Journal Description
Drugs and Drug Candidates
Drugs and Drug Candidates
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on drug discovery, development, and knowledge, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 15 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Drugs and Drug Candidates is a companion journal of Pharmaceuticals.
- Journal Clusters-Pharmaceutical Science: Scientia Pharmaceutica, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Pharmacy, Future Pharmacology, Pharmacoepidemiology, Drugs and Drug Candidates and Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry.
Latest Articles
Simulation of Plasma Level Changes in Cerivastatin and Its Metabolites, Particularly Cerivastatin Lactone, Induced by Coadministration with CYP2C8 Inhibitor Gemfibrozil, CYP3A4 Inhibitor Itraconazole, or Both, Using the Metabolite-Linked Model
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(3), 34; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4030034 - 4 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objective: Cerivastatin (Cer), a cholesterol-lowering statin, was withdrawn from the market due to fatal cases of rhabdomyolysis, particularly when co-administered with gemfibrozil (Gem), a strong CYP2C8 inhibitor. However, the pharmacokinetic (PK) mechanisms underlying these adverse events remain unclear. This study investigates the impact
[...] Read more.
Background/Objective: Cerivastatin (Cer), a cholesterol-lowering statin, was withdrawn from the market due to fatal cases of rhabdomyolysis, particularly when co-administered with gemfibrozil (Gem), a strong CYP2C8 inhibitor. However, the pharmacokinetic (PK) mechanisms underlying these adverse events remain unclear. This study investigates the impact of drug–drug interactions (DDIs) involving Gem and itraconazole (Itr), a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor, on plasma concentrations of Cer and its major metabolites—M23, M1, and cerivastatin lactone (Cer-L)—with a focus on the risk of excessive Cer-L accumulation. Methods: We applied a newly developed Metabolite-Linked Model that simultaneously characterizes parent drug and metabolite kinetics by estimating metabolite formation fractions (fM) and elimination rate constants (KeM). The model was calibrated using observed DDI data from Cer + Gem and Cer + Itr scenarios and then used to predict outcomes in an untested Cer + Gem + Itr combination. Results: The model accurately reproduced observed metabolite profiles in single-inhibitor DDIs. Predicted AUCR values for Cer-L were 4.2 (Cer + Gem) and 2.1 (Cer + Itr), with reduced KeM indicating CYP2C8 and CYP3A4 as primary elimination pathways. In the dual-inhibitor scenario, Cer-L AUCR reached ~70—far exceeding that of the parent drug—suggesting severe clearance impairment and toxic accumulation. Conclusions: Dual inhibition of CYP2C8 and CYP3A4 may cause dangerously elevated Cer-L levels, contributing to Cer-associated rhabdomyolysis. This modeling approach offers a powerful framework for evaluating DDI risks involving active or toxic metabolites, supporting safer drug development and regulatory assessment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Marketed Drugs)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Identification of Pharmacophore Groups with Antimalarial Potential in Flavonoids by QSAR-Based Virtual Screening
by
Adriana de Oliveira Fernandes, Valéria Vieira Moura Paixão, Yria Jaine Andrade Santos, Eduardo Borba Alves, Ricardo Pereira Rodrigues, Daniela Aparecida Chagas-Paula, Aurélia Santos Faraoni, Rosana Casoti, Marcus Vinicius de Aragão Batista, Marcel Bermudez, Silvio Santana Dolabella and Tiago Branquinho Oliveira
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(3), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4030033 - 4 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Severe malaria, mainly caused by Plasmodium falciparum, remains a significant therapeutic challenge due to increasing drug resistance and adverse effects. Flavonoids, known for their wide range of bioactivities, offer a promising route for antimalarial drug discovery. The aim of this
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Severe malaria, mainly caused by Plasmodium falciparum, remains a significant therapeutic challenge due to increasing drug resistance and adverse effects. Flavonoids, known for their wide range of bioactivities, offer a promising route for antimalarial drug discovery. The aim of this study was to elucidate key structural features associated with antimalarial activity in flavonoids and to develop accurate, interpretable predictive models. Methods: Curated databases of flavonoid structures and their activity against P. falciparum strains and enzymes were constructed. Molecular fingerprinting and decision tree analyses were used to identify key pharmacophoric groups. Subsequently, molecular descriptors were generated and reduced to build multiple classification and regression models. Results: These models demonstrated high predictive accuracy, with test set accuracies ranging from 92.85% to 100%, and R2 values from 0.64 to 0.97. Virtual screening identified novel flavonoid candidates with potential inhibitory activity. These were further evaluated using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations to assess binding affinity and stability with Plasmodium proteins (FabG, FabZ, and FabI). The predicted active ligands exhibited stable pharmacophore interactions with key protein residues, providing insights into binding mechanisms. Conclusions: This study provides highly predictive models for antimalarial flavonoids and enhances the understanding of structure–activity relationships, offering a strong foundation for further experimental validation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section In Silico Approaches in Drug Discovery)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Suzetrigine: A Novel Non-Opioid Analgesic for Acute Pain Management—A Review
by
Meaghan Jones, Aryanna Demery and Rami A. Al-Horani
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(3), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4030032 - 4 Jul 2025
Abstract
Suzetrigine represents a groundbreaking advancement in acute pain management as the first FDA-approved selective Nav1.8 inhibitor. This comprehensive review synthesizes data from clinical trials, pharmacological studies, and prescribing information to evaluate its mechanism, efficacy, safety, and clinical implications. With demonstrated superiority
[...] Read more.
