-
 Social Planning for eBRT Innovations: Multi-Criteria Evaluation of Societal Impacts
Social Planning for eBRT Innovations: Multi-Criteria Evaluation of Societal Impacts -
 Enabling Grid Services with Bidirectional EV Chargers: A Comparative Analysis of CCS2 and CHAdeMO Response Dynamics
Enabling Grid Services with Bidirectional EV Chargers: A Comparative Analysis of CCS2 and CHAdeMO Response Dynamics -
 Evaluating Unplug Incentives to Improve User Experience and Increase DC Fast Charger Utilization
Evaluating Unplug Incentives to Improve User Experience and Increase DC Fast Charger Utilization -
 EV and Renewable Energy Integration in Residential Buildings: A Global Perspective on Deep Learning, Strategies, and Challenges
EV and Renewable Energy Integration in Residential Buildings: A Global Perspective on Deep Learning, Strategies, and Challenges -
 A Novel Railgun-Based Actuation System for Ultrafast DC Circuit Breakers in EV Fast-Charging Applications
A Novel Railgun-Based Actuation System for Ultrafast DC Circuit Breakers in EV Fast-Charging Applications
Journal Description
World Electric Vehicle Journal
World Electric Vehicle Journal
(WEVJ) is the first international, peer-reviewed, open access journal that comprehensively covers all studies related to battery, hybrid, and fuel cell electric vehicles, and is published monthly online. It is the official journal of the World Electric Vehicle Association (WEVA) and its members, the E-Mobility Europe, Electric Drive Transportation Association (EDTA), and Electric Vehicle Association of Asia Pacific (EVAAP).
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), Ei Compendex, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Engineering, Electrical and Electronic) / CiteScore - Q2 (Automotive Engineering)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 17.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
2.6 (2024)
Latest Articles
Attack Detection of Federated Learning Model Based on Attention Mechanism Optimization in Connected Vehicles
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 679; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120679 (registering DOI) - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
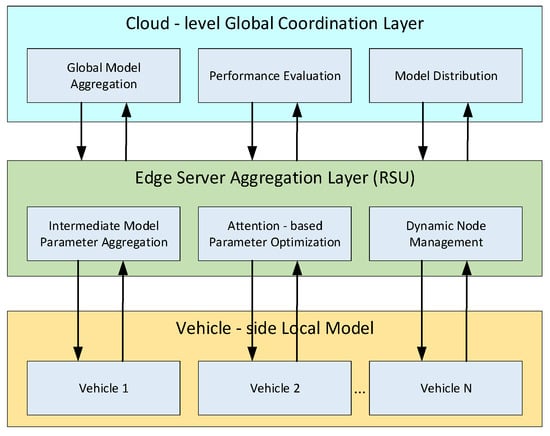
To address the problem of decreased model accuracy and poor global aggregation performance among existing methods in non-independent and identically distributed (non-IID) data backgrounds, the author proposes a method for attack detection in the Internet of Vehicles based on the attention mechanism optimization
[...] Read more.
To address the problem of decreased model accuracy and poor global aggregation performance among existing methods in non-independent and identically distributed (non-IID) data backgrounds, the author proposes a method for attack detection in the Internet of Vehicles based on the attention mechanism optimization of federated learning models. The author uses a combination of CNN and LSTM as the basic detection framework, integrating self-attention modules to optimize the spatiotemporal feature modeling effect. At the same time, an adaptive aggregation algorithm based on attention weights was designed in the federated aggregation stage, providing the model with stronger stability and generalization ability when dealing with data differences among nodes. In order to comprehensively evaluate the performance of the model, the experimental part is based on real datasets such as CICDDoS2019. The experimental results show that the federated learning model based on attention mechanism optimization proposed by the author demonstrates significant advantages in the task of detecting vehicle networking attacks. Compared with traditional methods, the new model improves attack detection accuracy by more than 5% in non-IID data environments, accelerates aggregation convergence speed, reduces aggregation epochs by more than 20%, and achieves stronger data privacy protection and real-time defense capabilities. Conclusion: This method not only improves the adaptability of the model in complex vehicle networking environments, but also effectively reduces the overall computational and communication overhead of the system.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Automated and Connected Vehicles)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Object Detection for Autonomous Vehicles in Low-Resolution Environments Using a Super-Resolution Transformer-Based Preprocessing Framework
by
Mokhammad Mirza Etnisa Haqiqi, Ajib Setyo Arifin and Arief Suryadi Satyawan
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 678; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120678 - 17 Dec 2025
Abstract
Low-resolution (LR) imagery poses significant challenges to object detection systems, particularly in autonomous and resource-constrained environments where bandwidth and sensor quality are limited. To address this issue, this paper presents an integrated framework that enhances object detection performance by incorporating a Super-Resolution (SR)
[...] Read more.
Low-resolution (LR) imagery poses significant challenges to object detection systems, particularly in autonomous and resource-constrained environments where bandwidth and sensor quality are limited. To address this issue, this paper presents an integrated framework that enhances object detection performance by incorporating a Super-Resolution (SR) preprocessing stage prior to detection. Specifically, a Dense Residual Connected Transformer (DRCT) is employed to reconstruct high-resolution (HR) images from LR inputs, effectively restoring fine-grained structural and textural information essential for accurate detection. The reconstructed HR images are subsequently processed by a YOLOv11 detector without requiring architectural modifications. Experimental evaluations demonstrate consistent improvements across multiple scaling factors, with an average increase of 13.4% in Mean Average Precision (mAP)@50 at ×2 upscaling and 9.7% at ×4 compared with direct LR detection. These results validate the effectiveness of the proposed SR-based preprocessing approach in mitigating the adverse effects of image degradation. The proposed method provides an improved yet computationally challenging solution for object detection.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Automated and Connected Vehicles)
Open AccessArticle
Four-Wheel Steering Control for Mining X-by-Wire Chassis Based on AUKF State Estimation
by
Qiang Ji, Yueqi Bi, Mingrui Hao, Jiaran Li and Long Chen
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 677; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120677 - 17 Dec 2025
Abstract
To address the challenges to driving stability caused by large-curvature steering of wire-controlled mining vehicles in narrow tunnels, a fused four-wheel steering (4WS) control strategy based on real-time estimation of vehicle state parameters is proposed. A comprehensive longitudinal–lateral–yaw dynamics model for 4WS is
[...] Read more.
