- Article
Method of Characterization and Classification of the Physicochemical Quality of Polished White Rice Grains Using VIS/NIR/SWIR Techniques and Machine Learning Models for Lot Segregation and Commercialization in Storage and Processing Units
- Letícia de Oliveira Carneiro,
- Nairiane dos Santos Bilhalva and
- Ênio Antônio Manfroi Filho
- + 4 authors
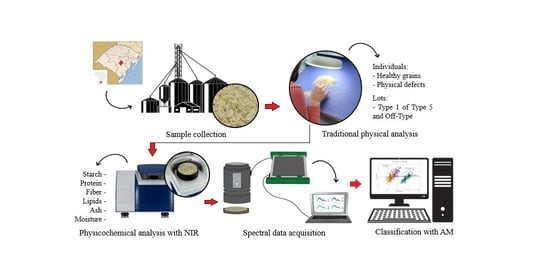
The quality of rice depends on physical, nutritional, and sensory attributes. However, in industrial practice, quality is predominantly based on physical characteristics evaluated by the conventional method for categorizing commercial atches. In this context, the present study aimed to characterize the physical quality and proximate composition and to classify commercial batches of polished white rice using machine learning (ML) algorithms based on spectral data. Individual samples (healthy grains and physical defects) and samples from commercial batches (Type 1 to Type 5 and Off-Type) were analyzed and prepared in accordance with current legislation. Spectral data were obtained using NIR and hyperspectral measurements covering the VIS/NIR/SWIR regions, and proximate composition was determined for moisture (MOI), starch (ST), protein (PRO), lipids (LIP), fiber (FIB), and ash (ASH). Multivariate analyses and ML classification models were applied to evaluate differences among grain types and commercial categories and to assess the discriminatory capacity of spectral information. The results showed that including physicochemical attributes to evaluate the quality of commercial batches simplifies the commercial categories currently used. For spectral behavior, batches classified as Type 1 and Type 2 showed low reflectance in the NIR and SWIR regions, suggesting greater interaction of radiant energy with compounds associated with nutritional and sensory quality. The MLP, LGBM, CAT, XGB and RF models performed best for the classification of commercial white polished rice batches, with metrics above 95%. The SWIR region, especially the 2173 nm spectral point, demonstrated high discriminatory power. In conclusion, the application of machine learning models based on VIS/NIR/SWIR spectroscopy proved highly efficient for classifying commercial batches of polished white rice, integrating physical and physicochemical attributes of the grains.
24 December 2025