Suzetrigine represents a groundbreaking advancement in acute pain management as the first FDA-approved selective Nav1.8 inhibitor. This comprehensive review synthesizes data from clinical trials, pharmacological studies, and prescribing information to evaluate its mechanism, efficacy, safety, and clinical implications. With demonstrated superiority over placebo in pivotal trials (SPID48: 29.3–48.4; p < 0.0001) and a favorable safety profile devoid of opioid-like addiction risks, suzetrigine offers a much-needed alternative in the opioid crisis era. However, its modest effect size compared to full-dose opioids, CYP3A-mediated drug interactions, and limited long-term data warrant judicious use. This article provides a balanced perspective on suzetrigine’s role in modern pain management protocols.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Marketed Drugs)
►▼
Show Figures
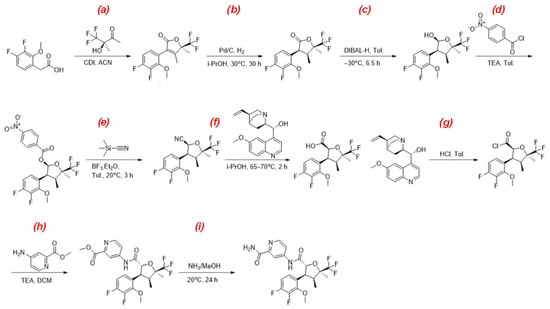
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Multifaceted Exploration of Shirakiopsis indica (Willd) Fruit: Insights into the Neuropharmacological, Antipyretic, Thrombolytic, and Anthelmintic Attributes of a Mangrove Species
by
Mahathir Mohammad, Md. Jahirul Islam Mamun, Mst. Maya Khatun, Md. Hossain Rasel, M Abdullah Al Masum, Khurshida Jahan Suma, Mohammad Rashedul Haque, Sayed Al Hossain Rabbi, Md. Hemayet Hossain, Hasin Hasnat, Nafisah Mahjabin and Safaet Alam
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(3), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4030031 - 1 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: Shirakiopsis indica (Willd.) (Family: Euphorbiaceae), a mangrove species found in the Asian region, is a popular folkloric plant. Locally, the plant is traditionally used to treat various types of ailments, especially for pain relief. Therefore, the current study investigates the neuropharmacological,
[...] Read more.
Background: Shirakiopsis indica (Willd.) (Family: Euphorbiaceae), a mangrove species found in the Asian region, is a popular folkloric plant. Locally, the plant is traditionally used to treat various types of ailments, especially for pain relief. Therefore, the current study investigates the neuropharmacological, antipyretic, thrombolytic, and anthelmintic properties of the S. indica fruit methanolic extract (SIF-ME). Methods: The neuropharmacological activity was evaluated using several bioactive assays, and the antipyretic effect was investigated using the yeast-induced pyrexia method, both in Swiss albino mice models. Human blood clot lysis was employed to assess thrombolytic activity, while in vitro anthelmintic characteristics were tested on Tubifex tubifex. Insights into phytochemicals from SIF-ME have also been reported from a literature review, which were further subjected to molecular docking, pass prediction, and ADME/T analysis and validated the wet-lab outcomes. Results: In the elevated plus maze test, SIF-ME at 400 mg/kg demonstrated significant anxiolytic effects (200.16 ± 1.76 s in the open arms, p < 0.001). SIF-ME-treated mice exhibited increased head dipping behavior and spent a longer time in the light box, confirming strong anxiolytic activity in the hole board and light–dark box tests, respectively. It (400 mg/kg) also significantly reduced depressive behavior during forced swimming and tail suspension tests (98.2 ± 3.83 s and 126.33 ± 1.20 s, respectively). The extract induced strong locomotor activity, causing mice’s mobility to gradually decrease over time in the open field and hole cross tests. The antipyretic effect of SIF-ME (400 mg/kg) was minimal using the yeast-induced pyrexia method, while it (100 μg/mL) killed T. tubifex in 69.33 ± 2.51 min, indicating a substantial anthelmintic action. SIF-ME significantly reduced blood clots by 67.74% (p < 0.001), compared to the control group’s 5.56%. The above findings have also been predicted by in silico molecular docking studies. According to the molecular docking studies, the extract’s constituents have binding affinities ranging from 0 to −10.2 kcal/mol for a variety of human target receptors, indicating possible pharmacological activity. Conclusions: These findings indicate that SIF-ME could serve as a promising natural source of compounds with neuropharmacological, anthelmintic, thrombolytic, and antipyretic properties.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Drug Candidates from Natural Sources)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Potentials of Silver Tungstate Nanoparticles, Cytotoxicity and Interference on the Activity of Antimicrobial Drugs
by
Washington de Souza Leal, Juliane Zacour Marinho, Isabela Penna Ceravolo, Lucas Leão Nascimento, Antonio Otávio de Toledo Patrocínio and Marcus Vinícius Dias-Souza
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(3), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4030030 - 23 Jun 2025
Abstract
Background: Bacterial resistance to antimicrobial drugs is a critical phenomenon that is hampering clinical treatments, raising the need for promising compounds that can be explored as pharmaceutical products. This study investigated the antimicrobial potential of α-Ag2WO4–alpha phase, orthorhombic structure
[...] Read more.
Background: Bacterial resistance to antimicrobial drugs is a critical phenomenon that is hampering clinical treatments, raising the need for promising compounds that can be explored as pharmaceutical products. This study investigated the antimicrobial potential of α-Ag2WO4–alpha phase, orthorhombic structure silver tungstate nanoparticles (STN), against clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli, alone and combined to clinically relevant antimicrobial drugs. Methods: We used classical methods (MIC/checkerboard) to investigate the antimicrobial activity of STN. We characterized STN using X-ray diffraction, photoluminescence and scanning electron microscopy. We also performed cytotoxicity tests on BGM cells and anti-inflammatory tests in vitro. Results: STN was effective at 128 µg/mL for S. aureus and at 256 µg/mL for E. coli, but was not effective against P. aeruginosa. When combined with antimicrobials, STN decreased their MIC values, and its anti-inflammatory potential was confirmed. CC50 of STN was of 16.23 ± 1.09 μg/mL against BGM cells. Conclusions: Our data open doors for further studies in animal models to investigate the effects on STN in infectious diseases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Medicinal Chemistry and Preliminary Screening)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Ex Vivo Molecular Studies and In Silico Small Molecule Inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum Bromodomain Protein 1
by
David O. Oladejo, Titilope M. Dokunmu, Gbolahan O. Oduselu, Daniel O. Oladejo, Olubanke O. Ogunlana and Emeka E. J. Iweala
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(3), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4030029 - 21 Jun 2025
Abstract
Background: Malaria remains a significant global health burden, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, accounting for high rates of illness and death. The growing resistance to frontline antimalarial therapies underscores the urgent need for novel drug targets and therapeutics. Bromodomain-containing proteins, which regulate gene expression
[...] Read more.
