Journal Description
Veterinary Sciences
Veterinary Sciences
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on veterinary sciences published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, PubAg, AGRIS, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Veterinary Sciences) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Veterinary)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 21.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Journal Cluster of Animal Science: Animals, Arthropoda, Birds, Insects, Journal of Zoological and Botanical Gardens, Pets, Poultry, Ruminants and Veterinary Sciences.
Impact Factor:
2.3 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.4 (2024)
Latest Articles
Molecular Detection and Prevalence of Equine Piroplasmosis and Other Blood Parasites in Equids of Western Aegean Türkiye
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 826; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090826 (registering DOI) - 27 Aug 2025
Abstract
Equine piroplasmosis (EP), caused by Theileria equi and Babesia caballi, is a tick-borne disease posing significant threats to equine health and the horse industry worldwide. Other vector-borne blood parasites, including Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Trypanosoma spp., and Leishmania spp., can also infect horses;
[...] Read more.
Equine piroplasmosis (EP), caused by Theileria equi and Babesia caballi, is a tick-borne disease posing significant threats to equine health and the horse industry worldwide. Other vector-borne blood parasites, including Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Trypanosoma spp., and Leishmania spp., can also infect horses; however, their prevalence remains poorly characterized in Türkiye. This study aimed to determine the molecular prevalence of T. equi, B. caballi, A. phagocytophilum, Trypanosoma spp., and Leishmania spp. in equids from the Western Aegean Region of Türkiye. Blood samples were collected from 388 clinically healthy equines across İzmir, Aydın, Denizli, and Muğla provinces. Species-specific PCR assays were performed, and T. equi and B. caballi were detected in 24.74% (96/388) and 12.89% (50/388) of samples, respectively, with co-infections in 3.09%. T. equi and B. caballi infections were detected in horses from all four sampled provinces—Aydın, İzmir, Denizli, and Muğla—except for B. caballi, which was not found in any samples from Muğla. No samples tested positive for A. phagocytophilum, Trypanosoma spp., or Leishmania spp. Prevalence significantly varied by province, breed, age, and sex (p < 0.05). This study demonstrates the considerable prevalence of T. equi and B. caballi in Western Türkiye, underlining the need for routine screening and vector control programs. The absence of other parasites suggests limited circulation; however, continued surveillance remains crucial to safeguard equine health and prevent disease spread.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Detection of Parasitic Diseases in Livestock)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Effects of Fennel Essential Oil Supplementation on Mitigating the Heat Stress Impacts on Growth Rate, Blood Biochemical Parameters, and Liver Histopathology in Broiler Chickens
by
Shimaa A. Amer, Ahmed Gouda, Rehab I. Hamed, Arwa H. Nassar, Hanaa S. Ali, Rania M. Ibrahim, Gehan N. Alagmy, Azza M. M. Abdelmoteleb, Fayez Althobaiti, Khalid S. Alotaibi, Shatha B. Albattal, Mohamed Mohamed Soliman, Saed A. Althobaiti and Gehan K. Saleh
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 825; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090825 (registering DOI) - 27 Aug 2025
Abstract
The current study evaluated the role of dietary fennel essential oil (FO) supplementation in ameliorating the effects of heat stress on growth performance, meat quality, antioxidant activity, inflammatory responses, and liver histopathology in broiler chickens. Six hundred male broiler chicks (three-day-old ROSS broilers)
[...] Read more.
The current study evaluated the role of dietary fennel essential oil (FO) supplementation in ameliorating the effects of heat stress on growth performance, meat quality, antioxidant activity, inflammatory responses, and liver histopathology in broiler chickens. Six hundred male broiler chicks (three-day-old ROSS broilers) were allocated into six experimental treatments (TRTs); the first was the negative control (Neg. CON, not subjected to hot temperature conditions), and the second was the positive control group (PS CON, subjected to hot temperatures). The control groups (Neg. and PS) were fed the basal diet without supplements. The third, fourth, and fifth groups were fed diets supplemented with 1 g FO/kg diet, 2 g FO/kg diet, and 3 g FO/kg diet, respectively and subjected to hot temperatures. The sixth group was fed the basal diet, received 500 mg of paracetamol per liter of drinking water, and subjected to hot temperatures. Hot temperature conditions (36 ± 0.5 °C) was applied for 6 h/day from the 22nd to the 25th day of the feeding period. The feeding period lasted for 35 days. The results showed that FO supplementation improved the body weight, weight gain, and feed conversion ratio compared to those in the PS CON and paracetamol groups. The growth hormone concentrations increased in the FO-supplemented TRTs and the paracetamol groups compared to those in the Neg. and PS CON groups. The serum total protein, albumin, and globulin concentrations significantly increased in the FO-supplemented TRTs compared to those in the Neg. and PS CON groups and the paracetamol TRTs. The serum TAC increased in the 3 g FO/kg TRT. The serum activity of CAT and SOD increased in the 3 and 2 g FO/kg TRTs and the paracetamol TRTs compared to those in the Neg. and PS CON groups. The serum MDA concentrations decreased in the FO-supplemented TRTs and paracetamol groups compared to those in the Neg. and PS CON groups. The IL1β and IFN-α concentrations decreased in the FO-supplemented and paracetamol groups compared to those in the PS CON groups. The HSP70 concentration was the highest in the 3 g FO/kg TRT. The immune expression of IL1-β and TGF-β in the liver tissues was downregulated in the FO-supplemented groups, especially the FO3 group, compared to those in the PS CON group. In conclusion, dietary supplementation with FO increased the broiler chickens’ growth more than that in the PS CON and paracetamol groups under hot temperatures. Fennel oil supplementation (3 g/kg diet) can alleviate the negative impacts of heat stress on broiler chickens’ antioxidant and inflammatory responses.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Evaluation of Feeds and Additives on Metabolic or Metabolomic Research on Animal Production)
►▼
Show Figures
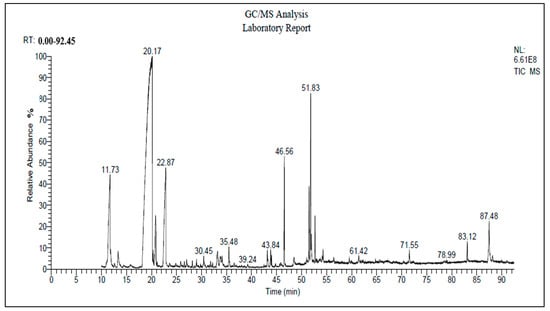
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Composition Heterogeneity and Low-Molecular-Weight Allergen Content of Dermatophagoides farinae House Dust Mite Allergen Extracts Used in Veterinary Medicine
by
Marie Welters, Ana Mas-Fontao, Silvia T. Auxilia and Thierry Olivry
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 824; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090824 (registering DOI) - 27 Aug 2025
Abstract
Extracts used for allergen sensitization testing in humans are heterogeneous in composition and may contain low levels of important allergens. In contrast, there is scant information on the variability of veterinary allergen extracts. We selected two batches of extracts of Dermatophagoides farinae house
[...] Read more.
