Pathological Findings of Nestling European Goldfinches (Carduelis carduelis) Co-Infected with Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Clinical Disease
2.2. Necropsy and Histopathology
2.3. Bacteriological Investigation
2.4. Molecular Identification of the Bacterial Colonies
2.5. PCR-Based Diagnostic for Viral Infectious Agents
3. Results
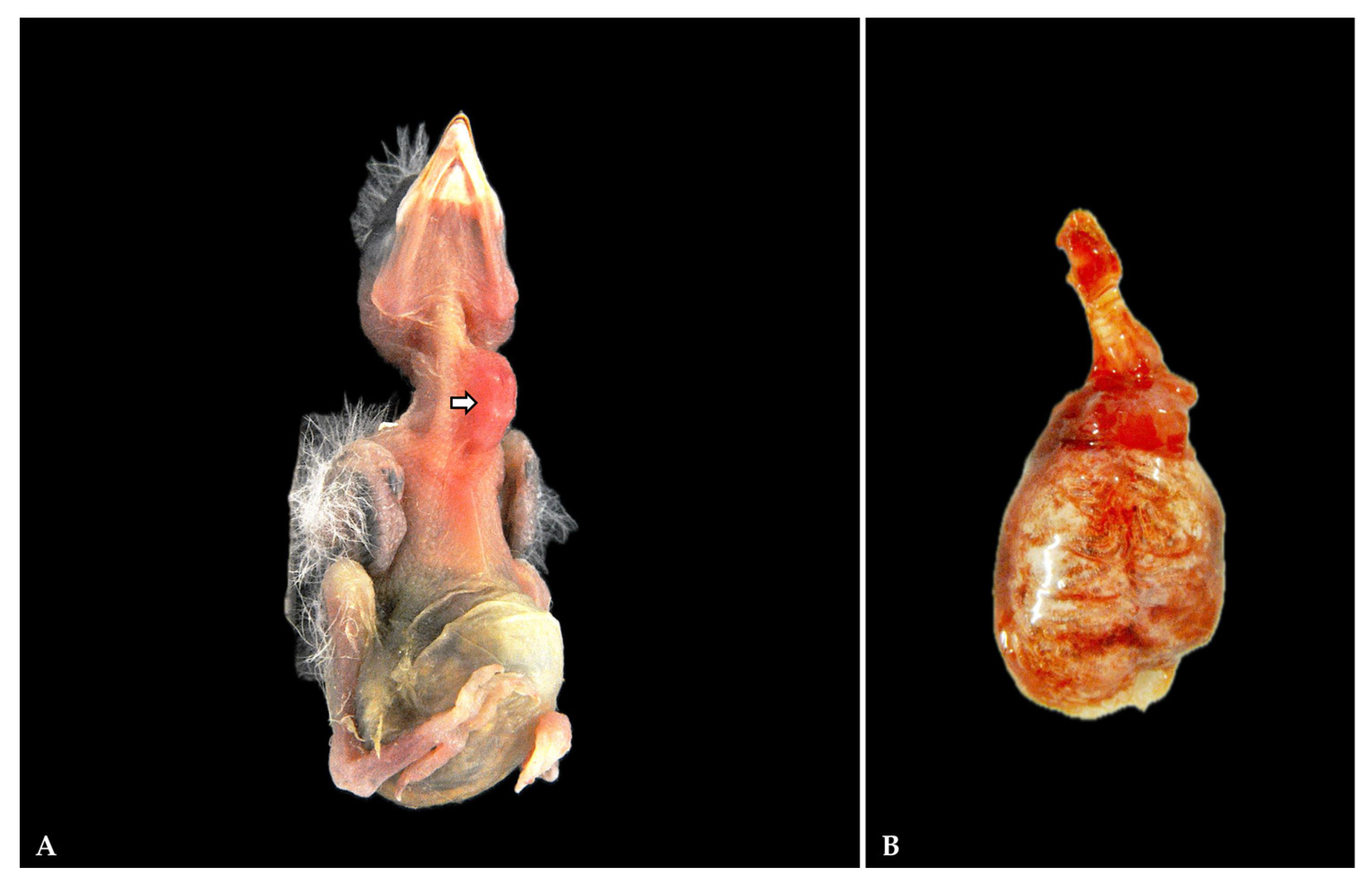
3.1. Gross Pathology
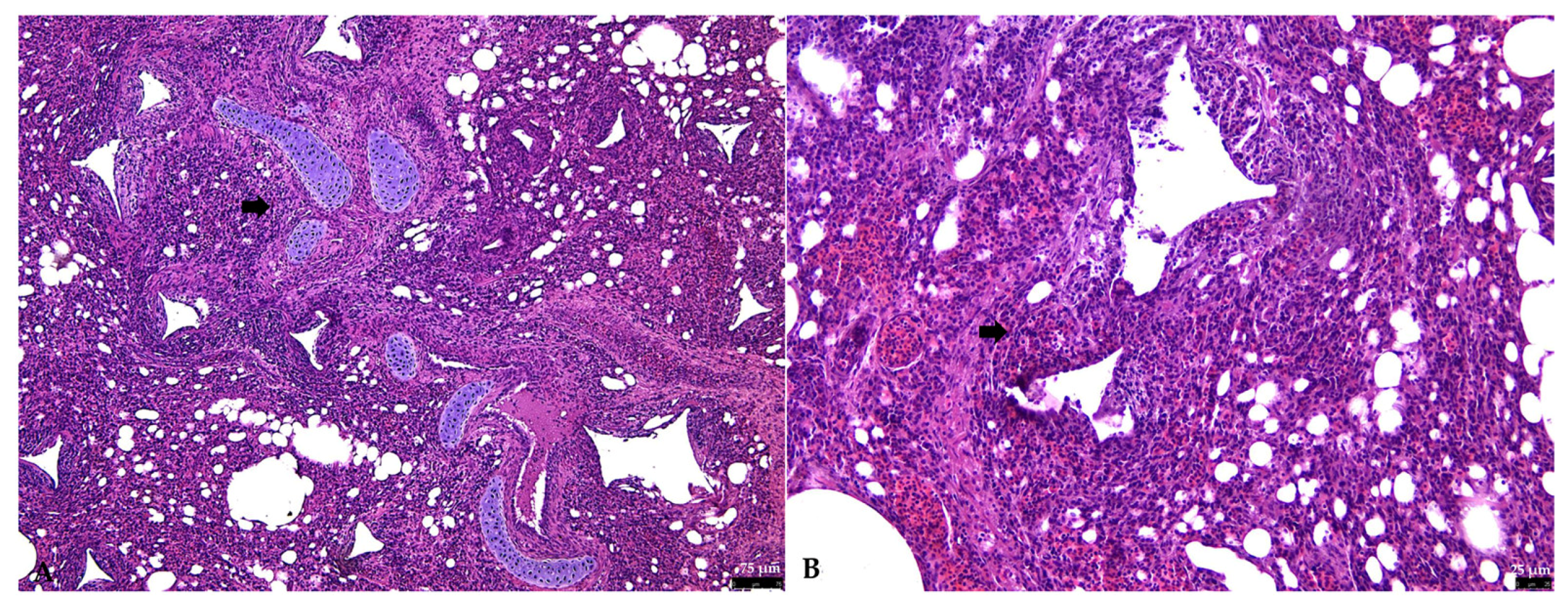
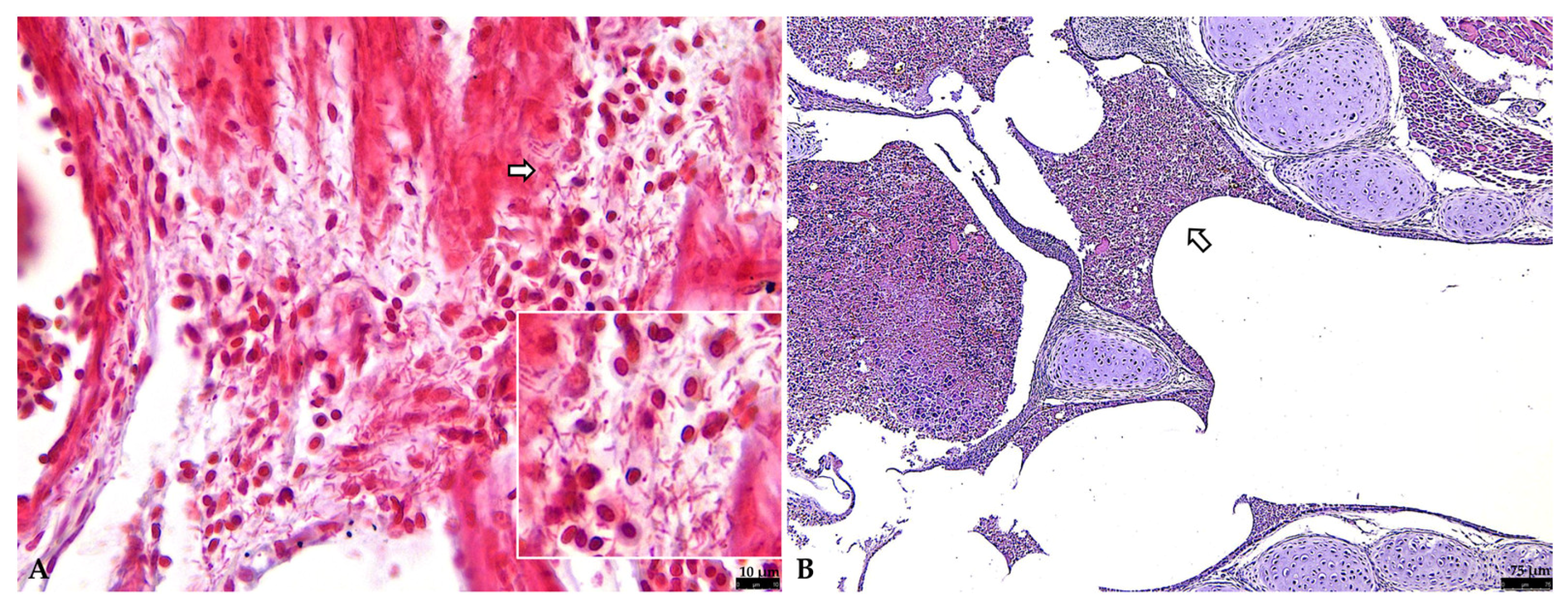
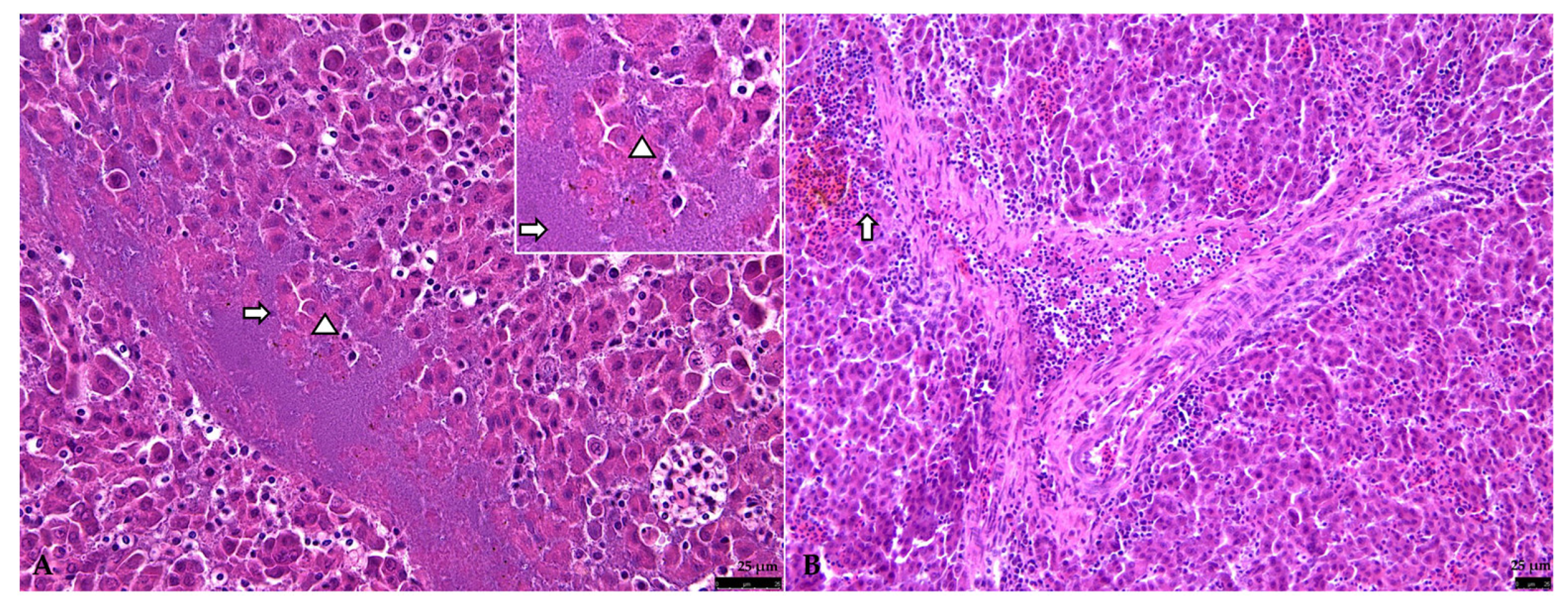
3.2. Histopathology
3.2.1. Respiratory Tract
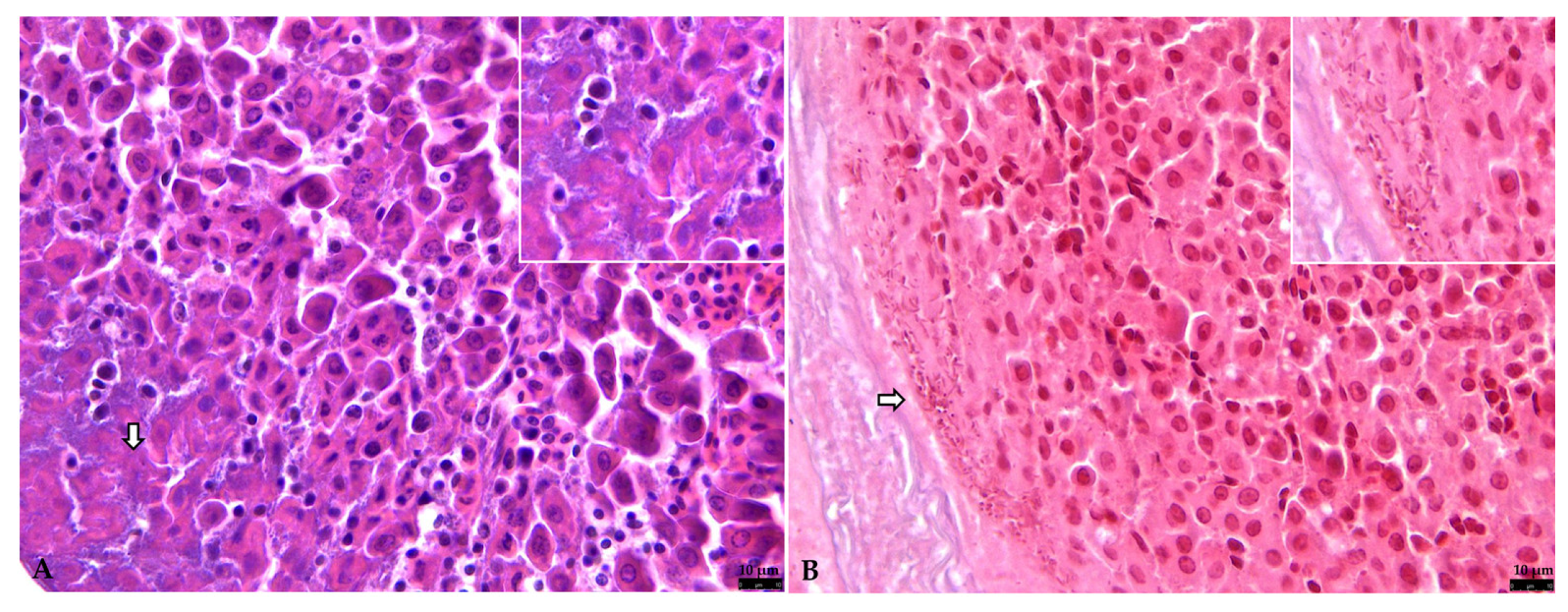
3.2.2. Liver
3.2.3. Other Organs
3.3. Bacterial Identification
3.4. Molecular-Based Diagnostic for Viral Agents
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dorrestein, G.M. Passerines. In Handbook of Avian Medicine, 2nd ed.; Tully, T.N., Jr., Dorrestein, G.M., Jones, A.K., Eds.; Sauders: Seneca Falls, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 169–208. ISBN 9780702028748. [Google Scholar]
- Zuccon, D.; Prys-Jones, R.; Rasmussen, P.C.; Ericson, P.G.P. The phylogenetic relationships and generic limits of finches (Fringillidae). Mol. Phylogenet Evol. 2012, 62, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boseret, G.; Losson, B.; Mainil, J.G.; Thiry, E.; Saegerman, C. Zoonoses in pet birds: Review and perspectives. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, V. Infectious and parasitic diseases of captive passerines. Semin. Avian Exot. Pet. Med. 2003, 12, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marouf, S.; Li, X.; Salem, H.M.; Ahmed, Z.S.; Nader, S.M.; Shaalan, M.; Awad, F.H.; Zhou, H.; Cheang, T. Molecular detection of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa of different avian sources with pathogenicity testing and in vitro evaluation of antibacterial efficacy of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoaib, M.; Tang, M.; Aqib, A.I.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Wen, Y.; Hou, X.; Xu, J.; Hao, R.; Wang, S.; et al. Dairy farm waste: A potential reservoir of diverse antibiotic resistance and virulence genes in aminoglycoside—And beta-lactam-resistant Escherichia coli in Gansu Province, China. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asokan, S.; Jacob, T.; Jacob, J.; AlSosowaa, A.A.; Cherian, T.