To address the challenges to driving stability caused by large-curvature steering of wire-controlled mining vehicles in narrow tunnels, a fused four-wheel steering (4WS) control strategy based on real-time estimation of vehicle state parameters is proposed. A comprehensive longitudinal–lateral–yaw dynamics model for 4WS is established, and a comparative study is conducted on three control methods: proportional feedforward control, yaw rate feedback control, and fused control. Expressions for steady-state yaw rate gain under different control modes are derived, and the stability differences in 4WS characteristics among these strategies are thoroughly analyzed. To overcome the difficulty in directly acquiring state information for chassis steering control, a vehicle state parameter estimator based on the unscented Kalman filter (UKF) is designed. To enhance the robustness to noise and computational real-time performance of vehicle state estimation in complex environments, a method for real-time estimation of noise covariance matrices using innovative sequences is adopted, improving the estimation accuracy of the algorithm. To validate the effectiveness of the control strategies, a co-simulation platform integrating Carsim and Matlab/Simulink is developed to simulate the performance of the three 4WS control methods under step steering and sinusoidal steering input conditions. The results show that, under low-speed conditions, 4WS strategies increase the yaw rate by approximately 50% and reduce the turning radius by over 45%, significantly enhancing steering maneuverability. Under medium-high speed conditions, 4WS strategies decrease the yaw rate by up to 68% and increase the turning radius by 17–29%, effectively suppressing oversteering tendencies to comprehensively improve stability, with the integrated control strategy demonstrating the best performance. Under both test conditions, the fused feedforward and feedback control strategy reduces the steady-state yaw rate by approximately 12.7% and 48.7%, respectively, compared to other control strategies, demonstrating superior stability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Design Theory and Methods of Intelligent Electric Vehicle Chassis)
Open AccessArticle
Research on Mobile Robot Path Planning Using Improved Whale Optimization Algorithm Integrated with Bird Navigation Mechanism
by
Zhijun Guo, Tong Zhang, Hao Su, Shilei Jie, Yanan Tu and Yixuan Li
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 676; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120676 - 17 Dec 2025
Abstract
In order to solve the problems of slow convergence speed, insufficient accuracy, and easily falling into the local optimum of the traditional whale optimization algorithm (WOA) in mobile robot path planning, an improved whale optimization algorithm (IWOA) combined with the bird navigation mechanism
[...] Read more.
In order to solve the problems of slow convergence speed, insufficient accuracy, and easily falling into the local optimum of the traditional whale optimization algorithm (WOA) in mobile robot path planning, an improved whale optimization algorithm (IWOA) combined with the bird navigation mechanism was proposed. Specific improvement measures include using logical chaos mapping to initialize the population to enhance the randomness and diversity of the initial solution, designing a nonlinear convergence factor to prevent the algorithm from prematurely entering the shrinking surround phase and extending the global search time, introducing an adaptive spiral shape constant to dynamically adjust the search range to balance exploration and development capabilities, optimizing the individual update strategy in combination with the bird navigation mechanism, and optimizing the algorithm through companion position information, thereby improving the stability and convergence speed of the algorithm. Path planning simulations were performed on 30 × 30 and 50 × 50 grid maps. The results show that compared with WOA, MSWOA, and GA, in the 30 × 30 map, the path length of IWOA is shortened by 3.23%, 7.16%, and 6.49%, respectively; in the 50 × 50 map, the path length is shortened by 4.88%, 4.53%, and 28.37%, respectively. This study shows that IWOA has significant advantages in the accuracy and efficiency of path planning, which verifies its feasibility and superiority.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Research on Intelligent Vehicle Path Planning Algorithm)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research on the Supply–Demand Evaluation and Configuration Optimization of Urban Residential Public Charging Facilities Based on Collaborative Service Networks: A Case Study of Hongshan District, Wuhan
by
Yanyan Huang, Yunfang Zha, You Zou, Xudong Jia, Zaiyu Fan, Hangyi Ren, Yilun Wei and Daoyuan Chen
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 675; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120675 - 17 Dec 2025
Abstract
The rapid growth of electric vehicles has intensified the spatial mismatch between the layout of charging infrastructure and user demand, resulting in a structural contradiction in which “local oversupply” and “local shortages” coexist. To systematically diagnose and optimize this issue, this study develops
[...] Read more.