Background: Malaria remains a significant global health burden, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, accounting for high rates of illness and death. The growing resistance to frontline antimalarial therapies underscores the urgent need for novel drug targets and therapeutics. Bromodomain-containing proteins, which regulate gene expression through chromatin remodeling, have gained attention as potential targets. Plasmodium falciparum bromodomain protein 1 (PfBDP1), a 55 kDa nuclear protein, plays a key role in recognizing acetylated lysine residues and facilitating transcription during parasite development. Methods: This study investigated ex vivo PfBDP1 gene mutations and identified potential small molecule inhibitors using computational approaches. Malaria-positive blood samples were collected. Genomic DNA was extracted, assessed for quality, and amplified using PfBDP1-specific primers. DNA sequencing and alignment were performed to determine single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP). Structural modeling used the PfBDP1 crystal structure (PDB ID: 7M97), and active site identification was conducted using CASTp 3.0. Virtual screening and pharmacophore modeling were performed using Pharmit and AutoDock Vina, followed by ADME/toxicity evaluations with SwissADME, OSIRIS, and Discovery Studio. GROMACS was used for 100 ns molecular dynamics simulations. Results: The malaria prevalence rate stood at 12.24%, and the sample size was 165. Sequencing results revealed conserved PfBDP1 gene sequences compared to the 3D7 reference strain. Virtual screening identified nine lead compounds with binding affinities ranging from −9.8 to −10.7 kcal/mol. Of these, CHEMBL2216838 had a binding affinity of −9.9 kcal/mol, with post-screening predictions of favorable drug-likeness (8.60), a high drug score (0.78), superior pharmacokinetics, and a low toxicity profile compared to chloroquine. Molecular dynamics simulations confirmed its stable interaction within the PfBDP1 active site. Conclusions: Overall, this study makes a significant contribution to the ongoing search for novel antimalarial drug targets by providing both molecular and computational evidence for PfBDP1 as a promising therapeutic target. The prediction of CHEMBL2216838 as a lead compound with favorable binding affinity, drug-likeness, and safety profile, surpassing those of existing drugs like chloroquine, sets the stage for preclinical validation and further structure-based drug design efforts. These findings are supported by prior experimental evidence showing significant parasite inhibition and gene suppression capability of predicted hits.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section In Silico Approaches in Drug Discovery)
►▼
Show Figures
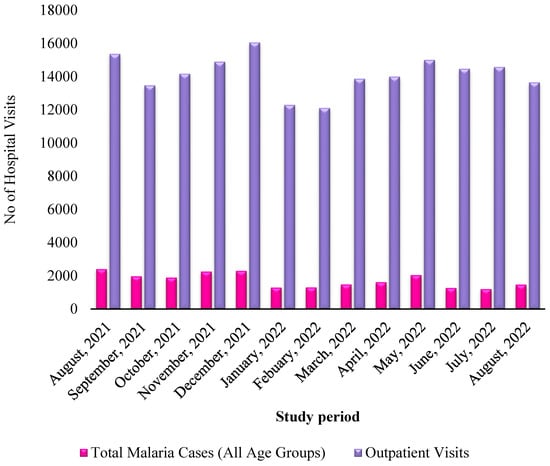
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
System Theoretic Methods in Drug Discovery and Vaccine Formulation: Review and Perspectives
by
Ankita Sharma, Yen-Che Hsiao and Abhishek Dutta
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(3), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4030028 - 21 Jun 2025
Abstract
The methods utilized in the drug discovery pipeline routinely combine machine learning and deep learning algorithms to enhance the outputs. The generation of a drug target, through virtual screening and computational analysis of databases used for target discovery, has increased the reliability of
[...] Read more.