Extracts used for allergen sensitization testing in humans are heterogeneous in composition and may contain low levels of important allergens. In contrast, there is scant information on the variability of veterinary allergen extracts. We selected two batches of extracts of Dermatophagoides farinae house dust mites from each of three different manufacturers. We observed a 3.4-fold difference in total protein content between the two extracts with the lowest and highest amounts of allergens. After electrophoresis, the band migration patterns were found to be similar between the two batches of extracts from two manufacturers and dissimilar in the third; the migration profiles were heterogeneous between manufacturers. The six extracts did not contain the same concentrations of Der f 1 and Der f 2, with fold changes between the highest and lowest concentrations measured to be 14.3× for Der f 1 and 8.0× for Der f 2. This allergen composition heterogeneity resulted in differences in ELISA seropositivity when allergic dogs had low serum concentrations of IgE against Der f 1 and Der f 2. Our findings demonstrate that, like in human allergology, allergen extracts for veterinary use are also heterogeneous in their protein content and allergen composition. This heterogeneity can impact results when determining allergen sensitizations using crude extracts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Veterinary Biomedical Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures
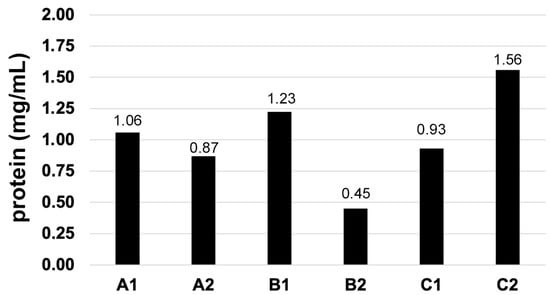
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Improving Cattle Health and Welfare in the Area Affected by the First Outbreak of Lumpy Skin Disease in Indonesia
by
Widi Nugroho, Hani Muhamad Mardani, Ando Fahda Aulia, Achmad Efendi and Michael Philipp Reichel
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 823; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090823 (registering DOI) - 27 Aug 2025
Abstract
This study aimed to investigate cattle farmer livelihoods that relate to cattle welfare in the region with the newly emerging Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) in Indonesia. A semi-structured interview survey was conducted with randomly selected cattle farmers (n = 102), in Riau. Cattle
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to investigate cattle farmer livelihoods that relate to cattle welfare in the region with the newly emerging Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) in Indonesia. A semi-structured interview survey was conducted with randomly selected cattle farmers (n = 102), in Riau. Cattle were bled for analysis of LSD-post-vaccinal seroconversion. The Sustainable Livelihood Framework (SLF) was used; data on livelihood assets, activities, and outcomes were analysed using Multiple Correspondence Analysis (MCA), two-step clustering, and the radar chart of asset possessions. The survey showed that vaccination and veterinary services covered 82.4% and 90.2% of farms. Seroconversion was detectable in vaccinated (15.0%, n = 173) and in non-vaccinated animals (23.1%, n = 13). Farmers mostly fed only grass to cattle (92.2%), with neither pastoral management nor ad libitum water provision. The MCA and cluster analyses indicated that cattle shelter roofing and flooring and manure disposal were the most important markers of the community’s livelihood. Poverty among cattle farmers was 23.5%. The cluster with lower income per capita had lower quality of shelter roofing and flooring, a lack of regular manure disposal, jobless second children, and the lowest possession of natural and physical assets. Helping to possess natural and physical assets might improve cattle farmers’ well-being and cattle welfare.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Special Issue for the 10th Anniversary of the Animal Welfare and Healthy Farming Branch of the Chinese Association of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
RNA Sequencing-Based Transcriptome Analysis of Liver in Laying Hens Supplemented with Dietary Probiotic Bacillus Species and Prebiotic Yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) Cell Walls
by
Ala E. Abudabos, Zafar M. Hakami, Ali R. Al Sulaiman, Riyadh S. Aljumaah, Valentino Palombo, Mashael R. Aljumaah, Mariasilvia D’Andrea, Abdulrahman S. Alharthi and Rashed A. Alhotan
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 822; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090822 - 27 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
To investigate the impacts of dietary Bacillus-based probiotics and yeast-derived prebiotics on the hepatic transcriptome profile, 500 Hisex White laying hens were randomly allotted into five dietary treatments from 37 to 52 weeks of age: control; control + Bacillus subtilis; control
[...] Read more.