The rapid growth of electric vehicles has intensified the spatial mismatch between the layout of charging infrastructure and user demand, resulting in a structural contradiction in which “local oversupply” and “local shortages” coexist. To systematically diagnose and optimize this issue, this study develops an innovative analytical framework for a “residential area–charging infrastructure” collaborative service network and conducts an empirical analysis using Hongshan District in Wuhan as a case study. The framework integrates actual facility utilization data, complex network analysis, and spatial clustering methods. The findings reveal that the collaborative service network in the study area is overall sparse, exhibiting a distinct “core–periphery” structure, with noticeable patterns of resource concentration and isolation. Residential areas can be categorized into three types based on their supply–demand characteristics: efficient-collaborative, transitional-mixed, and low-demand peripheral areas. The predominance of the transitional-mixed type indicates that most areas are currently in an unstable state of supply–demand adjustment. A key systemic mechanism identified in this study is the significant “collaborative reinforcement effect” between facility utilization rates and network centrality. Building on these insights, we propose a hierarchical optimization strategy consisting of “overall network optimization—local cluster coordination—individual facility enhancement.” This ultimately forms a comprehensive decision-support framework for “assessment—diagnosis—optimization,” providing scientific evidence and new solutions for the precise planning and efficient operation of urban charging infrastructure.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Charging Infrastructure and Grid Integration)
►▼
Show Figures
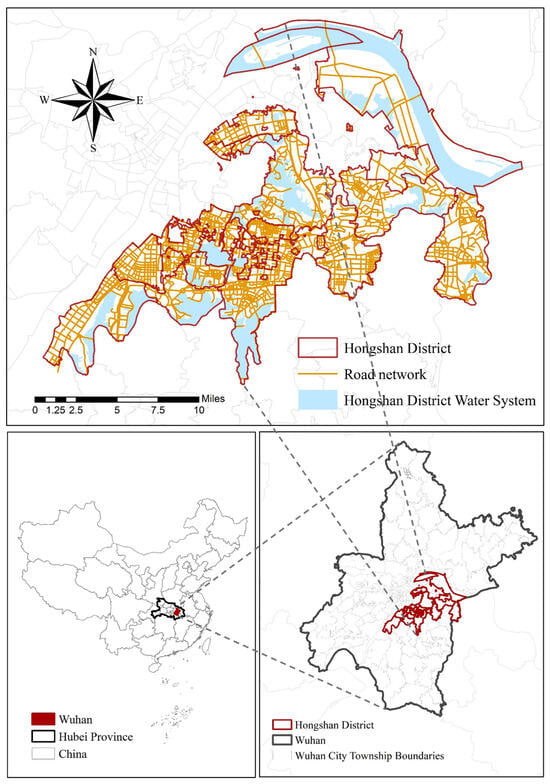
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research on Layout Planning of Electric Vehicle Charging Facilities in Macau Based on Spatial Syntax Analysis
by
Junling Zhou, Yan Li, Kuan Liu, Lingfeng Xie and Fu Hao
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 674; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120674 - 16 Dec 2025
Abstract
With the global trend towards “carbon neutrality,” the use of electric vehicles is becoming increasingly widespread, leading to new impacts on urban spaces. In the process of allocating resources for urban charging stations, there are widespread issues such as a singular planning approach
[...] Read more.
With the global trend towards “carbon neutrality,” the use of electric vehicles is becoming increasingly widespread, leading to new impacts on urban spaces. In the process of allocating resources for urban charging stations, there are widespread issues such as a singular planning approach and inadequate adaptation to actual travel demands. Therefore, this study adopts a method of integrating multi-source data to optimize the planning and layout of public electric vehicle charging facilities in Macau, striving to achieve breakthroughs in theoretical methods and key technologies. The study obtained a determination coefficient of R2 = 0.43 through quantitative analysis, which is within a reasonable range of fitting spatial syntax and charging facility layout. This indicates that there is a moderate positive correlation between the distribution of charging facilities and core indicators such as road network integration and accessibility—about 43% of layout differences can be explained by spatial syntax indicators, and the remaining 57% of differences reserve space for optimizing multiple factors such as population density and parking lot distribution. On this basis, this study compares the layout experience of medium to high-density cities such as Hong Kong and Singapore, and combines the common characteristics of old parishes on Macau Island and new urban areas on outlying islands to explore innovative sustainable development technology paths that are suitable for Macau. This study not only summarizes the key factors and optimization breakthroughs that affect the spatial distribution of charging facilities in Macau, providing basic data and methodological strategies for charging facility planning, but also helps Macau save energy and reduce emissions, build a green city through layout optimization, provide practical reference for the development of land reclamation areas, and provide reference for carbon neutrality and smart city construction in the Guangdong Hong Kong Macau Greater Bay Area.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Charging Infrastructure and Grid Integration)
►▼
Show Figures
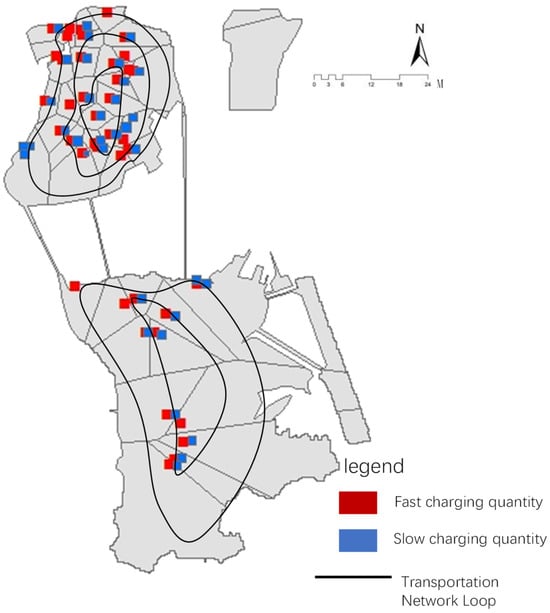
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research on Decoupling Control of Four-Wheel Steering Distributed Drive Electric Vehicles
by
Jie Zhu and Chengye Liu
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 673; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120673 - 14 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
To address the issue of limited accuracy in vehicle lateral and longitudinal dynamics control—caused by the strong coupling and nonlinearity between the four-wheel steering and distributed drive systems, particularly under crosswind disturbances—a control method integrating differential geometric decoupling with robust control is proposed.
