Hattami et al., 2024, 2025; Lutfi, 2022; Lutfi et al., 2022c). This study is based on a review of prior research that substantiates a direct correlation between DASs and associated IS domains and the quality of decision-making (Al-Okaily et al., 2022a; Fitrios, 2016; Nguyen & Nguyen, 2020; Saad, 2023). This study, related to comparable research in the literature (M. M. Alzoubi & Snider, 2020; Fadelelmoula, 2018), utilizes the De Lone and McLean (D&M) (DeLone & McLean, 2003) IS Success Model to examine the sustainability of managerial decision-making by assessing the quality parameters of DAS and user satisfaction.
This study adds to what is known about Information Systems (ISs) and Digital Accounting Systems (DASs) in a number of important ways. Initially, it builds upon previous research by empirically validating the IS Success Model (DeLone & McLean model) in the context of small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in Saudi Arabia, a developing economy with limited empirical evidence in this area. This study integrates business performance as a critical dimension and prioritizes user satisfaction as a central component of the effective utilization and successful implementation of DAS by analyzing the impact of DAS adoption on organizational outcomes. This study is one of the first empirical and theoretical attempts at explaining the link between DAS adoption and its affecting elements among Saudi SMEs. In doing so, it improves the D&M IS Success Model’s predictive and explanatory capabilities within the context of DAS. Additionally, the investigation emphasizes the importance of quality dimensions, including system quality, information quality, and service quality, in determining user satisfaction and the utilization of DAS. Consequently, it provides valuable insights into a relatively unexplored field of research.
This study also acknowledges the unique economic structure, cultural norms, and robust government support for digital transformation in Saudi Arabia, which may impact both the findings and their broader interpretation. The generalizability of these results to SMEs in other contexts should be approached with caution, as factors such as legislative frameworks, technological preparedness, and cultural differences may result in variations in IS success. Consequently, it is important to exercise caution. Even with these factors, the results show that using DAS can greatly improve the performance of a business by making it more competitive, efficient, and good at making decisions, which will eventually lead to growth and long-term success of the company. These insights are practical and relevant to policymakers, regulators, consultants, suppliers, and financial institutions, underscoring the strategic significance of DAS in facilitating economic transformation in emerging economies and promoting organizational success.
2. Literature Review
At the tail end of the twentieth century, wireless networking technologies like the extranet and intranet were invented, which completely changed how accountants could access and share information with their outside contexts. In addition, accountants and their clients can now communicate in a new way thanks to social media. The accounting profession is about to undergo a sea change due to recent technology developments (Abu Afifa et al., 2023; Al-Hattami, 2025; Al-Okaily et al., 2022a). These new digital tools have changed the way accountants do their jobs, making them more efficient and accurate (Mujalli et al., 2024). They have also changed the way professionals execute their duties, communicate with each other, and add value to their entities.
The digital revolution has dramatically transformed the corporate landscape through major shifts and advancements (Sidorova et al., 2024). Organizations have been compelled to acclimate to and manage new and forthcoming trends because of accelerated technological inventions and the necessity to implement rapidly changing technology (Al-Okaily et al., 2022a). Automation is advancing across interconnected industries, particularly in auditing, where experts have recognized four essential principles for automation: big data, cloud accounting, IoT, and blockchain (Zhang et al., 2020). These methodologies are being documented in the accounting arena, and scholars are emphasizing their ability to assist automation in accounting. Currently, accountants have the ability to be involved in more complex analyses and attain statistical accounting outcomes with enhanced proficiency to predict the organization’s financial status (Al-Okaily et al., 2022a).
The application of the four previously described principles in the accounting field, in differing degrees, enhances the electronic reading, analysis, and transfer of critical information for accounting processes (Mujalli et al., 2024; Saad et al., 2022). Effective cooperation significantly decreases the necessity for manual record-keeping, permitting a single individual to utilize technology for the comprehensive preparation of all accounting records (Mujalli et al., 2024). For instance, blockchain technology has facilitated various elements of the accounting field. All members possess access to all transactions on the blockchain, and this enhances audit capabilities and trustworthiness. Eventually, it reduces fraud, as alterations to the blocks are very challenging to execute; therefore, such incidents are rare, and if they occur, all participants can identify the modification and who did it. An additional benefit of employing blockchain in this situation is that two parties engaged in a transaction can exchange invoices via the blockchain, thus accelerating the transaction procedure, minimizing paperwork, and avoiding misappropriation (Fanning & Centers, 2016). Nonetheless, there are challenges associated with this new technology. Despite possessing several commendable attributes, individuals remain apprehensive about system stability, data privacy, and the adequacy of available tools to ensure optimal functionality (Barreto et al., 2025; Qasim & Kharbat, 2020). Transitioning entirely to digital systems necessitates substantial financial investment in education, infrastructure development, and the protection of sensitive financial information from cyber threats (Simatupang, 2024).
As a result of technological advancements, the term “business intelligence” (BI) has become more prevalent in the body of scholarly writing (Morshed & Khrais, 2025; Niu et al., 2021; Popovič et al., 2012). BI refers to the array of computerized techniques employed to transform data into information (Aljawarneh et al., 2023), ultimately utilized to advance procedures for making decisions (Al-Okaily et al., 2022a). These days, DASs play a significant role in business intelligence solutions used in the accounting industry. They assist organizations in monitoring their financial performance, identifying trends, and enhancing decision-making via data analysis (Aljawarneh et al., 2023; Morshed & Khrais, 2025). Consequently, business intelligence serves as both a technology and a managerial instrument, hence enhancing accountants’ strategic role in facilitating organizational success.
Conversely, the quality of decision evaluates the degree to which the results of a decision align with what the organization anticipates (Al-Okaily et al., 2022a; Al-Hattami et al., 2024, 2025; Saad, 2023; Visinescu et al., 2017). Prior research indicated that decision quality is affected by various issues, including the quality of information in the procedure for making decisions. Nevertheless, according to academic studies and practitioners, users in numerous organizations may not always associate their BI abilities with the procedure for making decisions (Morshed & Khrais, 2025; Visinescu et al., 2017). This gap highlights the need to strategically integrate BI systems with accounting services to ensure that data-driven insights are not only generated but also used for informed managerial decision-making. In conclusion, the ongoing advancements in accounting technology demonstrate the transition from traditional bookkeeping to intelligent, analytics-driven decision-making. Accountants are expected to serve as strategic advisors, using technology to facilitate organizational growth, manage risks, and derive new insights. To use these advantages, accountants in the contemporary digital economy must possess the ability to acquire new skills, demonstrate adaptability, and exhibit proficiency in technology utilization.
3. Theoretical Underpinning and Hypotheses Development
The D&M IS Success Model (2003) was chosen for this study because it has the capacity to assess intricate information systems, as well as the development, distribution, and application of process information and causal factors that could affect end users. Mason (Taufik, 2022) states that the D&M model (1992) classified IS success into six groups based on six factors: information Quality (IQ), System quality (SysQ), user satisfaction (US), individuals, and the influence of the organization. These groups originated from an analysis of 180 studies that measured the performance of IS/IT. DeLone and McLean (2003) revised the first model by incorporating SevQ and adjusting the individual’s and organization’s impacts with reference to net benefit. Belief in the system’s quality and one’s experience using it are said to influence the individual’s attitudes and subsequent actions in the revised model. The model postulates that users’ views of the net benefits are influenced by the interplay between IQ, SysQ, and SrvQ, as well as their intentions to utilize the system and their level of satisfaction with it (DeLone & McLean, 2003; Petter & McLean, 2009).