To investigate the impacts of dietary Bacillus-based probiotics and yeast-derived prebiotics on the hepatic transcriptome profile, 500 Hisex White laying hens were randomly allotted into five dietary treatments from 37 to 52 weeks of age: control; control + Bacillus subtilis; control + Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis; control + Bacillus coagulans; and control + Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast cell wall. Transcriptome analysis revealed a substantial number of differentially expressed genes exclusively between the control and prebiotic groups, identifying 2221 genes (FDR ≤ 0.05), with 980 genes upregulated (log2 fold change 0.69 to 24.62) and 1241 downregulated (log2 fold change −0.74 to −26.46). The top 10 upregulated KEGG pathways included protein export, glycerophospholipid metabolism, tryptophan metabolism, amino acid biosynthesis, alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism, cofactor biosynthesis, propanoate metabolism, ABC transporters, 2-oxocarboxylic acid metabolism, and protein processing within the endoplasmic reticulum. In contrast, the most prominently downregulated pathways encompassed fructose and mannose metabolism, hedgehog signaling, PPAR signaling, Notch signaling, GnRH signaling, cell adhesion molecules, cytokine–cytokine receptor interactions, apelin signaling, glycosaminoglycan degradation, and RIG-I-like receptor signaling. These findings advance understanding of the hepatic transcriptomic response to yeast-derived prebiotics and identify key molecular pathways that could be targeted to enhance metabolic function in laying hens.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pathological Findings of Nestling European Goldfinches (Carduelis carduelis) Co-Infected with Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
by
Jessica Maria Abbate, Giulia D’Annunzio, Rosa Falleti, Claudio Gervasi, Valentina Ravaioli, Elisabetta Lilliu, Emma Santo, Elena Carra, Giovanni Tosi and Giovanni Lanteri
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 821; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090821 - 27 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Bacterial diseases are widespread in pet birds, posing a severe threat in nestlings and birds with weakened immune systems, often resulting in high mortality during the first days after hatching. This study aimed to describe the pathological findings of a natural bacterial co-infection
[...] Read more.
Bacterial diseases are widespread in pet birds, posing a severe threat in nestlings and birds with weakened immune systems, often resulting in high mortality during the first days after hatching. This study aimed to describe the pathological findings of a natural bacterial co-infection with Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in nestling European goldfinches (Carduelis carduelis), as a cause of mortality after hatching. Eight nestlings kept in a breeding facility showed an inability to move, anorexia, and respiratory distress, and were found dead between 1 and 4 days of life. Gross pathological findings included diffuse pneumonia with edema and multifocal hemorrhages and occasionally hepatic necrosis. On histopathology, the main findings in all examined birds included severe, subacute bronchopneumonia and severe necrotizing hepatitis. Gram-negative bacilli were observed in parabronchial walls, within pulmonary arteries and surrounding hepatocellular necrotic foci. Lungs, livers and kidneys were sampled for bacteriological examination, resulting in two Gram-negative bacterial isolates. Four housekeeping genes (i.e., 16S rRNA; rpoB; khe; ecfX) were amplified and sequenced for bacterial identification at species level. Although K. pneumoniae and P. aeruginosa are common Gram-negative pathogens and are often co-isolated in human bacterial pneumonia, co-infection with these bacteria has not been documented in nestling goldfinches to date. Pathogen identification is essential for formulating a correct etiological diagnosis and further selecting the most appropriate therapeutic strategy.
Full article
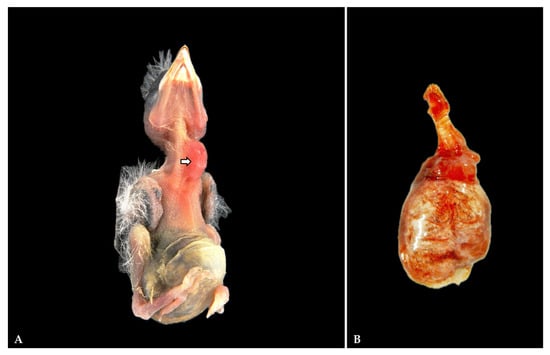
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Metagenomic Analysis of the Fecal Virome in Wild Mammals Hospitalized in Pisa, Italy
by
Maria Irene Pacini, Mario Forzan, Micaela Sgorbini, Dania Cingottini and Maurizio Mazzei
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 820; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090820 - 26 Aug 2025
Abstract
Emerging infectious diseases, particularly those of zoonotic origin, often originating from wildlife reservoirs represent a growing threat to global health. Human-driven environmental changes such as habitat fragmentation, climate change, and urban expansion have intensified interactions at the wildlife–domestic animal–human interface, facilitating cross-species viral
[...] Read more.
Emerging infectious diseases, particularly those of zoonotic origin, often originating from wildlife reservoirs represent a growing threat to global health. Human-driven environmental changes such as habitat fragmentation, climate change, and urban expansion have intensified interactions at the wildlife–domestic animal–human interface, facilitating cross-species viral transmission. Despite their epidemiological importance, systematic virological surveillance of wildlife remains challenging. In this study, we employed shotgun metagenomic sequencing to characterize the virome of wild animals rescued in the Pisa area and hospitalized at the “Mario Modenato” Veterinary Teaching Hospital (VTH) at the University of Pisa. Fecal samples collected from injured wildlife admitted between September 2020 and September 2021 were analyzed to detect both known and novel viruses. This approach builds upon previous PCR-based investigations of the same biological material, enabling a more comprehensive assessment of viral diversity. We adopted a shotgun approach for analyzing six sample pools—four were positive for at least one viral target—identifying diverse viral families, including Astroviridae, Circoviridae, Picornaviridae, Adenoviridae, and Retroviridae, in asymptomatic wildlife admitted to a veterinary hospital, highlighting their potential role as reservoirs. Our findings provide insights into the influence of environmental and anthropogenic factors on wildlife virome composition and highlight the value of hospital-based sampling strategies for urban viral surveillance. The results contribute to the development of integrated monitoring and prevention strategies within a One Health framework.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Veterinary Microbiology, Parasitology and Immunology)
Open AccessArticle
Prognostic Factors for Mortality Following Diaphragmatic Herniorrhaphy in Dogs and Cats: Multivariable Logistic Regression and Machine Learning Approaches
by
Irin Kwananocha, Sirirat Niyom, Pharkpoom Budsayaplakorn, Suwicha Kasemsuwan, Wutthiwong Theerapan and Kanawee Warrit
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 819; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090819 - 26 Aug 2025
Abstract
This study aimed to explore prognostic factors for mortality in dogs and cats following traumatic diaphragmatic herniorrhaphy using both multivariable logistic regression, a traditional statistical method, and the random forest algorithm, a machine learning approach. Associations between demographic and clinical variables and mortality
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to explore prognostic factors for mortality in dogs and cats following traumatic diaphragmatic herniorrhaphy using both multivariable logistic regression, a traditional statistical method, and the random forest algorithm, a machine learning approach. Associations between demographic and clinical variables and mortality were examined. Overall survival was 78.8% (149/189), 77% (97/126) in cats and 82.5% (52/63) in dogs. Key findings revealed that chronic diaphragmatic hernia (DH) significantly increased the odds of death compared to acute cases (adjusted odds ratio (OR) = 4.01, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.69–9.53). Elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN) increased mortality (adjusted OR = 3.24, 95% CI: 1.22–8.57). Cox proportional hazards analysis revealed that chronic DH (adjusted hazard ratio (HR) = 3.31, 95% CI: 1.51–7.30) and elevated BUN (HR = 2.88, 95% CI: 1.23–6.77) were associated with increased one-year mortality risk. The random forest analysis reinforced these findings, identifying hernia duration (Gini importance: 1.90) and BUN (Gini importance: 0.94) as the most crucial predictors. Among chronic DH patients, 55% of those with elevated BUN experienced fatal outcomes based on classification and regression tree (CART) analysis. The consistency of random forest results with logistic regression strengthens the reliability of these prognostic insights for DH patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Veterinary Surgery)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Machine Learning-Based Detection of Pig Coughs and Their Association with Respiratory Diseases in Fattening Pigs
by
Panuwat Yamsakul, Terdsak Yano, Kiettipoch Junchum, Wichittra Anukool and Nattinee Kittiwan
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 818; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090818 - 26 Aug 2025
Abstract
Respiratory infections are a major concern in pig farming as they negatively impact animal health and productivity. Coughing is a key symptom of respiratory disease and can be classified as productive or non-productive, but human assessment often leads to inconsistencies. This study aimed
[...] Read more.