[...] Read more.
To address the issue of limited accuracy in vehicle lateral and longitudinal dynamics control—caused by the strong coupling and nonlinearity between the four-wheel steering and distributed drive systems, particularly under crosswind disturbances—a control method integrating differential geometric decoupling with robust control is proposed. This integrated approach mitigates coupling effects among the vehicle motions in various directions, thereby enhancing overall robustness. The control architecture adopts a hierarchical structure: the upper layer takes the deviation between the ideal and actual models as input and generates longitudinal, yaw, and lateral control laws via robust control; the middle layer employs differential geometric methods to decouple the nonlinear system, deriving the total driver-required driving torque, additional yaw moment, and rear-wheel steering angle; and the lower layer utilizes a quadratic programming algorithm to optimize the distribution of driving torque across the four wheels. Finally, simulation verification is conducted based on a co-simulation platform using TruckSim 2022 and MATLAB R2024a/Simulink. The simulation results demonstrate that, compared to the sliding mode control (SMC) and the uncontrolled scenario, the proposed method improves the driving stability and safety of the four-wheel steering distributed drive vehicle under multiple operating conditions.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigating Barriers to EV Adoption in Morocco: Insights from an Emerging Economy
by
Sara Meskine, Hayat El Asri and Salah Al-Majeed
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 672; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120672 - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
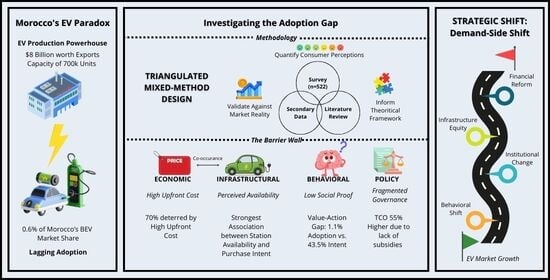
The global shift toward sustainable transport electric vehicles (EVs) is at the core of decarbonization efforts. While advanced economies have achieved their rapid adoption through strong policies and incentives, emerging markets face structural and behavioral barriers. This study investigates the paradox in Morocco,
[...] Read more.
The global shift toward sustainable transport electric vehicles (EVs) is at the core of decarbonization efforts. While advanced economies have achieved their rapid adoption through strong policies and incentives, emerging markets face structural and behavioral barriers. This study investigates the paradox in Morocco, whereby a significant automotive capacity contrasts with a minimal domestic BEV market share of 0.6%, despite 143% growth from a small base, using a four-dimensional framework encompassing financial, infrastructural and energy, policy and institutional, and behavioral–social factors. The research integrates a literature review, a survey (n = 522), and secondary data on charging infrastructure and EV sales. Findings reveal a strong value–action gap: 69% of respondents acknowledged EVs’ environmental benefits yet only 1.1% owned one and 42% had considered buying. The high upfront costs of EVs influenced over 70% of participants, and a significant association was confirmed between charging availability and purchase intent (χ2 = 34.80, p < 0.05). Urban-centric charging, fragmented governance, and skepticism persist as barriers. The study concludes that industrial strength alone cannot ensure adoption without targeted incentives, equitable infrastructure, and cultural shifts in ownership perception, offering key insights for policymakers in emerging economies pursuing sustainable mobility.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Marketing, Promotion and Socio Economics)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Rapid Evaluation of Off-Highway Powertrain Architectures
by
Rupert Tull de Salis
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 671; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120671 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Task-specific off-highway vehicles are typically produced in small volumes, so limited resources must be used in their design. The fuel efficiency benefits of hybridizing an off-highway vehicle are typically in the range of 10–30%, meaning that a simulation tool should ideally be able
[...] Read more.
Task-specific off-highway vehicles are typically produced in small volumes, so limited resources must be used in their design. The fuel efficiency benefits of hybridizing an off-highway vehicle are typically in the range of 10–30%, meaning that a simulation tool should ideally be able to predict fuel usage within about ±10%, to support stage-gate design decisions. However, such simulation tools typically require significant cost, setup effort, and simulation expertise. A wheel loader and four agricultural tractors were analyzed with a new tool, “ePOP Concept (v1.0)” from ZeBeyond Ltd. of Leamington Spa, UK, to estimate the benefits of electrification. This method is quick to set up, requiring minimal data preparation and simulation expertise. The results were compared with measured fuel consumption data, and with those of commercially available analysis tools. The errors deriving from ePOP Concept’s BSFC assumptions alone were large at 17% RMS when using a generic value for engine BSFC, but could be improved to 6.7% RMS when applying a readily available minimum BSFC value in the model setup. For future development, a target accuracy of ±10% could potentially be achieved with one-dimensional loss models, requiring minimal extra setup effort, while reducing the subject BSFC errors to 3.9% RMS.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Propulsion Systems and Components)
►▼
Show Figures
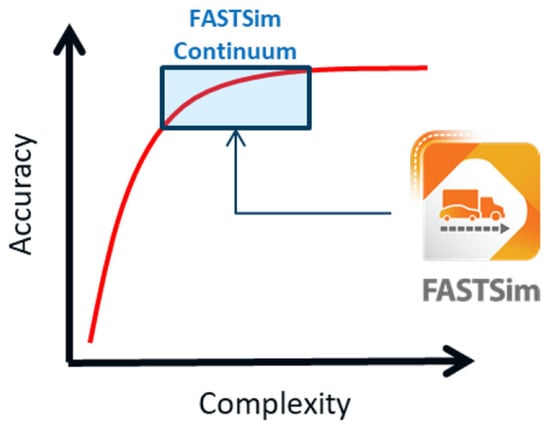
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Design and Sensorless Control in Dual Three-Phase PM Vernier Motors for 5 MW Ship Propulsion
by
Vahid Teymoori, Nima Arish, Hossein Dastres, Maarten J. Kamper and Rong-Jie Wang
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 670; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120670 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
Advancements in ship propulsion technologies are essential for improving the efficiency and reliability of maritime transportation. This study introduces a comprehensive approach that integrates motor design with sensorless control strategies, specifically focusing on Dual Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Vernier Motors (DTP-PMVM) for ship propulsion.