Furthermore and in regard to the tasks that were accomplished, we also took into account the model’s usefulness as a model for measuring the success (efficiency) of IS and its adaptability to different levels of analysis (Morshed & Khrais, 2025; Mujalli, 2024b; Petter et al., 2008). It is evident that the system’s successful performance is influenced by all three aspects of quality dimensions: information quality (IQ), system quality (SysQ), and service quality (SrvQ). These are clearly important to the system’s efficient operation. System utilization, user happiness, and net benefits are the metrics used to measure the effectiveness of a model. So, the revised and improved version of the IS success framework, which is the basis for the quality of IS assessment, makes it easier to use in many situations, including when DASs are adopted and used.
To attain this objective, the study integrates other elements pertaining to user pleasure that are distinct from the system’s technical characteristics, including IQ and SQ. This combination aims to represent certain organizational traits essential for the effective use of information systems (Urbach & Ahlemann, 2010). Considering that the objective of Information Systems (IS) is to initiate and enhance relationships among diverse business entities within a singular supply chain (Cullen & Taylor, 2009), it is essential to examine elements beyond the technical system components and incorporate factors that demonstrate how IS users engage and collaborate. Consequently, the present research study enhances the model by including the net advantages of DAS utilization, which have been overlooked in existing DAS research and the IS success framework. Despite the extensive application of the IS success model in prior research to assess information systems’ effectiveness, these studies have predominantly overlooked its application in evaluating decision support systems within organizational contexts (Ifinedo et al., 2010; Lutfi et al., 2022b) and the exploration of decision-making sustainability as an exogenous variable.
The study uses extra factors for user happiness that are specific to the technical aspects of the system, such as IQ and SevQ, in order to reach this objective. Among these variables are intelligence and social intelligence assessments. The purpose of this combination is to illustrate specific organizational characteristics that are indispensable for the effective implementation of information systems (Cullen & Taylor, 2009; Urbach & Ahlemann, 2010). These characteristics are intended to be reflected in this combination. Consequently, it is essential to examine the aspects that extend beyond the technical system components and to incorporate components that demonstrate the manner in which IS users interact and collaborate. This is due to the fact that the purpose of ISs is to forge and enhance relationships among a diverse array of business entities that operate within a singular supply chain (Cullen & Taylor, 2009). Consequently, the current research study expands the model’s scope. This is accomplished by incorporating the net benefits of utilizing DASs, which have not been taken into account in previous studies on DASs or in the framework for the success of ISs. Despite the fact that the model of IS success has been extensively employed to assess the success of ISs in previous studies, these studies have largely disregarded the investigation of the decision-making sustainability as an exogenous factor and the application of the framework to evaluate DASs within the organization (Al-Okaily et al., 2022a; Al-Hattami et al., 2025).
The D&M Success model was employed as the foundational model in previous research endeavors to evaluate the extent to which IT/IS technologies influence business performance (J.-S. Chou & Hong, 2013; Ifinedo et al., 2010; Xie et al., 2014). An examination of these attributes illustrated the model’s capacity to illuminate the correlations between enhanced organizational performance and IT/IS technologies. In this study, I will examine the impact of DASs on user satisfaction and the sustainability of decision-making, with IQ, SysQ, and SrvQ serving as independent variables. Additionally, the investigation investigates whether there is a correlation between the quality of sustainable decision-making, the utilization of DDAS, and the United States. The D&M Success model was employed as the fundamental model to assess the influence of IT/IS on the performance of enterprises in previous research (J.-S. Chou & Hong, 2013; Ifinedo et al., 2010; Xie et al., 2014). Based on the findings of their investigation, the model has the potential to illuminate the connections between improved organizational performance and IT/IS technologies. I will investigate the impact of the utilization of DASs on the sustainability of decision-making and user satisfaction in this study. SysQ, IQ, and SerQ will function as independent variables. The research also investigates the potential correlation between the use of DASs and the process of making sustainable decisions. Figure 1 displays the theoretical research framework that has been suggested.
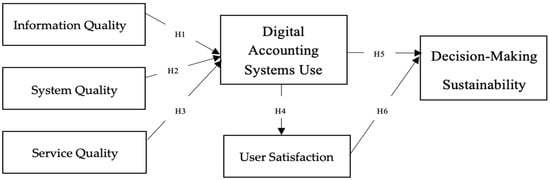
Figure 1.
Theoretical Research Framework.
3.1. Information Quality
Information quality (IQ) has been the subject of much study in the field of ISs because it is prominent in the adoption of IT in the business world. When we talk about the system’s capability to give users precise, complete, and up-to-date information, we are talking about IQ. The goal of the quality of IT guarantee is to evaluate the accuracy and usefulness of data created by IT systems in order to reduce the occurrence of transactional mistakes (DeLone & McLean, 1992, 2003). A clear conclusion has not been drawn from previous research on the association between intelligence and embracing of IT, because the results have been contradictory (Li & Wang, 2021). While some research has revealed that intelligence and embracing of IT have strongly influenced DAS (Al-Okaily et al., 2022a; Al-Hattami et al., 2025), other studies have discovered no such correlation (Daoud & Triki, 2013; Jaoua et al., 2022). Many aspects of intelligence, according to research (Al-Hiyari et al., 2013) have little bearing on the uptake of IT. The subsequent hypothesis is proposed for examination:
H1.
IQ significantly influences DASs.
3.2. System Quality
In addition to IQ, system quality (SysQ) is regarded as a principal construct of the model of success for IS in De Lone and McLean’s (DeLone & McLean, 2003) framework, characterized by the degree of technical effectiveness of the system, encompassing ease of use, reaction time, dependability, security, and adaptability. An effective DAS is one that enhances user experience, with evaluations grounded in users’ perceptions of the DASs and their usability. SysQ is a crucial factor affecting the utilization of DASs within organizations. According to DeLone and McLean (2003), information systems that are designed and implemented proficiently can be very consequential in efficient ISs. Even though this construct was not theorized to directly influence DASs usage in the framework of IS success, most dedicated studies have tested the direct association, resulting in inconsistent findings (M. M. Alzoubi & Snider, 2020).
Thus, this study updated De Lone and McLean’s IS success model to include human-related factors, taking into account the effect these factors have on decision-making and the use of DASs in businesses. A strong correlation between SysQ and IS usage was detected in the results (Almaiah et al., 2022; M. M. Alzoubi & Snider, 2020; Quintero et al., 2009). After analyzing the effects of IT deployment, Lutfi et al. (2022g) discovered that SysQ significantly affects IT utilization. This is consistent with the results given by Xu et al. (2013), who used the 3Q model—a combination model of technology utilization established by Nelson et al. (2005)—to study the effect of SysQ on the adoption of ISs. According to the authors’ findings, SysQ exerts a significant effect on the utilization of IT. Negash et al. (2003) reported a beneficial relationship between SysQ and customers’ web-based assistance systems, which accords with this line of research. However, since they focused on web-based IS within the organization, it is important to explore constructs in various settings. Therefore, the following hypothesis is suggested here:
H2.
SYSQ significantly influences DASs.
3.3. Service Quality (SerQ)
Another aspect in the model of IS success is SerQ, which consists of indicators such as assurance and empathy. The IS must deliver knowledge free from hazards and risks (Lutfi et al., 2022b; Mujalli, 2024b), and it should facilitate ease of utilization while conveying and comprehending the user’s requirements. SerQ assesses the caliber of services provided by ISs and serves as a tool for marketing researchers to assess SerQ (Dehghanpouri et al., 2020; Mujalli, 2024b). It is a factor of Information System effectiveness, facilitating user help via the IS department, and is frequently assessed throughout system trustworthiness, responsiveness, and empathy in support services (Saad, 2023).