Respiratory infections are a major concern in pig farming as they negatively impact animal health and productivity. Coughing is a key symptom of respiratory disease and can be classified as productive or non-productive, but human assessment often leads to inconsistencies. This study aimed to use a machine learning model to classify pig coughs and investigate their association with respiratory infections. Cough sounds from 49 fattening pigs were recorded and analyzed using a Python-based machine learning system. The model’s accuracy in detecting coughs was 0.72, compared to 0.69 for farmers. For classification of non-productive coughs, the machine learning results showed strong agreement with infection status by Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, with a Spearman’s correlation of 0.80 and a Cohen’s Kappa of 0.79. However, the association with Porcine Circovirus type 2 was weak, with correlation and Kappa values of 0.05 and 0.037, respectively. These findings indicate that machine learning can classify pig coughs more accurately than human evaluators and that non-productive coughs are strongly linked to Mycoplasma infection but not to PCV2. This suggests the potential use of machine learning for more reliable disease monitoring and early detection in swine production.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic AI, Deep Learning, and Machine Learning in Veterinary Science Imaging)
►▼
Show Figures
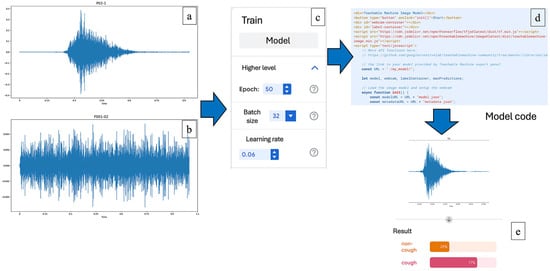
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Isolation of Lytic Bacteriophages of Escherichia coli and Their Combined Use with Antibiotics Against the Causative Agents of Colibacillosis in Calves
by
Pavel G. Alexyuk, Andrey P. Bogoyavlenskiy, Kuralay S. Akanova, Yergali S. Moldakhanov, Timur T. Kerimov, Nadezhda S. Sokolova, Vladimir E. Berezin and Madina S. Alexyuk
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 817; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090817 - 26 Aug 2025
Abstract
The spread of antibiotic-resistant pathogenic Escherichia coli poses a serious threat to calf health on livestock farms. With the decline in antibiotic therapy effectiveness, alternative approaches such as phage therapy are urgently needed. This study aimed to isolate lytic E. coli bacteriophages, characterize
[...] Read more.
The spread of antibiotic-resistant pathogenic Escherichia coli poses a serious threat to calf health on livestock farms. With the decline in antibiotic therapy effectiveness, alternative approaches such as phage therapy are urgently needed. This study aimed to isolate lytic E. coli bacteriophages, characterize their properties, and evaluate the synergistic effects of their combined use with veterinary antibiotics against colibacillosis pathogens in calves. As a result of the work, 4 bacteriophages were isolated from wastewater from various cities of Kazakhstan: vB_EcoS_ABO/4, vB_EcoM_PL/4, vB_Eco_CWW/26, vB_EcoM_ShWW/46. Morphological, biological, and genomic analyses showed that the phages belong to different genera of the Caudoviricetes class, possess high lytic activity, broad host range, environmental stability, and lack genes associated with lysogeny, antibiotic resistance, or virulence. Interaction studies with antibiotics revealed synergistic or additive effects in over 75% of cases. These findings highlight the strong potential of the isolated bacteriophages for independent or adjunctive use in the treatment and prevention of colibacillosis in calves. However, further in vivo studies are required to definitively confirm their therapeutic efficacy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Veterinary Biomedical Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures
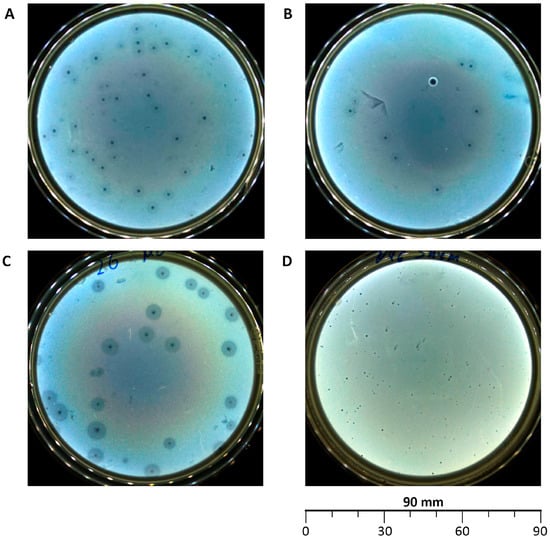
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Scutellaria baicalensis and Lonicera japonica: An In-Depth Look at Herbal Interventions Against Oxidative Stress in Non-Ruminant Animals
by
Vetriselvi Sampath, Yu Jin Beak and In Ho Kim
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 816; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090816 - 26 Aug 2025
Abstract
The use of antibiotics as growth promoters (AGPs) has been a common practice in animal production; however, concerns over microbial resistance have led organizations, such as the FAO, EU, and EFSA, to restrict or ban their use. This has prompted a growing interest
[...] Read more.