[...] Read more.
Advancements in ship propulsion technologies are essential for improving the efficiency and reliability of maritime transportation. This study introduces a comprehensive approach that integrates motor design with sensorless control strategies, specifically focusing on Dual Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Vernier Motors (DTP-PMVM) for ship propulsion. The initial section of the paper explores the design of a 5-MW DTP-PMVM using finite element method (FEM) analysis in dual three-phase configurations. The subsequent section presents a novel sensorless control technique employing a Prescribed-time Sliding Mode Observer (PTSMO) for accurate speed and position estimation of the DTP-PMSM, eliminating the need for physical sensors. The proposed observer convergence time is entirely independent of the initial estimation guess and observer gains, allowing for pre-adjustment of the estimation error settling time. Initially, the observer is designed for a DTP-PMVM with fully known model parameters. It is then adapted to accommodate variations and unknown parameters over time, achieving prescribed-time observation. This is accomplished by using an adaptive observer to estimate the unknown parameters of the DTP-PMVM model and a Neural Network (NN) to compensate for the nonlinear effects caused by the model’s unknown terms. The adaptation laws are innovatively modified to ensure the prescribed time convergence of the entire adaptive observer. MATLAB (R2023b) Simulink simulations demonstrate the superior speed-tracking accuracy and robustness of the speed and position observer against model parameter variations, strongly supporting the application of these strategies in real-world maritime propulsion systems. By integrating these advancements, this research not only proposes a more efficient, reliable, and robust propulsion motor design but also demonstrates an effective control strategy that significantly enhances overall system performance, particularly for maritime propulsion applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Design and Control of Electrical Machines in Electric Vehicles, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Experimental Evaluation of Pulsating and Rotating HFI Methods with Adaptive-Gain SMO for Sensorless IPM Compressor Drives
by
Tunahan Sapmaz and Ahmet Faruk Bakan
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 669; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120669 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
This paper presents a comprehensive sensorless control approach for interior permanent magnet (IPM) motors, integrating high-frequency injection (HFI) and model-based observer techniques to ensure accurate rotor position estimation across a wide speed range. Two HFI strategies—pulsating and rotating—are investigated experimentally and compared in
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a comprehensive sensorless control approach for interior permanent magnet (IPM) motors, integrating high-frequency injection (HFI) and model-based observer techniques to ensure accurate rotor position estimation across a wide speed range. Two HFI strategies—pulsating and rotating—are investigated experimentally and compared in combination with two observer structures: the conventional Sliding Mode Observer (SMO) and Adaptive-Gain SMO (AG-SMO). The AG-SMO dynamically adjusts its observer gain according to the estimated back-electromotive force (back-EMF) amplitude, significantly reducing chattering and improving estimation performance under varying load and noise conditions. A Frequency-Adaptive Complex Coefficient Filter (FACCF) and an Orthogonal Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) are incorporated to eliminate phase delay and enhance demodulation accuracy. Simulation and experimental results obtained using a 30 W, 20 V IPM motor demonstrate that the pulsating HFI + AG-SMO configuration achieves superior stability and noise immunity, while the rotating HFI + AG-SMO provides smoother and more accurate estimation. Overall, the proposed hybrid control framework achieves robust, high-precision, and sensorless operation for IPM motors over the wide speed range, offering a practical solution for applications such as inverter-driven compressor systems operating in noisy environments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Propulsion Systems and Components)
►▼
Show Figures
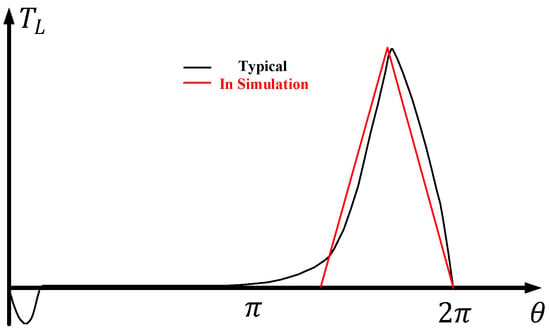
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessing the Economic Viability and Reliability of Advanced Truck Powertrains: A California Freight Case Study
by
Charbel Mansour, Amarendra Kancharla, Julien Bou Gebrael, Michel Alhajjar, Olcay Sahin, Natalia Zuniga-Garcia, Hoseinali Borhan, Sylvain Pagerit and Vincent Freyermuth
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 668; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120668 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
Heavy-duty trucking is central to the U.S. economy, and improving its long-term sustainability requires cost-effective, energy-efficient, and reliable operations. Emerging technologies—advanced powertrains, batteries, and alternative fuels—offer potential solutions, but their economic and operational viability remains uncertain. This study evaluates the performance of Class
[...] Read more.