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Vijayan, S. Klebsiella pneumoniae: A growing threat in the era of antimicrobial resistance. Microbe 2025, 7, 100333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.E.; Reavill, D.R.; Phalen, D.N. Pathology of Pet and Aviary Birds, 2nd ed.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 95–125. [Google Scholar]
- Nolan, L.K.; Vaillancourt, J.P.; Barbieri, N.L.; Louge, C.M. Colibacillosis. In Diseases of Poultry; Swayne, D.E., Ed.; Wiley Online Library: Ames, IA, USA, 2020; pp. 770–830. [Google Scholar]
- Qui, Y.; Lv, C.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Tang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.; et al. The global distribution and diversity of wild-bird-associated pathogens: An integrated data analysis and modeling study. Med 2025, 6, 100553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobuszewska, A.; Wysok, B. Pathogenic Bacteria in Free-Living Birds, and Its Public Health Significance. Animals 2024, 14, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantois, I.; Ducatelle, R.; Pasmans, F.; Haesebrouck, F.; Gast, R.; Humphrey, T.J.; Van Immerseel, F. Mechanisms of egg contamination by Salmonella enteritidis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 718–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gast, R.K.; Porter, R.E., Jr. Salmonella Infections. In Diseases of Poultry, 14th ed.; Swayne, D.E., Boulianne, M., Logue, S.M., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 719–753. [Google Scholar]
- Ottinger, M.A.; Mani, S.; Krüger, S.; Coverdale, B.; Willows-Munro, S.; Combrink, L. Microbiomes in Birds: A review of links to health and reproduction. Reprod. Fertil. 2024, 5, e230076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, H. Bacteria. In Avian Medicine: Principles and Application; Ritchie, B.W., Harrison, G.J., Harrison, L.R., Eds.; Wingers Publishing, Inc.: Lake Worth, FL, USA, 1994; pp. 949–983. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yan, H.; Zhong, J.; Wang, L.J.; Abdullah, H.M.; Wang, H.H. Antibiotic administration routes and oral exposure to antibiotic resistant bacteria as key drivers for gut microbiota disruption and resistome in poultry. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Chen, J.; Liu, K.; Tang, M.; Yang, Y. The avian gut microbiota: Diversity, influencing factors, and future directions. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 934272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benskin, C.M.H.; Rhodes, G.; Pickup, R.W.; Wilson, K.; Hartley, I.R. Diversity and temporal stability of bacterial communities in a model passerine bird, the zebra finch. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 5531–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Mazcorro, J.F.; Castillo-Carranza, S.A.; Guard, B.; Gomez-Vazquez, J.P.; Dowd, S.E.; Brightsmith, D.J. Comprehensive molecular characterization of bacterial communities in feces of bet birds using 16S marker sequencing. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 73, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteucci, G.; Binanti, D. Presence and Significance of Gram-negative bacteria in the cloacal microbiota of Psittacine and Passerine. In Proceedings of the ICARE 2017—International Conference of Avian Herpetological and Exotic Mammal Medicine, Venice, Italy, 25–29 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Coles, B.H.; Krautwald-Junghanns, M.; Orosz, S.E.; Tully, T. Essentials of Avian Medicine and Surgery, 3rd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- El Fertas-Aissani, R.; Messai, Y.; Alouache, S.; Bakour, R. Virulence profiles and antibiotic susceptibility patterns of Klebsiella pneumoniae strains isolated from different clinical specimens. Pathol. Biol. 2013, 61, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, Y.M.; Cunha, M.P.V.; Oliveira, M.G.X.; Oliveira, M.C.V.; Philadelpho, N.; Romero, D.C.; Milanelo, L.; Guimarães, M.B.; Ferreira, A.J.P.; Moreno, A.M.; et al. Virulence and antimicrobial resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from passerine and psittacine birds. Avian Pathol. 2016, 45, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.A.; Awad, N.F.S.; Abd El-Hamid, M.I.; Shaker, A.; Mohamed, R.E.; Elsohaby, I. Pet birds as potential reservoir of virulent and antibiotic resistant zoonotic bacteria. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 75, 101606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmyar, J.; Zamani, A.H. An outbreak of yolk sac infection and dead-in-shell mortality in common canary (Serinus canaria) caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2016, 17, 141–143. [Google Scholar]