The evaluation of the efficiency of IT service components has become increasingly significant, with SerQ representing a vital dimension of ISs in a competitive landscape for organizations seeking service improvement and assessment of IT utilization (M. M. Alzoubi & Snider, 2020). Concerning this concept, Al-Hattami et al. (2024) stated that effective SerQ in relation to DASs enhances and streamlines system integration across the business, including necessary user assistance, all of which leads to better organizational performance. In a comparable study, Chang et al. (2012) acknowledged there was a favorable association between SerQ and IS usage. Nevertheless, particular research studies (Al-Hattami, 2025; Lutfi et al., 2022b; Mujalli, 2024b; Negash et al., 2003) revealed no significant correlation between the two notions, resulting in persistent ambiguity regarding SerQ findings in the literature. According to the DeLone and McLean (2003) paradigm, the elements of SerQ might have differing significance depending on the analytical context and circumstances; consequently, the following hypothesis is posited:
H3.
SrvQ significantly influences DASs.
3.4. Digital Accounting Systems Usage
A study focused on system information characterized system utilization as the extent of effort invested in interacting with the information systems, reflecting the output made through the system relative to a time unit (Al-Hattami et al., 2025; Bokhari, 2005; Mujalli et al., 2024; Trice & Treacy, 1988). The use of the system fundamentally depends on users’ evaluations regarding its impact on work performance and decision quality (Lutfi et al., 2022b). This would inherently result in heightened user satisfaction and increased usage regularity (M. M. Alzoubi & Snider, 2020). According to research (H.-W. Chou et al., 2014; Lutfi et al., 2022e; Mujalli, 2024b), user satisfaction is the extent to which the system information meets the users’ needs. This implies that satisfaction is derived from the user’s experience with information inquiry, satisfaction, and decision-making outcomes.
Satisfaction among users is a concept within the DASs framework that pertains to system utilization (J.-S. Chou & Hong, 2013), wherein system usage facilitates decision-making and improves both efficiency and productivity (H.-F. Lin, 2010; Lutfi et al., 2022e). User satisfaction and usage are quantifiable characteristics, with previous studies highlighting three primary metrics of usage: duration in hours, frequency of use, and level of engagement (H.-W. Chou et al., 2014; H.-Y. Lin et al., 2006; Ramli, 2013). User satisfaction was evaluated using four different measures in other research (Hsu et al., 2015; Wixom & Todd, 2005). These measures were as follows: the satisfaction with the service, the satisfaction with the information, and the satisfaction with the overall DASs. The existing study aims to find if there is a correlation between DASs use and user satisfaction that significantly influences decision-making sustainability:
H4.
DAS use has a significant influence on user satisfaction with the system.
H5.
DAS use has a significant influence on decision-making sustainability.
3.5. User Satisfaction
Another measure of IS success is user satisfaction, which includes signs of recurrent visits and repeat purchases. Previous studies indicate there is variation between the information needed and the information obtained (Alsyouf et al., 2022; Alsyouf & Ishak, 2018). Information satisfaction generally arises from the comparison between the demands of the information system and its actual performance. On the other hand, recurrent purchases indicate overall contentment with the system, assessed by evaluating the satisfaction levels of the information system and the advantages derived from the input–output procedure (Alsyouf et al., 2021).
Concerning the sustainability of decisions, the quality as well as values inherent in the users’ choices determine the subsequent outcomes or consequences (Lutfi et al., 2022e; Wang et al., 2023). Within the DASs setting, the system’s delivery of precision, accuracy, and information reliability serves as the criterion for assessing the quality of decision-making (Alalwan et al., 2014; Arora & Kumar, 2022). According to one study (Bhattacherjee, 2001), the effective utilization of the system is somewhat contingent upon user happiness; hence, it is posited that the frequency of DAS usage, in conjunction with user satisfaction, will contribute to improved sustainability of decision-making. Therefore, it is suggested that:
H6.
User satisfaction has a significant impact on decision-making sustainability.
4. Research Methodology
4.1. Instrument Measurement
The study utilized a questionnaire originally created in English and subsequently translated into Arabic. The questions aimed to evaluate the study’s hypotheses (Mujalli, 2024b). The items have been chosen and derived from reputable research in DASs and information systems, preserving the original metrics to ensure their validity within the study’s framework. Four specialists in DASs and information systems participated in the formulation of the questionnaire, which was subsequently pre-tested to assess its clarity, relevance, comprehensibility, and ensure that any vagueness was removed, consistent with prior research (e.g., Almagrashi et al., 2023; Lutfi et al., 2022e; Mujalli, 2024b). Furthermore, five field specialists performed an exhaustive evaluation of the questionnaire. Minor adjustments were implemented to improve clarity and facilitate completion according to their feedback. The definitive iteration of the questionnaire employed a 5-point Likert scale, spanning from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree). Table 1 below indicates the measurement variables employed in the present study along with their corresponding sources.

Table 1.
Constructs, measurements and their source.
4.2. Sample, Data Gathering Process and Ethical Considerations
The study population comprises managers, accountants, and employees from SMEs in SA who execute DASs. The sample size was established according to the varied attributes of the population and the requisite accuracy of the results. A commonly endorsed criterion for establishing sample size in studies employing SEM recommends a minimum of ten participants for each observed variable (Hair et al., 2019). This study, which examines a single construct using 21 items, necessitates a minimum sample size of 210 (21 × 10). The sample size must not be smaller than this level. Kline (2023) additionally advocates for a minimum of 200 participants for SEM analysis, reinforcing this criterion.
The questionnaires were distributed both in person and via Google Forms, with all respondents permitted to complete the survey only once. Participants were requested to engage by providing their email addresses on the organization’s website. Ethical standards for human research were rigorously maintained, encompassing the acquisition of informed permission, the protection of participants’ rights, and the prevention of harm, the assurance of secrecy regarding their names and replies, and the preservation of professional research integrity. Participation was wholly voluntary, devoid of any coercion. All replies were maintained in confidence, and the data will be accessible upon request for scholarly reasons.
Eight hundred questionnaires were sent out to decision-makers, including accounting managers, who work in a variety of SMEs in SA. These people were requested to oversee the dissemination of the surveys to the real end users. This methodology was selected due to the direct accountability of accounting managers for organizational accounting operations and their good understanding of the target customers. Consequently, 348 complete surveys were submitted, resulting in a response rate of 43.5%. Table 2 presents a comprehensive summary of the respondents’ returns.

Table 2.
Presents a comprehensive summary of the respondents’ returns.
4.3. Demographic Characteristics of Respondents
The study included 348 participants, comprising 70.7% male and 29.3% female respondents. The majority were aged 30 to 39 (67.8%) and were employed as accountants (59.2%). The predominant group possessed a bachelor’s degree (74.7%) and had 5–9 years of experience in the position (68.1%). Likewise, 65.8% had utilized DAS for a duration of 5 to 9 years. Table 3 summarizes the demographic features of the study’s participants.

Table 3.
Participants’ characteristics.
5. Analysis of Data and Results
5.1. Statistical Approach
Utilizing two statistical programs, SPSS (v 29) and Smart PLS (v 4.1.0.8), the gathered data was examined. This study tested the hypothesized research model employing partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) (Almgrashi & Mujalli, 2024; Hair et al., 2019; Mujalli et al., 2022; Shmueli et al., 2019). In the context of SME, PLS-SEM is expected to profoundly influence upcoming research techniques (Mujalli, 2024a). The PLS-SEM approach was used because it works best in complex models with a large number of associated indicators. Previous studies have demonstrated that data does not need to be distributed widely to apply PLS-SEM (Hair et al., 2019). Again, it is a non-parametric method of estimation that is particularly efficient when the sample size is small or limited (Almagrashi et al., 2023; Mujalli, 2021).