The use of antibiotics as growth promoters (AGPs) has been a common practice in animal production; however, concerns over microbial resistance have led organizations, such as the FAO, EU, and EFSA, to restrict or ban their use. This has prompted a growing interest in natural alternatives, particularly medicinal herbs, for enhancing animal performance and health. Among these, Scutellaria baicalensis (Chinese Skullcap) and Lonicera japonica (Japanese Honeysuckle) have gained attention for their high medicinal value in monogastric animal diets. These plants contain bioactive compounds, such as flavones (baicalin, baicalein, oroxylin A), iridoids (loganin), and saponins (including loniceroside hederagenin), which exhibit a range of biological activities, including antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antiviral, and anti-stress effects. Notably, these herbal extracts are natural, safe, and unlikely to induce microbial resistance. Recent studies suggest that supplementation with S. baicalensis and L. japonica can improve livestock production performance by mitigating oxidative stress. This review aims to highlight the potential application of these plant-based additives in reducing oxidative damage and enhancing productivity in animal agriculture.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nutritional Health of Monogastric Animals)
►▼
Show Figures
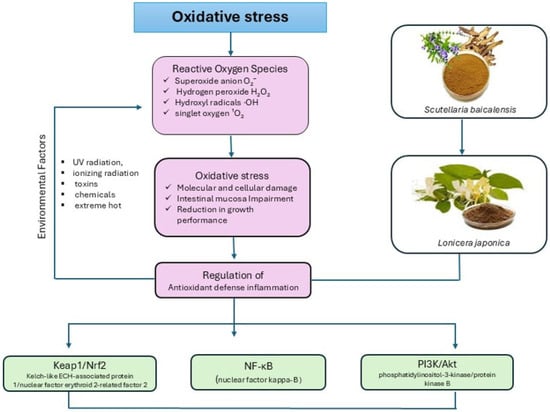
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Advancing In Vitro Tools for Oncologic Research in Cats and Dogs
by
Chang He and Sven Rottenberg
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 815; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090815 - 26 Aug 2025
Abstract
In vitro culture systems have advanced cancer biology, particularly through 2D and 3D tumor cultures. These have answered numerous scientific inquiries and propelled human oncologic research, with growing recognition of their potential to improve cancer treatment in companion animals, specifically cats and dogs.
[...] Read more.
In vitro culture systems have advanced cancer biology, particularly through 2D and 3D tumor cultures. These have answered numerous scientific inquiries and propelled human oncologic research, with growing recognition of their potential to improve cancer treatment in companion animals, specifically cats and dogs. These species develop cancer spontaneously, closely resembling specific human cancer subtypes. For example, canine and feline mammary tumors are especially valuable for studying tumor biology. In vitro models from these tumors therefore offer a unique opportunity for veterinary cancer research. Recent 3D cell culture advancements provide promising platforms for predicting therapeutic responses in human cancer and may be applied to mammary tumors in animals. However, while limitations in fully recapitulating in vivo conditions and predicting chemotherapy response have been observed in colorectal tumoroids, similar challenges are emerging in mammary and breast tumors. In particular, canine mammary tumors and human breast cancers share critical heterogeneity and microenvironmental factors usually inadequately modeled in vitro. This review critically examines the predictivity of 3D mammary tumoroids from humans and companion animals, highlighting challenges related to stromal and immune cell preservation, reproducibility, and the translational gap between in vitro findings and clinical outcomes. We propose future directions to optimize these models for both comparative oncology and veterinary-specific applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Focus on Tumours in Pet Animals: 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Molecular Survey for Major Canine Enteric Viral Pathogens in Wild Carnivores, Northwestern Italy
by
Vittorio Sarchese, Federica Di Profio, Serena Robetto, Riccardo Orusa, Beatrice Vuillermoz, Francesco Pellegrini, Fulvio Marsilio, Vito Martella and Barbara Di Martino
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 814; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090814 - 26 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Wild carnivores can harbor pathogens affecting wildlife conservation and domestic animal health. This study surveyed major viral pathogens in free-ranging wolves, red foxes, stone martens, and Eurasian badgers in Northwestern Italy. Duodenal samples from 140 carcasses were screened by consensus PCR for members
[...] Read more.
Wild carnivores can harbor pathogens affecting wildlife conservation and domestic animal health. This study surveyed major viral pathogens in free-ranging wolves, red foxes, stone martens, and Eurasian badgers in Northwestern Italy. Duodenal samples from 140 carcasses were screened by consensus PCR for members of the species Protoparvovirus carnivoran1 and for canine adenoviruses (CAdV-1/2). PCR-positive samples underwent sequence-independent amplification and Oxford Nanopore sequencing. Canine parvovirus type 2 (CPV-2) and feline panleukopenia virus (FPV) DNAs were identified in three wolves (6.4%) and one badger (4.3%), whereas CAdV-1 was detected in one red fox (1.8%). Nanopore sequencing yielded near-complete genomes of two CPV-new 2a, one CPV-2c, and one FPV strains, along with partial CAdV-1 sequences. Furthermore, the complete genome of a canine circovirus (CaCV) strain in co-infection with a CPV-2c-positive wolf and partial sequences of a canine kobuvirus (CaKoV) strain were also obtained. Phylogenetic analysis placed these viruses within known European lineages and linked them to domestic and wild hosts. These findings revealed the circulation of multiple viral pathogens among wild carnivores, reflecting ongoing cross-species spillover. Continuing molecular surveillance at the wildlife–domestic interface is recommended.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Computed Tomographic Findings in Dogs with Presumed Metaphyseal Osteopathy
by
Giulia Dalla Serra, Cliona Skelly and Olga Amorós Carafí
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 813; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090813 - 26 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Metaphyseal osteopathy (MO) is a rare systemic disease primarily affecting young large-breed dogs. Diagnosis of MO is usually based on a combination of signalment, presenting clinical signs, and imaging findings. While radiographic features of MO are well documented, reports describing Computed Tomography (CT)
[...] Read more.