The methods utilized in the drug discovery pipeline routinely combine machine learning and deep learning algorithms to enhance the outputs. The generation of a drug target, through virtual screening and computational analysis of databases used for target discovery, has increased the reliability of the machine learning and deep learning incorporated techniques. Recent technological advances in human immunology have provided improved tools that allow a better understanding of the biological and molecular mechanisms leading to the protective human immune response to pathogens, inspiring new strategies for vaccine design. Immunoinformatics approaches are more beneficial, and thus there is a demand for modern technologies such as reverse vaccinology, structural vaccinology, and system approaches in developing potential vaccine candidates. System theory, defined as a set of machine learning, control theory, and optimization-based methods applied to networked systems, provides a unifying framework for modeling and analyzing biological complexity. In this review, we explore the application of such computational methods at every stage of the therapeutic pipeline, including lead discovery, optimization, and dosing, as well as vaccine target prediction and immunogen design. Here, we summarize the system theoretic methods which provide insights into developed approaches and their applications in rational drug discovery and vaccine formulations. The approaches ranged in the review yield accurate predictions and insights. This review is intended to serve as a resource for researchers seeking to understand, adopt, or build upon system theoretic techniques in drug and vaccine development, offering both conceptual foundations and practical directions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section In Silico Approaches in Drug Discovery)
►▼
Show Figures
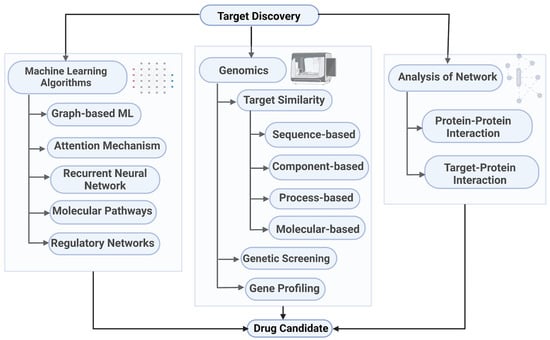
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Plants Metabolites as In Vitro Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Targets: A Systematic Review and Computational Analysis
by
Brendo Araujo Gomes, Diégina Araújo Fernandes, Thamirys Silva da Fonseca, Mariana Freire Campos, Patrícia Alves Jural, Marcos Vinicius Toledo e Silva, Larissa Esteves Carvalho Constant, Andrex Augusto Silva da Veiga, Beatriz Ribeiro Ferreira, Ellen Santos Magalhães, Hagatha Bento Mendonça Pereira, Beatriz Graziela Martins de Mattos, Beatriz Albuquerque Custódio de Oliveira, Stephany da Silva Costa, Flavia Maria Mendonça do Amaral, Danilo Ribeiro de Oliveira, Ivana Correa Ramos Leal, Gabriel Rocha Martins, Gilda Guimarães Leitão, Diego Allonso, Simony Carvalho Mendonça, Marcus Tullius Scotti and Suzana Guimarães Leitãoadd
Show full author list
remove
Hide full author list
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(2), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4020027 - 14 Jun 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Since the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the discovery of compounds with antiviral potential from medicinal plants has been extensively researched. This study aimed to investigate plant metabolites with in vitro inhibitory potential
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Since the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the discovery of compounds with antiviral potential from medicinal plants has been extensively researched. This study aimed to investigate plant metabolites with in vitro inhibitory potential against SARS-CoV-2 targets, including 3CLpro, PLpro, Spike protein, and RdRp. Methods: A systematic review was conducted following PRISMA guidelines, with literature searches performed in six electronic databases (Scielo, ScienceDirect, Scopus, Springer, Web of Science, and PubMed) from January 2020 to February 2024. Computational analyses using SwissADME, pkCSM, ADMETlab, ProTox3, Toxtree, and DataWarrior were performed to predict the absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) profiles as well as other medicinal chemistry parameters of these compounds. Results: A total of 330 plant-derived compounds with inhibitory activities against the proposed targets were identified, with compounds showing IC50 values as low as 0.01 μM. Our findings suggest that several plant metabolites exhibit significant in vitro inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 targets; however, few molecules exhibit drug development viability without further adjustments. Additionally, after these evaluations, two phenolic acids, salvianic acid A and protocatechuic acid methyl ester, stood out for their potential as candidates for developing antiviral therapies, with IC50 values of 2.15 μM against 3CLpro and 3.76 μM against PLpro; respectively; and satisfactory in silico drug-likeness and ADMET profiles. Conclusions: These results reinforce the importance of plant metabolites as potential targets for antiviral drug discovery.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fighting SARS-CoV-2 and Related Viruses)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Integrating Synthetic Accessibility Scoring and AI-Based Retrosynthesis Analysis to Evaluate AI-Generated Drug Molecules Synthesizability
by
Mokete Motente and Uche A. K. Chude-Okonkwo
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(2), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4020026 - 31 May 2025
Abstract
Background: One of the challenges of applying artificial intelligence (AI) methods to drug discovery is the difficulty of laboratory synthesizability for many AI-discovered molecules. Often, in silico techniques and metrics such as the computationally enabled synthesizability score and AI-based retrosynthesis analysis are used.
[...] Read more.
Background: One of the challenges of applying artificial intelligence (AI) methods to drug discovery is the difficulty of laboratory synthesizability for many AI-discovered molecules. Often, in silico techniques and metrics such as the computationally enabled synthesizability score and AI-based retrosynthesis analysis are used. Methods: In this paper, we present a predictive synthesizability method that integrates the gains of synthetic accessibility scoring and the benefits of AI-driven retrosynthesis analysis tools to evaluate the synthesizability of AI-generated lead drug molecules. Results: We explored the proposed method by using it to analyze the synthesizability of a set of 123 novel molecules generated using AI models. The analysis of the synthesis route of the four best molecules from the set in terms of synthesizability, as identified using the proposed method, is presented. Conclusions: This strategy enables quick initial screening and more comprehensive actionable synthetic pathways, thereby balancing speed and detail, and favoring simple routes to avoid the risk of pursuing non-synthesizable compounds in the drug development pipeline.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section In Silico Approaches in Drug Discovery)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Regulatory T Cell Function Is Not Affected by Antisense Peptide-Conjugated Phosphorodiamidate Morpholino Oligomer (PPMO)-Mediated TMPRSS2 Truncation
by
Sandra Gunne, Fiona K. Sailer, Lucas Keutmann, Marie Schwerdtner, Hong M. Moulton, Eva Böttcher-Friebertshäuser and Susanne Schiffmann
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(2), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4020025 - 27 May 2025
Abstract
Background: TMPRSS2 plays an important role in the viral entry mechanisms of influenza viruses and coronaviruses. Therefore, TMPRSS2 seems to be a suitable antiviral drug target. To exclude possible side effects of TMPRSS2 truncation in an early stage of drug in-vitro testing, this
[...] Read more.