In order to determine the significance of the factors, the researchers employed the well-known bootstrapping technique (Hair et al., 2019; Shmueli et al., 2019). For bootstrapping, the researchers used 5000 iterations. To achieve that, we investigated the variables’ path coefficients (Hair et al., 2019; Shmueli et al., 2019). The researchers used a two-stage technique to analyze the data correctly and followed the principle of PLS-SEM. The measurement model was broadly assessed in the first phase, and then the structural model was computed in the second phase.
5.2. Normality Test
The researchers employed an online calculator to conduct a multivariate normality test, evaluating the data’s adherence to multivariate normality as defined by Mardia (1970). Establishing multivariate normality is crucial for improving the model’s prediction accuracy. The test findings demonstrated substantial multivariate skewness (β = 170.666, p < 0.001) and kurtosis (β = 1047.357, p < 0.001), indicating a breach of the multivariate normalcy assumption (refer to Table 4). Due to its non-normality, Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) is appropriately utilized for analysis, as it adeptly manages non-normally distributed data (Hair et al., 2019; Shmueli et al., 2019). This additionally justifies the selection of PLS-SEM for this research.

Table 4.
Normality test.
5.3. Common Method Bias (CMB)
CMB typically arises when data originates from a singular source (Avolio et al., 1991) and poses challenges in self-reported data analysis (Spector, 2006). It influences the validity of the study and has an impact on the structural connection (MacKenzie & Podsakoff, 2012). The potential risk of CMB may be reduced in research in two different ways: firstly, through the usage of statistical control and secondly, through the usage of procedural design. The procedural design facilitated anonymous responses, the questionnaire was succinct, demographic items were positioned at the end, and the questionnaire was subjected to a pilot test before the final data collection stage. Privacy standards have been introduced to cultivate a setting of trust and promote genuine replies.
Conversely, the study utilized two stages of statistical control techniques for statistical control. In the first stage of the process, the CMB problem was verified by utilizing Harman’s one-factor test, which is also known as principal component analysis (PCA). The results of this test revealed that the highest variation explained was 43.71% of the total variance, which is lower than the standard of fifty percent recommended (MacKenzie & Podsakoff, 2012; Podsakoff et al., 2012). In the second stage of the procedure, a multicollinearity analysis was carried out in order to determine the degree of correlation that exists between the independent constructs. Following Kock’s (2015) recommendation, the full-collinearity test was utilized. The variance inflation factor (VIF) values over 3.3 signify the presence of collinearity among the variables (Hair et al., 2019). According to Table 3, every single VIF score fell within the acceptable range. As a result, it was suggested that multicollinearity did not impair the capacity of the predictors for accurately predicting the dependent construct. Consequently, the results confirm that CMB does not pose an issue for the present investigation.
5.4. Assessment of Measurement Model
Initially, the researchers assessed the measurement model to determine its overall accuracy and dependability. To do this, the researcher ensured the collection of comprehensive quality indices on various perspectives related to the influential factors. To ensure the constructs’ reliability, the factor loadings, Cronbach’s alpha (α), and composite reliability (CR) need to exceed 0.70 (Hair et al., 2019; Shmueli et al., 2019). The factor loading (λ) values exceeded the predicted threshold of 0.70 (Mujalli, 2024a). Furthermore, the α and CR results exceeded the minimum needed threshold (see Figure 2). In addition, to evaluate the components’ convergent validity, the average variance extracted (AVE) was used. Hair et al. (2019) state that AVE values greater than 0.50 are required. The study outcomes demonstrate that all AVEs meet the criterion of 0.5, confirming the presence of convergent validity (Almgrashi & Mujalli, 2024; Hair et al., 2019; Shmueli et al., 2019). These results are presented in Table 5.
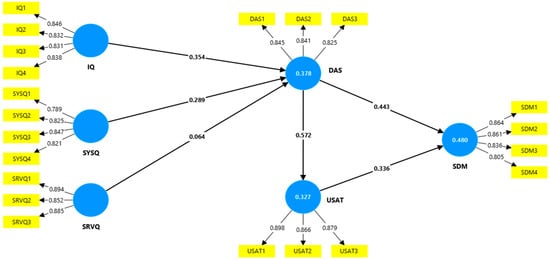
Figure 2.
Results of the measurement model.

Table 5.
Factor loadings, Cronbach’s alpha (α), composite reliability (CR), and average variance extracted (AVE) values.
Table 6 summarizes the evaluation of the discriminant validity of the constructs (DAS, SDM, IQ, SevQ, SysQ, UsaT) by utilizing two widely used methods: Heterotrait–Monotrait Ratio (HTMT) and the Fornell & Larcker criterion. Kline (2023) indicated that the HTMT ratio value needs to be a maximum of 0.85. All HTMT ratio values in this investigation remain below the threshold, indicating the absence of a discriminant validity issue. Table 6 represents the results of discriminant validity.

Table 6.
Discriminant validity and VIF values.
5.5. Structural Equation Model (SEM) Assessment
A SEM analysis was conducted using SmartPLS 4 to evaluate the hypothesized relationships between the constructs in the model. This study employed PLS-SEM methodologies to investigate the impact of various independent variables on several dependent variables. To analyze the results of the research framework, the researcher first determined the significance of the path coefficient (β) and then calculated the coefficient of determination (R2).
In Table 7, the analysis discovered that DAS is positively and significantly correlated with IQ (β = 0.354, p < 0.001) and SYSQ (β = 0.289, p < 0.001), thereby supporting hypotheses H1 and H2. In contrast, SRVQ has no significant impact on DAS (β = 0.064, p > 0.05), which does not support hypothesis H3. Again, DAS has a substantial effect on USAT (β = 0.572, p < 0.001) and SDM (β = 0.443, p < 0.001), supporting hypotheses H4 and H5. Finally, there is a strong and significant association between USAT and SDM (β = 0.336, p < 0.001). As a result, hypothesis H6 was supported. Figure 3 represents the results of the significance.

Table 7.
Assessment of the path relationships.
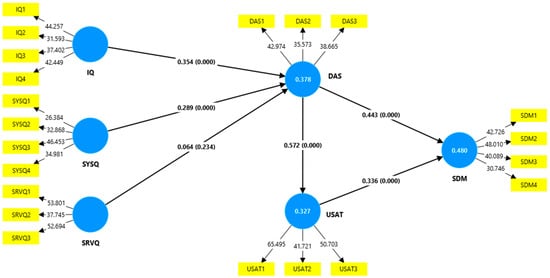
Figure 3.
Results of the structural equation modeling.
5.6. Estimation of the Explanatory Power of the Model
This research determined the explanatory power (R2) of the proposed research framework. It is a statistical measure that evaluates the level to which a regression model accurately reflects the observed data. It measures the extent to which the independent factors can forecast the dependent variable’s variability. R2 represents the degree to which the model accurately fits the data. A number close to 1 indicates a better fit, while a value of 0 suggests that the model does not account for any variation in the dependent variable (Hair et al., 2019). It plays a vital role in assessing the outcomes of regression models for: firstly, providing an understanding of actual events; and secondly, for making projections.
Concerning the total percentage of variation explained by each of the independent variables under consideration in the sample, the R2 values for DAS, USAT, and SDM were 0.378, 0.327, and 0.480, respectively. As a result, the exogenous constructs accounted for 37.8% of the variance in DAS, 32.7% in USAT, and 48.0% in SDM. So, the framework has a good explanatory power of these outcomes. Subsequently, the researchers assessed the predictive significance (Q2) of the framework (Shmueli et al., 2019). A Q2 score over zero signifies substantial predictive relevance. A Q2 value of 0.260, 0.248, and 0.336 for DAS, USAT, and SDM, respectively, indicated that the framework has outstanding predictive relevance.