- Nakhaee, P.; Zarif Moghadam, H.; Shokrpoor, S.; Razmyar, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in canaries (Serinus canaria domestica): A case report. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2022, 23, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kock, N.; Kock, R. Disease epidemic in lesser flamingos (Phoeniconauis minor) in Kenya. In Proceedings of the American Association of Zoo Veterinarians; American Association of Zoo Veterinarians: East Lansing, MI, USA, 1995; p. 115. [Google Scholar]
- Momotani, E.; Kiryu, M.; Ohshiro, M.; Murakami, Y.; Ashida, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Matsubara, Y. Granulomatous lesions caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Ostrich (Struthio camelus). J. Comp. Pathol. 1995, 112, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.A.; Silvanose, C.D.; Naldo, J.N.; Howlett, J.H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in kori bustards (Ardeotis kori). Avian Pathol. 2000, 29, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diancourt, L.; Passet, V.; Verhoef, J.; Grimont, P.A.D.; Brisse, S. Multilocus sequence typing of Klebsiella pneumoniae nosocomial isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4178–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavenir, R.; Jocktane, D.; Laurent, F.; Nazaret, S.; Cournoyer, B. Improved reliability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PCR detection by the use of the species-specific ecfX gene target. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 70, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Guo, X.; Xiang, S.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Xiang, H.; He, J.; Chen, D.; Chen, J. Comparative analyses of phenotypic methods and 16S rRNA, khe, rpoB genes sequencing for the identification of clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2016, 109, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzolo, S.; Gervasi, C.; Abbate, J.M.; Gjurčević, E.; Falleti, R.; Piro, M.G.; Lanteri, G.; Iaria, C.; Marino, F. Natural bacterial co-infection in farmed European sea bass intended for experimental research in Sicily, southern Italy: Pathological findings. Fishes 2024, 9, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, D.A.; Allen, D.P.; Fuller, C.M.; Mayers, J.; Mollett, B.C.; Londt, B.Z.; Reid, S.M.; Mansfield, K.L.; Brown, I.H. Development of an avian avulavirus 1 (AAvV-1) L-gene real-time RT-PCR assay using minor groove binding probes for application as a routine diagnostic tool. J. Virol. Methods 2019, 265, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigrist, B.; Geers, J.; Albini, S.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Wolfrum, N. A New Multiplex Real-Time RT-PCR for Simultaneous Detection and Differentiation of Avian Bornaviruses. Viruses 2021, 13, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johne, R.; Enderlein, D.; Nieper, H.; Müller, H. Novel polyomavirus detected in the feces of a chimpanzee by nested broad-spectrum PCR. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 3883–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, D.; Weston, J.; Ball, N.W.; Borghmans, B.J.; Smyth, J.A.; Gelmini, L.; Lavazza, A. Nucleotide sequence-based identification of a novel circovirus of canaries. Avian Pathol. 2001, 30, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, F.; Ando, Y.; Honda, K.; Nakayama, T.; Ono, A.; Tanoue, S.; Maeda, T.; Mori, H. Acute Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia alone and with concurrent infection: Comparison of clinical and thin-section CT findings. Br. J. Radiol. 2010, 83, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Ghany, W.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection of avian origin: Zoonosis and one health implications. Vet. World 2021, 14, 2155–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones-Nelson, O.; Hilliard, J.J.; DiGiandomenico, A.; Warrener, P.; Alfaro, A.; Cheng, L.; Stover, C.K.; Cohen, T.S.; Sellman, B.R. The Neutrophilic response to Pseudomonas damages the airway barrier, promoting infection by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 59, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchaim, D.; Perez, F.; Lee, J.; Bheemreddy, S.; Hujer, A.M.; Rudin, S.; Hayakawa, K.; Lephart, P.R.; Blunden, C.; Shango, M.; et al. “Swimming in resistance”: Co-colonization with carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae and Acinetobacter baumannii or Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am. J. Infect. Control 2012, 40, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzaki, M.Z.B.M.; Subramoni, S.; Summers, S.; Kjelleberg, S.; Rice, S.A. Klebsiella pneumoniae AI-2 transporters mediate interspecies interactions and composition in a three-species biofilm community. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, S.; Banin, E. Multi-species biofilms: Living with friendly neighbors. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 990–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Juárez, I.; Maeda, T.; Mandujano-Tinoco, E.A.; Tomás, M.; Pérez-Eretza, B.; García-Contreras, S.J.; Wood, T.K.; García-Contreras, R. Role of quorum sensing in bacterial infections. World J. Clin. Cases 2015, 3, 575–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Kim, E. Quorum sensing and antibiotic resistance in polymicrobial infections. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2024, 17, 2415598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Vivaldi, M.; Soler, J.J.; Peralta-Sánchez, J.M.; Arco, L.; Martín-Platero, A.M.; Martínez-Bueno, M.; Ruiz-Rodríguez, M.; Valdivia, E. Special structures of hoopoe eggshells enhance the adhesion of symbiont-carrying uropygial secretion that increase hatching success. J. Anim. Ecol. 2014, 83, 1289–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Veelen, H.P.J.; Salles, J.F.; Tieleman, B.I. Microbiome assembly of avian eggshells and their potential as transgenerational carriers of maternal microbiota. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Chen, C.K.; Chen, Y.Y.; Fang, A.; Shaw, G.T.W.; Hung, C.M.; Wang, D. Maternal gut microbes shape the early-life assembly of gut microbiota in passerine chicks via nests. Microbiome 2020, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, P.S.; Kasa, R.; Newbrey, J.L.; Petermann, S.R.; Wooley, R.E.; Winson, H.M.; Reed, W. Identification, antimicrobial resistance profiles and virulence of members from the family Enterobacteriaceae from the feces of yellow-headed blackbirds (Xanthocephalus xanthocephalus) in North Dakota. Avian Dis. 2007, 51, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, R.V.; Cardoso, E.M.; Lopes, E.S.; Teixeira, R.S.C.; Albuquerque, A.H.; Rocha-e-Silva, R.C.; Machado, D.N.; Bezerra, W.G.A. Identification and antimicrobial resistance of members from the Enterobacteriaceae family isolated from canaries (Serinus canaria). Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2015, 35, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenkat, J.; Krautwald-Junghanns, M.E.; Schmitz, O.A.; Eilers, A.; Schmidt, V. Aerobic cloacal and pharyngeal bacterial flora in six species of free-living birds. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raue, R.; Schmidt, V.; Freick, M.; Reinhardt, B.; Johne, R.; Kamphausen, L.; Kaleta, E.F.; Muller, H.; Krautwald-Junghanns, M.E. A disease complex associated with pigeon circovirus infection, young pigeon disease syndrome. Avian Pathol. 2005, 34, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, N.K.; Philips, S.N. Necrotizing hepatitis in pet birds associated with Pseudomonas fluorescens. Avian Dis. 1996, 40, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosta, L.; Sironi, G.; Rampin, T. Polyomavirus infection in Fringilidae. In Proceedings of the 4th Conference of the European AAV, London, UK, 19–24 May 1997; European Association of Avian Veterinarians: Madrid, Spain, 1997; pp. 128–131. [Google Scholar]
- Shivaprasad, D.L.; Hill, D.; Todd, D.; Smyth, J.A. Circovirus infection in a Gouldian finch (Chloebia gouldiae). Avian Pathol. 2004, 33, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. 16S rRNA gene sequencing for bacterial identification in the diagnostic laboratory: Pulses, perils, and pitfalls. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2761–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekambi, T.; Raoult, D.; Drancourt, M. The rpoB gene as a tool for clinical microbiologists. Trends Microbiol. 2009, 17, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin-Ching, C.; Jer-Horng, S.; Ching-Nan, L.; Ming-Chung, C. Cloning of a gene encoding a unique haemolysin from Klebsiella pneumoniae and its potential use as a species-specific gene probe. Microb. Pathog. 2002, 33, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Base Pairs | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16S rRNA | 1500 | AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG | TACGGYTACCTTGTTACGACTT |
| ecfX | 500 | ATGGATGAGCGCTTCCGTG | TCATCCTTCGCCTCCCTG |
| khe | 430 | TGATTGCATTCGCCACTGG | GGTCAACCCAACGATCCTG |
| rpoB | 1000 | GGCGAAATGGCWGAGAACCA | GAGTCTTCGAAGTTGTAACC |
| NAME | SEQUENCE | FINAL CONCENTRATION | TYPE OF PCR PERFORMED |
|---|---|---|---|