Heavy-duty trucking is central to the U.S. economy, and improving its long-term sustainability requires cost-effective, energy-efficient, and reliable operations. Emerging technologies—advanced powertrains, batteries, and alternative fuels—offer potential solutions, but their economic and operational viability remains uncertain. This study evaluates the performance of Class 8 battery electric (BEV), plug-in hybrid (PHEV), fuel cell electric (FCEV), and diesel trucks in terms of energy use and the levelized cost of driving (LCOD) to determine when these technologies become competitive without compromising operational reliability. The analysis explores how evolving fuel prices and vehicle technology improvements in 2023, 2035, and 2050 influence the cost competitiveness of each powertrain. By comparing the results at both the technology level and the fleet level, the study demonstrates that powertrains that appear cost-effective on individual routes may not always scale to fleet-wide viability, and vice versa. The analysis is based on real-world data from over 15,700 Class 8 truck trips recorded in California in 2022, capturing diverse driving scenarios, payload conditions, and operational constraints. The results show that BEV250 can deliver cost-effective performance in short-haul operations (0–250 miles) under depot electricity prices below USD 0.34/kWh and maintain this advantage through 2050 as battery costs decline. In the 250–500-mile segment, the technology-level analysis indicates that BEV500 often achieves the lowest LCOD on individual tours, particularly under low electricity prices, while the fleet-level results show that FCEVs provide a more consistent cost performance across all tours, especially when the route variability is high. For long-haul operations (>500 miles), where BEVs are assumed to operate without en-route charging, FCEVs emerge as the most cost-effective non-diesel option by 2050, provided hydrogen prices fall below USD 6/kg. PHEVs show a limited long-term competitiveness and are mainly viable under transitional fuel price conditions. Overall, the findings underscore that there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Powertrain adoption must be range-aware, infrastructure-sensitive, and fleet-structured. By integrating technology-level and fleet-level perspectives, this study provides actionable insights for fleet operators, policymakers, and industry stakeholders seeking to balance cost, reliability, and sustainability in heavy-duty freight.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Vehicle and Transportation Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Thermal Performance Assessment of Lithium-Ion Battery Packs Under Air-Cooling Conditions
by
Sumol Sae-Heng Pisitsungkakarn, Supanut Chankerd, Supawit Chankerd, Thansita Thomrungpiyathan and Anusak Bilsalam
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 667; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120667 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Electric vehicles (EVs) have garnered significant attention in recent years due to their near-zero carbon dioxide emissions and compatibility with sustainable transportation systems. However, the lack of high-performance batteries remains a major barrier to widespread EV adoption. This study examines the variations in
[...] Read more.
Electric vehicles (EVs) have garnered significant attention in recent years due to their near-zero carbon dioxide emissions and compatibility with sustainable transportation systems. However, the lack of high-performance batteries remains a major barrier to widespread EV adoption. This study examines the variations in heat transfer coefficient and surface temperature of prismatic lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) battery packs during discharge operations. Experiments were conducted using both forced air convection and natural convection. A wind tunnel was constructed to maintain an ambient temperature of 25 °C. The air flow rates were set at 0, 40, 80, and 120 g/s, while the battery pack spacings were 5, 10, and 15 mm. Discharge rates of 0.50, 0.75, and 1.00 C-rate were also examined. The results reveal that increasing the discharge rate led to a significant and uniform rise in surface temperature across the battery pack. Additionally, the voltage decreased gradually until an approximately 90% depth of discharge, after which it declined rapidly until the battery pack was depleted. Under forced convection, the voltage drop occurred slightly faster than that under natural convection. Greater spacing between battery packs enhanced cooling efficiency. Higher air flow rates increased the convection coefficient, whereas an increased discharge rate elevated the heat generation but reduced the heat convection coefficient. The highest heat dissipation was observed at a battery pack spacing of 15 mm, a discharge rate of 1.00 C, and an air flow rate of 120 g/s. The highest convection coefficient was achieved under the same spacing and air flow rate, but with a discharge rate of 0.50 C-rate.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimization of Mixed-Model Multi-Manned Assembly Lines for Fuel–Electric Vehicle Co-Production Under Workstation Sharing
by
Lingling Hu and Vatcharapol Sukhotu
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 666; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120666 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
With the rapid transformation of the automotive industry towards electric vehicles, how to achieve efficient mixed-line production of electric vehicles and fuel vehicles has become a key challenge for modern assembly systems. This study investigated the balancing problem of a mixed-model multi-manned assembly
[...] Read more.
With the rapid transformation of the automotive industry towards electric vehicles, how to achieve efficient mixed-line production of electric vehicles and fuel vehicles has become a key challenge for modern assembly systems. This study investigated the balancing problem of a mixed-model multi-manned assembly line, considering workstation sharing (MMuALBP-WS), and developed a deterministic multi-objective model that integrates the heterogeneity of tasks and the coordination of shared workstations. An improved genetic algorithm was proposed, whose decoding mechanism enables different types of electric vehicle and fuel vehicle tasks to achieve dynamic collaboration within the shared workstations. A real case study from the chassis assembly line of Company W demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed method, achieving a 25% reduction in the number of workstations, a 27% decrease in the total number of workers, and a 23.56% increase in average workstation utilization. The results confirmed that the workstation sharing mechanism significantly improved production balance, labor utilization, and flexibility, providing a practical and scalable optimization framework for the mixed-model assembly system in the era of the transition from electric vehicles to fuel vehicles. In addition to its practical significance, this study enhances the understanding of mixed-model multi-manned line balancing by incorporating workstation-sharing logic into both the mathematical modeling and optimization process, offering a theoretical basis for future extensions to more complex production environments.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Liability for Autonomous Vehicle Torts: Who Should Be Held Responsible?
by
Zhuo Ba, Ziyu Zhao and Bokang Zhang
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 665; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120665 - 9 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The swift advancement of autonomous driving technology in China renders the traditional driver-centred liability framework inadequate for the regulatory demands of advanced automation. Traffic accidents involving advanced autonomous cars frequently provide difficulties in identifying responsible parties and assigning liability. This study employs a
[...] Read more.