Background: TMPRSS2 plays an important role in the viral entry mechanisms of influenza viruses and coronaviruses. Therefore, TMPRSS2 seems to be a suitable antiviral drug target. To exclude possible side effects of TMPRSS2 truncation in an early stage of drug in-vitro testing, this study aims to analyze the impact of TMPRSS2 truncation via antisense peptide-conjugated phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PPMO) targeting immune cells, using the example of regulatory T cells (Treg). Methods: TMPRSS2 was truncated in human Tregs using a splice-modulating PPMO. Effects on Treg function were analyzed by evaluation of surface marker and transcription factor expression, cytokine secretion, and effector cell suppression capability. Results: PPMO treatment led to a slight concentration-dependent toxicity in Tregs. Tregs with truncated TMPRSS2 behave similarly to untreated and control PPMO-treated cells in the analyzed assays. Conclusions: Treg function is not altered after TMPRSS2 truncation and therefore, no unwanted side effects in regard of Tregs are expected when using TMPRSS2-truncating PPMO as an anti-viral drug.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fighting SARS-CoV-2 and Related Viruses)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Targeted but Troubling: CYP450 Inhibition by Kinase and PARP Inhibitors and Its Clinical Implications
by
Martin Kondža, Josipa Bukić, Ivan Ćavar and Biljana Tubić
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(2), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4020024 - 26 May 2025
Abstract
Cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes are pivotal in the metabolism of numerous anticancer agents, with CYP3A4 being the predominant isoform involved. Inhibition of CYP450 enzymes is a major mechanism underlying clinically significant drug-drug interactions (DDIs), particularly in oncology, where polypharmacy is frequent. This review
[...] Read more.
Cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes are pivotal in the metabolism of numerous anticancer agents, with CYP3A4 being the predominant isoform involved. Inhibition of CYP450 enzymes is a major mechanism underlying clinically significant drug-drug interactions (DDIs), particularly in oncology, where polypharmacy is frequent. This review aims to provide a comprehensive and critical overview of CYP450 enzyme inhibition, focusing specifically on the impact of kinase inhibitors (KIs) and poly adenosine diphosphate-ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors. A systematic review of the current literature was conducted, focusing on the molecular mechanisms of CYP450 inhibition, including reversible, time-dependent, mechanism-based, and pseudo-irreversible inhibition. Specific attention was given to the inhibitory profiles of clinically relevant KIs and PARP inhibitors, with analysis of pharmacokinetic consequences and regulatory considerations. Many KIs, such as abemaciclib and ibrutinib, demonstrate time-dependent or quasi-irreversible inhibition of CYP3A4, while PARP inhibitors like olaparib and rucaparib exhibit moderate reversible and time-dependent CYP3A4 inhibition. These inhibitory activities can significantly alter the pharmacokinetics of co-administered drugs, leading to increased risk of toxicity or therapeutic failure. Regulatory guidelines now recommend early identification of time-dependent and mechanism-based inhibition using physiologically based pharmacokinetic) (PBPK) modeling. CYP450 inhibition by KIs and PARP inhibitors represents a critical but often underappreciated challenge in oncology pharmacotherapy. Understanding the mechanistic basis of these interactions is essential for optimizing treatment regimens, improving patient safety, and supporting personalized oncology care. Greater clinical vigilance and the integration of predictive modeling tools are necessary to mitigate the risks associated with CYP-mediated DDIs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Marketed Drugs)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Targeting Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Breast Cancer Development and the Potential Protective Effect of Phytochemicals
by
Anchal Dubey and Bechan Sharma
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(2), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4020023 - 23 May 2025
Abstract
Breast cancer continues to represent one of the most widespread and lethal health afflictions on a global scale. The advancement of this malignancy is predominantly influenced by genetic mutations that precipitate unregulated cellular growth and proliferation, with oxidative stress being a crucial factor
[...] Read more.
Breast cancer continues to represent one of the most widespread and lethal health afflictions on a global scale. The advancement of this malignancy is predominantly influenced by genetic mutations that precipitate unregulated cellular growth and proliferation, with oxidative stress being a crucial factor in all phases of carcinogenic development. Oxidative stress emerges from a disruption in the equilibrium between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidants, which inflicts damage on cellular components and facilitates the onset of cancer. Although numerous studies have advocated the notion that augmenting antioxidant levels may confer protection against cancer, other investigations have yielded contradictory results. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of antioxidants in cancer prophylaxis remains contentious, with research exhibiting variable outcomes. Certain studies have indicated that a high consumption of fruits and vegetables abundant in antioxidants may lower cancer risk. However, the irrefutable evidence is currently absent. Furthermore, the chemotherapeutic agents, such as taxanes and cisplatin, utilized in breast cancer management are reported to produce ROS as an integral aspect of their therapeutic mechanisms, thereby highlighting the intricate interplay between redox equilibrium and oncological treatment. This review emphasizes the pro-oxidant hypothesis, which asserts that heightened levels of ROS may selectively annihilate cancer cells, given that normal cells generally sustain low levels of ROS. Some recent reports have indicated that the application of plant-based molecules as a therapeutic supplement may help treat breast cancer effectively. However, a comprehensive understanding of the role of oxidative stress in breast cancer and use of antioxidants could pave the way for more precisely targeted therapeutic strategies aimed at the modulation of redox homeostasis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Drug Candidates from Natural Sources)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s Disease: Focus on H3 Receptor Modulators and Their Implications
by
Nagaraju Bandaru, Sarad Pawar Naik Bukke, Veera Mani Deepika Pedapati, Gurugubelli Sowjanaya, Vangmai Swaroopa Suggu, Swathi Nalla, Prashik Bhimrao Dudhe, Joseph Obiezu Chukwujekwu Ezeonwumelu, Abdullateef Isiaka Alagbonsi and Hope Onohuean
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(2), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4020022 - 16 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Current treatment options for Alzheimer’s disease target neurotransmitters following the disease onset, and they offer limited efficacy without slowing down the disease progression. There has been an increasing concern in recent years targeting the histamine H3 receptor (H3R) in treating cognitive disorders, including
[...] Read more.