Metaphyseal osteopathy (MO) is a rare systemic disease primarily affecting young large-breed dogs. Diagnosis of MO is usually based on a combination of signalment, presenting clinical signs, and imaging findings. While radiographic features of MO are well documented, reports describing Computed Tomography (CT) findings are limited. Clinical records of a veterinary teaching hospital were searched for dogs with a presumed diagnosis of MO that underwent CT imaging. CT and available radiographic studies were retrospectively reviewed. Four dogs met the inclusion criteria. All presented with pyrexia, often associated with other clinical signs. CT lesions were bilateral and symmetric in all cases, characterised by an irregular metaphyseal band of lysis parallel to the physis with associated signs of bone sclerosis. Multiple long bones were affected, and mandibular involvement was suspected in two cases. Comparison with a radiographic study was available in two cases, and follow-up CT imaging was performed in one. Although radiographs remain the primary diagnostic tool for MO, understanding the CT features of the disease is valuable and may contribute to prompt diagnosis, particularly when evaluating young dogs with pyrexia and non-specific clinical signs.
Full article
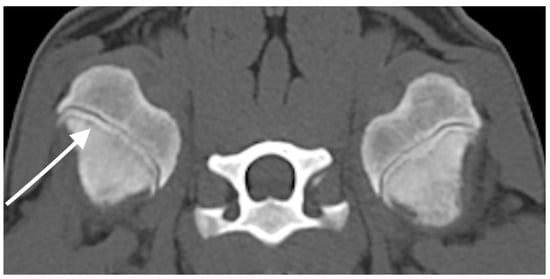
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Method for Automated Detection of Chicken Coccidia in Vaccine Environments
by
Ximing Li, Qianchao Wang, Lanqi Chen, Xinqiu Wang, Mengting Zhou, Ruiqing Lin and Yubin Guo
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 812; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090812 - 26 Aug 2025
Abstract
Vaccines play a crucial role in the prevention and control of chicken coccidiosis, effectively reducing economic losses in the poultry industry and significantly improving animal welfare. To ensure the production quality and immune effect of vaccines, accurate detection of chicken Coccidia oocysts in
[...] Read more.
Vaccines play a crucial role in the prevention and control of chicken coccidiosis, effectively reducing economic losses in the poultry industry and significantly improving animal welfare. To ensure the production quality and immune effect of vaccines, accurate detection of chicken Coccidia oocysts in vaccine is essential. However, this task remains challenging due to the minute size of oocysts, variable spatial orientation, and morphological similarity among species. Therefore, we propose YOLO-Cocci, a chicken coccidia detection model based on YOLOv8n, designed to improve the detection accuracy of chicken coccidia oocysts in vaccine environments. Firstly, an efficient multi-scale attention (EMA) module was added to the backbone to enhance feature extraction and enable more precise focus on oocyst regions. Secondly, we developed the inception-style multi-scale fusion pyramid network (IMFPN) as an efficient neck. By integrating richer low-level features and applying convolutional kernels of varying sizes, IMFPN effectively preserves the features of small objects and enhances feature representation, thereby improving detection accuracy. Finally, we designed a lightweight feature-reconstructed and partially decoupled detection head (LFPD-Head), which enhances detection accuracy while reducing both model parameters and computational cost. The experimental results show that YOLO-Cocci achieves an mAP@0.5 of 89.6%, an increase of 6.5% over the baseline model, while reducing the number of parameters and computation by 14% and 12%, respectively. Notably, in the detection of Eimeria necatrix, mAP@0.5 increased by 14%. In order to verify the application effect of the improved detection algorithm, we developed client software that can realize automatic detection and visualize the detection results. This study will help improve the level of automated assessment of vaccine quality and thus promote the improvement of animal welfare.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic AI, Deep Learning, and Machine Learning in Veterinary Science Imaging)
►▼
Show Figures
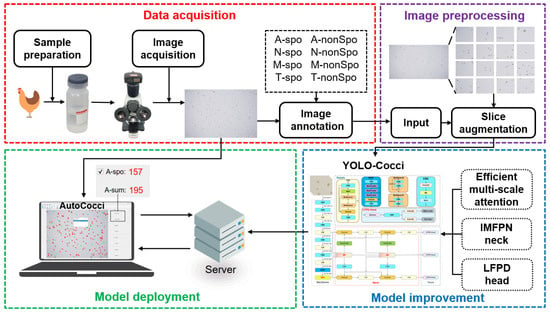
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Translation and Linguistic Validation into Spanish of the Owner-Reported Outcome Measure “Helsinki Chronic Pain Index” (HCPI)
by
María Olcoz, Miguel Ángel Cabezas and Ignacio A. Gómez de Segura
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 811; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090811 - 26 Aug 2025
Abstract
Due to the challenges in evaluating chronic pain in dogs, owner-reported outcome measures have been developed, such as the Helsinki Chronic Pain Index (HCPI), originally written in Finnish and published in English, limiting its use among Spanish-speaking veterinarians and owners/caretakers. The goal of
[...] Read more.