The swift advancement of autonomous driving technology in China renders the traditional driver-centred liability framework inadequate for the regulatory demands of advanced automation. Traffic accidents involving advanced autonomous cars frequently provide difficulties in identifying responsible parties and assigning liability. This study employs a comparative analytical approach to evaluate the liability regimes utilised across different jurisdictions, such as the driver liability, the system liability, the manufacturer and operator liability, and the composite liability regimes. It proposes that liability standards ought to differ according to levels of automation, mirroring the benefits and constraints of each regime within China’s legal and industrial framework. Liability should be assigned to the driver at Levels 0–2, divided between the driver and manufacturer or operator at Level 3, contingent upon road and system circumstances, and predominantly attributed to manufacturers, operators, and system providers at Levels 4–5. This study outlines a framework for enhancing China’s autonomous vehicle liability system and aligning legal accountability with technological advancements, while offering recommendations for other jurisdictions in regulating developing technology.
Full article
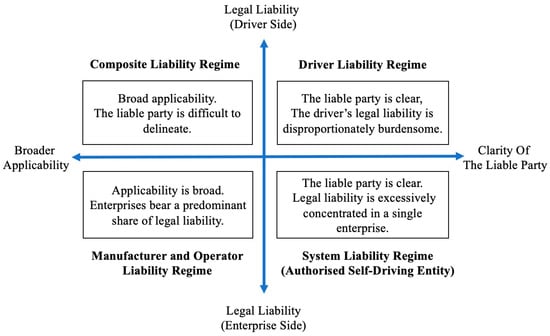
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prediction Method of Closing Action Time of Vehicle Pneumatic Main Circuit Breaker Based on PCA and GBDT Algorithm
by
Ruoyu Li, Qingfeng Wang, Jianqiong Zhang and Xiangqiang Li
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 664; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120664 - 9 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The switching action of the main circuit breaker of the train will produce switching overvoltage. In order to suppress the switching overvoltage, the phase selection control of the circuit breaker is required. However, the mechanical structure of the train-mounted electronically controlled pneumatic vacuum
[...] Read more.
The switching action of the main circuit breaker of the train will produce switching overvoltage. In order to suppress the switching overvoltage, the phase selection control of the circuit breaker is required. However, the mechanical structure of the train-mounted electronically controlled pneumatic vacuum main circuit breaker is too complicated, resulting in a large dispersion of its closing action time, which is not suitable for the traditional phase selection control system. In order to obtain the accurate closing action time, a method for predicting the closing action time of train electronically controlled pneumatic vacuum main circuit breaker based on the PCA and GBDT algorithm is proposed. The relationship between the closing phase of AC25 kV power supply train and the peak value of switching overvoltage is obtained by simulation and field test, and the accuracy requirement of the prediction model is determined, that is, the prediction error should be within ±3.3 ms. The final prediction results show that the prediction error of the on-board electronically controlled pneumatic vacuum main circuit breaker closing action time prediction model based on the PCA and GBDT algorithm is controlled within ±3.3 ms, and the probability is 92%, which meets the accuracy requirements of phase selection control.
Full article
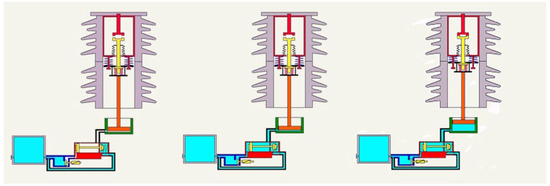
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Tacholess, Physics-Informed NVH Diagnosis for EV Powertrains with Smartphones: An Open Benchmark
by
Ignacio Benavides, Cristina Castejón, Víctor Montenegro and Julio Guerra
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 663; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120663 - 9 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper presents a physics-informed, tacholess pipeline for smartphone-grade Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH) diagnosis in electric vehicle powertrains. A configurable generator synthesizes labeled signals with order components (1×/2×/3×), AM/FM modulation, sub-harmonics, impact-driven ring-down near resonance, and realistic white/pink/ambient noise at phone bandwidths.
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a physics-informed, tacholess pipeline for smartphone-grade Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH) diagnosis in electric vehicle powertrains. A configurable generator synthesizes labeled signals with order components (1×/2×/3×), AM/FM modulation, sub-harmonics, impact-driven ring-down near resonance, and realistic white/pink/ambient noise at phone bandwidths. A ridge-guided harmonic comb recenters orders without a tachometer and splits tonal from residual content. Interpretable features—order-invariant ratios (

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Review of Emerging Hybrid Gas–Magnetic Bearings for Aerospace Electrical Machines
by
Mohammad Reza Karafi and Pedram Asef
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 662; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120662 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Hybrid Gas–Magnetic Bearings (HGMBs) are an emerging technology ready to completely change high-speed oil-free rotor support in aerospace electric motors. Because HGMBs combine the stiffness and load capacity of gas bearings with the active control of magnetic bearings, enabling oil-free, contactless rotor support
[...] Read more.