Current treatment options for Alzheimer’s disease target neurotransmitters following the disease onset, and they offer limited efficacy without slowing down the disease progression. There has been an increasing concern in recent years targeting the histamine H3 receptor (H3R) in treating cognitive disorders, including dementia. Preclinical studies have shown that antagonists of H3R or inverse agonists enhance the cognitive function in animal models with dementia by increasing the release of neurotransmitters associated with learning and memory. This review employed a systematic literature search across databases including PubMed, Scopus, Google Scholar, and ClinicalTrials.gov, selecting peer-reviewed studies. The results of this study illustrate the complex landscape of research on H3R modulators in dementia, highlighting both promising findings and ongoing challenges in translating preclinical discoveries into effective clinical interventions. Knowing the role of H3R in dementia and developing novel pharmacological interventions targeting these receptors represent a promising avenue for future research, leading to the development of new treatments for this devastating condition.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
The Role of a Glucal-Based Molecule in the Reduction of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma—An In Vitro and In Silico Approach
by
Pedro Alcântara, Henrique Siqueira, Anwar Shamim, Denise Gonçalves Priolli, Karine C. Q. Banagouro, Hélio A. Stefani and Juliana Mozer Sciani
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(2), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4020021 - 12 May 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Pancreatic cancer is the seventh most lethal type of cancer in the world, and its treatment, which is largely inefficient, is based on surgery and/or non-specific chemotherapy. Its malignant features are characterized by complex cell signaling pathways, which can be used
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Pancreatic cancer is the seventh most lethal type of cancer in the world, and its treatment, which is largely inefficient, is based on surgery and/or non-specific chemotherapy. Its malignant features are characterized by complex cell signaling pathways, which can be used as targets for new drugs. Methods: In this study, glucal-based compounds were synthetized, with substitution based on fluorine, nitrogen and aromatic ring addition. The compounds were tested in the pancreatic cell culture Mia-PaCa-2 and cell viability was assessed, with further IC50 calculation, stability and selectivity. Molecular docking was performed to evaluate the probable molecular target for 5b and in silico physicochemical properties were determined. Results: One molecule, named 5b, with two fluorine atoms inserted in the aromatic ring, exerted potent inhibitory activity on cell growth (IC50 = 1.39 µM), which was selective for pancreatic cells. Through molecular docking studies, the compound was found to be positioned in the active site of JAK3, indicating inhibition of such protein, which has a role in tumoral cell growth. Moreover, 5b was stable for 24 months and had physicochemical properties to permeate cell membranes, good oral absorption, and low potential to cause toxicity. Conclusions: These data suggest that 5b can be druggable and can be considered as a prototype for a new course of treatment in pancreatic cancer.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Medicinal Chemistry and Preliminary Screening)
►▼
Show Figures
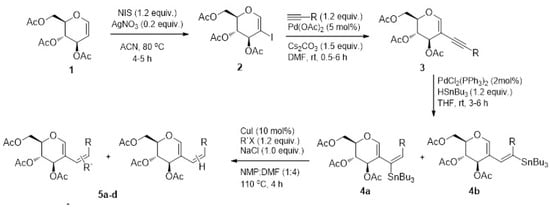
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Probing Redox Responses and DNA Interactions in Drug Discovery
by
Hüseyin Oğuzhan Kaya, Ceylin Bozdemir, Hüseyin İstanbullu and Seda Nur Topkaya
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(2), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4020020 - 29 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The thiazolo [5,4-d]pyrimidine scaffold is a class of drugs known for its anticancer, antitumor, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. In this study, the electrochemical properties of novel thiazolo [5,4-d]pyrimidine derivatives and their interactions with DNA were characterized for the first time using voltammetric
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The thiazolo [5,4-d]pyrimidine scaffold is a class of drugs known for its anticancer, antitumor, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. In this study, the electrochemical properties of novel thiazolo [5,4-d]pyrimidine derivatives and their interactions with DNA were characterized for the first time using voltammetric methods. Determining the interactions of new drug candidate molecules with DNA is crucial for drug development studies and is the main objective of this research. Methods: Both molecules were immobilized on the surface of the electrodes by passive adsorption, and their electrochemical properties were determined by voltammetric methods through reduction currents. Their interactions with DNA were carried out in the solution phase and examined by the changes in the oxidation peak potential and current of the guanine base. Results: For both molecules, it was determined that the electrochemical reduction processes are diffusion-controlled and irreversible, with an equal number of protons and electrons being transferred during this process. The detection limits for TP-NB (4-chloro-N-(5-chlorothiazolo [5,4-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)-3-nitrobenzamide) and TP-PC (1-(2-(4-(4-carbamoylpiperidin-1-yl)-3-nitrobenzamido)thiazolo [5,4-d]pyrimidin-5-yl)piperidine-4-carboxamide) were determined to be 12 µg/mL and 16 µg/mL, respectively. As a result of the interaction between both molecules with DNA, the guanine oxidation current decreased. It was found that TP-NB could act as an intercalator, while TP-PC could affect DNA electrostatically, both showing toxic effects on DNA. Conclusions: An electrochemical method was developed for the rapid, cost-effective, and sensitive detection of both molecules and their DNA interactions. Both compounds exhibited notable affinity towards DNA, as evidenced by significant changes in oxidation peak currents, shifts in peak potentials, and calculated toxicity values. These findings suggest their potential use as DNA-interacting drugs, such as anticancer and antimicrobial agents. Our study offers a quick, cost-effective, and reliable electrochemical approach for the evaluation of drug–DNA interactions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Medicinal Chemistry and Preliminary Screening)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Engineered Exosomes as Smart Drug Carriers: Overcoming Biological Barriers in CNS and Cancer Therapy
by
Tanvi Premchandani, Amol Tatode, Jayshree Taksande, Milind Umekar, Mohammad Qutub, Ujban Md Hussain and Priyanka Singanwad
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(2), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4020019 - 24 Apr 2025
Cited by 5
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Engineered exosomes have emerged as transformative drug carriers, uniquely equipped to overcome biological barriers in central nervous system (CNS) disorders and cancer therapy. These natural extracellular vesicles, derived from cell membranes, offer inherent biocompatibility, low immunogenicity, and the ability to traverse physiological obstacles
[...] Read more.