Furthermore, goodness of fit (GoF) is another metric for assessing model competence. Some authors (Hair et al., 2019; Shmueli et al., 2019) proposed a method to evaluate standardized root mean square residuals (SRMR) with an acceptable maximum value of 0.080. In this study, the SRMR value was 0.055, which was less than the threshold value. Based on this value, it is possible to state that the above-specified model adequately described the data.
6. Research Discussion
The current study contributes to the existing body of knowledge by evaluating the D&M model’s quality constructs and showing that, with the exception of SerQ, all of the parameters significantly affected DAS adoption. The study detected no significant influence of SerQ on DAS utilization, but it did corroborate and verify the conclusions of previous studies regarding information and SysQ and their impact on usage and user satisfaction (M. M. Alzoubi & Snider, 2020; Yakubu & Dasuki, 2018). The results are consistent with certain research studies (M. M. Alzoubi & Snider, 2020; Heo & Han, 2003; Lutfi et al., 2022g; Marble, 2003; Mujalli, 2024b), but they also disprove D&M claims that SerQ is a key factor in determining system performance and usage. This unexpected result is because many respondents were dissatisfied with the services provided by their accounting information systems department. They voiced concerns about communication breakdowns, unfulfilled promises, and delays caused by a lack of technical support. This could be because the study was conducted in a specific setting, where the lack of technical skills in developing nations’ organizations, especially in their respective IS departments, makes it impossible for them to fully utilize all of the features of the DAS. As a result, decision-makers utilizing DAS should undertake technical courses that teach them more than just basic computer skills.
The findings concerning the positive DAS usage and satisfaction usage correlation were anticipated, with SysQ and InfQ having an impact on DAS usage as well, which improved USat. Evidence suggests that SysQ is the most important factor in predicting DAS adoption; this might be due to the fact that different types of companies place different amounts of weight on the IS Success Model’s individual elements (M. M. Alzoubi & Snider, 2020; Heo & Han, 2003). According to some research (Al-Hattami et al., 2024; Mujalli, 2024b; Petter et al., 2008), firms that use centralized computing, for example AIS, emphasize a greater emphasis on SysQ than InfQ. Incorporating DAS‘s flexibility and dependability features, this discovery lends credence to earlier research that emphasized the SysQ in AIS (Hsu et al., 2015; H.-F. Lin, 2010; Lutfi et al., 2022b; Mujalli, 2024b). In the long run, this increases user satisfaction (USat) by encouraging the user to fully utilize DAS, which in turn increases their motivation to participate actively.
Previous research (Alalwan et al., 2014; Abidin, 2017; Hou, 2013; Al-Okaily et al., 2022a; Al-Hattami et al., 2025) demonstrated that the regular utilization of DAS by users, in particular executives, enhanced sustainability in decision-making. This conclusion indicates that USat plays a crucial role in enhancing executives’ decision-making, and the quality of information delivered through DAS facilitates dependable, sustainable and precise decisions, hence confirming the assertion that the DAS department fulfills user requirements (Al-Okaily et al., 2022a; Lutfi et al., 2022a; Rajan & Baral, 2015). Furthermore, the findings empirically substantiated the assertion posited by research (Al-Okaily et al., 2022a; Al-Hattami et al., 2024; Lutfi et al., 2022e; Ouiddad et al., 2018) that information systems adoption significantly enhances a company’s ability to make decisions.
The factors investigated in this study were shown to have a positive impact on the sustainability of DAS decision-making among businesses.
DAS-based decision-making necessitates the utilization of DAS data assessment and processes. It is essential for businesses to devise complex procedures in order to make the context clearer and to provide decision-makers with a meaningful understanding of the effectiveness and benefits of DAS. In turn, this necessitates a possible overview of the data sources and the manner in which they might be merged in order to throw light on the context (Lutfi et al., 2022f; Mujalli et al., 2024). DAS requires collaboration between the many stakeholders and specialists in domain systems in order to comprehend DAS processing and its ramifications. This kind of cooperation is essential for firms that use both IS and DAS. In the same vein, an overview of the quality evaluation of DAS sources and resources is another topic that requires additional research and investigation.
The findings can then be utilized to assess DAS’s capacity to improve decision-making sustainability using the theoretical framework. The theoretical foundation regarding the study can also guide subsequent research endeavors on this important subject. The links that are established by the D&M Successful Framework place an emphasis on the abilities of DAS, with the quality of decisions being determined by the complexity of the problem and the efficiency with which the system is utilized. It can be concluded that DAS enhances the decision-making and outcomes of managerial positions in a sustainable way.
In summary, the current study’s findings revealed the aspects that increase managers’ decision-making through the utilization of their DAS. DAS enables management to oversee and monitor diverse transactions, analyze situations from multiple viewpoints, and make decisions that are precise, educated, and grounded in fact. The study findings generate compelling evidence on the crucial impact of DAS utilization on the success of sustainable enterprises. According to this research finding, enterprises that extensively utilize DASs are likely to achieve significant value and impact from DAS usage, as posited by the D&M Success Model. This outcome has demonstrated relevance to various empirical studies across multiple IS or IT technology sectors (Lutfi et al., 2022b, 2022g), where extensive IS or IT utilization greatly changes decision-making equity, hence substantially affecting values and impacting company sustainability.
Despite Ramli (2013) indicating that DAS usage improves satisfaction of the users, reduces mistakes, and enhances information accessibility, studies examining the effects of DAS on the quality of decision-making and company sustainability have to date been scarce. Decision-making has emerged as a critical business objective for sustainability over the past decade. The utilization of DAS has attracted significant attention for the attainment of company sustainability and objectives. Sustainability significantly affects the survival of SMEs.
Furthermore, the D&M model’s (2003) extension, which included the inclusion of factors pertaining to the decision-making quality, makes a contribution to the literature on the use of information technology and information systems. The findings can be analyzed in other countries that have economic and social backgrounds that are comparable to the environment of the study. Nevertheless, due to the sample of this study incorporating specifically small and medium enterprises in Saudi Arabia, it is important to use caution when generalizing the findings and applying them to other developing countries.
7. Conclusions, Contributions, Limitations and Avenues for Future Research
In conclusion, DAS’s value is derived from its improvement of decision-making quality; however, despite its significance, the utilization of DASs in decision-making remains insufficiently explored. It is often presumed that DASs primarily enhance decisions, a generalization that may overlook the effect of various factors and how their relationships affect the sustainability of decision-making. This work sought to empirically develop and assess the suggested model to elucidate how DASs, such as InfQ, SysQ, and SerQ, affect user perspectives of system usage and satisfaction, hence, influencing the quality of decision-making. Consequently, data were collected from 348 decision-makers employed in SMEs in SA, specifically those knowledgeable with DAS and its application. The current study is distinctive in its emphasis on operational and transactional DAS’s abilities, as well as its exploration of DAS’s role in improving decision-making. Consequently, the study findings possess significant implications for the DeLone and McLean (2003) foundational model and its expansion, as well as insights into the diverse aspects influencing the decision-making sustainability.
The present study offers several significant theoretical contributions to the literature on innovations and the utilization of DAS. This study enhances the DAS literature regarding the acceptance and utilization of DAS, along with its effects (benefits) in a developing nation like Saudi Arabia. This study is, to the best of our knowledge, the first of its kind to empirically or conceptually examine the determinants of DAS utilization and its effect on corporate performance. The literature study indicates that, despite significant attention being paid to various technologies, little research has been performed specifically on the DAS setting. This research augments current information by presenting a robust conceptual model grounded in established frameworks (DM ISSM) that elucidates the influence of several quality criteria on DAS utilization and user satisfaction, along with its implications and advantages. Consequently, the predictive and explanatory efficacy of the DM ISSM model is enhanced, yielding outcomes beneficial to both scholars and practitioners.