Hybrid Gas–Magnetic Bearings (HGMBs) are an emerging technology ready to completely change high-speed oil-free rotor support in aerospace electric motors. Because HGMBs combine the stiffness and load capacity of gas bearings with the active control of magnetic bearings, enabling oil-free, contactless rotor support from zero to ultra-high speeds. They offer more load capacity of standalone magnetic bearings while maintaining full levitation across the entire speed range. Dual-mode operation, magnetic at low speeds and gas film at high speeds, minimizes control power and thermal losses, making HGMBs ideal for high-speed aerospace systems such as cryogenic turbopumps, electric propulsion units, and hydrogen compressors. While not universally optimal, HGMBs excel where extreme speed, high load, and stringent efficiency requirements converge. Advances in modeling, control, and manufacturing are expected to accelerate their adoption, marking a shift toward hybrid electromagnetic–aerodynamic rotor support for next-generation aerospace propulsion. This review provides a thorough overview of emerging HGMBs, emphasizing their design principles, performance metrics, application case studies, and comparative advantages over conventional gas or magnetic bearings. We include both a historical perspective and the latest developments, supported by technical data, experimental results, and insights from recent literature. We also present a comparative discussion including future research directions for HGMBs in aerospace electrical machine applications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Social Planning for eBRT Innovations: Multi-Criteria Evaluation of Societal Impacts
by
Maria Morfoulaki, Maria Chatziathanasiou and Iliani Styliani Anapali
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 661; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120661 - 6 Dec 2025
Abstract
This paper develops and applies an ex-ante methodological framework to assess the societal optimisation of eBRT innovations within the Horizon Europe eBRT2030 project, using Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) and the PROMETHEE method. The study evaluates 11 eBRT innovations to be deployed in five
[...] Read more.
This paper develops and applies an ex-ante methodological framework to assess the societal optimisation of eBRT innovations within the Horizon Europe eBRT2030 project, using Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) and the PROMETHEE method. The study evaluates 11 eBRT innovations to be deployed in five demonstration sites in Europe and one in Colombia. Twenty social parameters, including 10 risks and 10 benefits, were weighted and scored through expert and stakeholder engagement, to calculate the Societal Optimisation Index (SOI). Positive SOI values indicate that societal benefits outweigh risks, and negative values indicate the opposite, while close-to-zero values indicate socially neutral or ambiguous options requiring case-specific judgement. The results indicate that innovations such as Adaptive Fleet Scheduling and Planning, Intelligent Driver Support Systems, and IoT Monitoring Platforms provide strong societal benefits with manageable risks, while charging-related innovations are associated with social concerns. The study emphasises the importance of social impact assessment prior to implementing innovations, to enable inclusive decision-making for policymakers and transport planners and enable the development of socially optimised eBRT systems. Embedding experts’ perspectives and social criteria ensures that technological innovations are aligned with societal needs, assisting the transition towards more equitable, low-carbon transport systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Zero Emission Buses for Public Transport)
►▼
Show Figures
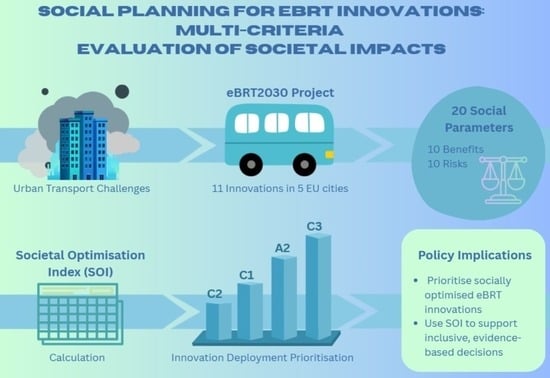
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Decarbonizing Transportation: Cross-Country Evidence on Electric Vehicle Sales and Carbon Dioxide Emissions
by
Burcu Yengil Bülbül and Maide Betül Baydar
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 660; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120660 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
The increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions are widely recognized as the primary driving force behind the phenomenon of global warming. Considering environmental concerns and the depletion of fossil fuel reserves, the use of electric vehicles (EVs) in transportation has emerged
[...] Read more.
The increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions are widely recognized as the primary driving force behind the phenomenon of global warming. Considering environmental concerns and the depletion of fossil fuel reserves, the use of electric vehicles (EVs) in transportation has emerged as one of the most promising technological alternatives to conventional gasoline-powered cars. Compared to their gasoline counterparts, EVs significantly reduce the costs associated with air pollution and mitigate adverse effects on human health. Owing to these characteristics, EVs have become one of the key components of the transition toward a sustainable future, while also steering the transformation of the global automotive industry. This transition is reshaping the structure of the global automobile industry. Many countries aim to achieve their greenhouse gas reduction targets by promoting the adoption of EVs. This study aims to empirically examine the effects of electric vehicles on CO2 emissions in 15 high-income countries during the period 2010–2023, highlighting both short- and long-term environmental impacts. The analysis also considers economic and socio-demographic variables such as gross domestic product (GDP), urbanization, and fossil fuel consumption. The findings indicate that the share of EVs significantly reduces CO2 emissions, whereas sales have a short-term increasing effect.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Energy Supply and Sustainability)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- WEVJ Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
WEVJ
Vehicle System Dynamics and Intelligent Control for Electric Vehicles
Guest Editors: Leilei Zhao, Liguo Zang, Yuewei Yu, Jian WangDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
WEVJ
New Trends in Electrical Drives for EV Applications
Guest Editors: Ayman Abdel-Khalik, Mohamed AbdelrahemDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
WEVJ
Vehicle-to-Grid in Coordinated Power and Transportation Systems: Challenges and Development
Guest Editors: Qinran Hu, Tao QianDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
WEVJ
Recent Advances in Intelligent Vehicle
Guest Editors: Biao Yu, Jiajia Chen, Xiang DongDeadline: 31 December 2025