Engineered exosomes have emerged as transformative drug carriers, uniquely equipped to overcome biological barriers in central nervous system (CNS) disorders and cancer therapy. These natural extracellular vesicles, derived from cell membranes, offer inherent biocompatibility, low immunogenicity, and the ability to traverse physiological obstacles such as the blood–brain barrier (BBB) and dense tumor stroma. Recent advances in exosome engineering—including surface modification (e.g., ligand conjugation for receptor-mediated targeting) and cargo loading (siRNA, CRISPR-Cas systems, and chemotherapeutics)—have enhanced their precision and therapeutic utility. For CNS delivery, exosomes functionalized with brain-homing peptides (e.g., RVG or TfR ligands) have enabled the efficient transport of neuroprotective agents or gene-editing tools to treat Alzheimer’s disease or glioblastoma. In oncology, engineered exosomes loaded with tumor-suppressive miRNAs or immune checkpoint inhibitors exploit tumor microenvironment (TME) features, such as acidity or enzyme overexpression, for spatially controlled drug release. Furthermore, hybrid exosome–liposome systems and exosome–biomaterial composites are being explored to improve payload capacity and stability. Despite progress, challenges persist in scalable production, batch consistency, and regulatory standardization. This review critically evaluates engineering strategies, preclinical success, and translational hurdles while proposing innovations such as AI-driven exosome design and patient-derived exosome platforms for personalized therapy. By bridging nanotechnology and biomedicine, engineered exosomes can represent a paradigm shift in targeted drug delivery, offering safer and more effective solutions for historically intractable diseases.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Photothermal Bacterial Clearance Using Gold Nanoshells Grown on Chitosan Nanoparticles Dielectric Templates
by
Patricia Dolores Martinez-Flores, Marisol Gastelum-Cabrera, Manuel G. Ballesteros-Monrreal, Pablo Mendez-Pfeiffer, Marco Antonio Lopez-Mata, Gerardo García-González, Gerardo Erbey Rodea-Montealegre and Josué Juárez
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(2), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4020018 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Bacterial infections remain among the top ten major public health concerns, contributing to a high number of incidences of disease and mortality worldwide, exacerbated by the rise of multidrug-resistant bacteria (MDRB). Consequently, it is crucial to develop novel antimicrobial strategies, including the
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Bacterial infections remain among the top ten major public health concerns, contributing to a high number of incidences of disease and mortality worldwide, exacerbated by the rise of multidrug-resistant bacteria (MDRB). Consequently, it is crucial to develop novel antimicrobial strategies, including the use of functional nanoparticles. Gold nanoparticles (GNPs) have emerged as promising candidates due to their unique optical properties, particularly their ability to efficiently convert absorbed light into heat through the photothermal (PT) effect, which can be harnessed for bacteria eradication. Methods: Chitosan was modified with 3-mercaptopropionic acid to introduce sulfur groups, facilitating gold deposition onto chitosan nanoparticle (TCNPs) surface. The gold shell was subsequently formed via a seed-mediated method, wherein gold seeds were adsorbed onto TCNPs and further grown to form the shell. Photothermal effect on the bacterial viability was evaluated. Results: TCNPs with a size of 178 nm and spherical morphology were obtained. After the gold shell (TCNP@Au) exhibited a photothermal conversion efficiency of 31%, making them a promising photothermal agent for bacterial clearance. Notably, the viability of Escherichia coli was significantly reduced in the presence of TCNP@Au and was almost eradicated upon PT treatment. In contrast, TCNP@Aus were non-toxic for Staphylococcus aureus. Conclusions: TCNP@Au demonstrated favorable photothermal properties, presenting a novel nanoplatform for antibacterial applications, particularly against Gram-negative bacteria. However, further investigation is required to optimize the PT-based strategies against Gram-positive bacteria, such as S. aureus.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Preclinical Research)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Development of Ofloxacin-Loaded CS/PVA Hydrogel for the Treatment of Metritis in Bovine
by
Priyanka Kumari, Manish Kumar Shukla, Ashutosh Tripathi, Janmejay Pandey and Amit K. Goyal
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(2), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4020017 - 16 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Metritis, a common postpartum uterine infection in bovines, poses substantial challenges in livestock management, including compromised fertility and economic losses. Poor uterine drug penetration and systemic side effects, necessitating innovative localised delivery systems and limiting current systemic antibiotic treatments. Aim:
[...] Read more.