This argument posits that the findings are contributions for government organizations, regulators, decision-makers, consultants, DAS providers, and the enterprises themselves. The benefits of DAS are substantiated by the validation of the substantial correlation between its utilization and business performance, suggesting that adoption of DAS can improve processes, competitiveness, efficiency, information accuracy, prompt decision-making, and general efficiency. From a policy standpoint, these results indicate that governments and legislative bodies are essential in assisting SMEs to optimize DAS advantages. These goals can be accomplished by instituting explicit norms and standards for the adoption of DAS, delivering specialized training programs for workers and DAS users, fostering investment in technology infrastructure, and offering incentives to enhance effective system utilization. Through the implementation of these measures, policymakers may guarantee that the adoption of DAS not only bolsters the growth and sustainability of individual enterprises but also improves the effectiveness, transparency, and sustainability of the wider SME sectors.
Nonetheless, every study has its limitations, since no research can comprehensively address all inquiries pertaining to the phenomena it investigates. This study’s primary limitation is its context, centered on SMEs in Saudi Arabia, which restricts the generalizability of the results to other nations. This constraint may be mitigated by future research utilizing samples from other developing countries in Africa and Asia. Secondly, another drawback pertains to the employed cross-sectional design, which omits data from various temporal intervals. It is significant that certain constructions, such as usage, necessitate the passage of time for accurate measurement. This restriction has often been noted in research utilizing D&M; hence, subsequent studies might undertake comparative analyses or examine the pre-adoption and post-adoption trajectories of DASs usage. Thirdly, the study’s incorporation of the sustainability of decision-making as a DAS net benefit is one of the new impact elements into the model, which presents a challenge. Future research should therefore concentrate on the contingent implications of additional elements like DAS efficacy or business performance in order to calculate the net advantages of systems.
In order to comprehend the potential indirect associations, future studies should evaluate the explicit mediating influence of DAS use between quality factors (IQ, SevQ, and SysQ) and the quality of decision-making; this study solely analyzed the quality factors DAS use as well as DAS use of quality decision-making relationships. Stakeholders might be better informed about the strategic benefits of DAS and its role in supporting decision-making if other variables, including training, user experience, internal control quality, and DAS development, were included in the analysis. Examining the elements may also reveal their crucial function in revealing the path that decision-makers ought to follow. Considering the lack of conclusiveness in this study, subsequent investigations can extend the duration of comparable DAS studies.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study due to the fac that the study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and ethical review and approval were waived for this study, for the reason that this study was conducted individually and independently by the institution where they work, respecting the anonymity of the interviewer.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Abidin, N. H. Z. (2017). Factors influencing the implementation of risk-based auditing. Asian Review of Accounting, 25(3), 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Afifa, M. M., Vo Van, H., & Le Hoang Van, T. (2023). Blockchain adoption in accounting by an extended UTAUT model: Empirical evidence from an emerging economy. Journal of Financial Reporting and Accounting, 21(1), 5–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alalwan, J. A., Thomas, M. A., & Weistroffer, H. R. (2014). Decision support capabilities of enterprise content management systems: An empirical investigation. Decision Support Systems, 68, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hattami, H. M. (2025). The impact of digital accounting systems on financial performance in the banking sector: Advancements in the digital era. International Journal of Intelligent Information Technologies (IJIIT), 21(1), 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hattami, H. M., Almaqtari, F. A., Abdullah, A. A. H., & Al-Adwan, A. S. (2024). Digital accounting system and its effect on corporate governance: An empirical investigation. Strategic Change, 33(3), 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hattami, H. M., Battour, M., & Al-Bukhrani, M. A. (2025). Digital accounting systems in SMEs: Do they influence marketing performance? A moderated mediation analysis. Strategic Change, 34(5), 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hiyari, A., Al-Mashregy, M. H. H., Mat, N. K. N., & Alekam, J. M. (2013). Factors that affect accounting information system implementation and accounting information quality: A survey in University Utara Malaysia. American Journal of Economics, 3(1), 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Aljawarneh, N. M., Huson, Y. A., Alqmool, T. J., & Jarbou, S. I. (2023, December 21–23). Tracing the evolution of auditing and digital accounting research in the digital business environment: A bibliometric analysis. 4th International Conference on Distributed Sensing and Intelligent Systems (ICDSIS 2023) (pp. 135–145), Dubai, United Arab Emirates. [Google Scholar]
- Almagrashi, A., Mujalli, A., Khan, T., & Attia, O. (2023). Factors determining internal auditors’ behavioral intention to use computer-assisted auditing techniques: An extension of the UTAUT model and an empirical study. Future Business Journal, 9(1), 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaiah, M. A., Hajjej, F., Lutfi, A., Al-Khasawneh, A., Shehab, R., Al-Otaibi, S., & Alrawad, M. (2022). Explaining the factors affecting students’ attitudes to using online learning (Madrasati Platform) during COVID-19. Electronics, 11(7), 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almgrashi, A., & Mujalli, A. (2024). The influence of sustainable risk management on the implementation of risk-based internal auditing. Sustainability, 16(19), 8455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Okaily, M., Alghazzawi, R., Alkhwaldi, A. F., & Al-Okaily, A. (2022a). The effect of digital accounting systems on the decision-making quality in the banking industry sector: A mediated-moderated model. Global Knowledge, Memory and Communication, 72(8/9), 882–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Okaily, M., Alkhwaldi, A. F., Abdulmuhsin, A. A., Alqudah, H., & Al-Okaily, A. (2022b). Cloud-based accounting information systems usage and its impact on Jordanian SMEs’ performance: The post-COVID-19 perspective. Journal of Financial Reporting and Accounting. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsyouf, A., & Ishak, A. K. (2018). Understanding EHRs continuance intention to use from the perspectives of UTAUT: Practice environment moderating effect and top management support as predictor variables. International Journal of Electronic Healthcare, 10(1–2), 24–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsyouf, A., Lutfi, A., Al-Bsheish, M., Jarrar, M., Al-Mugheed, K., Almaiah, M. A., Alhazmi, F. N., Masa’deh, R., Anshasi, R. J., & Ashour, A. (2022). Exposure detection applications acceptance: The case of COVID-19. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(12), 7307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsyouf, A., Masa’deh, R., Albugami, M., Al-Bsheish, M., Lutfi, A., & Alsubahi, N. (2021). Risk of fear and anxiety in utilising health app surveillance due to COVID-19: Gender differences analysis. Risks, 9(10), 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzoubi, A. (2011). The effectiveness of the accounting information system under the enterprise resources planning (ERP). Research Journal of Finance and Accounting, 2(11), 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Alzoubi, M. M., & Snider, D. H. (2020). Comparison of factors affecting enterprise resource planning system success in the Middle East. International Journal of Enterprise Information Systems (IJEIS), 16(4), 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arief, S. (2024). Digital transformation in accounting: The nexus between technology, leadership, and beyond. In Digital transformation in accounting and auditing: Navigating technological advances for the future (pp. 29–59). Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, M., & Kumar, A. (2022). An empirical study on make-or-buy decision making. International Journal of Education and Management Engineering, 12(1), 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avolio, B. J., Yammarino, F. J., & Bass, B. M. (1991). Identifying common methods variance with data collected from a single source: An unresolved sticky issue. Journal of Management, 17(3), 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balios, D. (2021). The impact of big data on accounting and auditing. International Journal of Corporate Finance and Accounting (IJCFA), 8(1), 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, A., Gomes, P., Quesado, P., & O’Sullivan, S. (2025). Advancements in management accounting and digital technologies: A systematic literature review. Accounting, Finance & Governance Review, 34, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacherjee, A. (2001). Understanding information systems continuance: An expectation-confirmation model. MIS Quarterly, 25(3), 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhari, R. H. (2005). The relationship between system usage and user satisfaction: A meta-analysis. Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 18(2), 211–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y., Zhang, X., Mokhtar, I. A., Foo, S., Majid, S., Luyt, B., & Theng, Y. (2012). Assessing students’ information literacy skills in two secondary schools in Singapore. Journal of Information Literacy, 6(2), 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.-W., Chang, H.-H., Lin, Y.-H., & Chou, S.-B. (2014). Drivers and effects of post-implementation learning on ERP usage. Computers in Human Behavior, 35, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.-S., & Hong, J.-H. (2013). Assessing the impact of quality determinants and user characteristics on successful enterprise resource planning project implementation. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 32(4), 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, A. J., & Taylor, M. (2009). Critical success factors for B2B e-commerce use within the UK NHS pharmaceutical supply chain. International Journal of Operations & Production Management, 29(11), 1156–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Dagiliene, L., & Šutiene, K. (2019). Corporate sustainability accounting information systems: A contingency-based approach. Sustainability Accounting, Management and Policy Journal, 10(2), 260–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, H., & Triki, M. (2013). Accounting information systems in an ERP environment and Tunisian firm performance. The International Journal of Digital Accounting Research, 13(1), 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanpouri, H., Soltani, Z., & Rostamzadeh, R. (2020). The impact of trust, privacy and quality of service on the success of E-CRM: The mediating role of customer satisfaction. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 35(11), 1831–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLone, W. H., & McLean, E. R. (1992). Information systems success: The quest for the dependent variable. Information Systems Research, 3(1), 60–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLone, W. H., & McLean, E. R. (2003). The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: A ten-year update. Journal of Management Information Systems, 19(4), 9–30. [Google Scholar]
- Diedrich, H. (2016). Ethereum: Blockchains, digital assets, smart contracts, decentralized autonomous organizations. Wildfire Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Fadelelmoula, A. A. (2018). The effects of the critical success factors for ERP implementation on the comprehensive achievement of the crucial roles of information systems in the higher education sector. Interdisciplinary Journal of Information, Knowledge, and Management, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanning, K., & Centers, D. P. (2016). Blockchain and its coming impact on financial services. Journal of Corporate Accounting & Finance, 27(5), 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitrios, R. (2016). Factors that influence accounting information system implementation and accounting information quality. International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research, 5(4), 192–198. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J. F., Risher, J. J., Sarstedt, M., & Ringle, C. M. (2019). When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. European Business Review, 31(1), 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J., & Han, I. (2003). Performance measure of information systems (IS) in evolving computing environments: An empirical investigation. Information & Management, 40(4), 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.-K. (2013). Measuring the impacts of the integrating information systems on decision-making performance and organisational performance: An empirical study of the Taiwan semiconductor industry. International Journal of Technology, Policy and Management, 13(1), 34–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.-F., Yen, H. R., & Chung, J.-C. (2015). Assessing ERP post-implementation success at the individual level: Revisiting the role of service quality. Information & Management, 52(8), 925–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifinedo, P., Rapp, B., Ifinedo, A., & Sundberg, K. (2010). Relationships among ERP post-implementation success constructs: An analysis at the organizational level. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(5), 1136–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaoua, F., Almurad, H. M., Elshaer, I. A., & Mohamed, E. S. (2022). E-learning success model in the context of COVID-19 pandemic in higher educational institutions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(5), 2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasim, T. A., & Ibrahim, M. A. (2023). The impact of adopting international financial reporting standards on the quality of financial reports using the accrual model. International Journal of Professional Business Review, 8(6), e02330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, R. B. (2023). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. Guilford Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Klisarova-Belcheva, S., Ilieva, G., & Yankova, T. (2017). Business intelligence and analytics–contemporary system model. Trakia Journal of Sciences, 15(1), 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock, N. (2015). Common method bias in PLS-SEM: A full collinearity assessment approach. International Journal of E-Collaboration (Ijec), 11(4), 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthi, S., & Mathew, S. K. (2018). Business analytics and business value: A comparative case study. Information & Management, 55(5), 643–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., & Wang, J. (2021). Evaluating the impact of information system quality on continuance intention toward cloud financial information system. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 713353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-F. (2010). An investigation into the effects of IS quality and top management support on ERP system usage. Total Quality Management, 21(3), 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-Y., Hsu, P.-Y., & Ting, P.-H. (2006). ERP systems success: An integration of IS success model and balanced scorecard. Journal of Research and Practice in Information Technology, 38(3), 215–228. [Google Scholar]
- Lutfi, A. (2022). Factors influencing the continuance intention to use accounting information system in Jordanian SMEs from the perspectives of UTAUT: Top management support and self-efficacy as predictor factors. Economies, 10(4), 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfi, A., Alkelani, S. N., Al-Khasawneh, M. A., Alshira’h, A. F., Alshirah, M. H., Almaiah, M. A., Alrawad, M., Alsyouf, A., Saad, M., & Ibrahim, N. (2022a). Influence of digital accounting system usage on SMEs performance: The moderating effect of COVID-19. Sustainability, 14(22), 15048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfi, A., Alkelani, S. N., Alqudah, H., Alshira’h, A. F., Alshirah, M. H., Almaiah, M. A., Alsyouf, A., Alrawad, M., Montash, A., & Abdelmaksoud, O. (2022b). The role of E-accounting adoption on business performance: The moderating role of COVID-19. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 15(12), 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfi, A., Al-Khasawneh, A. L., Almaiah, M. A., Alsyouf, A., & Alrawad, M. (2022c). Business sustainability of small and medium enterprises during the COVID-19 pandemic: The role of AIS implementation. Sustainability, 14(9), 5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfi, A., Alkilani, S. Z., Saad, M., Alshirah, M. H., Alshirah, A. F., Alrawad, M., Al-Khasawneh, M. A., Ibrahim, N., Abdelhalim, A., & Ramadan, M. H. (2022d). The influence of audit committee chair characteristics on financial reporting quality. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 15(12), 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfi, A., Al-Okaily, M., Alsyouf, A., & Alrawad, M. (2022e). Evaluating the D&M IS success model in the context of accounting information system and sustainable decision making. Sustainability, 14(13), 8120. [Google Scholar]
- Lutfi, A., Alsyouf, A., Almaiah, M. A., Alrawad, M., Abdo, A. A. K., Al-Khasawneh, A. L., Ibrahim, N., & Saad, M. (2022f). Factors influencing the adoption of big data analytics in the digital transformation era: Case study of Jordanian SMEs. Sustainability, 14(3), 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfi, A., Saad, M., Almaiah, M. A., Alsaad, A., Al-Khasawneh, A., Alrawad, M., Alsyouf, A., & Al-Khasawneh, A. L. (2022g). Actual use of mobile learning technologies during social distancing circumstances: Case study of King Faisal University students. Sustainability, 14(12), 7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, S. B., & Podsakoff, P. M. (2012). Common method bias in marketing: Causes, mechanisms, and procedural remedies. Journal of Retailing, 88(4), 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marble, R. P. (2003). A system implementation study: Management commitment to project management. Information & Management, 41(1), 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardia, K. V. (1970). Measures of multivariate skewness and kurtosis with applications. Biometrika, 57(3), 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z. A. I. (2025). The impact of artificial intelligence on digital accounting in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. In Generative AI in creative industries (pp. 117–128). Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, A., & Cepêda, C. (2021). Accounting information systems: Scientific production and trends in research. Systems, 9(3), 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, A., & Khrais, L. T. (2025). Cybersecurity in digital accounting systems: Challenges and solutions in the arab gulf region. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 18(1), 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujalli, A. (2021). Internal audit effectiveness in Saudi Arabia’s public sector higher education system [Ph.D. thesis, RMIT University]. [Google Scholar]