| NDV F | GAGCTAATGAACATTCTTTC | 0.5 µM | Real-Time PCR |
| NDV R | AATAGGCGGACCACATCTG | 0.5 µM | |
| LPROMGB (PROBE) | FAM-CCAATCAACTTCCC-MGBEQ | 0.2 µM | |
| LPROMGB2 (PROBE) | CY5-AATAGTGTATGACAACAC-MGBEQ | 0.2 µM | |
| BORNA PCA3 (+) F | CCCGCAGACAGYACGT | 0.25 µM | |
| BORNA PCA3 (+) F | GATCCGCAGACAGYACGT | 0.25 µM | |
| BORNA PCA6 (-) R | AAGAAYCCNTCCATGATCTC | 0.25 µM | |
| BORNAP (PROBE) | FAM-CGAATWCCCAGGGAGGCYCT-BHQ1 | 0.25 µM | |
| BORNAC (PROBE) | TexasRed-AGATGCATTGACCCARCCRGT-BHQ2 | 0.25 µM | |
| CIRCO-FOR | TTCACCCTTAAYAAYCCT | 0.5 µM | Conventional PCR |
| CIRCO-REV | CCRTSATATCCATCCCACCA | 0.5 µM | |
| VP1 POLY I FOR | CCAGACCCAACTARRAATGARAA | 0.9 µM | |
| VP1 POLY I REV | AACAAGAGACACAAATNTTTCCNCC | 0.9 µM | |
| VP1 POLY II FOR | ATGAAAATGGGGTTGGCCCNCTNTGYAARG | 0.9 µM | |
| VP1 POLY II REV | CCCTCATAAACCCGAACYTCYTCHACYTG | 0.9 µM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbate, J.M.; D’Annunzio, G.; Falleti, R.; Gervasi, C.; Ravaioli, V.; Lilliu, E.; Santo, E.; Carra, E.; Tosi, G.; Lanteri, G. Pathological Findings of Nestling European Goldfinches (Carduelis carduelis) Co-Infected with Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090821
Abbate JM, D’Annunzio G, Falleti R, Gervasi C, Ravaioli V, Lilliu E, Santo E, Carra E, Tosi G, Lanteri G. Pathological Findings of Nestling European Goldfinches (Carduelis carduelis) Co-Infected with Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(9):821. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090821
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbate, Jessica Maria, Giulia D’Annunzio, Rosa Falleti, Claudio Gervasi, Valentina Ravaioli, Elisabetta Lilliu, Emma Santo, Elena Carra, Giovanni Tosi, and Giovanni Lanteri. 2025. "Pathological Findings of Nestling European Goldfinches (Carduelis carduelis) Co-Infected with Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 9: 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090821
APA StyleAbbate, J. M., D’Annunzio, G., Falleti, R., Gervasi, C., Ravaioli, V., Lilliu, E., Santo, E., Carra, E., Tosi, G., & Lanteri, G. (2025). Pathological Findings of Nestling European Goldfinches (Carduelis carduelis) Co-Infected with Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Veterinary Sciences, 12(9), 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090821