Background: Metritis, a common postpartum uterine infection in bovines, poses substantial challenges in livestock management, including compromised fertility and economic losses. Poor uterine drug penetration and systemic side effects, necessitating innovative localised delivery systems and limiting current systemic antibiotic treatments. Aim: This study aimed to develop and evaluate the potential effect of the ofloxacin-loaded hydrogel as a localised drug delivery system to treat metritis in bovine. The focus was on achieving sustained drug release, enhanced antibacterial efficacy and reduced inflammation in the endometrium. Materials and Methods: The CS/PVA hydrogel was synthesised using a freeze–thaw method and further optimised for drug encapsulation efficiency (96.7 ± 2.1%), stability and biocompatibility. Physicochemical characterisation included swelling behaviour, mechanical properties and rheological analysis. In vitro drug release profiles in the simulated uterine fluid were assessed over 72 h and antibacterial activity was tested against common uterine pathogens such as Escherichia coli and S. aureus. In vivo studies were conducted on bovines diagnosed with endometritis to evaluate clinical recovery. Results: The SEM image of the ofloxacin-loaded CS/PVA hydrogel resulted in a smooth and porous structure demonstrating larger pore size than the blank. The rheological study suggested higher stability and elastic behaviour. Antibacterial assays on E. coli and S. aureus revealed significant inhibition zones, respectively, indicating potent efficacy. In vivo, evaluated on treated bovine, reduced bacterial loads were exhibited (2.86 × 105A CFU/mL → 6.37 × 102B CFU/mL), clinical improvement was marked and uterine inflammation was resolved. Conclusions: Ofloxacin-loaded hydrogels represent a promising localised treatment for bovine metritis, offering sustained antibacterial action and improved clinical outcomes. This approach addresses the limitations of systemic antibiotic therapies and provides a practical solution for enhanced veterinary care. Further studies are recommended to validate these findings in more extensive field trials and explore commercialisation potential.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Microbes and Medicine—Papers from the 2025 OBASM Meeting)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring Chalcone Derivatives as a Multifunctional Therapeutic Agent: Investigating Antioxidant Potential, Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition and Computational Insights
by
Sujatha M. Lokanath, Manjunatha S. Katagi, Girish S. Bolakatti, Johnson Samuel and Belakatte P. Nandeshwarappa
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(2), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4020016 - 14 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: The cholinergic hypothesis is an elementary approach employed for the research and drug discovery of novel anti-Alzheimer therapeutics. Method: In this context, the study focuses on synthesizing and evaluating a new series of chalcone derivatives (3a–3j) as multifunctional
[...] Read more.
Background: The cholinergic hypothesis is an elementary approach employed for the research and drug discovery of novel anti-Alzheimer therapeutics. Method: In this context, the study focuses on synthesizing and evaluating a new series of chalcone derivatives (3a–3j) as multifunctional therapeutic agents, specifically investigating their antioxidant potential using the DPPH method with ascorbic acid as a standard. Ellman’s protocol for acetylcholinesterase inhibition assay was performed using donepezil as a standard, and computational insights were explored through molecular docking and ADME profiling. Results: Compounds 3a, 3d, 3e, 3f, and 3h exhibited excellent antioxidant activity compared to the standard. Most of the compounds exhibited moderate to good (3b, 3c, and 3h) AChE inhibitory activity. Molecular docking studies revealed conventional hydrogen bonding and π-π interactions with the enzyme’s active residues, facilitated by their electronegative groups and phenyl rings, respectively. In addition, a pharmacokinetic study was conducted using computational approach to assess druggability. The results demonstrated that compound 3b is an outstanding lead candidate with appreciable AChE inhibitory activity. Conclusions: The combined experimental and computational results of this study highlight the multifunctional nature of chalcone derivatives, suggesting their potential as promising therapeutic agents for the discovery of novel AChE inhibitors that could be employed in the management of Alzheimer’s disease and oxidative stress-related diseases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Medicinal Chemistry and Preliminary Screening)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Epigenetic Alterations in Cancer: The Therapeutic Potential of Epigenetic Drugs in Cancer Therapy
by
Preeti Gupta
Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4(2), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc4020015 - 5 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
To date, numerous studies have emerged that indicate the possible role of epigenetic modulation in the development and progression of several diseases, including cancer. Epigenetic alterations participate in various steps of carcinogenesis. They play important regulatory roles in processes like cell division, proliferation,
[...] Read more.
To date, numerous studies have emerged that indicate the possible role of epigenetic modulation in the development and progression of several diseases, including cancer. Epigenetic alterations participate in various steps of carcinogenesis. They play important regulatory roles in processes like cell division, proliferation, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Thus, epigenetic modifications such as DNA methylation, histone modifications, and non-coding RNAs serve as attractive and promising targets for cancer prevention and anti-cancer therapy. Epigenetic drugs or epi-drugs possess the ability to reverse many such epigenetic alterations and thus can help manage the clinical manifestations of cancer. Epigenetic drugs broadly target epigenetic modifications, including DNA methylation and histone post-translational modifications, to manifest their effects. Several naturally occurring as well as chemically synthesized compounds have been recognized as epigenetic drugs. Some of them are clinically approved, while many are in their preclinical and clinical trials. In this review, we aim to present a broad overview of the epigenetic modifications implicated in carcinogenesis. The review also compiles various epigenetic drugs that are approved for clinical practice, as well as those that are in the preclinical and clinical stages of investigation for anti-cancer therapy.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
1–30 November 2025
The 1st International Electronic Conference on Medicinal Chemistry and Pharmaceutics

14–17 May 2026
Meet Us at the 5th MMCS: New Trends in Chemical Biology and Drug Discovery | 14–17 May 2026 | Beijing, China

31 August–4 September 2025
International Symposium on Advances in Synthetic and Medicinal Chemistry (EFMC-ASMC 2025)

Special Issues
Special Issue in
DDC
Fighting SARS-CoV-2 and Related Viruses
Guest Editors: Jean Jacques Vanden Eynde, Annie MayenceDeadline: 30 September 2025
Special Issue in
DDC
Microbes and Medicine—Papers from the 2025 OBASM Meeting
Guest Editors: Paul Hyman, Jennifer BennettDeadline: 30 October 2025
Special Issue in
DDC
Antioxidant Drug Candidates: Mechanistic and Computational Insights into Free Radical Scavenging and Redox Modulation
Guest Editor: Žiko B. MilanovićDeadline: 30 November 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
DDC
Bioinorganic Chemistry in Drug Discovery
Collection Editors: Tanja Soldatović, Snežana Jovanović-Stević
Topical Collection in
DDC
Chirality in Drugs and Drug Candidates
Collection Editors: Carla Fernandes, Maria Emília De Sousa
Topical Collection in
DDC
Heterocycles in Drug Discovery
Collection Editors: Thierry Besson, Nicolas Primas