- Mujalli, A. (2024a). Factors affecting the implementation of risk-based internal auditing. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 17(5), 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujalli, A. (2024b). The influence of E-auditing adoption on internal audit department performance amid COVID-19 in Saudi Arabia. Cogent Business & Management, 11(1), 2295608. [Google Scholar]
- Mujalli, A., & Almgrashi, A. (2020, December 16–18). A conceptual framework for generalised audit software adoption in Saudi Arabia by government internal auditing departments using an integrated institutional theory-TOE model. 2020 IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Computer Science and Data Engineering (CSDE) (pp. 1–8), Gold Coast, Australia. [Google Scholar]
- Mujalli, A., Khan, T., & Almgrashi, A. (2022). University accounting students and faculty members using the blackboard platform during COVID-19; Proposed modification of the UTAUT model and an empirical study. Sustainability, 14(4), 2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujalli, A., Wani, M. J. G., Almgrashi, A., Khormi, T., & Qahtani, M. (2024). Investigating the factors affecting the adoption of cloud accounting in Saudi Arabia’s Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs). Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 10(2), 100314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negash, S., Ryan, T., & Igbaria, M. (2003). Quality and effectiveness in web-based customer support systems. Information & Management, 40(8), 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R. R., Todd, P. A., & Wixom, B. H. (2005). Antecedents of information and system quality: An empirical examination within the context of data warehousing. Journal of Management Information Systems, 21(4), 199–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H., & Nguyen, A. (2020). Determinants of accounting information systems quality: Empirical evidence from Vietnam. Accounting, 6(2), 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y., Ying, L., Yang, J., Bao, M., & Sivaparthipan, C. B. (2021). Organizational business intelligence and decision making using big data analytics. Information Processing & Management, 58(6), 102725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouiddad, A., Chafik, O., Chroqui, R., & Hassani, I. B. (2018, November 21–23). Does the adoption of ERP systems help improving decision-making? A systematic literature review. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Technology Management, Operations and Decisions (ICTMOD) (pp. 61–66), Marrakech, Morocco. [Google Scholar]
- Petter, S., & McLean, E. R. (2009). A meta-analytic assessment of the DeLone and McLean IS success model: An examination of IS success at the individual level. Information & Management, 46(3), 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Petter, S., DeLone, W., & McLean, E. (2008). Measuring information systems success: Models, dimensions, measures, and interrelationships. European Journal of Information Systems, 17, 236–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirttimäki, V., Lönnqvist, A., & Karjaluoto, A. (2006). Measurement of Business Intelligence in a Finnish Telecom-munications Company. Electronic Journal of Knowledge Management, 4(1), 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2012). Sources of method bias in social science research and recommendations on how to control it. Annual Review of Psychology, 63, 539–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovič, A., Hackney, R., Coelho, P. S., & Jaklič, J. (2012). Towards business intelligence systems success: Effects of maturity and culture on analytical decision making. Decision Support Systems, 54(1), 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, A., & Kharbat, F. F. (2020). Blockchain technology, business data analytics, and artificial intelligence: Use in the accounting profession and ideas for inclusion into the accounting curriculum. Journal of Emerging Technologies in Accounting, 17(1), 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, J. M. M., Pedroche, E. G., & de la Garza Ramos, M. I. (2009). Influence of the implementation factors in the information systems quality for the user satisfaction. Journal of Information Systems and Technology Management, 6(1), 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, C. A., & Baral, R. (2015). Adoption of ERP system: An empirical study of factors influencing the usage of ERP and its impact on end user. IIMB Management Review, 27(2), 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, A. (2013). The impact of external factors on accounting information system (AIS) usage. Journal of Entrepreneurship and Business (JEB), 1(1), 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, J., Kaya, O., Mallick, S. K., & Rane, N. L. (2024). Influence of digitalization on business and management: A review on artificial intelligence, blockchain, big data analytics, cloud computing, and internet of things. Generative Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture, Education, and Business, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikhardsson, P., & Yigitbasioglu, O. (2018). Business intelligence & analytics in management accounting research: Status and future focus. International Journal of Accounting Information Systems, 29, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M. (2023). The influence of accounting information system adoption on business performance amid COVID-19. Computers in Human Behavior Reports, 10, 100286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M., Lutfi, A., Almaiah, M. A., Alshira’h, A. F., Alshirah, M. H., Alqudah, H., Alkhassawneh, A. L., Alsyouf, A., Alrawad, M., & Abdelmaksoud, O. (2022). Assessing the intention to adopt cloud accounting during COVID-19. Electronics, 11(24), 4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandner, P., Gross, J., & Richter, R. (2020). Convergence of blockchain, IoT, and AI. Frontiers in Blockchain, 3, 522600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, J., & Leoni, G. (2019). Accounting and auditing at the time of blockchain technology: A research agenda. Australian Accounting Review, 29(2), 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmueli, G., Sarstedt, M., Hair, J. F., Cheah, J.-H., Ting, H., Vaithilingam, S., & Ringle, C. M. (2019). Predictive model assessment in PLS-SEM: Guidelines for using PLSpredict. European Journal of Marketing, 53(11), 2322–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorova, M., Kopus, T., & Yurasova, I. (2024). Digital transformation for teaching management accounting: Training with a simulation in an authentic professional environment. Accounting Education, 33(5), 621–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simatupang, O. (2024). AI in accounting and finance: A literature review on challenges, opportunities, and ethical considerations. International Journal of Information System and Innovative Technology, 3(2), 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S. S. (2015). Accounting: Evolving for an integrated future. Journal of Accounting, Finance & Management Strategy, 10(1), 1. [Google Scholar]
- Spector, P. E. (2006). Method variance in organizational research: Truth or urban legend? Organizational Research Methods, 9(2), 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taufik, F. (2022). The success analysis of internal audit implementation on electronics through integrated instance accounting system of national data communication application. Indonesian Journal of Business, Accounting and Management, 1(1), 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trice, A. W., & Treacy, M. E. (1988). Utilization as a dependent variable in MIS research. ACM SIGMIS Database: The Database for Advances in Information Systems, 19(3–4), 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbach, N., & Ahlemann, F. (2010). Structural equation modeling in information systems research using partial least squares. Journal of Information Technology Theory and Application (JITTA), 11(2), 2. [Google Scholar]
- Visinescu, L. L., Jones, M. C., & Sidorova, A. (2017). Improving decision quality: The role of business intelligence. Journal of Computer Information Systems, 57(1), 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., Ferreira, F. A. F., & Yan, P. (2023). A multi-objective optimization approach for integrated risk-based internal audit planning. Annals of Operations Research, 346(2), 1811–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wixom, B. H., & Todd, P. A. (2005). A theoretical integration of user satisfaction and technology acceptance. Information Systems Research, 16(1), 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y., James Allen, C., & Ali, M. (2014). An integrated decision support system for ERP implementation in small and medium sized enterprises. Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 27(4), 358–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J., Benbasat, I., & Cenfetelli, R. T. (2013). Integrating service quality with system and information quality: An empirical test in the e-service context. MIS Quarterly, 37(3), 777–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubu, N., & Dasuki, S. (2018). Assessing eLearning systems success in Nigeria: An application of the DeLone and McLean information systems success model. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 17, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y., Xiong, F., Xie, Y., Fan, X., & Gu, H. (2020). The impact of artificial intelligence and blockchain on the accounting profession. IEEE Access, 8, 110461–110477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).