Due to the challenges in evaluating chronic pain in dogs, owner-reported outcome measures have been developed, such as the Helsinki Chronic Pain Index (HCPI), originally written in Finnish and published in English, limiting its use among Spanish-speaking veterinarians and owners/caretakers. The goal of this study was to obtain an equivalent Spanish version of the HCPI. The translation process followed established guidelines. First, two native Spanish speakers independently translated the HCPI from English to Spanish. A veterinary professional and a third translator then compared the translations to create a unified version. Next, an independent linguist translated the reconciled Spanish version back into English. The research team, alongside one of the linguists, reviewed the translation to resolve any discrepancies. To conclude, a cognitive assessment was conducted with 62 dog owners from diverse demographics to evaluate clarity and understanding of the translated HCPI. This resulted in a linguistically validated Spanish version of the HCPI that is conceptually aligned with the original, as a first step to validate its use by Spanish-speaking veterinarians and researchers to manage chronic pain in dogs. The next step in the process is psychometric validation, which will ensure the tool’s reliability and applicability in both clinical and research settings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Assessment and Management of Veterinary Anesthesia and Analgesia)
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of PD-L1 and TIM-3 Pathways in T Cells During Experimental Bovine Leukemia Virus Infection in Sheep
by
Wisa Tiyamanee, Tomohiro Okagawa, Shinji Yamada, Mari Ikehata, Hayato Nakamura, Maho Inoue, Naoya Maekawa, Yukinari Kato, Shiro Murata, Kazuhiko Ohashi, Kenji Murakami and Satoru Konnai
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 810; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090810 - 26 Aug 2025
Abstract
Bovine leukemia virus (BLV) infects B cells in ruminants and causes lymphoma after an extended latency period. Previous studies have demonstrated T-cell exhaustion through the upregulation of immunoinhibitory molecules, including programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-3 (TIM-3), in BLV-infected
[...] Read more.
Bovine leukemia virus (BLV) infects B cells in ruminants and causes lymphoma after an extended latency period. Previous studies have demonstrated T-cell exhaustion through the upregulation of immunoinhibitory molecules, including programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-3 (TIM-3), in BLV-infected cattle. However, studying T-cell exhaustion across all BLV infection stages remains challenging due to the virus’s prolonged latency in cattle. Sheep provide a valuable model, as they develop lymphoma more rapidly than cattle. This study examined PD-L1 and TIM-3 expression kinetics and T-cell function in BLV-infected sheep. During persistent infection, PD-L1 expression was correlated with BLV proviral load. TIM-3 expression increased in CD4+, CD8+, and γδTCR+ T cells. Functional analysis revealed that TIM-3 blockade enhanced T-cell activation markers (CD25 and CD69) in cultured PBMCs from infected sheep and increased CD69+IFN-γ+ and CD69+TNF-α+ populations, particularly among CD4+ T cells. Combined PD-L1 and TIM-3 blockade significantly enhanced cytokine production in both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, while PD-L1 blockade alone showed limited effects. These findings demonstrate the effect of TIM-3 blockade in restoring immune function during chronic BLV infection, effective both alone and in combination. This study validates sheep as a valuable model for investigating immune checkpoint dynamics and evaluating immunotherapies for BLV infection and other chronic diseases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Spotlight on Cattle Infectious Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Construction and Characterization of a Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Chimera Expressing Schmallenberg Virus Glycoproteins
by
Huijuan Guo, Zhigang Jiang, Jing Wang, Fang Wang, Qi Jia, Zhigao Bu, Xin Yin and Zhiyuan Wen
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 809; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090809 - 25 Aug 2025
Abstract
Schmallenberg virus (SBV) is a negative-sense RNA virus transmitted by insect vectors, causing arthrogryposis-hydranencephaly syndrome in newborn ruminants. Since its discovery in Germany and the Netherlands in 2011, SBV has rapidly spread across multiple European countries, resulting in significant economic losses in the
[...] Read more.
Schmallenberg virus (SBV) is a negative-sense RNA virus transmitted by insect vectors, causing arthrogryposis-hydranencephaly syndrome in newborn ruminants. Since its discovery in Germany and the Netherlands in 2011, SBV has rapidly spread across multiple European countries, resulting in significant economic losses in the livestock industry. With the increasing global animal trade and the expanded range of insect transmission, the risk of SBV introduction into non-endemic regions is also rising. As the gold standard for serological testing, the virus neutralization test (VNT) is crucial for tracking the spread of SBV and evaluating the efficacy of vaccines. However, in non-endemic regions, the lack of local viral strains and the biosafety risks associated with introducing foreign strains pose challenges to the implementation of VNT. In this study, we employed reverse genetics techniques using vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) to substitute the VSV G protein with the envelope glycoproteins of SBV, thereby successfully generating and rescuing the recombinant virus rVSVΔG-eGFP-SBVGPC. The recombinant virus was then thoroughly characterized in terms of SBV Gc protein expression, viral morphology, and growth kinetics. Importantly, rVSVΔG-eGFP-SBVGPC exhibited SBV-specific cell tropism and was capable of reacting with SBV-positive serum, enabling the measurement of neutralizing antibody titers. The results suggest that this recombinant virus can serve as a feasible alternative for SBV neutralization tests, with promising potential for application in serological screening and vaccine evaluation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Veterinary Microbiology, Parasitology and Immunology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Chinese Herbal Medicine Compound Microecological Agent (C-MEA) Improves Egg Production Performance in Caged Laying Ducks via Microbiota–Gut–Ovary Axis
by
Yanfeng Lu, Lei Zhang, Rui Zhu, Xiujun Duan, Guobo Sun and Yuying Jiang
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 808; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090808 - 25 Aug 2025
Abstract
This study was conducted to investigate the effects of a Chinese herbal medicine compound microecological agent (C-MEA) on the egg production performance, ovarian follicle development, ovary transcriptome, and cecal microbiota of caged laying ducks. A total of 108 black Muscovy ducks (150 days
[...] Read more.
This study was conducted to investigate the effects of a Chinese herbal medicine compound microecological agent (C-MEA) on the egg production performance, ovarian follicle development, ovary transcriptome, and cecal microbiota of caged laying ducks. A total of 108 black Muscovy ducks (150 days old) were randomly divided into three groups for 30 days in a formal feeding trial. Compared with the control basic diet (Group C) and 16 g/kg C-MEA dosage (Group B), the 8 g/kg C-MEA dosage (Group A) increased egg production (average laying rate 69.35%) and follicle development (5~7 Fs, 6~7 LYFs, 11~13 SYFs) mass (p < 0.05). According to RNA-Seq, the ovaries’ transcriptome among different dietary groups enriched six key pathways, including neuroactive ligand–receptor interaction, the PPAR signaling pathway, ECM–receptor interaction, focal adhesion, the adherens junction, and the FoxO signaling pathway, as well as 46 candidate key genes. According to 16S-Seq, the microbial diversity was significantly increased in Group A, and the genus abundances of Sphaerochaeta and UCG-004 were significantly changed among different dietary groups (p < 0.05). Supplementation with C-MEA may optimize the cecal microflora and the interactions between the intestinal microflora and the host. The results from combining RNA-Seq and 16S-Seq demonstrated that the relationship between Sphaerochaeta and the hub gene cluster (F2, KNG1, C5, PLG, F2RL1, FABP1, and GCG) is the most prominent. In conclusion, the egg performance of caged laying ducks can be modulated through the microbiota–gut–ovary axis. Our findings provide new insights for improving gut health and reproductive performance of caged laying ducks.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Interaction Between Intestinal Microorganisms and Hosts to Regulate Animal Growth)
►▼
Show Figures
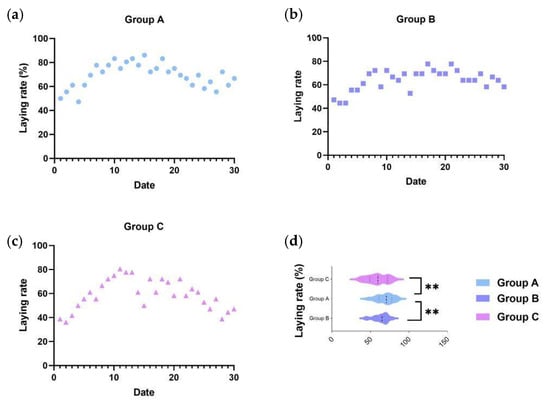
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Challenges and Enhancing Strategies of Equine Semen Preservation: Nutritional and Genetic Perspectives
by
Abd Ullah, Wenting Chen, Limeng Shi, Menghan Wang, Mingyang Geng, Jincheng Na, Muhammad Faheem Akhtar, Muhammad Zahoor Khan and Changfa Wang
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(9), 807; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090807 - 25 Aug 2025
Abstract
Equine semen preservation is fundamental to modern equine reproduction, supporting breeding programs, genetic conservation, and industry sustainability. However, significant challenges persist, including temperature sensitivity, oxidative stress, bacterial contamination, individual variability, and lack of standardized preservation protocols. These factors contribute to reduced sperm viability
[...] Read more.
Equine semen preservation is fundamental to modern equine reproduction, supporting breeding programs, genetic conservation, and industry sustainability. However, significant challenges persist, including temperature sensitivity, oxidative stress, bacterial contamination, individual variability, and lack of standardized preservation protocols. These factors contribute to reduced sperm viability and fertility following cryopreservation. This review examines critical obstacles in equine semen preservation, focusing on cryopreservation sensitivity, molecular damage mechanisms, economic constraints, and seasonal quality variations. We analyze the molecular and structural alterations (e.g., oxidative stress, membrane damage, and DNA fragmentation) and their impact on cryopreservation success. The review evaluates evidence-based enhancement strategies, including nutritional supplementation and genetic approaches, for improving semen quality. Nutritional interventions that utilize antioxidants, polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), and nutraceuticals have demonstrated promising results in enhancing sperm motility, preserving membrane integrity, and improving overall semen quality. Additionally, we discuss key candidate genes associated with equine semen-quality traits, including sperm motility, viability, and cryotolerance. The integration of nutritional supplementation and genetic selection strategies presents viable pathways for optimizing equine semen preservation techniques. These combined approaches offer potential solutions for overcoming current limitations, ultimately supporting sustainable breeding programs and advancing genetic conservation efforts in the equine industry.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Animal Sperm Conservation Techniques for Better Fertility—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Veterinary Sciences Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
19 August 2025
Empowering Academic Growth with MDPI Academic Publishing Workshop at Khon Kaen University, 29 August 2025, Bangkok, Thailand
Empowering Academic Growth with MDPI Academic Publishing Workshop at Khon Kaen University, 29 August 2025, Bangkok, Thailand

Topics
Topic in
Animals, Dairy, Microorganisms, Veterinary Sciences, Metabolites, Life, Parasitologia
The Complexity of Parasites in Animals: Impacts, Innovation, and Interventions
Topic Editors: Kun Li, Rongjun Wang, Ningbo Xia, Md. F. KulyarDeadline: 31 August 2025
Topic in
Animals, Fishes, Veterinary Sciences
Application of the 3Rs to Promote the Welfare of Animals Used in Scientific Research and Testing
Topic Editors: Johnny Roughan, Laura CalvilloDeadline: 20 September 2025
Topic in
Agriculture, Animals, Veterinary Sciences, Antibiotics, Zoonotic Diseases
Animal Diseases in Agricultural Production Systems: Their Veterinary, Zoonotic, and One Health Importance, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Ewa Tomaszewska, Beata Łebkowska-Wieruszewska, Tomasz Szponder, Joanna Wessely-SzponderDeadline: 30 September 2025
Topic in
Animals, Computers, Information, J. Imaging, Veterinary Sciences
AI, Deep Learning, and Machine Learning in Veterinary Science Imaging
Topic Editors: Vitor Filipe, Lio Gonçalves, Mário GinjaDeadline: 31 October 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Veterinary Sciences
Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Mechanisms in Food Animal Pathogens: Implications for Veterinary Health and Food Safety
Guest Editors: Sunghyun Yoon, Valentina Virginia EbaniDeadline: 30 August 2025
Special Issue in
Veterinary Sciences
Health and Welfare of Farm Animals and Their Impact on the Quality and Safety of the Derived Products
Guest Editors: Panagiotis Simitzis, Athanasios I. GelasakisDeadline: 31 August 2025
Special Issue in
Veterinary Sciences
Genetic Diversity, Conservation, and Innovative Breeding in Pigs—2nd Edition
Guest Editors: Ligang Wang, Hongbo ChenDeadline: 31 August 2025
Special Issue in
Veterinary Sciences
Interaction Between Intestinal Microorganisms and Hosts to Regulate Animal Growth
Guest Editors: Shifeng Pan, Yanhong Zhang, Penggang LiuDeadline: 31 August 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Veterinary Sciences
One-Health Approach to Bee Health
Collection Editors: Giovanni Cilia, Antonio Nanetti











